UbiPriSEQ—Deep Reinforcement Learning to Manage Privacy, Security, Energy, and QoS in 5G IoT HetNets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. UbiPriSEQ: System Requirements
3.1. QoS
3.2. Energy-Efficiency
3.3. Privacy
3.3.1. Location Privacy
3.3.2. Usage Pattern Privacy
3.3.3. Data Privacy
3.4. Security
3.4.1. Jamming
3.4.2. Rogue Fog Nodes and Users
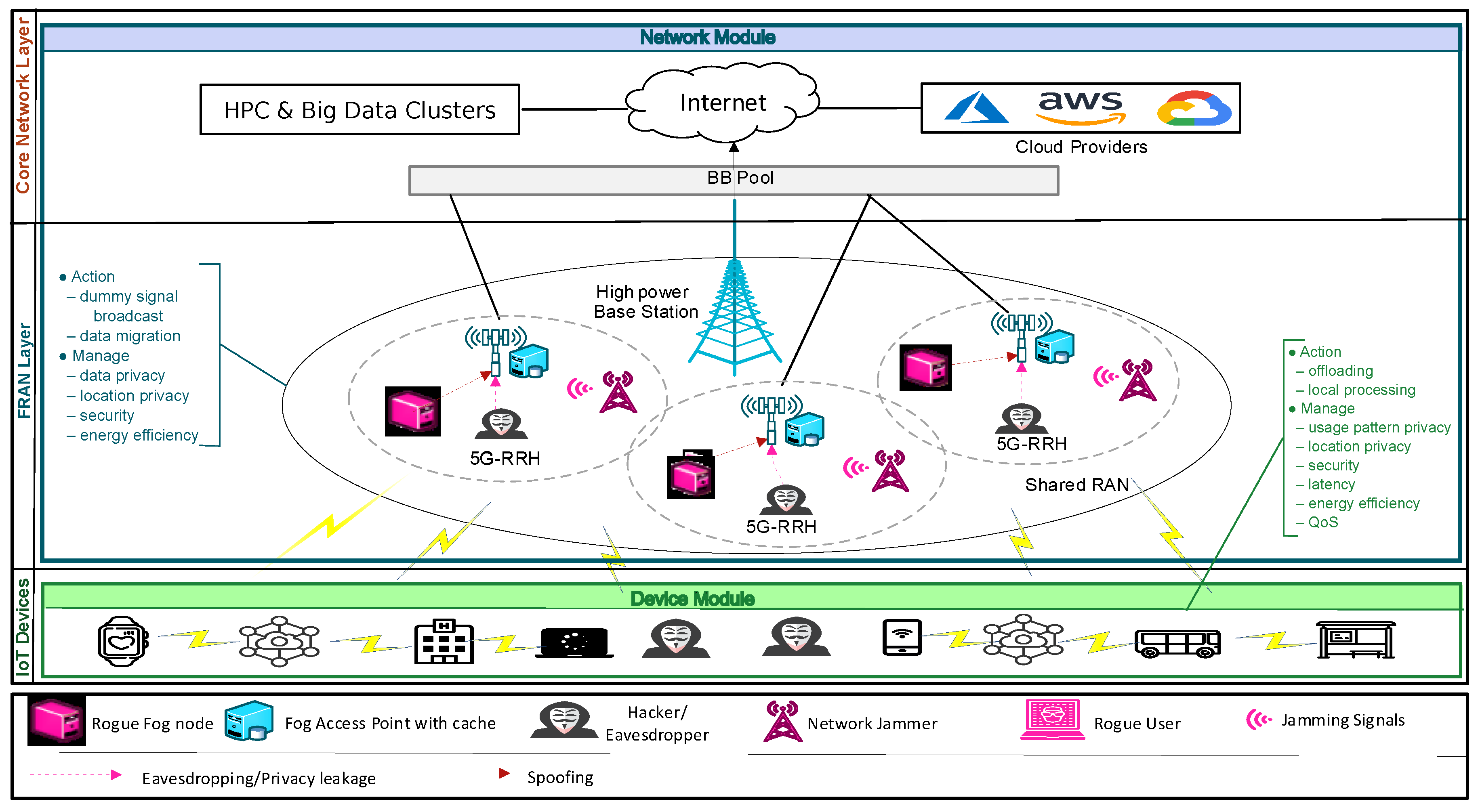
4. UbiPriSEQ: The Proposed Framework
4.1. UbiPriSEQ: Architectural Overview
4.2. UbiPriSEQ: Adaptive Learning Architecture
4.3. Device Module (DevM)
| Algorithm 1 Device Module (DevM) |
| Input:system state Output:action
|
4.3.1. DevM: Workflow
4.3.2. DevM: PrivacyMetric
4.3.3. DevM: QoS and Energy-Efficiency
4.3.4. DevM: Reward Function (Utility)
4.3.5. DevM: Q-Value
4.4. Network Module (NetM)
| Algorithm 2 Network Module (NetM) |
| Input:system state Output:action
|
5. UbiPriSEQ: System Evaluation
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Butler, L.; Windle, E.; Desouza, K.C.; Mehmood, R.; Corchado, J.M. Can Building “Artificially Intelligent Cities” Safeguard Humanity from Natural Disasters, Pandemics, and Other Catastrophes? An Urban Scholar’s Perspective. Sensors 2020, 20, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, R.; See, S.; Katib, I.; Chlamtac, I. (Eds.) Smart Infrastructure and Applications: Foundations for Smarter Cities and Societies; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; p. 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suma, S.; Mehmood, R.; Albeshri, A. Automatic Event Detection in Smart Cities Using Big Data Analytics. In Smart Societies, Infrastructure, Technologies and Applications; Mehmood, R., Bhaduri, B., Katib, I., Chlamtac, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Alomari, E.; Katib, I.; Mehmood, R. Iktishaf: A Big Data Road-Traffic Event Detection Tool Using Twitter and Spark Machine Learning. Mob. Networks Appl. 2020, 5, 9533–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqib, M.; Mehmood, R.; Alzahrani, A.; Katib, I.; Albeshri, A.; Altowaijri, S.M. Rapid Transit Systems: Smarter Urban Planning Using Big Data, In-Memory Computing, Deep Learning, and GPUs. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, E.; Mehmood, R. Analysis of Tweets in Arabic Language for Detection of Road Traffic Conditions. In Smart Societies, Infrastructure, Technologies and Applications; Mehmood, R., Bhaduri, B., Katib, I., Chlamtac, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Alotaibi, S.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I.; Rana, O.; Albeshri, A. Sehaa: A Big Data Analytics Tool for Healthcare Symptoms and Diseases Detection Using Twitter, Apache Spark, and Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosaeed, S.; Katib, I.; Mehmood, R. A Fog-Augmented Machine Learning based SMS Spam Detection and Classification System. In Proceedings of the 2020 Fifth International Conference on Fog and Mobile Edge Computing (FMEC), Paris, France, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Song, H.; Jara, A.J.; Bie, R. Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics for Smart and Connected Communities. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bie, R.; Yu, J. Advancing researches on IoT systems and intelligent applications. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2018, 22, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I.; Albogami, N.N.; Albeshri, A. Data Fusion and IoT for Smart Ubiquitous Environments: A Survey. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 9533–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D. How the Next Evolution of the Internet Is Changing Everything. 2011. Available online: http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac79/docs/innov/IoT_IBSG_0411FINAL.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Usman, S.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I. Big Data and HPC Convergence for Smart Infrastructures: A Review and Proposed Architecture. In Smart Infrastructure and Applications: Foundations for Smarter Cities and Societies; Mehmood, R., See, S., Katib, I., Chlamtac, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 561–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsch, P.; Silva, I.D.; Bulakci, O.; Tesanovic, M.; Ayoubi, S.E.E.; Rosowski, T.; Kaloxylos, A.; Boldi, M. 5G Radio Access Network Architecture: Design Guidelines and Key Considerations. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Lin, W.; Xu, X. Efficient computation offloading for Internet of Vehicles in edge computing-assisted 5G networks. J. Supercomput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; You, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. A Survey on Mobile Edge Computing: The Communication Perspective. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2322–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M.; Matam, R.; Shu, L.; Maglaras, L.; Ferrag, M.A.; Choudhury, N.; Kumar, V. Security and Privacy in Fog Computing: Challenges. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 19293–19304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Satpute, M.N.; Shan, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Yan, T. Computation Offloading for Mobile-Edge Computing with Multi-User. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 39th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Dallas, TX, USA, 7–10 July 2019; pp. 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Yin, H.; Huang, H.; Guo, D.; Lyu, Y. Computation Offloading for Multi-user Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 16th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 4th International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Exeter, UK, 28–30 June 2018; pp. 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Cheng, X.; Gao, H.; Zhou, X.; Wan, J. Toward Computation Offloading in Edge Computing: A Survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 131543–131558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, T.; Samdanis, K.; Mada, B.; Flinck, H.; Dutta, S.; Sabella, D. On Multi-Access Edge Computing: A Survey of the Emerging 5G Network Edge Cloud Architecture and Orchestration. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1657–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Chu, X.; Long, K.; Leung, V.C.M. Fog Radio Access Networks: Mobility Management, Interference Mitigation, and Resource Optimization. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.A.; Nasimi, M.; Han, B.; Schotten, H.D. A Comprehensive Survey of RAN Architectures toward 5G Mobile Communication System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 70371–70421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parwez, M.S.; Rawat, D.B. Resource Allocation in Adaptive Virtualized Wireless Networks with Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, P.; Banchs, A.; Berberana, I.; Breitbach, M.; Doll, M.; Droste, H.; Mannweiler, C.; Puente, M.A.; Samdanis, K.; Sayadi, B. Mobile network architecture evolution toward 5G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekki, S.; Featherstone, W.; Fang, Y.; Kuure, P.; Li, A.; Ranjan, A.; Purkayastha, D.; Feng, J.; Frydman, D.; Verin, G.; et al. MEC in 5G networks. ETSI White Pap. 2018, 28, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- ETSI GS MEC 003 V1.1.1. Mobile Edge Computing (MEC): Framework and Reference Architecture. 2016. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/MEC/001_099/003/01.01.01_60/gs_MEC003v010101p.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Zhang, K.; Mao, Y.; Leng, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Pan, L.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Energy-Efficient Offloading for Mobile Edge Computing in 5G Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 5896–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Letaief, K.B. Delay-optimal computation task scheduling for mobile-edge computing systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Barcelona, Spain, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, F.; Hu, R.Q. Joint Offloading and Computation Energy Efficiency Maximization in a Mobile Edge Computing System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3052–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Yu, G.; Cai, Y.; He, Y.; Qu, F. Partial Offloading for Latency Minimization in Mobile-Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2017—2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Li, L.; Gao, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, A. Partial Offloading Scheduling and Power Allocation for Mobile Edge Computing Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 6774–6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Dong, P.; Kong, X.; Xia, F. A Cooperative Partial Computation Offloading Scheme for Mobile Edge Computing Enabled Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 4804–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Ahmed, A.; Naeem, M.; Hong, Y. Partial Offloading in Energy Harvested Mobile Edge Computing: A Direct Search Approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 36757–36763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Ren, S. Online Learning for Offloading and Autoscaling in Energy Harvesting Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2017, 3, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, P.; Becvar, Z. Mobile Edge Computing: A Survey on Architecture and Computation Offloading. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1628–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.R.; Younis, M. Cross-layer traffic analysis countermeasures against adaptive attackers of wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 2019, 25, 2869–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, C.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Hu, G.; Ye, R.; Jiang, Y. CenLocShare: A centralized privacy-preserving location-sharing system for mobile online social networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 86, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Choo, K.K.R.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G. Enhancing privacy through uniform grid and caching in location-based services. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 86, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Lin, X.; Shen, X.S. Toward Edge-Assisted Internet of Things: From Security and Efficiency Perspectives. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, I.; Eckhoff, D. Technical Privacy Metrics: A Systematic Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2018, 51, 57:1–57:38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, G. Data Security and Privacy in Cloud Computing. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 10, 190903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, J.; Jin, R.; Dai, H. Privacy-Aware Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2017—2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jin, R.; Dai, H. Deep PDS-Learning for Privacy-Aware Offloading in MEC-Enabled IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 4547–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jin, R.; Dai, H. Peace: Privacy-Preserving and Cost-Efficient Task Offloading for Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Krikidis, I.; Li, J.; Petropulu, A.P.; Ottersten, B. Improving Physical Layer Secrecy Using Full-Duplex Jamming Receivers. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 4962–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Fakoorian, S.A.A.; Huang, J.; Swindlehurst, A.L. Principles of Physical Layer Security in Multiuser Wireless Networks: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1550–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Jin, R.; Dai, H. Physical-Layer Assisted Secure Offloading in Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 4054–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, B.; Bao, H.; Li, B. Secure Energy-Saving Resource Allocation on Massive MIMO-MEC System. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 137244–137253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Hanzo, L. Energy-Efficient Computation Offloading for Secure UAV-Edge-Computing Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 6074–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, F.R.; Pei, Q.; Chu, X.; Du, J.; Zhu, L. Cooperative Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation for Blockchain-Enabled Mobile-Edge Computing: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 6214–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, J.; Ma, M.; Li, H.; Niu, B.; Li, F. Privacy-Preserving Device Discovery and Authentication Scheme for D2D Communication in 3GPP 5G HetNet. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 February 2019; pp. 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangerter, B.; Talwar, S.; Arefi, R.; Stewart, K. Networks and devices for the 5G era. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.H.S.; Woungang, I.; Anpalagan, A.; Jaseemuddin, M.; Hossain, E. Intercloud and HetNet for Mobile Cloud Computing in 5G Systems: Design Issues, Challenges, and Optimization. IEEE Netw. 2017, 31, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogale, T.E.; Le, L.B. Massive MIMO and mmWave for 5G Wireless HetNet: Potential Benefits and Challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2016, 11, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servin, A.; Kudenko, D. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Intrusion Detection: A Case Study and Evaluation. In Multiagent System Technologies; Bergmann, R., Lindemann, G., Kirn, S., Pěchouček, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 159–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, S.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I.; Albeshri, A. ZAKI+: A Machine Learning Based Process Mapping Tool for SpMV Computations on Distributed Memory Architectures. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 81279–81296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, T.; Mehmood, R.; Albeshri, A.; Katib, I. SURAA: A Novel Method and Tool for Loadbalanced and Coalesced SpMV Computations on GPUs. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I.; Albeshri, A.; Altowaijri, S. ZAKI: A Smart Method and Tool for Automatic Performance Optimization of Parallel SpMV Computations on Distributed Memory Machines. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyahya, H.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I. Parallel Iterative Solution of Large Sparse Linear Equation Systems on the Intel MIC Architecture. In Smart Infrastructure and Applications: Foundations for Smarter Cities and Societies; Mehmood, R., See, S., Katib, I., Chlamtac, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 377–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAhmadi, S.; Muhammed, T.; Mehmood, R.; Albeshri, A. Performance Characteristics for Sparse Matrix-Vector Multiplication on GPUs. In Smart Infrastructure and Applications: Foundations for Smarter Cities and Societies; Mehmood, R., See, S., Katib, I., Chlamtac, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, R.; Crowcroft, J. Parallel Iterative Solution Method for Large Sparse Linear Equation Systems; Technical Report UCAM-CL-TR-650; University of Cambridge, Computer Laboratory: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, R.; Crowcroft, J.; Elmirghani, J.M.H. A Parallel Implicit Method for the Steady-State Solution of CTMCs. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation, Monterey, CA, USA, 11–14 September 2006; pp. 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, R. A Survey of Out-of-Core Analysis Techniques in Stochastic Modelling; Technical Report CSR-03-7; School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham: Birmingham, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, T.A.; Hu, Y. The University of Florida Sparse Matrix Collection. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 2011, 38, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolbeau, R. Theoretical peak FLOPS per instruction set: A tutorial. J. Supercomput. 2018, 74, 1341–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfat, Y.; Aqib, M.; Mehmood, R.; Albeshri, A.; Katib, I.; Albogami, N.; Alzahrani, A. Enabling Smarter Societies through Mobile Big Data Fogs and Clouds. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 109, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, T.; Mehmood, R.; Albeshri, A.; Katib, I. UbeHealth: A Personalized Ubiquitous Cloud and Edge-Enabled Networked Healthcare System for Smart Cities. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32258–32285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawalbeh, L.A.; Mehmood, R.; Benkhlifa, E.; Song, H. Mobile Cloud Computing Model and Big Data Analysis for Healthcare Applications. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 6171–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawalbeh, L.A.; Bakhader, W.; Mehmood, R.; Song, H. Cloudlet-Based Mobile Cloud Computing for Healthcare Applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]


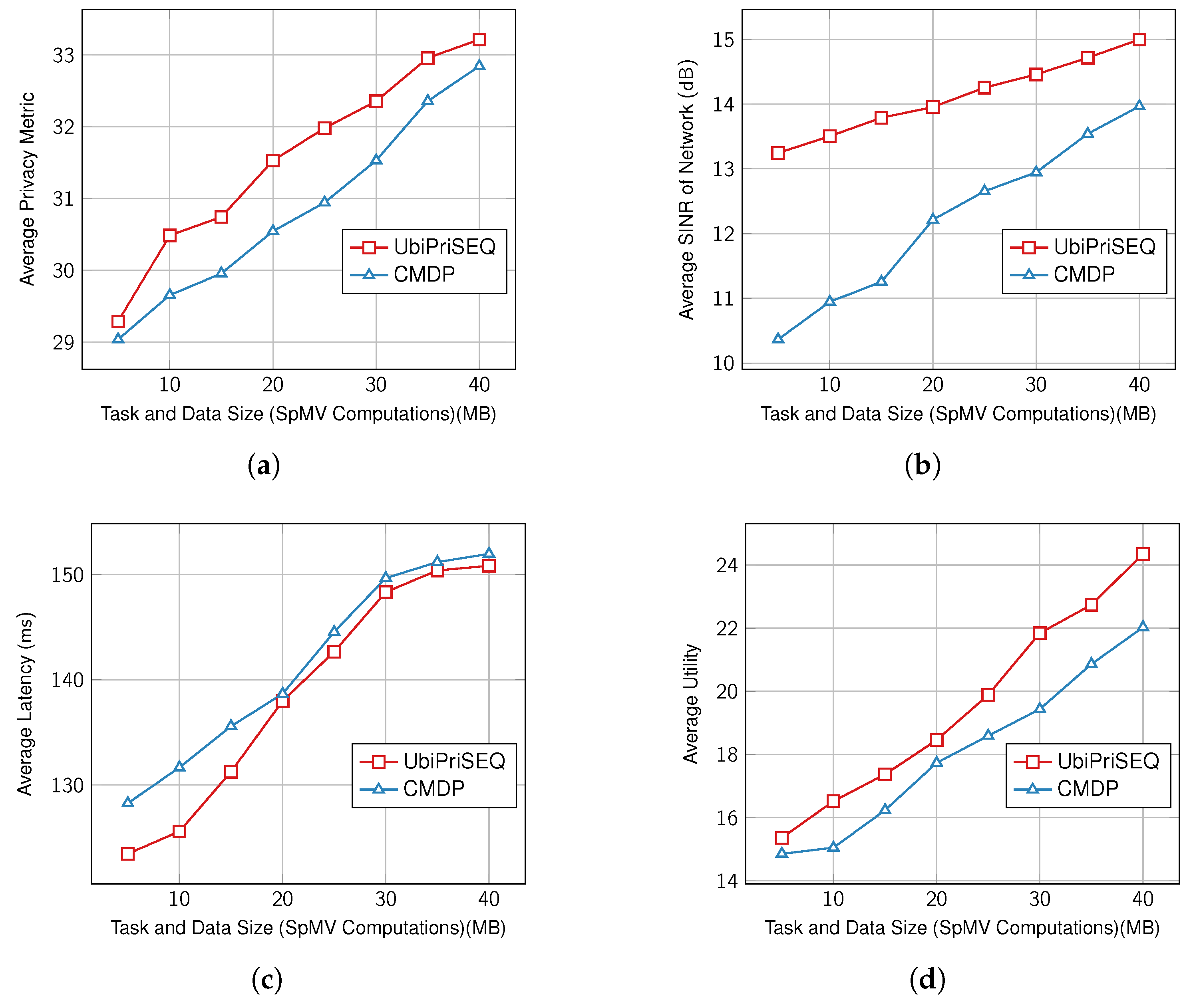
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| System bandwidth | 10 MHz |
| Transmit power of user nodes | 10 dBm |
| Number of fog nodes | 30 |
| Number of user nodes | 90 |
| Processing Density | 4 double-precision FLOPS/cycle [69] |
| Fog compute power | 10 GHz |
| Sparse Matrix Size | [10, 40,000] KB |
| Learning Rate | 0.8 |
| Discount Factor | 0.7 |
| Privacy weight | 5 |
| Task arrival rate | [0, 5] |
| Selection probability: | , |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammed, T.; Albeshri, A.; Katib, I.; Mehmood, R. UbiPriSEQ—Deep Reinforcement Learning to Manage Privacy, Security, Energy, and QoS in 5G IoT HetNets. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207120
Mohammed T, Albeshri A, Katib I, Mehmood R. UbiPriSEQ—Deep Reinforcement Learning to Manage Privacy, Security, Energy, and QoS in 5G IoT HetNets. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(20):7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207120
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammed, Thaha, Aiiad Albeshri, Iyad Katib, and Rashid Mehmood. 2020. "UbiPriSEQ—Deep Reinforcement Learning to Manage Privacy, Security, Energy, and QoS in 5G IoT HetNets" Applied Sciences 10, no. 20: 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207120
APA StyleMohammed, T., Albeshri, A., Katib, I., & Mehmood, R. (2020). UbiPriSEQ—Deep Reinforcement Learning to Manage Privacy, Security, Energy, and QoS in 5G IoT HetNets. Applied Sciences, 10(20), 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207120








