Energy Performance Forecasting of Residential Buildings Using Fuzzy Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fuzzy Methodologies
- -
- ANFIS is a pure fuzzy inference system, i.e., a fuzzy system is trained and a fuzzy inference process is performed for prediction. FIR identifies a fuzzy model that represents the system under study, but the prediction is performed applying a k-nearest neighbour (KNN) hybrid approach.
- -
- ANFIS models are trained by means of neural network training algorithms. FIR models are synthesized rather than trained, meaning that an optimization process is performed to organize the training data appropriately.
- -
- ANFIS models are Sugeno-type fuzzy systems where the antecedents are fuzzy sets and the consequent is not a fuzzy set, but a function. FIR, on the contrary, uses fuzzy sets to represent both the antecedents and the consequent, being more useful for obtaining explainable models that can be used for decision making.
- -
- FIR has an internal feature selection (FS) process that allows identifying the input variables that are most relevant in the inference process and their degree of individual relevance. ANFIS has no FS integrated in its structure, and it is necessary to apply a FS algorithm as a pre-process, if desired.
2.1. Fuzzy Inductive Reasoning (FIR)
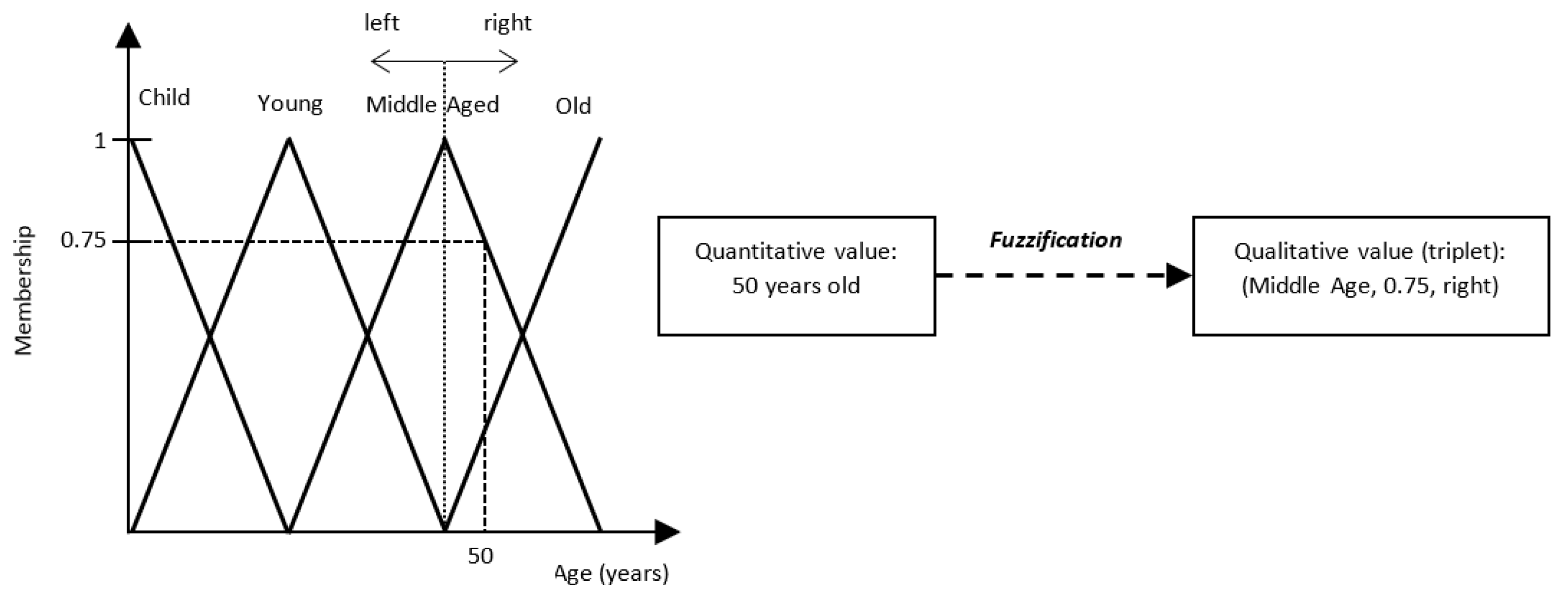
2.1.1. Fuzzification
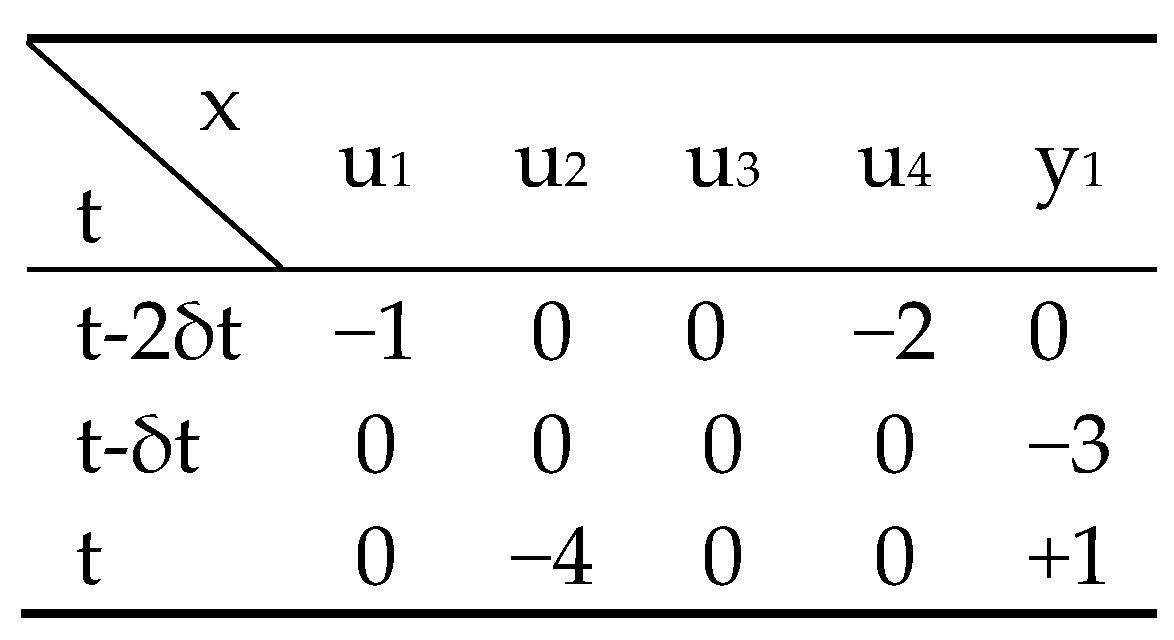
2.1.2. Qualitative Model Identification
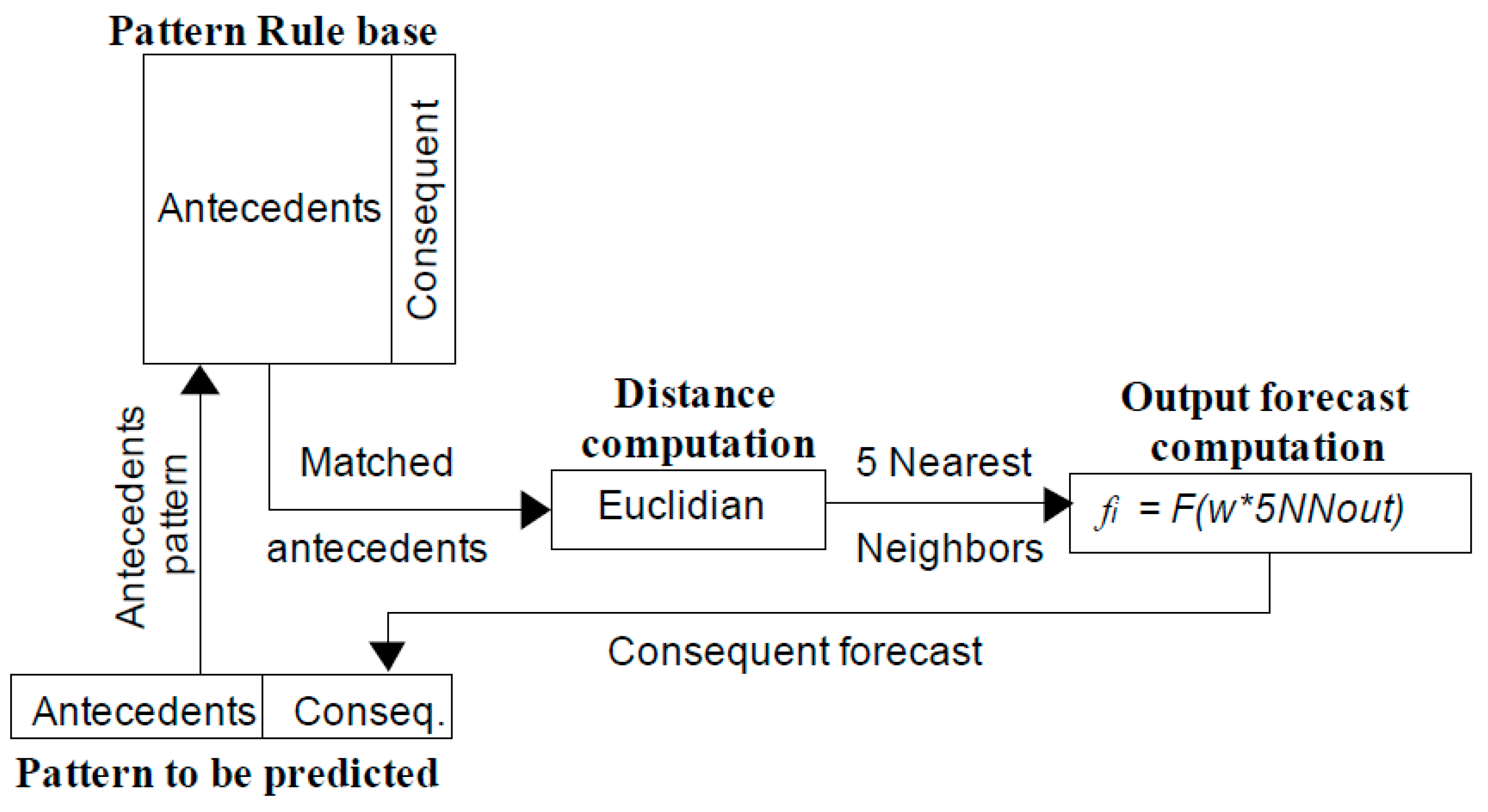
2.1.3. Fuzzy Forecasting
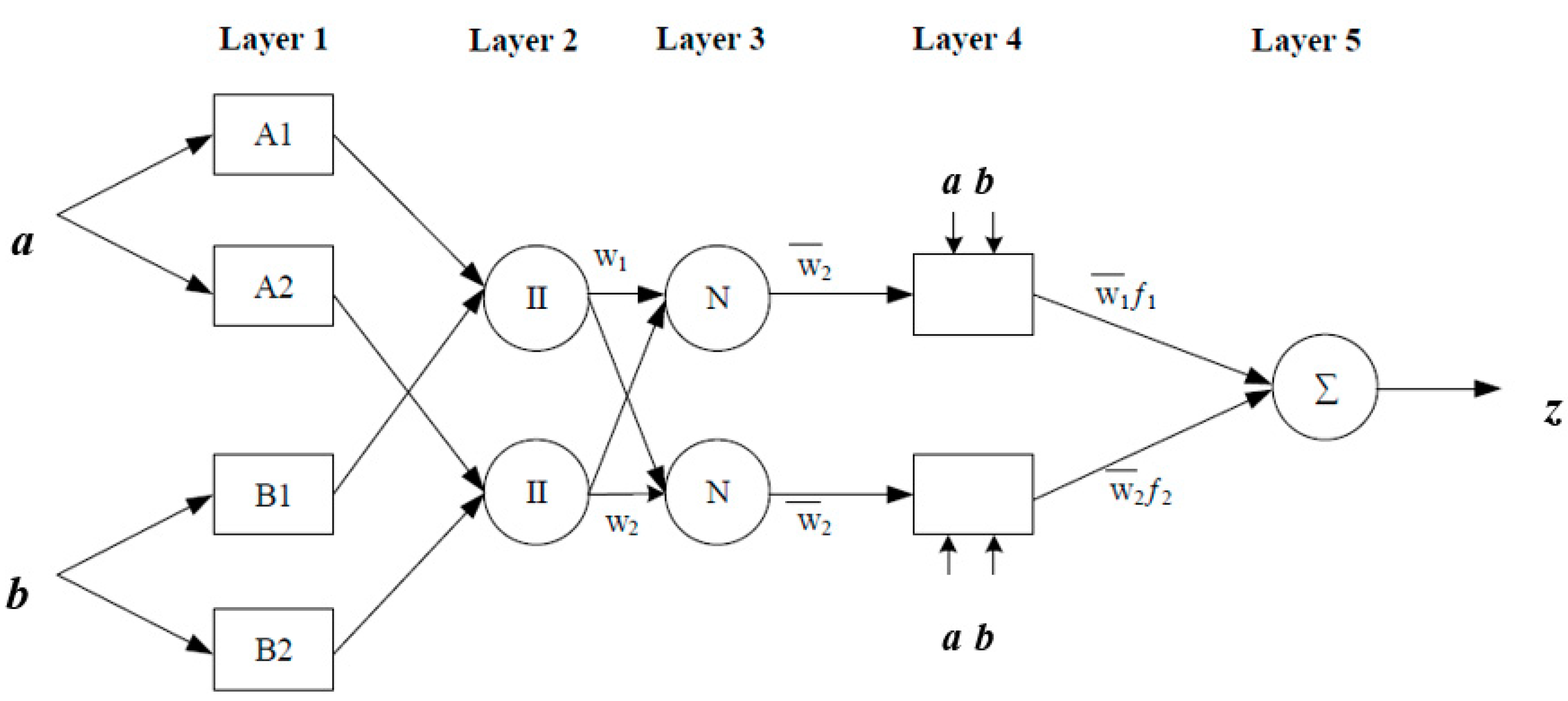
2.2. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS)
R2: If a is A2 and b is B2 then z = p2 × a + q2 × b + r2
3. Fuzzy Approaches for Energy Performance of Buildings Forecasting
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Performance Criteria
3.3. Fuzzy Models Identification
3.3.1. ANFIS Models
3.3.2. FIR Models
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Fuzzy Approaches Results and Discussion
4.2. Feature Selection Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/energy/en/topics/energy-efficiency/energy-performance-of-buildings (accessed on 14 October 2019).
- Deloitte. Energy Efficiency in Europe. The Levers to Deliver the Potential. Available online: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/global/Documents/Energy-and-Resources/energy-efficiency-in-europe.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Seyedzadeh, S.; Rahimian, F.; Glesk, I.; Roper, M. Machine learning for estimation of building energy consumption and performance: A review. Vis. Eng. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.G.; Baek, C.I.; Han, H. Prediction and Analysis of Building Energy Efficiency Using Artificial Neural Network and Design of Experiments. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2016, 819, 541–545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; O’Neill, Z.; Dong, B.; Augenbroe, G. Comparisons of inverse modeling approaches for predicting building energy performance. Build. Environ. 2015, 86, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascione, F.; Bianco, N.; De Stasio, C.; Mauro, G.M.; Vanoli, G.P. Artificial neural networks to predict energy performance and retrofit scenarios for any member of a building category: A novel approach. Energy 2017, 118, 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.; Cesarotti, V.; Introna, V.; Serranti, J. Energy consumption control automation using Artificial Neural Networks and adaptive algorithms: Proposal of a new methodology and case study. Appl. Energy 2016, 165, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Cho, S.; Chung, D.H. Analysis of energy and control efficiencies of fuzzy logic and artificial neural network technologies in the heating energy supply system responding to the changes of user demands. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuemei, L.; Lixing, D.; Jinhu, L.; Gang, X.; Jibin, L. A novel hybrid approach of KPCA and SVM for building cooling load prediction. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (WKDD), Phuket, Thailand, 9–10 January 2010; pp. 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Lian, Z. An application of support vector machines in cooling load prediction. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2009, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.C.; Kim, J.S.; Heo, H. Prediction of building energy consumption using an improved real coded genetic algorithm based least squares support vector machine approach. Energy Build. 2015, 90, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.W.; Mourshed, M.; Rezgui, Y. Trees vs Neurons: Comparison between random forest and ANN for high-resolution prediction of building energy consumption. Energy Build. 2017, 147, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuhus-Dubrow, D.; Krarti, M. Genetic-algorithm based approach to optimize building envelope design for residential buildings. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dounis, A.I.; Caraiscos, C. Advanced control systems engineering for energy and comfort management in a building environment—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1246–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S. Evaluating and ranking energy performance of office buildings using fuzzy measure and fuzzy integral. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebot, A.; Mugica, F. Fuzzy Approaches Improve Predictions of Energy Performance of Buildings. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Simulation and Modeling Methodologies, Technologies and Applications, Reykjavík, Iceland, 29–31 July 2013; Volume 1, pp. 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- Tsanas, A.; Xifara. Accurate quantitative estimation of energy performance of residential buildings using statistical machine learning tools. Energy Build. 2012, 49, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCI. Available online: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/ (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Chou, J.S.; Bui, D.K. Modeling heating and cooling loads by artificial intelligence for energy-efficient building design. Energy Build. 2014, 82, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.Y.; Cao, M.T. Accurately predicting building energy performance using evolutionary multivariate adaptive regression splines. Appl. Soft Comput. 2014, 22, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.; Trujillo, L.; Vanneschi, L.; Popovič, A. Prediction of energy performance of residential buildings: A genetic programming approach. Energy Build. 2015, 102, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klir, G.; Elias, D. Architecture of Systems Problem Solving, 2nd ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nebot, A.; Mugica, F. Fuzzy inductive reasoning: A consolidated approach to data-driven construction of complex dynamical systems. Int. J. Gen. Syst. 2012, 41, 645–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebot, A.; Mugica, F.; Cellier, F.; Vallverdú, M. Modeling and Simulation of the Central Nervous System Control with Generic Fuzzy Models. Simulation 2003, 79, 648–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, R.; Nebot, A. Growth Model for White Shrimp in Semi-intensive Farming using Inductive Reasoning Methodology. Comput. Electron. Agric. 1998, 19, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobet, A.; Nebot, A.; Cellier, F.E. Visual-FIR: A tool for model identification and prediction of dynamical complex systems. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2008, 16, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, D.; Klawonn, F.; Kruse, R. Neuro-Fuzzy Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ecotet. Available online: http://usa.autodesk.com/ecotect-analysis/ (accessed on 23 October 2019).


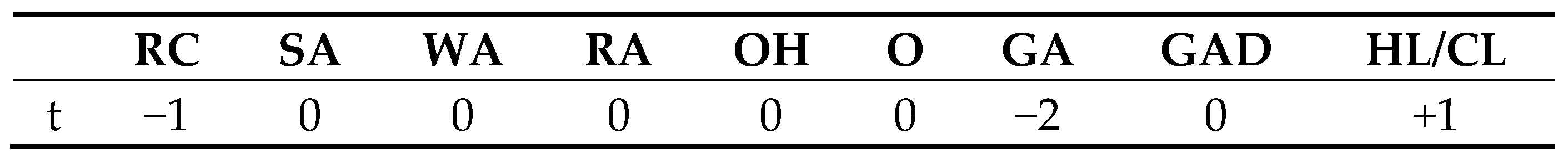

| RC | Relative Compactness | OH | Overall Height |
| SA | Surface Area | O | Orientation |
| WA | Wall Area | GA | Glazing Area |
| RA | Roof Area | GAD | Glazing Area Distribution |
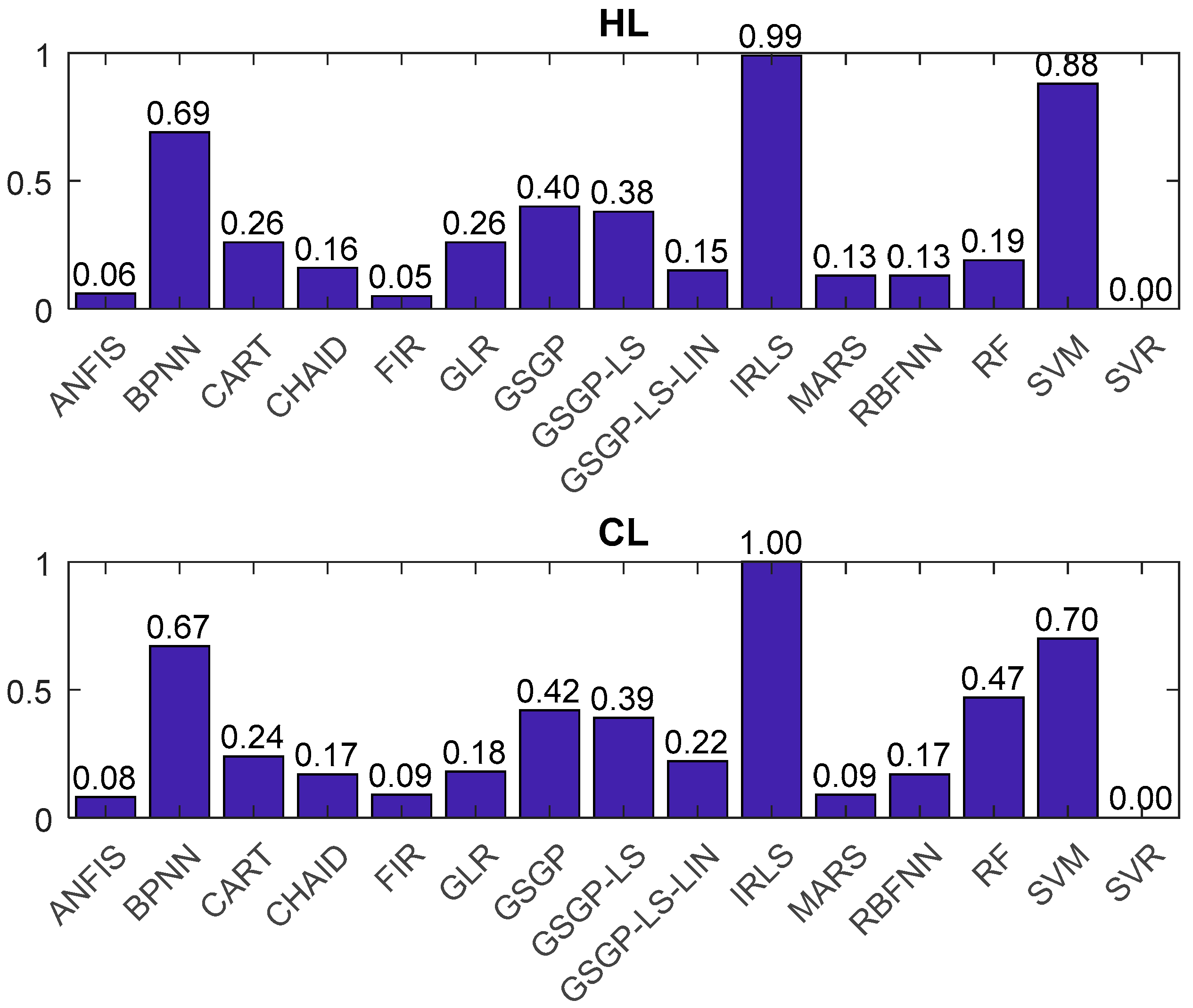
| Model [Reference] | Cooling Load | Heating Load | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | SI | MAE | RMSE | SI | |
| IRLS [17] | 2.21 | 3.38 | 1 | 2.14 | 3.14 | 0.99 |
| RF [17] | 1.42 | 2.57 | 0.47 | 0.51 | 1.01 | 0.19 |
| SVR [19] | 0.89 | 1.65 | 0 | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0 |
| GLR [19] | 1.29 | 1.74 | 0.18 | 0.79 | 1.04 | 0.26 |
| CHAID [19] | 1.17 | 1.86 | 0.17 | 0.47 | 0.91 | 0.16 |
| CART [20] | 1.31 | 1.94 | 0.24 | 0.73 | 1.11 | 0.26 |
| SVM [20] | 2.10 | 2.49 | 0.70 | 2.19 | 2.49 | 0.88 |
| RBFNN [20] | 1.30 | 1.69 | 0.17 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.13 |
| BPNN [20] | 1.92 | 2.63 | 0.67 | 1.61 | 2.25 | 0.69 |
| MARS [20] | 1.12 | 1.65 | 0.09 | 0.53 | 0.68 | 0.13 |
| GSGP [21] | 1.47 | 2.36 | 0.42 | 1.31 | 1.06 | 0.40 |
| GSGP-LS [21] | 1.37 | 2.36 | 0.39 | 1.26 | 1.04 | 0.38 |
| GSGP-LS-LIN [21] | 1.18 | 2.04 | 0.22 | 0.51 | 0.79 | 0.15 |
| ANFIS | 1.03 | 1.76 | 0.08 | 0.37 | 0.52 | 0.06 |
| FIR | 1.09 | 1.72 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.49 | 0.05 |
| Heating Load | #Epochs | Partition | RMSE | MAE | Exec. Time (min) |
| 50 | 3-2 | 1.71 | 1.34 | 0.1 | |
| 100 | 3-2 | 1.28 | 0.90 | 0.2 | |
| 500 | 3-2 | 1.13 | 0.85 | 0.7 | |
| 1000 | 3-2 | 1.10 | 0.83 | 1.3 | |
| 2000 | 3-2 | 1.09 | 0.81 | 2.6 | |
| 50 | 5-2 | 0.85 | 0.63 | 0.2 | |
| 100 | 5-2 | 0.55 | 0.40 | 0.3 | |
| 500 | 5-2 | 0.51 | 0.37 | 1.2 | |
| 1000 | 5-2 | 0.51 | 0.37 | 2.4 | |
| 2000 | 5-2 | 0.51 | 0.37 | 5 |
| Cooling Load | #Epochs | Partition | RMSE | MAE | Exec. Time (min) |
| 50 | 3-2 | 2.57 | 2.13 | 0.1 | |
| 100 | 3-2 | 2.26 | 1.69 | 0.2 | |
| 500 | 3-2 | 2.16 | 1.68 | 0.7 | |
| 1000 | 3-2 | 2.16 | 1.68 | 1.3 | |
| 2000 | 3-2 | 2.15 | 1.68 | 2.8 | |
| 50 | 5-2 | 1.68 | 1.09 | 0.2 | |
| 100 | 5-2 | 1.69 | 1.09 | 0.4 | |
| 500 | 5-2 | 1.69 | 1.09 | 1.2 | |
| 1000 | 5-2 | 1.69 | 1.09 | 2.5 | |
| 2000 | 5-2 | 1.69 | 1.09 | 5.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nebot, À.; Mugica, F. Energy Performance Forecasting of Residential Buildings Using Fuzzy Approaches. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020720
Nebot À, Mugica F. Energy Performance Forecasting of Residential Buildings Using Fuzzy Approaches. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(2):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020720
Chicago/Turabian StyleNebot, Àngela, and Francisco Mugica. 2020. "Energy Performance Forecasting of Residential Buildings Using Fuzzy Approaches" Applied Sciences 10, no. 2: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020720
APA StyleNebot, À., & Mugica, F. (2020). Energy Performance Forecasting of Residential Buildings Using Fuzzy Approaches. Applied Sciences, 10(2), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020720





