Abstract
We propose here a spectroscopic method to diagnose and differentiate inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) with pediatric onset, in a complete noninvasive way without performing any duodenal biopsy. In particular, the Raman technique was applied to proteic extract from fecal samples in order to achieve information about molecular vibrations that can potentially furnish spectral signatures of cellular modifications occurring as a consequence of specific pathologic conditions. The attention was focused on the investigation of the amide I region, quantitatively accounting the spectral changes in the secondary structures by applying deconvolution and curve-fitting. Inflammation is found to give rise to a significant increasing of the nonreducible (trivalent)/reducible (divalent) cross-linking ratio of the protein network. This parameter revealed an excellent marker in order to distinguish IBD subjects from non-IBD ones, and, among IBD patients, to differentiate between UC and CD. The proposed methodology was validated by statistical analysis using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
1. Introduction
An early and accurate detection of chronic diseases is crucial in view of a proper intervention [1,2,3]. It can also contribute in facilitating the monitoring of disease progression and therapeutic response. In many chronic diseases, especially regarding pediatric patients, the diagnostic process can be time consuming and invasive so the search for noninvasive and accurate diagnostic tools is underway.
In particular, the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in childhood, can be challenging [4,5,6]. The diagnosis is based on detection of chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and exclusion of other causes of inflammation. The differentiation of Crohn’s disease (CD) from ulcerative colitis (UC), and both of these from infectious diseases, allergic diseases, or primary immunodeficiency disorders (PIDs) with similar presentations is based on a combination of clinical suspicion, endoscopic and histological evaluation of the mucosa, and other additional tests in case of uncertainty [7]. An international group of European experts in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease (PIBD), mainly from the ‘‘Porto’’ IBD Working Group of the European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) stated that an “accurate diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease should be based on a combination of history, physical and laboratory examination, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and ileocolonoscopy with histology, and imaging of the small bowel [8]. It is critical to exclude enteric infections”. Even adhering to revised Porto IBD working group criteria for diagnosis, in some case distinguishing CD from UC and both from other disease is troublesome, especially in the subset of patients with early onset of disease. A noninvasive tool helpful, on the one hand, in reducing the burden of diagnosis and, on the other, in differentiating between CD and UC is a target for current and future research [9,10,11]. Nevertheless, the structural analysis of tissues didn’t reveal successful in differentiating among inflammation subtypes.
Calprotectin is a small calcium-binding protein of the S100 family of zinc-binding proteins, and is a major component of cytosol protein content in neutrophils and other cells involved in inflammatory process. In the presence of active intestinal inflammation, polymorphonuclear neutrophils migrate to the intestinal mucosa from the circulation. Any disturbance to the mucosal architecture due to the inflammatory process, results in leakage of neutrophils, and hence, calprotectin, into the lumen and its subsequent excretion in feces. The concentration of calprotectin in feces has been shown to correlate well with the disease activity in IBD and to help differentiate IBD from other functional intestinal disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome [12,13,14].
Raman spectroscopy is an inelastic light-scattering phenomenon according to which the illumination of a molecule by a monochromatic laser light will give rise to an exchange of a quantum vibrational energy between the two that will result in a difference in vibrational frequency between incident and scattered light [15,16,17]. Consequently, this experimental method provides a vibrational spectrum that contains information relative to chemical bonds and symmetry of a specific molecule [18,19]. As widely reported [20,21,22], it represents an essential methodology in chemistry, physics, biology and material science. For example, Raman spectroscopy is broadly employed in the investigation of changes in secondary structure at all stages of protein aggregation and amyloid fibril formation [23,24]. It is commonly used in unravelling molecule-specific spectral signatures of different biomolecules including nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates and complex biological systems like tissues, cells, that are made up of such biomolecules [25].
Most interesting, over the last decade Raman spectroscopy has proved to be a versatile tool in clinical diagnostics too, applied on tissues in order to detect a variety of diseases ranging from cancer [26] to infectious [27], neurodegenerative diseases [28] and in identification of cells [29]. This is because any altered biochemistry in the body that is specific to a particular disease and that will precede macroscopic tissue changes [30,31] will be reflected in a Raman spectrum. In particular, many inflammatory conditions have been investigated by Raman spectroscopy. For example, an endoscope-coupled Raman probe was used in vivo to investigate the colon mucosal composition in patients suffering from ulcerative colitis, for which a decrease in the phosphatidylcholine (720 cm−1) and total lipids (1303 cm−1) was detected [32]. In addition, colonoscopy-coupled fiber-optic probe-based Raman spectroscopy was applied in vivo for the diagnosis, in real time and in a nondestructive way, to inflammatory bowel disease, i.e., ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease [33].
With the aim of identifying a diagnostic procedural path for inflammatory bowel diseases, in particular CD and UC, that takes into consideration only a physical investigation technique, a noninvasive methodology has therefore been developed based on the analysis of the stool protein extract of patients, using Raman spectroscopy.
As is well known, the evaluation of diagnostic tests is a matter of concern in modern medicine not only for confirming the presence of disease but also to rule out the disease in healthy subjects [34]. In diagnostic tests with dichotomous outcome (positive/negative test results), the conventional approach of the diagnostic test evaluation uses sensitivity and specificity as measures of the accuracy of the test in comparison with gold standard status [35]. Here, the reliability of the proposed innovative methodology was evaluated by conducting statistical analysis by using, in particular, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the Youden index (), with its associated cutoff-point.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
Raman analysis was performed on fecal samples of patients with IBD (UC and CD). The same analysis was performed on fecal samples of patients for whom IBD was ruled out. All the patients were evaluated in the Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit of University Hospital “G Martino”, in Messina, Italy. In particular, we analyzed a proteic extract from fecal samples of 15 subjects with CD, nine subjects with UC (both the groups of subjects constituting the so-called IBD group) and 19 subjects for whom IBD was ruled out (non-IBD group, i.e., control group). For all subjects a fecal sample was collected in order to evaluate fecal calprotectin levels (Calprest® NG by Eurospital SpA, Trieste, Italy). In the IBD group the evaluation was necessary in order to assess disease activity (i.e., intensity of intestinal inflammation), in the non-IBD group the evaluation was performed as part of assessments to rule out IBD diagnosis. We selected patients in the IBD group both with CD and UC with different degrees of disease activity based on calprotectin levels. On the other hand, in the control group, we selected patients for whom an intestinal inflammation was excluded according to normal calprotetin levels (<100 mg/kg according to manufacturer indications) (see final diagnosis for these patients in Table 1). From the same sample prepared for the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test for fecal calprotectin incubated with an extraction buffer, in order to retrieve the proteic content, a liquid extract of 100 µl was collected in order to homogenize the sample for Raman analysis. In Table 1 demographic and clinical descriptions of subjects are summarized.

Table 1.
Demographic, clinical and baseline features of inflammatory bowel (IBD) and non-IBD group. * Standard deviation; ** irritable bowel disease; § recurrent abdominal pain.
2.2. Raman Measurements
Raman measurements were performed by means of a DXR-SmartRaman Spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) using a diode laser with the excitation wavelength of 785 nm. All the Raman spectra were acquired over the wavenumber range of 400–3300 cm−1, with a resolution of 1.9 cm−1 and irradiated with a laser power of 24 mW, coming out from a 50 µm spot.
Vials containing fecal extract were accommodated into their sample holder and the 180-degree sampling accessory for the DXR-SmartRaman Spectrometer was used for measurements. This sampling accessory, that has the typical 180-degree backscattering geometry for collecting Raman scattered radiation, is designed as a simple device to accommodate vials, tubes, powders and other samples in a variety of formats. It can allow the use of specialty cells, including cryogenic, high-temperature, electrochemical and controlled-humidity chambers, and results particularly useful in environments that value diverse sample formats over highly automated data collection. In order to obtain high signal-to-noise ratio (S/R) spectra, each Raman spectrum was obtained after collecting 32 sample frames, and the duration of each exposure for each frame was set equal to 60.0 s. Total acquisition time was 32 min for each spectrum.
Experimental data in the 1300–1800 cm−1 range were fitted by a multiple curve-fitting routine provided in the PeakFit 4.0 software package (Systat Software, Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). The fitting procedure we adopted was a nonlinear regression procedure (a nonlinear least squares fitting) that adjusts the parameters in small steps in order to improve the goodness of the fit, by minimizing the sum of the squares of the vertical deviations of a set of n data points from a function f. The analysis of the second derivative of the spectra was preliminary applied in order to gain, by evaluating the minima in the obtained profiles, a first indication of the minimum number of band components and their peak positions, according to a procedure already successfully applied in the analysis of Raman spectra of supramolecular systems [36].
In associated systems, the width of a vibrational band shape suffers homogeneous and non-homogeneous enlargement, therefore the Voigt profile, which is a convolution of Lorentzian with Gaussian, is suitable for band shape analysis. In the light of this, the experimental data were deconvoluted into the minimum number of Voigt fitting functions, defined as the following convolution of a Lorentzian with a Gaussian curve:
in which and are the amplitude and the center frequency, is related to the Gaussian half width at half maximum () and depends on the ratio of the Lorentzian half width at half maximum to (). All parameters (, , , ) were left free to vary upon iteration. For each fitting session, multiple iterations were performed until a converging solution (“best-fit”) was reached, by minimization of the value of . The well-known problem of finding a local (“false”) minimum was overcome by running each nonlinear regression several (20 on average) times, providing each time a different set of initial values of parameters. All fits generated the same parameters values, with the same sum-of squares, regardless the initial values, and this made us confident that we didn’t encounter a false minimum.
2.3. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve and Youden Index ()
The ROC curve is the graph of sensitivity vs. 1–specificity, where the sensitivity represents the true positive rate, while (1–specificity) is the false positive rate [37]. In this study, sensitivity and specificity of the diagnostic test were determined considering positive and negative test in the two different groups (IBD vs. non-IBD subjects). Sensitivity referred to the ability of Raman spectroscopy to correctly identify those patients with the inflammatory process. Instead, specificity referred to the ability of Raman spectroscopy to correctly identify those patients without the inflammation. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) represents the probability Pr (Y ≥ X), i.e., the probability of the marker value Y of a randomly selected subject from the diseased population to be higher than the marker value X of a randomly selected subject from the healthy population [38]. The obtained AUC result is an effective way to summarize the overall diagnostic accuracy of the test. It takes values from 0 to 1, where a value of 0 indicates a perfectly inaccurate test and a value of 1 reflects a perfectly accurate test. In general, an AUC value equal to 0.5 suggests no discrimination (i.e., ability to diagnose patients with and without the disease or condition based on the test), from 0.7 to 0.8 is considered acceptable, from 0.8 to 0.9 is considered excellent, and more than 0.9 is considered outstanding [39]. On the other hand, since AUC serves as a measure of a biomarker’s global diagnostic accuracy over all possible cut-points, it cannot directly provide an ‘optimal’ threshold or cut-point needed by clinicians for making diagnosis, i.e., for classifying a subject as either diseased or healthy. For this reason, the cut-point was determined using the Youden index , defined as = sensitivity + specificity − 1. This index represents the maximum vertical distance between the ROC curve and the diagonal, and is taken at the cut-point that optimizes the biomarker’s differentiating ability when equal weight is given to sensitivity and specificity [40]. It offers the optimal cutoff-point and, at the same time, it is a direct measure of the diagnostic accuracy at the optimal cut-point, that is, the maximum overall correct classification rate a marker can achieve [41,42].
3. Results
In Figure 1, we report the average Raman spectrum of fecal extract from non-IBD patients, obtained averaging the spectra collected for all the analyzed subjects, after having performed a baseline correction of each of them in order to compensate eventual technical and/or sample variations, and having normalized them to the total integrated area.
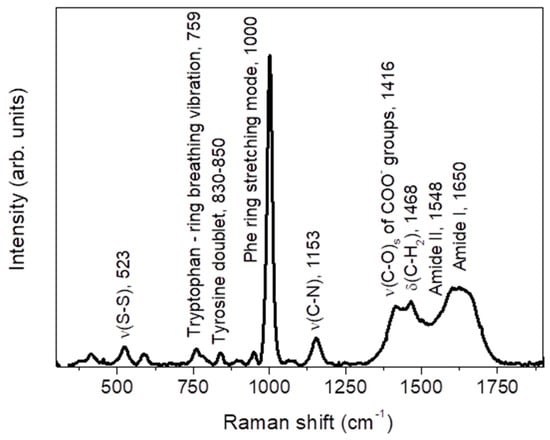
Figure 1.
Average Raman spectrum of non-IBD subjects, together with the main vibrational assignment. See text for details.
The spectrum highlights some of the main typical protein vibrational modes, associated to the polypeptide backbone (amide bands) and to the aromatic and nonaromatic amino acid residue side.
Based on comparison with literature [43,44], the band detected at ~523 cm−1 is associated to the ν(S-S) stretching vibration. The feature at ~759 cm−1 is assigned to the ring breathing vibration of tryptophan. Going on, the tyrosine doublet can be recognized in the ~830–850 cm−1 range, the high peak corresponding to the phenylalanine (Phe) ring stretching mode is well evident at ~1000 cm−1, and the ν(C-N) stretching mode is responsible of the band at ~1153 cm−1. Going to higher Raman shifts, a large and composite band is detected extending from ~1250 cm−1 up to ~1750 cm−1. It is the result of the overlapping of several contributions, among which we can distinguish the symmetric ν(C-O)s stretching vibration of COO- groups, at ~1416 cm−1, and the δ(C-H2) bending vibration, at ~1468 cm−1. Going on, the amide II band is recognized at ~1548 cm−1, consisting of an out-of-phase combination of ν(C-N) stretching and δ(N-H) bending motions. Finally, the amide I vibration is well evident as a large band centered at ~1650 cm−1. It is mainly due to the ν(C=O) stretching mode and a small amount of out-of-phase ν(C-N) stretching. The position of the amide I band will depend on the conformations of the polypeptide backbone, i.e., on the type of secondary structure, and on the intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bond of protein specimen [45]. Each type of secondary structure will have a typical ν(C=O) stretching frequency, and this justifies the broadening of the band.
Figure 2a,b depicts the average Raman spectra, in the 900–1200 cm−1 and 1300–1800 cm−1 wavenumber ranges respectively, of fecal extract from non-IBD subjects (black line), compared to those obtained from subjects within each disease class, i.e., CD (red line) and UC (green line) (the last two spectra were obtained following the same procedure described at the beginning of this section for the average Raman spectrum relative to non-IBD subjects). The spectra reported in Figure 2 were preliminarily normalized to the total integrated area.
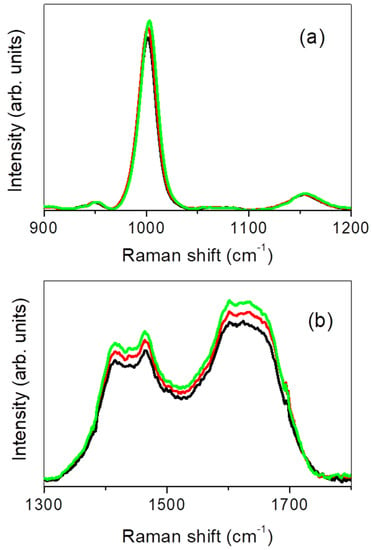
Figure 2.
Average Raman spectrum, collected in the 900–1200 cm−1 (a) and 1300–1800 cm−1 (b) region, of fecal extract from non-IBD subjects (black line), subjects with Crohn’s disease (CD; red line) and subjects with ulcerative colitis (UC; green line).
From an inspection of the figure it appears clear that, as disease occurs, an evident increasing is observed in spectral intensity of the band centered at ~1000 cm−1 and in the large band detected in the 1300–1800 cm−1 range. About this, it is worth remarking that significant variations in integrated Raman intensity, as active inflammation occurs and progresses in severity, were observed in previous studies by colonoscopy-coupled fiber-optic probe-based Raman spectroscopy for inflammatory bowel disease of the colon, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease [33].
The high quality of our spectra allowed us to quantitatively account spectral modifications eventually induced by the inflammatory state as a consequence of changes in the secondary structures, by focusing our attention into the amide I region. For the reasons explained above, and as already reported in literature [46,47], this band constitutes an excellent marker to quantify the secondary structure and conformational changes of proteins, as a consequence of the role played by the amide moiety in crosslinking [48].
In order to do so, the several secondary structures of proteins contributing to the unresolved amide I band need to be distinguished, by separating the corresponding components through second derivative computations, deconvolution and curve-fitting. About this, it is worth remarking that there are clearly other methods to process the Raman spectra without fitting. For example, quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics calculations were recently used for computing the Raman spectra of the Phycocyanobilin Chromophore in α-C-Phycocyanin [49]. Again, the quantification of protein secondary structure content was achieved by multivariate analysis of Raman spectra [50]. A multivariate approach, on the other hand, considers the entire spectral profile, not just a single Raman band or frequency. In the present study, our attention was mainly focused on the investigation of the amide I region, for which the interpretation of protein peaks relies upon curve-fitting to extract information about the protein structure.
In this sense, the main problem we encountered in the analysis of our spectra is the overlapping of several components that contribute to the Raman vibrational profile observed in the 1300–1800 cm−1 range. According to a well-established procedure [51], we decided to fit, first of all, the whole spectrum by means of Voigt lineshapes. After that, all those sub-bands falling out from the amide I range were subtracted from the total fits. A second, more detailed curve-fitting was then carried out only for the amide I region. The analysis of the second derivative of the spectra was applied in order to gain, by evaluating the minima in the obtained profiles, a first indication of the peak positions of the band components [14,52]. In this regard, it is worth remarking that second derivative computation has been already proved to be successful in quantifying secondary structure changes in proteins [53,54]. Starting from it, four main sub-bands were recognized, centered at ~ 1617 cm−1, ~ 1634 cm−1, ~ 1663 cm−1, and ~ 1694 cm−1 respectively. Based on comparison of the obtained center-frequencies with those reported in literature [43,53], they have been correlated to intermolecular β-sheet (), characterized by strong hydrogen bond (indicative of protein aggregates), antiparallel β-sheet (, ), and disordered secondary structures (). It is worth underlining that, in principle, the presence of the α-helix structures from the analysis of the amide I modes cannot be excluded. However, about this, we have to remark that the choice of the number of components for the spectral decomposition of the band was based on the following criteria: (1) minimum number of components; (2) acknowledged secondary structures present in the system; (3) spectral criteria (second derivative computation); and (4) generation of a reasonable fit. Hence, even if the evaluation of the second derivative profiles of the experimental Raman spectra indicated four main sub-bands and the curve fitting procedure was applied to the experimental profiles based on these values, the contribution of α-helix structures is also reasonably present in the 1640–1654 cm−1 region.
The results of a typical curve fitting procedure obtained for a non-IBD subject, and those for an example subject with CD and with UC are reported in Figure 3a–c. In the inset, the calculated second derivative profile of the experimental Raman spectrum of an example non-IBD subject is reported.
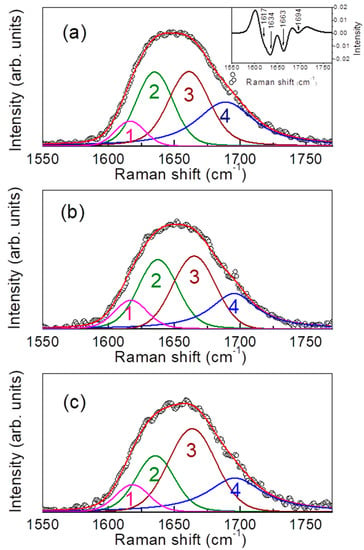
Figure 3.
Curve-fitting results in the amide I region for a non-IBD subject (a), for a subject with CD (b) and for a subject with UC (c). Experimental points: black circles; best-fit: red line; individual components: magenta, green, brown, and blue lines. In the inset, example of second derivative profile calculated for the experimental Raman spectrum of the non-IBD subject.
Even if we are conscious of the arbitrariness intrinsically related to the best-fit procedure, which can lead to an overinterpretation of the data, we want to underline that the minimum number of parameters was used in the protocol here adopted, and these furnished, at the same time, a very good reproduction of the data. For all the investigated samples best-fits are, in fact, characterized by ~ 0.9999.
Alterations in protein network as a consequence of the inflammatory state were monitored by evaluating the ratio , where and represent the areas and the curves corresponding to the and components, respectively. It is worth remarking, in this regard, that quantifying ratios of Raman bands is very advantageous, since they are least affected by background fluctuations and preprocessing methods [55]. In particular, as reported in [56], the parameter is related to the nonreducible (trivalent)/reducible (divalent) crosslinking ratio. The obtained values for all the analyzed subjects are reported in Figure 4.
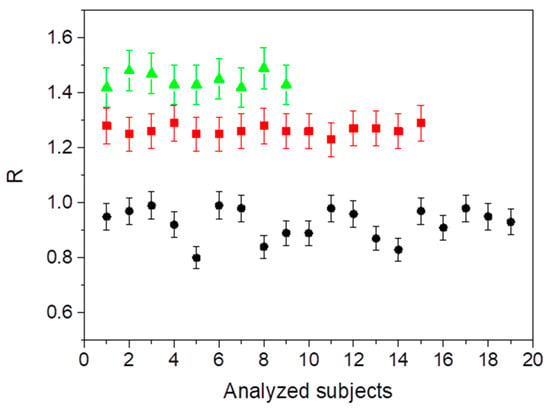
Figure 4.
Calculated values of the ratio for the analyzed non-IBD (black circles), with CD (red squares), and with UC (green triangles) subjects.
Active inflammation is found to give rise to a significant increase in the crosslinking ratio, which passes from an average value of 0.93 ± 0.05 in the case of non-IBD subjects up to 1.26 ± 0.06 and to 1.45 ± 0.07 in the case of subjects with CD and with UC disease, respectively.
Figure 5a illustrates the ROC curve for IBD and non-IBD subjects (AUC = 1, 95% confidence interval). Figure 5b shows the best cut-off point for maximizing sensitivity and specificity (threshold value = 1.2). These curves show that Raman spectroscopy is able to discriminate IBD from non-IBD subjects. In order to highlight the above results, in Figure 5c, the distribution graph for IBD and non-IBD subjects is depicted.
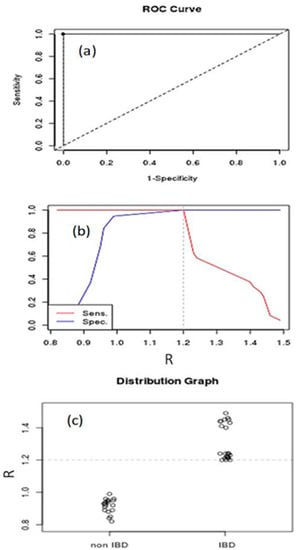
Figure 5.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (a), Youden index and optimal cutoff-point (b), and distribution graph (c) for IBD and non-IBD subjects.
Considering the values obtained from the ratio , we also performed the differentiation between CD and UC in IBD patients. Figure 6a illustrates the ROC curve for IBD subjects (AUC = 1, 95% confidence interval). Figure 6b shows the best cut-off point for maximizing sensitivity and specificity (threshold value = 1.4). These curves show that Raman spectroscopy is able to discriminate UC from CD in IBD subjects. In order to highlight the above results, in Figure 6c, the distribution graph for UC and CD subjects is depicted.
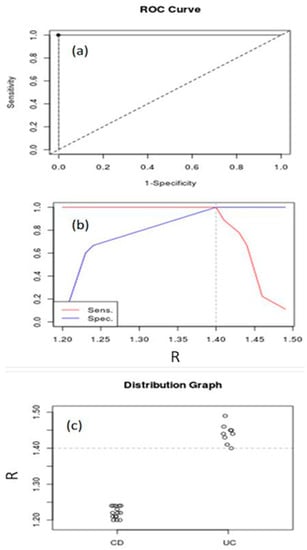
Figure 6.
ROC curve (a), Youden index and optimal cutoff-point (b) and distribution graph (c) for UC and CD in IBD subjects.
4. Discussion
The analysis of the amide I Raman band of calprotectin, deconvoluted in different sub-bands directly correlated with various protein secondary structures, revealed an excellent tool to look at their spectral variations as a consequence of two inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, in childhood.
Starting from this, the purpose of this study was furnishing an evaluation method whose peculiarity lies in its ability of detecting an inflammatory disease without any invasive procedure, such as in vivo analysis and/or biopsy, in an automated and highly efficient way.
This method, deeply described in the previous section, furnished at the same time some information regarding the quality of the protein network induced by the inflammatory state. As a matter of fact, the observed enhancement of the nonreducible (trivalent)/reducible (divalent) crosslinking ratio, as accounted by the parameter , is indicative of an increasing, upon inflammation, of the quantity of trivalent, nonreducible cross-links at the expenses of the divalent reducible ones, and/or as a consequence of their reduced formation. As a consequence, a more strongly interconnected protein network is conceivable, that will clearly result in altered mechanical and functional properties [57].
One could argue that an increase in the amide I band could be also ascribed to protein conformational changes induced by factors different from inflammatory state, including aging, dehydration and radiological conditions [58,59,60]. Nevertheless, these factors don’t affect the reported data, as the groups of subjects were very similar to each other, differing only regarding intestinal inflammation.
The obtained results demonstrated the feasibility of Raman spectroscopy as diagnostic modality for rapid detection of IBD and, among IBD subjects, for a clear and unequivocal distinction between CD and UC. Beyond noninvasiveness, the proposed method offers significant advantages, including ease of use, experimental repeatability and speed of execution. In addition, it is extremely low-cost, compared to the currently used diagnostic techniques requiring special diagnostic kits, and nondestructive, since the sample can be stored and analyzed several times after some time, being the only limit of analysis given by the degradation of the sample itself. Encouraged by the obtained results, the next step of the research will concern the possibility to apply the proposed Raman-based method for an early categorization of disease for patients with indeterminate colitis diagnoses.
5. Conclusions
In the present paper, a rapid, nondestructive, cost-effective and noninvasive diagnostic method for the detection and discrimination of pediatric onset inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), namely Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), is presented. The proposed methodology makes use of Raman spectroscopy in order to probe the changes in secondary structures occurring in proteic extract from fecal samples of pediatric patients that underwent to IBD, i.e., CD or UC, with respect to subjects for which any presence of IBD is excluded. The detected spectral modifications in the protein network were quantified, through a deconvolution procedure into Voigt profiles applied to the broad amide I vibrational band, by the evaluation of the cross-linking ratio between nonreducible (trivalent) and reducible (divalent) structures. The aforementioned parameter is found to significantly increase upon inflammation, suggesting a more interconnected proteic network, and in a different extent according to CD or UC disease. Based on its value, then, the distinction between non-IBD and IBD subjects, and among the last ones, between CD and UC, was achieved.
Accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the proposed diagnostic test were determined using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and Youden index (), which provided excellent results.
The overall results suggest a possible use of the Raman technique as an early diagnostic tool for such classes of inflammatory bowel diseases of very high incidence, with enormous implications in facilitating, for example, early specific treatments, and for which, at the same time, biopsy and/or any invasive procedure are no longer necessary.
6. Patents
A patent application from the work reported in this manuscript is pending.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.A., V.V., S.C. and D.M.; methodology, G.A., V.V., V.C. and D.M.; validation, G.A., V.V., S.C., S.P. and V.C.; formal analysis, G.A. and V.V.; investigation, G.A., S.C. and B.T.; data curation, G.A., V.V. and B.T.; writing—original draft preparation, G.A., V.V. and S.C.; writing—review and editing, G.A., V.V. and S.C.; visualization, G.A., V.V., S.C., S.P. and V.C.; supervision, D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Salarian, M.; Turaga, R.C.; Xue, S.; Nezafati, M.; Hekmatyar, K.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.; Ibhagui, O.Y.; Hai, Y.; et al. Early detection and staging of chronic liver diseases with a protein MRI contrast agent. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pefanis, A.; Botlero, R.; Langham, R.G.; Nelson, C.L. eMAP:CKD: Electronic diagnosis and management assistance to primary care in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ramón Fernández, A.; Ruiz Fernández, D.; Marcos-Jorquera, D.; Gilart Iglesias, V. Support System for Early Diagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on the Service-Oriented Architecture Paradigm and Business Process Management Strategy: Development and Usability Survey Among Patients and Health Care Providers. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, A.M. Specificities of inflammatory bowel disease in childhood. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2004, 18, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, M.J.; Dhawan, A.; Saeed, S.A. Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Children and Adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuffari, C. Diagnostic Considerations in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 5, 775–783. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgart, D.C. The diagnosis and treatment of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2009, 106, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.; Koletzko, S.; Turner, D.; Escher, J.C.; Cucchiara, S.; de Ridder, L.; Kolho, K.L.; Veres, G.; Russell, R.K.; Paerregaard, A.; et al. European Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. ESPGHAN revised porto criteria for the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 795–806. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, R. Recent advances in intestinal imaging. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2011, 21, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, E.; Atkinson, C.; Jepeal, L.I.; Berg, A.; Huang, C.S.; Cerda, S.R.; O’Brien, M.J.; Bigio, I.J.; Farraye, F.A.; Singh, S.K. Elastic scattering spectroscopy as an optical marker of inflammatory bowel disease activity and subtypes. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKalski, B.A.; Bernstein, C.N. New diagnostic imaging tools for inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2006, 55, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I. The Use of Fecal Calprotectin in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 13, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mumolo, M.G.; Bertani, L.; Ceccarelli, L.; Laino, G.; Di Fluri, G.; Albano, E.; Tapete, G.; Costa, F. From bench to bedside: Fecal calprotectin in inflammatory bowel diseases clinical setting. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3681–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsham, N.E.; Sherwood, R.A. Fecal calprotectin in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, E.J.; Sundberg, R.; Tannor, D. Simple aspects of Raman scattering. J. Phys. Chem. 1982, 86, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannor, D.J.; Heller, E.J. Polyatomic Raman scattering for general harmonic potentials. J. Chem. Phys. 1982, 77, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, S.A. UV resonance Raman studies of molecular structure and dynamics: Applications in physical and biophysical chemistry. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1988, 39, 537–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orkoula, M.G.; Kontoyannis, C.G. Raman spectroscopy for the study of biological organisms (biogenic materials and biological tissues): A valuable analytical tool. Spectrosc. Eur. 2014, 26, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Crupi, V.; Majolino, D.; Paciaroni, A.; Rossi, B.; Stancanelli, R.; Venuti, V.; Viliani, G. The effect of hydrogen bond on the vibrational dynamics of genistein free and complexed with β-cyclodextrins. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Longo, F.; Majolino, D.; Venuti, V. Raman spectroscopy: Probing dynamics of water molecules confined in nanoporous silica glasses. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2007, 141, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Majolino, D.; Mele, A.; Rossi, B.; Trotta, F.; Venuti, V. Modelling the interplay between covalent and physical interactions in cyclodextrin-based hydrogel: Effect of water confinement. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 6457–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Galli, G.; La Russa, M.F.; Longo, F.; Maisano, G.; Majolino, D.; Malagodi, M.; Pezzino, A.; Ricca, M.; Rossi, B.; et al. Multi-technique investigation of Roman decorated plasters from Villadei Quintili (Rome, Italy). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wan, Z.; Popov, M.; Carey, P.R.; Weiss, M.A. Insulin assembly damps conformational fluctuations: Raman analysis of amide I linewidths in native states and fibrils. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 330, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladepo, S.A.; Xiong, K.; Hong, Z.; Asher, S.A.; Handen, J.; Lednev, I.K. UV resonance Raman investigations of peptide and protein structure and dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2604–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venuti, V.; Crupi, V.; Fazio, B.; Majolino, D.; Acri, G.; Testagrossa, B.; Stancanelli, R.; De Gaetano, F.; Gagliardi, A.; Paolino, D.; et al. Physicochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Idebenone/Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almond, L.M.; Hutchings, J.; Lloyd, G.; Barr, H.; Shepherd, N.; Day, J.; Stevens, O.; Sanders, S.; Wadley, M.; Stone, N.; et al. Endoscopic Raman spectroscopy enables objective diagnosis of dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 79, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Nawaz, H.; Ditta, A.; Majeed, M.I.; Hanif, M.A.; Rashid, N.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nargis, H.F.; Saleem, M.; Bonnier, F.; et al. Raman spectral analysis for rapid screening of dengue infection. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2018, 200, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevaidi, M.; Morais, C.L.M.; Halliwell, D.E.; Mann, D.M.A.; Allsop, D.; Martin-Hirsch, P.L. Raman Spectroscopy to Diagnose Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies in Blood. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2786–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; McReynolds, N.; Campbell, E.C.; Mazilu, M.; Barbosa, J.; Dholakia, K.; Powis, S. The use of wavelength modulated Raman spectroscopy in label-free identification of T lymphocyte subsets, natural killer cells and dentritic cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125158. [Google Scholar]
- Malini, R.; Venkatakrishna, K.; Kurien, J.; Pai, K.M.; Rao, L.; Kartha, V.B.; Krishna, C.M. Discrimination of normal, inflammatory, premalignant, and malignant oral tissue: A Raman spectroscopy study. Biopolymers 2006, 81, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, J.; Mohammed, N.; Rotimi, O.; Magee, D.; Jha, A.; Subramanian, V. Raman spectroscopy of endoscopic colonic biopsies from patients with ulcerative colitis to identify mucosal inflammation and healing. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2022–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Dupont, A.W.; Singhal, S.; Scott, L.D.; Guha, S.; Younes, M.; Bi, X. In vivo analysis of mucosal lipids reveals histological disease activity in ulcerative colitis using endoscope-coupled Raman spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3426–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pence, I.J.; Beaulieu, D.B.; Horst, S.N.; Bi, X.; Herline, A.J.; Schwartz, D.A.; Mahadevanjansen, A. Clinical characterization of in vivo inflammatory bowel disease with Raman spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. ROC analysis applied to the evaluation of medical imaging techniques. Investig. Radiol. 1979, 14, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, J.A. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) methodology: The state of the art. Crit. Rev. Diagn. Imaging 1989, 29, 307–335. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglione, F.; Crupi, V.; Majolino, D.; Mele, A.; Rossi, B.; Trotta, F.; Venuti, V. Vibrational spectroscopy investigation of swelling phenomena in cyclodextrin nanosponges. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummar, R.; Indrayan, A. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for medical researchers. Indian Pediatr. 2011, 48, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajian, K. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis for Medical Diagnostic Test Evaluation. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 4, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Assessing the fit of the model. In Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Schisterman, E.F.; Perkins, N.J.; Liu, A.; Bondell, H. Optimal cut-point and its corresponding Youden Index to discriminate individuals using pooled blood samples. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Tian, L. Joint confidence region estimation for area under ROC curve and Youden index. Statist. Med. 2014, 33, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.J.; Schisterman, E.F. The inconsistency of optimal cut-points obtained using two criteria based on receiver operating characteristic curve. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurouski, D.; Van Duynea, R.P.; Lednev, I.K. Exploring the structure and formation mechanism of amyloid fibrils by Raman spectroscopy: A review. Analyst 2015, 140, 4967–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyaci, I.H.; Temiz, H.T.; Geniş, H.E.; Soykut, E.A.; Yazgan, N.N.; Güven, B.; Uysal, R.S.; Bozkurt, A.G.; İlaslan, K.; Torun, O.; et al. Dispersive and FT-Raman spectroscopic methods in food analysis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 56606–56624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Happillon, T.; Feru, J.; Brassart-Passco, S.; Angiboust, J.F.; Manfait, M.; Piot, O. Raman comparison of skin dermis of different ages: Focus on spectral markers of collagen hydration. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.Y.; Li, C.; Nguyen, X.; Muzammil, S.; Towers, E.; Gabrielson, J.; Narhi, L. Qualification of FTIR spectroscopic method for protein secondary structural analysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 4631–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Yu, S. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of protein secondary structures. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandekar, J. Amide modes and protein conformation. BBA Protein Struct. M. 1992, 1120, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroginski, M.A.; Mark, F.; Thiel, W.; Hildebrand, P. Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Calculation of the Raman Spectra of the Phycocyanobilin Chromophore ina-C-Phycocyanin. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshokoya, O.O.; Roach, C.A.; JiJi, R.D. Quantification of protein secondary structure content by multivariate analysis of deep-ultraviolet resonance Raman and circular dichroism spectroscopies. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorelli, S.; Cannistraro, S.; Bizzarri, A.R. Raman Evidence of p53-DBD Disorder Decrease upon Interaction with the Anticancer Protein Azurin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Majolino, D.; Mele, A.; Melone, L.; Punta, C.; Rossi, B.; Toraldo, F.; Trotta, F.; Venuti, V. Direct evidence of gel–sol transition in cyclodextrin-based hydrogels as revealed by FTIR-ATR spectroscopy. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 2320–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usoltsev, D.; Sitnikova, V.; Kajava, A.; Uspenskaya, M. Systematic FTIR Spectroscopy Study of the Secondary Structure Changes in Human Serum Albumin under Various Denaturation Conditions. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.; Luczak, A.; Ganesh, V.; Park, E.; Kalyanaraman, R. Protein Secondary Structure Determination Using Drop Coat Deposition Confocal Raman Spectroscopy. Spectroscopy 2016, 31, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Verma, T.; Mukherjee, R.; Ariese, F.; Somasundaram, K.; Umapathy, S. Raman and infra-red microspectroscopy: Towards quantitative evaluation for clinical research by ratiometric analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1879–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Bora, T.; Al Ghaithi, A.; Thukral, S.; Dutta, J. Raman Spectroscopy detects changes in Bone Mineral Quality and Collagen Cross-linkage in Staphylococcus Infected Human Bone. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orkoula, M.G.; Vardaki, M.Z.; Kontoyannis, C.G. Study of bone matrix changes induced by osteoporosis in rat tibia using Raman spectroscopy. Vib. Spectrosc. 2012, 63, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, C.B.; Einhorn, M.; Dagan, R.; Yagupski, P.; Porat, S. Fine-needle bone biopsy to diagnose osteomyelitis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1994, 76, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, R.A.; van Langevelde, P.; Kristjansson, M.; Maslow, J.N.; Arbeit, R.D. Persistent and relapsing infections associated with small-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1995, 20, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.C.; Ramp, W.K.; Nicholson, N.C.; Williams, A.S.; Nousiainen, M.T. Internalization of Staphylococcus aureus by cultured osteoblasts. Microb. Pathogenesis 1995, 19, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).