Formaldehyde Emission in Micron-Sized Wollastonite-Treated Plywood Bonded with Soy Flour and Urea-Formaldehyde Resin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Panel Production
2.2. Resin Application
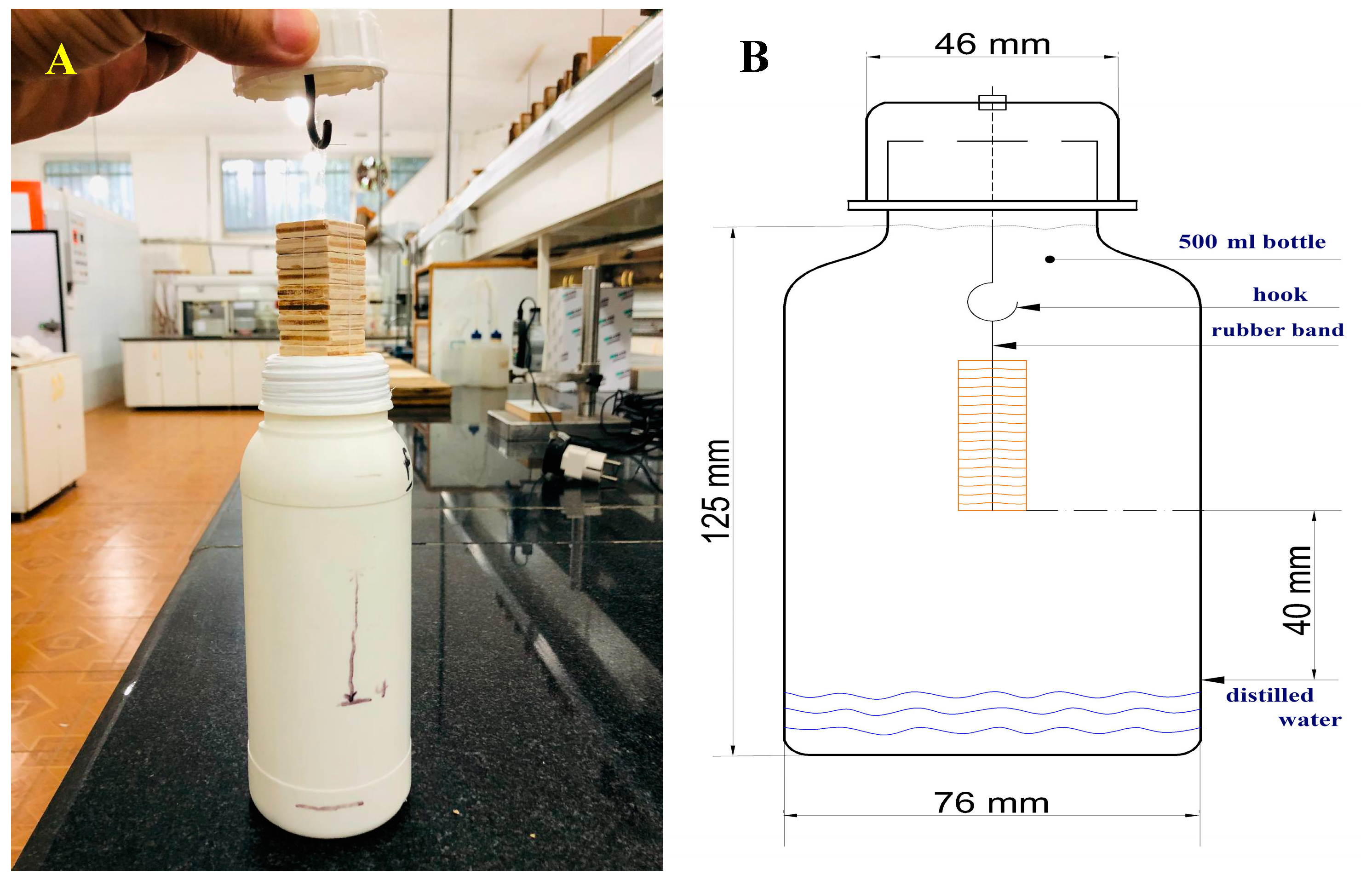
2.3. Measurement of Formaldehyde Emission
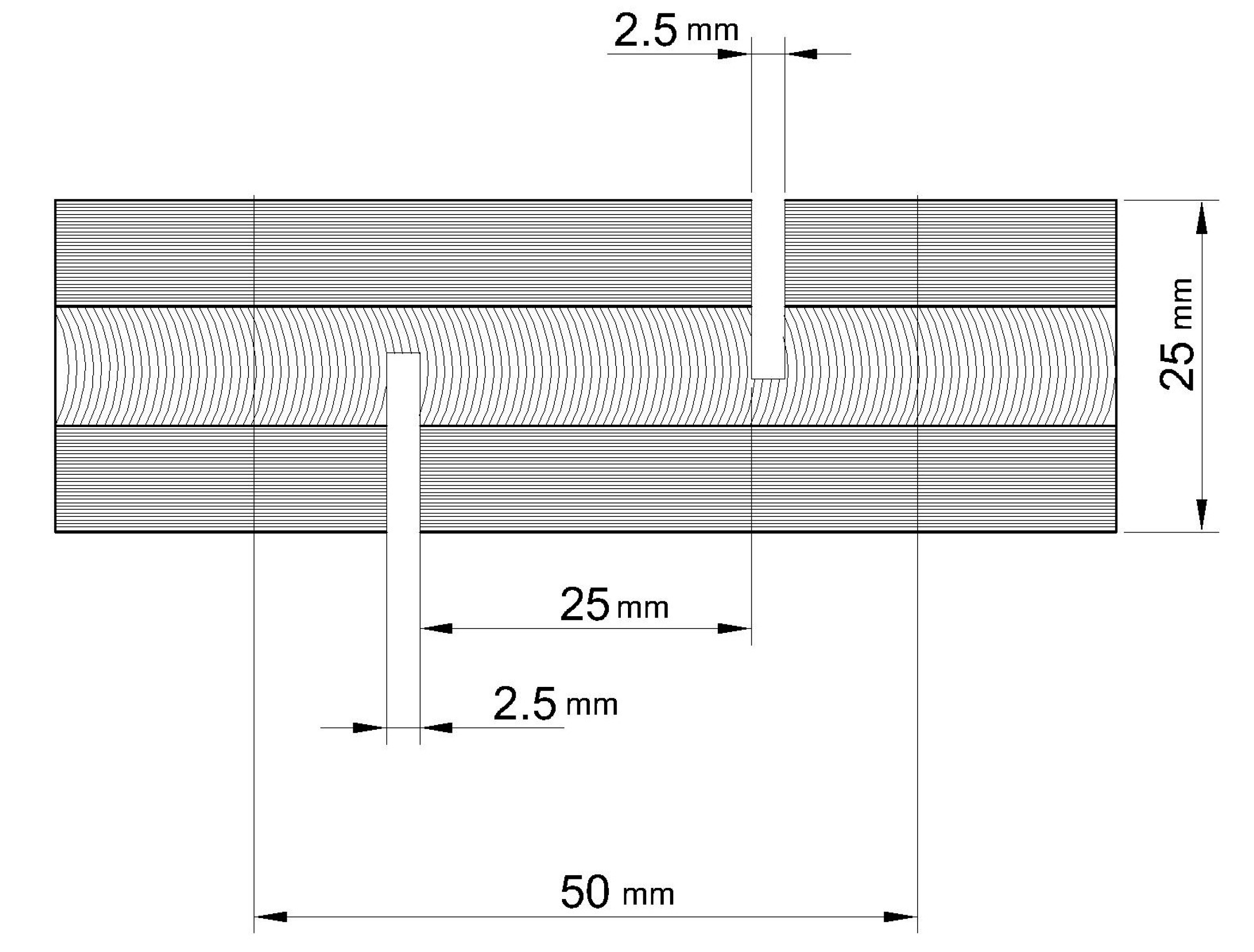
2.4. Shear-Strength Test
2.5. Delamination Test
2.6. Statistical Analysis
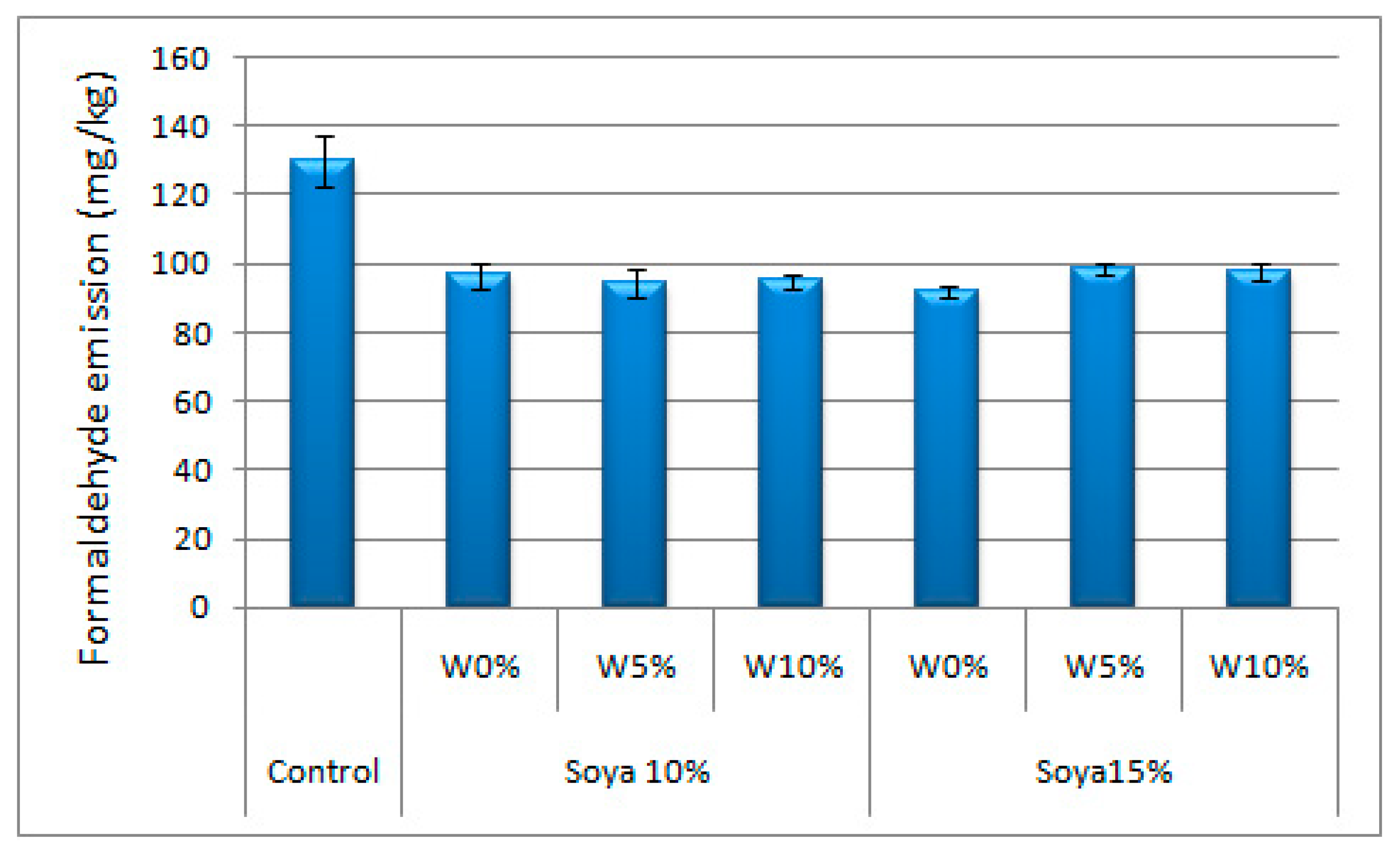
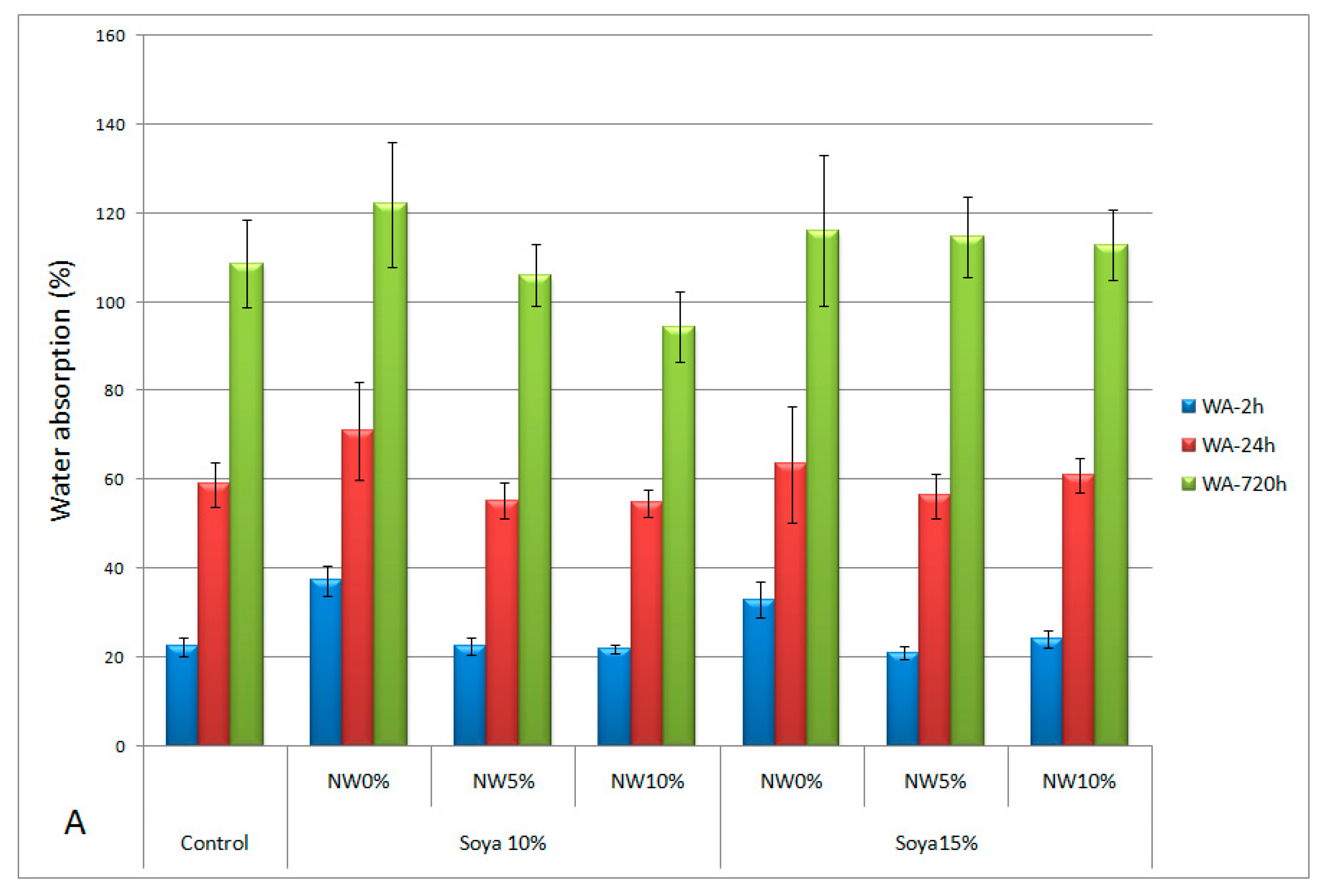
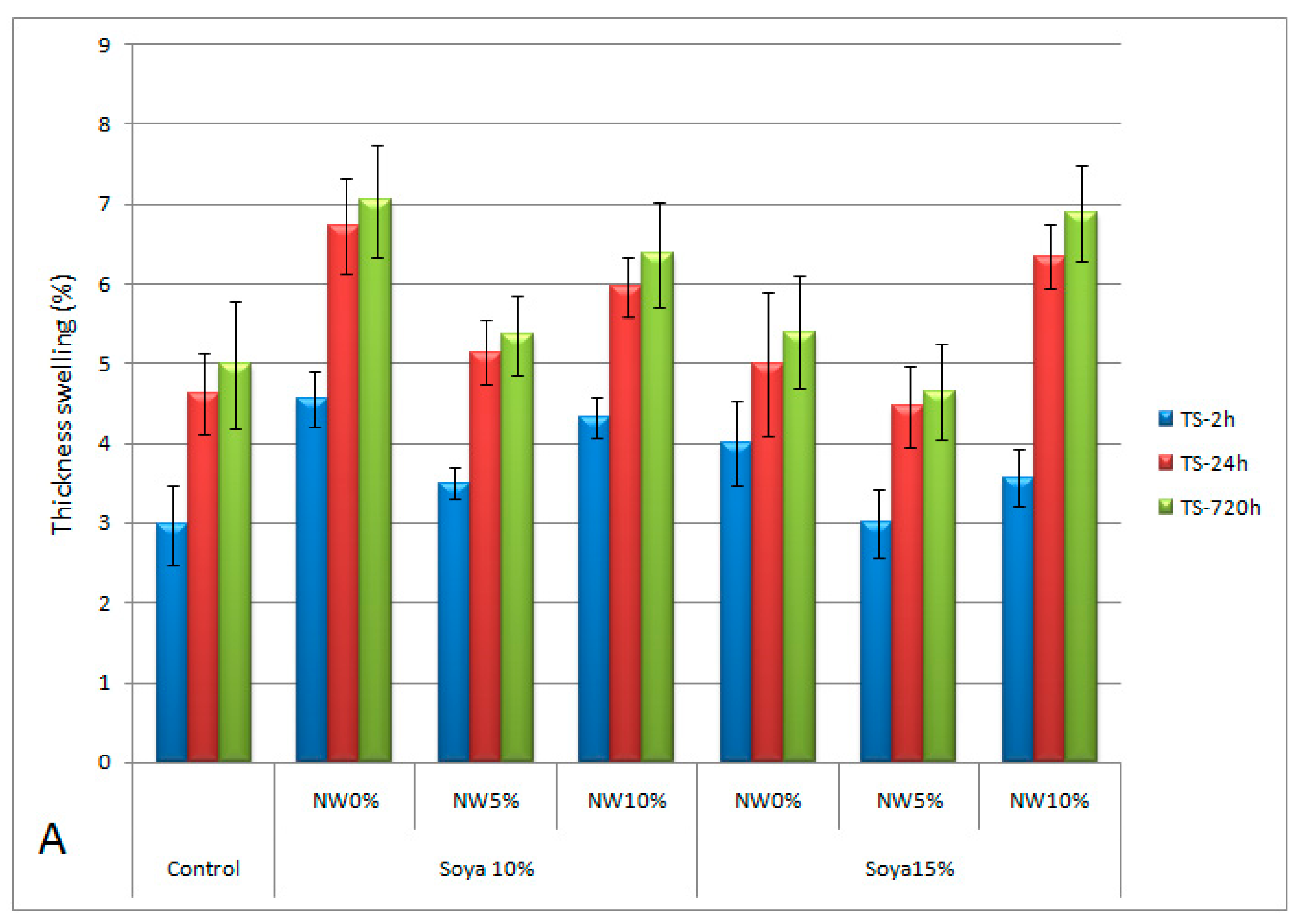
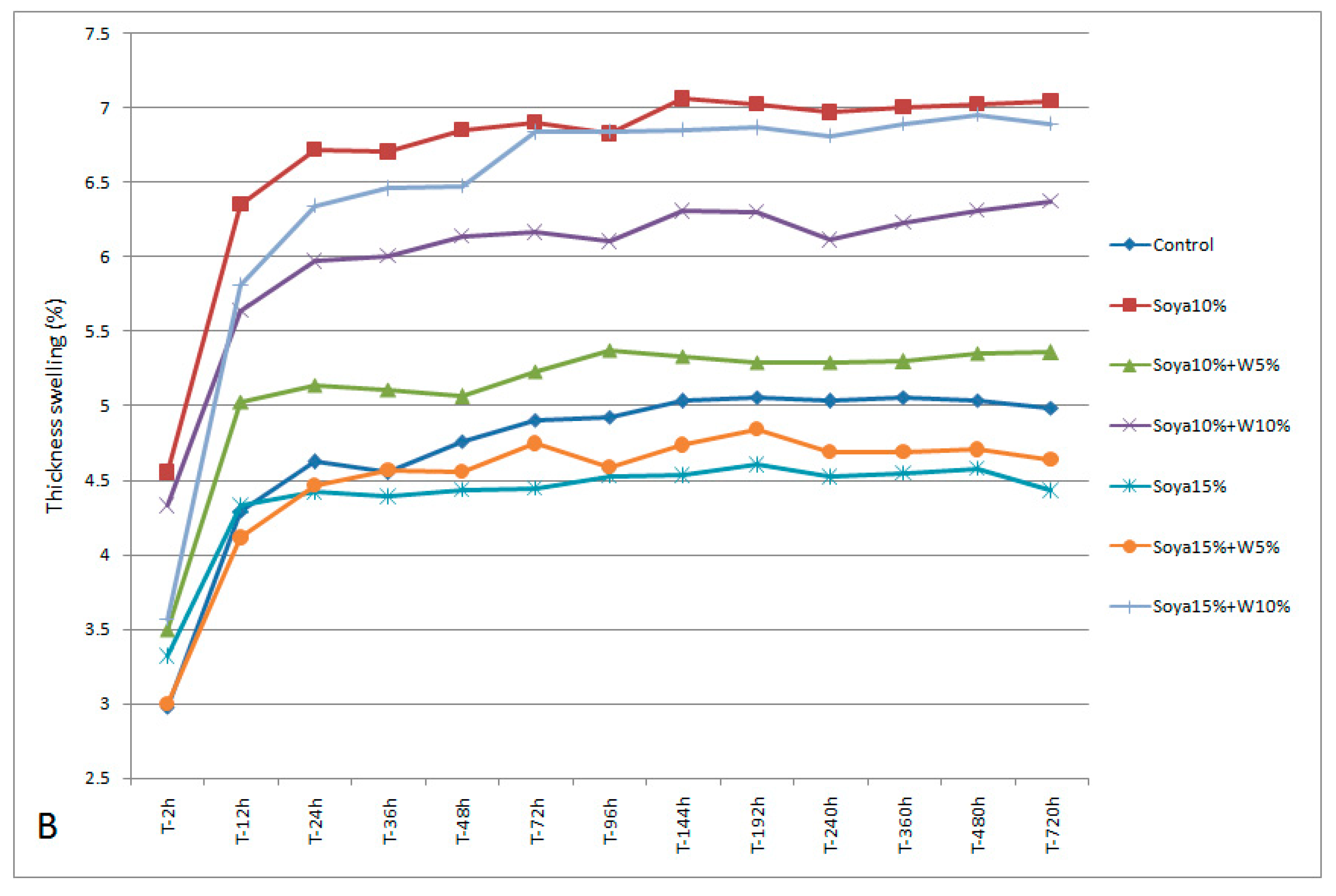
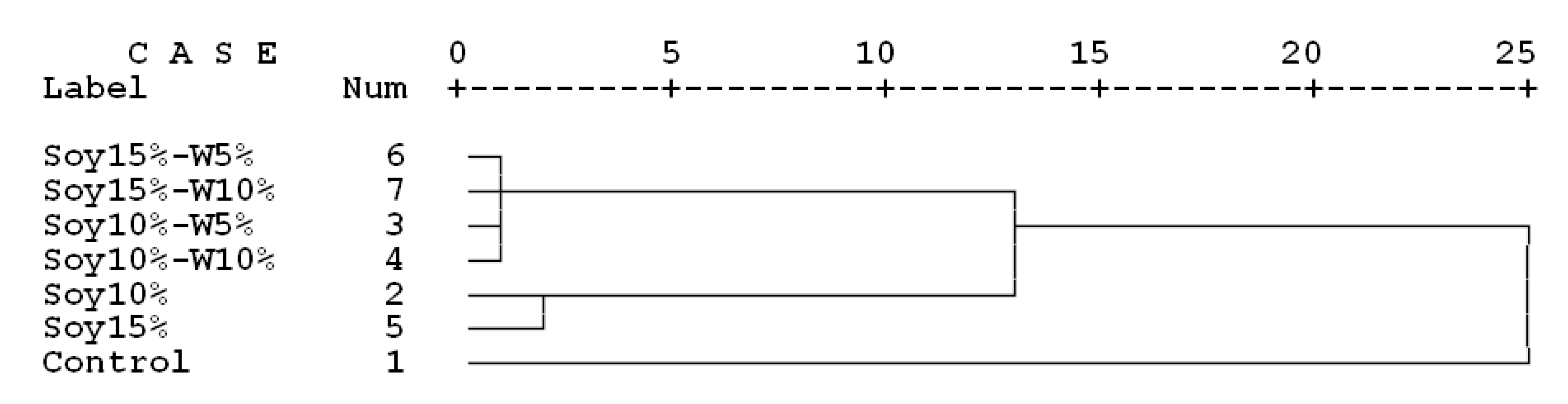
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Study
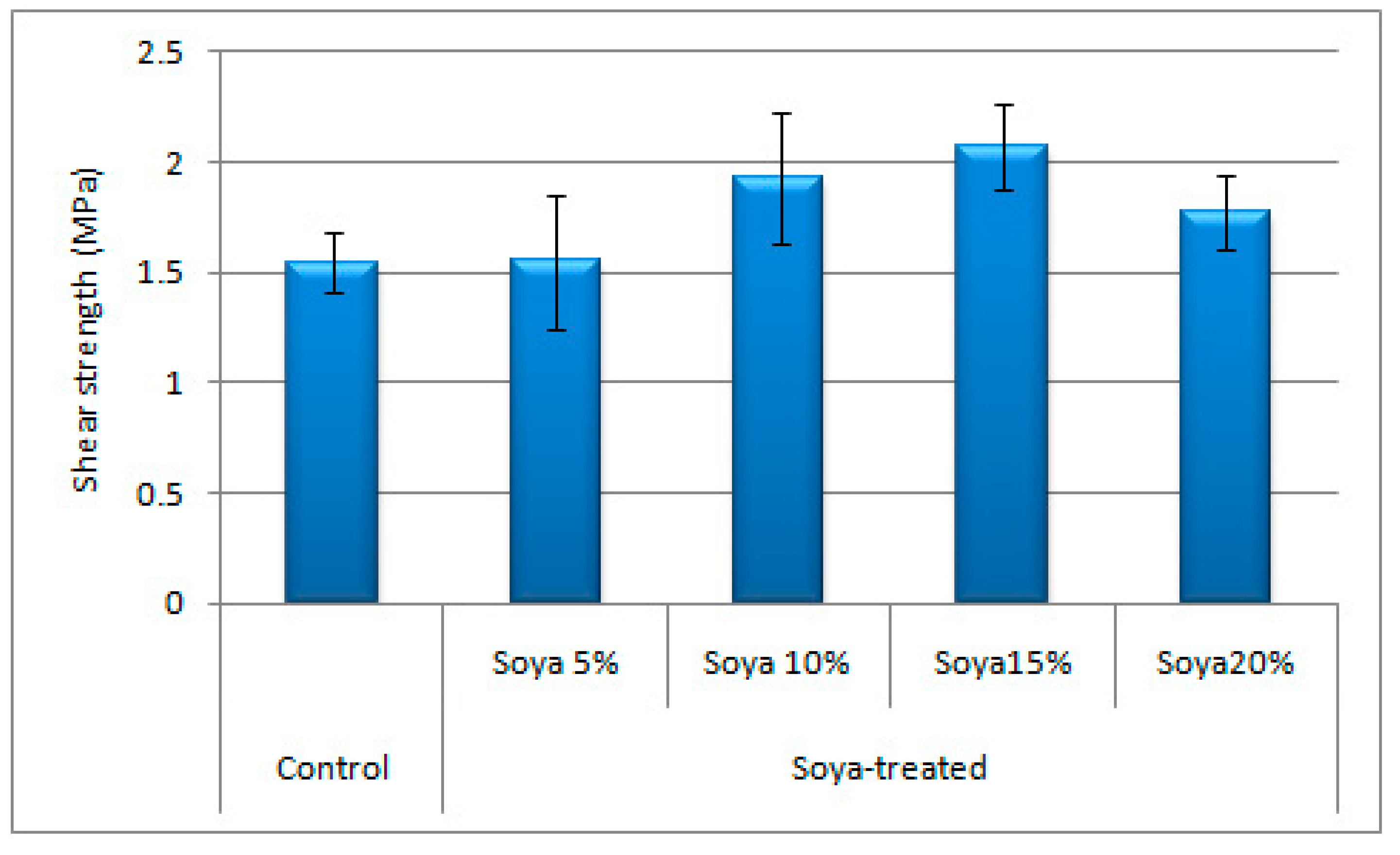
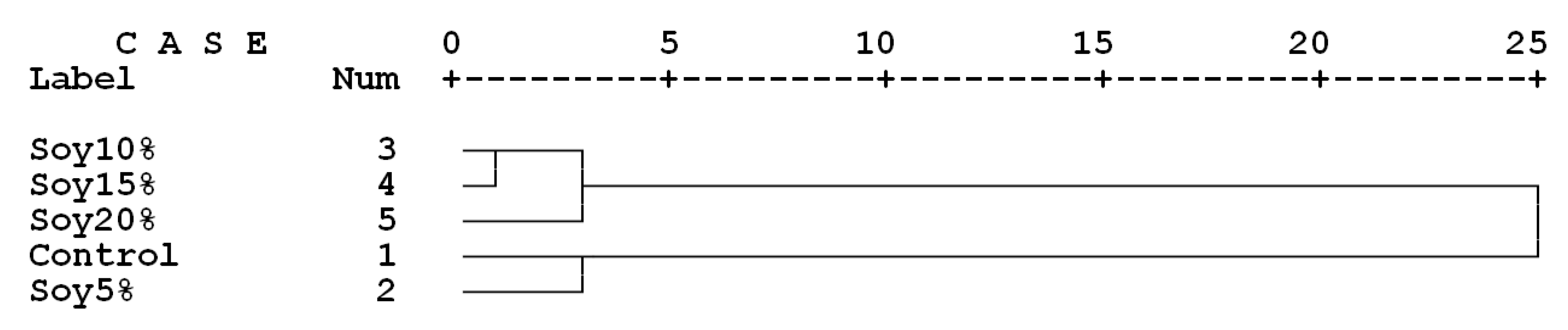
3.2. Main Phase of the Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pizzi, A.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Policardi, F. Wood composites and their polymer binders. Polymers 2020, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopt, P.; Konnerth, J.; Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Katner, W.; Moser, J.; Mitter, R.; van Herwijnen, H. Technological performance of formaldehyde-free adhesive alternatives for particleboard industry. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 94, 99–131. [Google Scholar]
- Roffael, E. Formaldehyde release from wood-based panels—A review. Holz als Roh Werkst 1989, 47, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthammer, T.; Mentese, S.; Marutzky, R. Formaldehyde in the indoor environment. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2536–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzi, A.; Lipschitz, L.; Valenzuela, J. Theory and practice of the preparation of low formaldehyde emission UF adhesives for particleboard. Holzforschung 1994, 48, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunker, A.K.; Johns, W.E.; Rammon, R.; Farmer, B.; Johns, S.Y. Slightly Bizarre Protein Chemistry: Urea-Formaldehyde Resin from a Biochemical Perspective. J. Adhes. 1986, 19, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levendis, D.; Pizzi, A.; Ferg, E.E. The correlation of strength and formaldehyde emission with the crystalline/amorphous structure of UF resins. Holzforschung 1992, 45, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferg, E.E.; Pizzi, A.; Levendis, D. A 13 C NMR analysis method for urea-formaldehyde resin strength and formaldehyde emission. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 50, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, M.A.R.; Park, B.D. Enhancing the performance of low molar ratio urea–formaldehyde resin adhesives via in-situ modification with intercalated nanoclay. J. Adhes. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, N.; Jarroux, N.; Robitzer, M.; Majdoub, M.; Habas, J.P. Optimized synthesis according to one-step process of a biobased thermoplastic polyacetal derived from isosorbide. Polymers 2016, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, M.; Li, T.; Yang, L.; Duan, Z.; Zhou, X.; Du, G. Characterization of the low molar ratio urea–formaldehyde resin with 13C NMR and ESI–MS: Negative effects of the post-added urea on the urea–Fformaldehyde polymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, H. Effect of bio-scavengers on the curing behavior and bonding properties of melamine-formaldehyde resins. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. The reduction of indoor air pollutant from wood-based composite by adding pozzolan for building materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2319–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réh, R.; Igaz, R.; Krišťák, Ľ.; Ružiak, I.; Gajtanska, M.; Božíková, M.; Kučerka, M. Functionality of beech bark in adhesive mixtures used in plywood and its effect on the stability associated with material systems. Materials 2019, 12, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Song, S.; Wu, G.; Pu, J. Modified nanocrystalline cellulose from two kinds of modifiers used for improving formaldehyde emission and bonding strength of urea-formaldehyde resin adhesive. BioResources 2011, 6, 4430–4438. [Google Scholar]
- Kawalerczyk, J.; Siuda, J.; Mirski, R.; Dziurka, D. Hemp flour as a formaldehyde scavenger for melamine-urea-formaldehyde adhesive in plywood production. BioResources 2020, 15, 4052–4064. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, A.; Corneau, D. Effectiveness of barriers to minimize VOC emissions including formaldehyde. For. Prod. J. 2006, 56, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dunky, M. Urea-formaldehyde (UF) adhesive resins for wood. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 1998, 18, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzkopf, M.; Huang, J.; Li, K. A formaldehyde-free soy-based adhesive for making oriented strandboard. J. Adhes. 2010, 86, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Labat, G.A.; Pizzi, A.; Gonc, A.R.; Celzard, A.; Rigolet, S.; Rocha, G.J.M.; Eel, D.E.; Paulo, S. Environment-friendly soy flour-based resins without. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Peshkova, S.; Geng, X. Investigation of soy protein-kymene ® adhesive systems for wood composites. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 81, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.B.; Assadollahzadeh, M.; Najfai, S.K.; Taherzadeh, J. Partial replacement of urea-formaldehyde adhesive with fungal biomass and soy flour in plywood fabrication. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalerczyk, J.; Dziurka, D.; Mirski, R.; Trocinski, A. Flour fillers with urea formaldehyde resin in plywood. BioResources 2019, 14, 6727–6735. [Google Scholar]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Karimi, A.; Tahir, P.M.D. Nano-wollastonite in particleboard: Physical and mechanical properties. BioResources 2013, 8, 5721–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Majidi, R.; Jahangiri, A. Adsorption of nano-wollastonite on cellulose surface: Effects on physical and mechanical properties of medium-density fiberboard (MDF). CERNE 2016, 22, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Mohammad-Panah, B.; Morrell, J.J. Effects of wollastonite on the properties of medium-density fiberboard (MDF) made from wood fibers and camel-thorn. Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2016, 18, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantanis, G.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Reducing the thickness swelling of wood based panels by applying a nanotechnology compound. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2010, 68, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanomaterials and chemical modification technologies for enhanced wood properties: A review. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Esmailpour, A.; Adamopoulos, S.; Zereshki, K.; Hosseinpourpia, R. Shear strength of heat-treated solid wood bonded with polyvinyl-acetate reinforced by nanowollastonite. Wood Res. 2020, 65, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailpour, A.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Ghorbanali, M.; Mantanis, G.I. Improving fire retardancy of medium density fiberboard by nano-wollastonite. Fire Mater. 2020, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.N.; Gkaraveli, A. Dimensional stabilisation and strength of particleboard by chemical modification with propionic anhydride. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2003, 61, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Majidi, R.; Mohseni Armaki, S.M.; Haghighatparast, M. Graphene as reinforcing filler in polyvinyl acetate resin. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Funk, M.; Wimmer, R.; Adamopoulos, S. Diatomaceous earth as an inorganic additive to reduce formaldehyde emissions from particleboards. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A. Construction of active bio-nanocomposite by inseminated metal nanoparticles onto activated carbon: Probing to antimicrobial activity. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, V.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Schmidt, O.; Maleki, S.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Mechanical and physical properties of oriented strand lumber (OSL): The effect of fortification level of nanowollastonite on UF resin. Polymers 2019, 11, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EN 717-3. Wood Based Panels-Determination of Formaldehyde Release-Part 3: Formaldehyde Release by the Flask Method; Comite Europeen de Normalisation: Brussels, Belgium, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, F.; Pereira, J.; Paiva, N.; Ferra, J.; Martins, J.; Magalhaes, F.; Carvalho, L. Natural additive for reducing formaldehyde emissions in urea-formaldehyde resins. J. Renew. Mater. 2016, 4, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.J.; Marcinko, J.J.; Wagler, T.A.; Sosnowick, A.J. Investigations of the molecular interactions of soy-based adhesives. For. Prod. J. 2010, 60, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Damodaran, S. Chemical phosphorylation improves the moisture resistance of soy flour-based wood adhesive. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahri, S.; Pizzi, A. Improving soy-based adhesives for wood particleboard by tannins addition. Wood Sci. Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahri, S.; Mohebby, B.; Pizzi, A.; Mirshokraie, A.; Mansouri, H.R. Improving water resistance of soy-based adhesive by vegetable tannin. J. Polym. Environ. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailpour, A.; Majidi, R.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Ganjkhani, M.; Mohseni Armaki, S.M.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Improving fire retardancy of beech wood by graphene. Polymers 2020, 12, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Component | Proportion (% w/w) |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 46.96 |
| CaO | 39.77 |
| Al2O3 | 3.95 |
| Fe2O3 | 2.79 |
| TiO2 | 0.22 |
| K2O | 0.04 |
| MgO | 1.39 |
| Na2O | 0.16 |
| SO3 | 0.05 |
| Water | 4.67 |
| Binder | First Round 1 | Third Round 2 | Result 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| UF 4 100% | 1/20 | 1/20 | P |
| UF 95% + SF 5 5% | 0/20 | 0/20 | P |
| UF 90% + SF 10% | 1/20 | 1/20 | P |
| UF 85% + SF 15% | 0/20 | 0/20 | P |
| UF 80% + SF 20% | 0/20 | 0/20 | P |
| Binder | First Round 1 | Third Round 2 | Result 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| UF 4 100% | 1/20 | 1/20 | P |
| UF 90% + SF 5 10% | 1/20 | 1/20 | P |
| UF 90% + SF 10% + W 6 5% | 1/20 | 2/20 | P |
| UF 90% + SF 10% + W 10% | 0/20 | 0/20 | P |
| UF 85% + SF 15% | 0/20 | 0/20 | P |
| UF 85% + SF 15% + W 5% | 0/20 | 0/20 | P |
| UF 85% + SF 15% + W 10% | 0/20 | 0/20 | P |
| Binder | pH | Gel Time (s) | Viscosity (6 rpm) (cP) | Viscosity (10 rpm) (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UF 1 100% | 7.4 | 75 | 449.9 | 455.9 |
| UF 95% + SF 2 5% | 5.4 | 105 | 564.9 | 566.9 |
| UF 90% + SF 10% | 5.2 | 128 | 824.8 | 794.8 |
| UF 90% + SF 10% + W 3 5% | 5.6 | 214 | 689.9 | 656.9 |
| UF 90% + SF 10% + W 10% | 5.2 | 230 | 569.9 | 551.9 |
| UF 85% + SF 15% | 5.6 | 146 | 1300 | 1302 |
| UF 85% + SF 15% + W 5% | 5.5 | 172 | 1120 | 1086 |
| UF 85% + SF 15% + W 10% | 5.1 | 158 | 949.8 | 902.8 |
| UF 80% + SF 20% | 5.6 | 172 | 2000 | 1911 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taghiyari, H.R.; Hosseini, S.B.; Ghahri, S.; Ghofrani, M.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Formaldehyde Emission in Micron-Sized Wollastonite-Treated Plywood Bonded with Soy Flour and Urea-Formaldehyde Resin. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196709
Taghiyari HR, Hosseini SB, Ghahri S, Ghofrani M, Papadopoulos AN. Formaldehyde Emission in Micron-Sized Wollastonite-Treated Plywood Bonded with Soy Flour and Urea-Formaldehyde Resin. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(19):6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196709
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaghiyari, Hamid R., Seyed Behzad Hosseini, Saman Ghahri, Mohammad Ghofrani, and Antonios N. Papadopoulos. 2020. "Formaldehyde Emission in Micron-Sized Wollastonite-Treated Plywood Bonded with Soy Flour and Urea-Formaldehyde Resin" Applied Sciences 10, no. 19: 6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196709
APA StyleTaghiyari, H. R., Hosseini, S. B., Ghahri, S., Ghofrani, M., & Papadopoulos, A. N. (2020). Formaldehyde Emission in Micron-Sized Wollastonite-Treated Plywood Bonded with Soy Flour and Urea-Formaldehyde Resin. Applied Sciences, 10(19), 6709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10196709







