Ultrasound DMAS Beamforming for Estimation of Tissue Speed of Sound in Multi-Angle Plane-Wave Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. BB-DMAS Beamforming
2.2. DMAS Beamforming in Multi-Angle PW Imaging
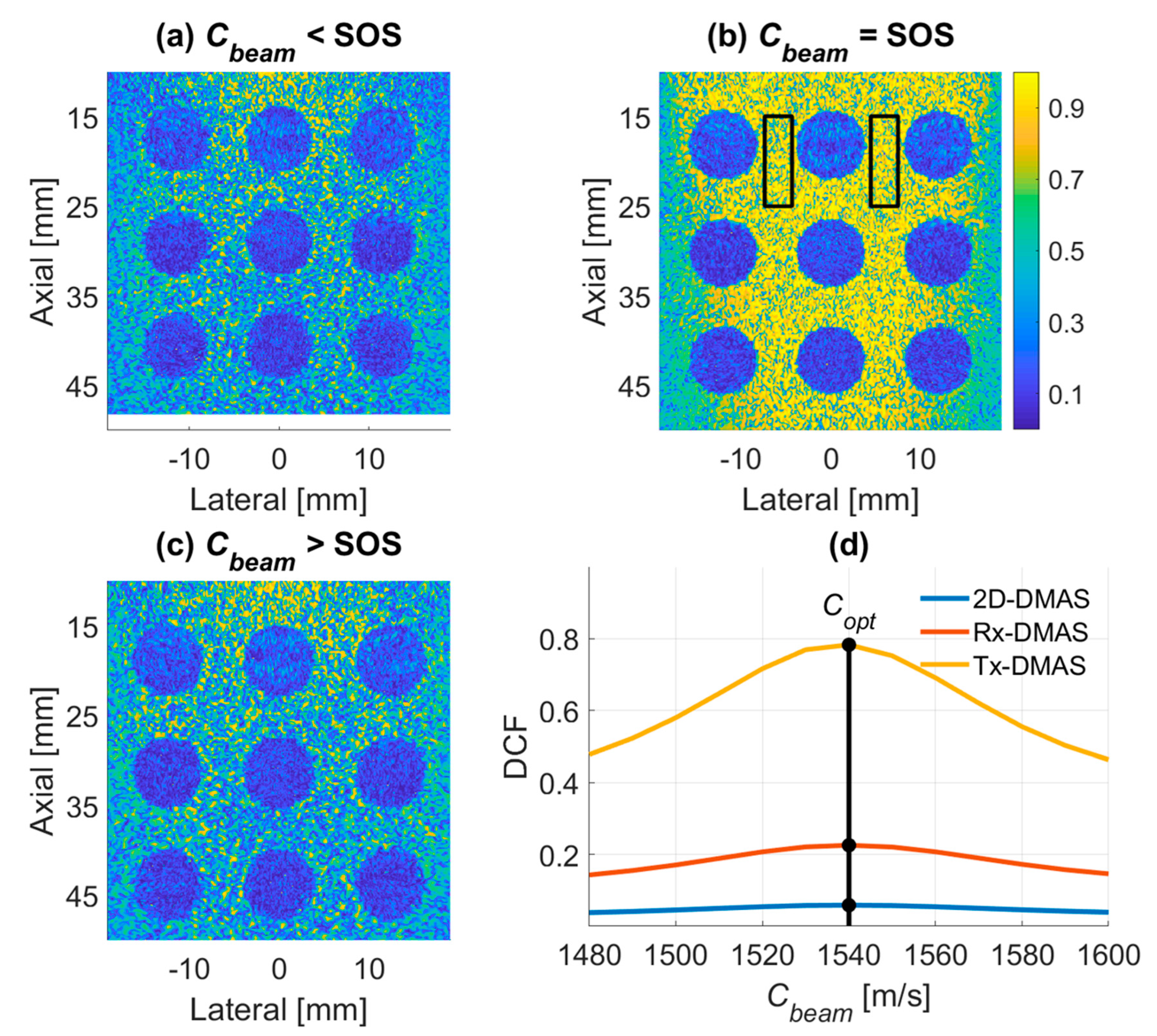
2.3. DCF of Multi-Angle PW Imaging for Tissue SOS Estimation
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
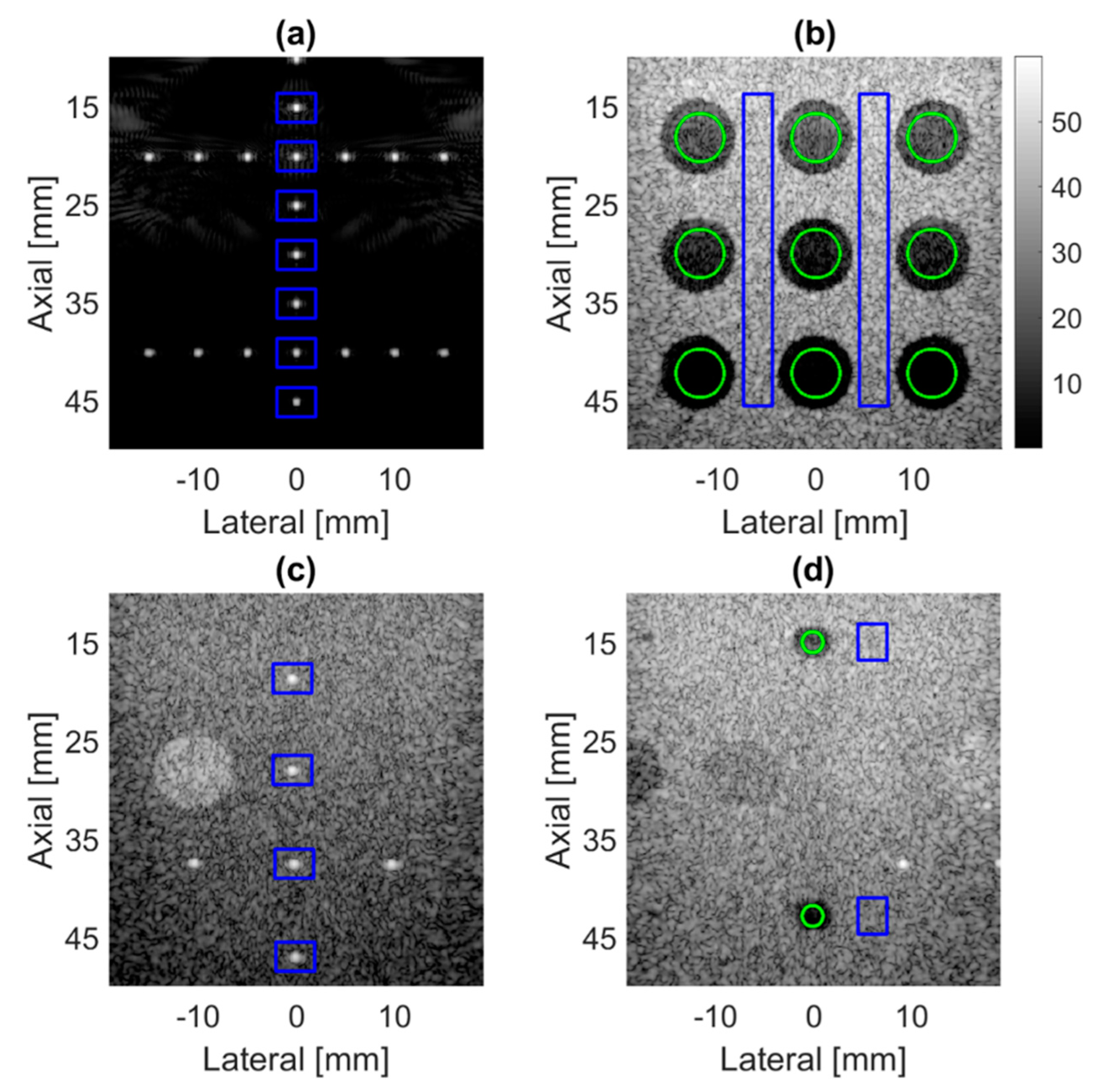
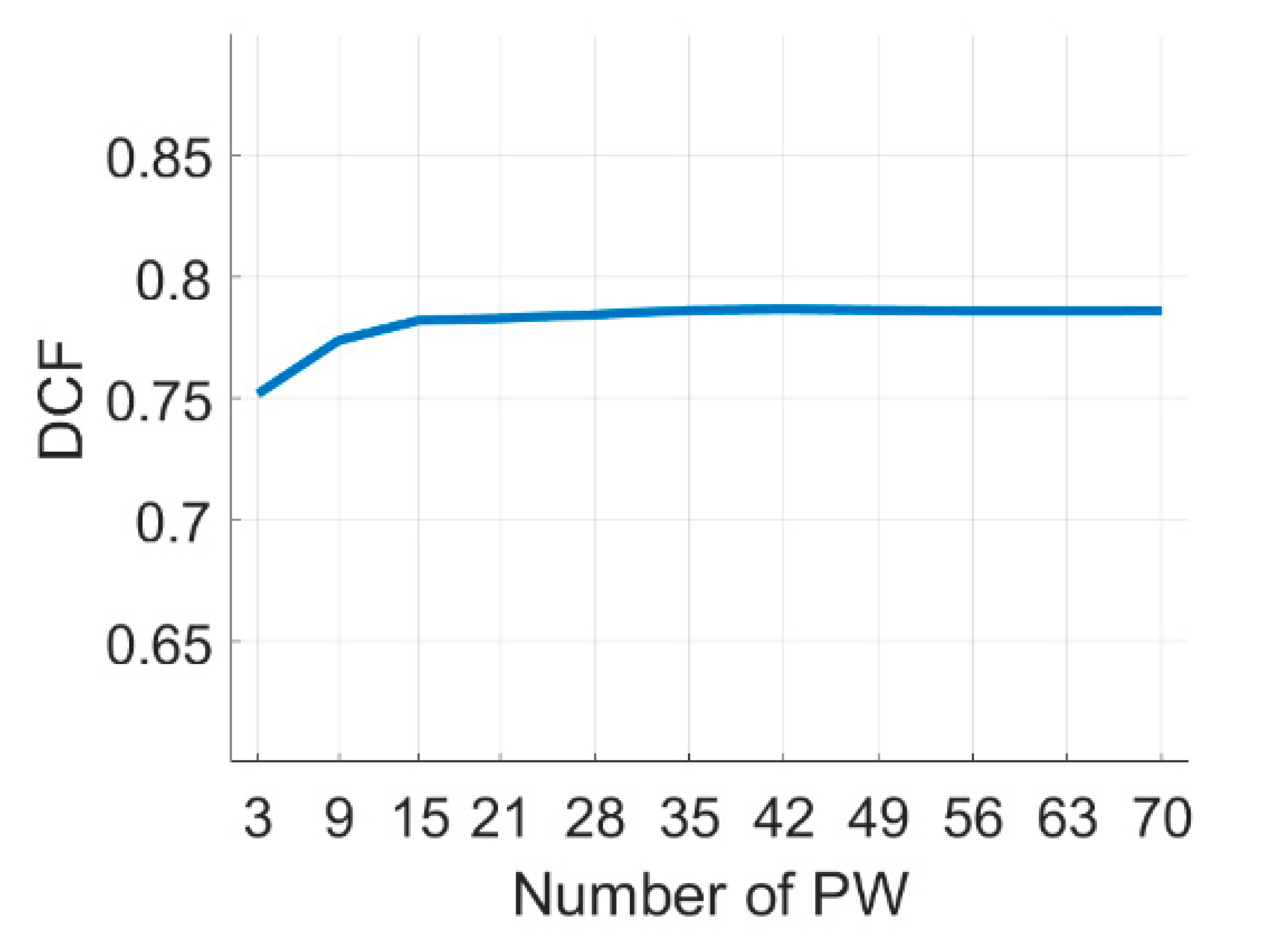
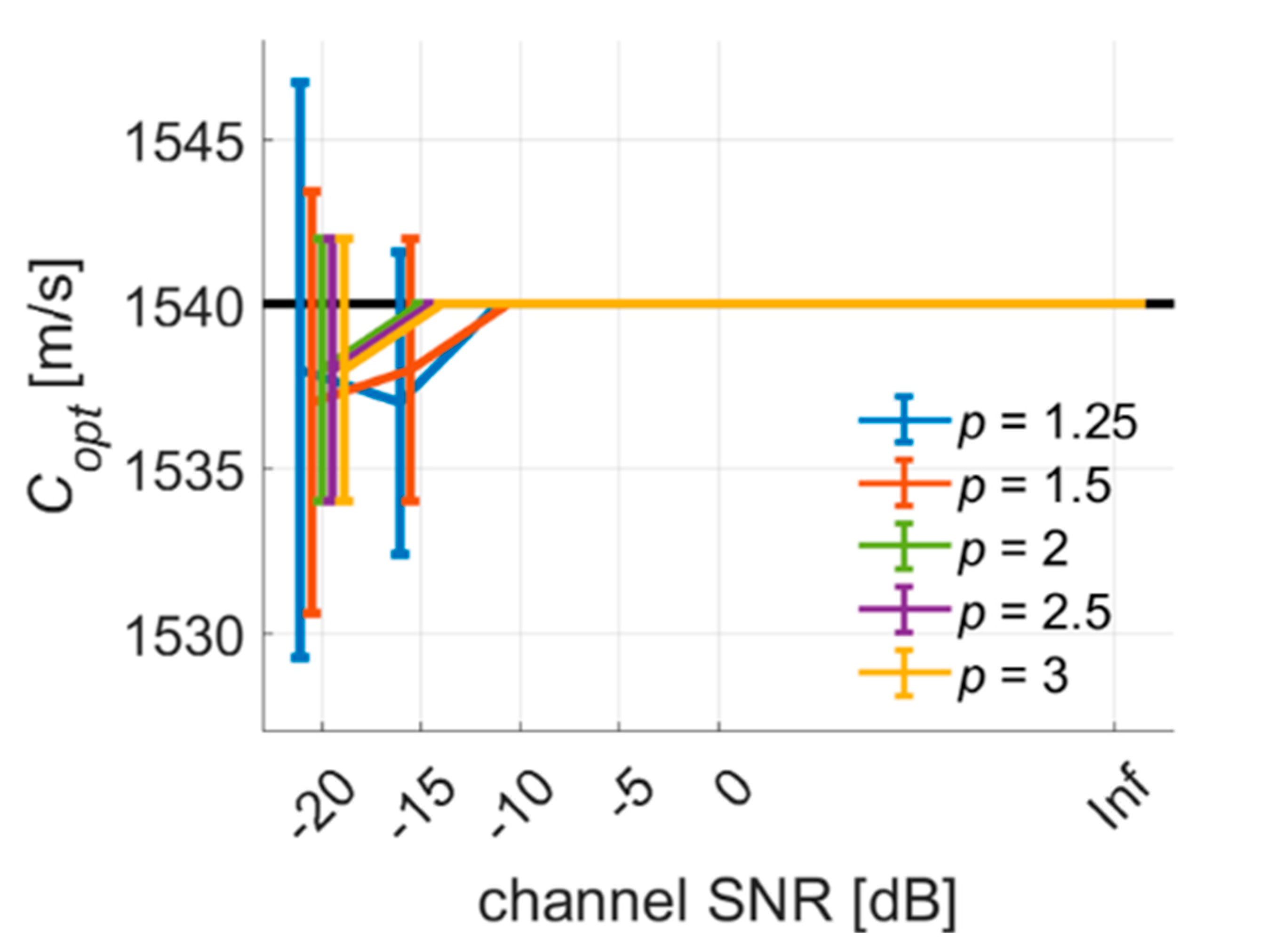
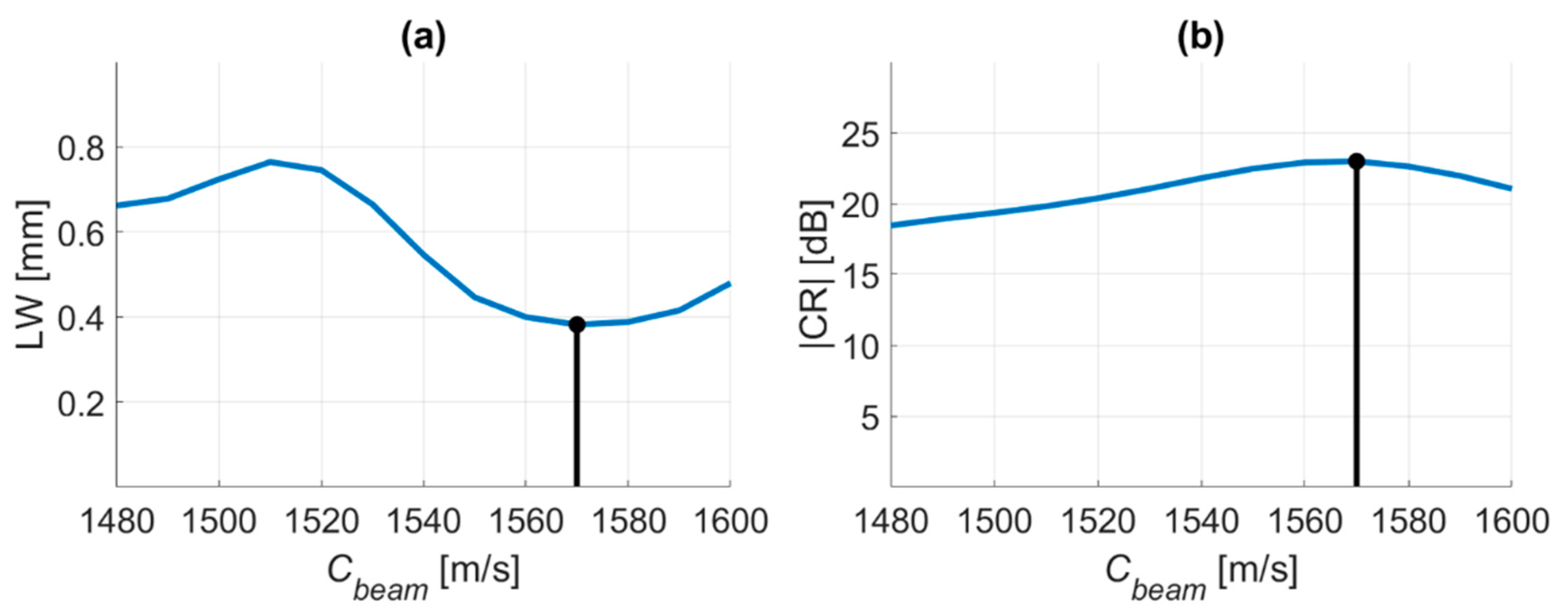
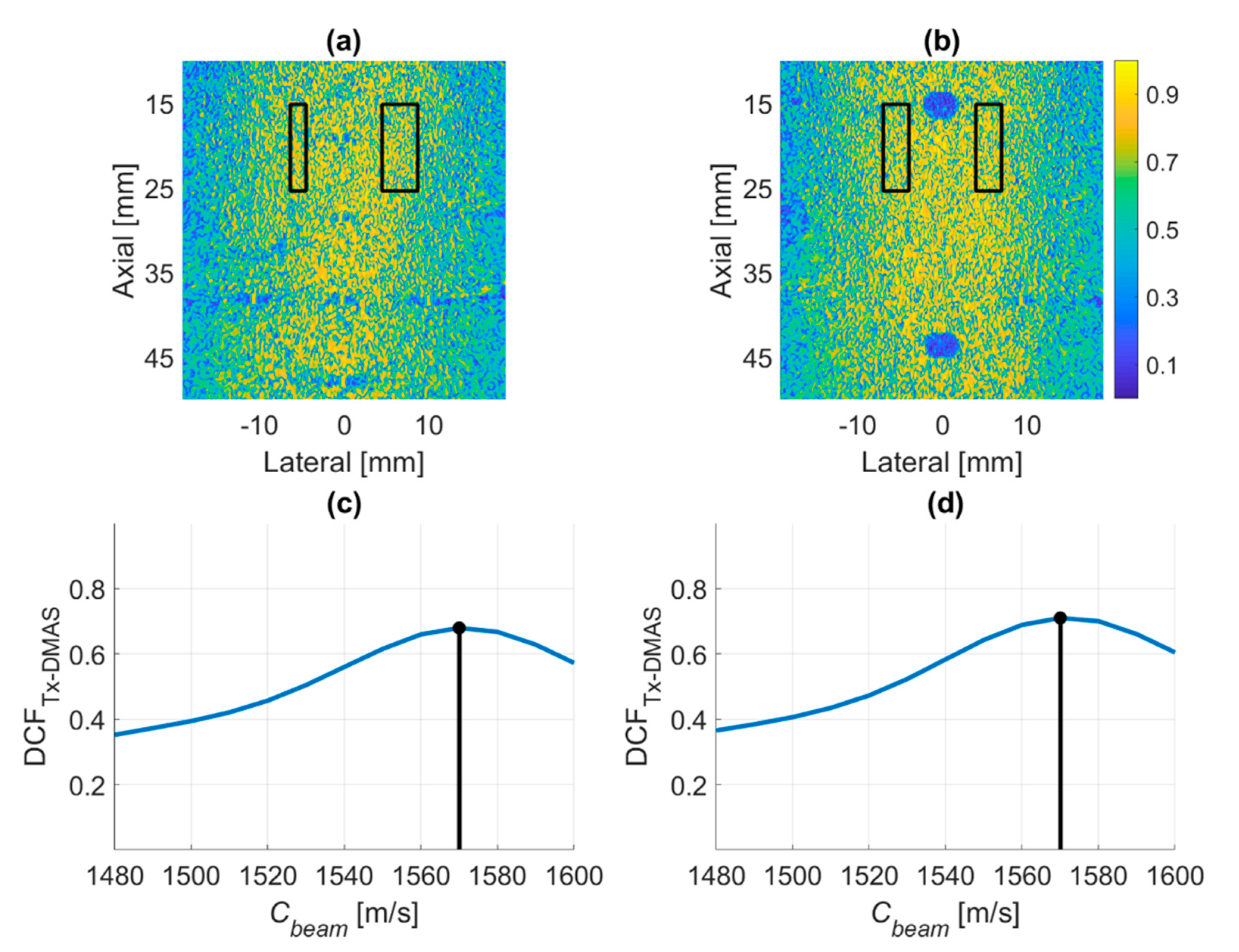
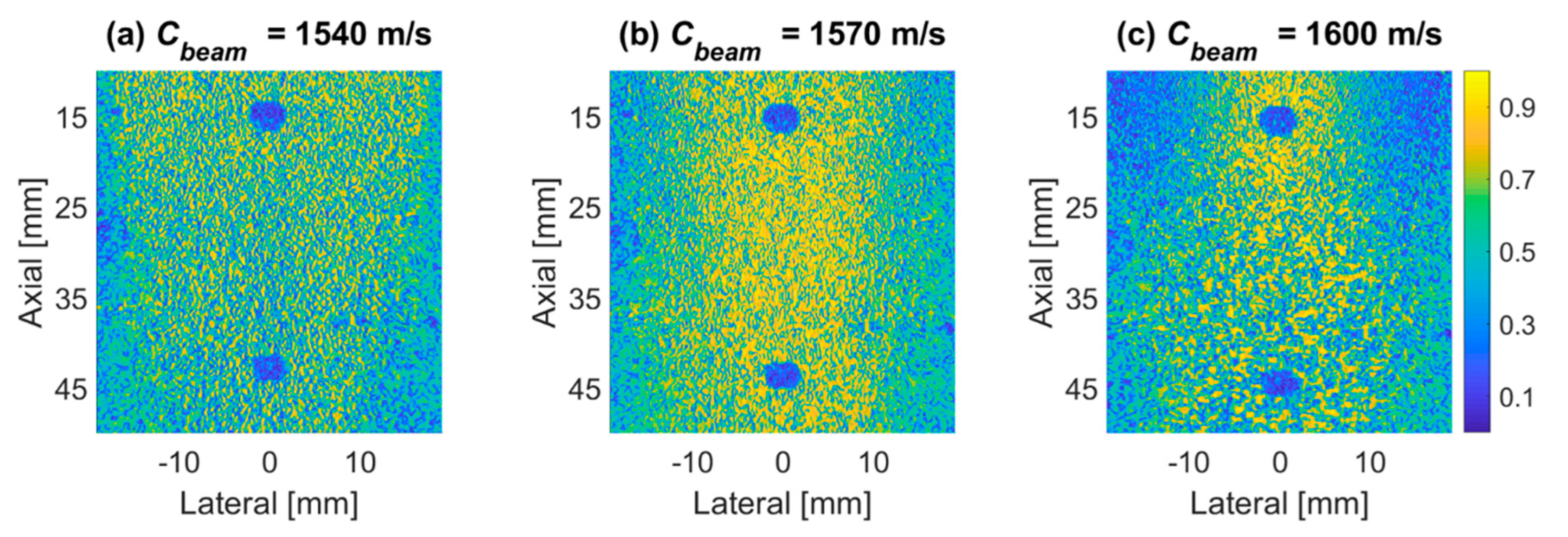
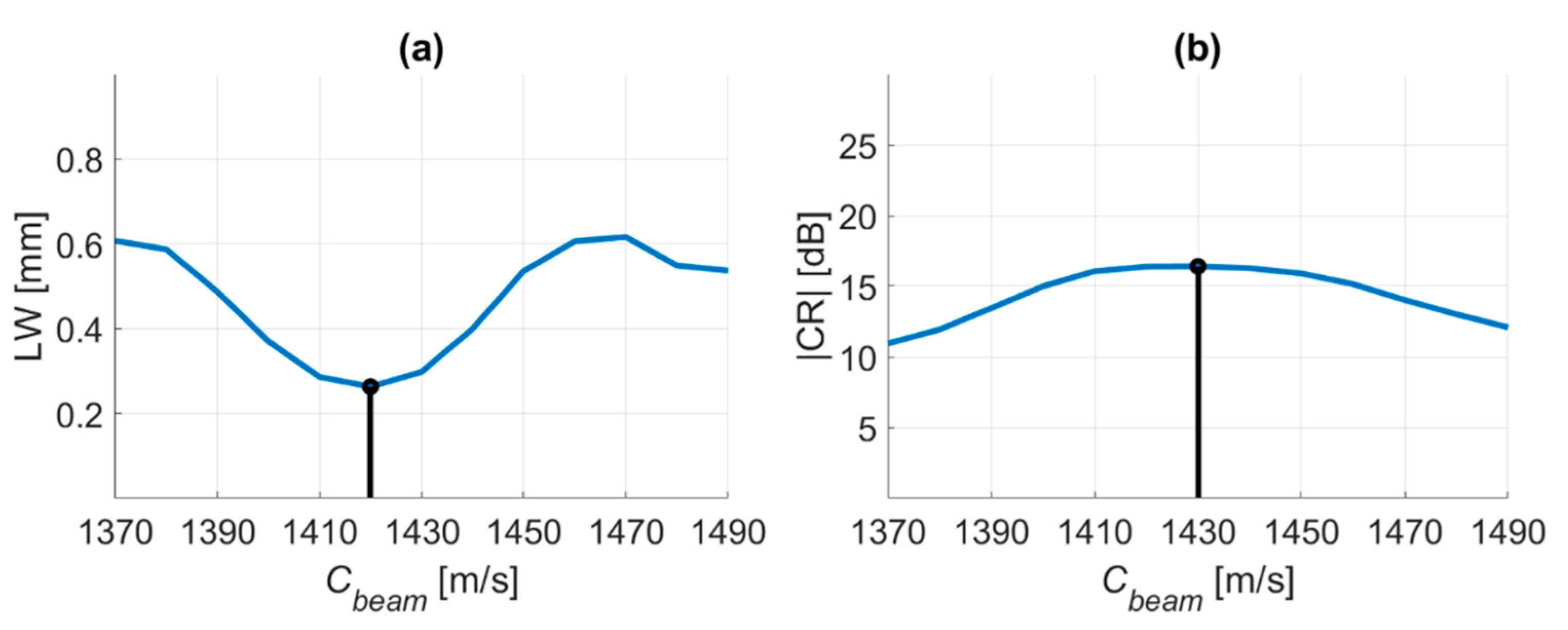
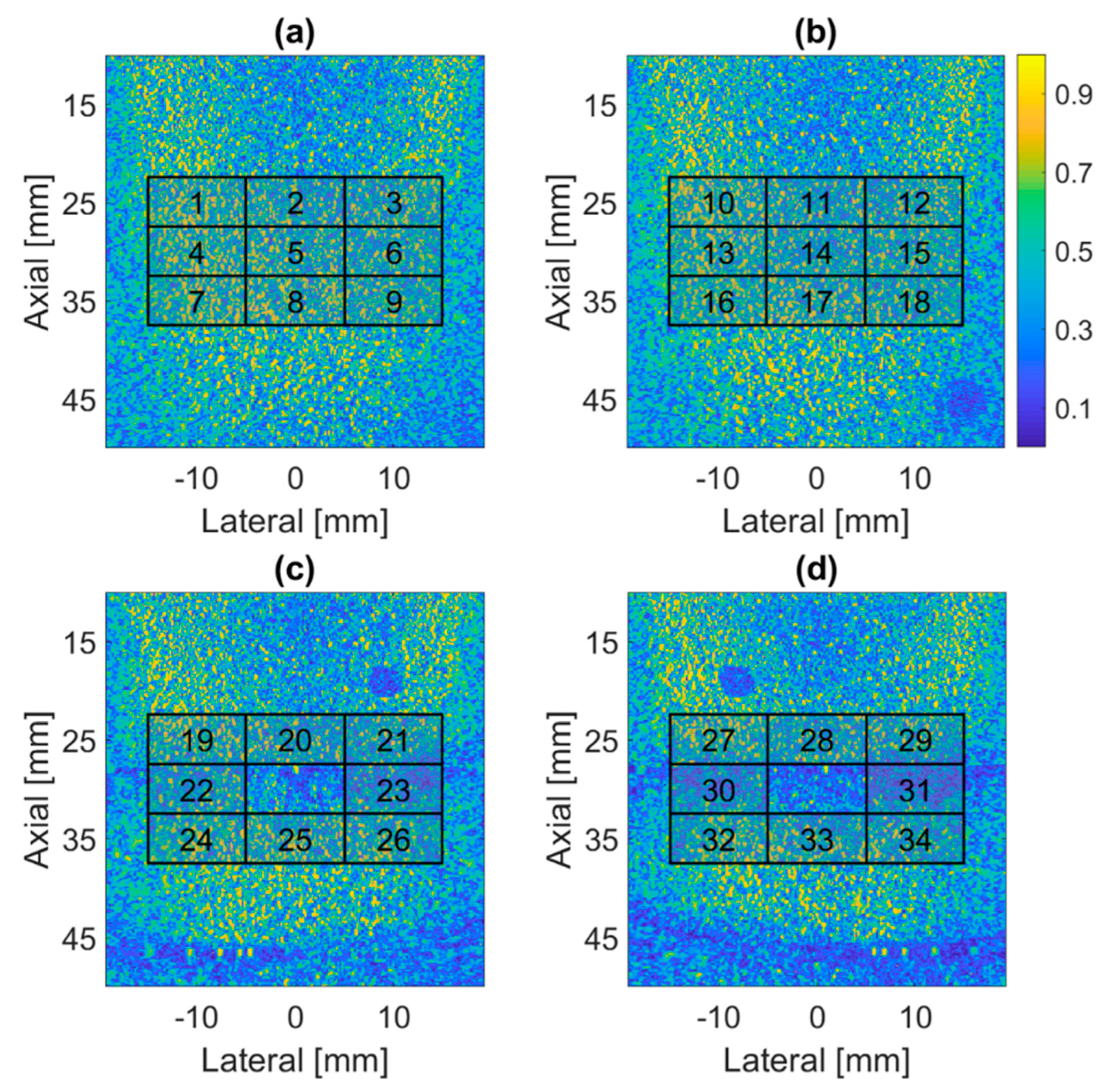
4.1. PICMUS Simulation Dataset
4.2. PICMUS Experimental Dataset
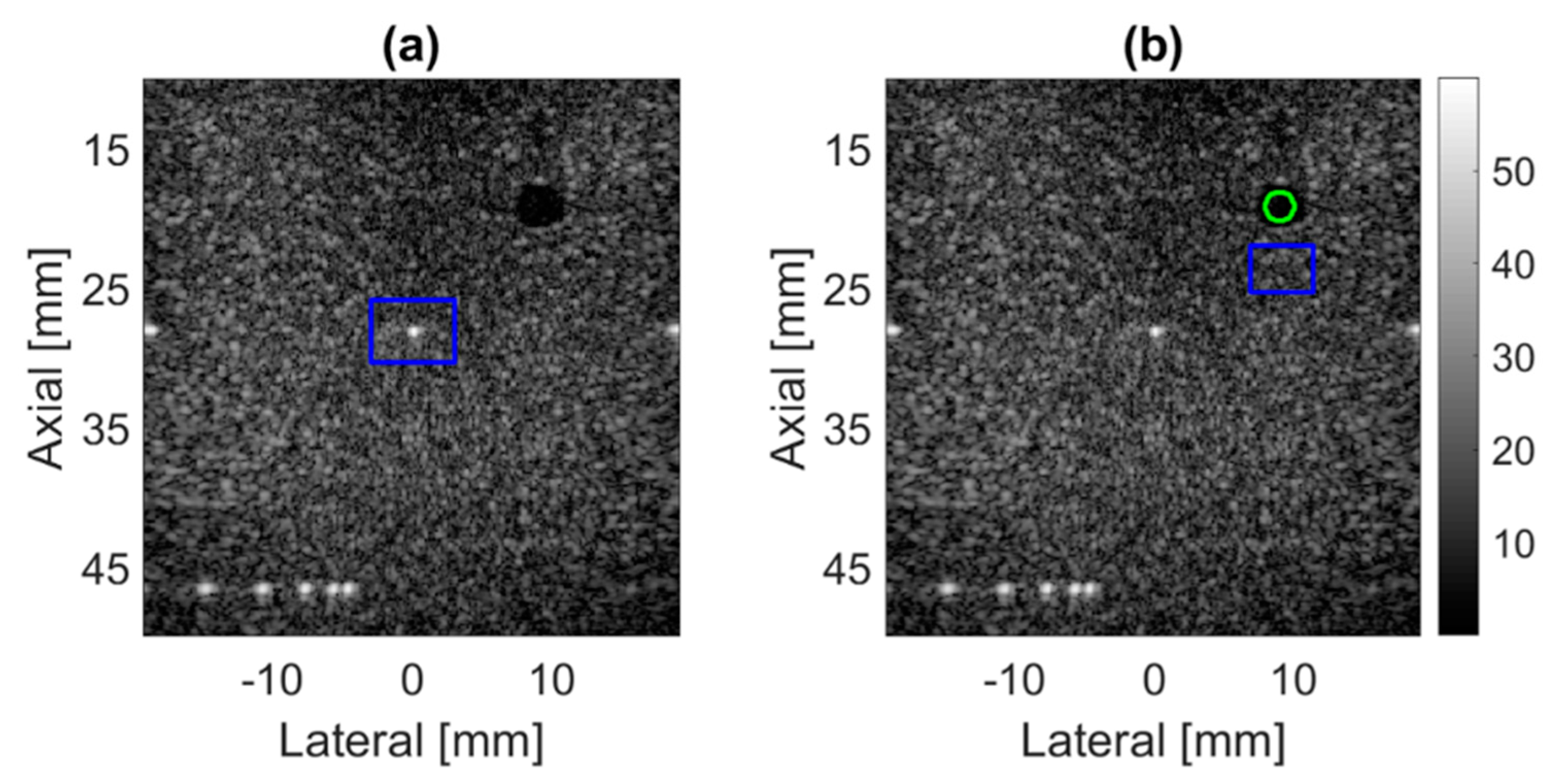
4.3. Prodigy Experimental Dataset
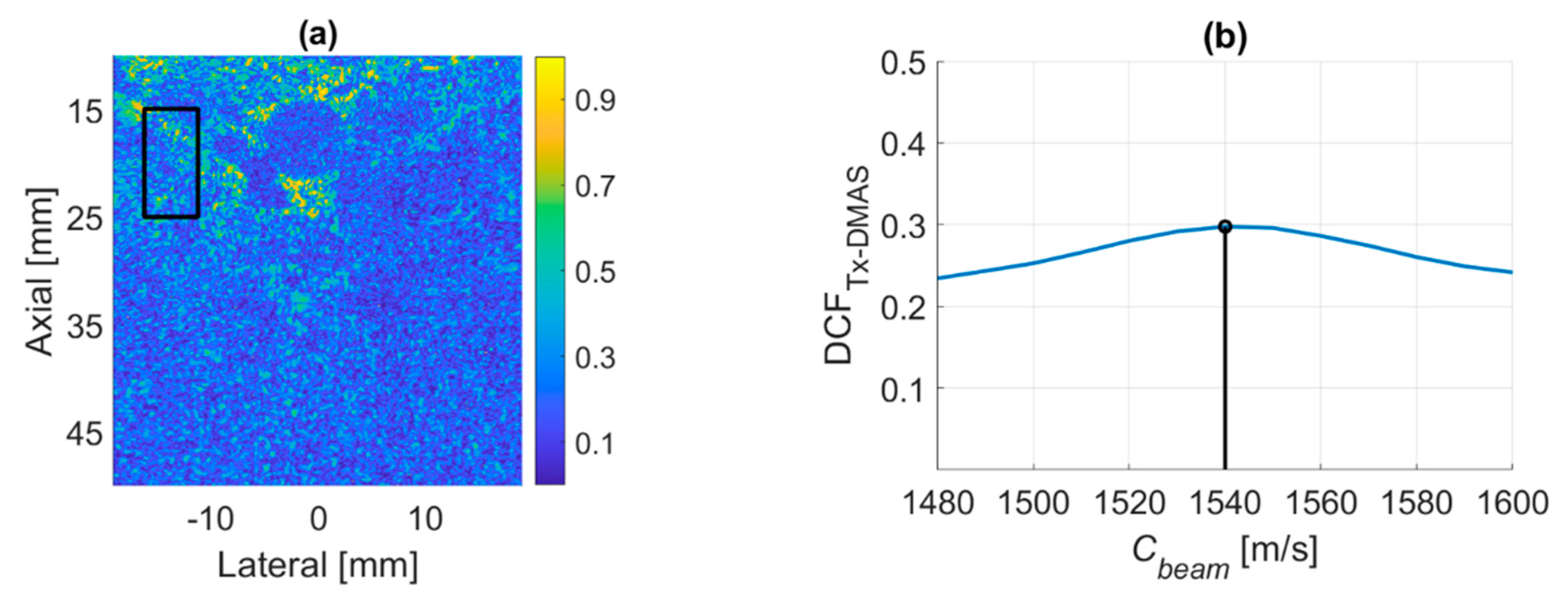
4.4. PICMUS In-Vivo Dataset
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montaldo, G.; Tanter, M.; Bercoff, J.; Benech, N.; Fink, M. Coherent plane-wave compounding for very high frame rate ultrasonography and transient elastography. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2009, 56, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrone, G.; Savoia, A.S.; Caliano, G.; Magenes, G. The delay multiply and sum beamforming algorithm in ultrasound b-mode medical imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 34, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrone, G.; Ramalli, A.; Savoia, A.S.; Tortoli, P.; Magenes, G. High frame-rate, high resolution ultrasound imaging with multi-line transmission and filtered-delay multiply and sum beamforming. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 36, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrone, G.; Ramalli, A.; Tortoli, P.; Magenes, G. Enhanced ultrasound harmonic imaging using the filtered-delay multiply and sum beamformer. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Matrone, G.; Ramalli, A.; D’Hooge, J.; Tortoli, P.; Magenes, G. Performance of F-DMAS beamforming with adjustable maximum spatial lag in multi-line transmission ultrasound imaging. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Kobe, Japan, 22–25 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.C.; Hsieh, P.Y. Ultrasound baseband delay-multiply-and-sum (BB-DMAS) nonlinear beamforming. Ultrasonics 2019, 96, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jeon, S.; Meng, J.; Song, L.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, C. Delay-multiply-and-sum-based synthetic aperture focusing in photoacoustic microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 36010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarzadeh, M.; Mahloojifar, A.; Orooji, M.; Adabi, S.; Nasiriavanaki, M. Double-Stage Delay Multiply and Sum Beamforming Algorithm: Application to Linear-Array Photoacoustic Imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 65, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, T.; Sattler, F.; Gröhl, J.; Maier-Hein, L. Signed real-time delay multiply and sum beamforming for multispectral photoacoustic imaging. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Park, E.Y.; Choi, W.; Managuli, R.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, C. Real-time delay-multiply-and-sum beamforming with coherence factor for in vivo clinical photoacoustic imaging of humans. Photoacoustics 2019, 15, 100136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, D.; Kang, J.; Yoo, Y. A new compounding method for high contrast ultrafast ultrasound imaging based on delay multiply and sum. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Kobe, Japan, 22–25 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Matrone, G.; Savoia, A.S.; Caliano, G.; Magenes, G. Ultrasound plane-wave imaging with delay multiply and sum beamforming and coherent compounding. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.C.; Hsieh, P.Y. Two-dimensional spatial coherence for ultrasonic DMAS beamforming in multi-angle plane-wave imaging. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.E.; Trahey, G.E. The direct estimation of sound speed using pulse–echo ultrasound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.; Lee, Y.; Chang, J.H.; Song, T.K.; Yoo, Y. In vitro estimation of mean sound speed based on minimum average phase variance in medical ultrasound imaging. Ultrasonics 2011, 51, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.C.; Yang, H.-C. Adaptive optimization of ultrasound beamforming sound velocity using sub-aperture differential phase gradient. Ultrasonics 2017, 79, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.C.; Hsiao, S.H.; Lin, Y.C. Synthetic transmit aperture beamforming for sound velocity estimation using channel-domain differential phase gradient—A phantom study. Ultrasonics 2019, 94, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbault, M.; Faccinetto, A.; Osmanski, B.F.; Tissier, A.; Deffieux, T.; Gennisson, J.L.; Vilgrain, V.; Tanter, M. Robust sound speed estimation for ultrasound-based hepatic steatosis assessment. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 3582–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, D.; Chou, C.H.; McLaughlin, G.; Ji, T.L.; Mo, L.; Debusschere, D.; Steins, R. Sound speed correction in ultrasound imaging. Ultrasonics 2006, 44, e43–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.; Seo, H.; Lee, Y.; Yoo, Y.; Song, T.K.; Chang, J.H. Optimal sound speed estimation using modified nonlinear anisotropic diffusion to improve spatial resolution in ultrasound imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2012, 59, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Azuma, T.; Liang, J.T.; Nakajima, Y. Average sound speed estimation using speckle analysis of medical ultrasound data. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2012, 7, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.C.; Prager, R.; Gomersall, H.; Kingsbury, N.; Treece, G.; Gee, A. Estimation of average speed of sound using deconvolution of medical ultrasound data. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindal, O.M.H.; Rodriguez-Molares, A.; Austeng, A. The dark region artifact in adaptive ultrasound beamforming. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho, J.; Romero, M.P.; Fritsch, C. Phase Coherence Imaging. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2009, 56, 958–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruza, J.; Camacho, J.; Fritsch, C. Plane-wave phase-coherence imaging for NDE. NDT E Int. 2017, 87, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Dahl, J.J. Distributed phase aberration correction techniques based on local sound speed estimates. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Kobe, Japan, 22–25 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liebgott, H.; Rodriguez-Molares, A.; Cervenansky, F.; Jensen, J.A.; Bernard, O. Plane-wave imaging challenge in medical ultrasound. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Tours, France, 18–21 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, J.E.; Ramnarine, K.V.; Watson, A.J.; Hoskins, P.R. Assessment of the acoustic properties of common tissue-mimicking test phantoms. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003, 29, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flax, S.W.; O’Donnell, M. Phase-aberration correction using signals from point reflectors and diffuse scatterers: Basic principles. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 1988, 35, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PICMUS Imaging System | |
| Pitch | 0.3 mm |
| Number of elements | 128 |
| Elevation focus | 20 mm |
| Sampling frequency | 20.832 MHz |
| PICMUS Transmit Pulse | |
| Center frequency | 5.208 MHz |
| Excitation | 2.5 cycles |
| Number of Tx angle | 21 (−16°~+16°) |
| Simulation Phantom | |
| Nominal SOS | 1540 m/s |
| Phantom | 20 wires Speckle with 9 cysts |
| Experimental Phantom | |
| Nominal SOS | 1540 m/s |
| Phantom | CIRS Model 040GSE |
| In-vivo Data | |
| Suggested SOS | 1540 m/s |
| Tissue | Carotid |
| Prodigy Imaging System | |
| Pitch | 0.3 mm |
| Number of elements | 128 |
| Elevation focus | 30 mm |
| Sampling frequency | 25.6 MHz |
| Prodigy Transmit Pulse | |
| Center frequency | 6.4 MHz |
| Excitation | 2 cycles |
| Number of Tx angle | 21 (−16°~+16°) |
| Experimental Phantom | |
| Nominal SOS | 1430 m/s |
| Phantom | CIRS Model 042 |
| Cbeamwith the Minimal −6-dB LW | ||||
| RxFn | 0.75 | 1 | 1.25 | 1.5 |
| Copt [m/s] | 1540 | 1540 | 1540 | 1530 |
| Cbeamwith the Maximal CR | ||||
| RxFn | 0.75 | 1 | 1.25 | 1.5 |
| Copt [m/s] | 1540 | 1540 | 1540 | 1540 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, C.-C.; Tu, K.-L. Ultrasound DMAS Beamforming for Estimation of Tissue Speed of Sound in Multi-Angle Plane-Wave Imaging. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186298
Shen C-C, Tu K-L. Ultrasound DMAS Beamforming for Estimation of Tissue Speed of Sound in Multi-Angle Plane-Wave Imaging. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(18):6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186298
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Che-Chou, and Kuan-Lin Tu. 2020. "Ultrasound DMAS Beamforming for Estimation of Tissue Speed of Sound in Multi-Angle Plane-Wave Imaging" Applied Sciences 10, no. 18: 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186298
APA StyleShen, C.-C., & Tu, K.-L. (2020). Ultrasound DMAS Beamforming for Estimation of Tissue Speed of Sound in Multi-Angle Plane-Wave Imaging. Applied Sciences, 10(18), 6298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10186298





