Abstract
This study presents an innovative stabilization method of fly ash derived from co-combustion of municipal solid waste and sewage sludge. Bottom ash, obtained from the same process, is used as a stabilizing agent. The stabilization method involved the use of two other components—flue gas desulfurization residues and coal fly ash. Leaching tests were performed on stabilized samples, aged in a laboratory at different times. The results reveal the reduction of the concentrations of heavy metals, particularly Zn and Pb about two orders of magnitude lower with respect to fly ash. The immobilization of heavy metals on the solid material mainly depends on three factors—the amount of used ash, the concentrations of Zn and Pb in as-received fly ash and the pH of the solution of the final materials. The inert powder, obtained after the stabilization, is a new eco-material, that is promising to be used as filler in new sustainable composite materials.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the diffuse practice of sewage sludge (SS) land spreading has generated several concerns, due to the presence of potential contaminants (such as pathogenic agents, toxic inorganic substances, and microorganisms) [1,2], with the consequence of emerging alternatives for SS treatments strategies, such as mono- and co-combustion. For example, co-combustion has been realized with municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI). The co-combustion has several advantages, the main related to the possibility to use the already existing plants (such as MSW incineration plants), avoiding investments costs, due to the need to construct new incinerators expressly devoted to mono-combustion. Moreover, the wastes generated from co-combustion of MSW and SS, i.e., fly ash (FA), and bottom ash (BA), must be properly managed to avoid landfilling and/or pollution, generated by unsuitable treating strategies. MSWI-FA is generally considered the most problematic incineration waste, due to the presence of leachable heavy metals [3]. Several technologies for MSWI-FA stabilization have been already proposed [4,5,6,7,8] with the aim to promote its reuse [9,10,11]. Even though some recently proposed MSWI-FA treatments were defined as zero-waste technologies [12], they often require MSWI-FA pre-treatments, which need the use of some additional processes and raw materials.
In a very recently published paper, we have demonstrated that MSWI-BA can be used to stabilize MSWI-FA [13]. Indeed, after metal separation, BA is generally recovered for use in the building industry. On the contrary, FA is generally destined to landfill. However, the recently proposed strategy allows the use of a waste (BA) to stabilize another waste (FA). It is important to highlight that the proposed procedure has several advantages—it employs wastes produced at the same location, strongly suggesting the possibility to directly apply the new technology on the incinerator plant sites; in addition, it avoids the transport of wastes in different locations and the landfilling of MSWI-FA. The idea to combine different wastes to take advantage of their valuable components to reduce the contained pollutants is not new [8,14,15]. In particular, the suggestion to use wastes and by-products to minimize energy, materials, and emissions for remediation was recently defined as the Azure Chemistry approach [16]. In the present work, the results recently proposed, that involve the combination of Sewage-MSWI BA and Sewage-MSWI FA to obtain a new safe eco-material, are considered to investigate if the process can be applied also to Sewage-MSWI FA derived from co-combustion. The obtained inert can be defined as eco-materials due to the low energies and emissions required to perform the proposed stabilization [14]. In particular, the aim of this work is the investigation if different amounts of SS in the co-combustion can influence the FA stabilization procedure that must be used to reduce the leachable pollutants.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
In this study, FA and BA from the co-incineration of MSW and SS were recovered from the incineration plant located in Brescia (Northern Italy). In this plant, Sewage-MSWI-FA is collected with APC (air-pollution-control) residues, originating from cleaning the flue gases before emission to air. These residues consist of fine particulates, that are generally defined FA.
The co-incineration of MSW and SS was implemented in this plant since 2017. The plant normally processes an SS concentration of 7% on the flow rate of MSW. Because the aim of the present experiment is to study the effects of different SS flow rates on the co-incineration residue stabilization, the plant worked for one day, with the three separate combustion lines at different SS concentrations—0, 2, and 4 tons/h. The amount of MSW incinerated on each line was 31 tons/h.
The schema representing the operation of the first, second and third combustion lines (also reporting the SS concentrations) is shown in Figure 1.
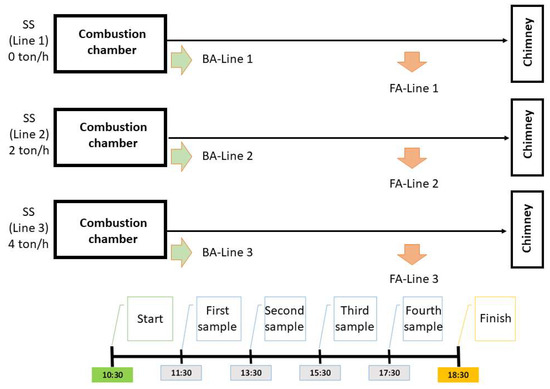
Figure 1.
Schema of the co-incineration experiment made on the industrial plant, where the three different combustion lines are represented.
During the experimentation day, Sewage-MSWI FA and Sewage-MSWI BA were collected from the three separated lines at predetermined time intervals of two hours (see Figure 1). At the end of the day, the ashes collected at different interval times were adequately mixed to obtain a homogeneous and representative sample of Sewage-MSWI FA and Sewage-MSWI BA for each line. In total, 6 ash samples (2 samples for each line) were recovered (see Figure 1).
The samples obtained and considered in this study can be divided into two categories—three samples of Sewage-MSWI BA obtained from the bottom of the combustion chamber and three samples of Sewage-MSWI FA obtained from the bag filters.
After sampling, Sewage-MSWI BA was manually sorted—metals and particles with diameter higher than 2 cm were separated. Then, due to the Sewage-MSWI BA moisture, a thermal treatment at 100 °C for about 2 h was made. After drying, Sewage-MSWI BA was grounded with Mixer Mill Retsh (MM400) and sieved until 106 µm.
Other as-received ashes are used with the aim to stabilize FA. In particular, CFA (coal combustion ash) is a by-product in thermal coal power plants. This ash is removed by a dust-collection system from the combustion gases before they are emitted into the atmosphere [17].
Flue gas desulphurization (FGD) residues are produced during the removal of sulphur oxides from coal-burning power plants. In this process, insoluble calcium sulphite and calcium sulphate solids are formed because absorbed SO2 reacts with lime in scrubbing liquor [18]. They also are a by-product of the coal combustion system. FGD residues contain high amounts of S and Ca [5]. Calcium hydroxide is very important to promote the carbonation reactions.
Both CFA and FGD residues were collected from Brescia pulverized coal thermal power plant.
2.2. Stabilization Procedure
The as-received Sewage-MSWI FA samples were stabilized following a very recent proposed technology based on the use of MSWI-BA deriving from the corresponding combustion line to stabilize FA [4]—for each FA, the procedure (defined procedure a) involved the mix of about 130 g of FA with of 20 g of BA, about 30 g of CFA, and about 40 g of FGD [4,13] (see Table 1). Another procedure, with the same amount of ashes reported for procedure a)), but that did not involve the BA addition, was also realized (defined procedure b)). Procedure b) was selected to have a comparative procedure suitable to allow us to evaluate the BA role in the stabilization. In this case, all samples exhibited a relative weight percentage, already used for similar stabilization technology [5], as follows—65% FA, 15% CFA and 20% FGD. For both stabilization procedures, all powders were carefully mixed before adding approx. 200 mL of milliQ water (Millipore DirectQ-5 TM, Millipore S.A.S., 67120, Molsheim, France); then they were additionally mixed for 20 min. The obtained eco-materials were aged in laboratory for 3 months at room temperature.

Table 1.
Sample descriptions.
2.3. Leaching Test and TXRF Analysis
Leaching tests were carried out according to CEN EN 12457-2 regulation (EN 13055-1:2002-CN/TC 154-CEN-CEN, 2002) on all as-received powders and stabilized samples (in this case the test was made each month, after the stabilization). The procedure for the leaching test, reported by [5,19,20], consists of mixing at room temperature approximately 20 g of each sample with 200 mL of milliQ water (1:10) by means of an agitator for 2 h [20]. pH measurement by a pH-meter (Metrohm, model 827 Lab, Origgio, Italy) is conducted immediately after the leaching test on the samples filtered by 0.45 µm pore membranes.
After filtration, elemental chemical analysis is realized by Total-reflection X-ray Fluorescence (TXRF) using a S2 Picofox system from Bruker (Bruker AXS Microanalysis GmbH, Berlin, Germany) equipped with Mo tube operating at 50 kV and 750 µA and a Silicon Drift Detector (SDD). For this aim, 0.010 g of a Ga solution with a concentration of 100 mg/L is used as internal standard (Ga-ICP Standard Soluyion, Fluka, Sigma Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA). It is added to the leachate solutions and homogenized by a mean of vortex shaker at 2500 rpm for 1 min. Three replicates are always prepared for each sample by adding a droplet of 10 µL of sample. By the use of a dedicated instrumental software based on mono-element profiles, the spectra are deconvolution to evaluate the peak areas. The TXRF lower detection limits (LOD) evaluated with similar experimental conditions are reported [21]. Chemical analysis of soluble elements, with atomic numbers less than 19, such Na, cannot be made by TXRF due to their low fluorescence yield [22]. Furthermore, Si cannot be evaluated, because the sample holder for TXRF analysis is made of quartz.
3. Results and Discussion
In order to understand the effects of the addition of different SS amounts to the three combustion lines, all starting ashes (FA and BA) and the obtained stabilized eco-materials were analyzed. Elemental chemical analysis using TXRF was performed to estimate the amount of leachable metals that can be found in the ashes. As reported in the experimental section, as-received FAs were analyzed as well; BA samples were pre-treated before the analysis with a reduction of the grains dimension to 106 µm. Table 2 reports the results of the leaching tests made on these ashes (BA and FA). It shows the concentration of soluble elements derived from the three combustion lines, as resulted from the TXRF analysis. Furthermore, data about BA leaching are shown.

Table 2.
Results of the Total-reflection X-ray Fluorescence (TXRF) analysis and pH values of leachate solutions of Sewage-MSWI FA and Sewage-MSWI BA derived from different combustion lines.
The leaching data of the BA and FA derived from different lines are in agreement with results reported in literature, also considering the alkaline pH of the solutions [23,24,25]. The major leachable elements in FA are Cl, Ca, K, S and Br. Relevant quantities of other elements such as Zn, Pb and Rb are also found. The main soluble elements found in the BA solutions are Ca, Cl, K and S. The presence of a high amount of Ca in FA in comparison to BA is expected, due to the addition of lime as a stabilizing agent. Indeed, during the incineration process, acid gases are produced (like HCl and SO2) and lime is normally added to absorb these gases. A higher amount of Pb and Zn are present in FA, in comparison to BA, due to the fact that these metals are moderately volatile elements, then they are generally found in ashes collected at the chimney after a combustion process carried out at a maximum temperature about 1000 °C [15]. Comparing the leaching data of different combustion lines, it is very interesting to notice that in FA, the concentration of leachable Zn is substantially irrespective of the amount of co-incinerated SS. On the contrary, the amount of soluble Pb increases with the amount of SS, probably due to the presence of this metal in sewage sludge [26]. Concerning P, an element that is well-known to be abundant in SS [27], its concentration appears to decrease in FA with the increase of co-incinerated SS. On the contrary, in BA the leachable P shows an inverse behavior. These results are substantially due to the presence of this element in soluble phases (leaching tests only allow to detect soluble elements). Moreover, it means that the increase of SS amount in co-incineration seems to increase the P leachability in BA (see Table 2). Similar consideration can be extended to Cu, for BA.
After the stabilization procedure, a significant decrease in heavy metal leachability can be noticed, if samples are analyzed one, two, and three months after the stabilization (see Table 3 and Table 4), in comparison to data reported in Table 2. In particular, three months after the stabilization the concentration of Pb is sometimes lower than LOD by TXRF spectrometry, which is 0.002 mg/L, thus demonstrates that the stabilization procedure was effective in reducing the solubility of heavy metals and that the stabilization efficacy increases with time. Moreover, comparing data reported in Table 3 and Table 4 (considering the corresponding month of stabilization), it seems that the use of BA is not so fundamental in reducing the heavy metal mobility. Indeed, eco-materials obtained applying the procedures a) and b) (the procedure b) is made without the addition of BA) sometimes show comparable Pb concentrations in their leaching solutions. Another difference concerns the Cu concentration, that is higher in samples treated by BA addition. Even if this metal appears to be stabilized after aging, it is evident that this origin can be attributed to BA due to its higher concentrations in the BA than FA (see Table 2).

Table 3.
Results of the TXRF analysis and pH values of samples stabilized following the a) procedure with Sewage-MSWI FA from different lines after (1), (2) and (3) months.

Table 4.
Results of the TXRF analysis and pH values of samples stabilized following the b) procedure with Sewage-MSWI FA from different lines after (1), (2) and (3) months.
In a very recent paper, the stabilization mechanism was proposed and discussed—it was shown that dissolved amorphous silica and alumina (derived from BA) in the presence of calcium ions (and in a highly alkaline environment) promote a pozzolanic reaction with FA, with the formation of cementitious compounds such as C–S–H and calcium aluminate hydrates (C-A-H). Furthermore, carbonation reactions occurred, due to the calcium hydroxide that is present in the used wastes (for example in FGD residues) [28,29].
In particular, considering the pH of all raw FA and final stabilized eco-materials, it means that all FAs have a starting pH about 12 (see Table 2). Instead, stabilized materials have a pH of about 11 (see Table 3) and 8 (see Table 4), depending on the procedure used for stabilization. Indeed, carbonation produces a reduction of pH [30].
Both pozzolanic and carbonation reactions have been demonstrated to be effective in heavy metal mobilization [31], but the comparison between procedures a) and b) highlights the fundamental contribution of carbonation. As explained in the introduction part, the difference in the amount of SS in the co-combustion with MSW is considered to evaluate if the addition of this waste plays a role in the stabilization mechanism. For this aim, the procedure not involving the use of BA (procedure b) is considered. Moreover, this procedure allows for the reaching of lower pH values of the obtained eco-materials (see Table 4), increasing the efficacy of stabilization.
Figure 2 reports the concentration of Pb and Zn in the leaching solutions of stabilized samples, considered after different times, versus the pH of the solution (for both procedures a) and b)). Zn and Pb are found in a high concentration in the raw FA (ranging from 9–11.7 and 92–127.1 mg/L, respectively) with high pH values (about 12), while in the stabilized samples the concentration of these elements is found to be often two orders of magnitude lower. Figure 2 clearly highlights that an increase of the aging time corresponds to a decrease of pH of the solutions [32], in agreement with the already reported evidence of carbonation. This also corresponds to a decrease of the heavy metal leachability, as already observed and discussed [4,33]. In particular, concerning Pb, three months after stabilization it is sometimes lower than LOD by TXRF spectrometry, as reported in Table 3 and Table 4, therefore it cannot be found in Figure 2.
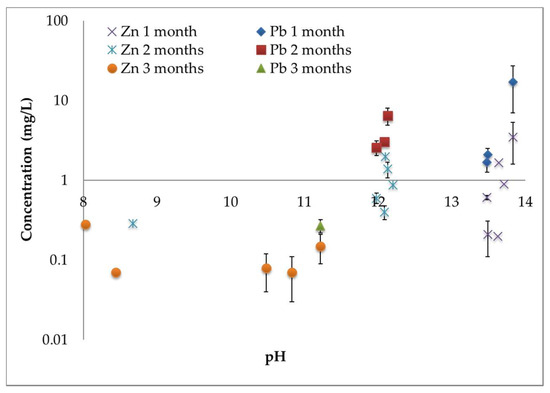
Figure 2.
Concentration values of Pb and Zn in the leaching solution of stabilized samples (involving both procedures a) and b)) during the first three months versus the pH.
To better highlight the pH role, the variation of the concentration of Pb and Zn in the leaching solutions of stabilized samples can be considered analyzing data reported in Figure 3. In this Figure, the concentration of Pb and Zn in the solutions of stabilized samples (considering both procedures a) and b)), are plotted versus their values in the leaching solution of raw FA (initial metals concentrations, before the stabilization). Figure 3 allows for the comparison of the results of stabilization, considering that raw FA (corresponding to different combustion lines) had a different amount of leachable Pb and Zn. In particular, it is evident that all samples show a reduction of the Pb and Zn concentration, after the stabilization. Obviously, samples that contained a lower amount of leachable heavy metals in raw FA show a lower concentration of corresponding metals in the solutions of stabilized eco-materials. This means that samples with higher initial concentrations of Pb and Zn need more time (or more stabilizing agents) to reduce the leachable elements concentration.
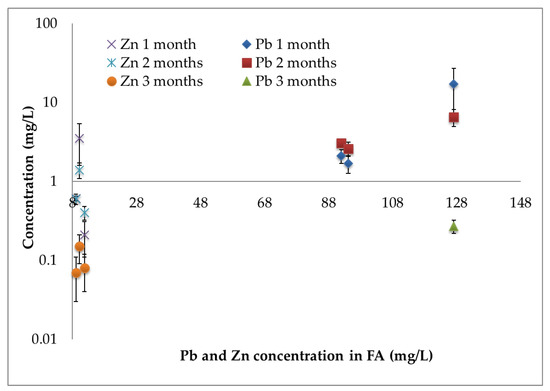
Figure 3.
Concentration values of Pb and Zn in the leaching solution of stabilized samples (involving both procedures a) and b)) during the first three months versus the concentration of Pb and Zn in MSWI FA.
The role of BA in the stabilization can be highlighted by analyzing data reported in Figure 4, that show the concentration of Pb and Zn during the first three months evaluated in the leaching solutions of all stabilized samples (considering both procedures a) and b)), versus the ratio between the total amount of ash (FA, CFA, FGD, and BA) and the sum of CFA and BA amount. It means that the samples that contain the higher CFA + BA amount are better stabilized in comparison to those containing a lower amount of these stabilization agents (the concentration of Pb and Zn are lower). Indeed, it is important to highlight that BA contains amorphous silica [4] and CFA contains aluminosilicate glass [13,34]. Then, it is possible to suppose that dissolved amorphous silica in the presence of calcium ions (and in a highly alkaline environment) promotes a pozzolanic reaction with FA. Then, it is possible to conclude that BA plays a fundamental role in reducing the Pb and Zn presence in solution of the produced eco-materials. Obviously, it was also shown that the pH role is fundamental, and it must be controlled and possibly adjusted to obtain the best results in terms of stability of the obtained eco-materials.
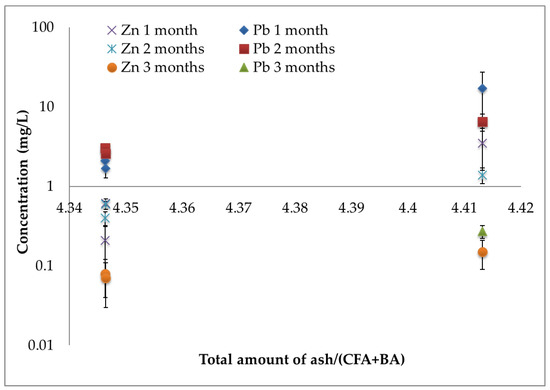
Figure 4.
Concentration values of Pb and Zn in the leaching of stabilized samples (involving procedure a)) during the first three months versus the partition of total amount of ash and the sum of CFA and BA quantities.
The obtained stabilized eco-material is a powder that is very similar to the inert material obtained by using similar treatments but using other by-products (such as silica fume) instead of BA for stabilization. This allows for us to suppose that the obtained eco-materials may be used in some applications, already explored for similar products, as a substitute of natural resources [10,33,35,36]. In particular, it was shown that the obtained eco-materials are biologically safe [37,38,39], opening the interesting opportunity of the investigation of their aquatic toxicity in the next future.
4. Conclusions
The present paper concerns the study of a method for the stabilization of heavy metals contained in FAs derived from the co-combustion of MSW and SS. BA, a residue of the same process, is used as a stabilizing agent. Leaching test reveals the reduction of heavy metals in the stabilized samples, that increases with the aging (to three months). In particular, the concentration of leachable Zn and Pb in the as-received FAs decreased to two orders of magnitude in the solution of stabilized samples. In addition, the reduction of pH of the same solutions confirms the occurring of carbonation reactions, that also contributed to reduce the heavy metal leachability.
In summary, these results show that the efficacy of the stabilization procedure depends on several factors—the pH is fundamental to reduce the heavy metal leachability. In addition, the amount of leachable Pb and Zn in as-received FA is an important parameter to consider obtaining the better results—as expected, ashes containing higher quantities of contaminants require higher quantities of stabilizing agents (or more time for the stabilization). Indeed, an increase in the sum of the concentration of CFA and BA corresponds to a better result in terms of metals reduced mobility.
The obtained stabilized eco-material may be used in different applications as a substitute of natural resources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.B. and M.N.; methodology, E.B.; software, A.A.; formal analysis, F.B., A.Z. and L.B.; investigation, A.A., A.Z. and F.B.; data curation, F.B. and A.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A. and E.B.; writing—review and editing, L.E.D., E.B., F.B., L.B. and M.N.; supervision, E.B.; project administration, E.B.; funding acquisition, E.B. and M.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially supported by FANGHI project, financed by Regione Lombardia, in the frame of the call HUB Ricerca e Innovazione.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Chang, Z.; Long, G.; Zhou, J.L.; Ma, C. Valorization of sewage sludge in the fabrication of construction and building materials: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 154, 104606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, L.; Zanoletti, A.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Sewage sludge ash recovery as valuable raw material for chemical stabilization of leachable heavy metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, Z.; Giannis, A.; Dong, Z.L.; Lisak, G.; Ng, W.J. Characteristics of incineration ash for sustainable treatment and reutilization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 16974–16997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, A.; Bilo, F.; Zanoletti, A.; Ponti, J.; Valsesia, A.; La Spina, R.; Zacco, A.; Bontempi, E. Zero-waste approach in municipal solid waste incineration: Reuse of bottom ash to stabilize fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodella, N.; Bosio, A.; Dalipi, R.; Zacco, A.; Borgese, L.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Waste silica sources as heavy metal stabilizers for municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3676–S3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, L.; Bosio, A.; Dalipi, R.; Borgese, L.; Rodella, N.; Pasquali, M.; Depero, L.E.; Bergese, P.; Bontempi, E. Comparison between rice husk ash grown in different regions for stabilizing fly ash from a solid waste incinerator. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 159, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benassi, L.; Franchi, F.; Catina, D.; Cioffi, F.; Rodella, N.; Borgese, L.; Pasquali, M.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Rice husk ash to stabilize heavy metals contained in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: First results by applying new pre-treatment technology. Materials 2015, 8, 6868–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosio, A.; Rodella, N.; Gianoncelli, A.; Zacco, A.; Borgese, L.; Depero, L.E.; Bingham, P.A.; Bontempi, E. A new method to inertize incinerator toxic fly ash with silica from rice husk ash. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacco, A.; Borgese, L.; Gianoncelli, A.; Struis, R.P.W.J.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Review of fly ash inertisation treatments and recycling. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, A.; Bilo, F.; Zanoletti, A.; Ponti, J.; Valsesia, A.; La Spina, R.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Review of the Reuse Possibilities Concerning Ash Residues from Thermal Process in a Medium-Sized Urban System in Northern Italy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacco, A.; Gianoncelli, A.; Ardesi, R.; Sacrato, S.; Guerini, L.; Bontempi, E.; Tomasoni, G.; Alberti, M.; Depero, L.E. Use of colloidal silica to obtain a new inert from municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash: First results about reuse. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2012, 14, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diliberto, C.; Meux, E.; Diliberto, S.; Garoux, L.; Marcadier, E.; Rizet, L.; Lecomte, A. A zero-waste process for the management of MSWI fly ashes: Production of ordinary Portland cement. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assi, A.; Fabjola, B.; Federici, S.; Zacco, A.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Bottom ash derived from municipal solid waste and sewage sludge co-incineration: First results about characterization and reuse. Waste Manag. 2020, 116, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontempi, E. A new approach for evaluating the sustainability of raw materials substitution based on embodied energy and the CO2 footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benassi, L.; Pasquali, M.; Zanoletti, A.; Dalipi, R.; Borgese, L.; Depero, L.E.; Vassura, I.; Quina, M.J.; Bontempi, E. Chemical Stabilization of Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash without Any Commercial Chemicals: First Pilot-Plant Scaling Up. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5561–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoletti, A.; Bilo, F.; Depero, L.E.; Zappa, D.; Bontempi, E. The first sustainable material designed for air particulate matter capture: An introduction to Azure Chemistry. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 218, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanianpour, A.A. Cement Replacement Materials, Properties, Durability, Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 7, ISBN 978-3-642-36720-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, R.A.; Biswas, R.; Chakrabarti, T.; Devotta, S. Flue gas desulfurization: Physicochemical and biotechnological approaches. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 35, 571–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempi, E.; Zacco, A.; Borgese, L.; Gianoncelli, A.; Ardesi, R.; Depero, L.E. A new method for municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash inertization, based on colloidal silica. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 2093–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosio, A.; Zacco, A.; Borgese, L.; Rodella, N.; Colombi, P.; Benassi, L.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. A sustainable technology for Pb and Zn stabilization based on the use of only waste materials: A green chemistry approach to avoid chemicals and promote CO2 sequestration. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, M.; Zanoletti, A.; Benassi, L.; Federici, S.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Stabilized biomass ash as a sustainable substitute for commercial P-fertilizers. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, P.; Agnihotri, D.K.; Asadchikov, V.E.; Bontempi, E.; Bowen, D.K.; Chang, C.H.; Depero, L.E.; Farnworth, M.; Fujimoto, T.; Gibaud, A.; et al. Reproducibility in X-ray reflectometry: Results from the first world-wide round-robin experiment. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, N.; Kato, S.; Kojima, T. Compositions and leaching behaviours of combustion residues. Fuel 2006, 85, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youcai, Z.; Ziyang, L. Pollution Control and Resource Recovery, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9780128116395. [Google Scholar]
- Seniunaite, J.; Vasarevicius, S. Leaching of Copper, Lead and Zinc from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Bottom Ash. Energy Procedia 2017, 113, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytła, M. Identification of the Chemical Forms of Heavy Metals in Municipal Sewage Sludge as a Critical Element of Ecological Risk Assessment in Terms of Its Agricultural or Natural Use. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kooij, S.; Van Vliet, B.J.M.; Stomph, T.J.; Sutton, N.B.; Anten, N.P.R.; Hoffland, E. Phosphorus recovered from human excreta: A socio-ecological-technical approach to phosphorus recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 157, 104744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosio, A.; Rodella, N.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Rice Husk Ash Based Composites, Obtained by Toxic Fly Ash Inertization, and their Applications as Adsorbents. Chem. Eng. 2014, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, A.; Federici, S.; Bilo, F.; Zacco, A.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Increased sustainability of carbon dioxide mineral sequestration by a technology involving fly ash stabilization. Materials 2019, 12, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Yu, H. Carbon dioxide sequestration by direct mineralization of fly ash. In Carbon Dioxide Sequestration in Cementitious Construction Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 13–37. ISBN 9780081024447. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, R.J.; Davidson, D.T. Pozzolanic reactivity study of fly ash. Highw. Res. Board Bull. 1959, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Cetin, B.; Likos, W.J.; Edil, T.B. Impacts of pH on leaching potential of elements from MSW incineration fly ash. Fuel 2016, 184, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodella, N.; Pasquali, M.; Zacco, A.; Bilo, F.; Borgese, L.; Bontempi, N.; Tomasoni, G.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Beyond waste: New sustainable fillers from fly ashes stabilization, obtained by low cost raw materials. Heliyon 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Huang, R.; Tang, Y. Comprehensive Understandings of Rare Earth Element (REE) Speciation in Coal Fly Ashes and Implication for REE Extractability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5369–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junakova, N.; Junak, J.; Balintova, M. Reservoir sediment as a secondary raw material in concrete production. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2015, 17, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, A.; Bilo, F.; Zanoletti, A.; Ducoli, S.; Ramorino, G.; Gobetti, A.; Zacco, A.; Federici, S.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. A Circular Economy Virtuous Example—Use of a Stabilized Waste Material Instead of Calcite to Produce Sustainable Composites. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarienti, M.; Gianoncelli, A.; Bontempi, E.; Moscoso Cardozo, S.; Borgese, L.; Zizioli, D.; Mitola, S.; Depero, L.E.; Presta, M. Biosafe inertization of municipal solid waste incinerator residues by COSMOS technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilo, F.; Moscoso, S.; Borgese, L.; Delbarba, M.V.; Zacco, A.; Bosio, A.; Federici, S.; Guarienti, M.; Presta, M.; Bontempi, E.; et al. Total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy to study Pb and Zn accumulation in zebrafish embryos. X-ray Spectrom. 2015, 44, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarienti, M.; Cardozo, S.M.; Borgese, L.; Lira, G.R.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E.; Presta, M. COSMOS-rice technology abrogates the biotoxic effects of municipal solid waste incinerator residues. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).