Laboratory Study on the Performance of Asphalt Mixes Modified with a Novel Composite of Diatomite Powder and Lignin Fiber
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Aggregate and Mix Gradation
2.1.2. Asphalt Binder
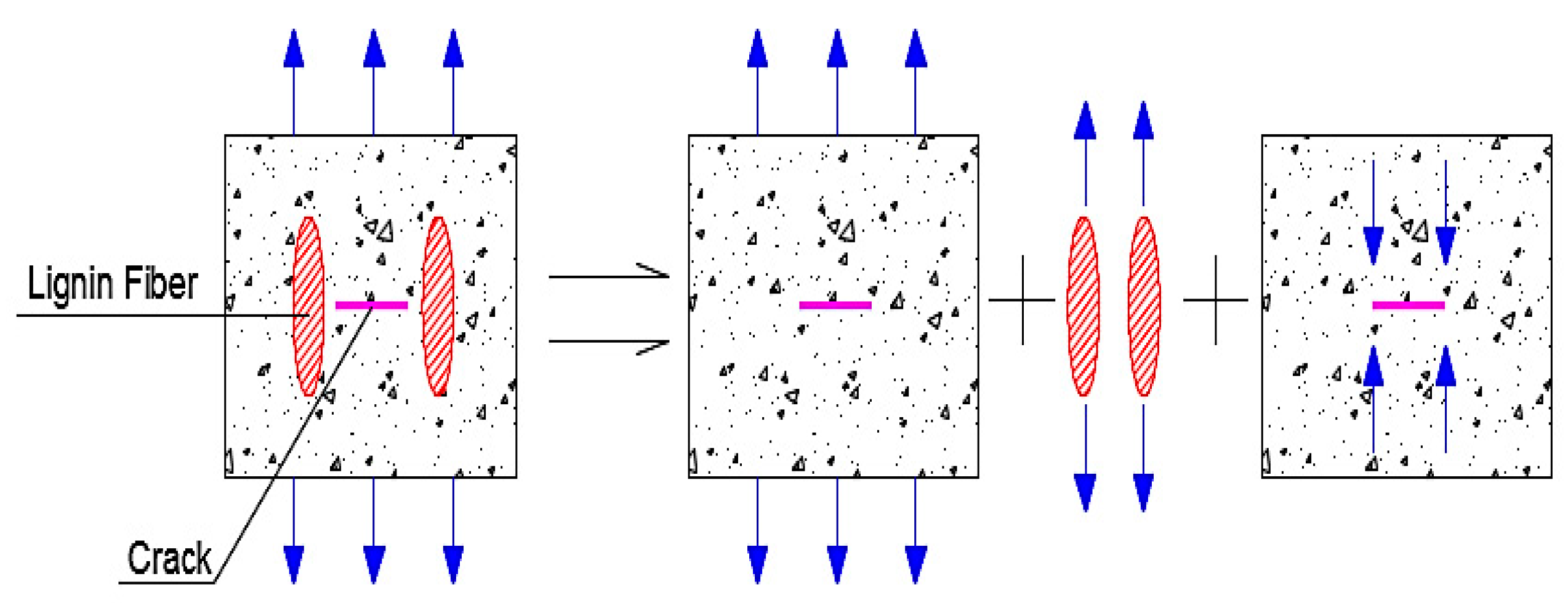
2.1.3. Lignin Fiber
2.1.4. Diatomite
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Preparation of the Samples
- Aggregates and asphalt were heated to temperatures of 170 °C and 160 °C, respectively, till the material temperature was stable.
- The preheated aggregates were mixed at a temperature of 175 °C in the mixing pot for 90 s.
- Lignin fiber was added to aggregates, and then they were mixed together about 90 s in order to improve the dispersion of fibers in the asphalt mix.
- Asphalt binder (Bitumen) was poured into the mixer and mixed for 90 s.
- Finally, diatomite and mineral filler were added and mixed 90 s to form DLFMAM.
2.4. Test Methods
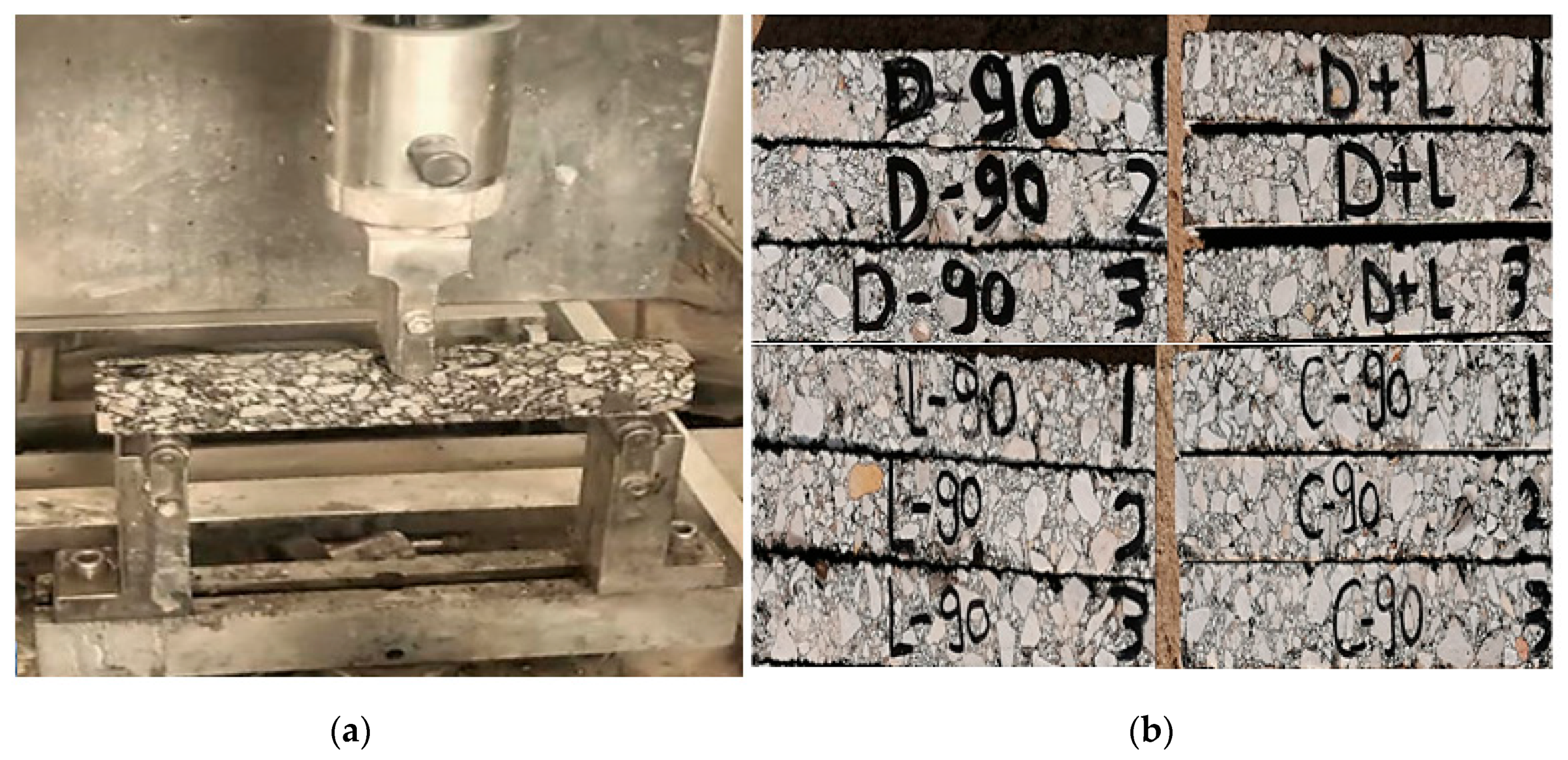
2.4.1. Three-Points Bending Test (Beam Bending Test)
2.4.2. Marshall Immersion Test
2.4.3. Freeze-Thaw Splitting Test
3. Results Analysis and Discussion
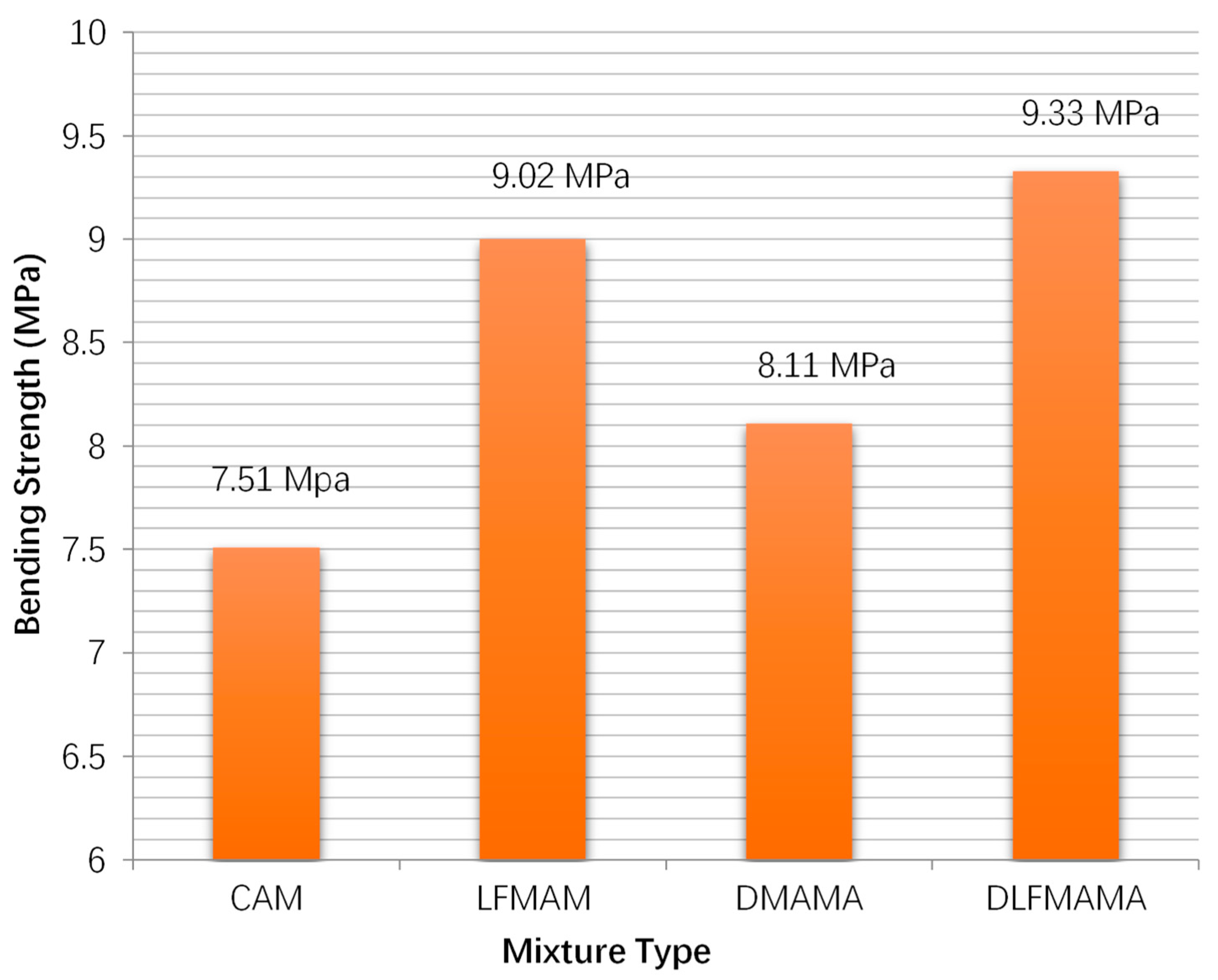
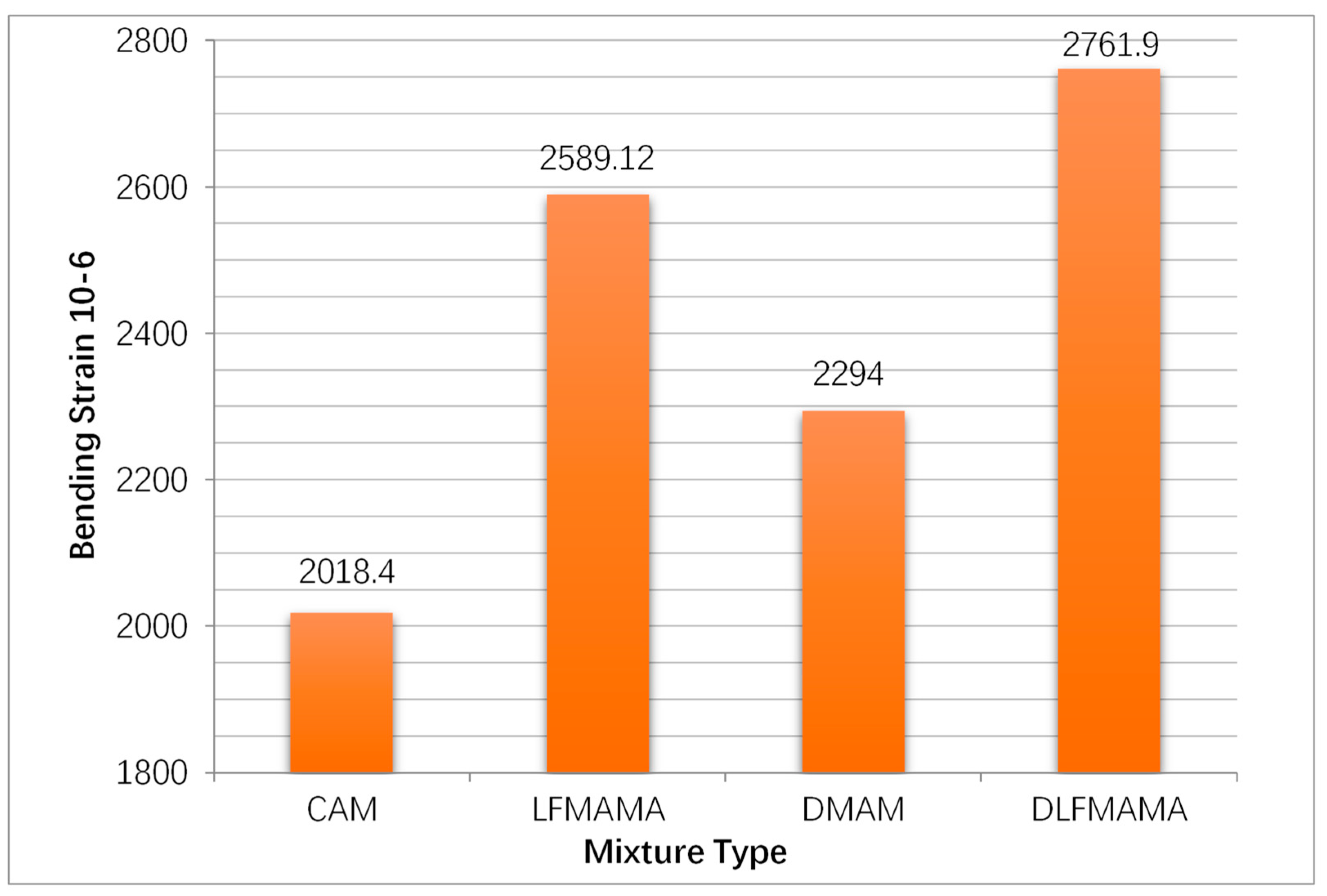
3.1. Low-Temperature Bending Test Results and Analysis
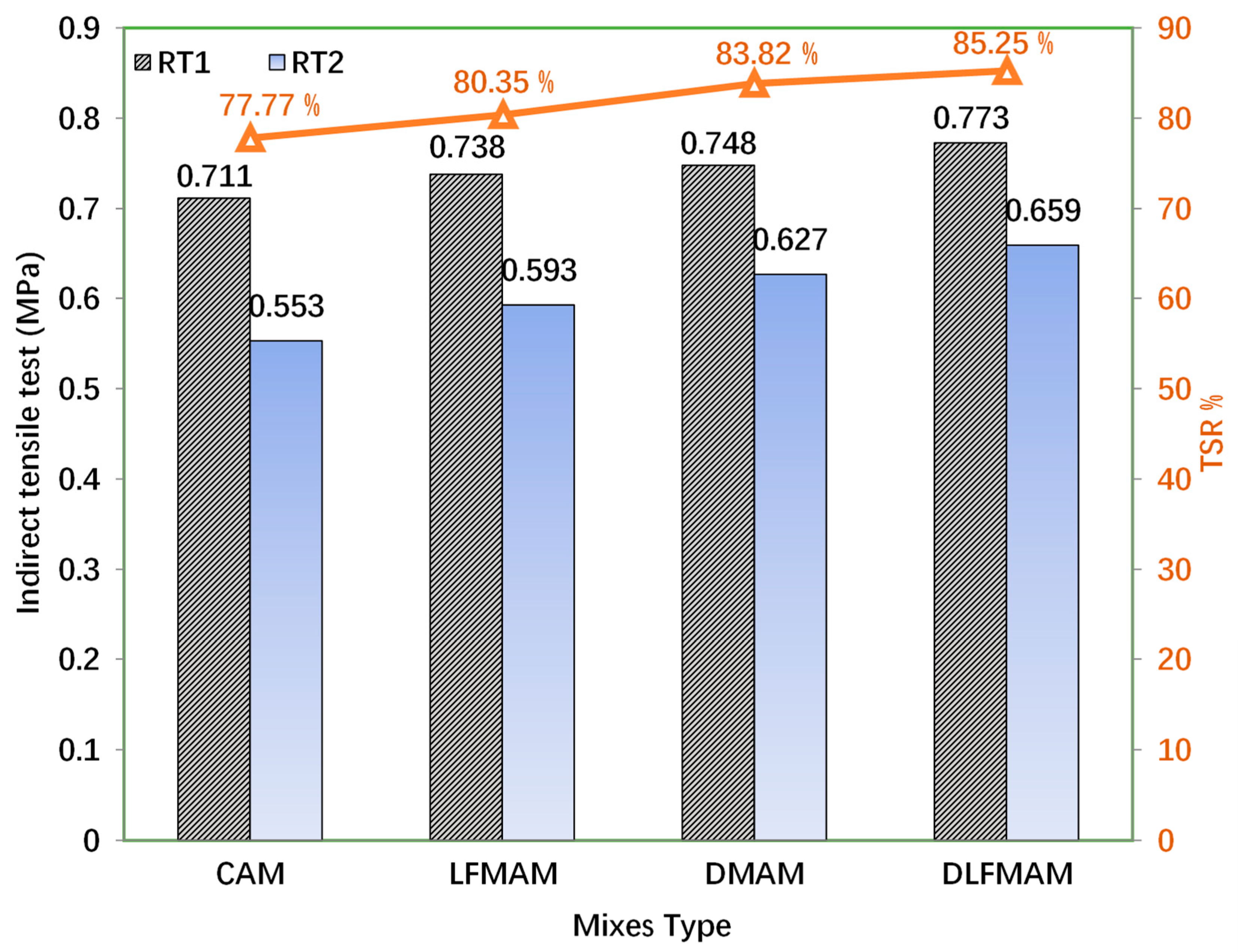
3.2. Water Stability Test Results
3.2.1. Marshall Immersion Test Results
3.2.2. Freeze-Thaw Splitting Test Results
4. Conclusions
- The addition of diatomite and lignin fiber increase the low-temperature performance of asphalt mixes compared to the control mix. Moreover, the lignin fiber has a greater improvement in the bending strength and failure strain than the diatomite.
- Diatomite and lignin fiber improve water damage resistance of asphalt mixture significantly. However, the influence of diatomite on water damage resistance property is more significant than that of lignin fiber.
- The composite asphalt mix of diatomite and lignin fiber (DLFMAM) is the best alternative to resist low-temperature cracking and moisture sustainability in asphalt pavements since it has the highest low-temperature performance, MSR, and TSR than other mixes.
- The Asphalt mixes modified with single additives cannot enhance the overall properties of asphalt mixes significantly, while the double-adding technology can improve the overall asphalt mixes performance at the same time.
- Using the composite asphalt mix of DLFMAM in construction of pavement will have a greater advantage in enhancing the service life and ride quality than the usage of single additives in pavements constructed.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Pang, L.; Xie, J. Function investigation of stone mastic asphalt (SMA) mixture partly containing basic oxygen furnace (BOF) slag. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2016, 14 (Suppl. S1), 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghnejad, M.; Arabani, M.; Taghipoor, M. Predicting the impact of temperature and stress on the glasphalt mixtures’ rutting behavior. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2018, 11, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Khater, A.; Yue, Y.; Abdelsalam, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Iseley, D.T. The performance of asphalt mixtures modified with lignin fiber and glass fiber: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Wu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Cui, P.; Zhou, H. VOCs reduction and inhibition mechanisms of using active carbon filler in bituminous materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 181, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohod, M.V.; Kadam, K. A comparative study on rigid and flexible pavement: A review. IOSR J. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2016, 13, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Xing, M.; Chen, S.; He, R.; Cong, P. Influence of the chloride-based anti-freeze filler on the properties of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 51, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Q. Experimental study of fibers in stabilizing and reinforcing asphalt binder. Fuel 2010, 89, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei-Wen, H.; Deng-Liang, Z.; Xi-Ning, H. Evaluation method for low temperature anti-cracking performance of asphalt mixture. J. Xi’an Highw. Unversity 2000, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kanerva, H.K.; Vinson, T.S.; Zeng, H. Low-Temperature Cracking: Field Validation of the Thermal Stress Restrained Specimen Test; Strategic Highway Research Program SHRP-A: NW Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Marker, V. Introduction to Non-Traffic Load Associated Cracking of Asphalt Pavements. In Proceedings of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists, Lino Lakes, MN, USA, 27 April 2012; pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Mashaan, N.S.; Ali, A.H.; Koting, S.; Karim, M.R. Performance evaluation of crumb rubber modified stone mastic asphalt pavement in Malaysia. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, H.; Khodaii, A.; Saleh, M. Long term effectiveness of anti-stripping agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Lutif, J.S.; Bhasin, A.; Little, D.N. Evaluation of moisture damage mechanisms and effects of hydrated lime in asphalt mixtures through measurements of mixture component properties and performance testing. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2008, 20, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R. Modeling of Asphalt Concrete; ASCE Press: Reston, VA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sienkiewicz, M.; Kucinska-Lipka, J.; Janik, H.; Balas, A. Progress in used tyres management in the European Union: A review. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, R. Novel Application of Carbon Fiber for Hot Mix Asphalt Reinformortar and Carbon-Carbon Pre-Forms. Master’s Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Abdelsalam, M.; Luo, D.; Khater, A.; Musanyufu, J.; Chen, T. Evaluation of the Properties of Asphalt Mixes Modified with Diatomite and Lignin Fiber: A Review. Materials 2019, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Dang, Y.; Guo, B.; Huang, Y. Laboratory investigation on the properties of asphalt mixtures modified with double-adding admixtures and sensitivity analysis. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2016, 3, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Shen, W.; Huang, Y.; Hang, G.; Li, X. Laboratory evaluation of pavement performance using modified asphalt mixture with a new composite reinforcing material. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2017, 10, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuya, H. The road performance of lignin and rubber powder composite modified asphalt mixture. Highw. Eng. 2014, 39, 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, R.; Fang, J.; Xu, A.; Guan, B.; Liu, Z. Laboratory investigation on the brucite fiber reinforced asphalt binder and asphalt concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 83, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, H.; Prozzi, J.A. Performance of fiber reinforced asphalt concrete under environmental temperature and water effects. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhao, J. Research on Performance of Basalt Fiber-Enhanced SMA. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 4323–4327. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, D.V.; Feng, C.P.; Long, L.H. Analysis of high temperature stability and water stability of SMA mixture using orthogonal experiments. Int. J. Civil. Struct. Eng. 2011, 2, 635–647. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, Q.L. Application of Diatomite Modified Asphalt. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 959–963. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tan, G.; Lv, Z.; Yang, J.; Ma, J. Laboratory Study on Properties of Diatomite and Basalt Fiber Compound Modified Asphalt Mastic. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, L.; Jiao, Y.; Tao, J.; Wang, X. Short-term aging effect on properties of sustainable pavement asphalts modified by waste rubber and diatomite. Sustainability 2017, 9, 996. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; He, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, M. Evaluation of anti-icing performance for crumb rubber and diatomite compound modified asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 107, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xie, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Pang, L. Performance Evaluation and Improving Mechanisms of Diatomite-Modified Asphalt Mixture. Materials 2018, 11, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiusheng, H.; Gang, Z. The Research on Improvement of Low Temperature Stability for Diatomite Modified Asphalt Mixture with PE Particles. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2015, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tao, J.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, D.; Xiao, B. Effects of Diatomite–Limestone Powder Ratio on Mechanical and Anti-Deformation Properties of Sustainable Sand Asphalt Composite. Sustainability 2018, 10, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davar, A.; Tanzadeh, J.; Fadaee, O. Experimental evaluation of the basalt fibers and diatomite powder compound on enhanced fatigue life and tensile strength of hot mix asphalt at low temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H. Evaluation of low-temperature performance of asphalt paving mixtures. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2012, 70, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, L.; Cheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Xu, C. Laboratory evaluation on performance of diatomite and glass fiber compound modified asphalt mixture. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukry, N.A.M.; Hassan, N.A.; Abdullah, M.E.; Hainin, M.R.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Jaya, R.P.; Mohamed, A. Effect of various filler types on the properties of porous asphalt mixture. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 342, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Chen, N.; Xu, H.; Tan, B.; Chen, Q. Study on Indoor Pavement Performance of Diatomite-Modified Asphalt Mixture. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Innovative Material Science and Technology (IMST 2016), Shenzhen, China, 19–21 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- JTGF 40-2004. Technical Code for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavement; Ministry of Communication of China: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- JTJ 052-2000. Specification for Highway Engineering Asphalt and Asphalt Concrete Mixture Experiments; C.M.o.T.: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, Y.-J.; Xue, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Y. Study on durability of high-modulus asphalt mixture based on TLA and fibre composite modification technology. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, D.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tao, J.; Wang, W. Laboratory evaluation on performance of eco-friendly basalt fiber and diatomite compound modified asphalt mixture. Materials 2018, 11, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abtahi, S.; Hejazi, S.; Sheikhzadeh, M.; Semnani, D. An investigation on the use of textile materials to mechanical reinforcement of asphalt-concrete (AC) structures and analysis of results by an artificial neural network (ANN). In Proceedings of the 4th National Congress on Civil Engineering, Tehran, Iran, 6 May 2008. NCCE04-127. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.Y. Research on the Modification Mechanism of Diatomite and Dry Mixing of Diatomite-Modified Asphalt Miture. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Solaimanian, M. Measurement and evaluation of asphalt concrete thermal expansion and contraction. J. Test. Eval. 2008, 36, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- JTG E20-2011. Standard Test Methods of Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures for Highway Engineering; Ministry of Transport: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L.; Liu, K.; Wu, S.; Lei, M.; Chen, Z. Effect of LDHs on the aging resistance of crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Property | Measured Value | Specified Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20–10 mm | 10–5mm | ||
| Crushing value (%) | 9.9 | 9.2 | ≤ 25 |
| Los Angeles abrasion value (%) | 13.2 | 15.1 | ≤ 30 |
| Apparent relative density | 2.726 | 2.722 | ≥ 2.5 |
| Water absorption (%) | 0.354 | 0.829 | ≤ 3 |
| > 9.5 mm needle and plate particle content (%) | 6.53 | ------- | ≤ 15 |
| < 9.5 mm needle and plate particle content (%) | -------- | 3.285 | ≤ 20 |
| Property | Measured Value | Specified Value |
|---|---|---|
| Apparent relative density | 2.692 | ≥ 2.5 |
| Sand equivalent | 82 | ≥ 60 |
| Mud content (< 0.075 content) (%) | 16.78 | --------- |
| Material | Item | Values | Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original asphalt binder | Specific gravity (g/cm 3) | 1.017 | N/A |
| Penetration at 25 °C (0.1 mm) | 93 | (80–100) | |
| Penetration Index PI | −1.27 | −1.5 ~ +1.0 | |
| Ductility at 15 °C (cm) | 145 | ≥ 100 | |
| Softening point (°C) | 45.9 | ≥ 45 | |
| RTOF asphalt binder | Mass loss (%) | 0.07 | ≤ ± 0.8 |
| Ductility at 15 °C (cm) | 73.7 | ≥ 20 | |
| Residual Penetration ratio (%) | 72.8 | ≥ 60 |
| Index | Length (mm) | Diameter (mm) | Aspect Ratio (mean) | Specific Surface Area (10-3 m2/g) | Density (g/cm3) | Melt Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 1.1 | 0.045 | 24 | 118.1 | 1.28 | > 200 |
| Property | Measured Value |
|---|---|
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 0.45 |
| Specific gravity (g/cm3) | 2.3 |
| The average particle diameter (µm) | 20 |
| pH | 9.87 |
| Mix ID | Modifier | Modifier Amount | O.A.C. % |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAM | NON | 0 | 4.2 |
| LFMAM | Lignin fiber | 0.3% * | 4.6 |
| DMAM | Diatomite | 13% ** | 4.27 |
| DLFMAM | Lignin fiber + Diatomite | 0.3% * + 13% ** | 4.52 |
| Asphalt Mix ID | Low-Temperature Cracking Test | Marshall Immersion Test | Freeze-Thaw Splitting Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stress (Mpa) | Strain (10−6) | MS1 (KN) | MS2 (KN) | MSR (%) | RT1 (Mpa) | RT2 (Mpa) | TSR (%) | |
| CAM | 7.51 | 2018.4 | 10.95 | 9.09 | 83.0 | 0.711 | 0.553 | 77.77 |
| LFMAM | 9.02 | 2589.12 | 11.02 | 9.93 | 90.11 | 0.738 | 0.593 | 80.35 |
| DMAM | 8.11 | 2294 | 11.71 | 10.79 | 92.14 | 0.748 | 0.627 | 83.82 |
| LFDMAM | 9.33 | 2762 | 12.11 | 11.51 | 95.05 | 0.773 | 0.659 | 85.25 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelsalam, M.; Yue, Y.; Khater, A.; Luo, D.; Musanyufu, J.; Qin, X. Laboratory Study on the Performance of Asphalt Mixes Modified with a Novel Composite of Diatomite Powder and Lignin Fiber. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165517
Abdelsalam M, Yue Y, Khater A, Luo D, Musanyufu J, Qin X. Laboratory Study on the Performance of Asphalt Mixes Modified with a Novel Composite of Diatomite Powder and Lignin Fiber. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(16):5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165517
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelsalam, Moustafa, Yanchao Yue, Ahmed Khater, Dong Luo, Josephine Musanyufu, and Xiaoli Qin. 2020. "Laboratory Study on the Performance of Asphalt Mixes Modified with a Novel Composite of Diatomite Powder and Lignin Fiber" Applied Sciences 10, no. 16: 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165517
APA StyleAbdelsalam, M., Yue, Y., Khater, A., Luo, D., Musanyufu, J., & Qin, X. (2020). Laboratory Study on the Performance of Asphalt Mixes Modified with a Novel Composite of Diatomite Powder and Lignin Fiber. Applied Sciences, 10(16), 5517. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10165517







