Abstract
R. raciborskii is known for growing under wide ranges of temperature and light. In temperate regions, however, low temperature and high light may serve as a stressful condition for invading tropical populations. The genetic basis of R. raciborskii’s adaptation to this combination of stresses are unknown. In this study, the growth rate and the expression of genes that may be crucial in the response to the chill/light stress of two R. raciborskii strains (differing in their climatic origin and toxicity) exposed to low temperature and high light were examined. Results showed that AMU-DH-30, a non CYN (cylindrospermopsin) producing strain isolated from the temperate region, exhibited under stress the upregulation of genes involved in the protein translation (rbp1, nusG, hflX), membrane fluidity (desA), photosynthetic activity (ccr2 and ftsH), and the accumulation of compatible solutes (asd). In contrast, a CYN producing Australian strain CS-505 was not able to adapt quickly and to continue growth during stress conditions. Intriguingly, CS-505 and AMU-DH-30 had a similar ability to resume growth when the stress conditions subsided. Moreover, in strain CS-505 the cyrB gene was significantly upregulated under the stress conditions. The presented results shed new light on the possible mechanisms involved in the response of R. raciborskii to chill/light stress.
1. Introduction
Increased eutrophication of surface water results in a common occurrence of toxic or potentially toxic cyanobacterial blooms. Several species originally thought to proliferate only in more tropical regions of the world are now being detected in temperate climates, suggesting that these cyanobacteria are highly adaptive, which has important implications for water safety [1]. The best example of a cyanobacterium well adapted to different conditions is Raphidiopsis (formerly Cylindrospermopsis) raciborskii which has considerable flexibility with respect to light and nutrients [2]. The successful expansion of this taxa from subtropical regions toward colder temperate regions has been explained by its ability to rapidly adapt to new environments through high intraspecific variability. These so-called ecotypes vary in their ecophysiology with respect to factors driving their occurrence including temperature, light, and nutrients. Recent studies have shown high degree of strain variability within populations of this cyanobacterium originating from different geographic regions [3]. Chemotypes of R. raciborskii isolated from China, Australia, and New Zealand can synthesize cylindrospermopsins (CYNs), some isolates from South America produce saxitoxins, while strains from the temperate zone including North America and Europe are considered, so far, as incapable of producing any of these toxic compounds [2]. However, several studies have shown R. raciborskii strains isolated from Polish lakes are capable of producing as-yet unknown metabolites that have in vitro cytotoxicity in human lymphocytes and neutrophils [4] and evoking neurotoxic effects [5]. Interestingly, the high physiological or chemical variability of R. raciborskii strains can occur even within one waterbody [3]. There is a relatively broad knowledge regarding the distribution and toxicity of freshwater cyanobacteria, on the other hand, the cellular response of cyanobacteria to different abiotic and biotic factors influencing their growth, abundance, and toxin production is still poorly understood.
Cyanobacteria need to manage several stress conditions generated by different abiotic factors [6]. As a response, some species have developed efficient strategies that allow them to invade and dominate new habitats. One of the most crucial problems for species that inhabit surface water in the temperate climate is to survive the cold period and to respond to high light stress. The combination of cold and high solar radiation may induce photooxidative stress. Moreover, the so-called phenomenon of low-temperature-induced photoinhibition is well established [7]. The high plasticity of R. raciborskii in response to key environmental factors—temperature and light intensity [8,9,10] may explain its gradual domination in changing environments. Additionally, the formation of akinetes is crucial during the winter period [11]. Akinetes could serve as a dispersal unit and only those filaments that formed akinetes are able to hibernate and to establish a new population [12]. However, when populations are well developed, growth may be continued even at relatively low temperatures combined with high light intensity. This is probably associated with the occurrence of genetically and ecophysiologically different ecotypes of R. raciborskii [13] and its greater plasticity in response to environmental factors [8].
Cyanobacteria that do not form akinetes, have developed a capability to overwinter when water temperatures decrease and then to reinvade the water column. This is called acquired chill-light tolerance (ACLT) which depends on gene regulation and the accumulation of certain metabolites during preconditioning. The crucial role of such mechanisms in ACLT has been documented mainly for the laboratory strain Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 [14,15,16] and Microcystis sp. [17]. R. raciborskii has been found to succeed in all climates and at temperatures as low as 11 °C. Therefore, the successful establishment of populations is not only dependent on akinete production but also on other processes [18]. This species must have developed physiological mechanisms which has allowed for survival and growth during cold periods associated with temperate winters.
Many genes regulated during cold or light stress have been identified in various species of cyanobacteria, although mostly in Synechocystis. In response to cold stress, cyanobacteria regulate the expression of genes involved in overcoming cold-induced damages and resume growth when favourable weather conditions occur [19]. Some categories of upregulated genes induced by a low-temperature have been distinguished in cyanobacteria. Among them are genes encoding: Desaturase, proteins involved in RNA and DNA metabolism, proteins involved in crucial metabolic pathways, GTP binding proteins, or high-light inducible proteins [19]. However, despite numerous field and laboratory research the genetic grounds of the adaptation of R. raciborskii strains to a low temperature and high light irradiation (chill/light stress) are not known. It is extremely important to understand the mechanisms which have allowed potentially toxic cyanobacteria to invade and dominate new environments. In the case of R. raciborskii it seems that its high level of physiological variability may be a key factor that contributes to its successful worldwide expansion. The current study aimed to investigate the expression of key genes involved in the adaptation mechanisms of R. raciborskii strains isolated from two different habitats: First, the strain was isolated from temperate Lake Bytyńskie (Poland) and the second from Solomon Dam, Palm Island (Australia). In addition, these two strains differ in their toxicity, the strain from Poland is non-CYN producing while the strain from Australia is a CYN producer. The analyzed genes were those that are crucial in the response to the stress of high light and/or low temperature, involved in: (i) Protein translation (rbp1, nusG, hflX), (ii) membrane fluidity (desA), (iii) photosynthetic activity (ccr2) including the PSII repair function (ftsH and fabZ), (iv) accumulation of compatible solutes (asd), and (v) involved in the synthesis of cytotoxic cylindrospermopsin (cyrB and cyrJ; CYN strain only).
Our hypothesis assumed that gene upregulation has an essential role in adaptation of toxic or potentially toxic R. raciborskii strains to chill/light stress. For this reason, we compared: (i) The growth of the two investigated strains during and after chill/light stress and (ii) the expression patterns of selected genes that could play an important role in response to this stress.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains
R. raciborskii AMU-DH-30 strain was isolated from Lake Bytyńskie (western Poland). It was confirmed to be non CYN-producing [20]. Australian R. raciborskii CS-505, with confirmed CYN production was isolated from Solomon Dam, Palm Island, Queensland and was supplied by the Australian National Algae Culture Collection. Strains were cultured in a WC medium with reduced nitrogen concentration (25% of the recommended dose), in 20 °C, and light intensity of 40 µmol m−2 s−1 in POL-EKO thermostatic cabinets equipped with cool white light (Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands).
2.2. Experimental Condition
The cultures in the early exponential growth phase (with the initial OD730 about 0.2) were split into two groups (control and stress) in three independent biological replicates. Cultures were kept in 250 mL glass flasks and incubated for one day in standard conditions (20 °C and 40 µmol m−2 s−1). The next day (time 0) cultures from the stress group were moved to a lower temperature (10 °C) and higher irradiance (100 µmol of photons m−1 s−1) for 10 d (the logarithmic growth of investigated strains), and then moved back to optimal conditions for five days which allowed observing, if the strains are able to resume the growth. Cultures from the control group were incubated in the standard conditions during the whole experiment. Fifteen milliliters of liquid culture for RNA isolation was collected in time 0 and then in 1, 6, 24, and 120 h (five days) of incubation for the analysis of gene expression connected to chill/light stress, and time 0, 48, 120 (five days), and 240 h (ten days) for the analysis of the expression of cyr genes. The growth was controlled by optical density measurement at 730 nm and the specific growth rate has been calculated based on the formula:
where Nt is the amount of cells at time t, N0 is the amount of cells at time 0, r is the growth rate, and t is the time passed.
Nt = N0 × (1 + r)t
2.3. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
RNA isolation was carried out using the TRI reagent (Molecular Research Center, Cincinnati, OH, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol with some modifications. Fifteen milliliters of liquid culture fixed with 10 mL of 96% ethanol in 50 mL falcon tubes was centrifuged (5 min, 5000× g, 4 °C). The cells were resuspended in 500 μL of the TRI Reagent mixed with glass beads (ratio 1:1 v/v). Samples were shaken intensively for 10 min at room temperature. An amount of 100 μL of chloroform was added in order to separate RNA and the mixture was shaken for 15 s and incubated for 15 min, then centrifuged for 15 min at 16,000× g at 4 °C. The water phase containing RNA was transferred into new Eppendorf tubes and 250 μL of isopropanol was added in order to precipitate RNA. Samples were mixed gently and incubated for 1 h at 4 °C, then centrifuged for 20 min at 16,000× g at 4 °C. The supernatant was discarded and the pellet was washed twice with 750 μL of 85% ethanol. The pellet was air dried and suspended in 30 μL of DEPC treated water. An amount of 500 ng of RNA, quantified with a spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA), were incubated with DNase I (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) to remove residual genomic DNA and used for cDNA synthesis using the High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions.
2.4. Real-Time PCR
Each sample was analyzed in two technical replicates. Primers for qPCR were designed on the base of genes sequences deposited in the Nucleotide NCBI database using the PrimerQuest Tool (https://eu.idtdna.com/Primerquest) (Table 1). The sequences were verified using the OligoAnalyzer software (https://eu.idtdna.com/calc/analyzer) to avoid the formation of secondary structures.

Table 1.
List of primers used in the qPCR reactions.
Real-time PCR was performed as described previously [21] using the PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) and the CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The temperature program was as follows: 2 min at 50 °C, 2 min at 95 °C, and 40 cycles of 15 s at 95 °C, and 60 s at 60 °C. An end-point melt-curve analysis was generated after each run and analyzed to assure the absence of nonspecific PCR products.
To establish standard curves a 10-fold dilution series of linearized pJET1.2 plasmids containing target genes were used. The plasmids were prepared by cloning the amplicons of the target genes fragments using the CloneJET PCR Cloning Kit (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) and linearized with a FastDigest NotI restriction enzyme (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Target gene fragments were prepared using Dream Taq DNA polymerase (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) and the same primers as in real-time PCR. The temperature program of PCR was as follows: 3 min at 95 °C, 30 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 60 °C, 1 min at 72 °C, and 10 min at 72 °C for the final extension.
2.5. Real-Time PCR Results Analysis
Gene expression was described as a ratio of the target gene copy number to a reference gene copy number, as follows:
where Ntarget is the target gene copy number and Nreference is the reference gene copy number. The copy numbers were estimated using the standard curve. Reference genes prs and rnpA were chosen as the most stable in the used experimental conditions [22].
RQ = Ntarget/Nreference
2.6. Statistical Analyses
Two independent experiments, each containing three independent replications were performed. Thus, all qPCR data used in the statistical analyses were based on six samples. The growth and qPCR results were analyzed statistically using ANOVA (Statistica 13.3, TIBCO Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Growth Pattern
The investigated strains expressed a different growth pattern in the control condition (Figure 1(1,2)) with the growth rate during the whole experiments (1–15 d) 0.137 and 0.116 for AMU-DH-30 and CS-505 strains, respectively. In comparison, the stress groups had the growth rate approximately 0.094 and 0.062. The most evident effect of the response to stress could be observed during the 10 d of incubation in high light irradiation and low temperature. In this period, the growth rate of both strains was much lower in stress groups in comparison to the control one (0.068 vs. 0.156 for AMU-DH-30 and 0.034 vs. 0.136 for CS-505). Moreover, the CS-505 strain grew two times slower than AMU-DH-30 during the stress condition (Figure 1(2)). Interestingly, both strains manifested the ability to resume their growth after 10 d of stress, when placed under favorable conditions. During this period the growth rate of both strains was similar.
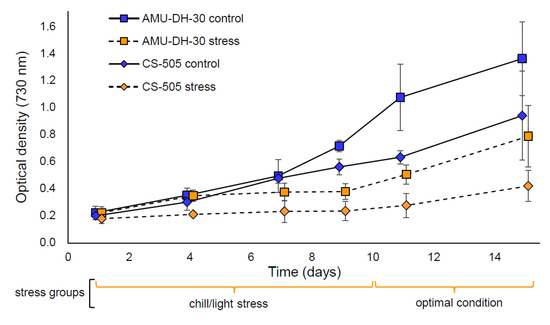
Figure 1.
The growth of Raphidiopsis raciborskii AMU-DH-30 (squares) and CS-505 (rhombs) strains in the control conditions and under the chill/light stress (10 °C and 100 µmol of photons m−1 s−1 for 10 d). The blue colour with solid lines represents control groups, the orange colour with dashed lines represents the stress group. Statistically significant differences between: (1) AMU-DH-30 control and AMU-DH-30 stress in 9, 11, and 15 d; (2) CS-505 control and CS-505 stress in 7, 9, 11, and 15 d; (3) AMU-DH-30 stress and CS-505 stress in 11 and 15 d.
3.2. Gene Expression
The transcript levels of eight genes of R. raciborskii AMU-DH-30 strain that theoretically could be involved in response to the chill/light stress were determined (Figure 2a and Figure 3). Most of the genes were upregulated in the stress group. Based on the results, three patterns of the gene expression of the AMU-DH-30 strain were distinguished: (i) The increase of the transcript level after 1 h of incubation in the chill/light stress (three genes: ccr2, hflX, nusG); (ii) the increase of the mRNA level in the chill/light stress both in 1 h and five days of incubation or in 24 and 120 h (asd and desA) or in 24 and 120 h (ftsH and rbp1); (iii) the lack of the influence of the chill/light stress on the mRNA levels (fabZ). The most spectacular changes were observed for nusG, asd, and hlfX.

Figure 2.
The heat maps of normalized relative gene expression intensities of investigated R. raciborskii strains: (a) AMU-DH-30; (b,c) CS-505. Each horizontal line represents a probe set (control and stress), with light green indicating low expression and dark-green indicating high expression in the various time intervals. Heat maps were prepared using the Multiple Experiment Viewer. Each t0 control value was normalized to 1.
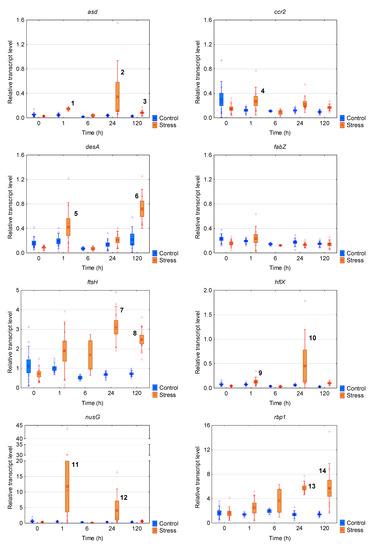
Figure 3.
The box plots with a relative gene expression level of each analyzed gene of Raphidiopsis raciborskii AMU-DH-30 in reference to the prs house-keeping gene transcript level. Means are indicated by squares, bars represent standard deviation, whereas boxes represent the standard error. Raw data are marked as triangles. Statistically significant differences: (1) increased in comparison to stress t0, control 1, 24, and 120 h; (2) increased in comparison to stress t0, control t0, 1, 24, and 120 h; (3) increased in comparison to stress t0, control t0, 1, 24, and 120 h; (4) increased in comparison to each control, stress t0 and 120 h; (5) increased in comparison to each control; (6) increased in comparison to each control, stress t0, 6, 24, and 120 h; (7,8) increased in comparison to each control and stress t0; (9) increased in comparison to each control and stress; (10) increased in comparison to each control and stress 6 h; (11,12) increased in comparison to each control and stress t0; (13, 14) increased in comparison to each control, stress t0, and 1 h.
R. raciborskii CS-505 strain from Australia expressed a much weaker transcriptomic response to the chill/light stress (Figure 2b,c and Figure 4). The mRNA levels of eight (ccr2, hflX, desA, fabZ, nusG, ftsH, rbp1, ccrJ) of the ten genes tested were not affected during the whole experiment. The increased mRNA amount was observed only for asd and cyrB after 120 h of the treatment.
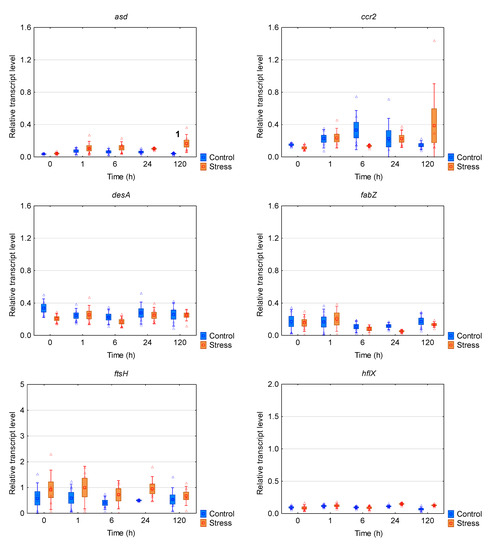
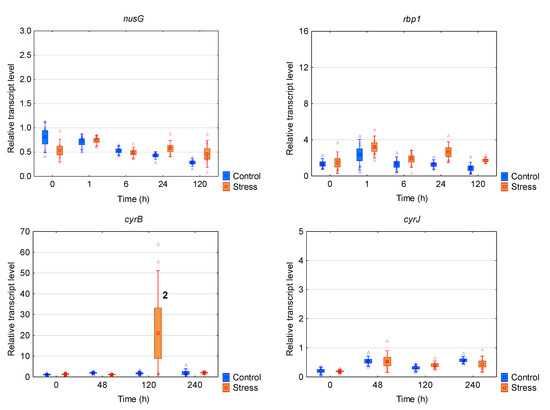
Figure 4.
The box plots with a relative gene expression level of each analyzed gene of Raphidiopsis raciborskii CS-505 in reference to the prs house-keeping gene transcript level. Means are indicated by squares, bars represent the standard deviation whereas boxes represents the standard error. Raw data are marked as triangles. Statistically significant differences: (1) increased in comparison to stress t0 and control 120 h; (2) increased in comparison to each control and stress.
4. Discussion
The successful range expansion of R. raciborskii species occurs through phenotypic plasticity, allowing it to rapidly adapt to new conditions, and physiological attributes that allow it to thrive in inhospitable environments [2]. For example, its high affinity for phosphorus uptake and strain variation in phosphorus storage [23] has allowed its dominance in habitats with phosphate deficiency [24]. Growth under a broad range of temperature and light conditions is also an important capability for successful invasion [18,25,26,27]. The dual roles of light and temperature in the dominance of certain species is not fully understood, and field and laboratory studies have shown contrasting results [7,28,29].
While the temperature optima of R. raciborskii strains isolated both from temperate and (sub)tropical regions is reported as 19 to 32 °C [26,30] in the field, R. raciborskii populations can sustain biomass at temperatures as low as 11 °C [11]. In this study, the strains isolated from different climatic zones varied in their ability to grow under low temperature and high light irradiance (Figure 1). The temperate Polish strain AMU-DH-30 performed better under the stress conditions (10 °C and 100 µmol of photons m−1 s−1) than strain CS-505 from tropical Australia. Unsurprisingly, strain AMU-DH-30 appears to be better adapted to cold conditions, however, both strains had the ability to regenerate under favorable conditions, suggesting that both strains would proliferate similarly. Therefore, increasing water temperatures and longer vegetation season are factors that could increase the opportunities for tropical strains of R. raciborskii to establish in temperate regions [30,31]. In the temperate zone in Poland, the maximum abundance of this species is limited to summer when water temperatures range from 22–25 °C [28]. Recknagel et al. [32] showed a strong correlation between seasonal population dynamics of R. raciborskii and water temperature in two temperate lakes, compared to a greater temperature dependence in tropical lakes. On the other hand, a different study reported only a weak influence of temperature on the phytoplankton community composition and R. raciborskii spread [29]. Overall, climate warming has been suggested frequently to explain the successful expansion of R. raciborskii.
Similarly, a high tolerance to changes in light intensity has been demonstrated for R. raciborskii [1,23]. The dual roles of light and temperature in the dominance of certain species is not fully understood. Briand et al. [33] revealed strain dependent differences in the growth rate under a wide range of light conditions from 50 to 500 µmol m−2 s−1, however, general preference appears to be for low light between 50 and 120 µmol m−2 s−1 [2]. Moreover, R. raciborskii is known to be a shade tolerant species and its growth can be maintained in light as low as 10 µmol m−2 s−1 and below [2]. Such a high variability in light tolerance does not seem to correlate with the biogeographical origin of the strains [2,34]. Changes in the photosynthetic structures (cell pigment quota and effective absorption cross-sectional area of PSII) were indicated as a possible mechanism that allows R. raciborskii to adapt to varied environments with relatively stable light conditions [35]. However, importantly, recent evidence indicates that the growth of R. raciborskii at low temperatures is light dependent, with high irradiance hampering its growth [7]. Our study is in line with this finding, additionally showing that the phenomenon of low-temperature/high light-induced photoinhibition is also strain specific. However, the above-mentioned findings do not explain how some R. raciborskii strains have adapted to chill/light. This adaptation requires the development of mechanisms that ensure survival with the combination of two stresses, typical of the temperate climate.
The mechanisms of adaptation to chill/light have been explored only accidentally. For example, such conditions may induce the accumulation of carotenoids and phycobilins in R. raciborskii cells [36,37] which allows better protection from light and results in lower photoinhibition compared to a native species, Aphanizomenon gracile [37]. However, neither genetic nor physiological characteristics of this adaptation are well understood. The pattern of gene expression of the selected genes in this study, which are involved in the basic metabolic processes (Figure 5), give insights into this phenomenon.
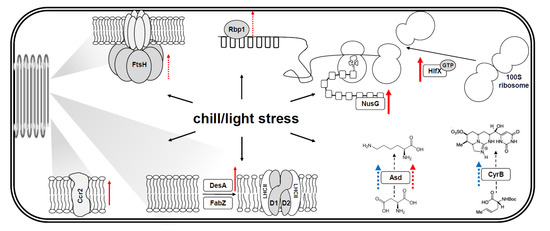
Figure 5.
Schematic indicating the role of analyzed genes in a cyanobacterial cell and their response to chill/light stress. Red and blue arrows represent the gene upregulation in AMU-DH-30 and CS-505 strains, respectively (solid—indicates early response (1 h), dotted—response after prolonged exposure to stress (120 h), bold arrows—at least 4-fold, thus biologically relevant upregulation). Rbp1—RNA-binding protein, involved in posttranscriptional regulation; DesA—delta(12)-fatty-acid desaturase, and FabZ (3R)—hydroxymyristoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]-dehydratase, both involved in unsaturation of fatty acids of the membrane lipids; FtsH—ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease responsible for the thylakoid membranes biogenesis and control of the photosystem II repair cycle; Ccr2—assumable thylakoid protein important in maintaining the membrane functionality and affecting the PS II-mediated electron transport rate; NusG—a transcription factor that may participate in transcription attenuation and translational control mechanisms; HflX—GTPase, a dissociation factor of the 100S ribosome that plays a role in the regulation of 70S and 100S ribosome homeostasis; Asd—aspartate-beta-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, enzyme involved in lysine biosynthetic pathway and the further accumulation of AASA participating in stress response; CyrB—enzyme involved in cytotoxic CYN synthesis pathway. See details in the main text.
The gene expression results suggest a broad response to chill/light stress on mRNA level (seven of the eight investigated genes upregulated) in AMU-DH-30 strain (Figure 2a, Figure 3 and Figure 5). The biologically relevant upregulation impacting the physiological level can be assumed at least for hflX, nusG, and asd. Furthermore, the increased expression of other genes also suggest their involvement in this type of response. Particularly important seems to be the upregulation of rbp1 as it has been documented that RNA-binding proteins (Rbp), involved in many posttranscriptional regulation processes may regulate the cyanobacterial physiology at low temperature. The accumulation of Rbp1 and 2 in Synechocystis sp. during preconditioning [14] was correlated with the increased chill/light tolerance. Our results suggest that the upregulation of rbp1 in R. raciborskii may allow the initiation of other processes necessary for adaptation, mainly those responsible for enhanced membrane fluidity and photosynthesis maintenance. In Synechocystis, Rbp3 may influence the mRNA levels of desA, desB, desD [38], which has a role in the modifications of membrane fluidity. In our study, the increased level of desA was observed only in AMU-DH-30 strain after 1 h and five days of acclimation to chill/light stress whereas in CS-505 strain this gene was not upregulated. These results suggest that cells of R. raciborskii AMU-DH-30 exposed to chill/light stress were induced to a rapid increase in the desaturation of fatty acids chains and this process is prolonged for several days, indicating the mechanism of chill/light adaptation. Another investigated gene encoding (3R)—hydroxymyristoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein]-dehydratase (FabZ) [39] is involved in a fatty acid elongation cycle that leads the biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids. However, fabZ was not upregulated neither in AMU-DH-30 nor CS-505 strain which indicates that this gene does not play any role in chill/light stress.
The modification of thylakoid membrane composition and fluidity provides an optimal condition leading to homeostasis of proteins involved in photosynthesis and their functionality under stressful condition [40]. The homeostasis of proteins relies on the mechanisms necessary to remove photodamaged and misfolded proteins. One of the most limiting steps in the photosynthetic repair cycle is the replacement rate of damaged D1, an integral component of PSII, which is particularly sensitive to oxidative stress induced by chill/light. The ATP-dependent zinc metalloprotease (FtsH) plays a crucial role in the control of the photosystem II repair cycle in model cyanobacterium species Synechocystis PCC 6803 [41] and in Prochlorococcus marinus MED 4 [42]. The upregulation of ftsH observed in our study under chill/light stress after 24 h (which was prolonged in the following days) suggests that in AMU-DH-30 ftsH supports the assembly of protein complexes in the photosynthetic electron-transport pathways. Other genes that are required to support the photosynthetic activity at a low temperature, crucial in the response to chill/light stress belong to ccr (cyanobacterial cold resistance genes) [15,16]. Their expression can be influenced by Rbp proteins [38] as discussed above. Ccr2 has previously been reported as a representative of a novel thylakoid protein required for survival in lower temperatures [16]. Our results seem to confirm the importance of this protein in the adaptation to lower temperature. The increased level of ccr2 observed in AMU-DH-30 strain may affect a membrane functionality and the PSII-mediated electron transport rate, by interaction with PSII or electron carriers, as was suggested by Li et al. [16].
Other metabolic processes important in the response to low temperature are those triggering the protein synthesis inhibited under low temperature. The upregulation of such genes required to reinitiate the translation (such as nusG and hlfX) occur after prolonged to low temperature [40,41]. A conserved transcription factor NusG may participate in transcription attenuation and translational control mechanisms [43]. Its expression in AMU-DH-30 increased after 1 h of chill/light stress and was upregulated after 120 h, as well, suggesting that the transcriptional and translational machineries can be controlled by the mechanism involving NusG. The expression of hflX in this strain was significantly increased in the same manner. Conserved GTPase HflX has recently been found as a dissociation factor of the S. aureus 100S ribosome [44] that plays a key role in the regulation of 70S and 100S ribosome homeostasis, which is closely connected with the bacterial survival during different stress conditions. The expression of hflX, that may be regulated in a temperature-dependent manner [45], is necessary to reuse the ribosome for new cycles of translation. The upregulation of hflX observed in our study may promote the 70S ribosomes disassembly and suggests that R. raciborskii AMU-DH-30 cells can maintain cell viability by reversible conversion of silent 100S to a translationally active 70S ribosome.
An alternative and widely used protective strategy to overcome the challenges of a changing environment is based on the accumulation of low-molecular-weight, water-soluble, organic compounds, known as compatible solutes [46]. Among them, the lysine derivatives are of particular interest because of their close connection between lysine catabolism and temperature stress protection [47]. In the present paper, the asd gene encoding aspartate-beta-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in the lysine biosynthetic pathway was analyzed. The further conversion of lysine allows the accumulation of α -aminoadipic-δ -semialdehyde (AASA), a physiological intermediate that participates in stress response [48]. The expression level of this gene was enhanced in both investigated strains which may suggest that the accumulation of compatible solute (AASA) [46] was stimulated. The induced expression of this gene involved in the lysine conversion suggests its importance to survive during the chill/light stress.
To summarize the aforementioned findings—both the growth and expression patterns of R. raciborskii AMU-DH-30 strain indicate that its adaptation to the temperate climate of central Europe is displayed by the fast initiation of different mechanisms required to maintain the main metabolic functions, particularly ones sensitive to chill/light stress. On the contrary, a different behaviour of R. raciborskii CS-505 (Figure 2b) was noted—lower growth rate in stressful conditions but, similar to AMU-DH-30, ability to resume the growth—may suggest other mechanisms involved in the response to chill/light. Indeed, it is an intriguing finding that from the analyzed list of genes reported previously known to encode proteins involved in a stress protection [19], no genes were activated in CS-505 during the chill/light stress. On the other hand, in the CS-505 cyrB gene involved in cytotoxic CYN production was significantly overexpressed on day 5 in stress conditions (Figure 2c). It is interesting to note this upregulation although previous studies have not found a link between cyr gene expression and toxin yield [49] and CYN production in R. raciborskii is generally considered constitutive [50,51].
5. Conclusions
Although R. raciborskii initially occurred in more tropical regions, it has invaded freshwaters in the temperate climate. The results provided in this paper suggest that the temperate strain, R. raciborskii AMU-DH-30, is better adapted to chill/light stress. Its expression pattern implies broad physiological response and the stimulation of several processes crucial for the cell functioning under stress. On the other hand, the tropical strain, R. raciborskii CS-505, was unable to grow and respond to the chill/light stress; it seems to halt physiological response and “wait” until conditions improve and then continues to grow. Gene expression of the same genes can vary significantly between the strains, and the results from our study suggest that the chill/light stress, relatively common in the temperate climate, imposes the adaptive evolution that allows such ecological success of invasive species through the flexible modification of the structure and physiology of cyanobacterial cells. Recent genome analysis suggests that speciation in Raphidiopsis occurs through geographic isolation [52,53]. This adaptation can occur through changes in the genome via the horizontal gene transfer but also through changes in gene expression, as has been seen previously in closely related strain CS-505 and CS-506 [54]. It is confirmed in the present study with strains with much greater geographic isolation. Comparing such different strains gives a broader insight into the adaptation of strains to local environments. However, further research would be needed to investigate more definitively which stress response mechanisms are activated in different strains of R. raciborskii.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.D., M.K., A.W., A.K.B., and W.S.; methodology, A.A., M.K., and D.D.; investigation, A.A., N.T., A.B., and R.M.; resources, M.K., A.B., and A.W.; data curation, A.A. and D.D.; writing—original draft preparation, D.D., W.S., A.K.B., and M.K.; writing—review and editing, D.D., W.S., A.K.B., A.W., A.A., A.B., N.T., R.M., and M.K.; visualization, D.D. and A.A.; supervision, A.W.; project administration, D.D. and M.K.; funding acquisition, D.D. and W.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Faculty of Biochemistry, Biophysics, and Biotechnology, JU. Nada Tokodi was supported by postdoctoral funding from Narodowa Agencja Wymiany Akademickiej (NAWA) with ULAM grant number PPN/ULM/2019/1/00219.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I., Bertram, J., Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1999; pp. 1–416. [Google Scholar]
- Burford, M.A.; Beardall, J.; Willis, A.; Orr, P.T.; Magalhaes, V.F.; Rangel, L.M.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.E.; Neilan, B.A. Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, M.A.; Willis, A.; Chuang, A.; Man, X.; Orr, P.T. Recent insights into physiological responses to nutrients by the cylindrospermopsin producing cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniedziałek, B.; Rzymski, P.; Kokociński, M.; Karczewski, J. Toxic potencies of metabolite(s) of non-cylindrospermopsin producing Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolated from temperate zone in human white cells. Chemosphere 2015, 120, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfushynska, H.; Horyn, O.; Brzozowska, A.; Fedoruk, O.; Buyak, B.; Poznansky, D.; Poniedziałek, B.; Kokociński, M.; Rzymski, P. Is the presence of Central European strains of Raphidiopsis (Cylindrospermopsis) raciborskii a threat to a freshwater fish? An in vitro toxicological study in common carp cells. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 206, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, A.; Ruiz, M.; Zhang, C.C. Oxidative stress in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, A.W.; Présing, M.; Vörös, L. Thermal-dependent growth characteristics for Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanoprokaryota) at different light availabilities: Methodological considerations. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L.; Soares, M.C.S.; Gonzalez-Piana, M.; Fabre, A.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Lurling, M.; Antoniades, D.; Padisak, J.; Kruk, C. What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Willis, A.; Burford, M.A. Differences in cyanobacterial strain responses to light and temperature reflect species plasticity. Harmful Algae 2017, 62, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Hamilton, D.P.; O’Brien, K.R.; Adams, M.P.; Willis, A.; Burford, M.A. Are laboratory growth rate experiments relevant to explaining bloom-forming cyanobacteria distributions at global scale? Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan-Levy, R.N.; Hadas, O.; Summers, M.L.; Rücker, J.; Sukenik, A. Akinetes: Dormant cells of cyanobacteria. In Dormancy and Resistance in Harsh Environments, Topics in Current Genetics; Lubzens, E., Cerda, J., Clark, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 21, pp. 5–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sukenik, A.; Hadas, O.; Kaplan, A.; Quesada, A.; Marine, H.S.; Morgan-kiss, R.M. Invasion of Nostocales (cyanobacteria) to subtropical and temperate freshwater lakes—Physiological, regional, and global driving forces. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccini, C.; Aubriot, L.; Fabre, A.; Amaral, V.; González-Piana, M.; Giani, A.; Figueredo, C.C.; Vidal, L.; Kruk, C.; Bonilla, S. Genetic and eco-physiological differences of South American Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolates support the hypothesis of multiple ecotypes. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zhu, T.; Shen, S.; Yin, C.; Gao, H.; Xu, X. Role of Rbp1 in the acquired chill-light tolerance of cyanobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 2675–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Li, W.; Du, Y.; Kong, R.; Xu, X. Identification of a gene, ccr-1 (sll1242), required for chill-light tolerance and growth at 15 degrees C in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Microbiology 2017, 1, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Gao, H.; Yin, C.; Xu, X. Identification of a novel thylakoid protein gene involved in cold acclimation in cyanobacteria. Microbiology 2012, 158, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, C.; Li, W.; Xu, X. α-Tocopherol Is Essential for Acquired Chill-Light Tolerance in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC 6803. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mehnert, G.; Leunert, F.; Cires, S.; Johnk, K.D.; Rucker, J.; Nixdorf, B.; Wiedner, C. Competitiveness of invasive and native cyanobacteria from temperate freshwaters under various light and temperature conditions. J. Plankton Res. 2010, 32, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Pearson, L.; Kumar, A. Stress Biology of Cyanobacteria: Molecular Mechanisms to Cellular Responses; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781466504783. [Google Scholar]
- Kokociński, M.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J.; Jurczak, T.; Spoof, L.; Meriluoto, J.; Rejmonczyk, E.; Hautala, H.; Vehniäinen, M.; Pawełczyk, J.; Soininen, J. Aphanizomenon gracile (Nostocales), a cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacterium in Polish lakes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5243–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziga, D.; Tokodi, N.; Drobac, D.; Kokociński, M.; Antosiak, A.; Puchalski, J.; Strzałka, W.; Madej, M.; Svirčev, Z.; Meriluoto, J. The Effect of a combined hydrogen peroxide-MlrA treatment on the phytoplankton community and microcystin concentrations in a mesocosm experiment in Lake Ludoš. Toxins 2019, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, J.; Chang, T.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.; He, H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; et al. Stable reference gene selection for RT-qPCR analysis in Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 under abiotic stresses. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7630601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Hamilton, D.P.; Chuang, A.; Burford, M.A. Intra-population strain variation in phosphorus storage strategies of the freshwater cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis raciborskii. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, V.; Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L. Growth optimization of the invasive cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in response to phosphate fluctuations. Eur. J. Phycol. 2014, 49, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; González-Piana, M.; Soares, M.C.S.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Becker, V.; Somma, A.; Marinho, M.M.; Kokociński, M.; Dokulil, M.; Antoniades, D.; et al. The success of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in freshwaters is enhanced by the combined effects of light intensity and temperature. J. Limnol. 2016, 75, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Pearson, L.A.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Orr, P.T.; Neilan, B.A. Increased incidence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in temperate zones—Is climate change responsible? Water Res. 2012, 46, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Dokulil, M.T. Vegetative survival of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) at low temperature and low light. Hydrobiologia 2016, 764, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolius, S.; Wiedner, C.; Weithoff, G. Low invasion success of an invasive cyanobacterium in a chlorophyte dominated lake. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.N.; Thomas, M.K.; Litchman, E. The effects of phosphorus and temperature on the competitive success of an invasive cyanobacterium. Aquat. Ecol. 2017, 51, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.K.; Litchman, E. Effects of temperature and nitrogen availability on the growth of invasive and native cyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 2016, 763, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokociński, M.; Gągała, I.; Jasser, I.; Karosienė, J.; Kasperovičienė, J.; Kobos, J.; Koreivienė, J.; Soininen, J.; Szczurowska, A.; Woszczyk, M.; et al. Distribution of invasive Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in the East-Central Europe is driven by climatic and local environmental variables. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recknagel, F.; Zohary, T.; Rücker, J.; Orr, P.T.; Castelo, C.; Nixdorf, B.; Max, M.M. Causal relationships of Raphidiopsis (formerly Cylindrospermopsis) dynamics with water temperature and N:P-ratios: A meta-analysis across lakes with different climates based on inferential modelling. Harmful Algae 2019, 84, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, J.-F.; Leboulanger, C.; Humbert, J.-F.; Bernard, C.; Dufour, P. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) invasion at mid-latitudes: Selection, wide physiological tolerance or global warming? J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.T.; Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: Review of the distribution, phylogeography, and ecophysiology of a global invasive species. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierangelini, M.; Stojkovic, S.; Orr, P.T.; Beardall, J. Photo-acclimation to low light—Changes from growth to antenna size in the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 2015, 46, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, R. Comparative studies on photosynthesis and phosphate metabolism of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii with Microcystis aeruginosa and Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, G.; Rücker, J.; Nicklisch, A.; Leunert, F.; Wiedner, C. Effects of thermal acclimation and photoacclimation on lipophilic pigments in an invasive and a native cyanobacterium of temperate regions. Eur. J. Phycol. 2012, 47, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Tan, X.; Xu, X. Effects of a type-II RNA-binding protein on fatty acid composition in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 2416–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeamton, W.; Mungpakdee, S.; Sirijuntarut, M.; Prommeenate, P.; Cheevadhanarak, S.; Tanticharoen, M.; Hongsthong, A. A combined stress response analysis of Spirulina platensis in terms of global differentially expressed proteins, and mRNA levels and stability of fatty acid biosynthesis genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 281, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Taira, Y.; Emi, T.; Yamane, Y.; Kashino, Y.; Koike, H.; Satoh, K. Acclimation to the Growth Temperature and the High-Temperature Effects on Photosystem II and Plasma Membranes in a Mesophilic Cyanobacterium, Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001, 42, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, M.; Yu, J.; Krynicka, V.; Barker, M.; Tichy, M.; Komenda, J.; Nixon, P.J.; Nield, J. Subunit organization of a Synechocystis hetero-oligomeric thylakoid FtsH complex involved in Photosystem II repair. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3669–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonisteel, E.M.; Turner, B.E.; Murphy, C.D.; Melanson, J.; Duff, M.; Beardsall, B.D.; Xu, K.; Campbell, D.A.; Id, A.M.C. Strain specific differences in rates of Photosystem II repair in picocyanobacteria correlate to differences in FtsH protein levels and isoform expression patterns. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Krishna, P.; Shivaji, S. Sensing and molecular responses to low temperature in cyanobacteria. In Stress Biology of Cyanobacteria; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, A.; Yap, M.-N.F. Disassembly of the Staphylococcus aureus hibernating 100S ribosome by an evolutionarily conserved GTPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8165–E8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Yap, M.-N.F. Ribosome hibernation factor promotes Staphylococcal survival and differentially represses translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4881–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Xue, Y.; Ma, Y. Identification of N α-acetyl-α-lysine as a probable thermolyte and its accumulation mechanism in Salinicoccus halodurans H3B36. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neshich, I.A.; Kiyota, E.; Arruda, P. Genome-wide analysis of lysine catabolism in bacteria reveals new connections with osmotic stress resistance. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2400–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mello Serrano, G.C.; e Silva Figueira, T.R.; Kiyota, E.; Zanata, N.; Arruda, P. Lysine degradation through the saccharopine pathway in bacteria: LKR and SDH in bacteria and its relationship to the plant and animal enzymes. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangelini, M.; Sinha, R.; Willis, A.; Burford, M.A.; Orr, P.T.; Beardall, J.; Neilan, B.A. Constitutive Cylindrospermopsin Pool Size in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii under Different Light and CO2 Partial Pressure Conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3069–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.; Adams, M.P.; Chuang, A.W.; Orr, P.T.; O’Brien, K.R.; Burford, M.A. Constitutive toxin production under various nitrogen and phosphorus regimes of three ecotypes of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii ((Wołoszyńska) Seenayya et Subba Raju). Harmful Algae 2015, 47, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, P.T.; Willis, A.; Burford, M.A. Application of first order rate kinetics to explain changes in bloom toxicity—The importance of understanding cell toxin quotas. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vico, P.; Bonilla, S.; Cremella, B.; Aubriot, L.; Iriarte, A.; Piccini, C. Biogeography of the cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis (Cylindrospermopsis) raciborskii: Integrating genomics, phylogenetic and toxicity data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 148, 106824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.; Jason, N.; Woodhouse, J.N. Defining cyanobacterial species: Diversity and description through genomics. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2020, 39, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.; Chuang, A.W.; Dyhrman, S.; Burford, M.A. Differential expression of phosphorus acquisition genes in response to phosphorus stress in two Raphidiopsis raciborskii strains. Harmful Algae 2019, 82, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).