Platelet Rich STROMA, the Combination of PRP and tSVF and Its Potential Effect on Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material & Methods
2.1. Patient Population
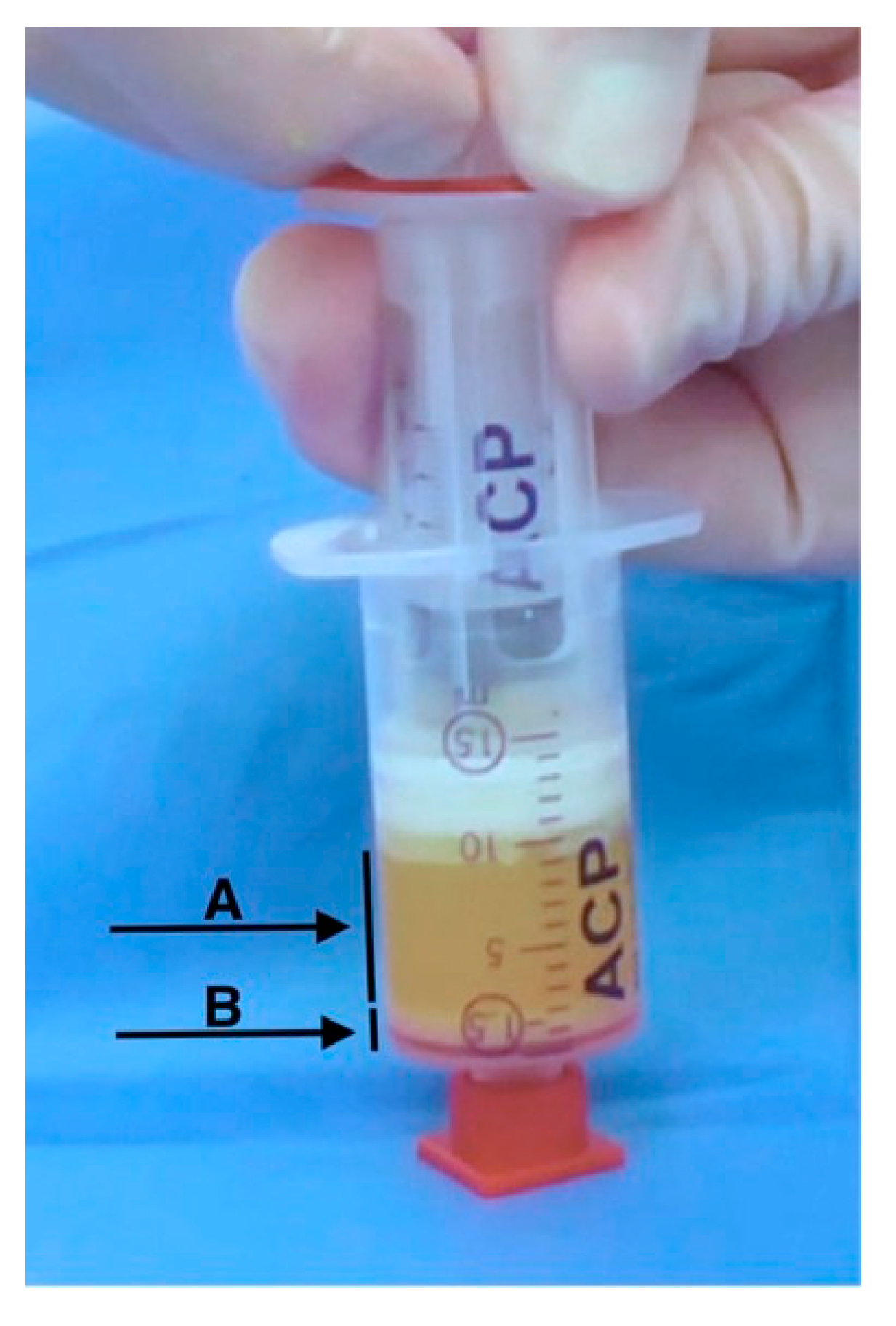
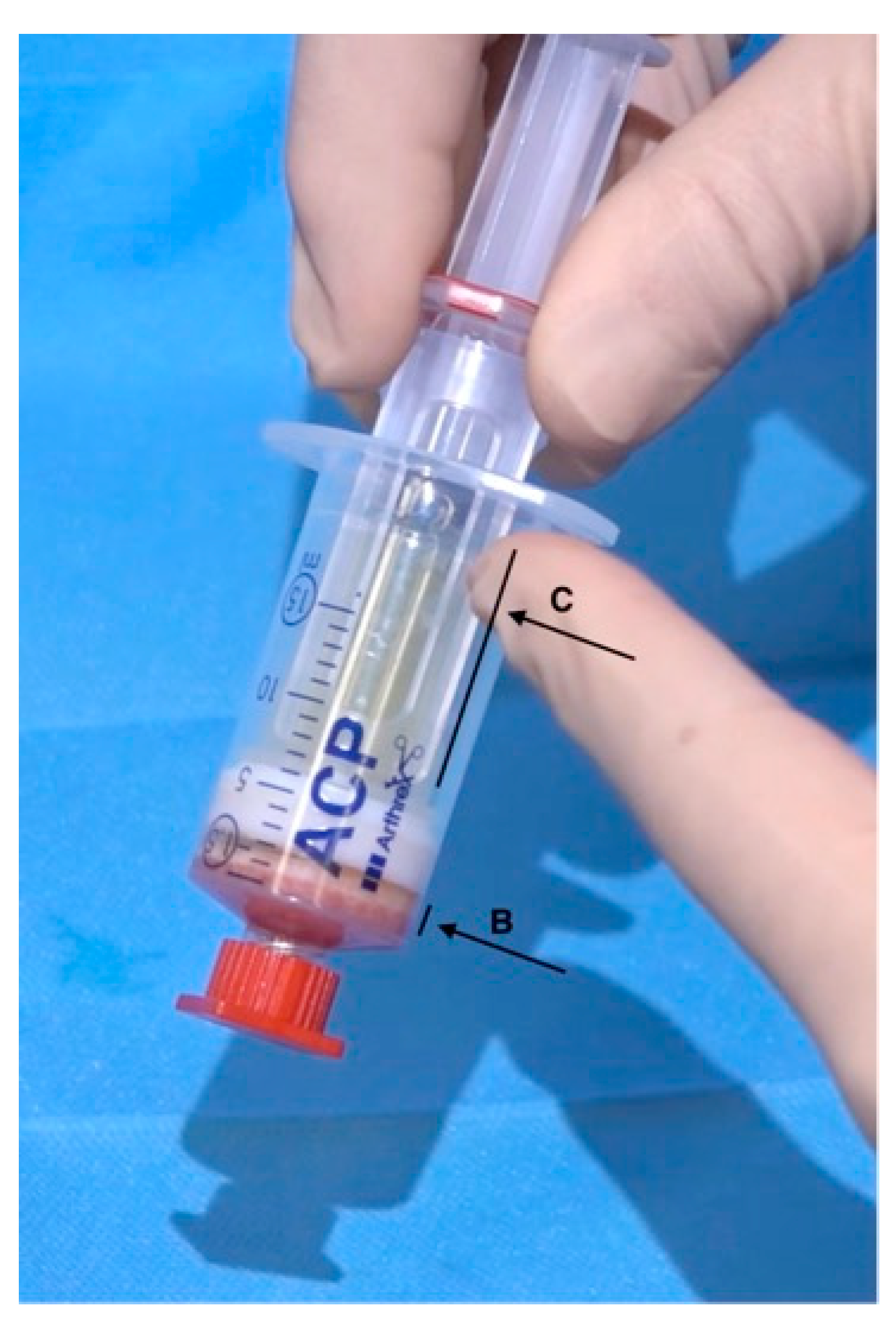
2.2. Preparation of Platelet-Rich Plasma
2.3. Lipoharvesting and the Fractionation of Adipose Tissue (FAT) Procedure
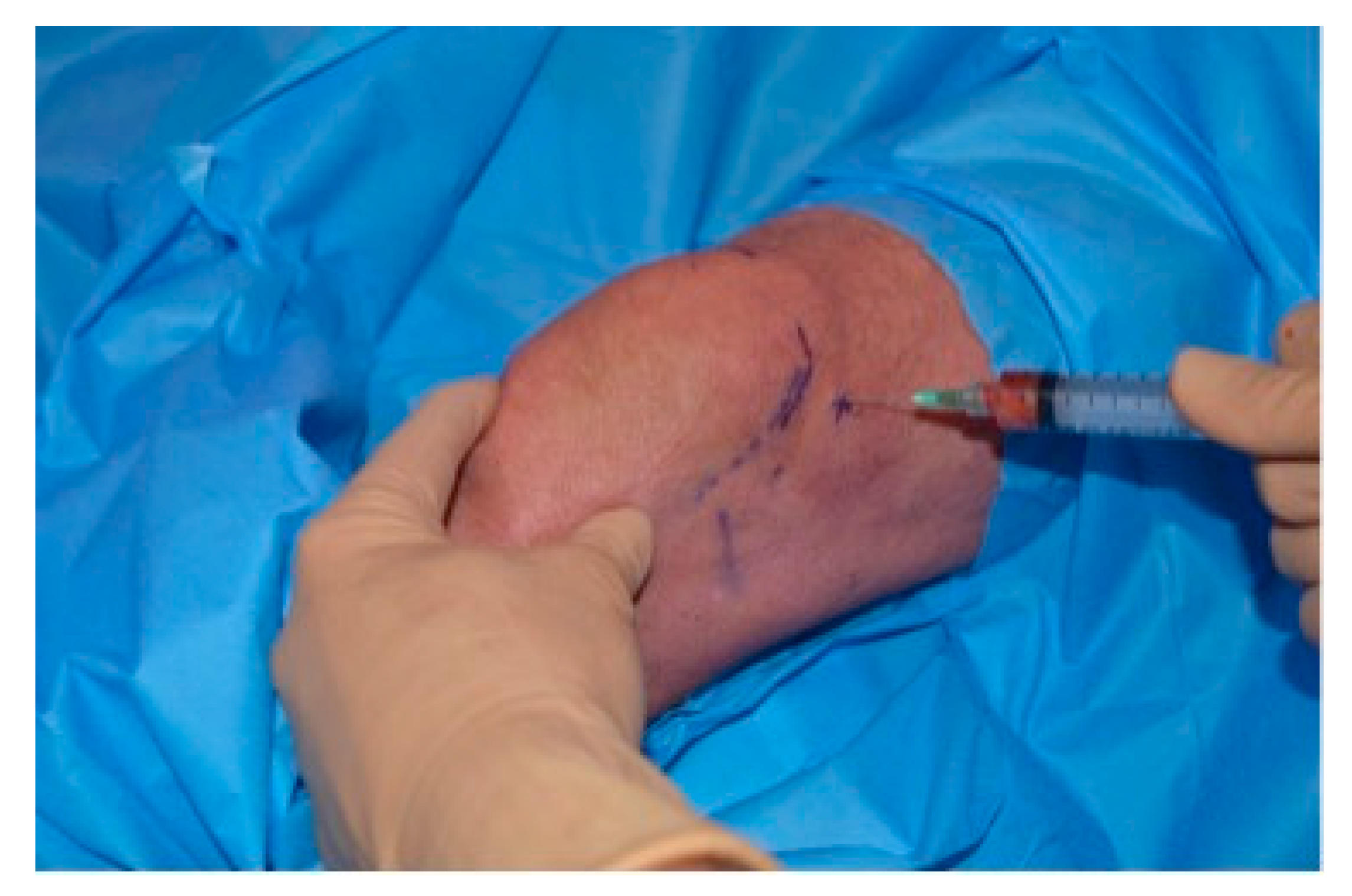
2.4. Platelet Rich Stroma (PRS) Injection
2.5. Evaluation of the Effect of PRS on Knee Osteoarthritis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
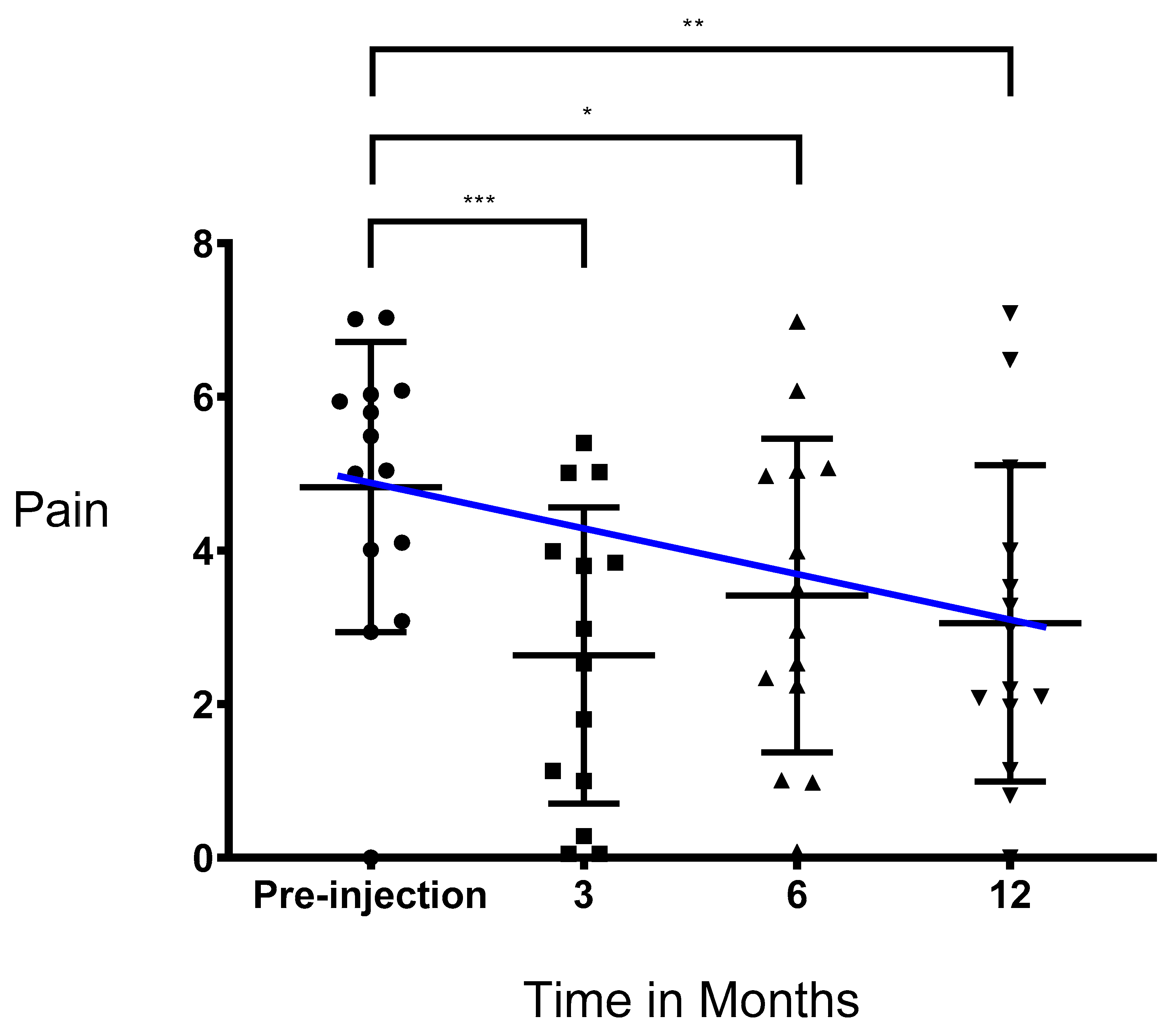
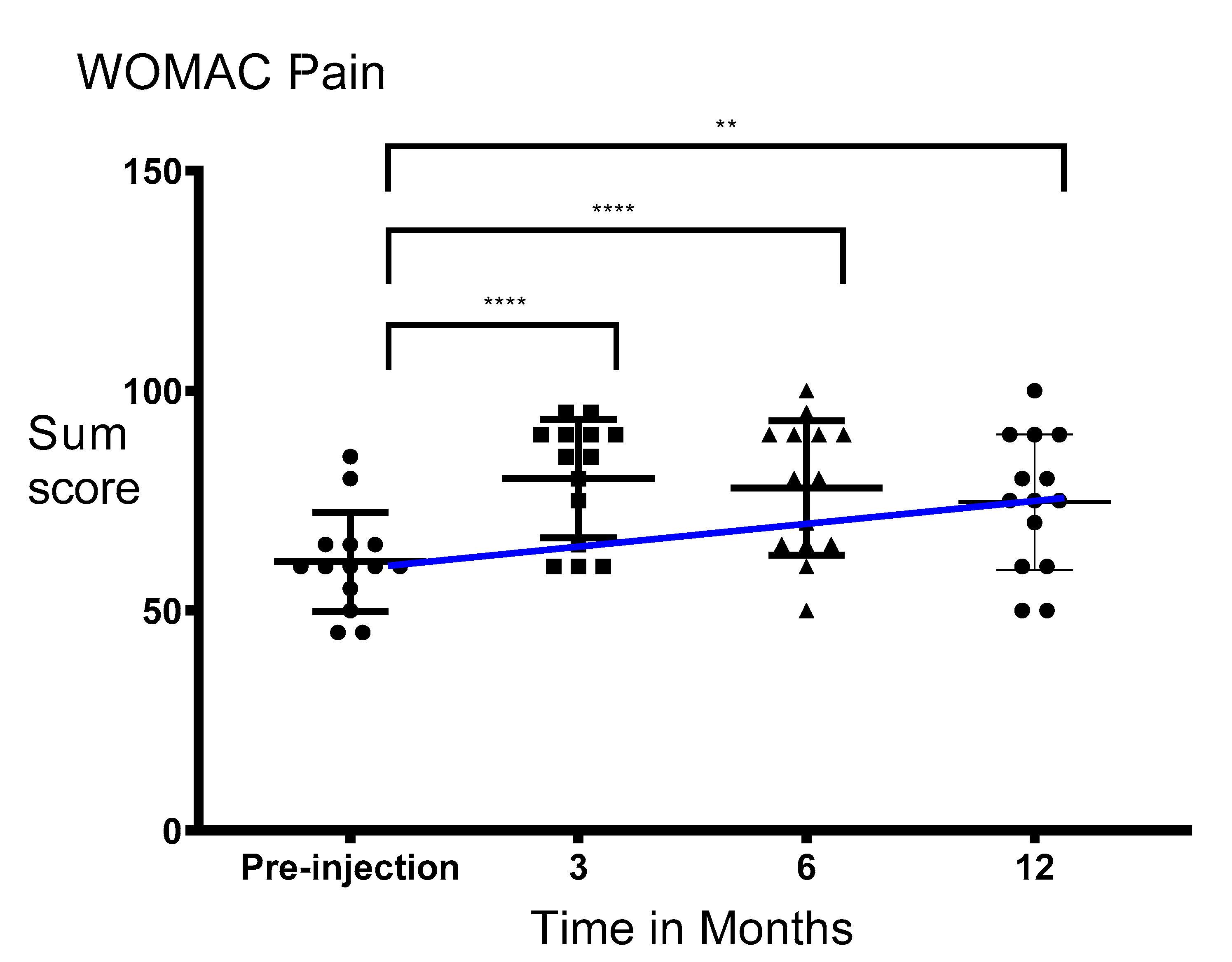
3.2. Pain Significantly Decreased after Injection of PRS
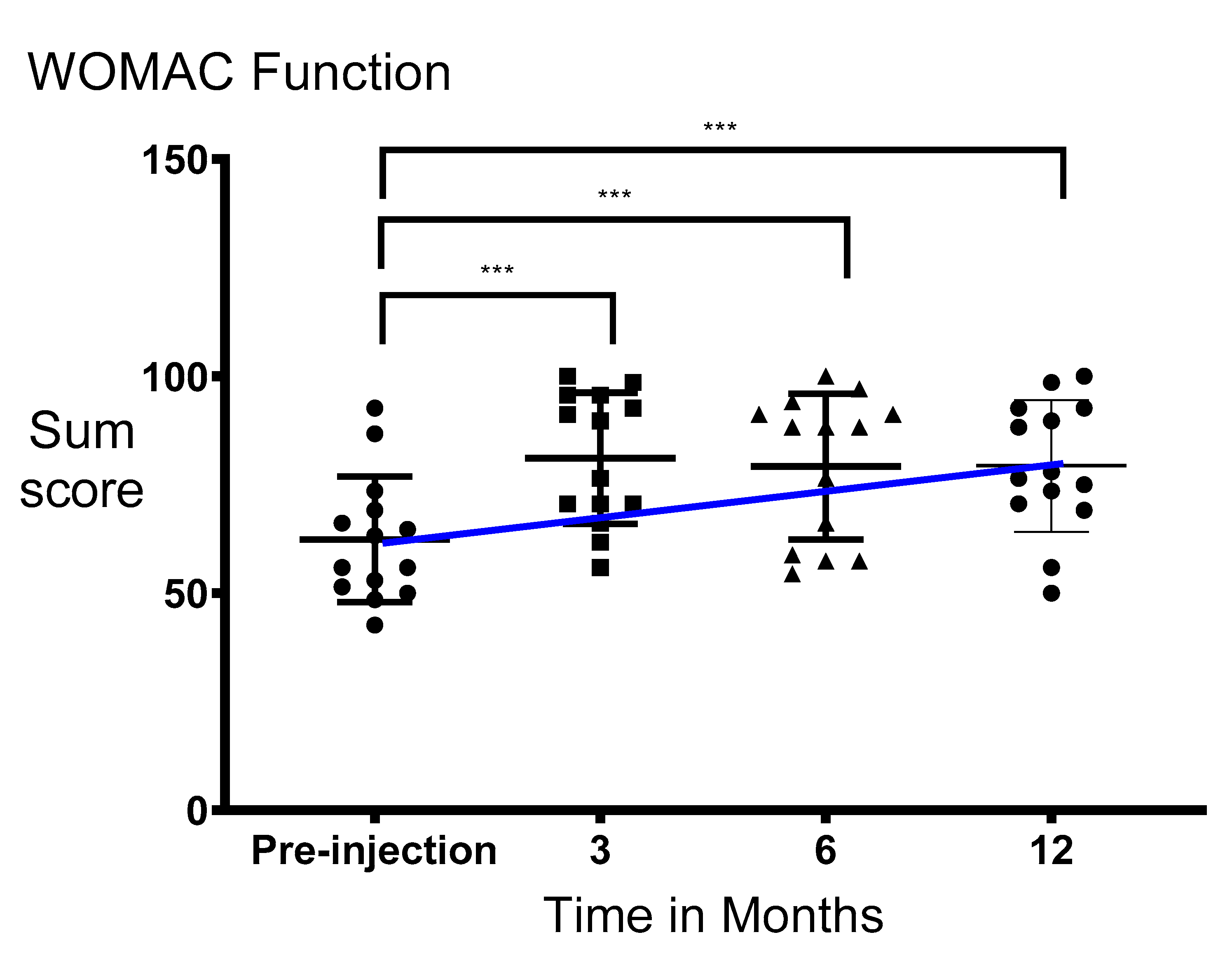
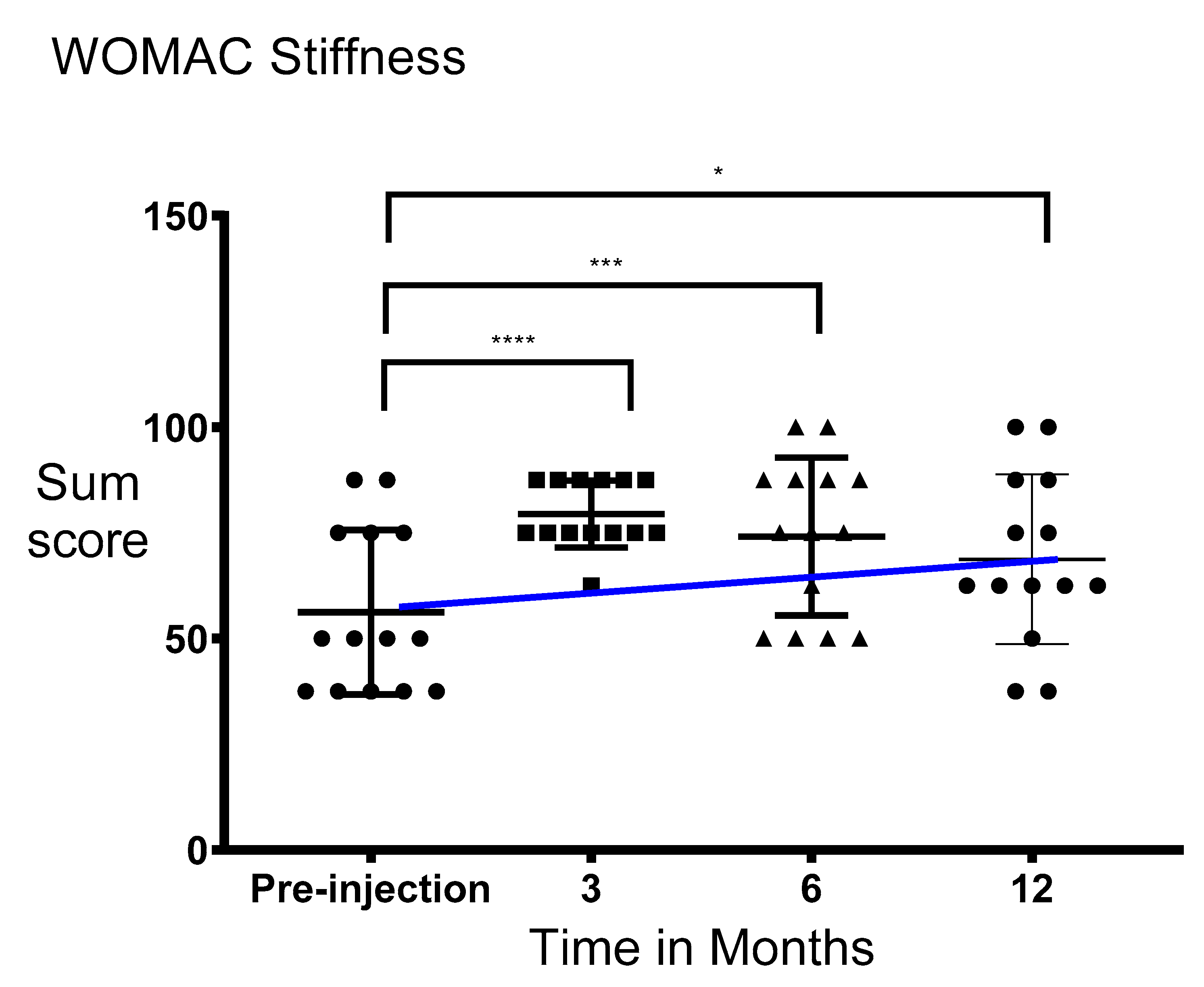
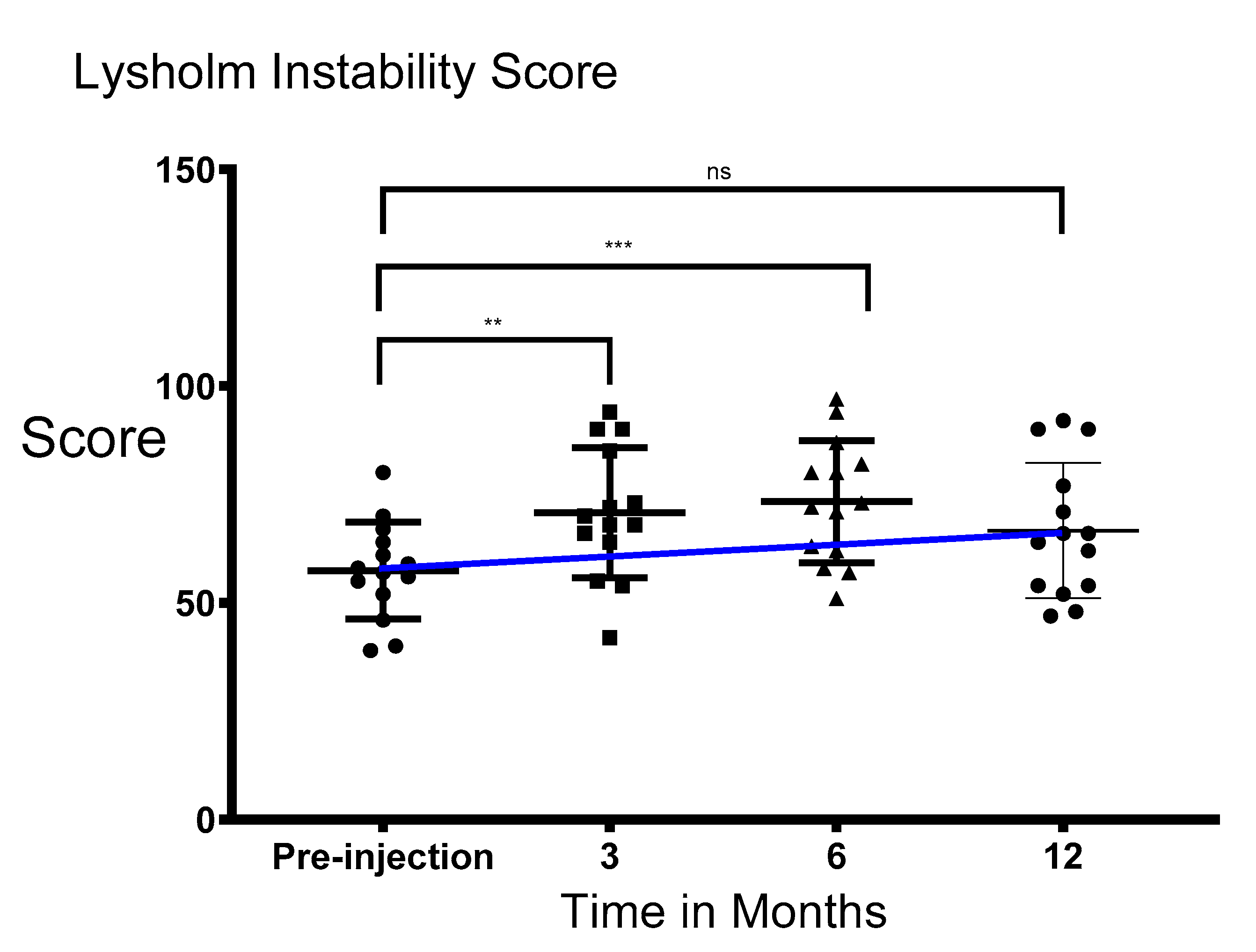
3.3. Functionality and Stiffness of the Knee Significantly Improved after Injection of PRS
3.4. No Significant Changes on MRI Were Seen after Injection of PRS
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silverwood, V.; Blagojevic-Bucknall, M.; Jinks, C.; Jordan, J.L.; Protheroe, J.; Jordan, K.P. Current evidence on risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day-Williams, A.G.; Southam, L.; Panoutsopoulou, K.; Rayner, N.W.; Esko, T.; Estrada, K.; Helgadottir, H.T.; Hofman, A.; Ingvarsson, T.; Jonsson, H.; et al. A variant in MCF2L is associated with osteoarthritis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, L.; Schwartz, T.A.; Helmick, C.G.; Renner, J.B.; Tudor, G.; Koch, G.; Dragomir, A.; Kalsbeek, W.; Luta, G.; Jordan, J.M. Lifetime risk of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis analysis and interpretation of data HHS public access. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2008, 59, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torio, C.M.; Andrews, R.M. National Inpatient Hospital Costs: The Most Expensive Conditions by Payer, 2011: Statistical Brief #160. In Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Neogi, T. The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. Vol. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Ong, K.L.; Lau, E.; Bozic, K.J. Impact of the economic downturn on total joint replacement demand in the United States: Updated projections to 2021. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. Vol. 2014, 96, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardo, G.; Kon, E.; Longo, U.G.; Madry, H.; Marchettini, P.; Marmotti, A.; Assche, D.V.; Zanon, G.; Peretti, G.M. Non-surgical treatments for the management of early osteoarthritis. Knee Surg. Sport Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibel, K.H. State-of-the-Art management of knee osteoarthritis. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, A.; Penrose, C.T.; Seyler, T.M.; Mather, R.C.; Wellman, S.S.; Bolognesi, M.P. Outcomes after total knee arthroplasty for post-traumatic arthritis. Knee 2015, 22, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, J.A.J.; Smith, H.K.; Jonas, S.C.; Greenwood, R.; Weale, A.E. Return to work following knee arthroplasty. Knee 2010, 17, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, N.; Diamond, R.; Sekyere, E.O.; Thomas, W.D. Management of knee osteoarthritis by combined stromal vascular fraction cell therapy, platelet-rich plasma, and musculoskeletal exercises: A case series. J. Pain Res. 2015, 8, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobita, M.; Tajima, S.; Mizuno, H. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma: Stem cell transplantation methods that enhance stemness Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells-An update. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourin, P.; Bunnell, B.A.; Casteilla, L.; Dominici, M.; Katz, A.J.; March, K.L.; Redl, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoshimura, K.; Gimble, J.M. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: A joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 641–648. [Google Scholar]
- Corselli, M.; Chen, C.W.; Sun, B.; Yap, S.; Rubin, J.P.; Péault, B. The tunica adventitia of human arteries and veins as a source of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Garcia, M.; Ning, H.; Banie, L.; Guo, Y.-L.; Lue, T.F.; Lin, C.-S. Defining stem and progenitor cells within adipose tissue. Stem Cells Dev. 2008, 17, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.A.; Tuin, A.J.; Spiekman, M.; Jansma, J.; van der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. Comparison of intraoperative procedures for isolation of clinical grade stromal vascular fraction for regenerative purposes: A systematic review. J. Tissue Eng. Regen Med. 2018, 12, e261–e274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.A.; Stevens, H.P.; Harmsen, M.C.; van der Lei, B. Mechanical micronization of lipoaspirates: Squeeze and emulsification techniques. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 1369e–1370e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dongen, J.A.; Stevens, H.P.; Parvizi, M.; van der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. The fractionation of adipose tissue procedure to obtain stromal vascular fractions for regenerative purposes. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocca, A.D.; McCarthy, M.B.; Chowaniec, D.M.; Dugdale, E.M.; Hansen, D.; Cote, M.P.; Bardley, J.P.; Romeo, A.A.; Arciero, R.A.; Beitzelet, K. The positive effects of different platelet-rich plasma methods on human muscle, bone, and tendon cells. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dongen, J.A.; Gostelie, O.F.E.; Vonk, L.A.; De Bruijn, J.J.; Van Der Lei, B.; Harmsen, A.C.; Stevens, H.P. Fractionation of adipose tissue procedure with a disposable one-hole fractionator. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricar, N.; Parkes, M.J.; Callaghan, M.J.; Felson, D.T.; O’Neill, T.W. Where and how to inject the knee—A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; Lo, G.H.; Gale, D.; Grainger, A.J.; Guermazi, A.; Conaghan, P.G. The reliability of a new scoring system for knee osteoarthritis MRI and the validity of bone marrow lesion assessment: BLOKS (Boston-Leeds Osteoarthritis Knee Score). Ann. Rheumatol. Dis. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sophia Fox, A.J.; Bedi, A.; Rodeo, S.A. The basic science of articular cartilage: Structure, composition, and function. Sports Health 2009, 1, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnans, C.; Chou, J.; Werb, Z. Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andia, I.; Maffulli, N. Platelet-rich plasma for managing pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Nuñez, G. Sterile inflammation: Sensing and reacting to damage. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcu, K.B.; Otero, M.; Olivotto, E.; Maria Borzi, R.; Goldring, M.B. NF-kappaB Signaling: Multiple angles to target OA. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buul, G.M.; Koevoet, W.L.M.; Kops, N.; Bos, P.K.; Verhaar, J.A.; Weinans, H.; Bernsen, M.R.; van Osch, G.J. Platelet-rich plasma releasate inhibits inflammatory processes in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.C.; Chen, W.H.; Zao, B.; Lai, P.-L.; Lin, T.-C.; Lo, H.-Y.; Shieh, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Deng, W.-P. Regenerative potentials of platelet-rich plasma enhanced by collagen in retrieving pro-inflammatory cytokine-inhibited chondrogenesis. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5847–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehranfar, S.; Abdi Rad, I.; Mostafav, E.; Akbarzadeh, A. The use of stromal vascular fraction (SVF), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cells in the treatment of osteoarthritis: An overview of clinical trials. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, H.; Comella, K.; Leon, J.; Verma, P.; Agrawal, D.; Koka, P.; Ichim, T. Intra-Articular injection in the knee of adipose derived stromal cells (stromal vascular fraction) and platelet rich plasma for osteoarthritis. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, C.; Bi, M.; Chen, X.; Bi, Q. Intra-articular injection of autologous adipose-derived stromal vascular fractions for knee osteoarthritis: A double-blind randomized self-controlled trial. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dongen, J.A.; Getova, V.; Brouwer, L.A.; Liguori, G.R.; Sharma, P.K.; Stevens, H.P.; van der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. Adipose tissue-derived extracellular matrix hydrogels as a release platform for secreted paracrine factors. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willemsen, J.C.N.; Spiekman, M.; Stevens, H.P.J.; Van Der Lei, B.; Harmsen, M.C. Platelet-Rich plasma influences expansion and paracrine function of adipose-derived stromal cells in a dose-dependent fashion. Plast Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 554e–565e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, H.P.; Donners, S.; De Bruijn, J. Introducing platelet-rich stroma: Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) and Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) combined for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2018, 38, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.T.; Riches, P.E.; Picard, F. The assessment of instability in the osteoarthritic knee. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, B.M.; Leroux, T.; Meyer, M.A.; Basques, B.A.; Chahal, J.; Bach, B.R., Jr.; Yanke, A.B.; Cole, B.J. The therapeutic effect of intra-articular normal saline injections for knee osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of evidence level 1 studies. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stevens, H.P.; van Boxtel, J.; van Dijck, R.; van Dongen, J.A. Platelet Rich STROMA, the Combination of PRP and tSVF and Its Potential Effect on Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4691. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144691
Stevens HP, van Boxtel J, van Dijck R, van Dongen JA. Platelet Rich STROMA, the Combination of PRP and tSVF and Its Potential Effect on Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(14):4691. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144691
Chicago/Turabian StyleStevens, Hieronymus P., Joeri van Boxtel, Robbert van Dijck, and Joris A. van Dongen. 2020. "Platelet Rich STROMA, the Combination of PRP and tSVF and Its Potential Effect on Osteoarthritis of the Knee" Applied Sciences 10, no. 14: 4691. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144691
APA StyleStevens, H. P., van Boxtel, J., van Dijck, R., & van Dongen, J. A. (2020). Platelet Rich STROMA, the Combination of PRP and tSVF and Its Potential Effect on Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Applied Sciences, 10(14), 4691. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144691




