Abstract
The influence of copper addition (0.5–2 mol%) on the crystal structure, densification microstructure, and electrochemical properties of Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.9 synthesized in a one-step sol–gel combustion synthesis route has been studied. It has been found that Cu is very active as sintering aids, with a significative reduction of GDC firing temperature. A reduction of 500 °C with a small amount of copper (0.5 mol%) was observed achieving dense bodies with considerable ionic conductivities. Rietveld refined was used to investigate the crystal structure while relative density and microstructural examination were performed in the sintering temperature range of 1000–1200 °C after dilatometer analysis. High dense bodies were fabricated at the lowest sintering temperature, which promotes the formation of Ce0.8(1−x)Gd0.2(1−x)CuxO[1.9(1−x)+x] solid solution and the absence of secondary phase Cu-rich or the segregation or copper at the grain boundary. As compared to the pure GDC an improvement of total conductivity was achieved with a maximum for the highest copper content of 2.23·10−3–9.19·10−2 S cm−1 in the temperature range of 200–800 °C.
1. Introduction
The development of ceramic ceria-based powders doped with rare earth elements is extensively regarded as favorable electrolytes type-component for intermediate and low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). The selection of these materials as electrolytes gives rise in their high ionic conductivity and good compatibility with high performing Cu-content anode or cathode [1,2]. Despite the enhanced ionic properties, compared to the standard yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), ceria-based ceramic materials needs processing temperatures higher than 1400 °C to achieve full densification. However, during sintering at high temperatures, many drawbacks can occur. For example, the formation of microcracks due to the O2− migration, as a consequence of the reduction of Ce4+ to Ce3+, or the development of undesirable interfacial reactions during co-sintering can influence the fabrication procedure and the electrolyte durability. If a dense sintered body could be fabricated at a lower temperature, the overall fabrication process can be simplified and the electrolytes can be fully exploited its potential with an additional reduction of production costs.
To improve the sinterability of doped ceria ceramics, several methods are proposed in literature which can be classified into two classes: (i) use of ultrafine powders and (ii) addition of sintering aid in a moderate amount according to their solubility in ceria solid solution. The first method implies the utilization of extremely sensitive particles derived from wet synthesis as sol–gel [3,4,5], hydrothermal [6], co-precipitation [7], polymeric precursor methods [8], etc. These syntheses can produce nanometer and submicron powders which facilitate the growth of dense bodies even if the sintering temperature is lower than 1500 °C. With the second methodology instead, ceria-based electrolytes can be sintered at lower temperatures by the direct addition of sintering promoters into commercial or synthesized powders with mechanochemical methods combined to heat treatments. The use of low melting point agents increases the atom mobility at the grain boundaries and encourages the liquid phase sintering. In fact, the aids influence the atomic diffusivity of the grain boundary inducing a closed packing. Combining the two approaches, it is possible to reduce the heating temperature until 950–1000 °C as reported in our previous works [4,9] where lithium precursor was added to gadolinium doped ceria. The direct addition of metal precursors during synthesis is a simple process to fabricate high homogenous powders with a faithful composition inducted by the molecular and not mechanical mixing of precursors. This promotes the microstructure and electrochemical properties at the same time.
Among the many types of sintering aids investigated for doped ceria, precursors of bismuth, cobalt, copper, iron, lithium, and praseodymium showed a good compromising between electrochemical properties and sintering temperature [10,11,12,13].
CuO-doped SDC, for example, is a promising anode for LT-SOFCs and the influence of copper precursors on the sintering and morphology of ceria based materials is interesting to understand the compatibility between anode and electrolyte. As known from the literature [14,15], CuO can form a Gd2O3-CeO2-CuO in the grain boundary. This ternary phase, can melt at a definite temperature and promote liquid phase sintering. As a consequence, dense bodies can be formed quickly due to the diffusion of liquid phase under capillary action, along with grain rearrangement with an effect on total conductivity. In a very recent work, Tori and Croiset [16] achieved a value of 0.0642 S cm−1 at 800 °C by adding the 0.5 mol% to SDC. The authors found that the continuous addition of copper, imply the segregation of a CuO on the surface and grain boundaries of SDC with a consequent decrease of total conductivity. Dong et al. [15] instead divided the sintering mechanism of Cu doped GDC into two steps: (i) at 900–1000 °C, rapid densification for the liquid phase sintering process; (ii) at 1100–1200 °C, grain coarsening, related with a slight reduction in the total density due the evaporation–condensation sintering process. The authors found a conductivity of 0.026 S·cm−1 at 600 °C by doping with 1 at.% of copper precursor after sintering at 1100 °C. Santos et al. [17] evaluated the effect of gadolinium composition on the microstructure, densification, and electrochemical properties of ceria based electrolytes co-doped with 1 mol% of CuO. The best composition Ce0.84Gd0.15Cu0.01O2-δ sintered at 1050 °C had a total conductivity of 7.81 × 10−3 S·cm−1 at 600 °C. According to the literature background, many studies have been established in the field of copper doped GDC electrolytes, reported here [15,18,19,20,21,22]. However, most of these researches concern the development of the traditionalSintering aids were added to commercial or synthesized electrolytes powders with mechanical reactions which requires a long milling period with solvents to ensure homogenization. Additional polishing steps to remove the contaminants added during milling are also often required before calcination and the inclusion of dispersants during compaction of the pellets can be a supplementary stage in the electrolyte preparation.
In this scenario, this work purposes to evaluate the effect of copper precursor on the microstructure, densification, and ionic conductivity of Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.9 by mean a very simple and fast reproducible synthesis procedure as sol–gel combustion synthesis. During synthesis, all starting precursors are added directly in one stage. Sol–gel reaction encourages the molecular, and not mechanical, mixing of all reagents with the consequent reduction of the reaction times and the fabrication of sinterable powders.
After synthesis, only the calcination stage was performed and no other additives, such as organic binders or dispersants, were used in pellet formation to elude contamination or extra porosity. Sintering behavior was studied by dilatometer analysis in the temperature range of 1000–1200 °C to fix the appropriate temperature and avoid the segregation of copper at the grain boundary. This study is the starting point to the optimization of the fabrication process of the anode-supported cells where the electrolyte should be densified even if the firing temperature is less than 1500 °C to prevent the additional and unwanted densification of the supporting anode substrate. For these reasons, the electrochemical properties were evaluated in the range of 200–800 °C by impedance spectroscopy after the identification of the best sintering temperature.
2. Materials and Methods
Nano-crystalline Ce0.8(1−x)Gd0.2(1−x)CuxO[1.9(1−x)+x] electrolytes were prepared by modified sol–gel combustion synthesis. All precursors with high purity, Sigma Aldrich > 99.9%, (Ce(NO3)3∙6H2O, Gd(NO3)3∙6H2O, (Cu(NO3)2∙2.5H2O, and C6H8O7∙H2O) were mixed in the desired molar ratio in deionized water according to the procedure reported in previous works [23,24,25]. Calcination temperature was fixed at 600 °C for 2 hours to obtain the final crystalline structure.
A reference of un-doped GDC was prepared as a reference was additionally prepared. The list of all electrolytes with the general formula of Ce0.8(1−x)Gd0.2(1−x)CuxO[1.9(1−x)+x] (0.005 ≤ x ≤ 0.02 and their designation are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Composition of electrolyte powders prepared.
The effect of copper addition on lattice parameters and crystalline nature of calcined powders was examined by X-ray spectroscopy using a Miniflex II (Rigaku Co., Japan) diffractometer (CuKα radiation, 2 range 5–90°). MAUD software was used to fit the diffractometer data and to calculate the cell parameters and crystallite size.
Transmission electron microscopy, TEM (Tecnai G II, FEI Co., United States), was used to understand the morphology features of powders while thermo-dilatometer analysis was accomplished to investigate the sintering behavior, i.e. sintering mechanism and shrinkage, of the various samples. Dilatometer tests were carried out in air using an instrument (DIL 402PC Netzch Instruments, Germany) in the temperature range 25–1400 °C. For the examination, a suitable quantity of calcined powder was uniaxially pressed at 140 MPa for 2 min to form small pellets with a diameter of 10 mm and a thickness of approx. 3.5 mm. The suitable firing temperature was fixed in the temperature range of 1000–1200 °C for 3 h and the microstructure of thin sintered pellets was studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Inspect F, FEI Co., USA). According to the ASTM C373-88 procedure, the relative density of the sintered electrolytes was measured by Archimedes’ principle. The achieved density values were compared with the theoretical densities calculated from crystallographic parameters, allowing by the equation:
From the Equation (1), υi is the stoichiometric coefficient, Z is the number of formula units per unit cell (i.e., 4 for the fluorite structure of ceria), Mi is the molar mass of atom i in g·mol−1, a is the lattice parameter from XRD patterns, and NA is Avogadro’s number.
Finally, a frequency response analyzer (FRA, Solartron 1260, Ametek, UK) coupled with a dielectric interface (Solartron 1296, Ametek, UK) was used for impedance analysis (EIS). Nyquist plots were recorded in the temperature range of 200–800 °C by means the frequency range of 0.1 Hz–1 MHz applying an AC voltage amplitude of 100 mV. Data fit of impedance spectra was carried out by using ZPlot and Zview software (Scribner Associates Inc, North Carolina, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Calcined Powders
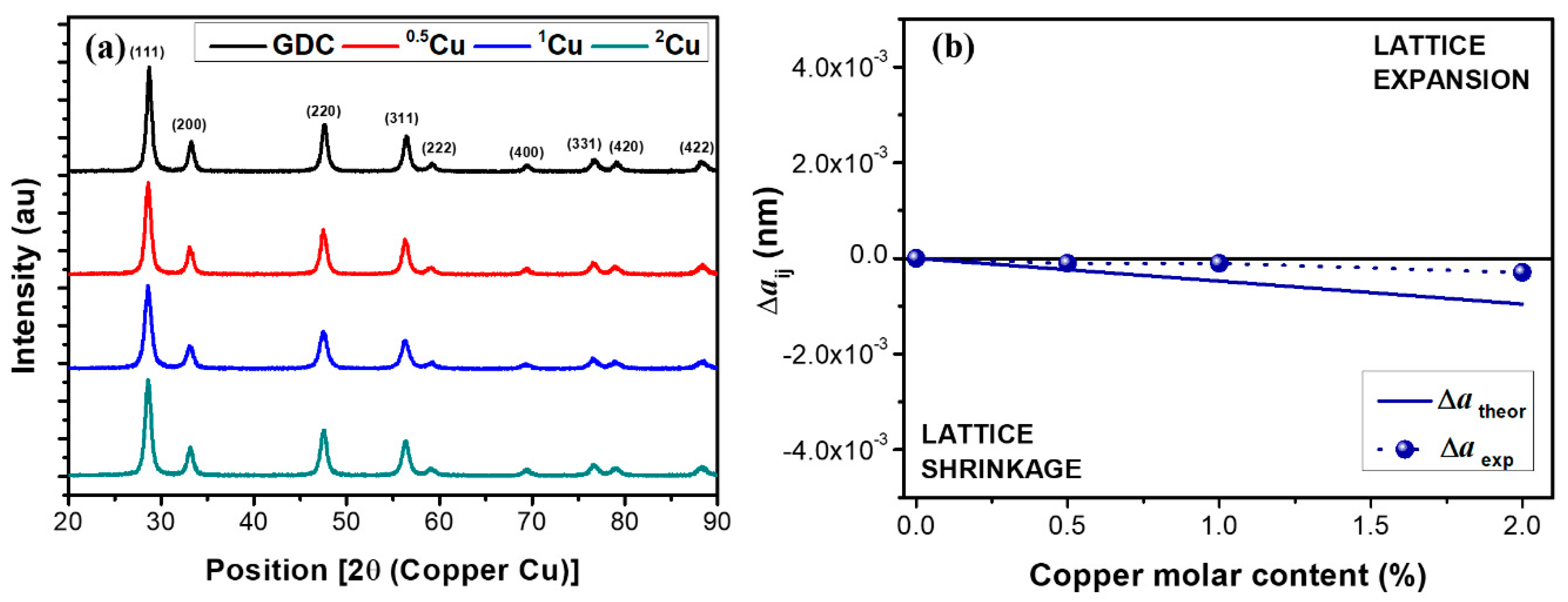
Figure 1a shows the XRD spectra of electrolyte powders where a single fluorite phase of ceria was detected. The peaks reflect the Fm3m cubic unit cell with crystalline direction 111, 200, 220, 311, 222, 400, 331 420, and 422. The ICDD card no. 01-075-0162 was employed as a reference during fit with MAUD software.
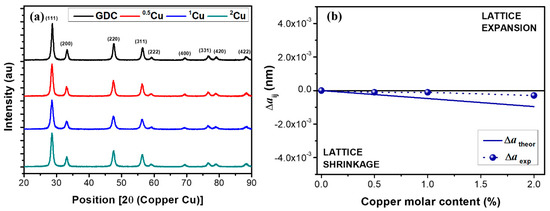
Figure 1.
XRD spectra for (a) Cu-doped GDC powders and (b) Vegard model
As reported in Table 2, the improvement of copper leads to the reduction of crystallographic parameters as the unit cell, the theoretical density, and the crystallite size. The results are in agreement with Vegard’s law. The experimental data illustrated in Figure 1b, are aligned with Vegard’s theory even if the values are slightly higher than calculated from the semiempirical equation for ionic radii in eightfold coordination [26]:
where Δri is the ionic radii difference (in nm) between the dopant and Ce4+ in 8-fold coordination and zi is the difference in charge between the dopant and Ce4+.

Table 2.
Composition of electrolyte powders prepared.
Using the Vegard’s slope theory and the knowledge of dopants size and charge, it is possible to identify the moderately undersized acceptor dopants, most likely to induce low-temperature sintering in GDC, through either liquid phase sintering or heterogeneous doping. The dopants with a negative and moderate value of Vegard’s slope (as the case of copper where Vegard’s slope is –4.76 × 10−4 affect the reduction of sintering temperature with an upright effect on the densities due to the increase of the concentration of oxygen vacancies near the grain boundary. So, the results indicate an improvement of density during sintering reducing the sintering temperature.
From XRD results, it is reasonable to think the inclusion of copper inside the crystal structure of doped ceria, as the dopant has a smaller ionic radius (0.73 Å) compared to cerium (0.97 Å). In fact, copper addition induces the lattice shrinkage ensuing the decrease in the lattice parameter with the increase of Cu composition in GDC. This effect depends on the attainable molecular mixing of copper during the sol–gel synthesis which favors the dopant distribution and substitution in the lattice.
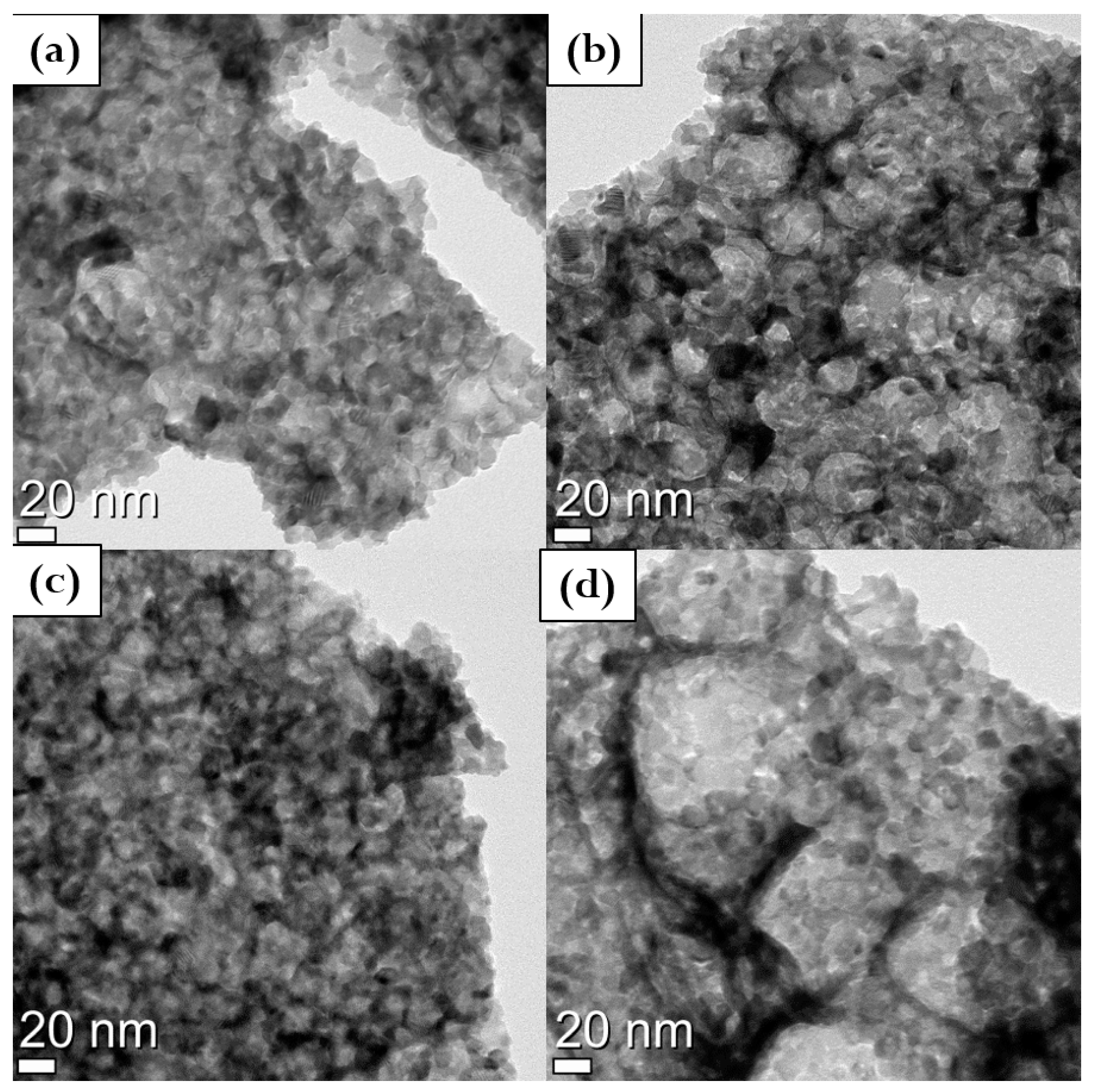
The decrease in the crystallographic parameters along with the copper addition is predictable due to its lower molecular weight compared to cerium and gadolinium. The powders morphology is reported in the TEM micrographs of Figure 2. Hard agglomerated and quasi-spheroid crystals were detected. The shape of the powders can be easily predicted due to the synthesis route performed [26,27]. In fact, sol–gel combustion synthesis leads to an irregular distribution even if the average particle size domain remains almost constant. Powders are arranged in spherical elements agglomerated in 10–20 nm small sub-units. However as reported in Figure 2d, the sample with 2 mol% of copper shows big spherical agglomerates, (1 to 5 µm), shaped by many smaller elements of 10–20 nm in size. The small units have a particle size comparable with the calculated crystallite size reported in Table 2.
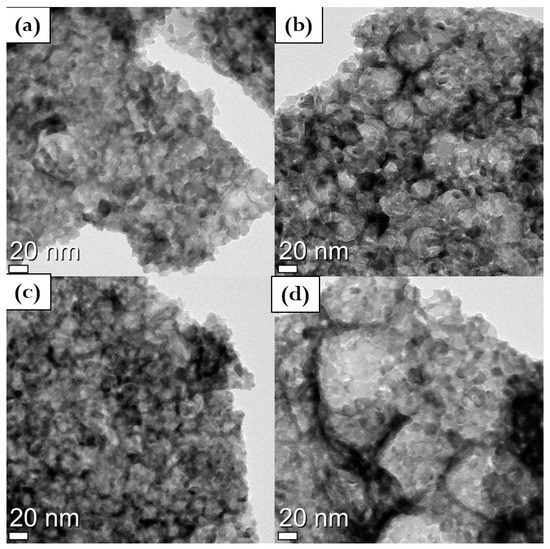
Figure 2.
TEM micrographs of (a) pure GDC, (b) 0.5Cu, (c) 1Cu, and (d) 2Cu calcined powders.
3.2. Sintering Behavior
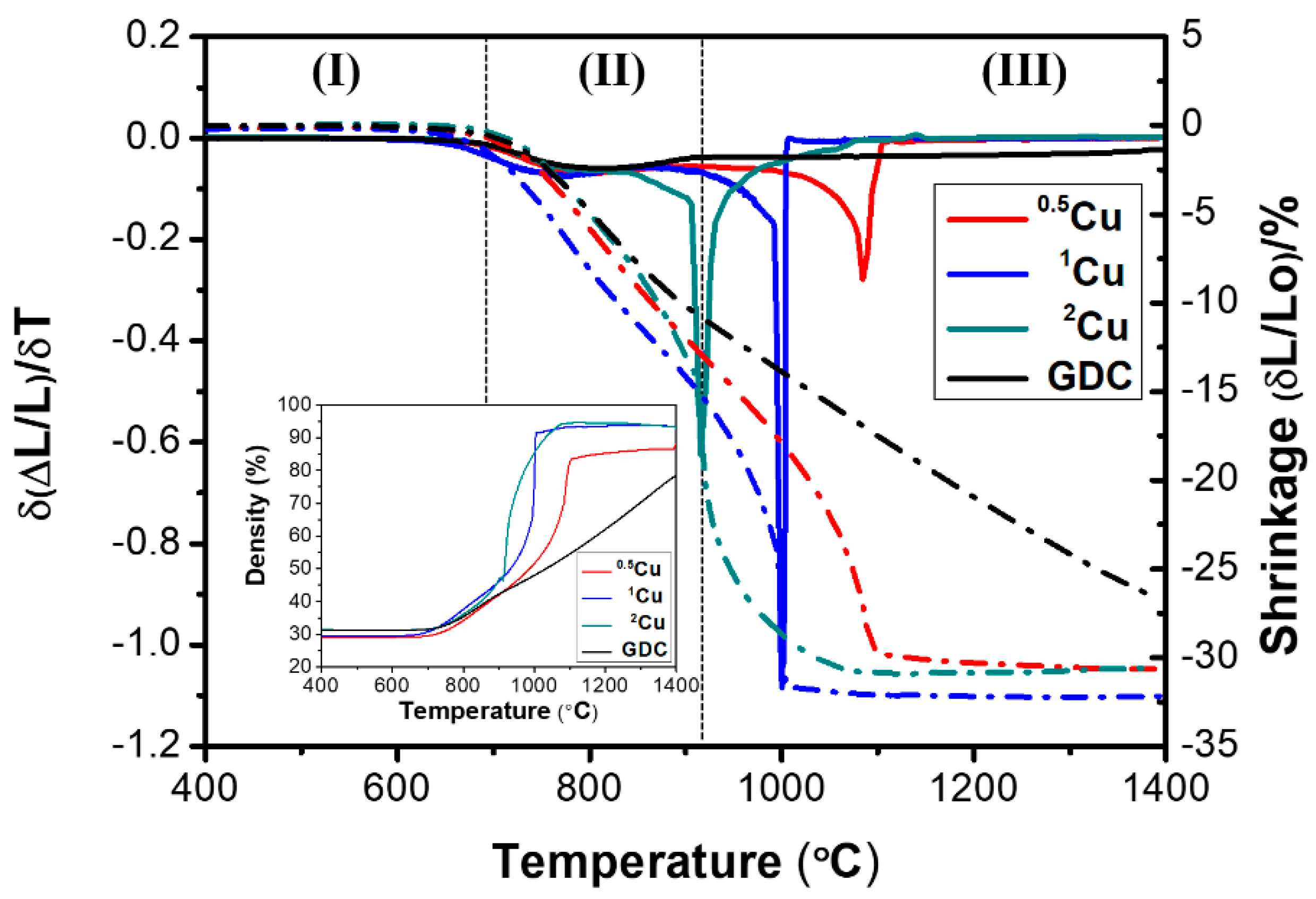
The shrinkage, δL/L0, and the shrinkage rate, δ(δL/L0)/δT, are showed in Figure 3. As reported in the dilatometer analysis, Cu accelerates the sintering process with marked enhancement in the relative densities compared to the undoped GDC (inset of Figure 3). In fact, GDC shrinkage behavior shows a weak sinterability in the temperature range investigated while Cu-doped samples show a prominent peak in the shrinkage rate profile for all compositions investigated. The maximum rate is detected at the highest concentration of copper. The sintering mechanism follows three distinctive stages (denoted by roman numerals, from I to III). The phases are intensely affected by the aid amount. For example, during the first stage, 2Cu densification begins at approximately 690 °C with an adequate increase in the shrinkage degree. After this stage, the second phase occurs with the maximum shrinkage rate at 915 °C and the densification process slows down until the end of the last stage (III). Similar sintering behavior can be observed in the other electrolytes with a shrinkage rate delayed, i.e. by ~100 °C in the sample with the lowest copper content. The effect of the copper composition can be furthermore evaluated by the density behavior, as a function of the temperature, in the insets of Figure 3. In this case, 2Cu and 1Cu show a similar value of a final density of 93–94%. According to Lima et al. [14], the rapid densification for Cu-doped GDC samples in the temperature range 910–1050 °C, suggests a liquid phase sintering mechanism due to the formation of a Gd2O3–CeO2–CuO ternary system. The liquid phase sintering is encouraged by the incorporation of copper oxide, which has a lower melting point (1326 °C) then ceria (2400 °C) and gadolinia (2420 °C), decreasing the total melting point of the ternary composition. However, from dilatometer analysis, the significant result is that the temperatures of maximum shrinkage rate: 915 °C for 2Cu, 1000 °C for 1Cu, and 1090 °C for 0.5Cu are greatly lower than pure GDC (above 1500 °C).
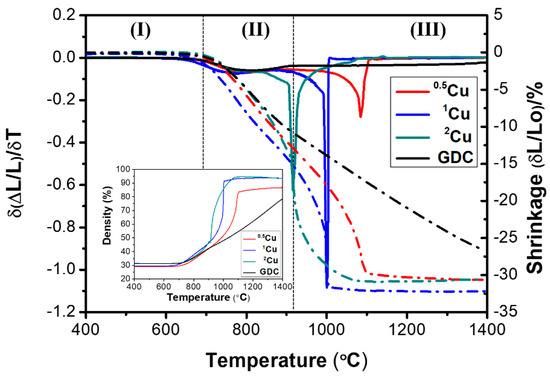
Figure 3.
Shrinkage rate (solid) and linear shrinkage (dotted) as a function of temperature for GDC and Cu co-doped samples and densification curves as a function of temperature (inset).
According to shrinkage outcomes, to achieve dense electrolytes bodies sintering temperature was fixed in the range 1000–1200 °C. The values of relative densities after sintering are reported in the following Table 3.

Table 3.
Density values of sintered bodies.
Compared to densities illustrated in the inset of Figure 3, a slight but acceptable variance is visible. The difference can be ascribed to the different types of analysis. The densities achieved by dilatometer were continuously measured isotropically without fix a dwell time. Table 3 instead shows the relative density after sintering at fixed temperature with a dwell of three hours and final geometrical measurements were found on compacted sintered pellets.
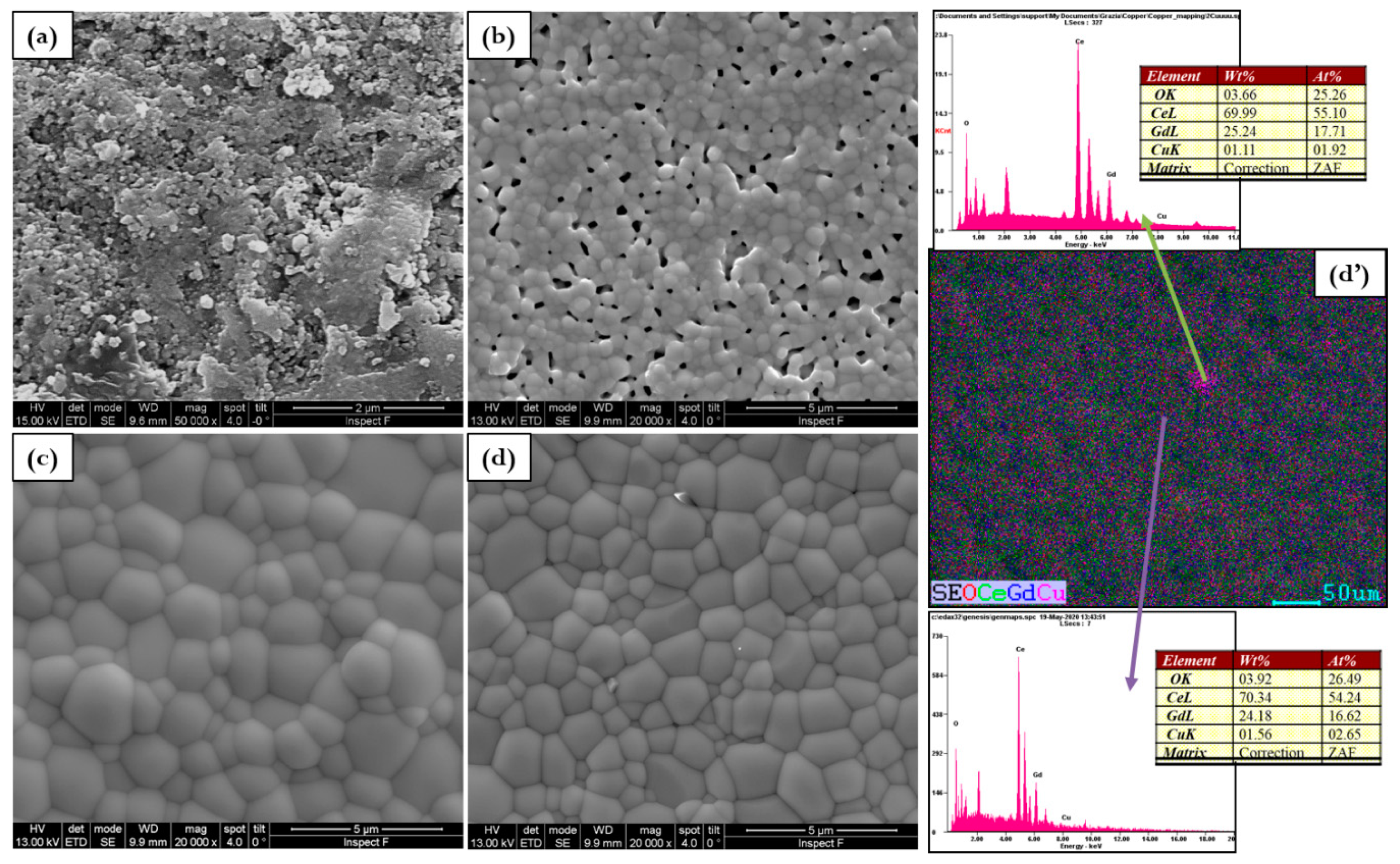
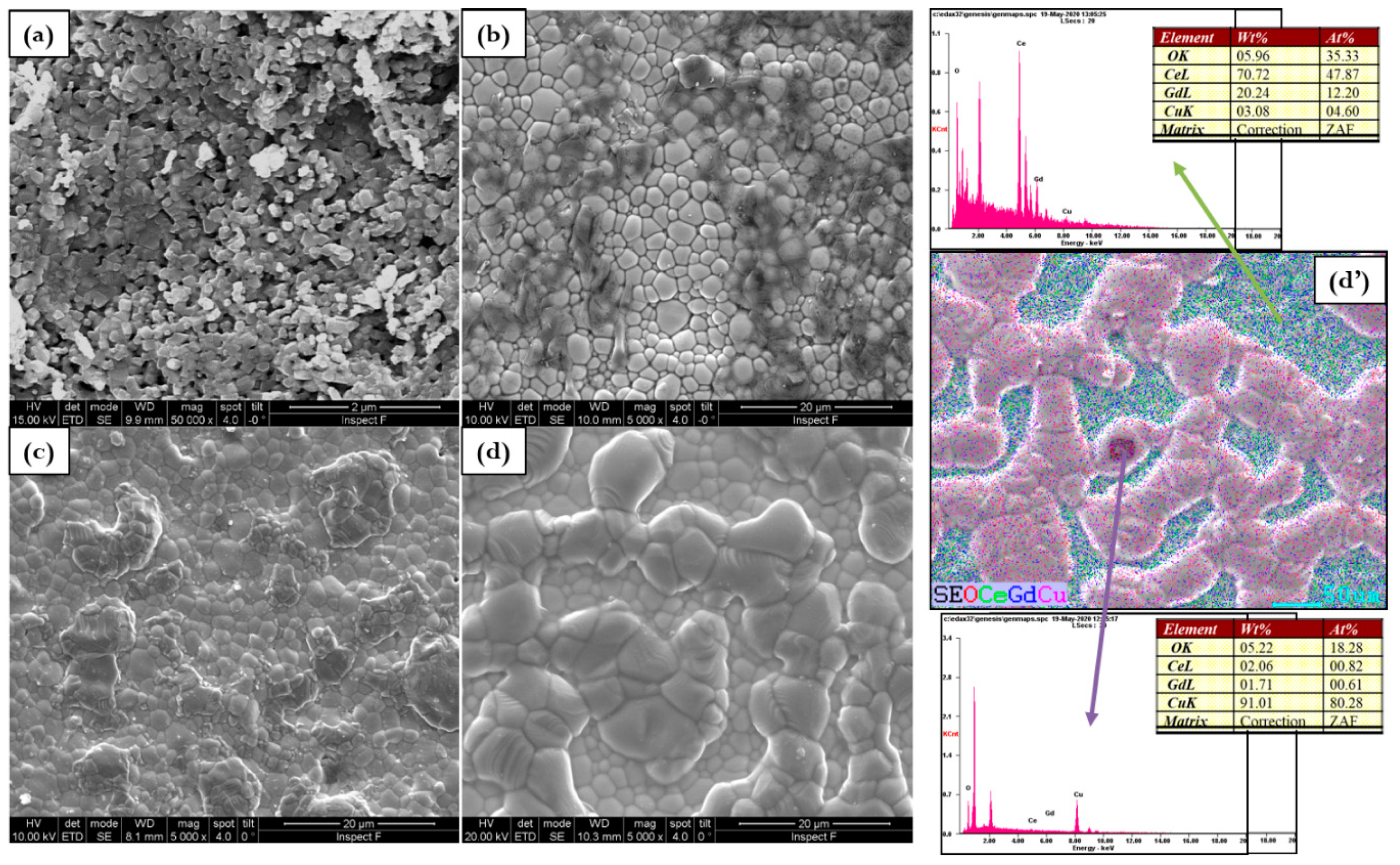
The effect on morphology and density cannot be predicted by preliminary analyses because at a comparable density, the microstructure is completely different as visible in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6. At sintering temperatures of 1000 °C and 1100 °C, pure electrolytes have small grains with a similar uneven and rough morphology. These samples are affected by the poorest densification with an inadequate microstructure for the lowest sintering temperatures. By increasing temperature GDC microstructure is always reveals small grains, many cracks, and voids, but the morphology became more uniform, and the relative density increases. The addition of copper, make obvious a change in the microstructure according to sintering temperature. As reported in Figure 4 microstructure with clean grain boundaries was formed at the lowest temperature
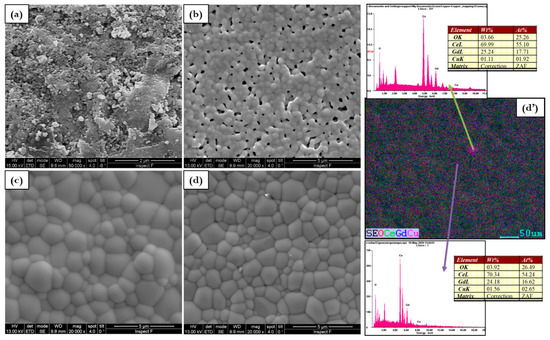
Figure 4.
Microstructure evolution for (a) GDC, (b) 0.5Cu, (c) 1Cu, (d) 2Cu, and (d’) EDS mapping of 2Cu sintered at 1000 °C.
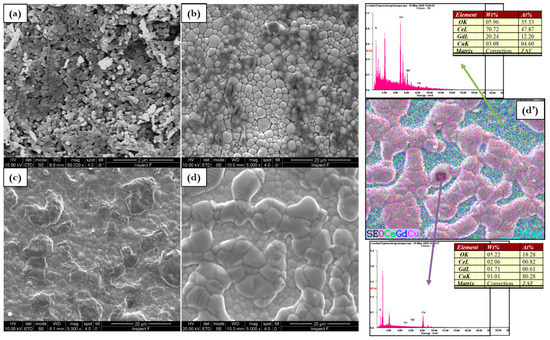
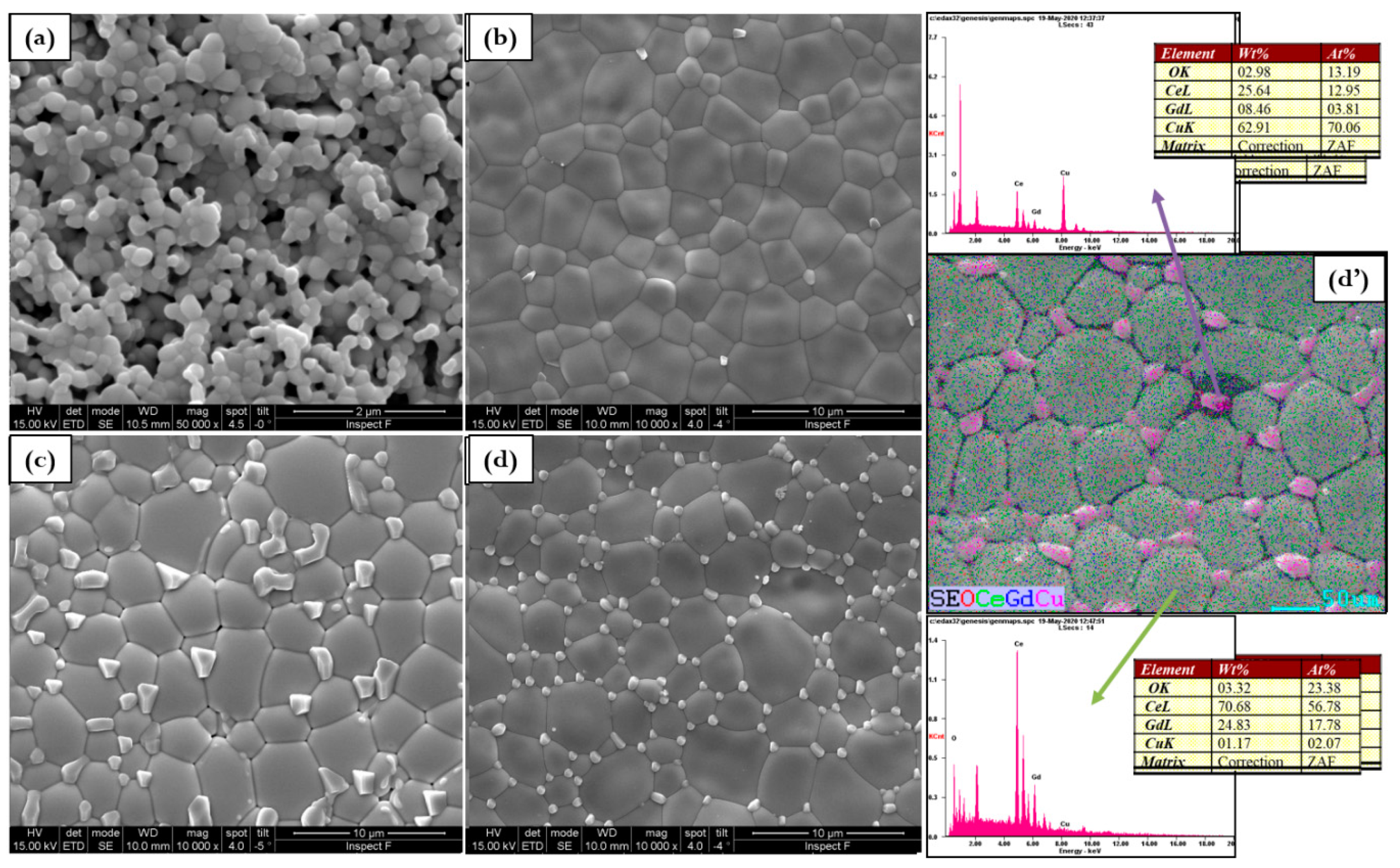
Figure 5.
Microstructure evolution for (a) GDC, (b) 0.5Cu, (c) 1Cu, (d) 2Cu, and (d’) EDX mapping of 2Cu (d’) sintered at 1100 °C.
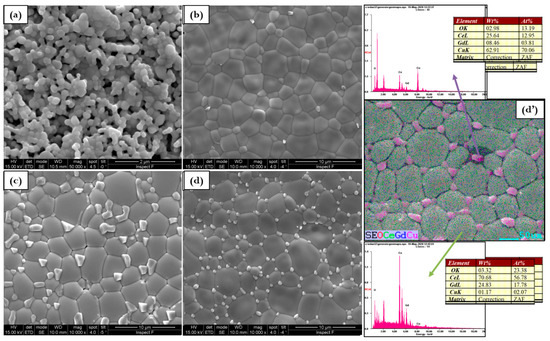
Figure 6.
Microstructure evolution for (a) GDC, (b) 0.5Cu, (c) 1Cu, (d) 2Cu, and (d’) EDX mapping of 2Cu sintered at 1200 °C.
The sintering temperature of 1000 °C gives rise to a considerable microstructure according to the calculated highest relative density. The element distribution reported in the EDS mapping of Figure 5d’ (for 2Cu) is quite homogenous indicating that at this temperature copper is well distributed in the overall GDC lattice. In fact, at 1100 °C electrolytes surface is slightly rough and Cu grains with a poorly defined geometry and different sizes are visible as reported in Figure 5.
The addition of copper at 1100 °C favors well-sintered electrolytes however, large grains related to copper oxide (CuO) occur at the surface. This effect is also influenced by the copper composition. For example, by a close look of the 2Cu micrographs, the SEM and the EDS results show different areas: Ce-Gd-rich regions composed by spherical grains in the order of 2 m where copper is well distributed in the GDC and regions with the presence of Cu at the large grain sites. EDS demonstrates the existence of CuOx mixed with nearly 80% of copper and less than 0.1% of cerium and gadolinium.
When samples are sintered at 1200 °C, the dense bodies are still embodied by the identification of two types of constituents but in this case, the Ce–Gd-rich regions represent the most intense area as reported in Figure 6. However, besides the formation of the Ce0.8(1−x)Gd0.2(1−x)CuxO[1.9(1−x)+x] solid solution (in Ce–Gd-rich regions), micrometer grains due to the segregation of copper at the grain boundary can be observed. The segregation suggests that the copper addition alters the atomic mobility along the grain boundary only, due to the formation of a second segregated phase [28]. The chemical mapping of 2Cu confirms the accumulation of copper in the micrometer grain and the formation of mixed oxide (Cu-rich). Ce and Gd elements are homogeneously distributed in the segregated grains suggesting that a small amount of Ce and Gd is dissolved in the copper oxide agglomerated phase. The segregation of copper oxide phases is extremely sensitive to copper composition.
These outcomes are partially in agreement with the literature. Lima et al. [14] found similar results in the GDC pellets co-doped with 1 mol% of Cu after sintering at 1000 °C. The authors observed a slight reduction of relative density from 1050 to 1100 °C, due to the volatilization of the liquid phase. The sintering temperature of 1000 °C was also studied by Zhang et al. [29] to fabricate samarium doped ceria electrolytes co-doped with copper and they found Ce–Sm rich and Cu-rich regions. In contrast to these works, in our results, the heating temperature of 1000 °C leads to the formation of very dense bodies where the different Cu-rich constituents are not observed. The segregation or copper or the formation of Cu poorly defined geometry grains start from 1100 °C. The segregation at these temperatures suggests the proposed following mechanism [30,31]
According to Dong et al. [15], the presence of a liquid phase leads to a densification process due to transport through the liquid and the elimination of solid–vapor interface by the liquid. This is in contrast to un-doped GDC where sintering is mainly dominated by a solid-state diffusion mechanism [32].
3.3. Electrochemical Properties
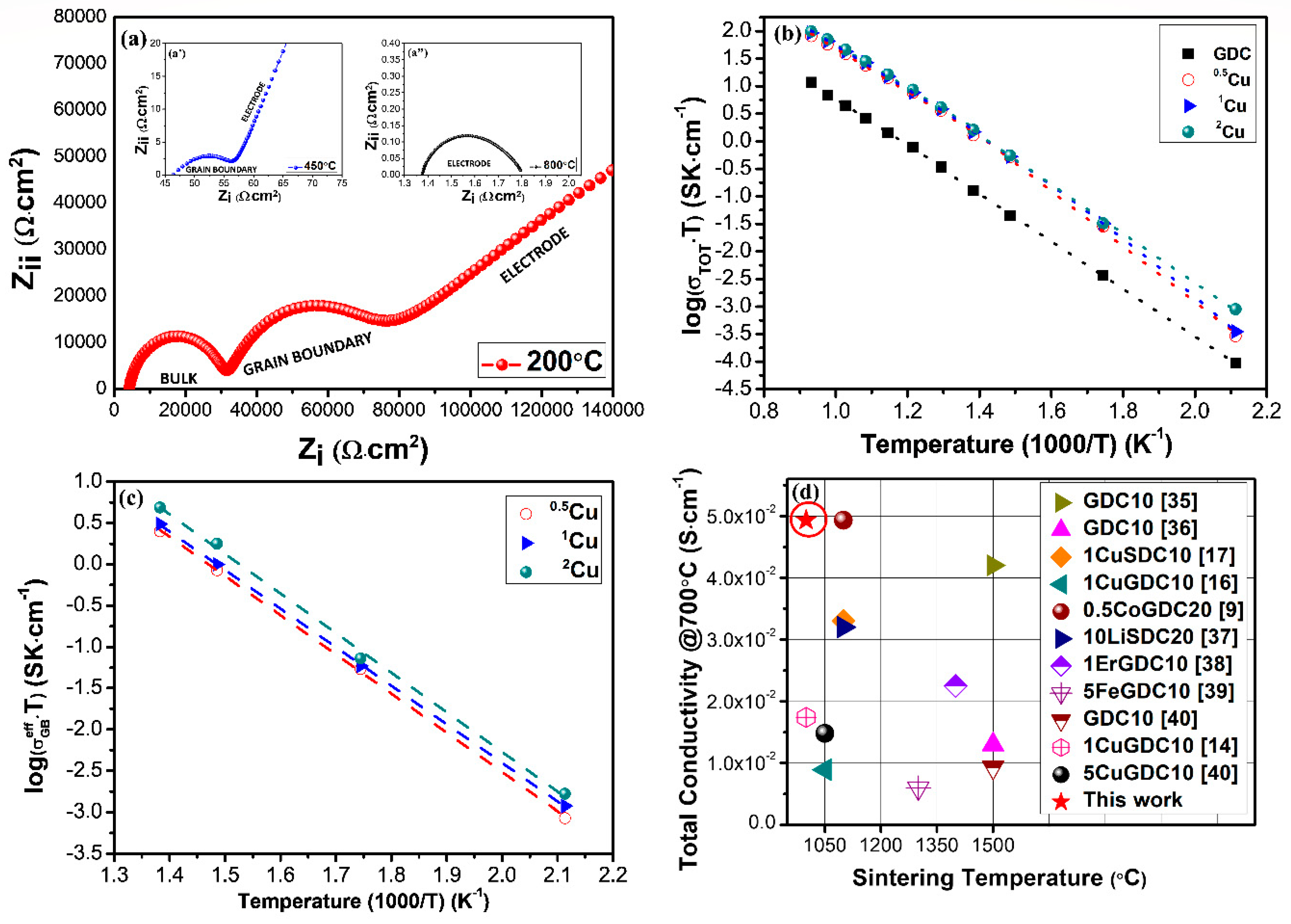
Electrochemical properties were evaluated on the samples sintered at 1000 °C due to the best morphology achieved. Data were recorded in the air between 200 and 800 °C to evaluate the influence of copper precursors on conductivity as well as to separate the bulk and the grain interior influences.
The impedance data can be fitted with three equivalent circuits connected in series. Each circuit is founded by a resistance and a constant phase element in parallel corresponding to the different responses (semi-circles or arcs) of the grain interior, grain-boundary, and electrode to the electrochemical properties. Generally, due to the microstructure and the relaxation properties of the different electrolytes, the separation of the three semi-circles cannot be always identified during the tests. At the same time, the occurrence of these contribution depends also by the operating temperatures, However, as described in the brick-layer theory [33], the Nyquist plots of the copper-doped GDC samples show in the experimental frequency range all three arcs only at 200 °C as reported in Figure 7a. In the temperature range of 300–450 °C, both the grain boundary contribution and electrode polarisation influence the electrochemical properties, and the bulk response is not visible or is more difficult to record (Figure 7a’). Increasing the operative temperature (T > 450 °C), the electrochemical semi-circles related to the bulk and grain boundaries cannot be examined, and only the electrode contribution lies inside the studied frequency range [34], as reported in Figure 7a’.
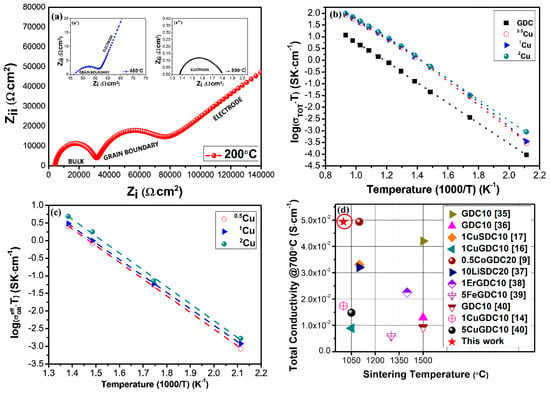
Figure 7.
(a) Nyquist plots at several temperatures, (b) Arrhenius plot of total conductivity, (c) Arrhenius plot of grain boundary conductivity, and (d) comparison with literature.
The electrochemical data are arranged in the form of Arrhenius plots in Figure 7b,c. Compared to un-doped GDC the electrochemical data of total conductivity are not fitted with a single straight line because of a change in the slope at 450 °C relieves the presence of the grain boundary contribution. As a consequence, the Arrhenius plots of total conductivity can be separated into two different areas correlated to different temperatures and related to two activation energies as reported in Table 4. For GDC, in the temperature range of 200–700 °C, the conductivity is an order of magnitude lower in comparison to Cu co-doped samples. Additionally, there is no significant difference in Ea below and above 450 °C because according to SEM images un-doped GDC has a rough microstructure and very low densification. This behavior reflects the ohmic resistance recorded at all temperatures investigated and the insignificant incidence of grain boundary resistance. Copper doped samples instead have a similar behavior above 450 °C indicating that electrochemical properties are comparable while at temperatures lower than 450 °C the differences are ascribed to the grain boundary conductivities.

Table 4.
Total conductivities and activation energies.
Figure 7d summarizes an extensive examination of literature to compare the results obtained in this study at 700 °C, using the impedance values, the sintering temperatures, and the different types of co-dopants [9,14,16,17,35,36,37,38,39,40]. In this work, the value of conductivity increases with dopant composition reaching a maximum for 2Cu of 2.23·10−3–9.19·10−2 S cm−1 in the operative temperature of 200–800 °C. The achieved result is an improvement considering samples with similar compositions and sintered at high temperatures. These improvements can be directly associated with the sol–gel synthesis procedure. Compared to the traditional synthesis process where aids are mixed and milled to the electrolyte powders by mechanical methods, during the sol–gel process nanometer and submicron powders can be produced. These powders simplify the growth of dense bodies even if the sintering temperature is 1000 °C. As a consequence, very dense sintered electrolytes with high electrochemical properties can be fabricated [22,41,42] avoiding many drawbacks [43,44].
4. Conclusions
The influence of copper precursors as sintering aid on microstructure, combined with impedance analysis was carried out on Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.9 prepared with sol–gel combustion synthesis. From XRD analysis was found that copper is incorporated as an additive in the lattice structure and after dilatometer analysis, the best sintering temperature was fixed at 1000 °C. At this temperature, the addition of copper promotes the fabrication of high dense bodies as confirmed by SEM observations due to the absence of secondary phase Cu-rich or the segregation or copper at the grain boundary.
At the same time, the enhancement in the ionic properties lies in the more defects in the doped samples which can promote ion mobility and the conduction mechanism. The results are very interesting considering the application of copper doped ceria electrolytes in the anode supported cells sintered in a single co-firing process
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.A. and S.P.Y.; methodology, G.A.; investigation, G.A. and J.K.B.; data curation, G.A. and J.K.B.; writing—original draft preparation, G.A.; writing—review and editing, S.P.Y. and G.A.; and supervision S.P.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by KRF—the Korean Research Fellowship Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Republic of Korea (Grant Number: 2016H1D3A1908428) and by the In-house Program (2E30380) of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- De Marco, V.; Iannaci, A.; Rashid, S.; Sglavo, V.M. Effect of anode thickness and Cu content on consolidation and performance of planar copper-based anode-supported SOFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 12543–12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurlo, F.; Iannaci, A.; Sglavo, V.M.; Di Bartolomeo, E. Copper-based electrodes for IT-SOFC. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, G.; Spiridigliozzi, L.; Dell’Agli, G.; Yoon, S.P.; Frattini, D. Morphology and structural stability of bismuth-gadolinium co-doped ceria electrolyte nanopowders. Inorganics 2019, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, G.; Kim, G.S.; Ham, H.C.; Yoon, S.P. Optimized lithium-doped ceramic electrolytes and their use in fabrication of an electrolyte-supported solid oxide fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 12138–12150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Shao, L.; Ji, D.; Yang, J.; Xie, J.; Yin, Q.; Le, H. Synthesis and characterization of tungsten and barium co-doped La2Mo2O9 by sol-gel process for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridigliozzi, L.; Ferone, C.; Cioffi, R.; Accardo, G.; Frattini, D.; Dell’Agli, G. Entropy-stabilized oxides owning fluorite structure obtained by hydrothermal treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, M.; Spiridigliozzi, L.; Frasnelli, M.; Dell’Agli, G.; Sglavo, V.M. Rapid densification of Samarium-doped Ceria ceramic with nanometric grain size at 900–1100 °C. Mater. Lett. 2017, 190, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sındıraç, C.; Ahsen, A.; Ozturk, O.; Akkurt, S.; Birss, V.I.; Buyukaksoy, A. Fabrication of LSCF and LSCF-GDC nanocomposite thin films using polymeric precursors. Ionics 2020, 26, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, G.; Frattini, D.; Ham, H.C.; Yoon, S.P. Direct addition of lithium and cobalt precursors to Ce0.8Gd0.2O1.95 electrolytes to improve microstructural and electrochemical properties in IT-SOFC at lower sintering temperature. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 9348–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Suda, E.; Pacaud, B.; Murai, K.; Moriga, T. Effect of components on the sintering characteristics of Ce0.9Gd0.1O1.95 electrolyte in intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells during fabrication. J. Power Sources 2006, 157, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridigliozzi, L.; Pinter, L.; Biesuz, M.; Dell’Agli, G.; Accardo, G.; Sglavo, V.M. Gd/Sm-Pr co-doped ceria: A first report of the precipitation method effect on flash sintering. Materials 2019, 12, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, J.P.F.; Macedo, D.A.; Nascimento, R.M.; Marques, F.M.B. Electronic conductivity in Gd-doped ceria with salt additions. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 318, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagaynov, I.; Fedorov, S. Gd0.05Bi0.15M0.05Ce0.75O2 solid solutions for IT-SOFC electrolyte application. Lett. Mater. 2019, 9, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.G.M.; Santos, T.H.; Grilo, J.P.F.; Dutra, R.P.S.; Nascimento, R.M.; Rajesh, S.; Fonseca, F.C.; Macedo, D.A. Synthesis and properties of CuO-doped Ce0.9Gd0.1O2-δ electrolytes for SOFCs. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 4161–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Hampshire, S.; Lin, B.; Ling, Y.; Zhang, X. High sintering activity Cu–Gd co-doped CeO2 electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 6510–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, S.Y.; Croiset, E. Reducing sintering temperature while maintaining high conductivity for SOFC electrolyte: Copper as sintering aid for Samarium Doped Ceria. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.H.; Grilo, J.P.F.; Loureiro, F.J.A.; Fagg, D.P.; Fonseca, F.C.; Macedo, D.A. Structure, densification and electrical properties of Gd3+ and Cu2+ co-doped ceria solid electrolytes for SOFC applications: Effects of Gd2O3 content. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 2745–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagg, D.P.; Kharton, V.V.; Frade, J.R. P-type electronic transport in Ce0.8Gd0.2O2-δ: The effect of transition metal oxide sintering aids. J. Electroceramics 2002, 9, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicollet, C.; Waxin, J.; Dupeyron, T.; Flura, A.; Heintz, J.-M.; Ouweltjes, J.P.; Piccardo, P.; Rougier, A.; Grenier, J.-C.; Bassat, J.-M. Gadolinium doped ceria interlayers for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells cathodes: Enhanced reactivity with sintering aids (Li, Cu, Zn), and improved densification by infiltration. J. Power Sources 2017, 372, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Choi, G.M. The effect of alumina and Cu addition on the electrical properties and the SOFC performance of Gd-doped CeO2 electrolyte. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Hampshire, S.; Zhou, J.; Meng, G. Synthesis and sintering of Gd-doped CeO2 electrolytes with and without 1 at.% CuO dopping for solid oxide fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 5054–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Xu, W.; Ling, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, K.; Xiong, C.; Zhou, Y. Electrical performance of fine-grained Y-TZP/TiC composites obtained through a hydrothermal-assisted sol-gel process. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, D.; Accardo, G.; Kwon, Y. Perovskite ceramic membrane separator with improved biofouling resistance for yeast-based microbial fuel cells. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 599, 117843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, G.; Frattini, D.; Yoon, S.P. Enhanced proton conductivity of Gd–Co bi-doped barium cerate perovskites based on structural and microstructural investigations. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 834, 155114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, G.; Frattini, D.; Ham, H.C.; Han, J.H.; Yoon, S.P. Improved microstructure and sintering temperature of bismuth nano-doped GDC powders synthesized by direct sol-gel combustion. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 3800–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-J. Lattice Parameters, Ionic Conductivities, and Solubility Limits in Fluorite-Structure MO2 Oxide [M = Hf4+, Zr4+, Ce4+, Th4+, U4+] Solid Solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1989, 72, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrosz-Gómez, I.; Gómez-García, M.Á.; Bojarska, J.; Kozanecki, M.; Rynkowski, J.M. Combustion synthesis and properties of nanocrystalline zirconium oxide. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2015, 18, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.; Balluffi, R. The mechanism of sintering of copper. Acta Met. 1957, 5, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Decès-Petit, C.; Yick, S.; Robertson, M.; Kesler, O.; Maric, R.; Ghosh, D. A study on sintering aids for Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinlogel, C.; Gauckler, L.J. Sintering and properties of nanosized ceria solid solutions. Solid State Ion. 2000, 135, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, J.D.; Jonghe, L.C. De Prediction and evaluation of sintering aids for Cerium Gadolinium Oxide. Solid State Ion. 2007, 178, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hing, P.; Huang, H.; Kilner, J. Densification, microstructure and grain growth in the CeO2–Fe2O3 system (0⩽Fe/Ce⩽20%). J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 21, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, E.C.C.; Chueh, W.C.; Jung, W.; Muccillo, E.N.S.; Haile, S.M. Ionic and Electronic Conductivity of Nanostructured, Samaria-Doped Ceria. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardo, G.; Dell’ Agli, G.; Frattini, D.; Spiridigliozzi, L.; Nam, S.W.; Yoon, S.P. Electrical Behaviour and Microstructural Characterization of Magnesia Co-doped ScSZ Nanopowders Synthesized by Urea Co-precipitation. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 57, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-L.; Su, Y.-M.; Chou, H.-L. A facile synthesis of high quality nanostructured CeO2 and Gd2O3 -doped CeO2 solid electrolytes for improved electrochemical performance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 14193–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medisetti, S.; Ahn, J.; Patil, S.; Goel, A.; Bangaru, Y.; Sabhahit, G.V.; Babu, G.U.B.; Lee, J.H.; Dasari, H.P. Synthesis of GDC electrolyte material for IT-SOFCs using glucose & fructose and its characterization. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2017, 11, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, V.; Zunic, M.; Traversa, E. Improved total conductivity of nanometric samaria-doped ceria powders sintered with molten LiNO3 additive. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.; Muhammed Ali, S.A.; Baharuddin, N.A.; Raduwan, N.F.; Muchtar, A.; Somalu, M.R. Structural, optical and electrical properties of Ce0.8Sm0.2-xErxO2-δ (x = 0–0.2) Co-doped ceria electrolytes. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 13639–13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehranjani, A.S.; Cumming, D.J.; Sinclair, D.C.; Rothman, R.H. Low-temperature co-sintering for fabrication of zirconia/ceria bi-layer electrolyte via tape casting using a Fe2O3 sintering aid. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 3981–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonov, A.V.; Spirin, A.V.; Khrustov, V.R.; Paranin, S.N.; Pavzderin, N.B.; Kuterbekov, K.A.; Nurakhmetov, T.N.; Atazhan, Y.K. Synthesis and properties of solid electrolyte Ce0.9Gd0.1O2–δ with Co, Cu, Mn, Zn doping. Inorg. Mater. 2016, 52, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, C.A.; Pintilie, I.; Surdu, A.; Truşcă, R.; Vasile, B.S.; Eftimie, M.; Ianculescu, A.C. Influence of Sintering Strategy on the Characteristics of Sol-Gel Ba1−xCexTi1−x/4O3 Ceramics. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayden, N.J.; Accardo, G.; Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A.; Pernice, P.; Vergara, A.; Ferone, C.; Aronne, A. Phosphorus stably bonded to a silica gel matrix through niobium bridges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15986–15995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, B.J.; Hekner, B.; Sopicka-Lizer, M. The Influence of High Energy Ball Milling on the Morphology of Metal-Ceramic Composite Powders. Solid State Phenom. 2016, 246, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andini, S.; Montagnaro, F.; Santoro, L.; Accardo, G.; Cioffi, R.; Colangelo, F. Mechanochemical Processing of Blast Furnace Slag for its Reuse as Adsorbent. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 2299–2304. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).