The Effects of Signal System and Traffic Flow on the Sound Level
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Site Measurement and Data Collection
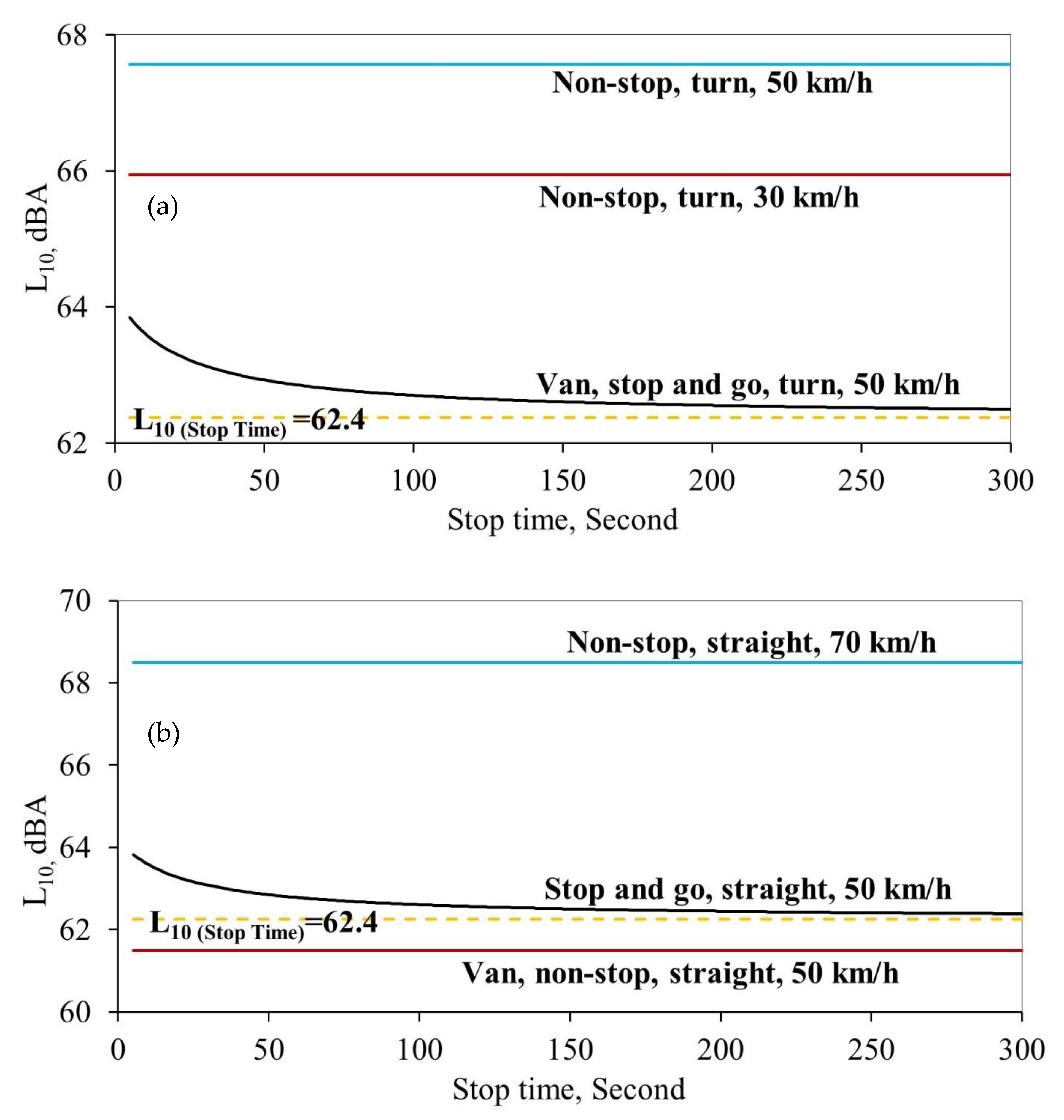
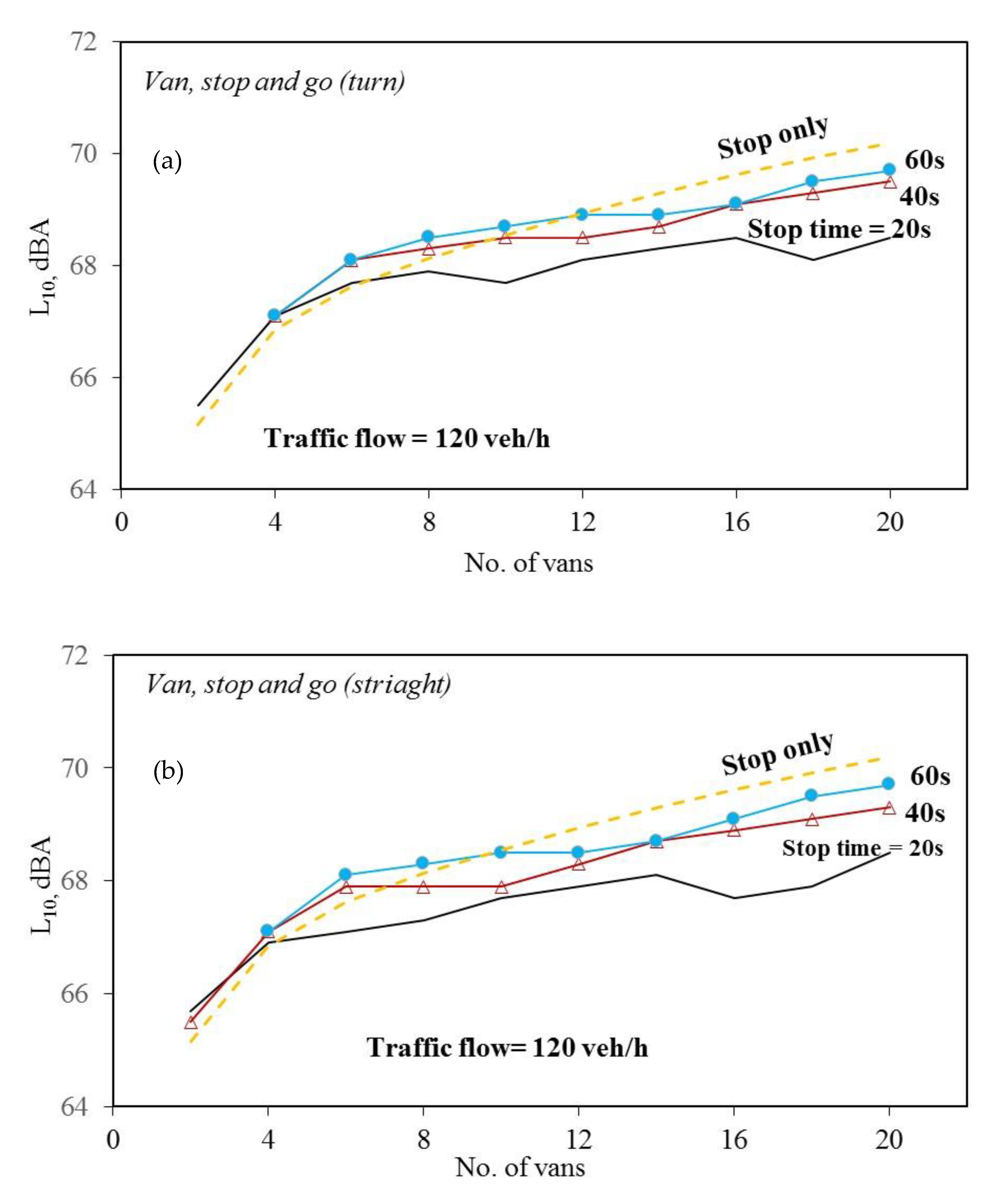
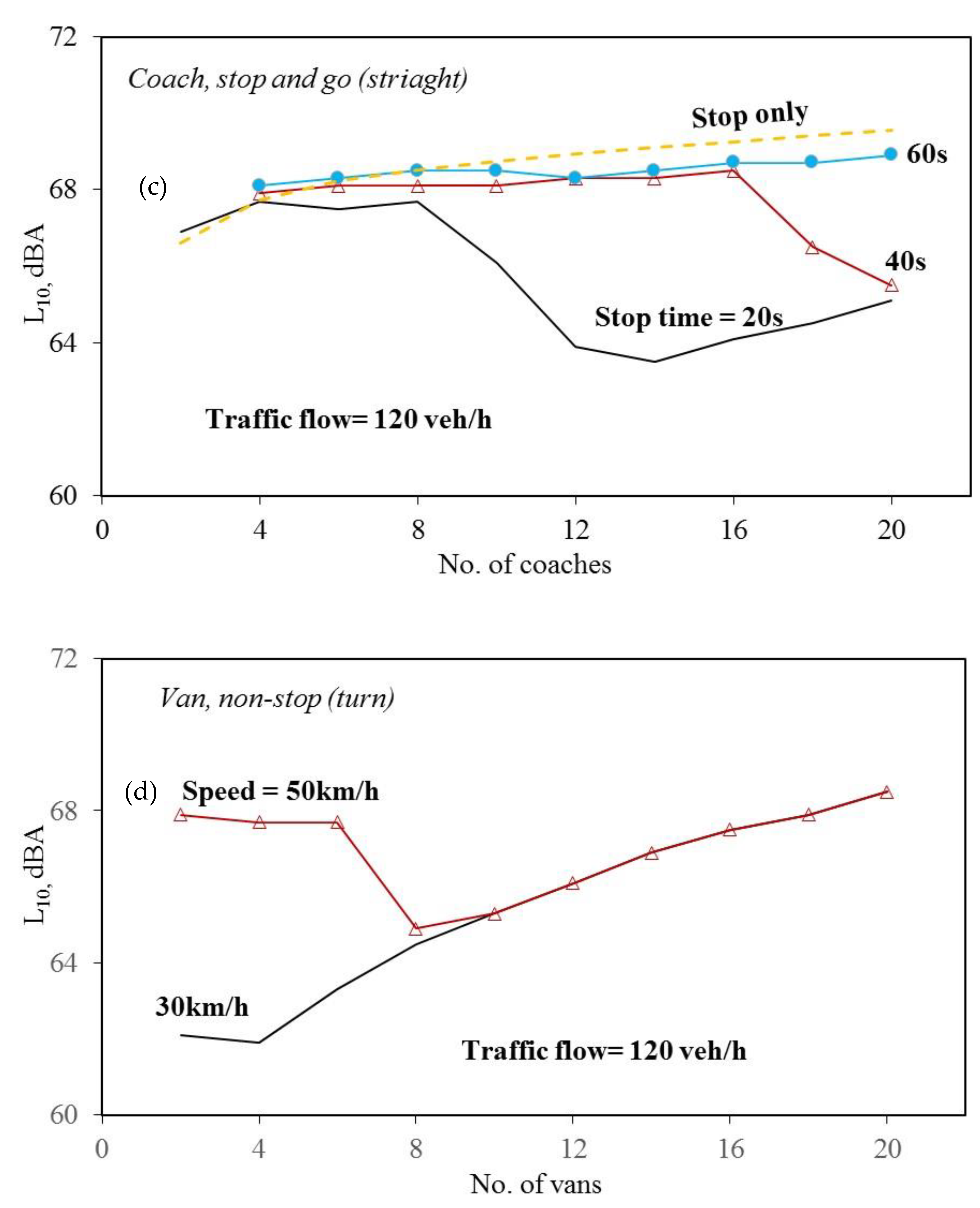
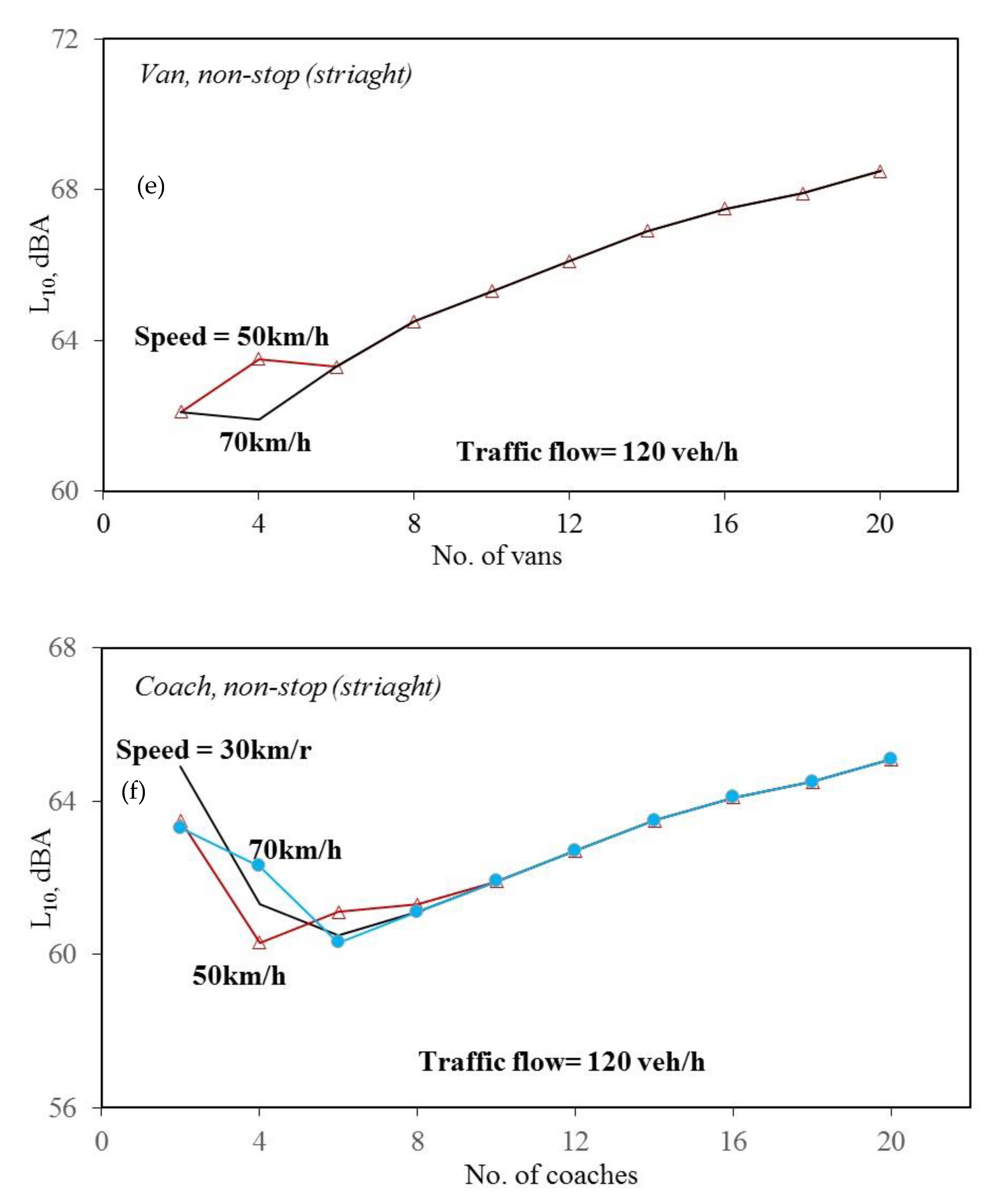
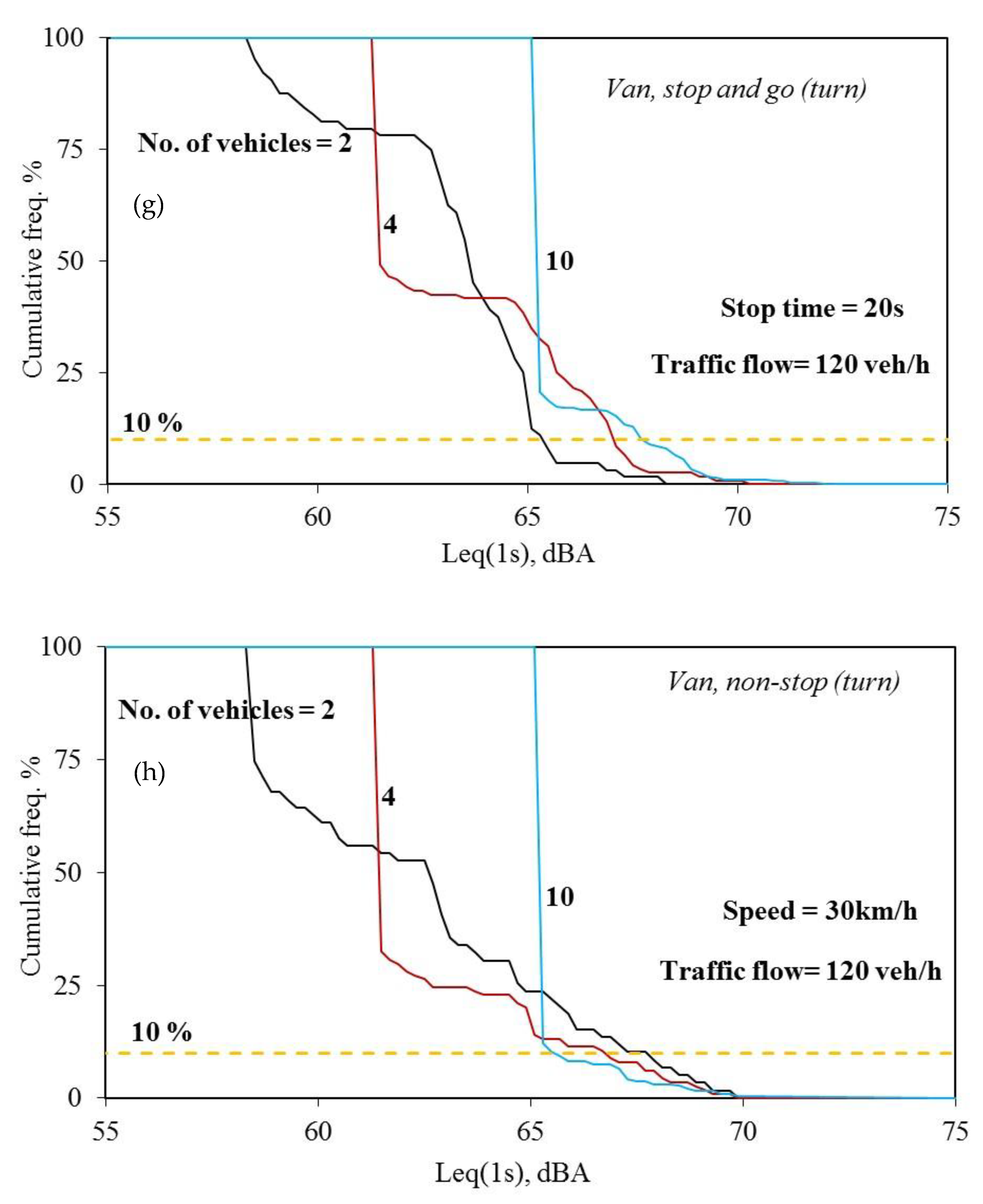
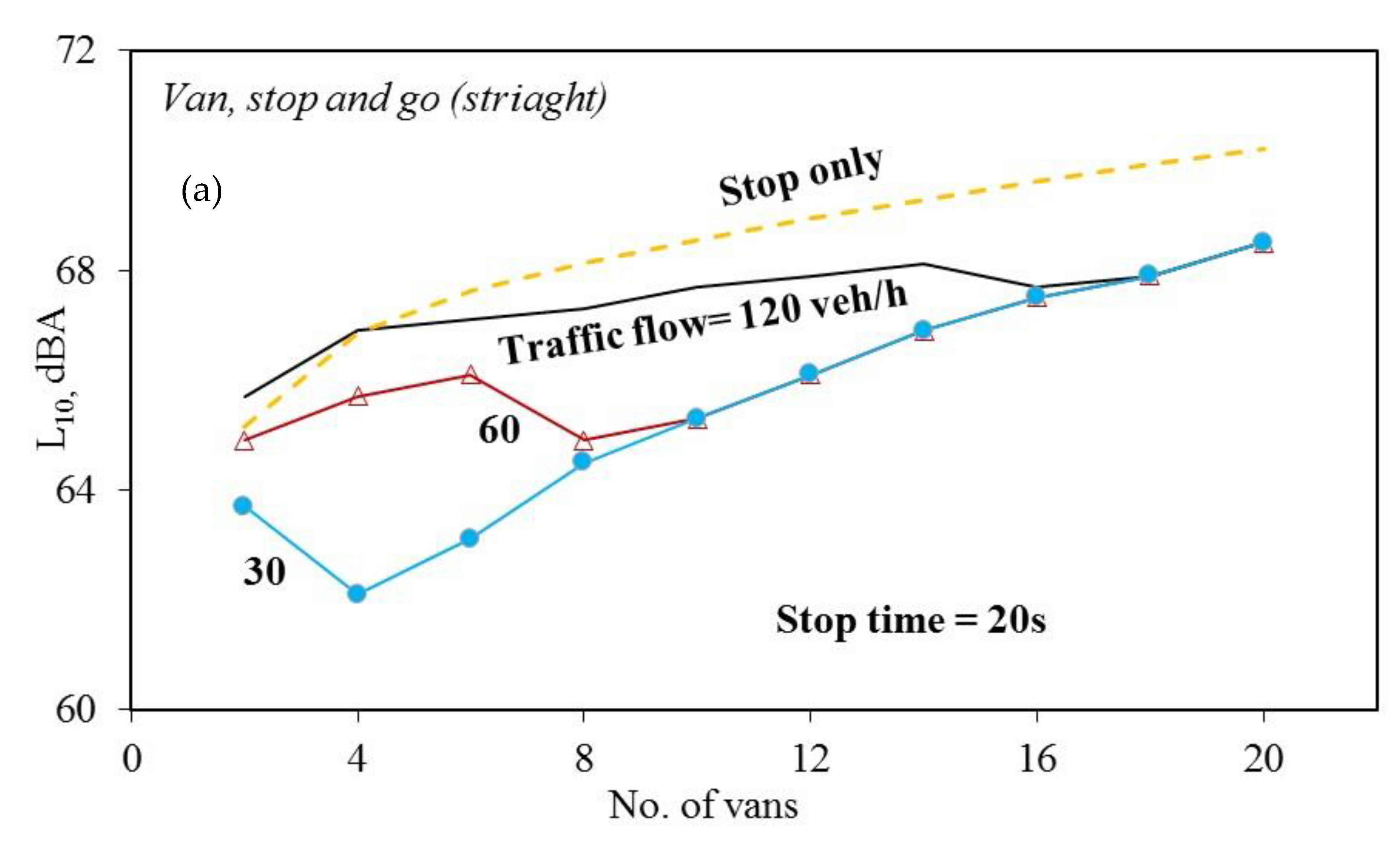
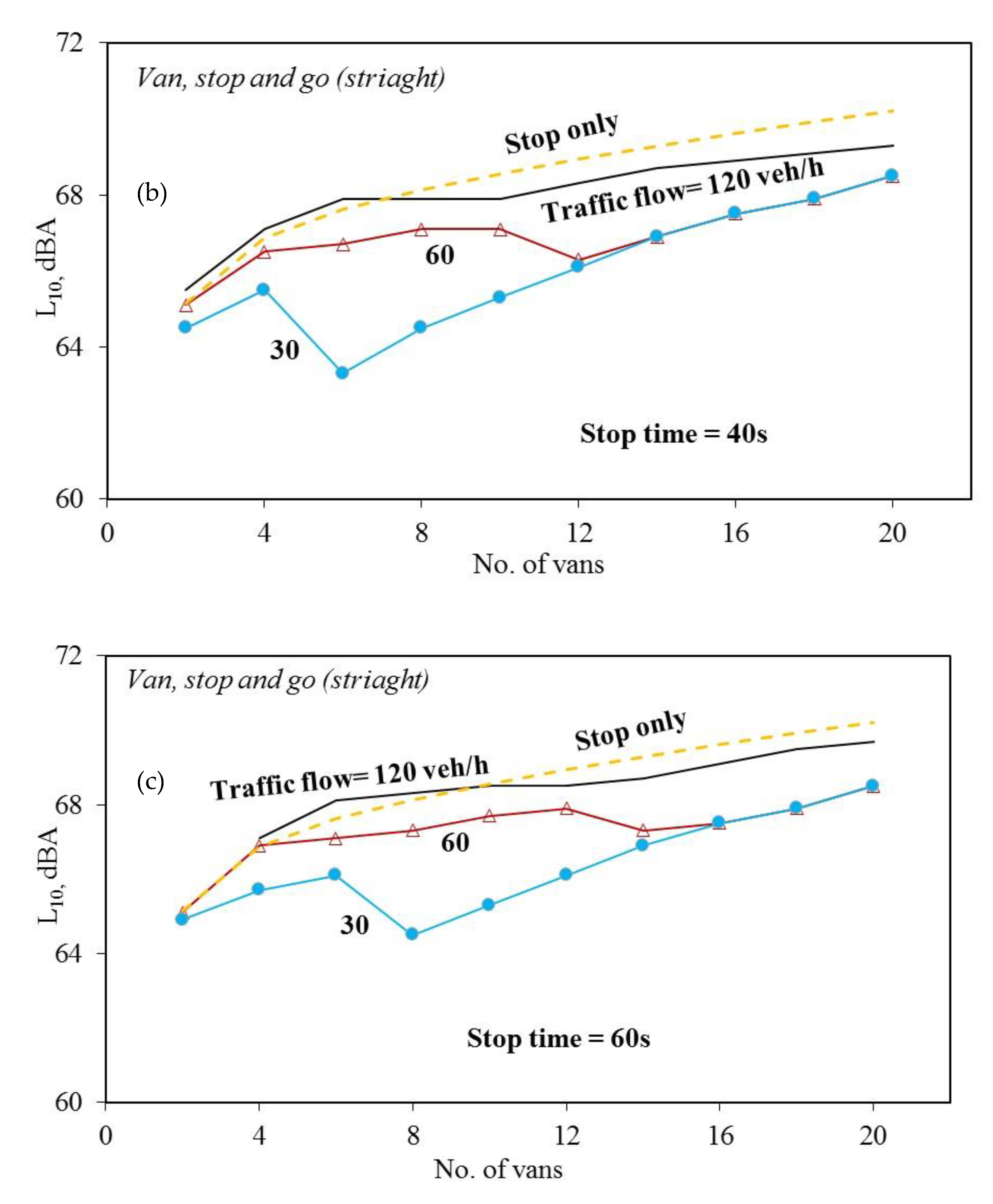
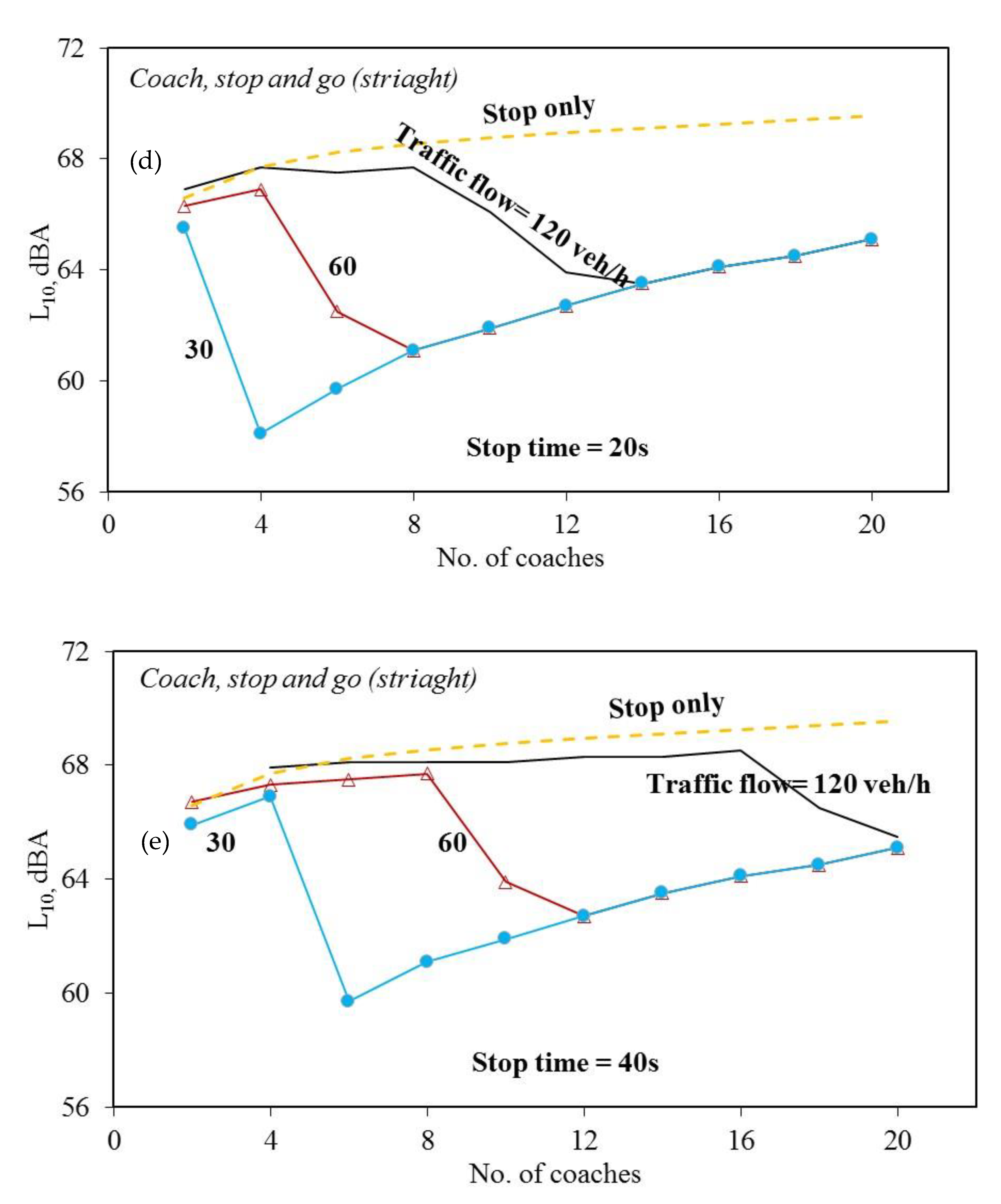
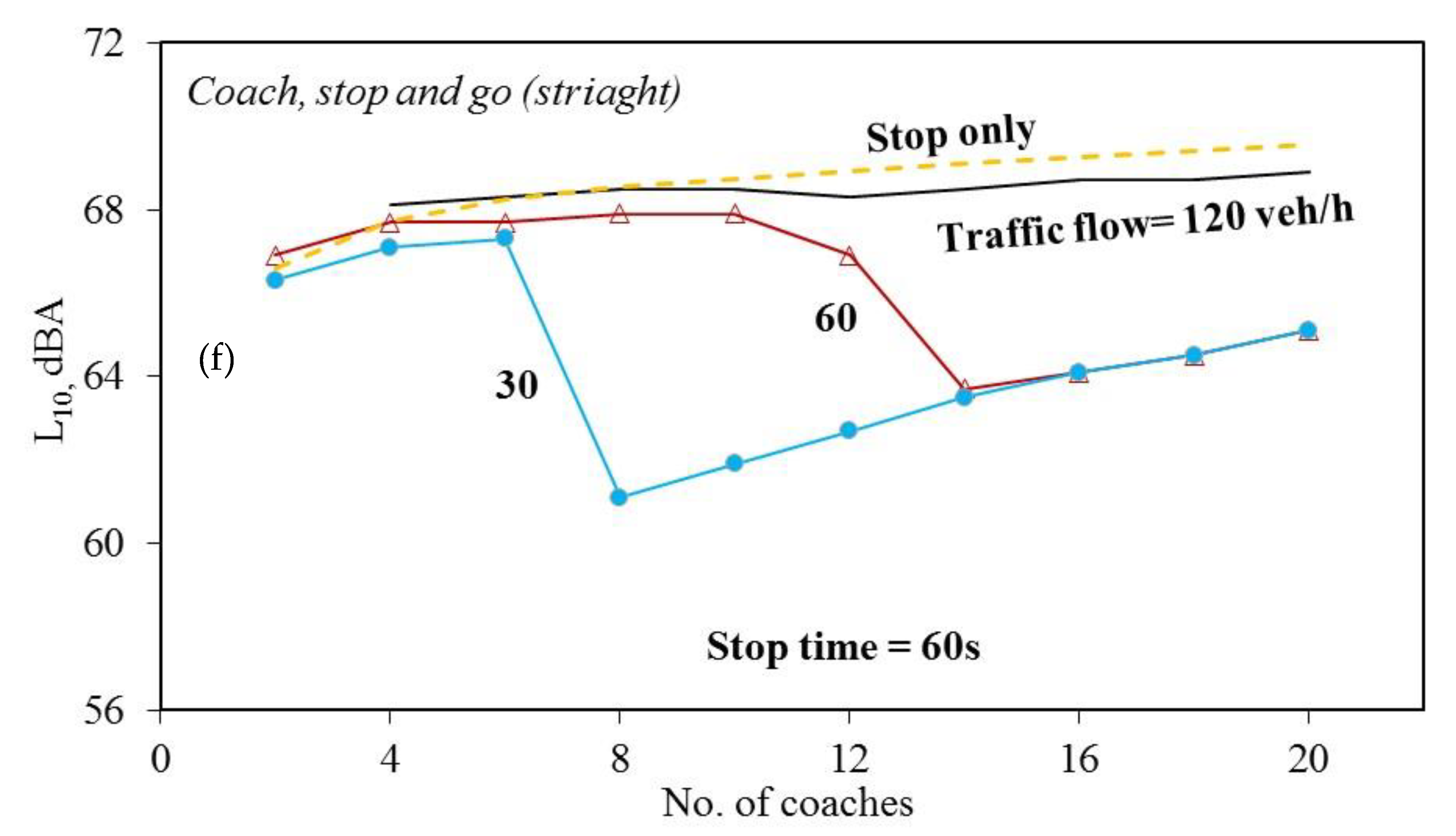
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Licitra, G.; Fredianelli, L.; Petri, D.; Vigotti, M.A. Annoyance evaluation due to overall railway noise and vibration in Pisa urban areas. Sci. Total. Env. 2016, 568, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, F.; Zannin, P.H.T. Assessment of railway noise in an urban setting. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 104, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, P.; Teti, L.; Licitra, G. A statistical evaluation on flight operational characteristics affecting aircraft noise during take-off. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 134, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Merchan, C.; Balteiro, L.D.; Soliño, M. Transportation planning and quiet natural areas preservation: Aircraft overflights noise assessment in a National Park. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Env. 2015, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredianelli, L.; Gallo, P.; Licitra, G.; Carpita, S. Analytical assessment of wind turbine noise impact at receiver by means of residual noise determination without the wind farm shutdown. Noise Control. Eng. J. 2017, 65, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, D.; Feder, K.; Keith, S.; Voicescu, S.A.; Marro, L.; Than, J.; Guay, M.; Denning, A.; McGuire, D.; Bower, T.; et al. Exposure to wind turbine noise: Perceptual responses and reported health effects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, M.; Fredianelli, L.; Fidecaro, F.; Gagliardi, P.; Nastasi, M.; Licitra, G. Noise Assessment of Small Vessels for Action Planning in Canal Cities. Environments 2019, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognese, M.; Fidecaro, F.; Palazzuoli, D.; Licitra, G. Port Noise and Complaints in the North Tyrrhenian Sea and Framework for Remediation. Environments 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredianelli, L.; Nastasi, M.; Bernardini, M.; Fidecaro, F.; Licitra, G. Pass-by Characterization of Noise Emitted by Different Categories of Seagoing Ships in Ports. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzet, A. Environmental noise, sleep and health. Sleep Med. Rev. 2007, 11, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacarías, F.F.; Hernández-Molina, R.; Ancela, J.L.C.; Lubián-López, P.; Alonso-Ojembarrena, A. Noise Exposure in Preterm Infants Treated with Respiratory Support Using Neonatal Helmets. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2013, 99, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Gallo, P.; Rossi, E.; Brambilla, G. A novel method to determine multi-exposure priority indices tested for Pisa action plan. Appl. Acoust. 2011, 72, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Fredianelli, L.; Castro, F.L.; Gagliardi, P.; Fidecaro, F.; Licitra, G. Stabilization of a p-u Sensor Mounted on a Vehicle for Measuring the Acoustic Impedance of Road Surfaces. Sensors 2020, 20, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licitra, G.; Cerchiai, M.; Teti, L.; Ascari, E.; Bianco, F.; Chetoni, M. Performance Assessment of Low-Noise Road Surfaces in the Leopoldo Project: Comparison and Validation of Different Measurement Methods. Coatings 2015, 5, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, D.; De Hoogh, K.; Fecht, D.; Fabbri, F.; Bell, M.; Goodman, P.; Elliott, P.; Hodgson, S.; Hansell, A.L.; Gulliver, J. International scale implementation of the CNOSSOS-EU road traffic noise prediction model for epidemiological studies. Env. Pollut. 2015, 206, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, R.P.; Diego, P.R.; Antonio, J.T.; Ángel, R.R. Selection of suitable alternatives to reduce the environmental impact of road traffic noise using a fuzzy multi-criteria decision model. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2016, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Miedema, H.M.E.; Oudshoorn, C.G.M. Annoyance from transportation noise: Relationships with exposure metrics DNL and DENL and their confidence intervals. Env. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, J.L.; Petrovici, A.M.; Hernández, R.; Fernández, F. Analysis of the Impact of Bus Signal Priority on Urban Noise. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2017, 103, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dratva, J.; Phuleria, H.C.; Foraster, M.; Gaspoz, J.-M.; Keidel, D.; Künzli, N.; Liu, L.-J.S.; Pons, M.; Zemp, E.; Gerbase, M.W.; et al. Transportation Noise and Blood Pressure in a Population-Based Sample of Adults. Env. Heal. Perspect. 2011, 120, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babisch, W.; Beule, B.; Schust, M.; Kersten, N.; Ising, H. Traffic Noise and Risk of Myocardial Infarction. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Annual Traffic Census; Transport Department of the HKSAR Government: Hong Kong, China, 2015.
- Hong Kong: The Facts-Highways; Highway Department of the HKSAR Government: Hong Kong, China, 2016.
- De Coensel, B.; Can, A.; Degraeuwe, B.; De Vlieger, I.; Botteldooren, D. Effects of traffic signal coordination on noise and air pollutant emissions. Env. Model. Softw. 2012, 35, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilova, K.; Stoilov, T. Traffic noise and traffic light control. Transp. Res. Part D: Transp. Env. 1998, 3, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, M.; Kuno, K.; Sone, T. New Mathematical Model to Estimate Road Traffic Noise in View of the Appearance Rate of Heavy Vehicles. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2011, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, A.; Orimoto, H.; Siddique, N.H.; Maguire, L.P. Statistical Evaluation of Complex Sound Environment with Background Noise. Int. J. Acoust. Vib. 2015, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, L.-A.; Marquis-Favre, C.; Klein, A.; Laure-Anne, G.; Catherine, M.-F.; Achim, K. Noise Annoyance Due To Urban Road Traffic with Powered-Two-Wheelers: Quiet Periods, Order and Number of Vehicles. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2016, 102, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Tong, K. Estimating traffic noise for inclined roads with freely flowing traffic. Appl. Acoust. 2004, 65, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.S.; Mun, S. Development of a highway traffic noise prediction model that considers various road surface types. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.-C.; Ma, W.-C. Road traffic noise exposure in residential complexes built at different times between 1950 and 2000 in Hong Kong. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Gayah, V.V. Continuum signalized junction model for dynamic traffic networks: Offset, spillback, and multiple signal phases. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2015, 77, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mirchandani, P.B.; Zhou, X. Solving simultaneous route guidance and traffic signal optimization problem using space-phase-time hypernetwork. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2015, 81, 103–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number of Sound Level Meters | 6 |
|---|---|
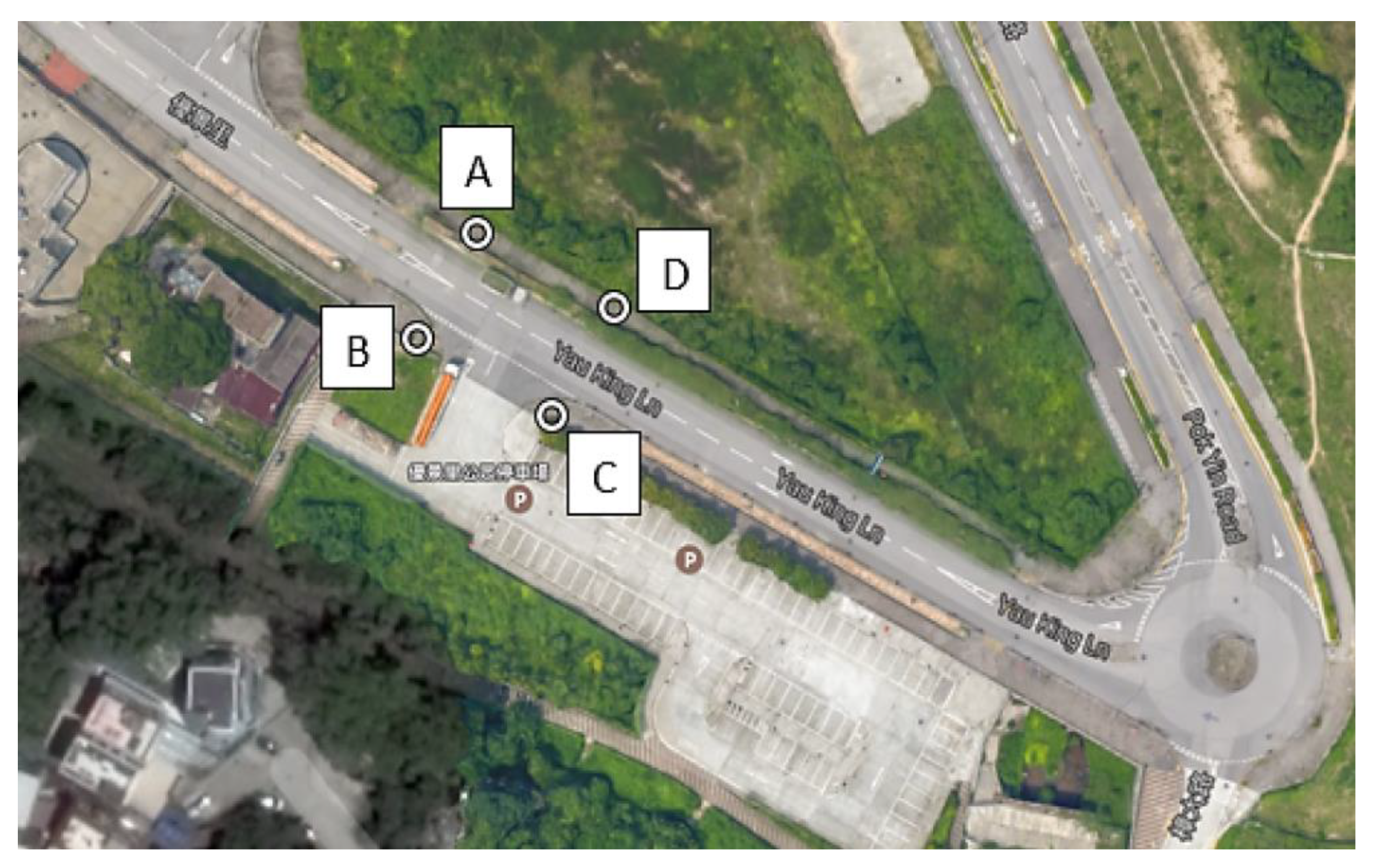
| Number of measurement locations | 4 (i.e., A, B, C, D in Figure 2) |
| Measurement heights | 1.2 m, 4.0 m and 6.5 m |
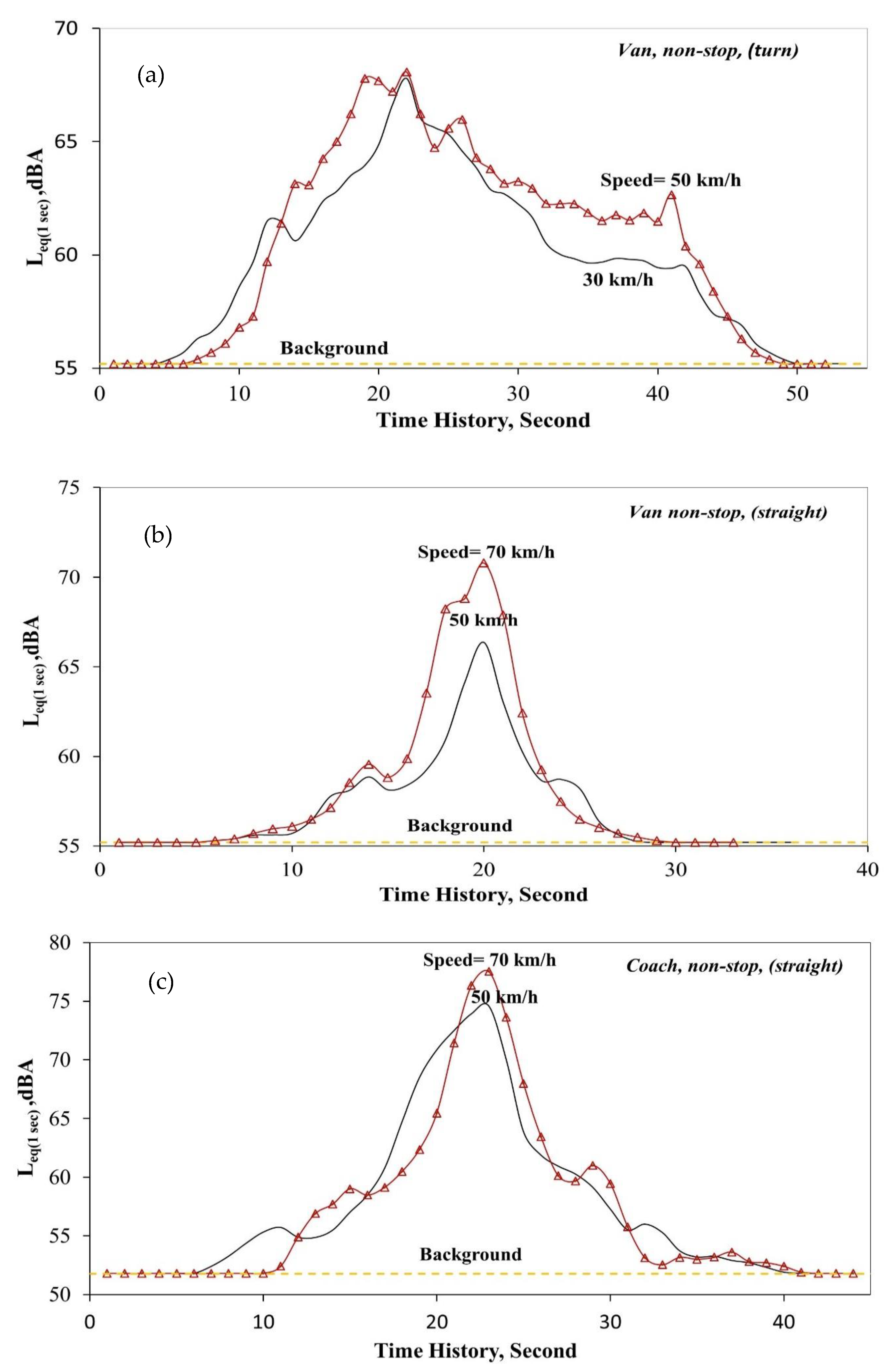
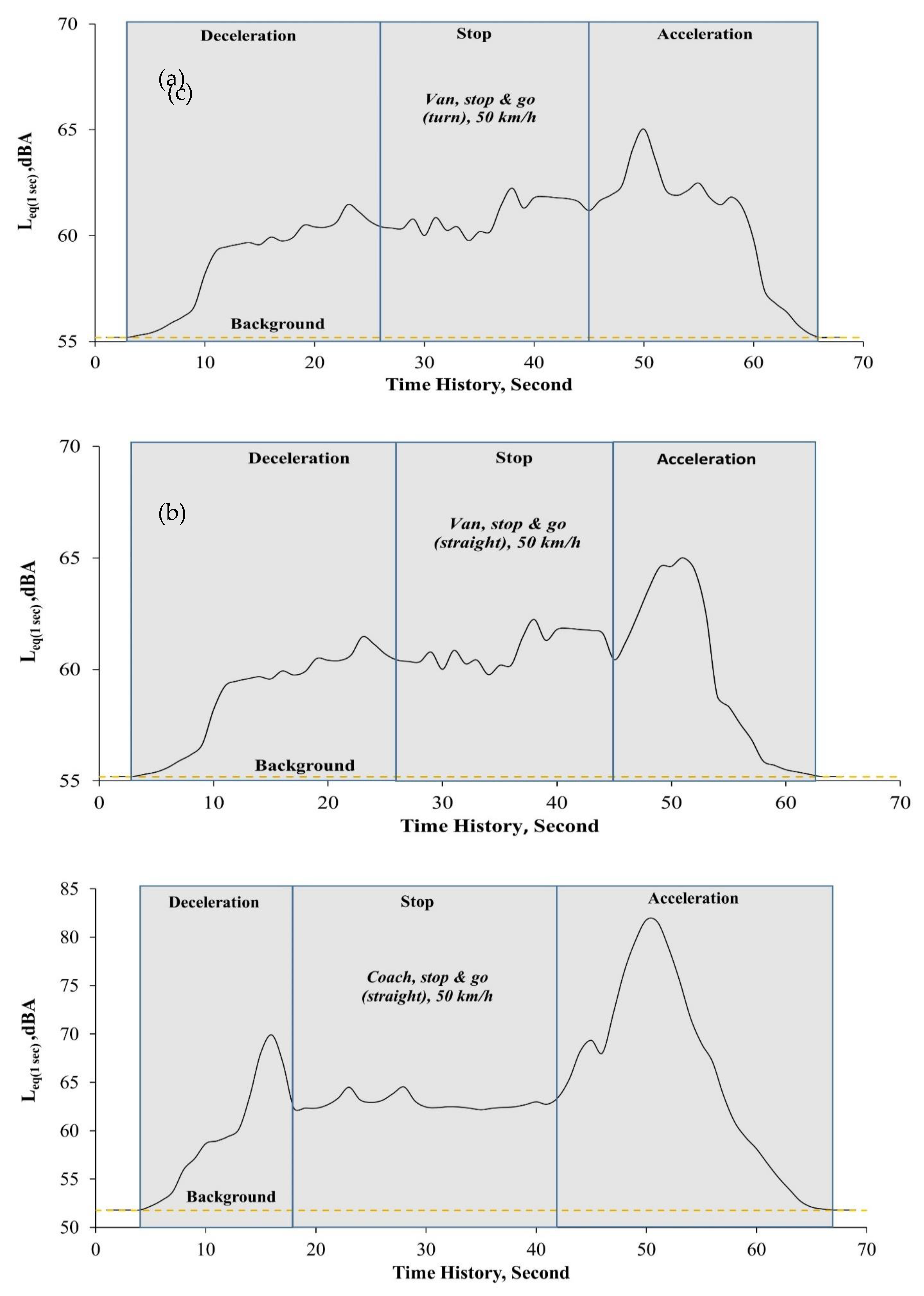
| Vehicle type | Van and Coach |
| Vehicle speed | 30, 50, and 70 km/h |
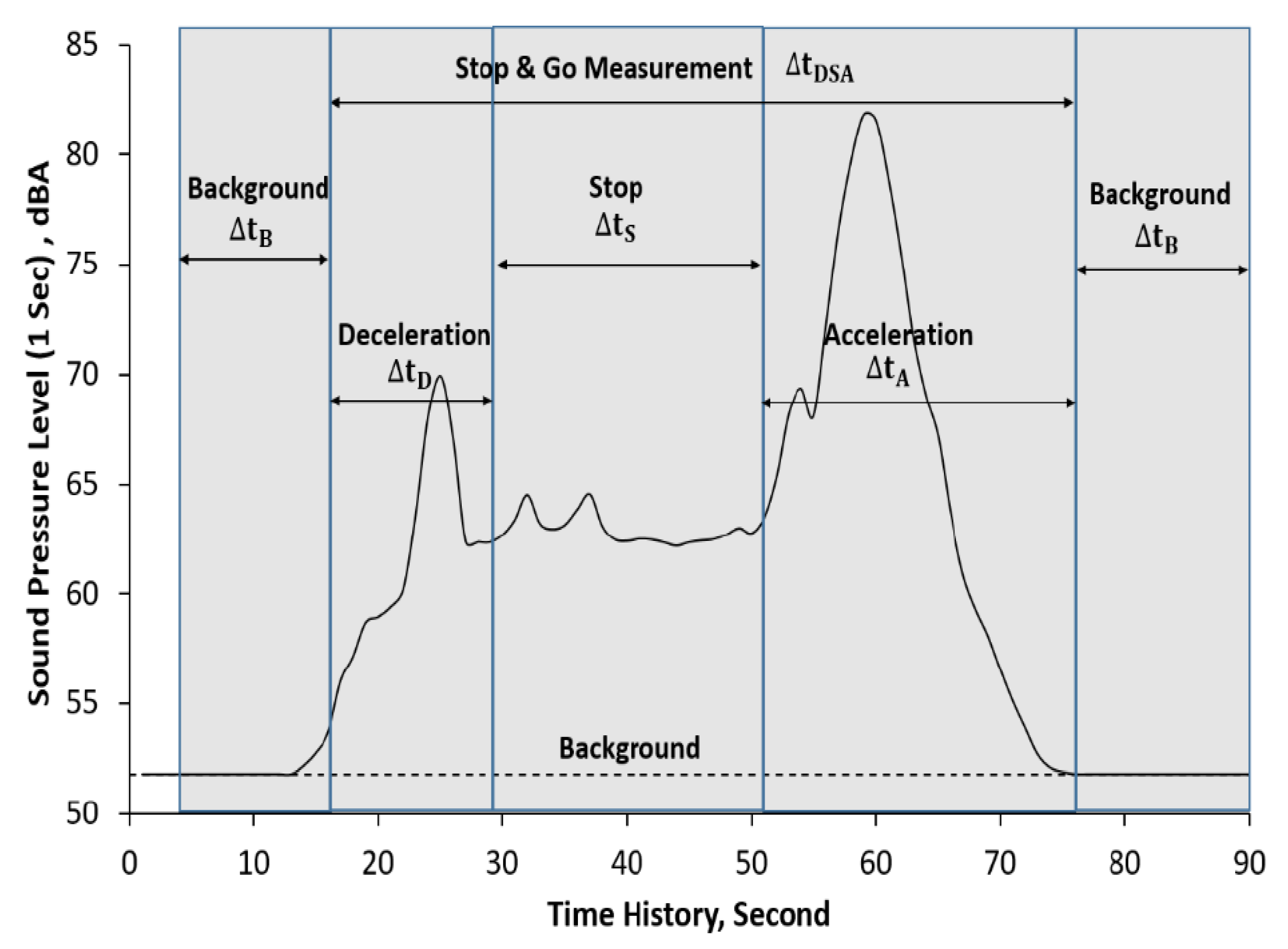
| Measurement scenarios | “non-stop” and “stop and go” |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, C.-k.; Lee, Y.-y. The Effects of Signal System and Traffic Flow on the Sound Level. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134454
Wong C-k, Lee Y-y. The Effects of Signal System and Traffic Flow on the Sound Level. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(13):4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134454
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Chi-kwong, and Yiu-yin Lee. 2020. "The Effects of Signal System and Traffic Flow on the Sound Level" Applied Sciences 10, no. 13: 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134454
APA StyleWong, C.-k., & Lee, Y.-y. (2020). The Effects of Signal System and Traffic Flow on the Sound Level. Applied Sciences, 10(13), 4454. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10134454





