2. Introduction
Information and telecommunications technologies are the fastest growing industry in the modern world. For companies that want to be competitive, it is essential to be interested in new technologies, whether it is a new software solution or a new hardware solution. New technologies bring efficiency to large companies in terms of saving money and simplifying work for individual employees and saving time that is wasted inefficiently. The technologies that surround us constantly increase over time.
Progress and technological advancement are essential in various sectors of society and in organizations around the world. Companies use various technological solutions to increase efficiency, productivity, and their privacy. Modern trends in cloud technologies and network solutions bring a certain comfort to employees. As a result, employees are more satisfied and can better devote themselves to their responsibilities. One such area is the press. Print management in a large organization is crucial. The printing of documents takes place in different areas, departments, or offices. Ensuring the printing needs of larger organizational units may not be a daunting task. Due to the degree of complexity of each organization, the solution is almost always different in each organization. Many aspects must be considered, such as the need for already implemented printing technology, compatibility with existing hardware, and many other factors. An important aspect is the need to ensure the correct access rights and to monitor printouts from a security perspective [
1,
2].
This work will focus on a company that has a problem with an unsustainable, old, and declining document printing system. The article is divided into three main parts.
The second section of the article is focused on defining the basic theoretical concepts that are necessary for this work and necessary to achieve the goal. From the composition and operation of computer networks, through selected network devices, we reach new, interesting solutions. Such solutions are not so often used in practice, but bring with them new possibilities that make work easier not only for employees, but can replace several small subtasks within the organization with one system. The section will also focus on the creation of analyses, projects, and their application, from the implementation of proposals into operation to the impact of these changes on employees.
The third section of the article describes the goals of the work and ways to achieve them. It turns out that by choosing the right methodology, it is possible to implement the individual steps and obtain the necessary information to develop this work.
The fourth section introduces the selected company, describes the current state, problems, and specifies the desired state. When designing a new solution, the printing model is analyzed, the current state of the organization, and the strengths and weaknesses of the company are identified. This data will then help to create a proposal that would be the most appropriate and would meet all the financial and time requirements that the company expects from the solution. The final state of the new system and a detailed description of the implementation in the selected company will be presented. On the basis of this proposal, a list of opportunities and threats posed by the new system has also been drawn up. Preparation of financial analysis and budget provides an overview of the price of the solution. The proposed schedule created using a Gantt chart will allow the project to start according to predetermined activities. Finally, the results, achievement of goals, and benefits of work are defined.
5. Results of This Work
This section will introduce the organization in which the analysis and implementation of the new printing system will be performed. By precisely defining the problem, asking for a solution to the problems and formulating the desired state, it was possible to present the first suggestions that would solve the problems.
The first issue was to evaluate the current state and collect strong and weak organization pages. After defining these pages, it will be possible to create the initial design solutions for which a suitable provider will be sought. After addressing potential providers based on the submitted offers, a financial budget for a specific solution will be prepared. After the budget was approved by the organization, the first phase of the solution will be launched in cooperation with the company, and a model solution will be implemented. After implementation, a test group was created, in order to test the solution after it had been in operation for a certain period of time. After the tests of the solution, it will be possible to define the new state of the organization and, thus, create new opportunities and threats related to the adoption of the new system.
5.1. Description of the Organization
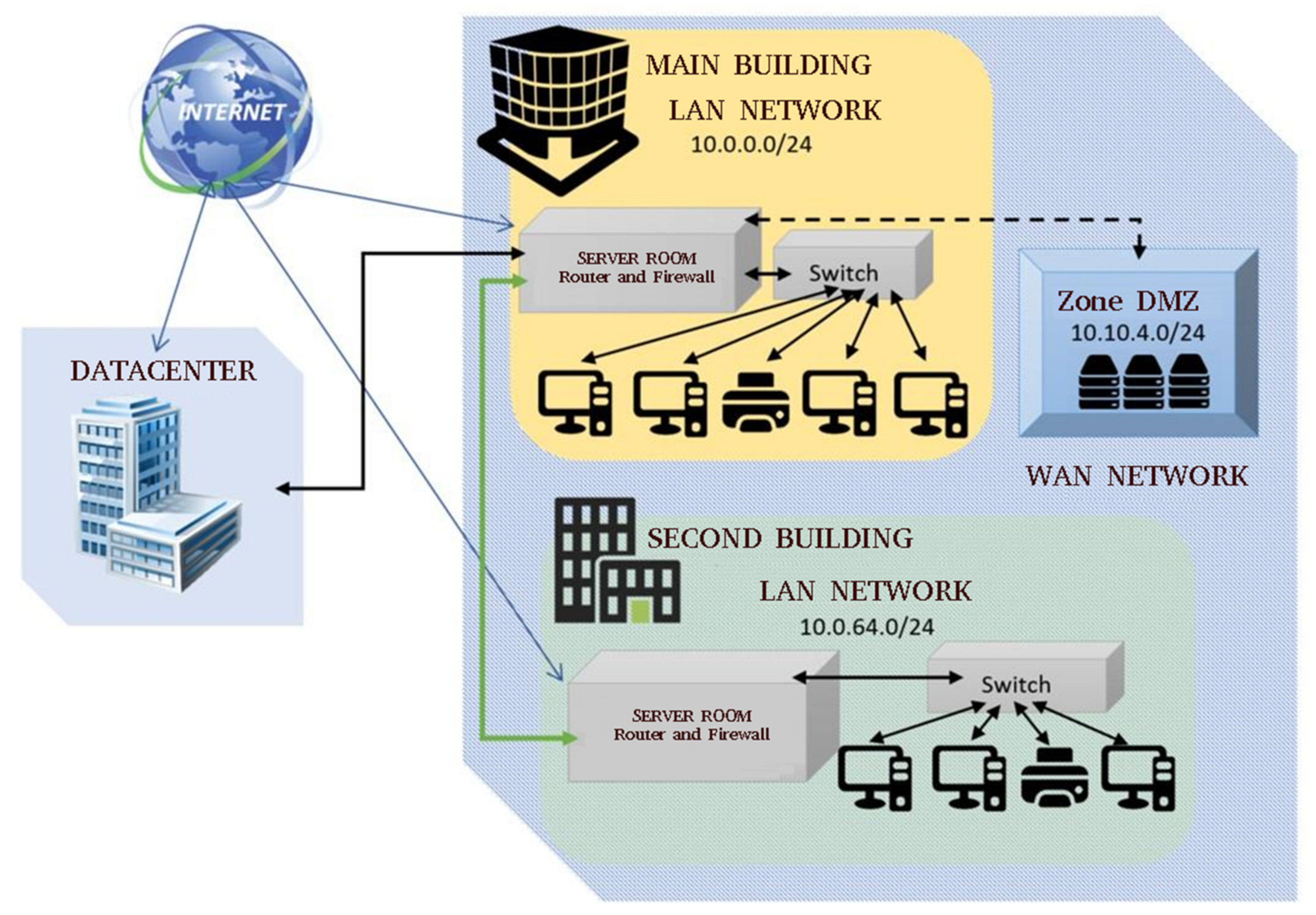
The organization in which the solution will be applied wished to be unnamed or otherwise mentioned. However, the solution is more or less universal for other companies with the same problem. It can be said that the company belongs among the larger companies operating in Slovakia with several smaller branches throughout the territory. The company is engaged in legal and international activities and is dominated by a lineage (hierarchical) organizational structure. The main building employs approximately 400 employees, each working mostly on a computer and needing access to a printer. The building consists of five floors and four main corridors that connect in an “O” shape. On each floor, offices are divided into cells, themselves 12–36 square meters. The distribution of employees depends on their functions. Directors have separate offices to which the relevant secretariat is assigned. Then there are offices occupied with 1–4 employees, or more. The organization comprises several sections, which are further divided into departments. Each of these departments has a dedicated independent activity, but cooperates upwards within the section. There are also four separate branches of the company in the same city, all belonging to one organizational structure.
The layout of the company is important from the perspective of employees’ access to printers for the reason of maintaining the security of personal data, or other reasons (confidentiality of sensitive data, etc.). Therefore, it is also important for the employee to have a printer as close as possible and larger; remote printers are not satisfactory.
However, the most important problem is the large number of printed pages. For this reason, the company has purchased a number of printers over the years, as well as other copying machines of different kinds. Maintaining and managing them is demands significant resources for the organization. Due to the poorly structured arrangement and planning of the purchase of these machines, there are many types of printers and, thus, many types of consumables that are not compatible. This means that the company has to order individual consumables for each type of printer material, toners, but also other materials, such as image drums, belt units, fusers or waste containers. Frequent repairs are necessary supplying the warehouse, which is very demanding in terms of time and money.
Small printers are cheaper, but materials like toner and other consumables make it more expensive to print more pages than with larger, more modern machines (
Table 1).
Table 1 lists two printers from each of the most commonly used printers in organizations. Toner prices were obtained from the average price from various retailers (via heureka.sk). To make the price as accurate as possible, the original toner black (base) with the specified number of pages printed manufacturer is used for each printer.
When calculating, it is possible see that the price of toner for small printers is, proportionally, significantly larger for printed pages than for large-volume machines. The most common small local printer price per printed page after rounding is 0.07€. The price of a large network printer per printed page is 0.002€. If one divided these two amounts by the result, we see that printing on a small printer is 35 times more expensive.
The company also has newer and more environmentally friendly equipment, but not every employee has access to them. Managing a large device and restoring consumables is easy. With network printing, the printer can be used by almost everyone who has access to it. As with small printers, damage often occurs by unprofessional staff intervention and technical assistance is only called when the printer is in particularly poor condition. In such cases, even if it is just a paper jam, it is recommended to call technical assistance. However, with many printers, there is a wait time for action, and the time delay and the need for the employee to print becomes very unsatisfactory.
Despite the era of digital media and mobile devices, the business is inevitably reliant on paper-based processes. These are mainly contracts, invoices received requests, letters, and many other documents received or sent for approval or correspondence.
5.1.1. Technical Support
The organization’s helpdesk is responsible for ensuring the operation of the organization’s printers. The helpdesk takes care of corporate problems from both an administrative and technical side. The printing system is in the technical category. Management of printing machines, maintenance, and restoration of consumables is recorded and managed by the Technical Department helpdesk. The internal technicians are responsible for ensuring that the organization runs smoothly. One of their tasks is caring for printers. Since its in closed, non-public areas where the printers are located they cannot be maintained externally in the form of a careful service. This is also true for large network printers in corridors and secretariats. Technicians accept requests from employees and resolve problems or requests to replace consumables. Any interventions (except paper refilling) equipment and printers are prohibited by employees. In the absence of technical workers in the workplace, the situation was unmanageable. This is why the company decided to take action and phase out small, inefficient printers from their assets.
5.1.2. Required Company Status
The company would need to prepare a complete analysis of the state and design of a new solution, which would solve all the problems at once. The targeted state of the company is to abandon the current complicated system and solve its already mentioned problems. The new system should be able to cover a large burst of press for all employees with coverage throughout the building without walking post-printed materials too far. The new system is not only about software but also about purchasing new equipment needed to implement the new design. The system should be easy to operate for both the employee and internal technical support.
Likewise, the system should have a backup solution, and in the event of major problems it must be easily repairable or replaced. It is also necessary to solve the security of printing, which is a significant problem in the current social system. Managing the new system’s hardware issues must be made available for internal technical support because the premises of the building are inaccessible to the public and waiting times for the securing business are too long. For the same reason, it is not acceptable to design services that uses an external company to provide printer rental and maintenance. The solution and transition to the new system is required as quickly as possible. The transition to the solution shall not exceed 30 working days.
5.2. Analysis of the Current State and Proposal of a New Solution
To analyze the status and design of the solution, it is necessary to recapitulate the main problems that the firm desires to remove with the new solution. The biggest problem is the chaotic structure of the press, improper placement of printers, variations and quantity is relatively difficult to maintain. Furthermore, print access is not guaranteed evenly for everyone, printers are not secured against theft of printed materials, and there is no condition and balance monitoring system.
The solution to the problem of the organization is to propose a new system layout of devices and consider renewal, or adopt a new, more modern system, i.e., apply a new information management system and monitor printing on all devices. However, for a detailed proposal, a complete analysis of the current situation is required.
5.2.1. Current Situation Analysis
Based on observations and data obtained in cooperation with the technical department of the company, it is necessary to process the necessary information into a SWOT analysis on the basis of the evaluation of the current state of the organization.
Already at the beginning of processing the current state it is possible to determine that the main problem is an outdated print structure that is unreliable and opaque. Complete assembly of the machines used to consist mainly of locally-connected printers located directly in the employees’ offices. Locally means the printer is connected using a USB cable directly to the computer, limiting printing to just one computer. This type represents approximately 70% of the printers used. It is also the most widespread, and this is mainly due to the many requests from employees for a personal printer and a refusal attitude of workers to give up the printer. There are more than 27 different types and brands of printer in this organization. Each type requires a different type of toner and others consumables. Another common problem with small printers is the unprofessional intervention by employees who have a paper jam or other error that has caused a printing stoppage. If the paper is jammed, one must be sure to open the printer carefully and follow precisely the specified steps by the manufacturer, pulling the paper in one piece. When the paper is torn inside the printer, the printer must be opened and cleaned gradually. If the printer shows any remaining dirt, it is inoperative. This means that the problem cannot be solved on-site and one needs to remove the printer and replace it with a new one be added to spare network printers nearby.
The second type is a network printer. This printer is set up so that, when connected, it obtains its own network IP address, making it available to anyone connected to that network. However, this does not mean that any employee can use it. Firstly, someone from the technical department must set up the printer on a specific computer and install the necessary drivers so that a computer can communicate with and send to the printer documents required for printing. The employee does not have the necessary knowledge and administrative rights for such an installation. For new employees, or when relocating an employee inside the building and connecting to another printer, or if the printer is unavailable, technicians install a new/different printer locally on every single computer. The advantage of a network printer is that it can be located anywhere when it is connected to a network. This type of printer is located mainly in corridors, secretariats, or larger offices. Network printers can be small or large, and provide scanning, sorting, stapling, and other functions. Another advantage of multifunction network printers is the possibility to send scanned materials directly to the employee’s mail. It does not require a storage device or manual setting. One simply chooses an address or addressee, selects their name from the list, and sends the scanned documents directly to mail.
However, the share of network printers is only 30%. That is, the network layout of the printers is very important, and since there are not many and the office space is very large, there are areas where no printer is available. This is a problem for the workers that have network printers (that is, they have the printer installed), but they must go to other parts of the building or to another floor to retrieve printed materials. The specification of the number and type of network printers is shown in
Table 2.
According to
Table 2, the organization has 89 printers. The division consists of 62 local printers of 27 types, and 27 network printers of seven types. The ratio between local and network printers is 70/30. The number of types means different types of printers of the same category that do not use the same consumables. For each type one needs to provide unique supplies that are not compatible with other printer types.
However, the main problem of downstream printers is not their localization or unavailability, but the printing system. The system prints on ordinary printers as soon as it receives a file, prints the documents, and must be picked up in person. During the normal day it often happens that several people print documents independently at the same time, and they need to be sorted after printing. It often happens that someone accidentally takes the documents of another, who then looks in vain for their printed materials. There is a great risk of losing materials, compromising personal data, or to the security of classified information. In such situations, many personal requests arise with respect to the printers, and the condition is getting worse [
5].
5.2.2. Breakdown and Recap of Strengths and Weaknesses
Based on the current information on the state of the company problem it is possible define the basic strengths and weaknesses of the company. The strengths of the company include, firstly, a functional printing system. This means that even if the system is not perfect, it is functional and, as such, it manages the current onslaught of printing traffic. Another strength is that there is sufficient good hardware within the company. There are enough quality printers that cover a large amount of usage, and, thus, a number of print jobs. Another important strength is the qualified professional help desk. These employees are also proficient in the onslaught of tasks. The company is free of use external companies to ensure operation or provide solutions to more complex problems. This is very important because the new system can be designed with the ultimate goal of being managed by company technicians and not by an external company—that is, the system vendor [
33,
34].
One of the weaknesses is the outdated print structure. It is a chaotic structure of different printers that are not compatible with each other and cannot work with multiple computers. In most cases they only cooperate with, at maximum, one computer. The second major problem is the mood of printers.
The lack of central network printers represents the blind spot where printers are not located. Therefore, small printers are needed, which, over time, have covered areas where no printers were before. This solution caused the purchase of small cheap printers which are expensive to maintain and do not have a controllable system of printed pages, as well as disorders. Such maintenance is relatively expensive and, compared to the new large network printers, is several times more expensive than modern printing technology. Many small inexpensive printers are not only expensive to run on supplies, but are also unreliable. Small printers are not adapted to a business where the printer is printing on a daily basis. Frequent use also requires regular maintenance that requires additional funding and technical support time. The most serious problem is not to use network printers that may result in information leakage or violate the GDPR. It is not possible to secure a network printer to prevent theft of printed material by another person. Such alienation of printed pages may also be purely random when multiple people print at the same time. Another disadvantage that has already been mentioned is that of printing monitoring. Small local printers cannot be monitored for the number printed pages and it is not possible to determine whether an employee is printing a number of authorized documents or printing for their own needs. The last weakness is the fear of change, although this is basically a risk when deploying any new system.
By defining strengths and weaknesses it is possible to evaluate the current situation, i.e., the current state of the organization by the printing system and the press in use. Detailed strengths and weaknesses are listed in
Table 3.
5.2.3. Creating a Proposal
In order to create a proposal it is necessary take into account the current status and requirements of the company. The design of the solution consists of creating a central network printing solution to manage overall organization-wide printing, including designing a user-friendly application with a notification system in the event of a problem or the need for intervention by a technician.
The solution consists of a print server that will be the center of all printed jobs. The essence of the system is to identify the job and send it to the desired place to print from. However, to create secure printing printers will be protected by security features, that is, printers will require user security identification. The most commonly used are PIN (digital) codes or smart cards. After identifying and authenticating the user directly to the printer that prints the job, it is created and sent to the system, and the print server sends the data to its present printer, which then prints the materials, already in the presence of the author.
Such a system must be deployed internally within the network infrastructure. After deployment, the system will be configured and, along with others necessary hardware (printers), access to the administrative part will be handed over to technical support.
Application settings will be made according to the requirements of the organization. The application will include a complete system report, providing a complete overview of all connected printers, their current status, and the status of users’ print jobs.
Users will be added to the system through synchronization with, for example, Active Directory, i.e., when an employee account is created or disabled, the account is activated or deactivated. By setting up, internal technicians will be able to define security features for logged-on users. The generated PIN will be delivered to the user via email directly from the system after creating an employee account. In case of a lost PIN, it can be re-generated.
The application will also include a power consumption notification system, warning a predetermined person (technical support) of the status of the device, such as a paper jam, device damage/error, or a current alert level of consumables. Such notifications can be sent directly to the helpdesk employee responsible to solve the problem. No communication from the employee is required towards the helpdesk. This system also prevents damage caused by the intervention of employees in order to (unprofessionally) repair the printer.
In the second part of the new solution it is necessary to work out which printers are suitable or, rather, if they are compatible with the implementation of the new solution. Since it is a networked printer, we can assume that local USB printers are not compatible. The new system can only be downloaded to printers that have: network access, touch display, numeric keypad, smart card reader, or other form of security.
According to the table, only 15 downloadable printer drivers are compatible with new system. These are the latest and most powerful printers that have been most recently purchased. From the ratio table it is known that the new system will be subject to 17% of all printers.
When designing a new layout, it is possible use data on the company building. According to such information, the building consists of five floors and four main corridors no more than 50 meters in length on each floor. That is, reflects a space of 20 corridor sections (5 × 4) and if the printer placed in the center of the hall, each employee will have a printer at a maximum distance of 25 m from the office, which is acceptable. This means that, for 400 employees, in an even distribution 20 devices are needed. Recommended hardware is a classic multifunction printer with an easy-to-use display with PIN input and chip reader cards. It will be suggested that the firm purchases the same printer type for easy management and compatibility of consumables. The minimum sufficient solution requires five devices with new system support.
Thanks to the new layout of printers with the printing system, this covers the complex area of the corridors of the building. This means that regardless of the section or the employee, one can use any printer in the building. However, there are still other printers that do not support this system. In the next section the proposal to deal with the current (old) system is discussed in detail.
5.2.4. Switching to the New System (Old System Solution)
The greatest advantage is the routing of the entire area of corridors and secretariats. This system also solves the possibility of equipment failure, because the employee (in case of device shutdown) has the option to go to another nearby printer and print the material right there. The print server sends jobs to the printer only after it has identified the employee, regardless of their location. That is, even in the event of long-term failure it is possible to replace the device with another (replacement or new) and there is no need for intervention by technicians in the form of installing a new printer or configuring a new IP address for the device.
The old solution is completely replaceable. It is not recommended that old printers are immediately decommissioned, but that employees gradually learn to print in the corridors, disconnecting old printers as needed, in the case of malfunctions or when there is a lack of consumables. Consumables in new the network printers last a few weeks to months in heavy traffic, so interventions in replacing material is minimal, which removes the burden on technical support (helpdesk).
Old network printers can be used directly at the secretariat or larger enclosed offices where other employees do not have access. By the information in
Table 4, the number of incompatible network printers is 12 and, therefore, it is possible to cover 12 separate sections as needed by the organization. However, it must be assumed that these printers remain the current printing system, either networked, without security or compatibility for all employees.
For both local and network printers, it is up to the organization to decide if it is necessary to continue using the printer in order to purchase the material. We recommend to separate older printers from newer ones, limiting redemption, and discarding outgoing printers. A transitional period for staff to adapt to the new system will be maintained. By limiting the purchase, the employee will have to accept that, over time, the printer will be disconnected and they will no longer be able to use it.
5.2.5. Final State of the New System
The layout of printers, including the purchase of new equipment to cover the remaining sections, is secured throughout the building. In every single corridor is a large multifunction device that is under the new printing solution system. The maximum distance from the printer to any office is 25 m. Employees, after registration in the system, receive an installation link (without administrator permission) and personal PIN to identify the printer. They will see an option in the menu when printing documents to the print server. All jobs that can be printed are stored in a so-called print job. When the employee decides that they need to print the materials, they arrive at any printer and after identification gains access to the system. Here they have the opportunity to print individual documents. The advantage is that the printer does not print the documents until they are identified, and will not be confused for another employee’s printed materials and removed materials by another person. After printing the employee has either the option to continue with another activity or log out of the system. Other options are available to scan when you sign in documents directly with an email address or portable device, make a copy, or send a scan to other employees. By synchronizing with the system, the entire contact directory is available. If the machine malfunctions, it may be sent to another printer and finish printing there. In case of malfunction or other defect, the system informs a technician of the type of error.
The advantage of the whole system is that, even after the purchase of new devices, these devices will still be able to be added directly into the system without having to locally set the device to the place of operation. Simply pair with the system when connecting to the network and the print solution itself configures it according to the pre-set settings by the organization.
With the adoption of a new printing solution, new opportunities will be created. The main task is to deploy printers to evenly cover the organization. Each will have at least one printer with a new system available, and the employee will be independent of technical support when the access is generated.
No further installation or configuration of the printer from the technical side will be necessary. The new system will take care of everything and after making the manuals, employees will be able to print fully autonomously. After a gradual reduction of used old printers and focusing on one type, organizations will also reduce the number of types of consumables materials. One kind of consumables will relieve warehouses and problems in planning and ordering toner cartridges for small local printers. The new system offers a notification system to simplify traffic and support new printers. By monitoring not only can the organization immediately identify the printer error, but it can collect the necessary data and obtain output reports from the system about the number of pages printed per specific employee. This will reduce the number of printed pages from people who have printed regardless if for work or for other needs. It will also unify printers with the new system in a way that one printer is not tied to one location. Employees can print regardless of its location on any printer in the building. Additionally, a malfunction of one printer does not stop the printing operation and it is possible to use the nearest printer without any intervention. In case of long-term failure it is possible to have a place where the printer is missing, moving another, or new printer (after quick configuration it is possible use immediately), without additional intervention by technical personnel. The last new opportunity is independence from other systems or from supplier support. After the implementation is complete, the organization manages the new system itself.
Among the newly emerging threats, we are primarily afraid of change from the employees. The new system or new printer layout, or the removal of personal printers from employees, can trigger a refusal to adapt. The fear of change is expected to adequately prepare the employees concerned. Among the threats related to the deployment of the new system from a technical point of view, we can only include implementation or implementation issues with respect to system outages. However, such threats can be minimized with thoroughness in planning and control.
The adoption of the new system creates certain opportunities and threats that are summarized in
Table 5.
5.3. Financial Analysis and Budget
During the planning before the presentation to the manager, it is necessary to prepare the price of the new solution. With the new system, it is necessary to define the necessary requirements, which will be priced and the price will depend on them. The financial plan is divided into the following categories:
Price for software and application and printing solution licenses
Hardware price
Price for implementation and other additional services
It is necessary adhere to minimum requirements when searching.
Support for Kyocera, HP—Hewlett Packard and others
Application support for Windows Server 2008 and later
Secure printing support (PIN, RFID—Radio-frequency identification chips, encryption, etc.)
Suitable for large organizations of 400+ employees
Operating on the Slovak market with the Slovak interface of the application
Modified application for easy operation
Generate reports to a specific user
Analysis of print jobs
Web access
Remote automatic installation and access
Direct printing
Monitoring network devices
Monitor alerts and reports
Print failure protection
The price of the software depends on the particular provider. In the detailed analysis, together with the type of printer to which we want to apply the system, it is taken into account separately as one system. The MyQ application combines the functions of the print and service module into one system, covering all print jobs and customer needs (learn more about the product in
Section 3.2.2.).
By contacting providers and requesting a quote from our requirements, the most suitable offer is shown in
Table 6.
For each single printer it is necessary to buy a contactless reader for RFID chips and a license to activate USB inputs. Next, it is necessary to buy a printer terminal license and a license to activate the printer in an application that runs on the internal company environment (virtual machine or cloud). Finally, it is necessary apply the license to the virtual machine on which the entire application will run. It implements these tasks, including annual support by the supplier, directly inside the organization. Finally, the amount for initial training of responsible helpdesk administrators is required.
As the Kyocera TASKalfa 3552ci is out of stock, it is necessary look for similar model. Its successor is the Kyocera TASKalfa 3553ci printer, which has similar functionality as its predecessor and with the exception of a few visual changes is identical. The previous model has identical consumables, which will make it easier to manage and order supplies. The price of hardware is for five multifunction printers, up to a total of 20. The final price of all operations is 27.955,20 € incl. VAT. The price includes all the aforementioned services and products, including delivery, annual technical support, and a lifetime warranty on MyQ.
5.4. Proposal for Implementation
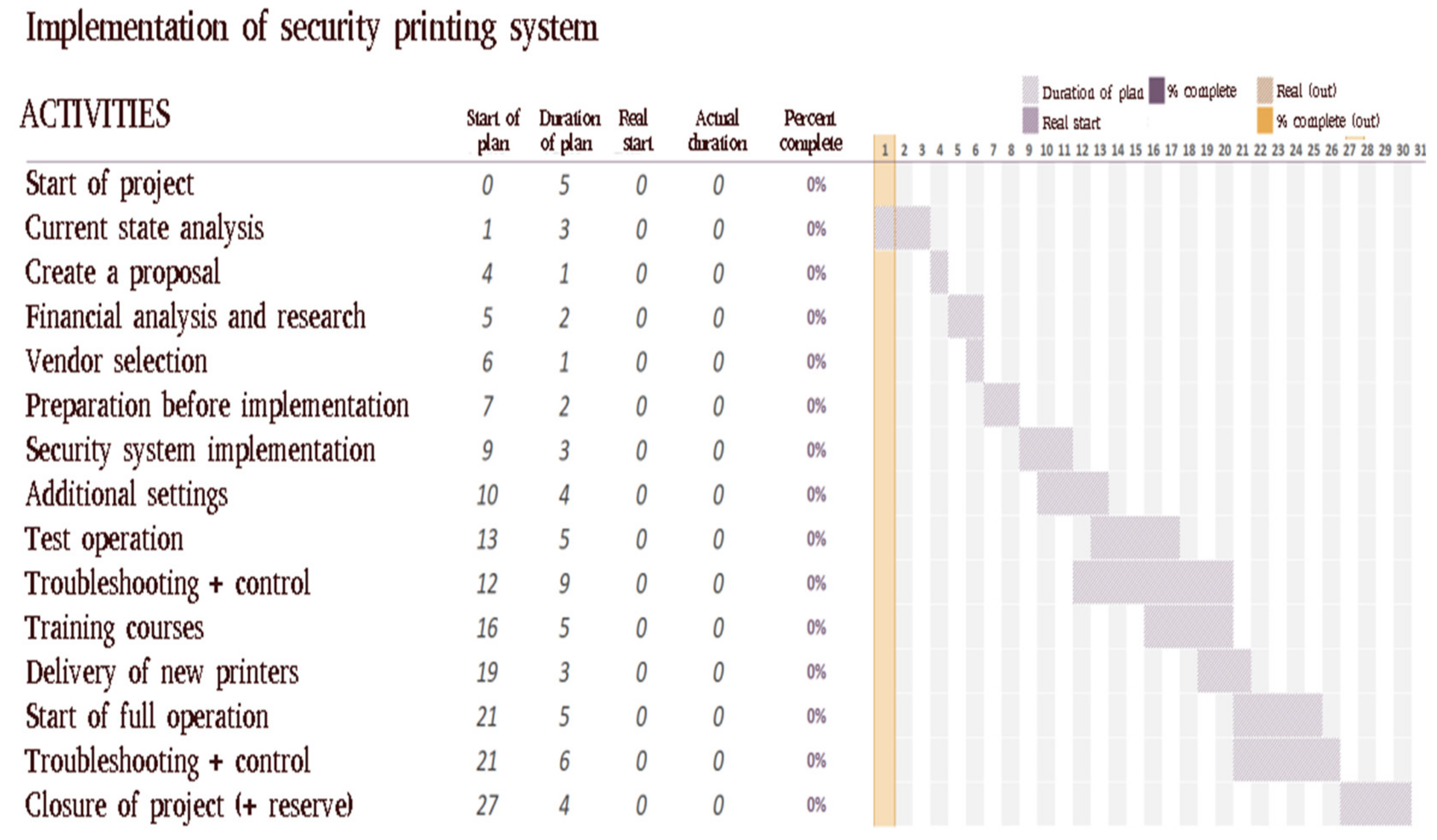
The whole implementation process is divided into individual sections. First of all, it is necessary to focus on the preparation of the necessary elements that are required for both the company and the supplier. It begins with detailed pre-installation preparation, where the supplier is provided with all the necessary documentation and the implementation environment is prepared. After implementation, it is necessary to fine-tune all specific settings. We work closely here with a vendor who guides us through the steps. After the setup is finished, it is possible to conduct a test run to test each feature and it is necessary look for system errors or flaws. Additional adjustment follows, such as program troubleshooting. Finally, it is possible to define and compare the current state and the final state. We compare the final state with the desired state that we originally wanted to reach. If it meets all desired aspects, such as functionality, safety, etc., we can switch to real operation. Before starting the system for others employees, technicians must be provided the necessary train training. At the end the implementation period is the period of correct operation, after which the project is closed (
Figure 2).
The planned timetable is divided as follows:
Project launch (five days)
Current situation analysis (three days)
Creating a suitable solution model (one day)
Financial plan and market research + supplier selection (two days)
Preparation before implementation (two days)
Implementation + Additional settings (3–5 days)
Test run + troubleshooting (5–9 days)
Training (1 day) + delivery of new printers (1–5 days)
System start-up + troubleshooting (5–6 days)
Project closure + reserve (1–4 days)
The maximum duration of the project was planned for 30 working days. The shortest duration was 21 days (first day of operation). A nine-day reserve has been created to stabilize the operation of the new system.
5.4.1. Preparation before Implementation
In preparation before implementation by the supplier it is necessary to create a space where all processes will take place. It is necessary to create a virtual space (server) on which the supplier implements everything necessary for the realization of printing operation management. Server requirements are nothing special and are only basic specifications. Since an organization requires an application to be internally designed, it must be localized within the company. It is, therefore, necessary for the organization to be given space for the implementation provided.
The minimum requirements according to official MyQ sources are shown in
Table 7.
Based on the minimum requirements, the company has prepared a Windows Server 2002 R2 virtual machine with a quad-core Intel Xeon CPU E5-2603 v4 2.20 Ghz and allocated memory at 16 GB. Storage disk size is limited to 120 GB for programs and databases. If necessary, the space will be scalable. After creating the virtual machine, a domain account will also be created to serve as access to the virtual machine and will be the key (identifier) of the program to the domain. After these simple preparations, the computer is ready for implementation.
5.4.2. Description of Implementation by the Contractor
After simple preparation of the virtual server, the next step is the implementation of printing management. Contractors use an auxiliary prepared account with permissions they start remotely by an auxiliary VPN connection to implement the necessary applications and software. Implemented applications include MyQ Terminal Manager, MyQ Easy Config, and MyQ Web Administrator.
MyQ Terminal Manager provides all processes of print and print management, connecting directly to the Active Directory database and sync servers from where it can retrieve data, such as user accounts and their properties. MyQ Easy Configurator is the basic application for the initial setup of all processes, creating backups of databases and other settings, identifying threats, and logging all printing events. The last application is the MyQ Web Administrator, which provides access to applications over a web connection. Using a web connection provides the ability to monitor processes as well as solve user sessions. Thus, access for IT server administrators will only be required if the web client is unavailable.
After the necessary software is completely installed, it is necessary to configure all settings that will in accordance with the organization’s technician (
Figure 3).
5.4.3. Description of Specific Settings
Once the vendor implementation is complete, one will be able to join using the master manager account, which can access the entire interface. Others will need to be configured before starting the first test print/operation. Between network settings one will need to define additional settings, such as the name of the access account that will be use the application for domain verification. It will also be important to set up an http proxy server for communication and notification through the application. The setup procedure before the first test run is shown below.
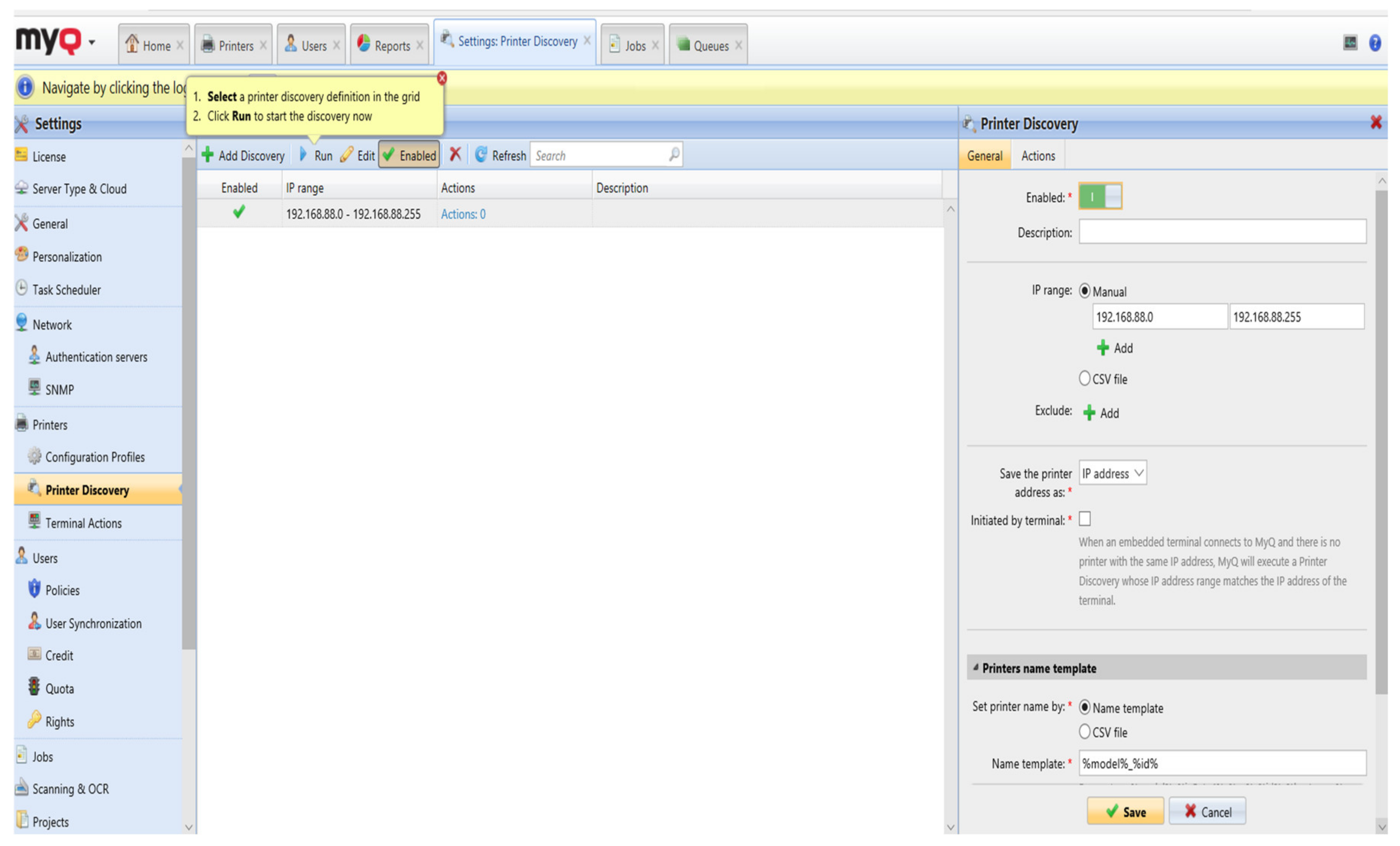
In the first step it is necessary to define the end stations, e.g., printers, which will be managed by MyQ. Since the appropriate printers have been pre-defined, they are selected from the list of printers with the exact IP addresses. The program also defines a range of IP addresses that are normally assigned to printers in the format (10.10.0.0–10.10.3.255). In this case, it is not necessary to have predefined printer IP addresses, but from an IP range address, the program searches for and identifies the printer that is found to be suitable or compatible with the MyQ interface (
Figure 4). Likewise, if a new printer is involved in the future suitable for management, the MyQ program performs regular checks to identify such printers and adds them to the list. After identifying all the printers it is necessary to reinstall the software and activate a contactless card reader locally on the printer.
To maintain uninterrupted operation, one must reinstall the printer without disruption of employees’ printing, therefore, a schedule of all printers will be created, which will be reinstalled at certain times. This breakdown will be provided to employees concerned with a warning of interruption. Installation readers and reinstall software is expected to take 5–10 min per printer, which is hardly any time at all. After the software is reinstalled the printer will still work with its original features. That is, except for a different graphical display, it works the same way. No additional work requires intervention. The printers will be ready to switch to the new available mode directly in the web application. This will enable enhanced mode or deactivate the publisher as needed.
The second essential step is to synchronize employee accounts directly from Active Directory. The sync users option is selected in the settings tab and the synchronization source from Active Directory is added. By setting up a domain LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) server and a network database access account, it accesses the Active Directory structure tree to define the necessary organizational features and folder trees. In this case, the organizational units of the individual sections and departments of the organization are defined.
Due to the number of impersonal accounts, each department or section is defined separately so that there are no non-user accounts in the MyQ management system. This can be the manager accounts of the supplier’s business, and so on. This way, they can be filtered out and only employees’ accounts will be added or removed with regular sync.
In the properties one can define individual data that will be synchronized with the user account. It can be mail, phone number, personal number, assigned chip card, address, class, or other. All this data will help in identifying the user for further settings. After selecting the necessary data, one can start the synchronization and check the functionality of the program.
After successful synchronization, a list of employee accounts will be available to define additional settings. Since test operation has not yet started, there will be no need to assign PIN access codes and installation servers.
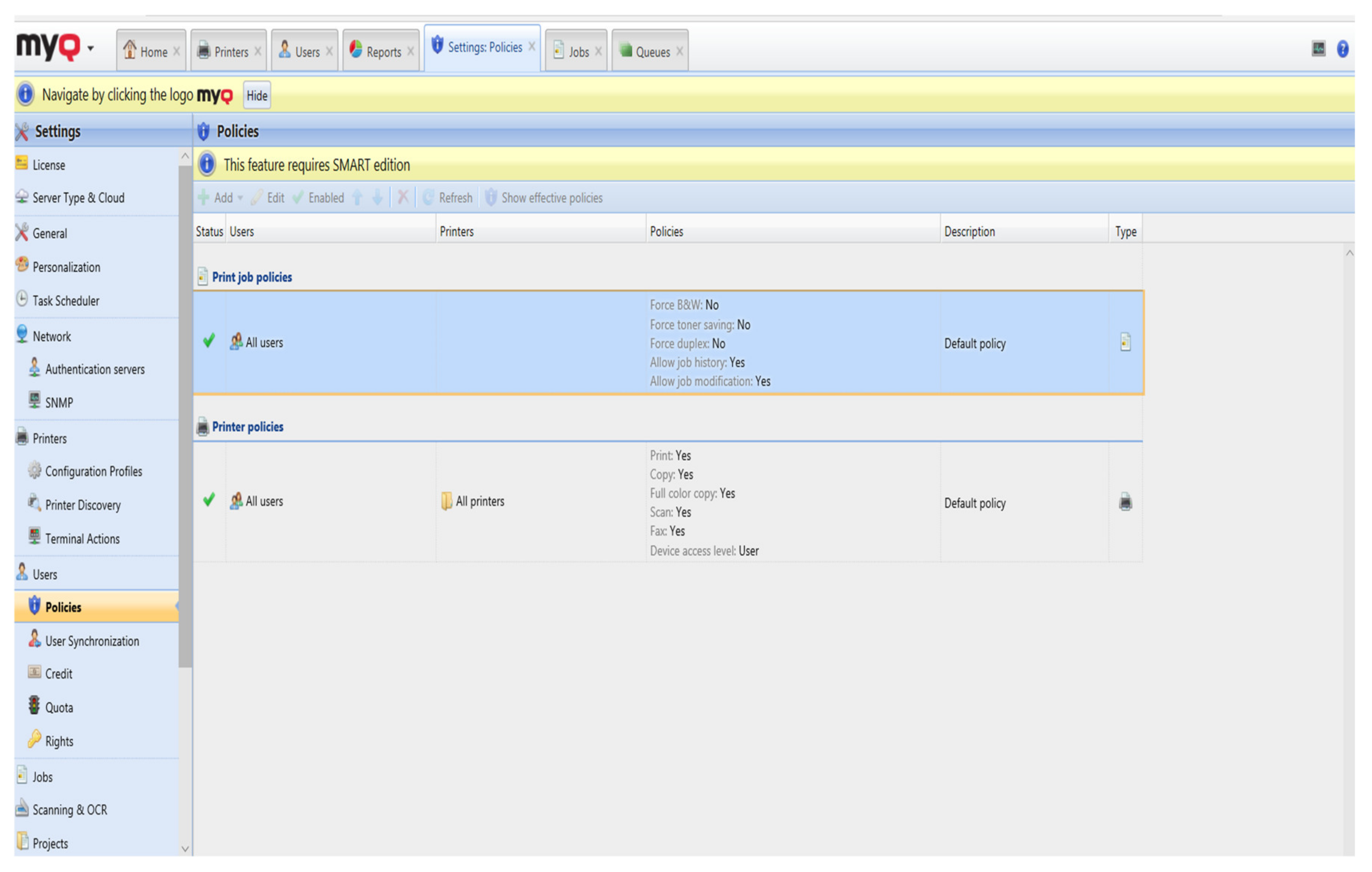
In the meantime, one can set up a basic setup policy that will apply when they print and use MyQ (
Figure 5). There is no need for specific settings, but it will be possible to define default settings for each print, if necessary. We will be able to force document printing in black and white, which is not an option in this case. However, we will be able to set automatic printing on both sides, thus reducing the consumption of material, e.g., paper. These settings can be set for predefined created groups or individually for specific printers. For example, a trainee or intern can restricted from color printing or to certain printers. However, these constraints for the real organization will not be necessary, as each user must have full access to each printer, in full.
The third important step is to set up backups via the task scheduler. Task Scheduler is one of the many features of the application. Among the most important are the backup of the database and settings. In the event of a problem or failure, these settings are easily restored from backups and all processes need not be set up from the beginning. This option is important, but the settings are not made daily, so the automatic backup is set to every 24 h. More regular checks also include checking drive vacancies. In case of heavy traffic or system load (number of prints; bulky tasks) is a scan of disk space that registers the threat, performs a backup, and suspends the operation as a rescue against system overload. This task is set to minute intervals because of the possibility of a sudden increase in space usage by users. Other regularly recurring tasks include the backup of the log, which monitors and saves every single activity and task created in the system print management.
Furthermore, system maintenance (deleting old users or long unprinted jobs) and regular synchronization of new users is conducted. There is an option to create several other tasks in Task Scheduler, which we can also add the frequency of repetitive operations (
Figure 6).
It is necessary to print in the printing system before sending the first authorizations defined by the email notifications, which are fully modifiable. Although it is an international organization it has decided to define all announcements and draw attention in both English and Slovak. Basic notifications include:
It is also possible to define the complexity of the password that users can connect to the web interface and manage their tasks. A predefined password is sent to the account PIN.
Notifications will only be sent when new PIN codes are generated or automatically when you create new accounts (via the Task Scheduler). They will be in the notification, including base data, defined login name and PIN, and installation link, together with instructions on how to use the printer for the first time.
After all these settings, the first tests can be run on the selected printer and predetermined users. In this case it will be a printer at the computer science department and test users will be the technical support staff.
5.4.4. Putting into Test Operation
After the first setup check tests, the first test operation can be started. In order to minimize the risk of problems, the introduction of a new system (as outlined in
Section 3.4) will apply to printers gradually, and a newly introduced printer will always have a technician to monitor responses and assist users in getting to know the new system. However, before deploying to the first printer, an informative email will be sent with all the detailed information about the introduction of the new printer and print management system, so that the user will not be confused at the first meeting with the new interface.
The first implementation wave will be started by defining the printer in the system. Printer settings define printing with forced printing exclusively through MyQ. This causes the printer to no longer be displayed at the original address (IP address printing). It is also defined on the printer with a security lock, or PIN. Once these settings have been made, the printer will be reconfigured within a few minutes and the numeric keypad will replace the original display asking the user to enter their security key (
Figure 7).
In this step, the printer is set up. Welcome groups were sent to the test group along with instructions and a new generated PIN. A technician present at the printer willingly presents the new system and answers all questions.
After testing of all features, the most frequently asked questions will be recorded and a prepared response sheet created, which will be inserted into outgoing notifications with a new PIN. After the first test run, it is now the turn of the others to switch over printers to the new mode. The test operation was scheduled for five working days. All questions or complaints that are submitted will be recorded for further processing and evaluation.
5.4.5. Troubleshooting
Periodically recurring after the first week of operation of the new system questions about the need to secure printers. These questions were answered and forwarded to new incremental members.
Problems in using the system were also evaluated. On this basis a simple manual was created, which is available on the company intranet or close to the printer to study. Furthermore, problem readers were recorded: devices that were unable to recognize older smart cards on the first try. This problem, however, will be solved in exchange for new hassle-free smart cards. After these steps, it is possible to assess the success of the new system and further explore its more detailed functions.
5.4.6. State of Play
A better understanding of the present and future state will be helped by the before and after state diagram in
Figure 8. In the first section, a classically connected printing system can be seen. Local printers are connected to only one computer at a time. Network printers are always connected to the nearest computer station. It can happen that one computer has more than one connected network printer, or the opposite situation, where the computer does not even have a printer assigned. In this case the employee is unable to print and must ask for a manual local installation or the nearest network printer. Portable devices, such as laptops or other data-free computers, also have the ability to print from other locations as long as they are plugged into the network. However, this does not solve the problem that they are always available only one pre-installed printers. There is a possibility to install other printers, but it may happen that the employee has something to print, and they forget which printer has sent it. Here one can see the problem of unmanageable printing and poor printer layout.
In the diagram in
Figure 8 of the future state, the complex connection and control of printing (and other functions) through the central printing solution system can be seen. All computers on the network automatically have unlimited access to the printing system. It does not matter on the printer location, but on the network connection status. After authorization (explained in
Figure 9), the desired file is sent to the print server, from which the print job is sent to the desired printer. The main difference of the new solution compared to the old one is that, regardless of whether the printer is broken or up-to-date and used for other activity, it makes printing uninterruptible. Another important aspect of the difference in the conditions described is that the solution does not affect previous local or network printing on devices that were not modified or enhanced with MyQ. The old system works as long as the organization does not change itself.
5.4.7. Final Status
To describe the final state, the system can be displayed using the final diagram future state. In the first part we can identify classical computer stations that send printed documents over the network directly to the print server. The print server registers the request and stores it in the database. The print job is assigned to the registered sender. The name is compared with the database in Active Directory. This means that the print job can only be printed or canceled by the user themself or, alternatively, an administrator. If the user decides they need to print the sent documents, they need to go to any printer with a secure print interface and enter their code on the display identification keypad. The default key is a six-digit PIN code. After logging into the system, the user has the option to print documents or cancel their printing (this option via a web application directly from their computer). After the jobs have been printed, if they do not sign out, the user will be automatically signed out within one minute for security reasons. The printer has the possibility of using other printer features, such as scanning or faxing. The employee needs to specify the addressee before scanning the necessary materials. One option is to automatically send everything to the logged-in user email. The second option is to select one or more recipients from a list that is synchronized with Active Directory and contains all contacts of employees, or other important addresses. The greatest difference from ordinary network printing is in document security throughout the time of sending to receipt of printed documents. The final solution model is outlined in
Figure 9.
5.5. Print Security
Printing security was one of the most important reasons for the recovery of the original system. General security protects the user from unwanted printing on devices that were not previously desired in situations where the user has preset another network printer. All data, whether it is user–server–printer communication or reading the status data from printers, is encrypted. Additionally, MyQ can encrypt the entire database containing sensitive data about users and their scanning and print jobs.
After printing the materials one can simply can forget to go pick up their printed material, or it can be stolen by someone else who printed materials before or after. Likewise, the author can mistake two identical printers and send the wrong document, and one can only wonder why the document did not print. In the same way duplicate IP addresses may be confused when configuring other new printers. In this case, the printed document can be printed on both printers, respectively, and there is a situation where one cannot print to either printer. The new security system is infallible, the user simply prints what he needs. It may happen that the employee printed something then changed their mind, made a few changes, and printed again. Due to this mistake, the new system does not need to print both documents and the user can simply choose which printer they want to print the document. Additionally, via the web, after logging in, the system page can modify or cancel all print jobs. The new system also provides the ability to repeat printing. The user simply sets up the application. Regular or popular files that do not need to be sent before each print but they simply remain in the system and can be printed out at any time computer use. Furthermore, the user is protected from unwanted (anonymous) takes of scanned documents, because when the email is received, the sender that was logged on to the printer is informed. In such case, the sender is immediately identified and marks the perpetrator of the mistake.
The second form of security when logging in is the option to register a chip card. Every employee is obliged to carry this card or chip at all times. Since these cards serve as identification at entry and record in turnstiles, everyone has such a card available. This card can be registered directly in the printer and a forgotten PIN can be identified by the printer. Additionally, if one forgets, or there is a malfunction of the reading device, it is still possible to verify with a numeric code.
In case of the permanent loss of a PIN, it is possible to request technical support for a new PIN, which is generated directly in the application. When a new PIN is generated, the number combination is encrypted and sent directly to the user’s email. If one loses their card they can get a new card registered on any printer without limiting the number of used cards.
At the same time, the printer is protected from unauthorized access to the system by strangers. Foreign persons or employees without a personal account assigned and the login code do not have the ability to perform any action on the printer. This will eliminate anonymous copying operations on unattended printers. Furthermore, the printer is protected against unauthorized interventions when replacing consumables. The printer is protected by an administrator password, which allows access to advanced settings and detailed analysis during a physical check. Toner inputs are also protected in an area that is only accessible after an administrator is identified. Since it is set in notification system, it is not necessary to report low levels of consumables, as this would duplicate toner replacement requirements.
Since the responsibility of printer and system management falls to the helpdesk department, it is at their discretion whether or not they will use secure access. The system can manage the printer without the need for passwords and IDs. For smaller printers (not in in our case) there is the possibility to activate the so-called safe mode on the printer, which does not require user identification and simply prints documents as soon as they are received. We recommend using this option for smaller- or medium-sized devices, which are otherwise secured. For example, these can be printers that are directly in the office or in closed secretariats where the printed documents can be taken over by someone who it does not pose a threat of leakage of sensitive information. These printers are also secure against unwanted actions, such as changing settings or misusing sending messages/scans from other sender addresses. Additionally, this type of printer is in the system management and is fully monitored. That is, it records the number of pages printed per person or by groups created (departments, floors, or any partition settings in the system).
5.6. Monitoring and Administration of the New System
The technical department receives requests to the information system on the basis of requests from employees. Such a request is assigned to a free technician who is assigned to solve the issue. The application was in a pending state when technicians were unavailable. Due to long wait-times of ongoing requests, the employees decided to act on their own and chose to solve the problem separately. In such cases, further damage occurred and subsequent retirement of printers was due to damage, such as broken plastic, holders, or other moving parts of the printer.
The new system uses a system of notifications on consumables. This system is fully adjustable and informs competent staff about the condition of the equipment. With the deployment of the new system, one technician manages to provide printer support. Forced use of network printers and gradual reduction of small local printer consumption has also been reduced due to frequent printing errors. Network printers that use high-capacity printer toners that last several times more than small toners. For large installations, the number of reported failures has decreased by more than half. With the notification system, a technician alerted states is determined between 1% to 5% failures. After these reports it is ready for recovery and the toner is always refilled the next day or, in case of heavy load, on that day, and the toner balance status is reported. The technician knows when a misfeed or other fault is reported, and intervenes almost immediately. In the event that a problem, such as a paper jam, or other, is identified the problem is resolved before the user reports an error. The most common problems caused by user errors are incorrectly loaded paper in the trays (A4 loaded in tray A3), which causes a printer malfunction or immediate paper misfeed in the feeder. Forgotten materials in devices, such as printed documents or USB memory keys with the new security system printing are reduced to zero.
The Technical Department delegates unresolvable requirements to either the printer supplier (technical issues) or system vendor (MyQ issues).
Training and Manual Creation
The last step of the implementation is to document the system and train the personnel. A training package for the System Management Technical Department was also purchased for delivery. The complexity of the system is not very high, so it can be operated by one technician. However, in order to ensure substitutability, everyone will participate (
Table 8).
All these points were addressed in the implementation or additional settings, however, they need to be controlled by other technicians to represent them at the inception of problems. The possibility of allocating powers to technicians is recommended, maintaining the chief technician and allocating other work tasks to other technicians to avoid unwanted errors when using or changing the system. A technician who only assigns new security keys or a technician that can produce reports or monitor supplies status, will not be authorized to other configuration settings, whether terminals or the web interface. Thus, there is the ability to assign simple permissions to untrained helpdesk employees, maintaining wide substitutability in the absence of technicians (e.g., late evening or in the morning with a lost PIN, another authorized worker may generate a new PIN but will not be entitled to other things).
5.7. Closing a Project
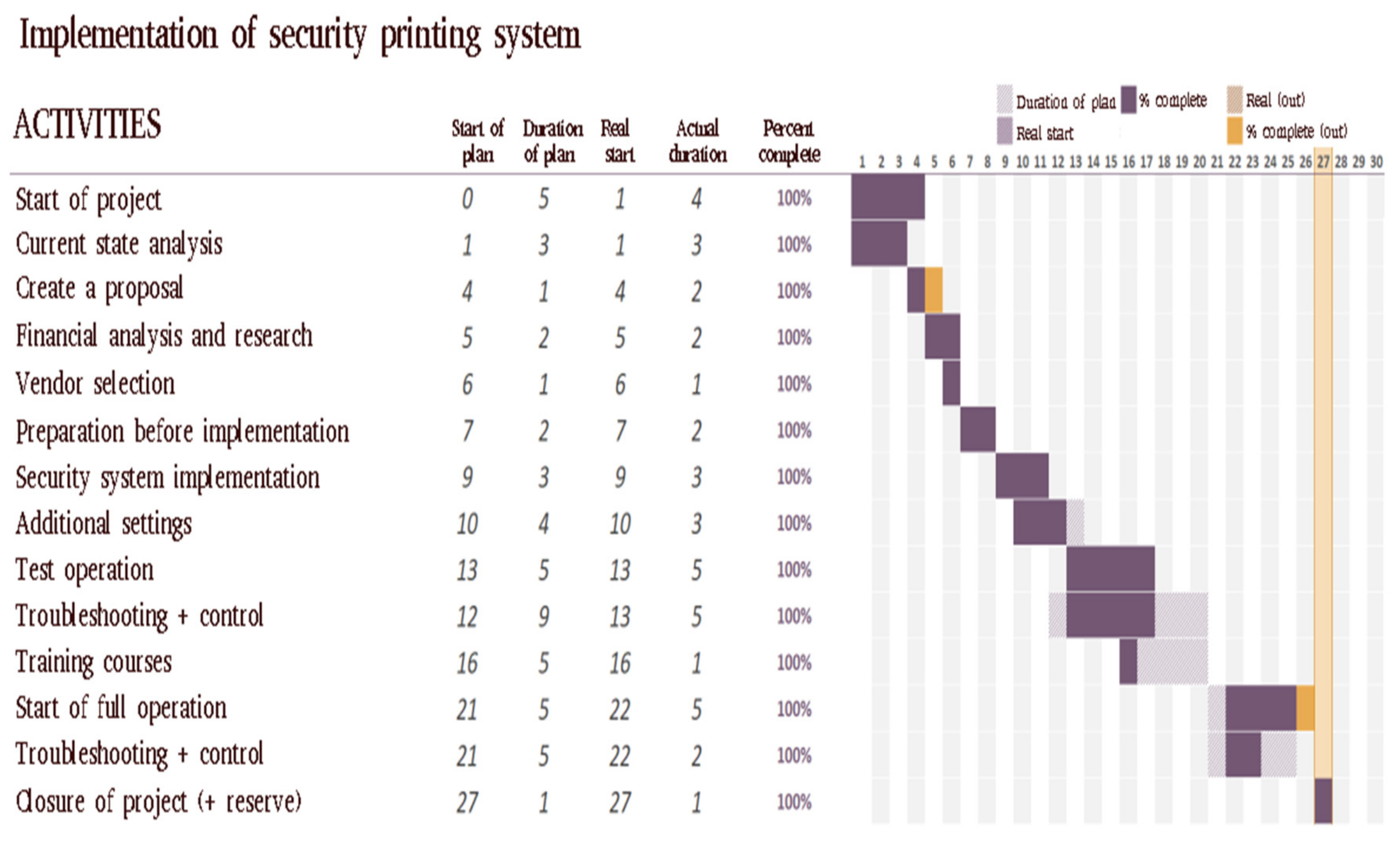
At the end of the project it is possible to compare the realization of the real project with the plan. The progress of the project is recorded in the Gantt chart in
Figure 10.
The final check is very important and, before submitting the project, it is checked whether the project progress has met the pre-set limits and fulfilled the individual points of the tasks according to the plan. Since it is a project in an organization chart, it is shown only on business days and not on calendar days.
Project start was set to day 0, and five working days were reserved. During these days, the groundwork for meetings with the observer was discussed and prepared. The next point included the individual observations of operation, environment and functionality of the current system. On the basis of that observation and discussion with authorized persons, the prepared materials served as a basis for the design of a new solution. Creating a proposal as the next point was realized the next day with a reserve the next day for the presentation of organization solutions. The analysis was performed on an ongoing basis which was chosen by a suitable supplier, who also submitted a price offer. After successful approval of the proposed model, the organization could have started to implement the solutions phase. Once the proposed model was successfully approved for the organization, the solution phase itself could start. On the seventh day, the preparations needed before the implementation of the new system began. Two days were reserved for these preparations. Since the delivery of new printers was not necessary at the implementation of the new system, the deadline was set for day 21, when the supplier had to deliver and operate the remaining (newly purchased) printers. Operation of new printers did not exceed one day. After the preparations, the implementation phase of the new system could start, for which three days were allocated for the implementation and configuration of existing printers.
The test operation was scheduled to start on day 13 with a five-day run. Prior to this phase it was necessary to inform the persons using the given printer to change and provide other information about the new system. During this time, a new phase called Bug Fixing and Control was launched. This phase was conducted at the same time to fine-tune printer and system settings, or collect data errors to provide users with answers to questions. At this stage said response sheet was created already, which is used to inform other employees after full operation. After the test operation was completed, there is a period where other helpdesk employees will receive the necessary training to operate the new system. After successfully completing the training phase, we could proceed to the final, and most important, phase, namely, full operation. Employees were informed before this launch on the following steps and received prepared answers to questions and instruction manuals for using the system. Outputs and inquiries of employees were checked during the entire period of operation. After five days of operation without significant errors, the deficiencies phase is completed and after the checks are completed we can terminate the project.
As can be seen from the Gantt diagram of the course of activities performed over time, the project was carried out within the deadline of 30 working days. Thanks to sufficient reserves soon all phases met the standard, as planned. The closing of the project was four working days earlier than expected.
6. Conclusions
At the end of the article, it is possible to confirm the achievement of the main objective, namely, the creation of a new model of print management, its implementation, and commissioning. The solution focused on a company with a large number of printers and a poorly designed printing system. Thanks to the good attitude of the company, as well as the possibility of observation of the company, the issue was identified and the strengths and weaknesses of the printing process were defined. After the analysis, an alternative solution was proposed and a new model was created to replace the existing system. The article discusses in detail the whole process from the selection of the solution to the planning of individual procedures for its implementation into operation during the continuous operation of the organization. It was also proposed to remove the old system with regard to environmental impacts, as well as to deal with the problem of possible resistance by employees when deploying the new system. Opportunities and threat analysis, which was carried out during the project implementation, contributed to these solutions. Real project data was used for the project. The data were obtained from market research, on the basis of which the financial and time assumptions of the price of the whole implementation could be specified.
The main benefits of the work include not only the analysis of the status of the selected organization, which it was used to design a new printing model, but also the model itself, which is applicable to a general society with similar printing problems. The work brings a solution that has minimal disadvantages and threats and brings a system with a great benefit not only from the viewpoint of security and distribution of the press, but also from a high degree of autonomy. The installation of local printers in the organization is a thing of the past, and this work can serve as a basis for realizing new projects for other companies with the same problems.
Problems, such as rejecting the new system and adapting to new printing habits in the corridors, are only a temporary question. However, negative attitudes were expected. After a sufficient presentation and a presentation of the positive aspects, it is possible to replace the old printing system in its entirety with this system.
Another recommendation for the company is to include other branches in the new system, which can be managed directly from the main central building. Under one system there may be several subsidiaries and the parent may control, or monitor, printer management. Since the parent company manages subsidiary networks and other IT security, the transition of printer management can relieve the individual branches, thus saving on trips or working hours of branch IT professionals.