Do Progressive Sensorimotor Training Devices Produce A Graded Increase in Centre of Mass Displacement During Unipedal Balance Exercises in Athletes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
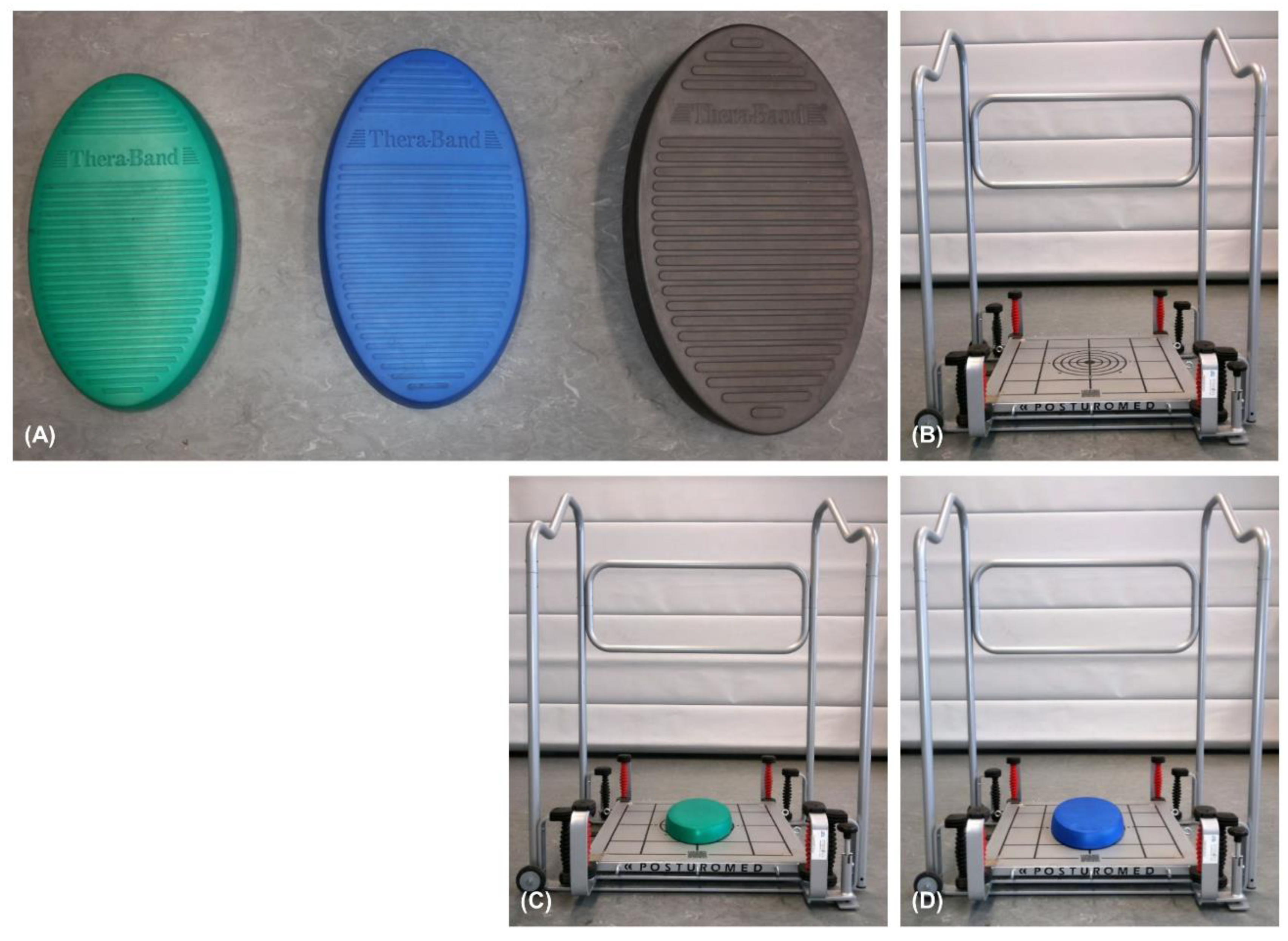
2.2. Balance Devices
2.3. Protocol
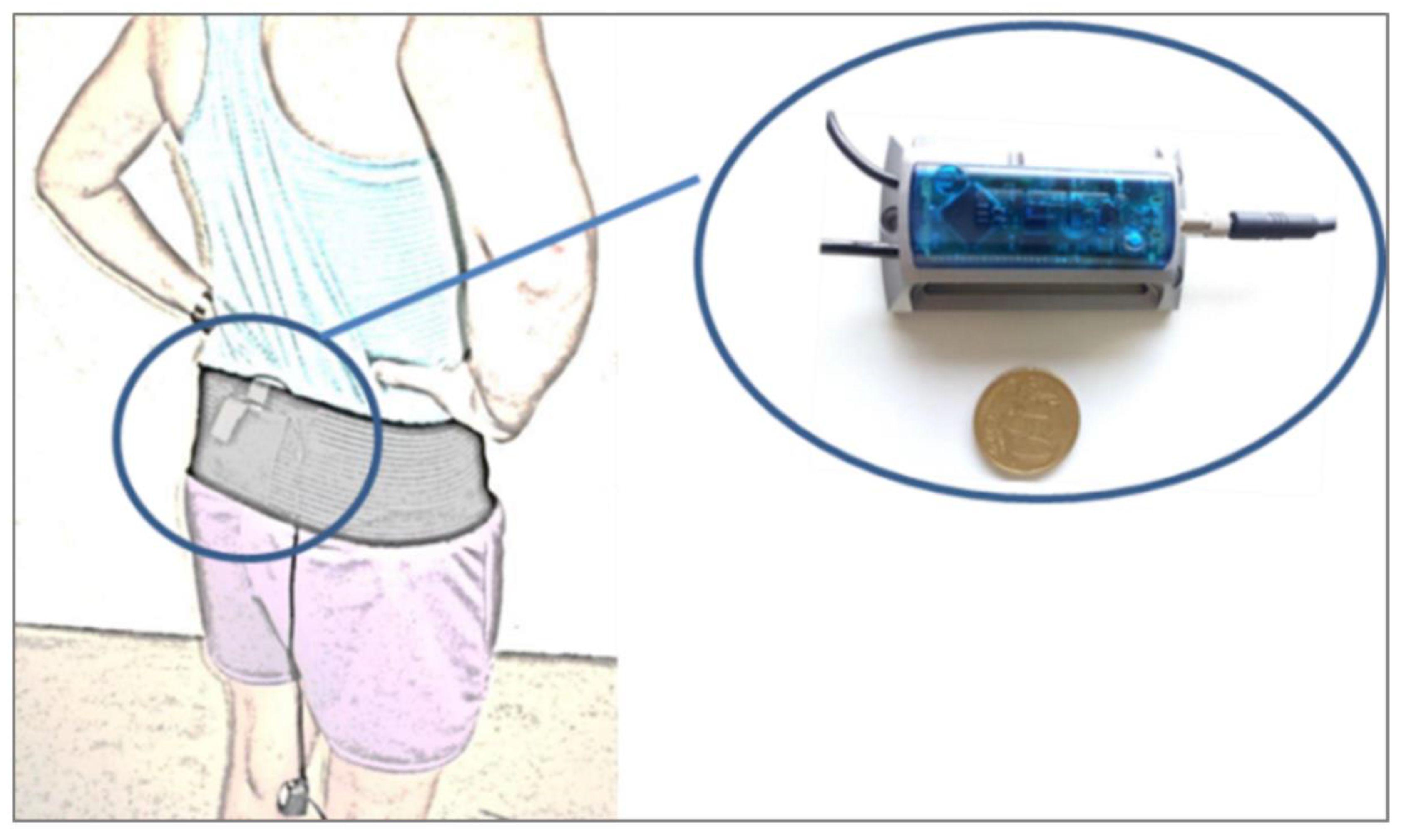
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
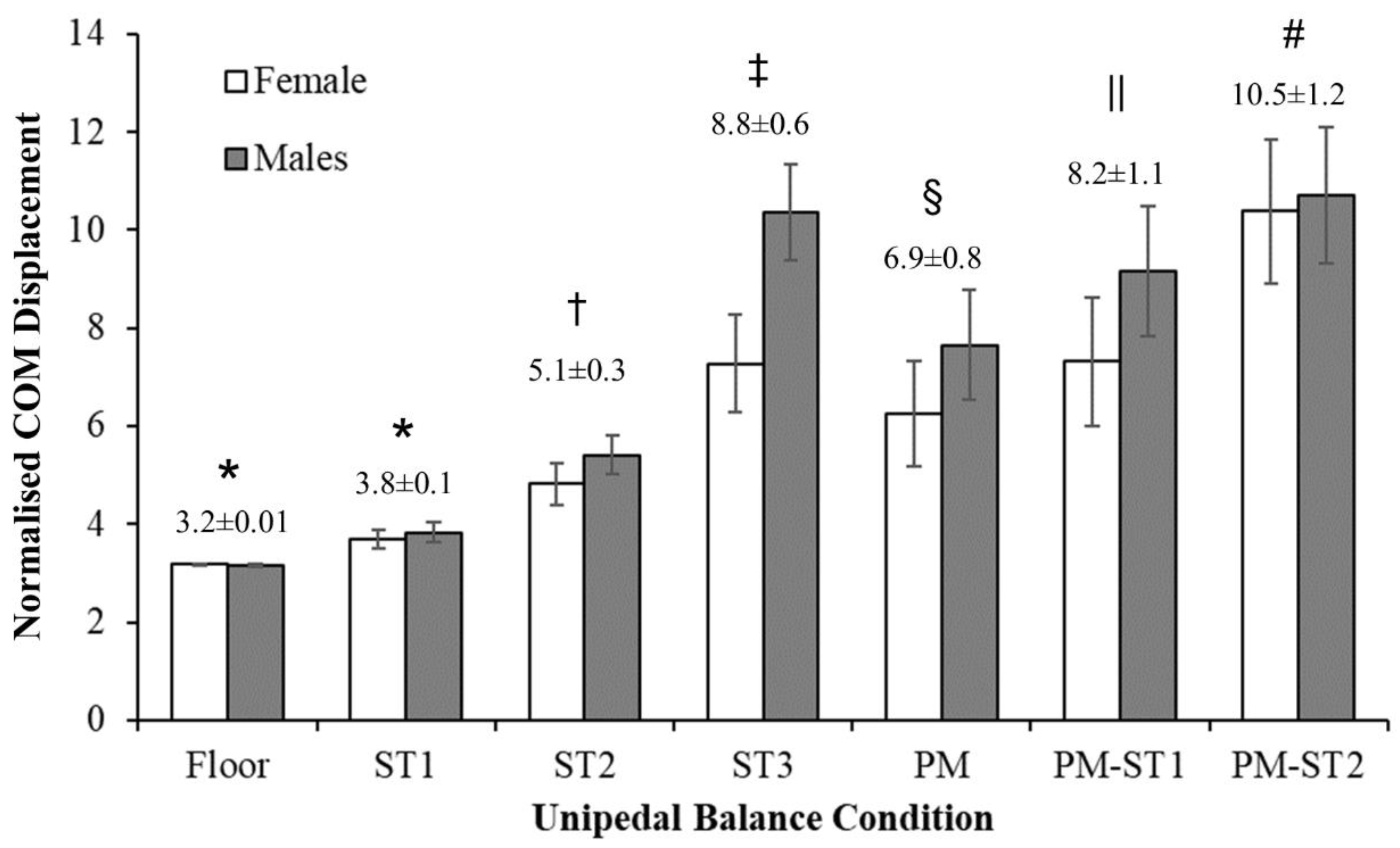
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hübscher, M.; Zech, A.; Pfeifer, K.; Hänsel, F.; Vogt, L.; Banzer, W. Neuromuscular training for sports injury prevention. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, A.; Hübscher, M.; Vogt, L.; Banzer, W.; Hänsel, F.; Pfeifer, K. Neuromuscular training for rehabilitation of sports injuries: A systematic review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zech, A.; Hübscher, M.; Vogt, L.; Banzer, W.; Hänsel, F.; Pfeifer, K. Balance training for neuromuscular control and performance enhancement: A systematic review. J. Athl. Train. 2010, 45, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, S.; Taube, W.; Gruber, M.; Amtage, F.; Gollhofer, A.; Schubert, M. Task-specific changes in motor evoked potentials of lower limb muscles after different training interventions. Brain Res. 2007, 1179, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granacher, U.; Gollhofer, A.; Kriemler, S. Effects of balance training on postural sway, leg extensor strength and jumping height in adolescents. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2010, 81, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, M.; Bruhn, S.; Gollhofer, A. Specific adaptations of neuromuscular control and knee joint stiffness following sensorimotor training. Int. J. Sports Med. 2006, 27, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, I.; Fosdahl, M.A.; Friis, A.; Risberg, M.A.; Myklebust, G.; Steen, H. Effect of neuromuscular training on proprioception, balance, muscle strength, and lower limb function in female team handball players. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2004, 14, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuğ, M.; Duncan, A.; Wikstrom, E. Comparative effects of different balance-training-progression styles on postural control and ankle force production: A randomized controlled trial. J. Athl. Train. 2016, 51, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brachman, A.; Kamieniarz, A.; Michalska, J.; Pawłowski, M.; Słomka, K.J.; Juras, G. Balance training programs in athletes—A systematic review. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 58, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borreani, S.; Calatayud, J.; Martin, J.; Colado, J.C.; Tella, V.; Behm, D. Exercise intensity progression for exercises performed on unstable and stable platforms based on ankle muscle activation. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Martel, V.; Santuz, A.; Ekizos, A.; Arampatzis, A. Neuromuscular organisation and robustness of postural control in the presence of perturbations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolburg, T.; Rapp, W.; Rieger, J.; Horstmann, T. Muscle activity of leg muscles during unipedal stance on therapy devices with different stability properties. Phys. Ther. Sport 2016, 17, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behm, D.; Colado, J.C. The effectiveness of resistance training using unstable surfaces and devices for rehabilitation. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2012, 7, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Behm, D.G.; Anderson, K.; Curnew, R.S. Muscle force and activation under stable and unstable conditions. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2002, 16, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wahl, M.J.; Behm, D.G. Not all instability training devices enhance muscle activation in highly resistance-trained individuals. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muehlbauer, T.; Roth, R.; Bopp, M.; Granacher, U. An exercise sequence for progression in balance training. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesinski, M.; Hortobágyi, T.; Muehlbauer, T.; Gollhofer, A.; Granacher, U. Dose-response relationships of balance training in healthy young adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringhof, S.; Stein, T. Biomechanical assessment of dynamic balance: Specificity of different balance tests. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 58, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, M.; Micarelli, A.; Viziano, A.; Pavone, I.; Costantini, G.; Casali, D.; Paolizzo, F.; Saggio, G. Body-worn triaxial accelerometer coherence and reliability related to static posturography in unilateral vestibular failure. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Moe-Nilssen, R. Test-retest reliability of trunk accelerometry during standing and walking. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1998, 79, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Era, P.; Sainio, P.; Koskinen, S.; Haavisto, P.; Vaara, M.; Aromaa, A. Postural balance in a random sample of 7,979 subjects aged 30 years and over. Gerontology 2006, 52, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Eom, G.M.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, B.K.; Hong, J. Sex differences in the postural sway characteristics of young and elderly subjects during quiet natural standing. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2010, 10, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, E.V.; Rose, J.; Rohlfing, T.; Pfefferbaum, A. Postural sway reduction in aging men and women: Relation to brain structure, cognitive status, and stabilizing factors. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taube, W.; Gruber, M.; Gollhofer, A. Spinal and supraspinal adaptations associated with balance training and their functional relevance. Acta Physiol. 2008, 193, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, D.W.; So, U.; Kawato, M.; Milner, T.E. Impedance control balances stability with metabolically costly muscle activation. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 3097–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selen, L.P.J.; Franklin, D.W.; Wolpert, D.M. Impedance control reduces instability that arises from motor noise. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12606–12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, C.F.; Shupert, C.L.; Horak, F.B.; Zajac, F.E. Ankle and hip postural strategies defined by joint torques. Gait Posture 1999, 10, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.B.; Nashner, L.M. Central programming of postural movements: Adaptation to altered support-surface configurations. J. Neurophysiol. 1986, 55, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.C.; Luna, N.M.; Mochizuki, L.; Barbieri, F.; Santos, S.; Greve, J.M. The influence of anthropometric factors on postural balance: The relationship between body composition and posturographic measurements in young adults. Clinics 2012, 67, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kejonen, P.; Kauranen, K.; Vaharanta, H. The relationship between anthropometric factors and body-balancing movements in postural balance. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cug, M.; Wikstrom, E.A. Learning effects associated with the least stable level of the biodex® stability system during dual and single limb stance. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2014, 13, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brueckner, D.; Göpfert, B.; Kiss, R.; Muehlbauer, T. Effects of motor practice on learning a dynamic balance task in healthy young adults: A wavelet-based time-frequency analysis. Gait Posture 2019, 70, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.; Salarian, A.; Carlson-Kuhta, P.; Zampieri, C.; King, L.; Chiari, L.; Horak, F.B. ISway: A sensitive, valid and reliable measure of postural control. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adlerton, A.K.; Moritz, U.; Moe-Nilssen, R. Forceplate and accelerometer measures for evaluating the effect of muscle fatigue on postural control during one-legged stance. Physiother. Res. Int. 2003, 8, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Female | Male | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 13 | 12 | 25 |
| Age (years) | 26 | 28 | 26 |
| (3) | (2) | (3) | |
| Height (m) | 1.68 | 1.84 * | 1.76 |
| (0.06) | (0.05) | (0.10) | |
| Body Mass (Kg) | 61 | 78 * | 69 |
| (7) | (9) | (12) | |
| Body Mass Index (Kg/m2) | 21.7 | 22.9 * | 22.3 |
| (2.1) | (1.9) | (2.1) |
| Floor | ST1 | ST2 | ST3 | PM | PM-ST1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST1 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - | - |
| dz | 0.82 | |||||
| ST2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - | - | - | - |
| dz | 1.54 | 1.13 | ||||
| ST3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | - | - | - |
| dz | 1.99 | 1.61 | 1.30 | |||
| PM | 0.00 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | - |
| dz | 1.02 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.45 | ||
| PM-ST1 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 1.00 | - |
| dz | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.74 | 0.09 | 0.44 | |
| PM-ST2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.02 | 1.00 |
| dz | 1.53 | 1.09 | 3.81 | 0.31 | 0.81 | 0.35 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gras, N.; Brauner, T.; Wearing, S.; Horstmann, T. Do Progressive Sensorimotor Training Devices Produce A Graded Increase in Centre of Mass Displacement During Unipedal Balance Exercises in Athletes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113893
Gras N, Brauner T, Wearing S, Horstmann T. Do Progressive Sensorimotor Training Devices Produce A Graded Increase in Centre of Mass Displacement During Unipedal Balance Exercises in Athletes. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(11):3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113893
Chicago/Turabian StyleGras, Nina, Torsten Brauner, Scott Wearing, and Thomas Horstmann. 2020. "Do Progressive Sensorimotor Training Devices Produce A Graded Increase in Centre of Mass Displacement During Unipedal Balance Exercises in Athletes" Applied Sciences 10, no. 11: 3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113893
APA StyleGras, N., Brauner, T., Wearing, S., & Horstmann, T. (2020). Do Progressive Sensorimotor Training Devices Produce A Graded Increase in Centre of Mass Displacement During Unipedal Balance Exercises in Athletes. Applied Sciences, 10(11), 3893. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113893




