Integration of Wavelet Denoising and HHT Applied to the Analysis of Bridge Dynamic Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
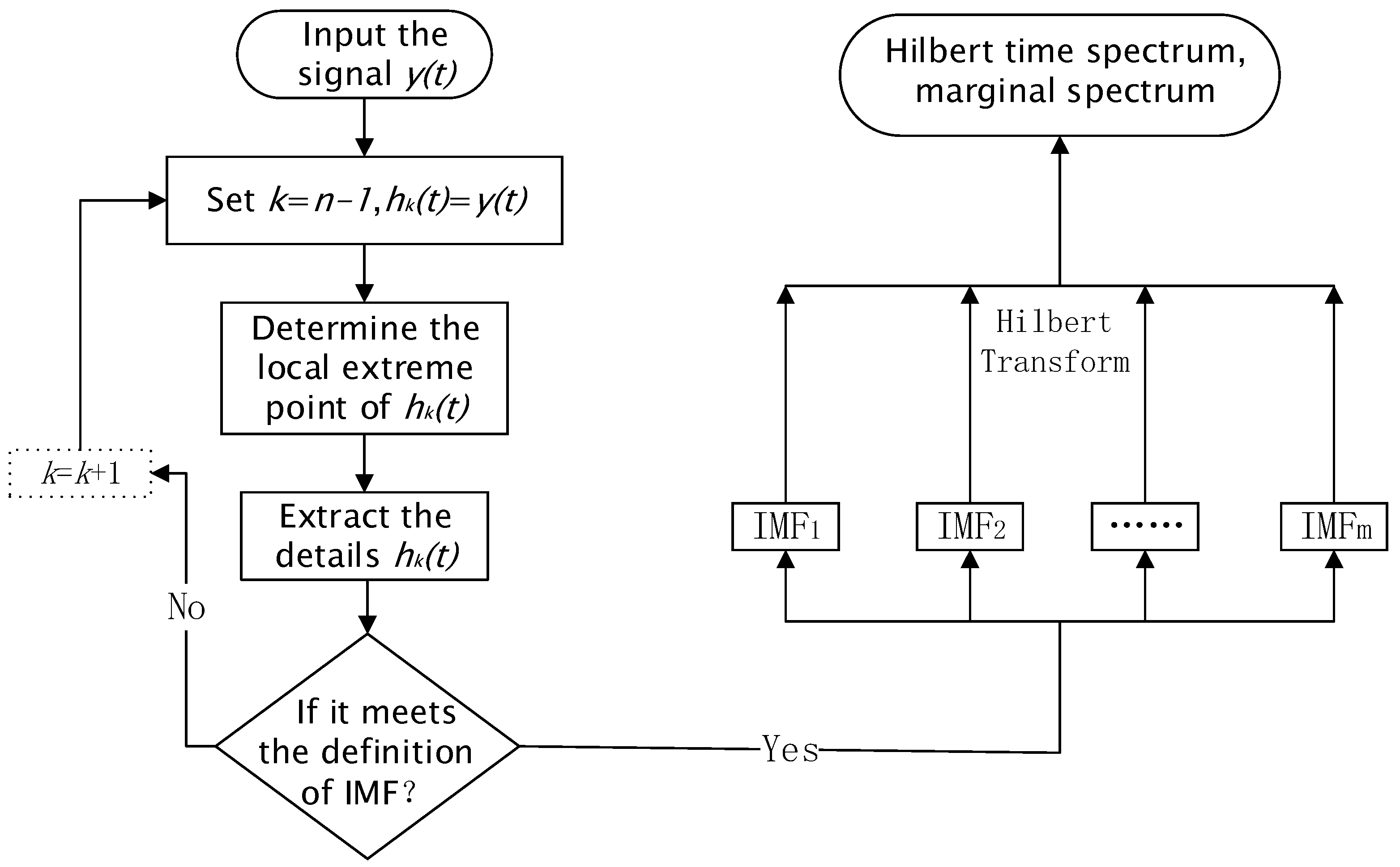
2. Basic Principle of HHT
3. Time-Frequency Analysis Method Based on Wavelet Threshold Denoising and HHT
3.1. Wavelet Threshold Denoising
3.2. Time-Frequency Analysis Method Combining Wavelet Threshold Denoising and HHT
3.3. Comparative Analysis of the Denoising Effect on Simulation Signals
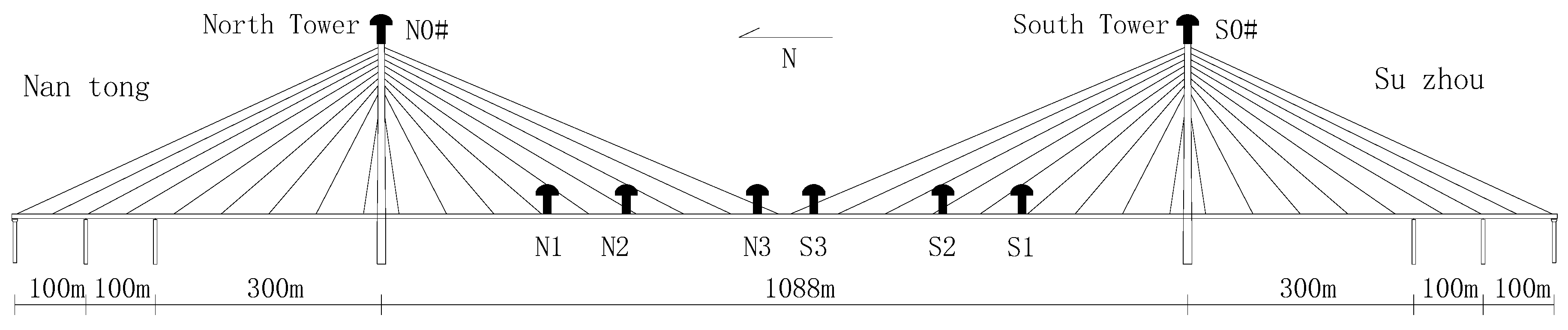
4. Application Analysis
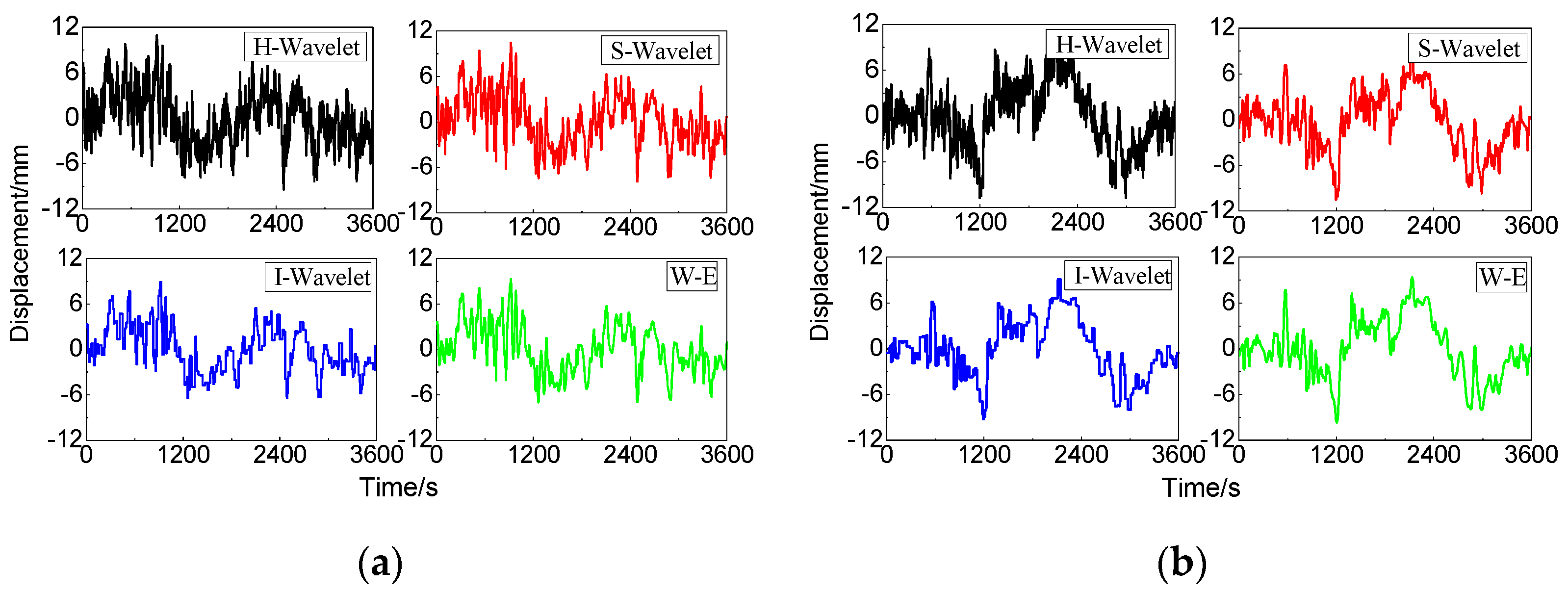
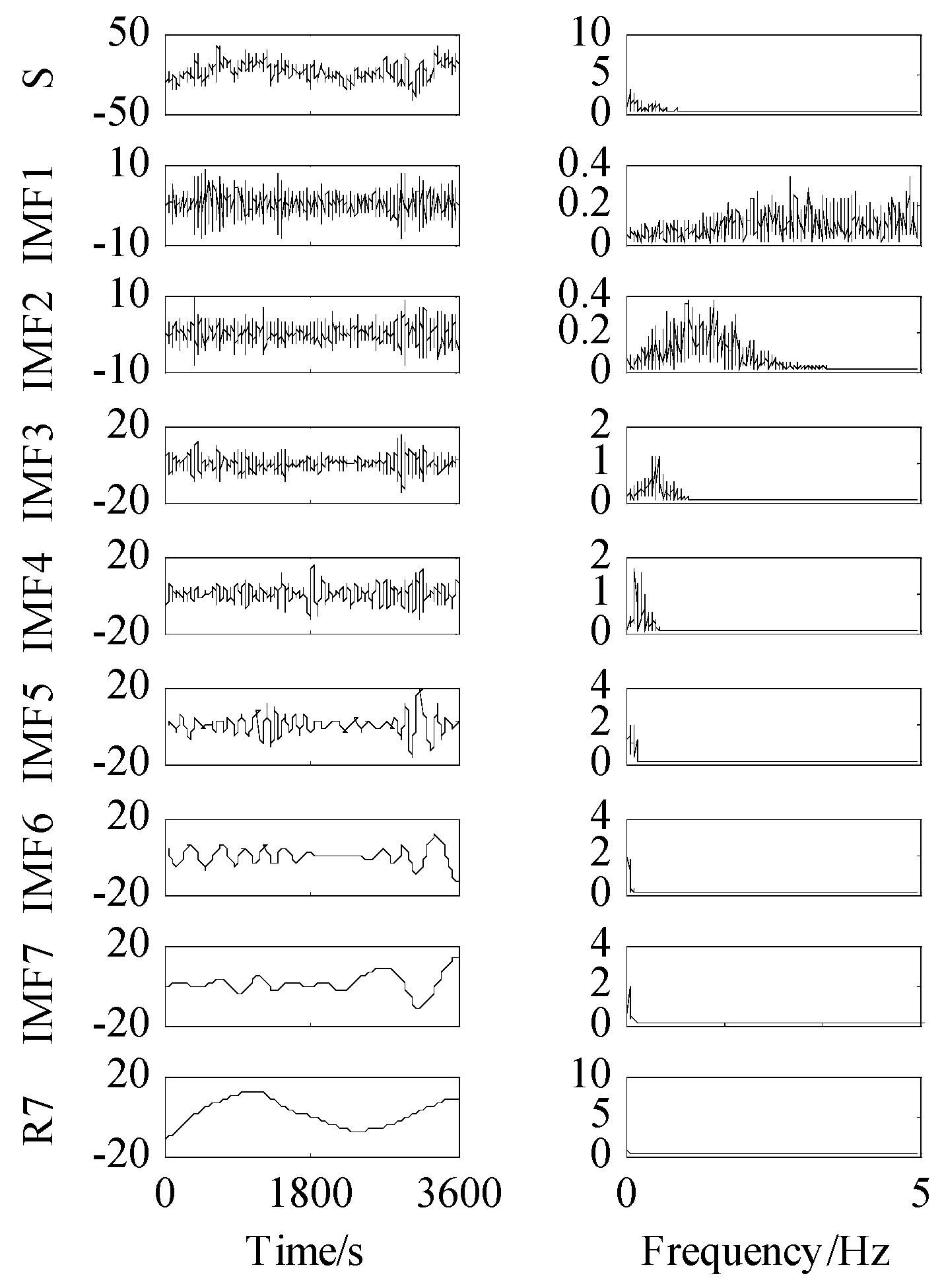
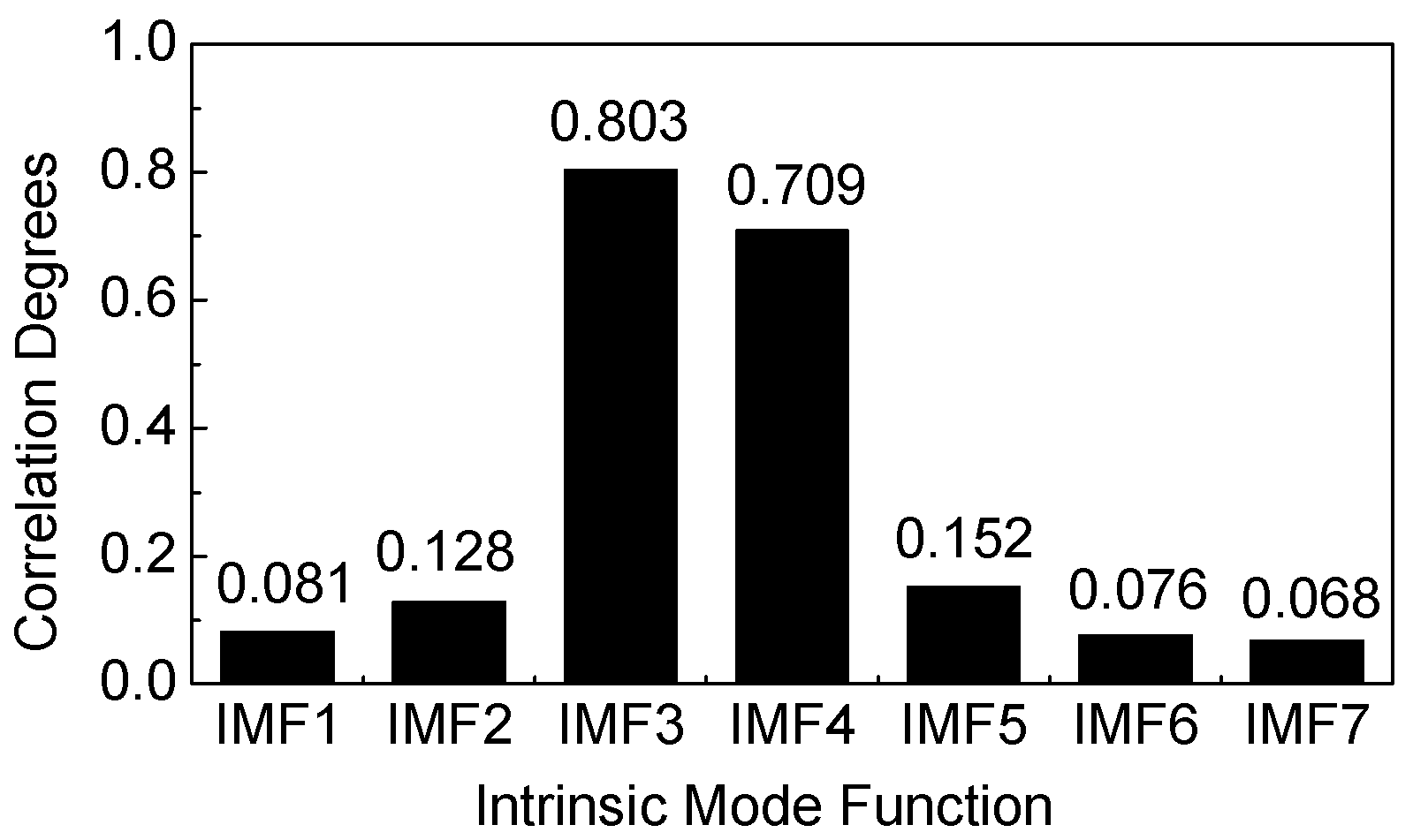
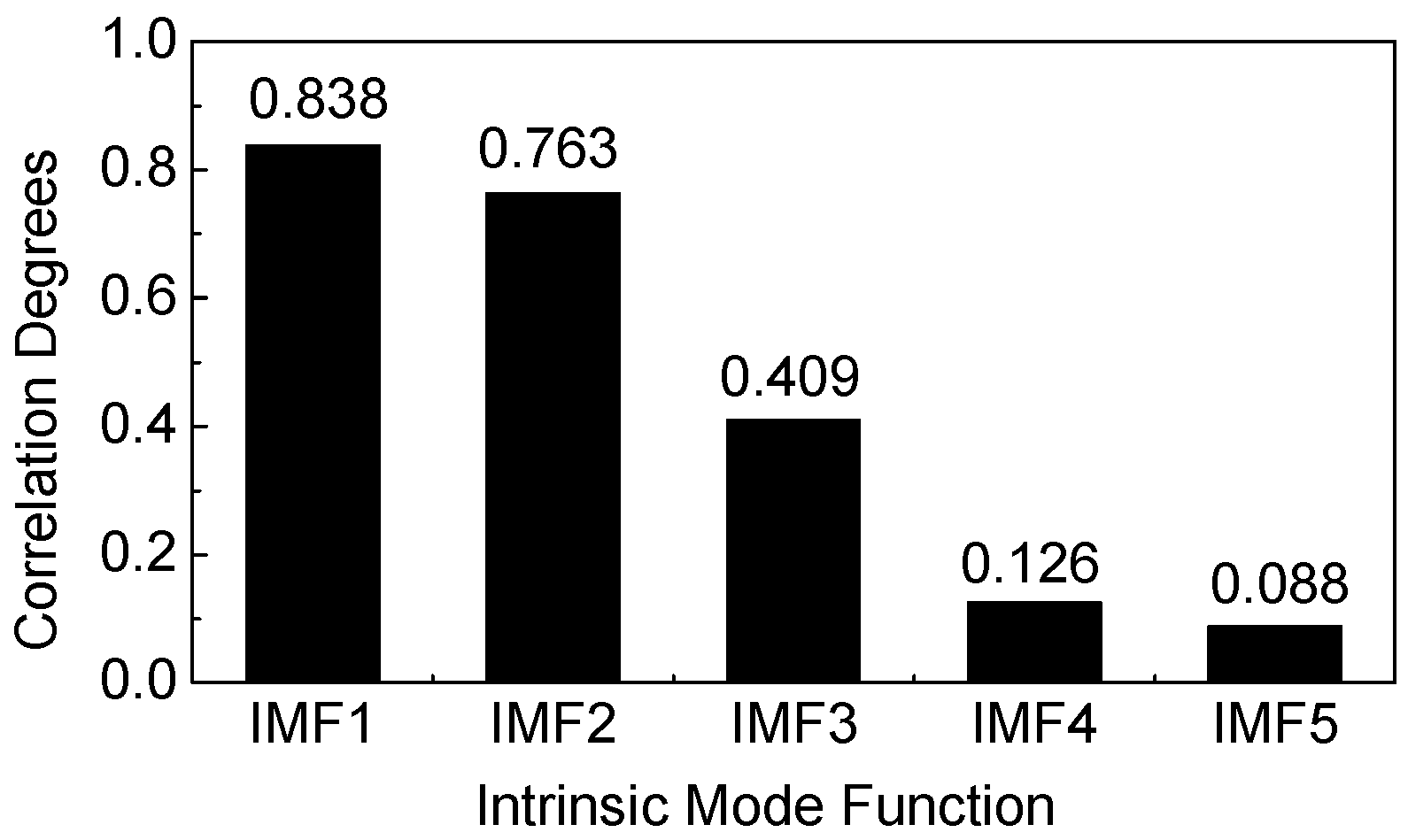
4.1. Comparative Analysis of the Denoised Results
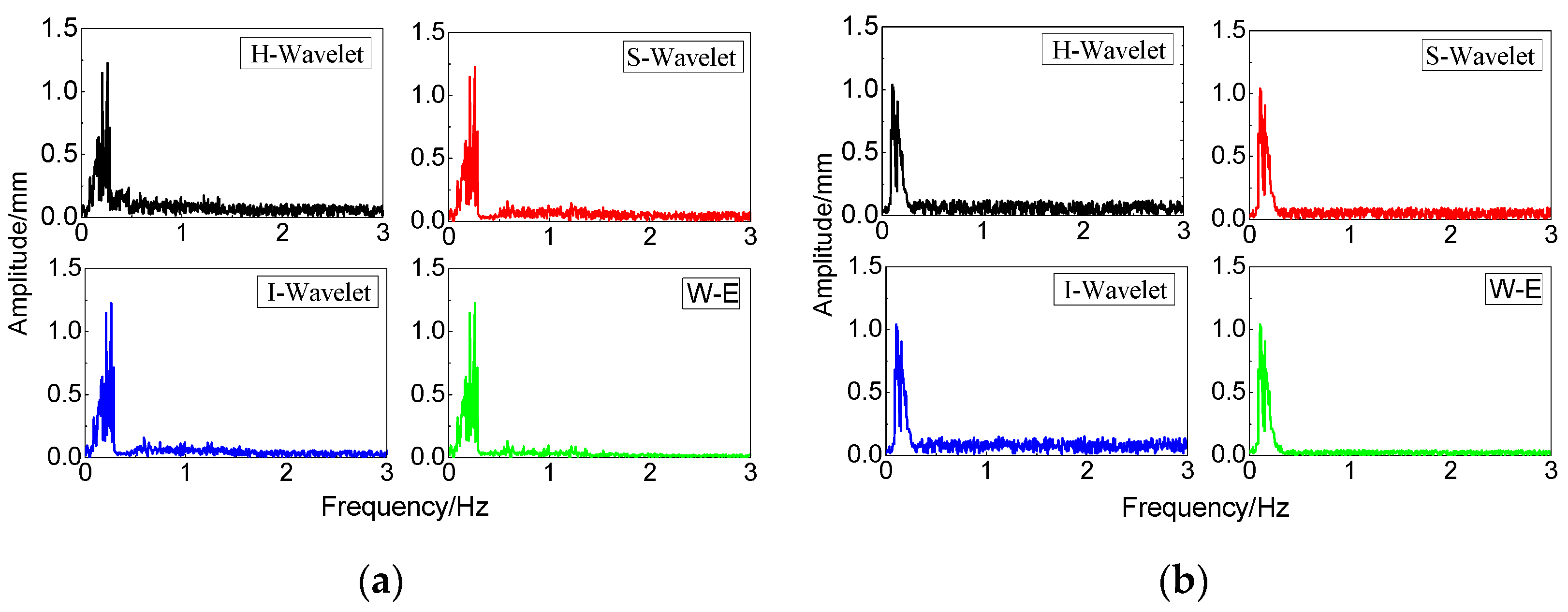
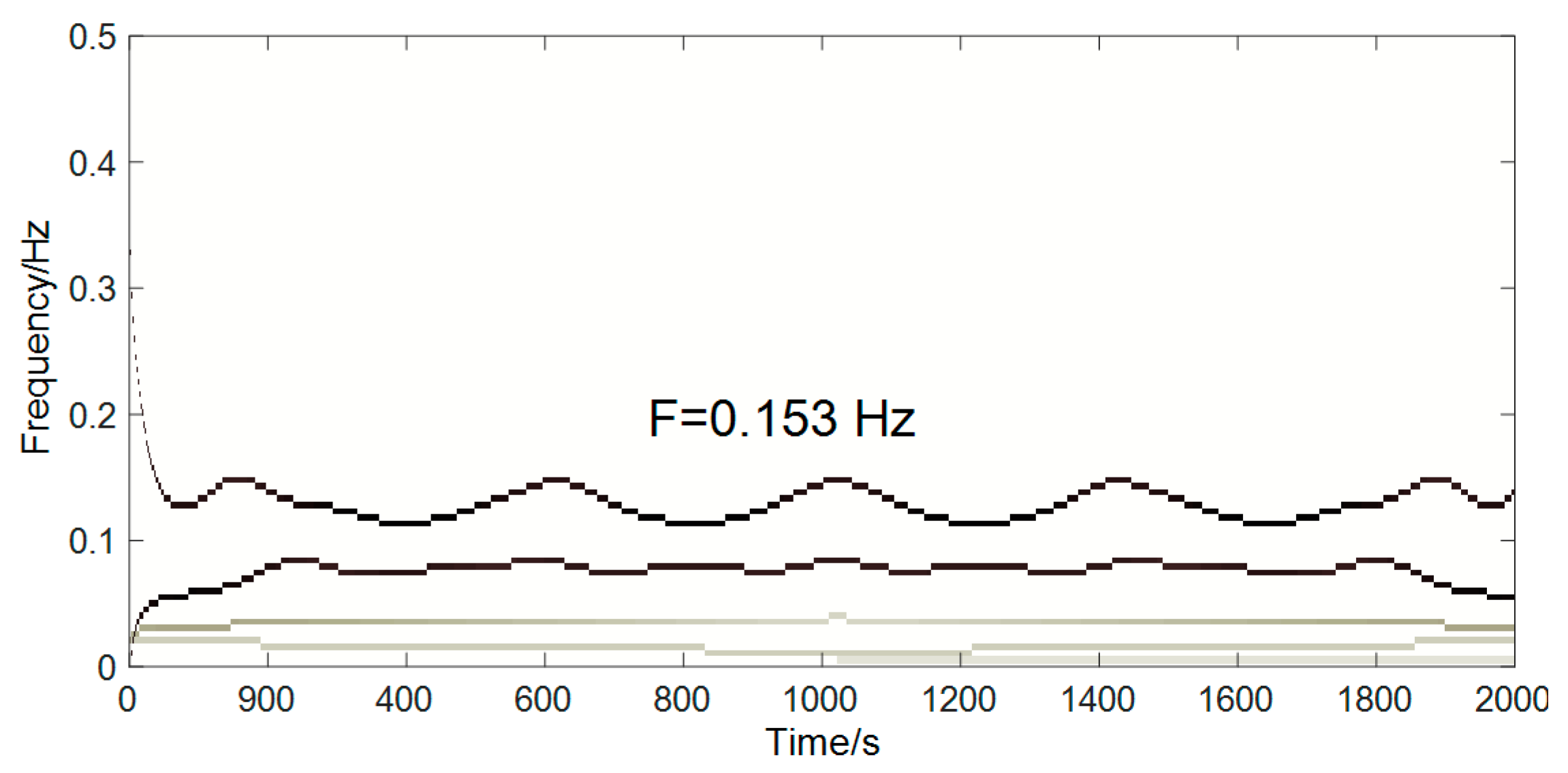
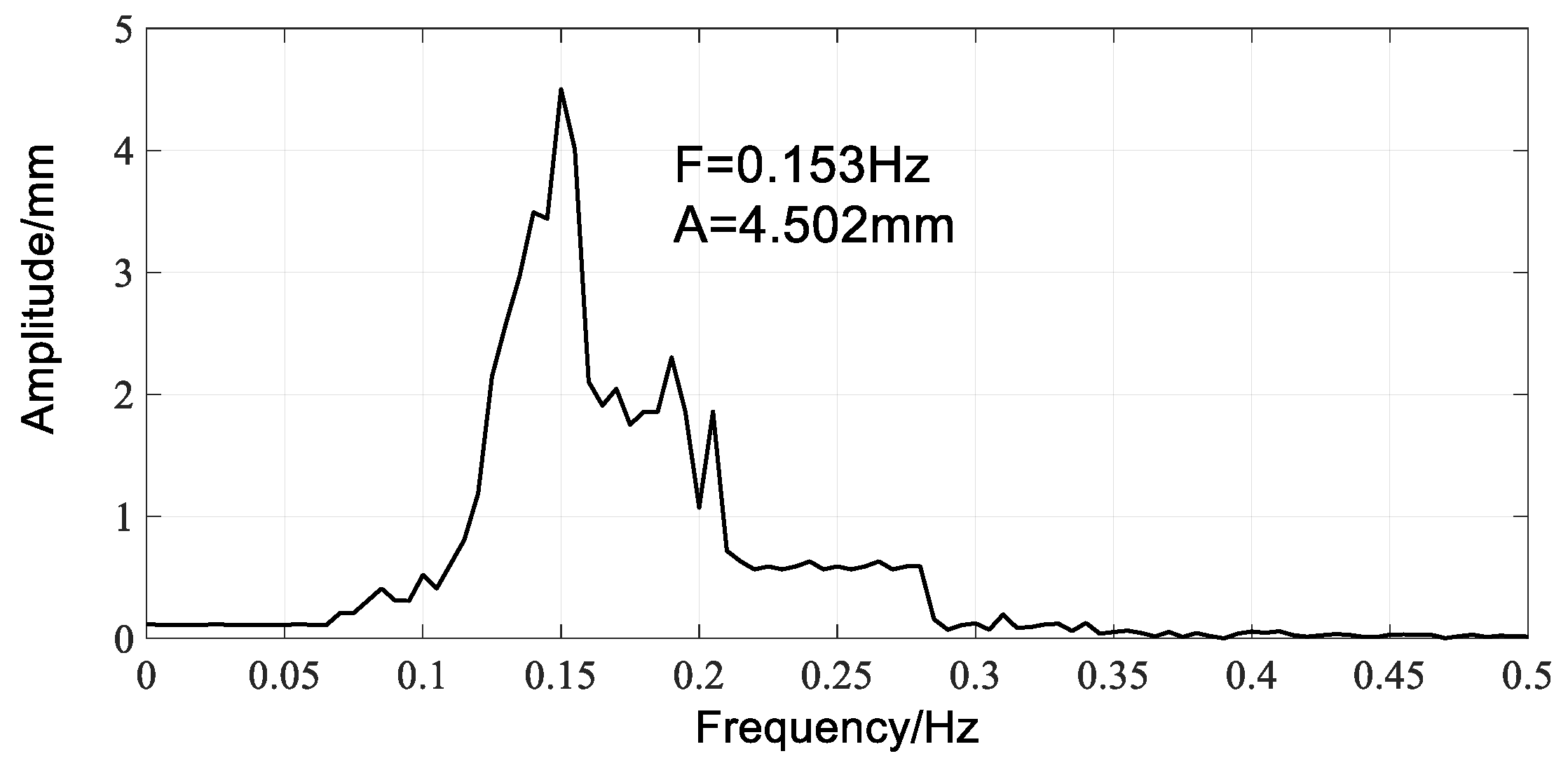
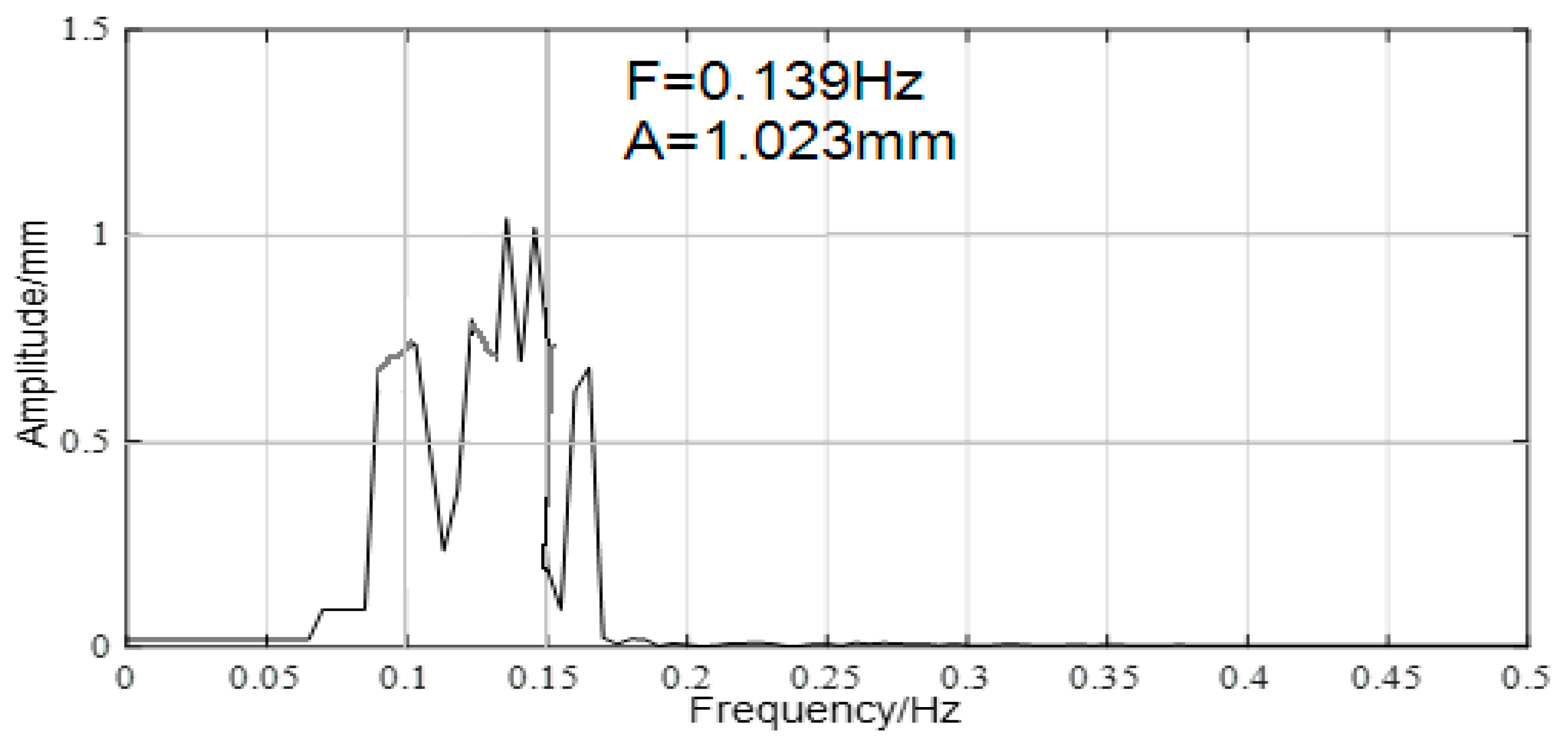
4.2. First Natural Frequency Identification from the Denoised Results
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed wavelet-EMD method suppressed high-frequency noise effectively, decreased the decomposition layers of EMD, and reduced the margin effects on the quality of effective signal decomposition. The SNR and linear correlation coefficient of the denoised signal were the largest, and RMSE was the smallest. The method had a stable denoising effect in the horizontal and vertical directions.
- (2)
- The Hilbert spectrum analysis of the denoised data clearly reflected the spectral value of the bridge structure, and the numerical results agreed well with the theoretical calculations. The relative errors of the natural frequency identification in the horizontal and vertical directions were 5.52% and 4.67%, respectively, which meant that the natural vibration characteristics of the bridge structure were identified effectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability of Data and Materials
Abbreviations
| HHT | Hilbert–Huang transform |
| EMD | Empirical mode decomposition |
| wavelet-EMD | Wavelet-empirical mode decomposition |
| IMF | Intrinsic modal component |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| HT | Hilbert transform |
References
- An, Y.H.; Chatzi, E.; Sim, S.H.; Laflamme, S.; Blachowski, B.; Ou, J.P. Recent progress and future trends on damage identification methods for bridge structures. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2019, 26, e2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Z.B.; Tan, C.; Si, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.H. Adaptive Wavelet Threshold Denoising Method for Machinery Sound Based on Improved Fruit Fly Optimization Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatir, S.; Belaidi, I.; Khatir, T.; Hamrani, A.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wahab, M.A. Multiple damage detection in unidirectional graphite-epoxy composite beams using particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm. Mechanika 2017, 23, 514–521. [Google Scholar]
- Khatir, S.; Brahim, B.; Capozucca, R.; Wahab, M.A. Damage detection in CFRP composite beams based on vibration analysis using proper orthogonal decomposition method with radial basis functions and cuckoo search algorithm. Compos. Struct. 2018, 187, 344–353. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, G.R.; Gao, G.W.; Zhang, B.Y. Application of Improved Wavelet Thresholding Method and an RBF Network in the Error Compensating of an MEMS Gyroscope. Micromachines 2019, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khatir, S.; Wahab, M.A.; Djilali, B.; Khatir, T. Structural health monitoring using modal strain energy damage indicator coupled with teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm and isogoemetric analysis. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 448, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Ngoc, H.; He, L.Q.; Reynders, E.; Khatir, S.; Le-Xuan, T.; Roeck, G.D.; Bui-Tien, T.; Wahab, M.A. An efficient approach to model updating for a multispan railway bridge using orthogonal diagonalization combined with improved particle swarm optimization. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 476, 115315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.Z.; Dong, L.L.; Dai, D.; Shen, L. Study of Blockage Diagnosis for Hydrocyclone Using Vibration-Based Technique Based on Wavelet Denoising and Discrete-Time Fourier Transform Method. Processes 2020, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.Y.; Meng, X.L.; Yan, B.F.; Xu, B.; Fan, Q.; Xie, Y.L. Global Navigation Satellite System-based positioning technology for structural health monitoring: A review. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2020, 27, e2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Xu, L.; Dai, L.; Mcdonald, M.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. Application of the Real-Time Kinematic Global Positioning System in Bridge Safety Monitoring. J. Bridge. Eng. 2005, 3, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.X.; Wang, X.P.; Li, C.F.; Kang, C. Data decomposition method combining permutation entropy and spectral substitution with ensemble empirical mode decomposition. Measurement 2019, 139, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogundipe, O.; Lee, J.K.; Roberts, G.W. Wavelet De-noising of GNSS Based Bridge Health Monitoring Data. J. Appl. Geod. 2014, 8, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, A.A.; Zhang, C.W.; Masri, S.F.; Gholipour, G. Structural Damage Localization and Quantification Based on a CEEMDAN Hilbert Transform Neural Network Approach: A Model Steel Truss Bridge Case Study. Sensors 2020, 20, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, S.P.E. GPS measurement of wind-induced suspension bridge girder displacements. J. Struct. Eng. 2000, 10, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbeh, R.; Kaloop, M.; Li, H. Monitoring of Bridge Deformation Using GPS Technique. J. Civ. Eng. 2009, 13, 423–431. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.X.H.B.C.; Zhang, H.; Mei, W.S. Real-time Dynamic Monitoring with GPS and Georobot During Sutong Bridge Construction. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2009, 38, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.X.; Luo, L.; He, C. Comparative Test Analysis for Determining Bridge Deflection by Using Ground-Based SAR and GPS. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2012, 37, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Liu, H. Analysis of the dynamic response of a long span bridge using GPS/accelerometer/anemometer under typhoon loading. Eng. Struct. 2016, 122, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloop, M.R.; Kim, D. GPS-structural health monitoring of a long span bridge using neural network adaptive filter. Surv. Rev. 2014, 46, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.J.; Huang, D.W.; Cai, C.S. Multipath mitigation via component analysis methods or GPS dynamic deformation monitoring. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, E.; Feng, J.; Chen, L.; Li, N.; Kong, X. Extraction of microseismic waveforms characteristics prior to rock burst using Hilbert–Huang transform. Measurement 2016, 91, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.X.; Liu, J.N.; Liu, X.L. Deformation Analysis Based on Wavelet and Its Applicationin Dynamic Monitoring for High-rise Buildings. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2003, 32, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, W.; Niu, X.; Liu, J. Weak GPS signal tracking using FFT discriminator in open loop receive. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, A.E.; Edwards, S.J.; Clarke, P.J. Using Filtered and Semi-continuous High Rate GPS for Monitoring Deformations. J. Surv. Eng. 2010, 136, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Feng, C.J. A Time-frequency Representation Method of STFT with Combining Window Functions. J. Detect. Control. 2010, 45–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Zhao, S.Y.; Wang, Q. De-nosing of acoustic emission signals based on empirical mode decomposition and wavelet transform. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 2011, 43, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F.X.; Dai, W.J.; Tang, C.J.; Huang, D.W.; Wu, X.X. EMD-ICA with reference signal method and its application in GPS multipath. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2012, 41, 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Huang, S.X.; Ma, F.H. The Dynamic Characteristics Analysis for the Large Bridge Based on the Improved Hilbert-Huang Transformation. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2010, 35, 801–805. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Y. Partly ensemble empirical mode decomposition: An improved noise-assisted method for eliminating mode mixing. Signal. Process. 2014, 96, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W. Neighboring adaptive Bayes Shrink image denoising in dual-tree complex wavelet transform. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2012, 48, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Yang, X.L. A Dyadic Wavelet Filtering Method for 2-D Image Denoising. J. Signal Inf. Process. 2011, 2, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, M.X.; Yang, B.C.; Huang, S.X.; You, X.P.; Tian, W. Analysis and Research of the Dynamic Characteristics of Large Cable-stayed Bridge During Construction. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. (Transp. Sci. Eng.) 2011, 35, 516–519. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.Y.; Chen, A.R. 3-D flutter analysis of Sutong bridge. Eng. Mech. 2008, 25, 139–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.X.; Wang, H.; Xun, Z.X. Comparison Study on Modal Parameter Identification of Large Span Cable Stayed Bridge with Time-frequency Method. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2016, 44, 996–1001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

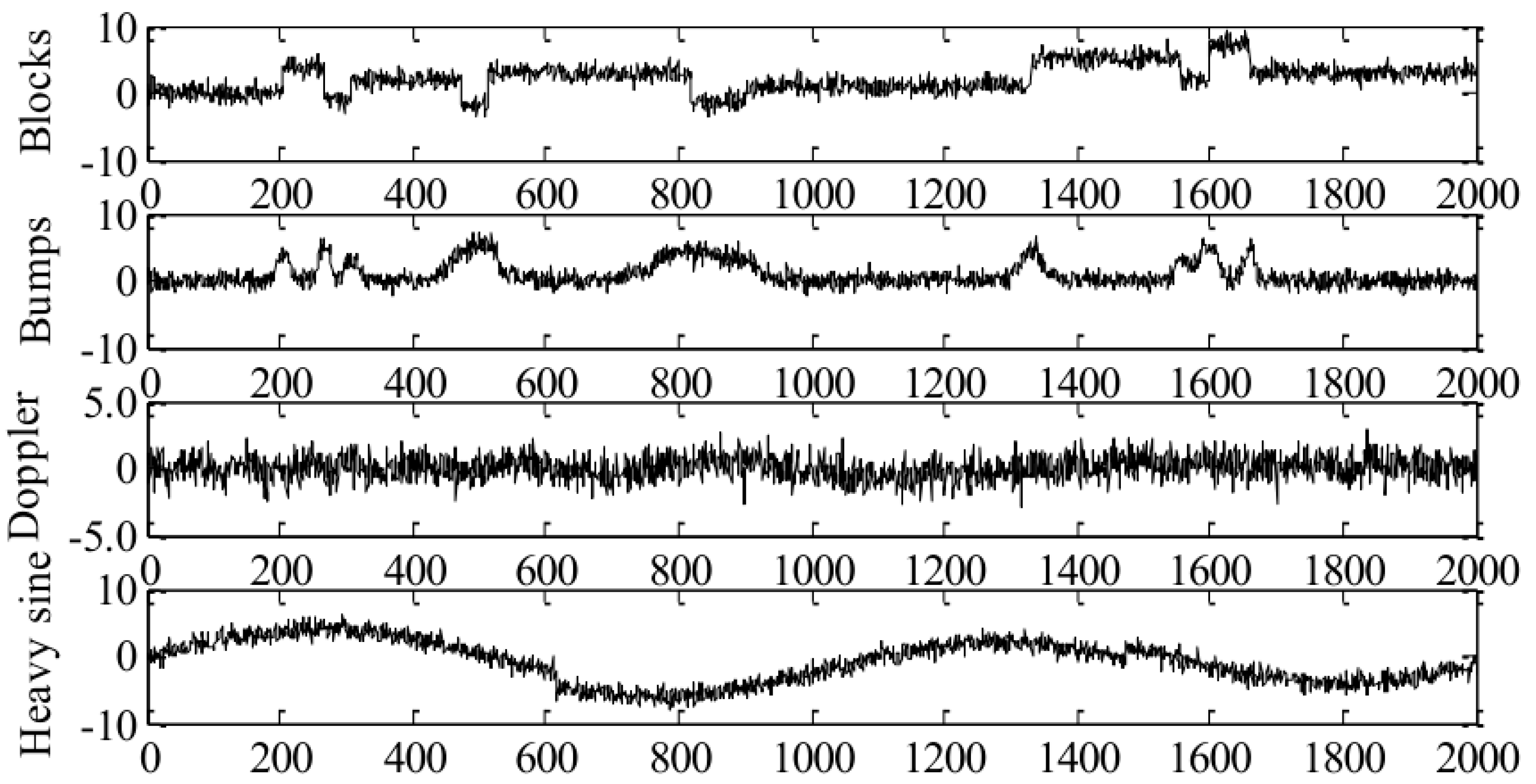
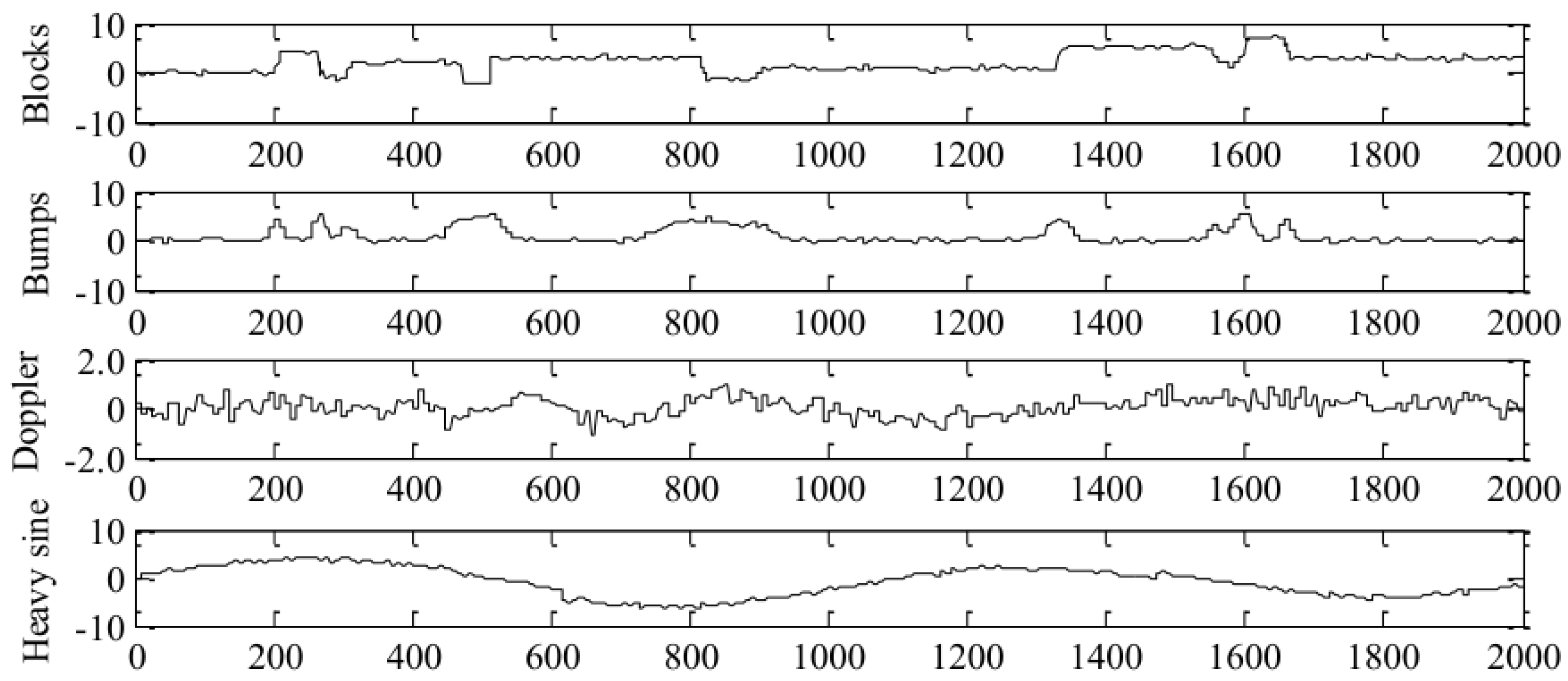
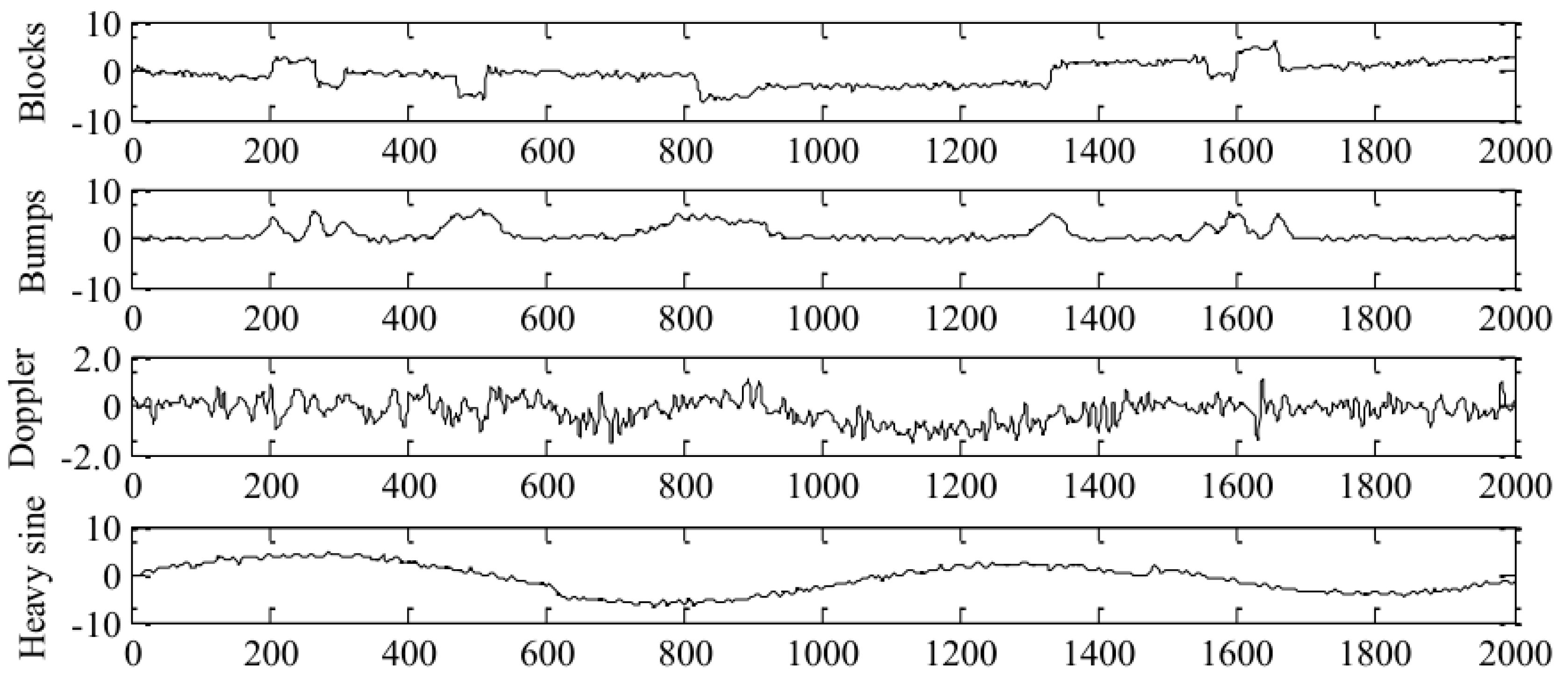
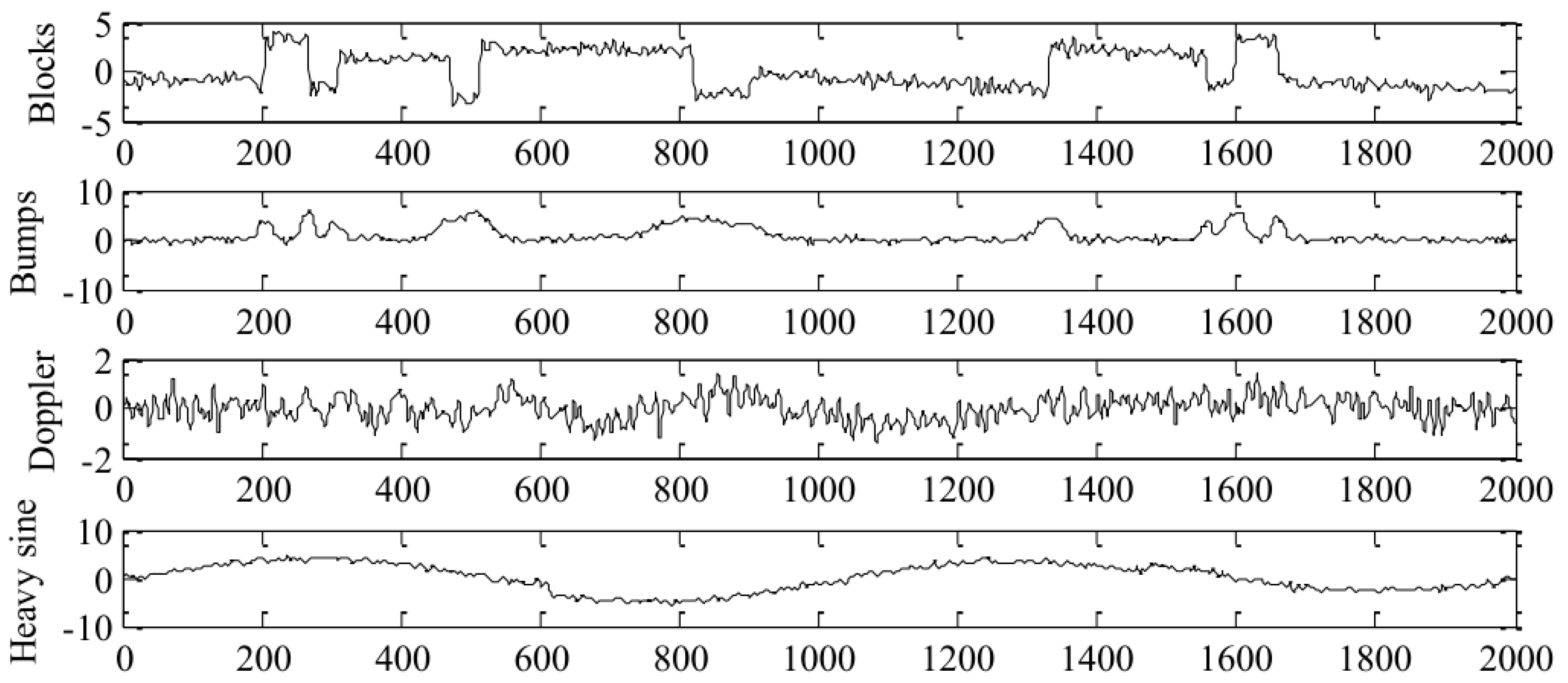

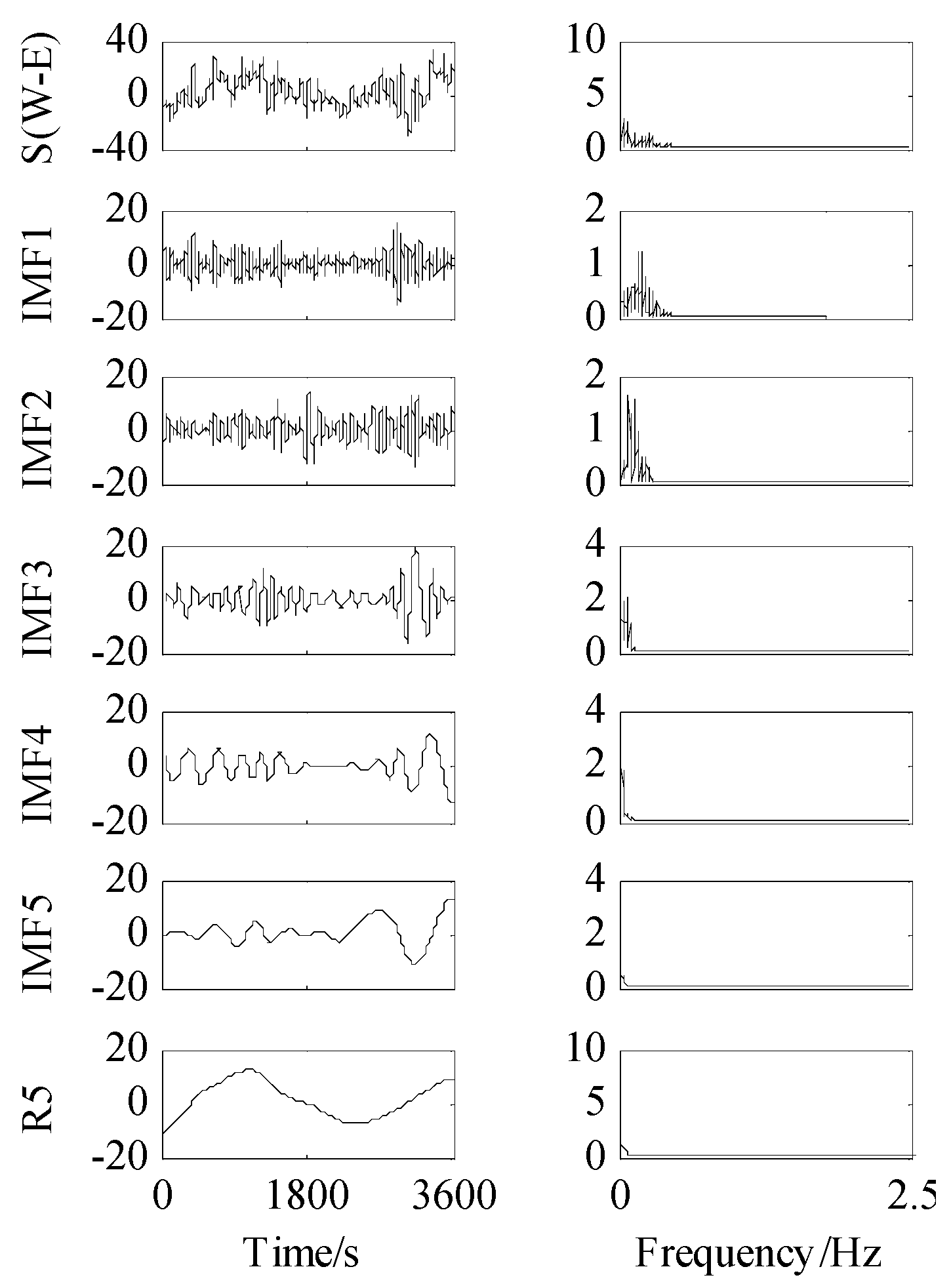

| Denoising Methods | Blocks Signal | Bumps Signal | Doppler Signal | Heavy Signal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | RMSE | SNR | RMSE | SNR | RMSE | SNR | RMSE | |
| Noisy signal | 11.593 | - | 8.855 | - | 7.403 | - | 6.357 | - |
| Wavelet denoising | 20.035 | 0.855 | 15.872 | 0.455 | 15.896 | 0.354 | 14.156 | 0.558 |
| EMD denoising | 21.065 | 0.413 | 16.828 | 0.448 | 14.017 | 0.417 | 15.384 | 0.491 |
| Wavelet-EMD | 21.428 | 0.362 | 18.147 | 0.362 | 20.548 | 0.252 | 19.285 | 0.328 |
| Signal SNR | Denoising Methods | Blocks Signal | Bumps Signal | Doppler Signal | Heavy Signal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | RMSE | SNR | RMSE | SNR | RMSE | SNR | RMSE | ||
| 6 dB | Noisy signal | 15.573 | - | 15.467 | - | 13.403 | - | 12.357 | - |
| Wavelet denoising | 19.038 | 0.578 | 16.872 | 0.655 | 15.896 | 0.454 | 14.156 | 0.558 | |
| EMD denoising | 21.372 | 0.316 | 17.538 | 0.888 | 16.017 | 0.316 | 15.354 | 0.491 | |
| Wavelet-EMD | 20.819 | 0.376 | 18.147 | 0.369 | 17.643 | 0.202 | 16.069 | 0.343 | |
| 2 dB | Noisy signal | 6.593 | - | 5.855 | - | 4.403 | - | 4.357 | - |
| Wavelet denoising | 11.168 | 0.555 | 10.364 | 0.462 | 9.764 | 0.409 | 9.156 | 0.306 | |
| EMD denoising | 12.083 | 0.413 | 10.905 | 0.491 | 10.375 | 0.438 | 7.874 | 0.492 | |
| Wavelet-EMD | 13.575 | 0.362 | 12.643 | 0.359 | 12.871 | 0.252 | 9.018 | 0.330 | |
| −2 dB | Noisy signal | −2.451 | - | −3.855 | - | −4.313 | - | −5.357 | - |
| Wavelet denoising | 5.035 | 0.455 | 6.872 | 0.563 | 6.831 | 0.684 | 3.876 | 0.678 | |
| EMD denoising | 6.362 | 0.417 | 5.828 | 0.431 | 7.707 | 0.586 | 4.321 | 0.529 | |
| Wavelet-EMD | 7.352 | 0.335 | 8.847 | 0.369 | 9.353 | 0.309 | 6.963 | 0.338 | |
| Denoising Methods | Horizontal Direction | Vertical Direction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | RMSE (mm) | R | SNR | RMSE (mm) | R | |
| H-Wavelet | 8.434 | 3.609 | 0.938 | 8.704 | 0.689 | 0.928 |
| S-Wavelet | 8.856 | 3.019 | 0.951 | 8.387 | 0.784 | 0.920 |
| I-Wavelet | 10.082 | 2.169 | 0.962 | 9.186 | 0.369 | 0.953 |
| Wavelet-EMD | 11.134 | 1.904 | 0.971 | 10.246 | 0.365 | 0.965 |
| Direction | Measured Frequency (Hz) | Theoretical Calculation (Hz) | Relative Error (%) | Amplitude (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | 0.153 | 0.145 | 5.52 | 4.50 |
| Vertical | 0.139 | 0.133 | 4.67 | 1.02 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Kang, C.; Li, G.; Li, C. Integration of Wavelet Denoising and HHT Applied to the Analysis of Bridge Dynamic Characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3605. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103605
Wang X, Huang S, Kang C, Li G, Li C. Integration of Wavelet Denoising and HHT Applied to the Analysis of Bridge Dynamic Characteristics. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3605. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103605
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinpeng, Shengxiang Huang, Chao Kang, Guanqing Li, and Chenfeng Li. 2020. "Integration of Wavelet Denoising and HHT Applied to the Analysis of Bridge Dynamic Characteristics" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3605. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103605
APA StyleWang, X., Huang, S., Kang, C., Li, G., & Li, C. (2020). Integration of Wavelet Denoising and HHT Applied to the Analysis of Bridge Dynamic Characteristics. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3605. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103605




