Spectral Optimization of White LED Based on Mesopic Luminance and Color Gamut Volume for Dim Lighting Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Test Spectra
2.2. Mesopic Luminance and Color Appearance
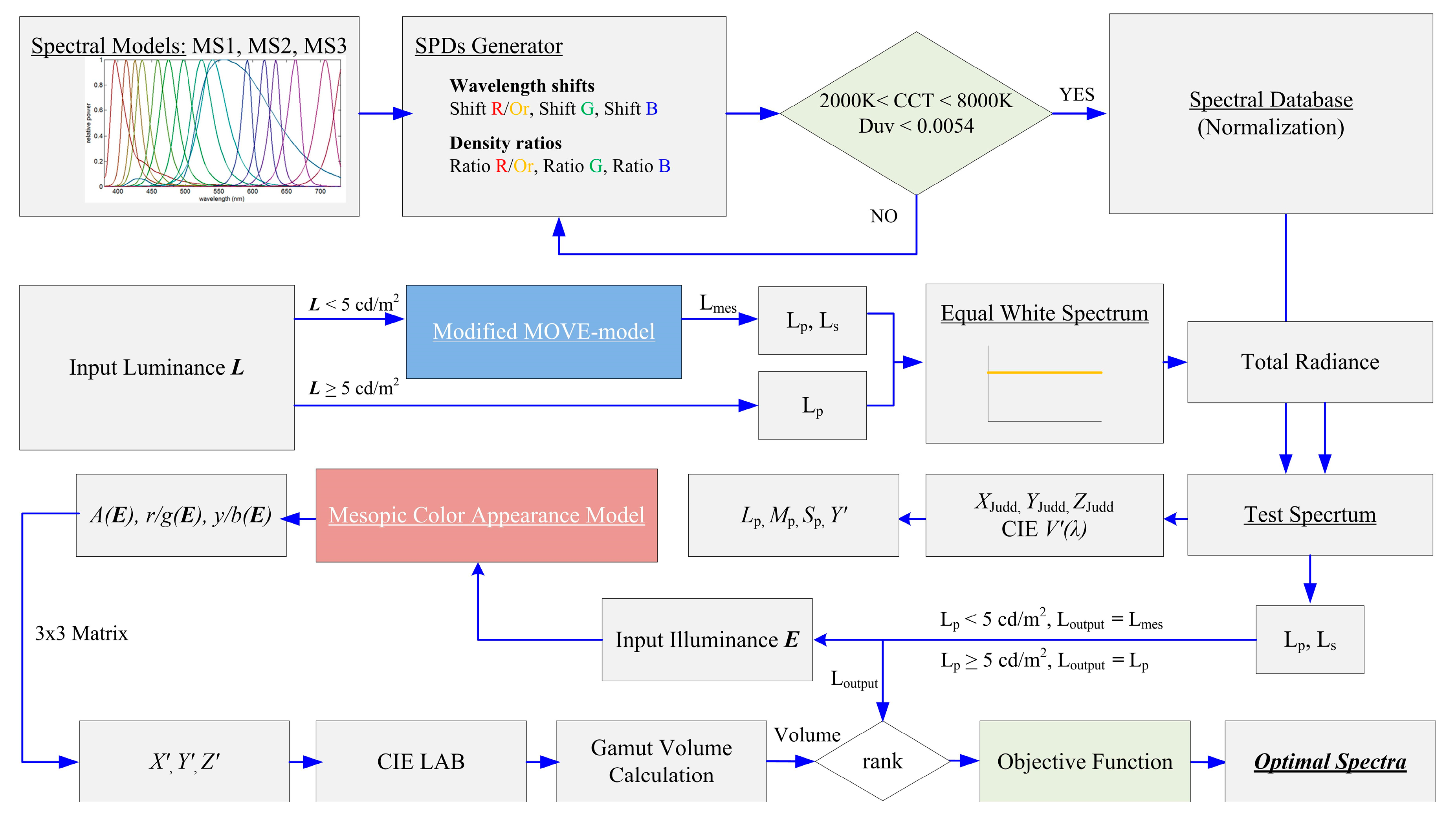
2.3. Optimization Procedure
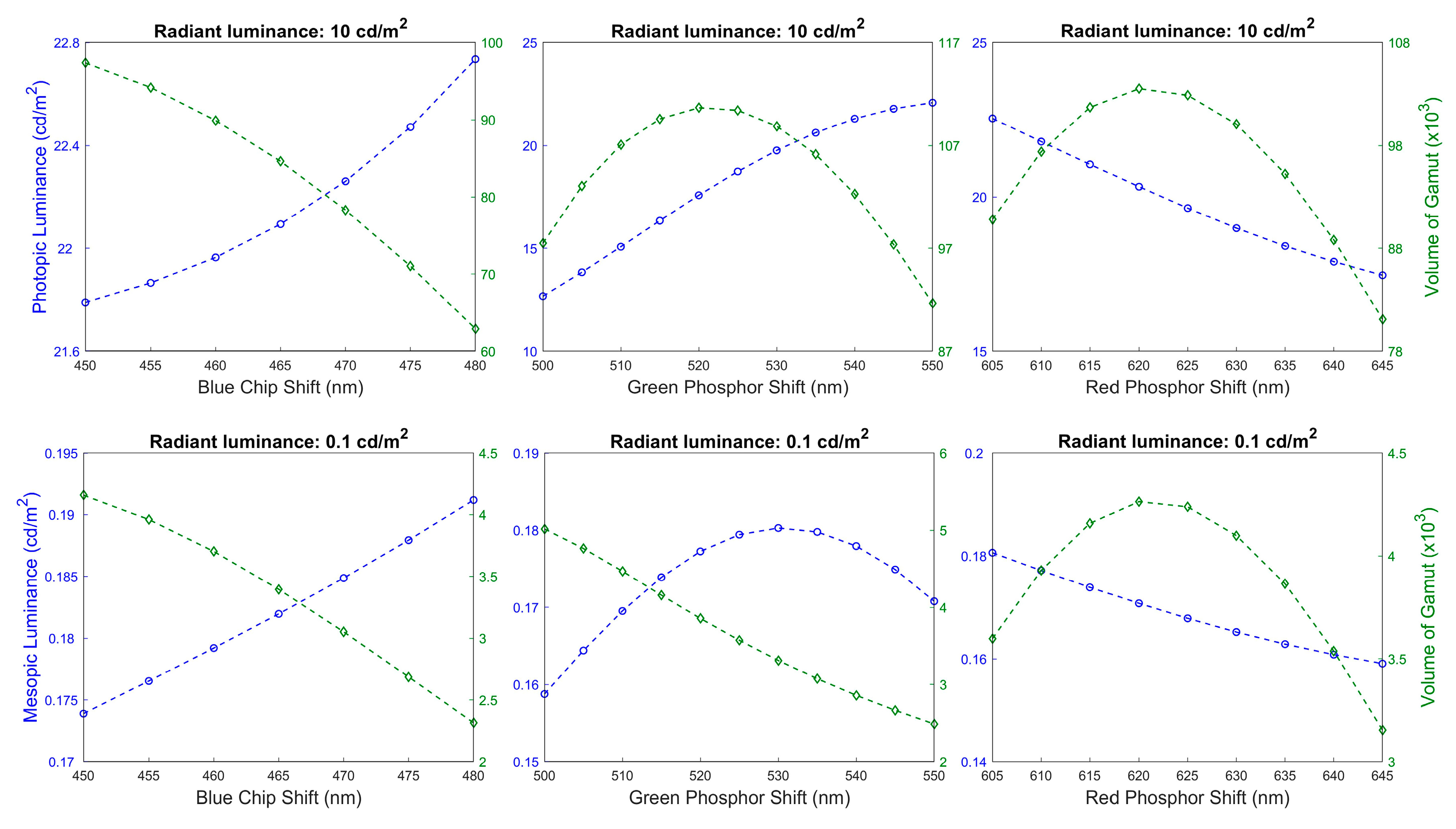
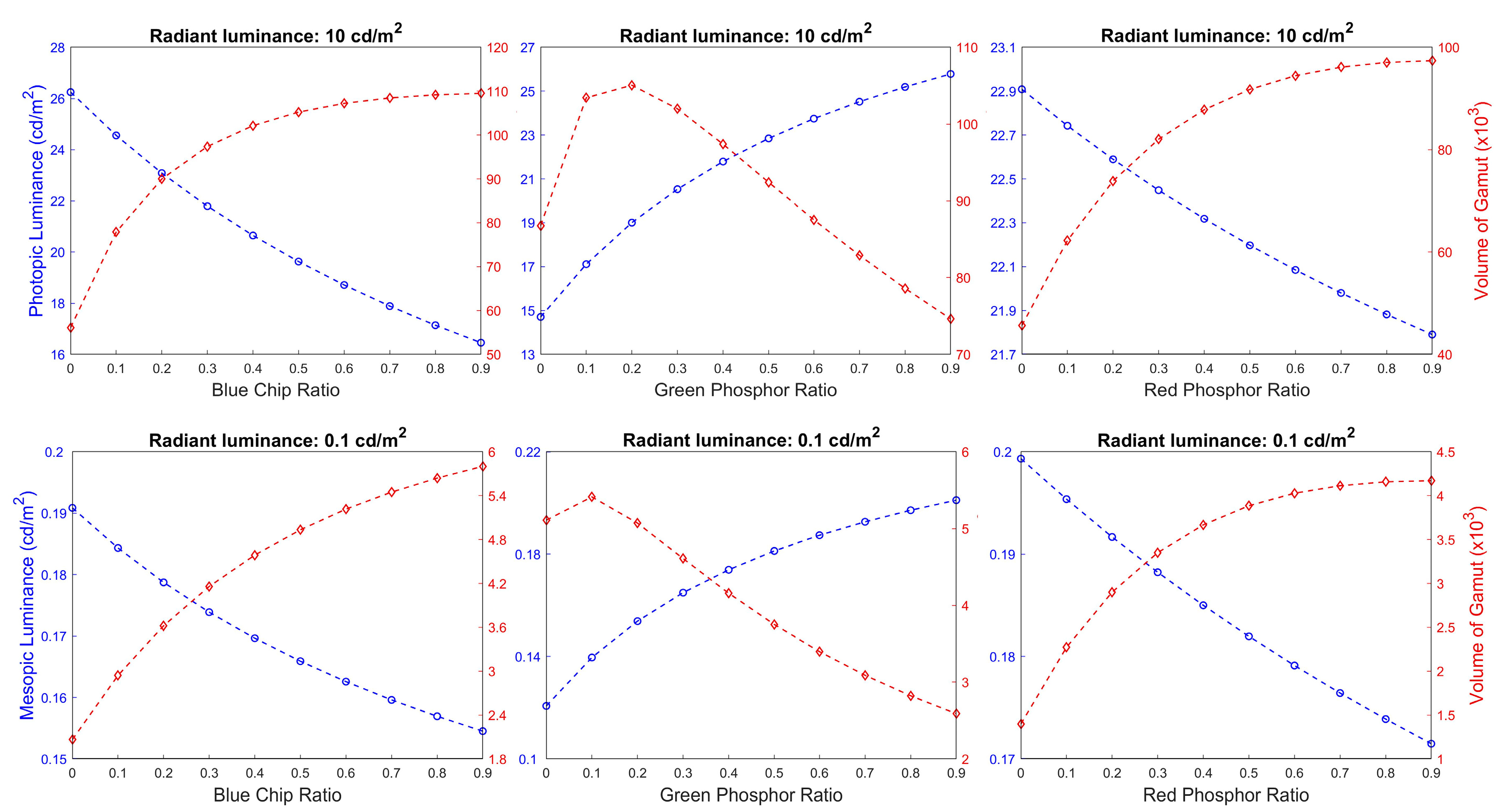
3. Results and Discussion
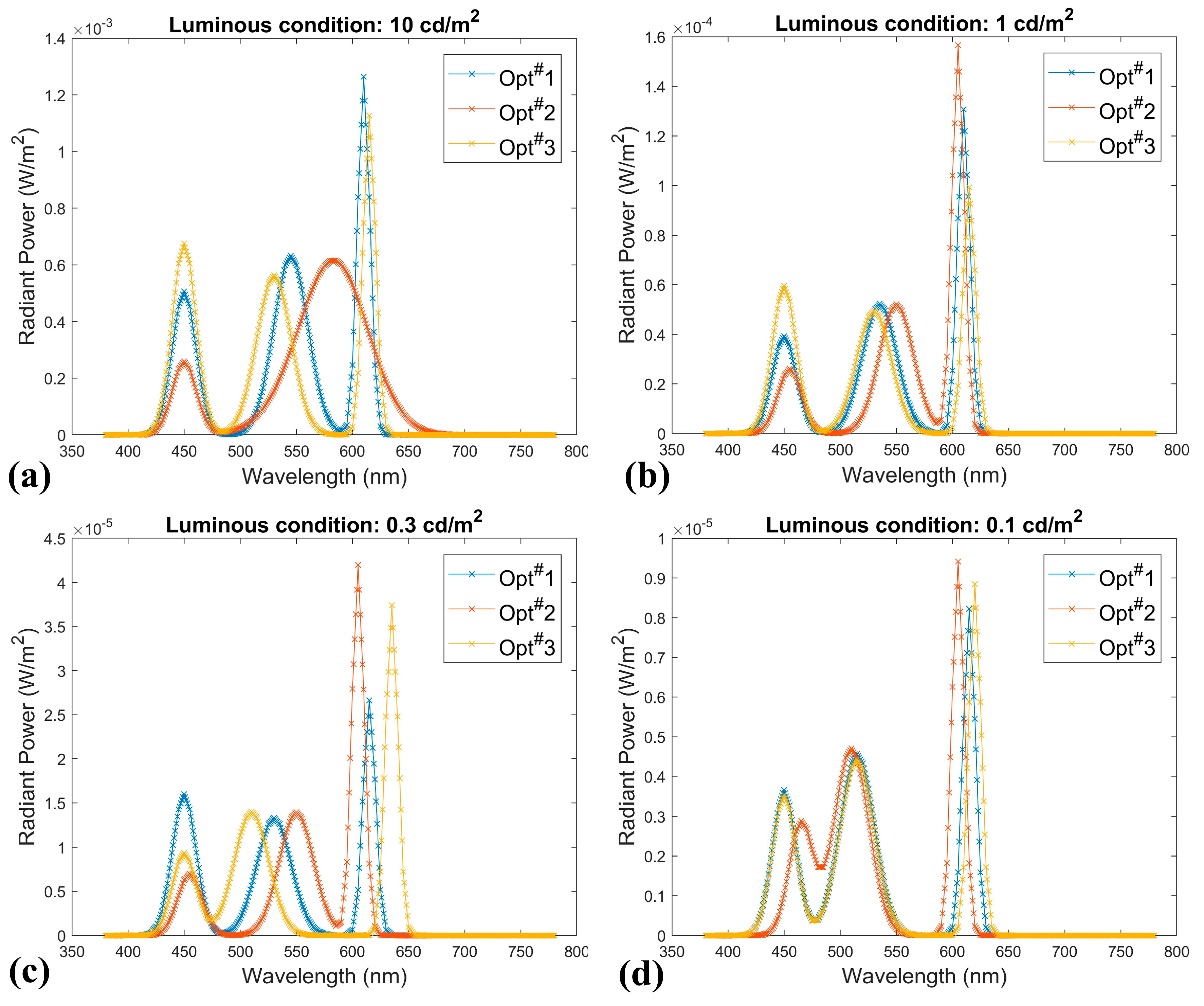
3.1. Optimal White LED Spectra
3.2. Characteristic of White LED Spectra
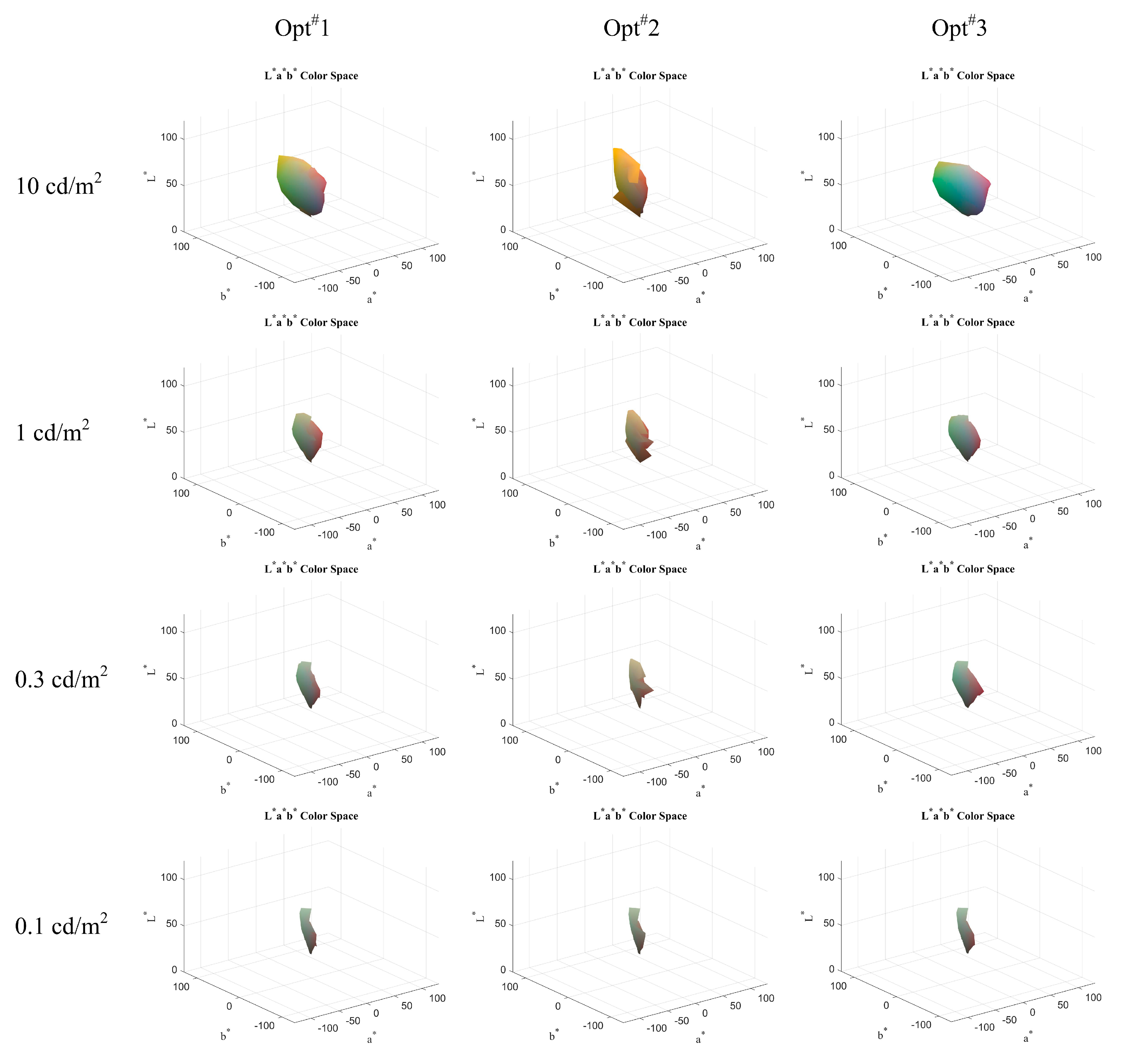
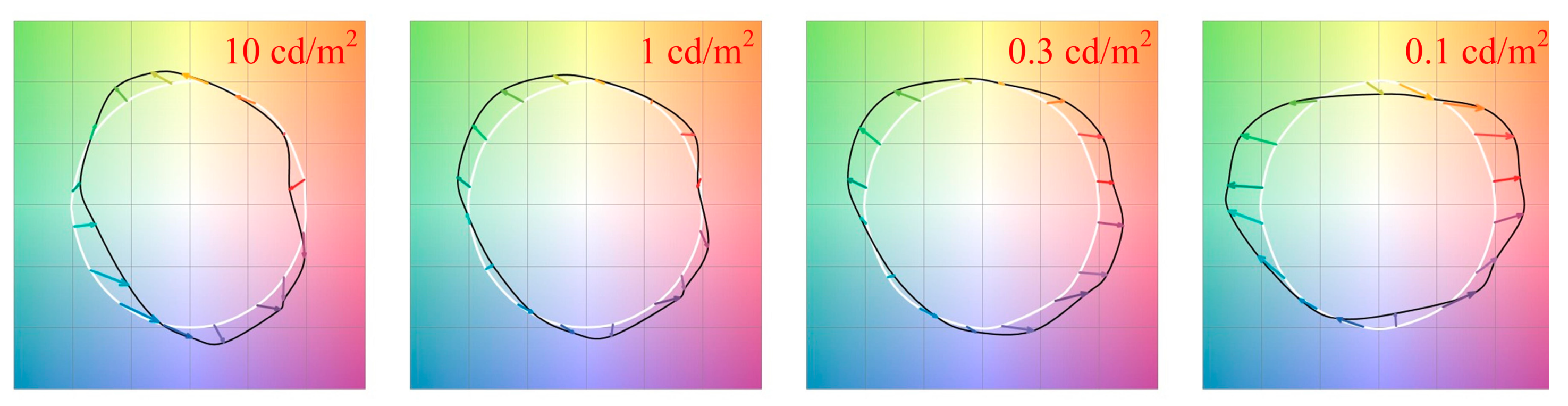
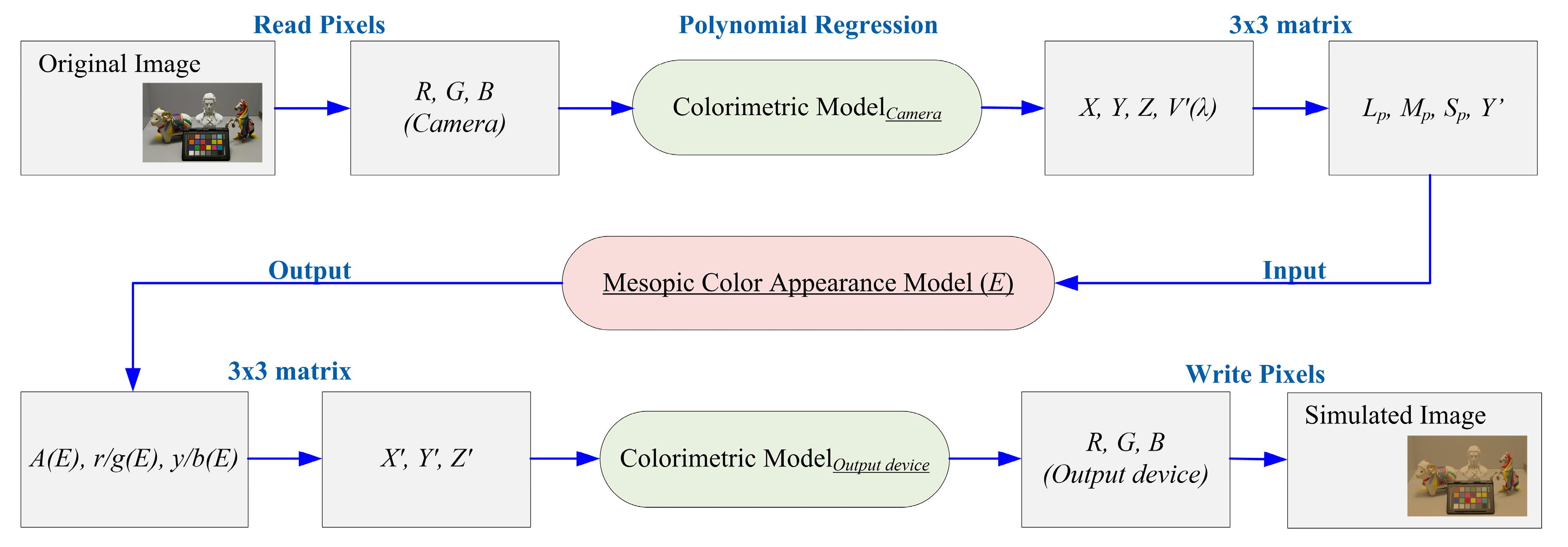
3.3. Mesopic Color Reproduction
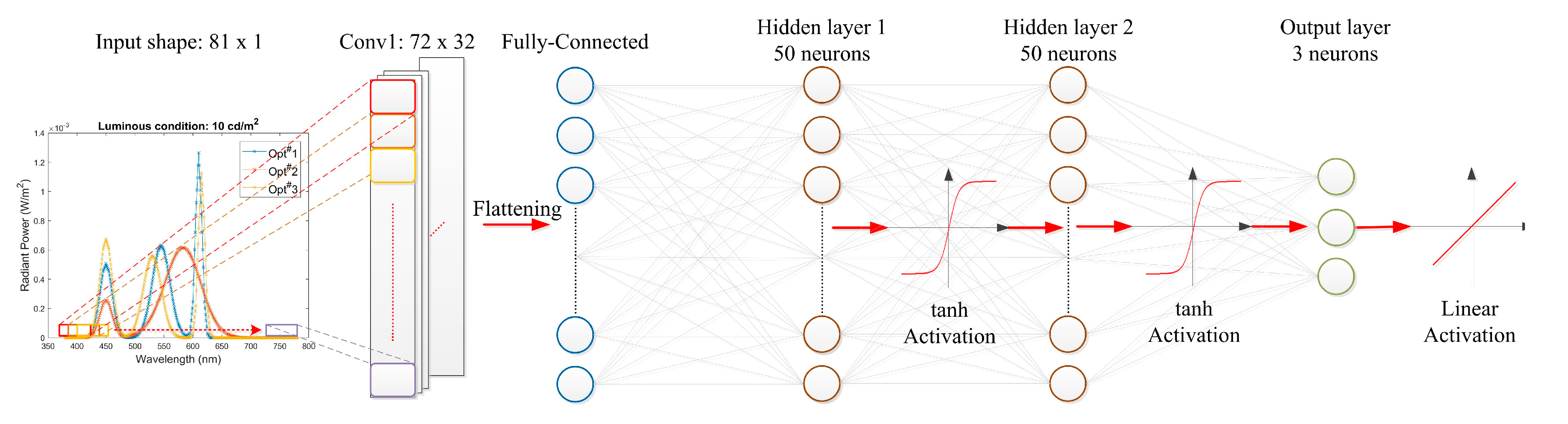
4. Evaluation Model
4.1. Modeling
4.2. Model Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eloholma, M.; Viikari, M.; Halonen, L.; Walkey, H.; Goodman, T.; Alferdinck, J.; Freiding, A.; Bodrogi, P.; Várady, G. Mesopic models—From brightness matching to visual performance in night-time driving: A review. Light. Res. Technol. 2005, 37, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, M.S.; Bullough, J.; Freyssinier-Nova, J.; Bierman, A. A proposed unified system of photometry. Light. Res. Technol. 2004, 36, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eloholma, M.; Halonen, L. New model for mesopic photometry and its application to road lighting. Leukos 2006, 2, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, L.; Puolakka, M. CIE and mesopic photometry. CIE NEWS, 2010; 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Halonen, L.; Puolakka, M. Development of mesopic photometry—The new CIE recommended system. Light Eng. 2012, 20, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Eloholma, M.; Ketomäki, J.; Orreveteläinen, P.; Halonen, L. Visual performance in night-time driving conditions. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2006, 26, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkey, H.; Harlow, J.; Barbur, J. Characterising mesopic spectral sensitivity from reaction times. Vision Res. 2006, 46, 4232–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viikari, M.; Ekrias, A.; Eloholma, M.; Halonen, L. Modeling spectral sensitivity at low light levels based on mesopic visual performance. Clin. Ophthalmol. (Auckland, NZ) 2008, 2, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, P.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhou, Q.-F.; Rooymans, J.; Yu, C.-Y. Luminous efficacy of white LED in the mesopic vision state. Optoelectron. Lett. 2009, 5, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Cen, S.; Liang, P.; Wang, L.; Li, X. The mesopic effect of different correlated color temperature LED light sources on road lighting. In Proceedings of the Asia Communications and Photonics Conference and Exhibition, Shanghai, China, 8–12 December 2010; p. 799106. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, T.; Ohno, Y. Simplified field measurement methods for the CIE mesopic photometry system. Light. Res. Technol. 2017, 49, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Ayama, M.; Akashi, Y.; Hara, N.; Kitano, T.; Kodaira, Y.; Sakai, K. Adaptation luminance simulation for CIE mesopic photometry system implementation. Light. Res. Technol. 2016, 48, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zan, L.; Lin, D.; Zhong, P.; He, G. Optimal spectra of white LED integrated with quantum dots for mesopic vision. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 7643–7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CIE191, C. Recommended System for Mesopic Photometry Based on Visual Performance; CIE: Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Shih, T.-M.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Z. Improvements of mesopic luminance for light-emitting-diode-based outdoor light sources via tuning scotopic/photopic ratios. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 4887–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Xia, G.; Ting, L.; Xiaoling, G.; Ming, L.Q.; Guangdi, S. Color rendering and luminous efficacy of trichromatic and tetrachromatic LED-based white LEDs. Microelectron. J. 2007, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiandong, Z.; Shuo, M. Dynamic Visual Performance of LED with Different Color Temperature. Int. J. Signal Process. Image Process. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 9, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Melgosa, M.; Pointer, M.; Luo, M.R.; Xiao, K.; Li, C. Improved computation of the adaptation coefficient in the CIE system of mesopic photometry. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 18365–18377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Melgosa, M.; Quesada-Molina, J.J.; Xiao, K.; Li, C. Theoretical consideration on convergence of the fixed-point iteration method in CIE mesopic photometry system MES2. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 31351–31362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.; Fotios, S. Effectiveness of an alternative model for establishing mesopic luminance. Light. Res. Technol. 2019, 51, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; You, L.; Nie, C.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, X.; Li, H.; Gu, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q. Quantum dot white light emitting diodes with high scotopic/photopic ratios. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 21901–21913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, T.L.; Zheng, P.; Liang, P. An optimal spectral model for phosphor-converted white light-emitting diodes used in the mesopic vision. J. Am. Cer. Soc. 2019, 102, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, P.; He, G. Spectral optimization of phosphor-coated white LED for road lighting based on the mesopic limited luminous efficacy and IES color fidelity index. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Dai, Q.; Uttley, J. Quantification of Trichromatic Light Sources to Achieve Tunable Photopic and Mesopic Luminous Efficacy of Radiation. LEUKOS 2019, 15, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimainen, M.; Kurkela, M.; Bhusal, P.; Hyyppä, H. Calculation of mesopic luminance using per pixel S/P ratios measured with digital imaging. LEUKOS 2019, 15, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Matsuki, N.; Yaguchi, H.; Shioiri, S. A color appearance model applicable in mesopic vision. Opt. Rev. 2004, 11, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, P.K.; Boynton, R.M. Human Color Vision; Optical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]

| Components | FWHM (nm) | Wavelength Shifts (nm) | Density Ratios | Records | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS1 | Blue, green, red | (25, 36, 13) | B: 450–480 G: 500–550 R: 605–645 Or: 580–620 | 0.1–1.0 | 5273 |
| MS2 | Blue, green, red | (22, 73, 88) | 0.1–1.0 | 45,382 | |
| MS3 | Blue, green, orange | (25, 70, 70) | 0.1–1.0 | 39,076 |
| cd/m2 | Peak Wavelength (nm) | Density Ratios | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opt#1 | Opt#2 | Opt#3 | Opt#1 | Opt#2 | Opt#3 | |
| 10 | 450, 545, 610 | 450, 550, 585 | 450, 530, 615 | 0.4, 0.5, 1.0 | 0.4, 1.0, 0.9 | 0.6, 0.5, 1.0 |
| 1 | 450, 535, 610 | 455, 550, 605 | 450, 530, 615 | 0.3, 0.4, 1.0 | 0.1, 0.2, 0.6 | 0.6, 0.5, 1.0 |
| 0.3 | 450, 530, 615 | 455, 550, 605 | 450, 510, 635 | 0.6, 0.5, 1.0 | 0.1, 0.2, 0.6 | 0.2, 0.3, 0.8 |
| 0.1 | 450, 515, 615 | 465, 510, 605 | 450, 515, 620 | 0.4, 0.5, 0.9 | 0.3, 0.5, 1.0 | 0.4, 0.5, 1.0 |
| cd/m2 | Luminance (cd/m2) | Color Gamut Volume (×103) | S/P Ratio | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opt#1 | Opt#2 | Opt#3 | Opt#1 | Opt#2 | Opt#3 | Opt#1 | Opt#2 | Opt#3 | |
| 10 | 21.79 | 24.52 | 17.16 | 97.40 | 51.40 | 122.98 | 1.57 | 0.94 | 2.46 |
| 1 | 1.92 | 2.17 | 1.67 | 20.60 | 12.71 | 26.61 | 1.78 | 1.10 | 2.46 |
| 0.3 | 0.50 | 0.59 | 0.42 | 11.84 | 4.59 | 13.17 | 2.46 | 1.10 | 3.72 |
| 0.1 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 4.16 | 2.70 | 4.30 | 3.16 | 3.09 | 3.20 |
| 10 cd/m2 | 1 cd/m2 | 0.3 cd/m2 | 0.1 cd/m2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEROpt#1 | 395 | 394 | 387 | 450 |
| LEROpt#2 | 444 | 446 | 450 | 480 |
| LEROpt#3 | 311 | 343 | 319 | 436 |
| CRIOpt#1 | 74 | 79 | 63 | 42 |
| CRIOpt#2 | 41 | 62 | 62 | 39 |
| CRIOpt#3 | 63 | 63 | -8 | 27 |
| Rf,Opt#1 | 66 | 76 | 71 | 54 |
| R f,Opt#2 | 44 | 60 | 60 | 44 |
| R f,Opt#3 | 71 | 71 | 24 | 47 |
| Rg,Opt#1 | 99 | 111 | 119 | 117 |
| Rg,Opt#2 | 76 | 90 | 80 | 86 |
| Rg,Opt#3 | 119 | 119 | 121 | 122 |
| CCTOpt#1 | 4607 | 4350 | 7456 | 7394 |
| CCTOpt#2 | 3036 | 3083 | 3083 | 5314 |
| CCTOpt#3 | 7456 | 7456 | 7975 | 7248 |
| DuvOpt#1 | 0.0046 | 0.0029 | 0.0010 | 0.0042 |
| DuvOpt#2 | 0.0048 | 0.0032 | 0.0032 | 0.0045 |
| DuvOpt#3 | 0.0010 | 0.0010 | 0.0006 | 0.0006 |
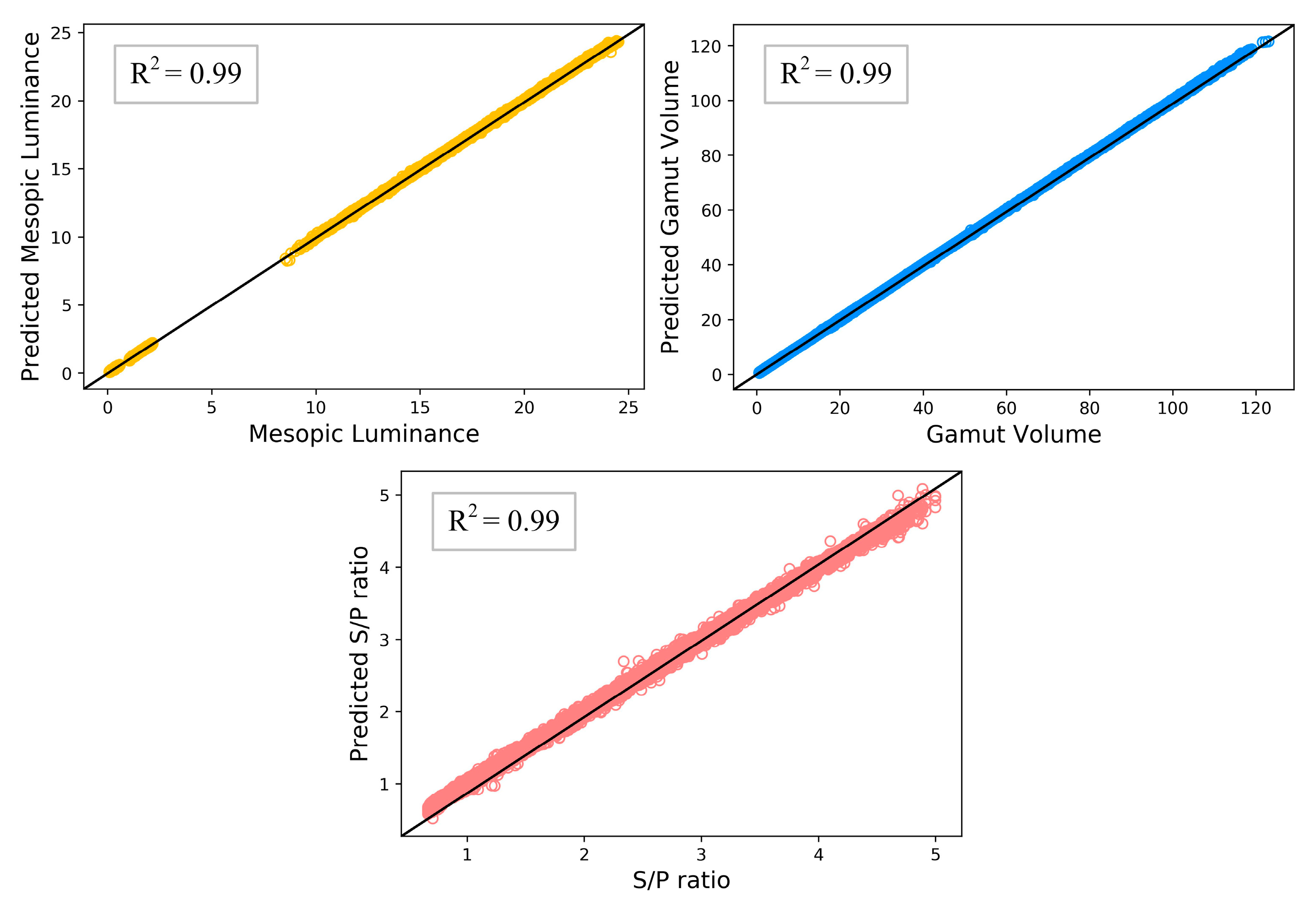
| (×10−2) | Mesopic Luminance | Color Gamut Volume | S/P Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean RMSE ± SD | 1.6025 ± 0.9088 | 5.2161 ± 4.3522 | 1.2786 ± 0.1880 |
| Mean R2 ± SD | 99.999 ± 0.0010 | 99.999 ± 0.0006 | 99.955 ± 0.0128 |
| Mean MAE ± SD | 0.9343 ± 0.4938 | 3.1094 ± 2.0530 | 0.8929 ± 0.1710 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.-C.; Sun, P.-L.; Huang, Y.; Luo, M.R. Spectral Optimization of White LED Based on Mesopic Luminance and Color Gamut Volume for Dim Lighting Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103579
Li H-C, Sun P-L, Huang Y, Luo MR. Spectral Optimization of White LED Based on Mesopic Luminance and Color Gamut Volume for Dim Lighting Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103579
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hung-Chung, Pei-Li Sun, Yennun Huang, and Ming Ronnier Luo. 2020. "Spectral Optimization of White LED Based on Mesopic Luminance and Color Gamut Volume for Dim Lighting Conditions" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103579
APA StyleLi, H.-C., Sun, P.-L., Huang, Y., & Luo, M. R. (2020). Spectral Optimization of White LED Based on Mesopic Luminance and Color Gamut Volume for Dim Lighting Conditions. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103579








