The Mechanical Properties of Centrifuged Concrete in Reinforced Concrete Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixture Design and Reinforcement Frames
2.3. Centrifuged Concrete and Reinforced, Centrifuged Concrete Specimens Preparation and Curing
2.4. Mechanical Tests of Specimens
3. Assessment of Mechanical Properties for Specimens
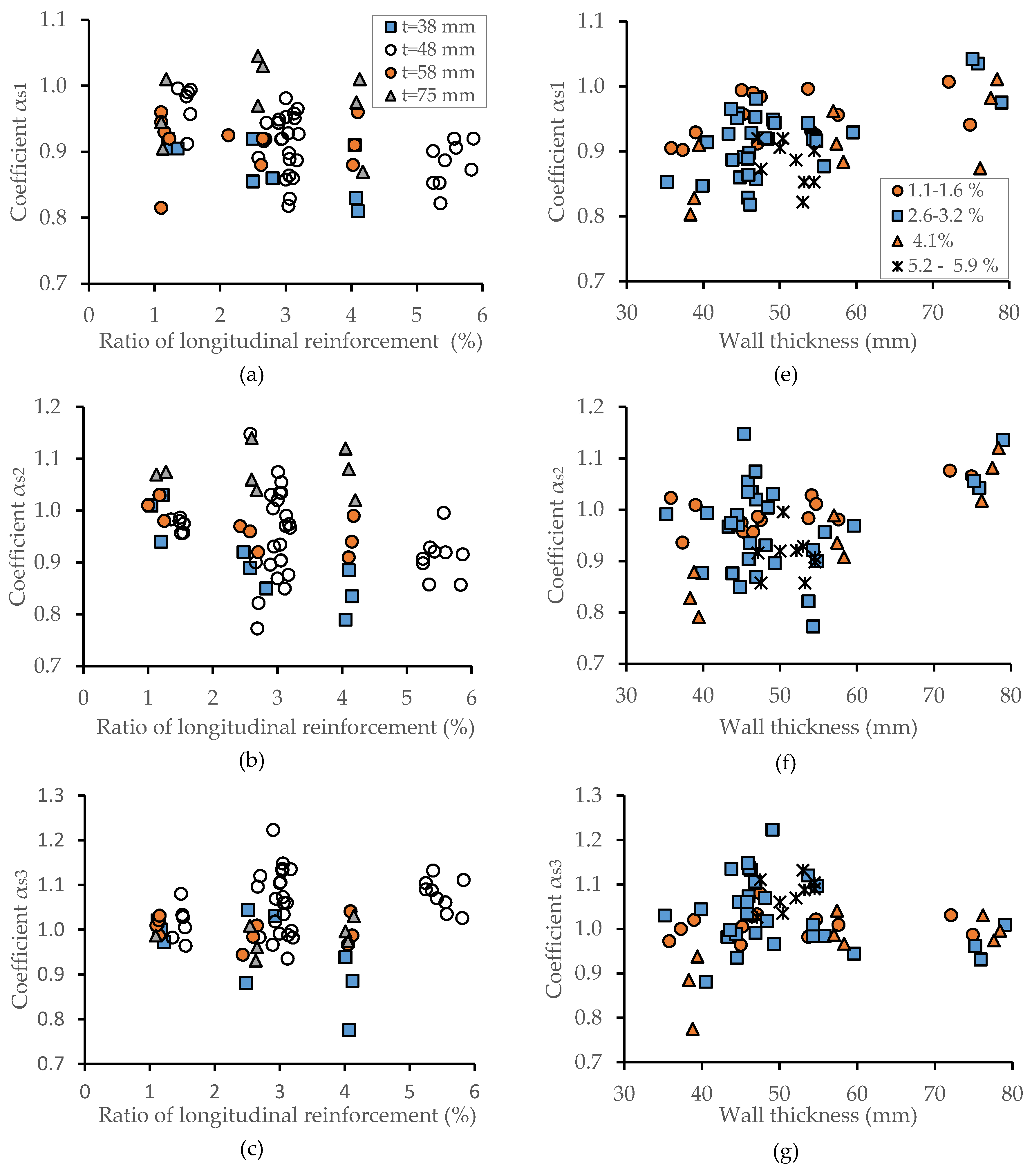
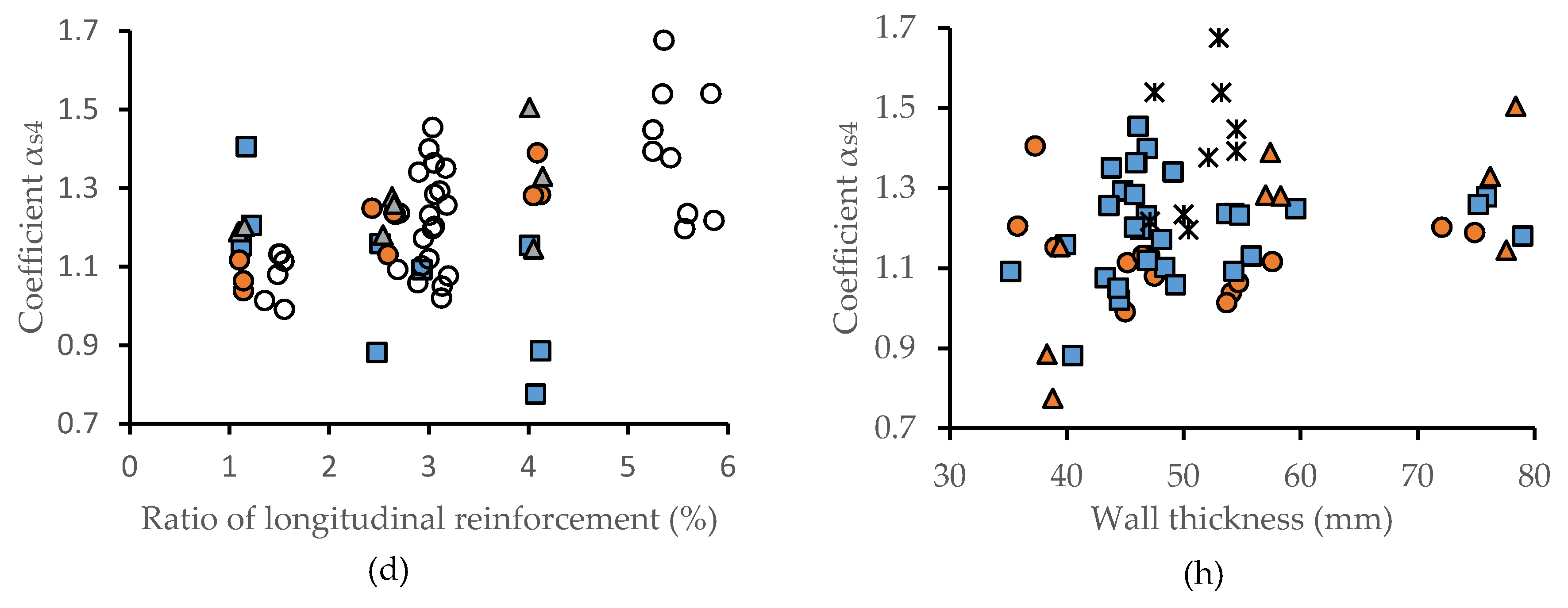
3.1. The Effect of Transverse Reinforcement for Mechanical Properties of Reinforced, Centrifuged Concrete Elements
3.2. The Effect of Longitudinal Reinforcement for Mechanical Properties of Reinforced, Centrifuged Concrete Elements
3.3. The Combined Effect of Longitudinal and Transverse Reinforcement for Mechanical Properties of Reinforced, Centrifuged Concrete Members
4. Experimental Results and Their Analysis
4.1. The Effect of Transverse Reinforcement
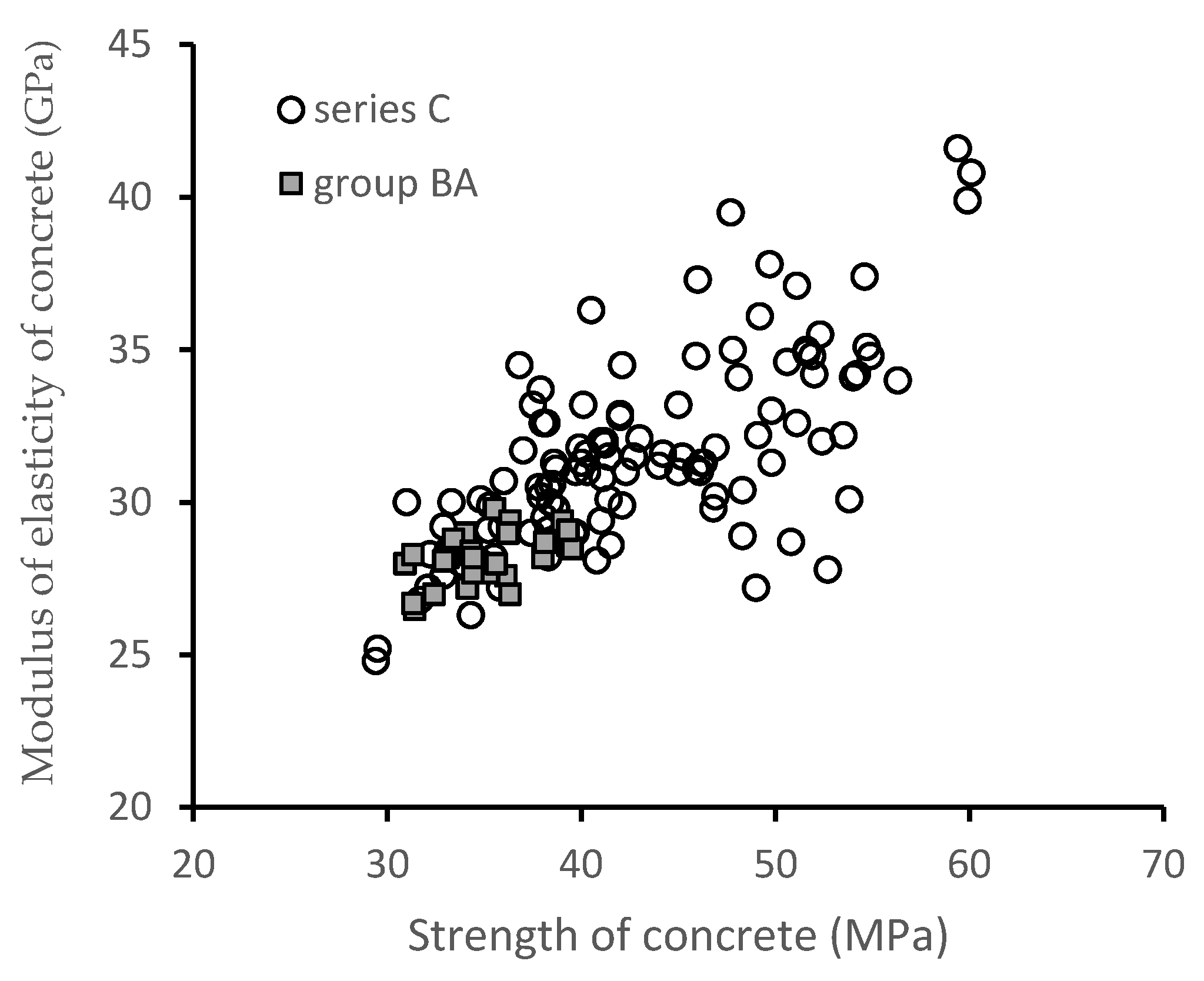
4.2. The Impact of Longitudinal Reinforcement
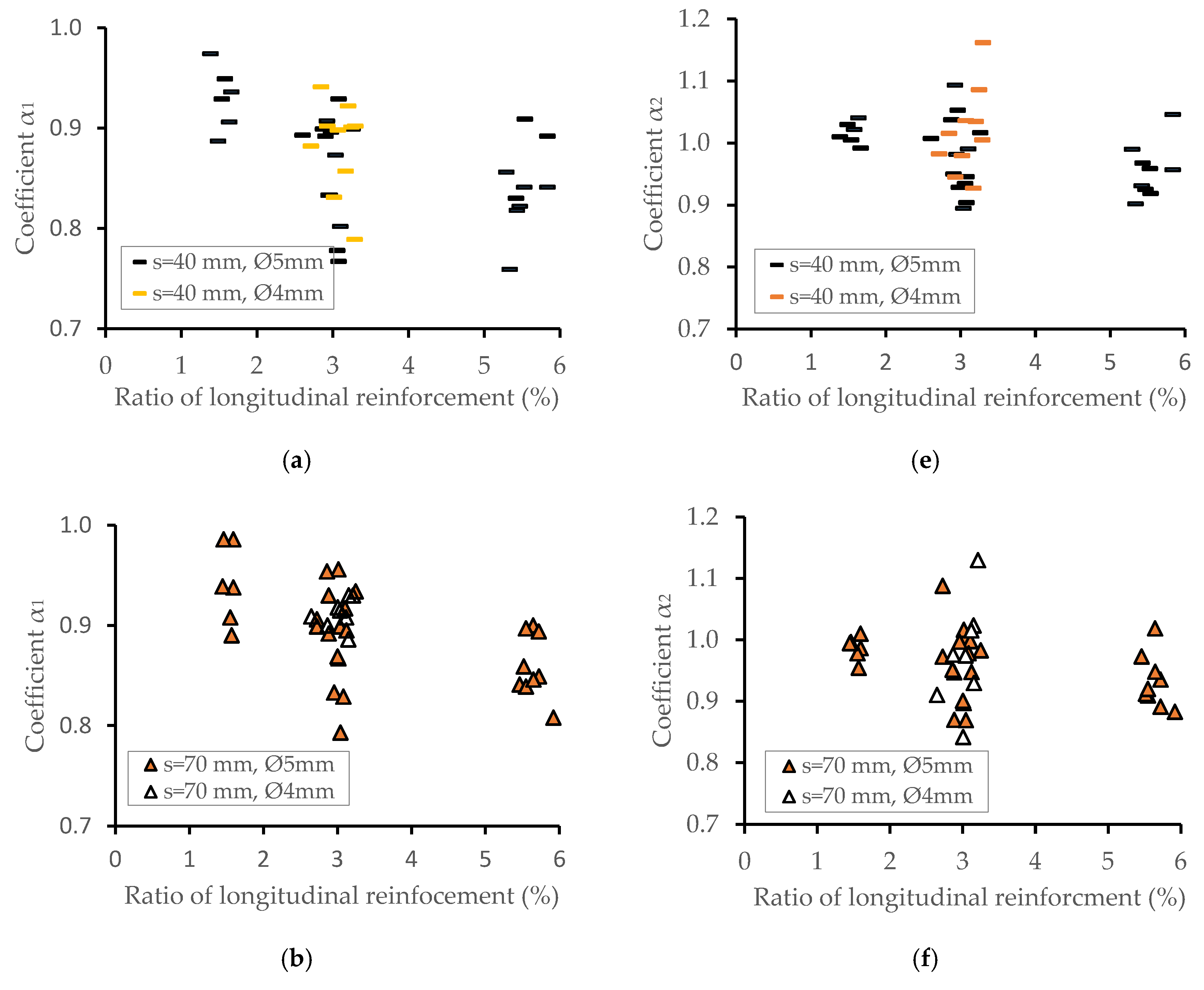
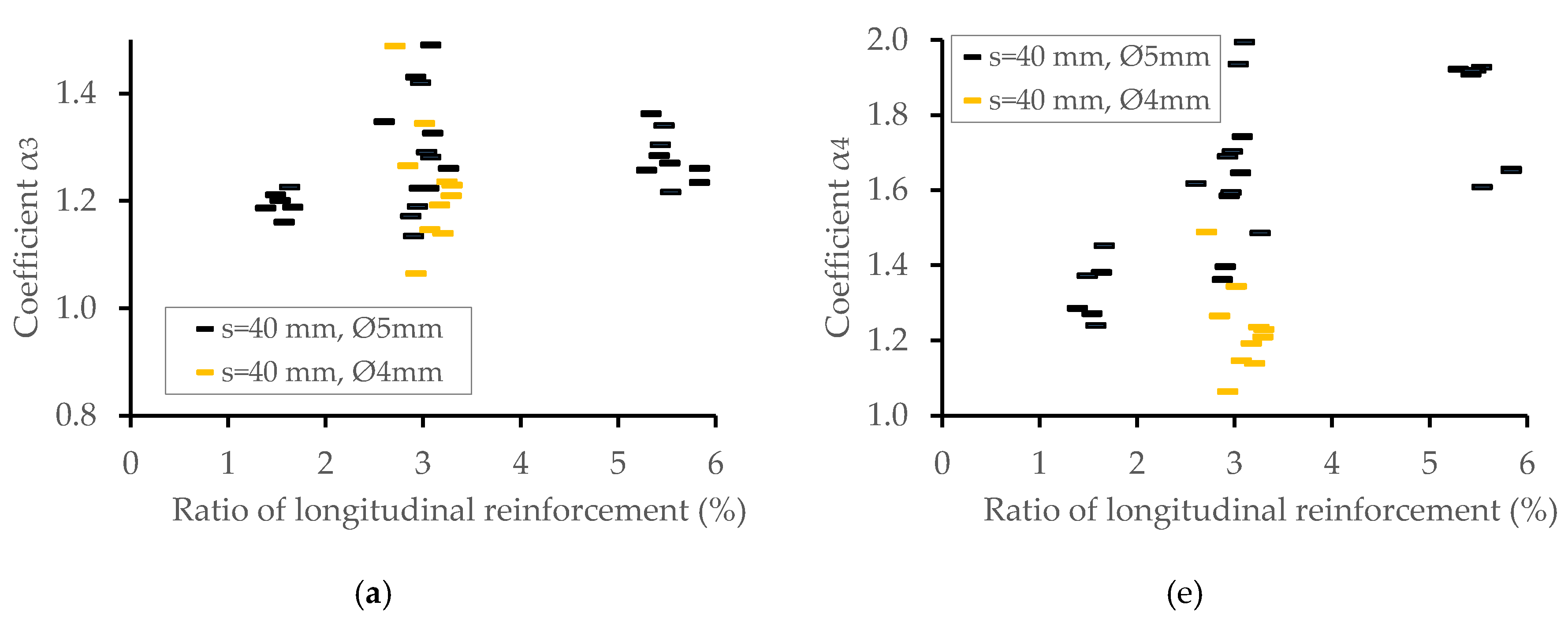
4.3. The Combined Effect of Longitudinal and Transverse Reinforcement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kliukas, R.; Vadlūga, R. Analysis of Structural Spun Concrete properties. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conferences SDSMS’03, Klaipėda, Lithuania, 17–19 September 2003; pp. 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Kudzys, A.; Kliukas, R. The resistance of compressed spun constrete members reinforced by high-strength steel bars. Mater. Struct. 2008, 41, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliukas, R.; Daniunas, A.; Gribniak, V.; Lukoševičienė, O.; Vanagas, E.; Patapavičius, A. Half a century of reinforced concrete electric poles maintenance: Inspection, field-testing, and performance assessment. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 14, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebler, M.; Polak, M.A. Torsion test on spun-cast prestressed concrete poles. PCI J. 2012, 57, 120–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziński, K.; Winnicki, A. Experimental research and analysis of load capacity and deformability of slender high strength concrete columns in biaxial bending. Eng. Struct. 2016, 107, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remitz, J.; Wichert, M.; Empelmann, M. Ultra-High Performance Spun Concrete Poles—Part I: Loading-Bearing Behaviour. In Proceedings of the 11th High Performance Concrete (HPC) and the 2nd Concrete Innovation Conference (CIC), Tromso, Norway, 6–8 March 2017; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317248474 (accessed on 26 July 2019).
- Remitz, J.; Wichert, M.; Empelmann, M. Ultra-High Performance Spun Concrete Poles—Part II: Tests on Grouted Pole Joints. In Proceedings of the 11th High Performance Concrete (HPC) and the 2nd Concrete Innovation Conference (CIC), Tromso, Norway, 6–8 March 2017; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317248608 (accessed on 26 July 2019).
- Quaranta, G.; Trentadue, F.; Marano, G. Closed-form approximation of the axial force-bending moment interaction diagram for hollow circular reinforced concrete cross-sections. Eng. Struct. 2017, 153, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J.; Hesselbarth, D. High Performance Composites in Spun-Cast Elements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgyi, I.; Farkas, G.; Nehme, S.G. Concrete strength tendency in the wall of cylindrical spun-concrete elements. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2010, 54, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volgyi, I.; Farkas, G. Rebound testing of Cylindrical spun-cast concrete elements. Period. Polytech. Civ. Eng. 2011, 55, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, J.; Pachnicz, M.; Sobotka, M. Application of Nanoindentation and 2D and 3D Imaging to Characterise Selected Features of the Internal Microstructure of Spun Concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achverdov, I.N. Centrifuged Reinforced Concrete Pressure Pipes; Stroyizdat: Moscow, USSR, 1969; p. 164. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kudzys, A. Reinforced Concrete Structures of Annular Cross-Section; Mintis: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1975; p. 224. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, A.S. Centrifugation of concrete mixtures in continuous and perforated moulds. In The Collection of Works of NIIZhB “Calc. and Manuf. Techn. of Reinf. Concr. Pres. Pipes”; Stroyizdat: Moscow, USSR, 1969; p. 56. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kliukas, R.; Jaras, A.; Lukoševičienė, O. Reinforced spun concrete poles—Case study of using chemical admixtures. Materials 2020, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aksomitas, G.; Kudzys, A. The strength estimation of centrifuged concrete in compressed elements. In Scientific Paper of the Universities of the Lithuanian SSR; Reinforced Concrete Structures. No. 14. The Reinforced Concrete Strength Assessment; Mokslas: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1985; pp. 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Vadlūga, R.; Kliukas, R.; Garalevičius, R. The strength and deformability estimation of centrifuged concrete. Civ. Eng. 1996, 2, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afifi, M.Z.; Mohamed, H.M.; Benmokrane, B. Theoretical stress–strain model for circular concrete columns confined by GFRP spirals and hoops. Eng. Struct. 2015, 102, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, W.J.; Wong, C.J. Spun Concrete Poles for Electrical Transmission Structure Applications—Continuing to Push the Envelope of the Technology. In Proceedings of the ASCE Conf. “Electrical Transmission in a New Age”, Omaha, NE, USA, 9–12 September 2002; Jackman, D.E., Ed.; ASCI: Reston, VA, USA, 2002; pp. 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Dittmar, F.; Bahous, H. Spun prestressed concrete poles: Alternative to wooden and steel poles for low, medium, and high voltage. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2011), Frankfurt, Germany, 6–9 June 2011. Paper No 0392. [Google Scholar]
- Parvin, A.; Wang, W. Behavior of FRP jacketed concrete columns under eccentric loading. J. Compos. Constr. 2001, 5, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, A. Development of a novel pole using spun-cast concrete inside glass-fiber-reinforced polymer tubes. PCI J. 2008, 53, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanesi, T.; Lavorato, D.; Nuti, C.; Santini, S. Experimental program for pseudodynamic tests on repaired and retrofitted bridge piers. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2009, 13, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, N.; Oprisan, G.; Budescu, M.; Gosav, I. Hollow Concrete Poles with Polymeric Composite Reinforcement. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 9, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.M.; Fouad, F.H.; Albanese, R. Strength and deflection behavior of spun concrete poles with CFRP reinforcement. PCI J. 2011, 56, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-F.; Jiang, C. Effect of load eccentricity on the stress-strain relationship of FRP-confined concrete columns. Compos. Struct. 2013, 98, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.-F.; Jiang, C. Stress-strain relationship of FRP confined concrete columns under combined axial load and bending moment. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 134, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, A.; Eslami, A.; Mohamed, M.H.; Benmokrane, B. Strength of compression lap-spliced GFRP bars in concrete columns with different splice lengths. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 182, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAjarmeh, O.S.; Manalo, A.C.; Benmokrane, B.; Karunasena, K.; Ferdous, W.; Mendis, P. Axial performance of hollow concrete columns reinforced with GFRP composite bars with different reinforcement ratios. Compos. Struct. 2019, 213, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAjarmeh, O.S.; Manalo, A.C.; Benmokrane, B.; Karunasena, K.; Ferdous, W.; Mendis, P. Hollow concrete columns: Review of structural behavior and new designs using GFRP reinforcement. Eng. Struct. 2020, 203, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvedaras, A.B. The study of the work of centrifuged concrete elements with spiral reinforcement under short-term and long-term loading. In Reinforced Concrete Structures; Vilnius Civil Engineering Institute: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1969; pp. 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Stroyizdat. Guidelines for the Design, Manufacture and Use of Reinforced Concrete Centrifuged Structures of Annular Cross-Section; Stroyizdat: Moscow, USSR, 1979; 145p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- CEN. EN 12843:2005 Precast Concrete Products—Masts and Poles; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C1089-19. Standard Specification for Spun Cast Prestressed Concrete Poles; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.astm.org (accessed on 26 July 2019).




| Series | Cement (kg) | Sand (kg) | Crushed Stone (kg) | Water (kg) | w/c | (w/c)residual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 320 to 450 | 680 to 755 | 1080 to 1120 | 155 to 195 | 0.41 to 0.56 | 0.31 to 0.33 |
| BK | 460 | 750 | 1080 | 175 | 0.38 | 0.32 |
| BA | 350 to 400 | 700 | 1080 | 202 | 0.52 to 0.58 | 0.31 to 0.33 |
| C | 360 to 460 | 750 to 850 | 1010 to 1100 | 175 to 210 | 0.44 to 0.65 | 0.31 to 0.33 |
| Series | Group | Strength of Concrete, MPa | Number of Control Annular Cross-Section Specimens of Concrete | Series Specimens | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Reinforcement Characteristics | Geometrical Characteristics | ||||
| Investigation of the effect of transverse (spiral) reinforcement | ||||||
| A | A | 30 to 50 | 21 | 34 | μs = 0 μcir = 0.25% to 1.25% s = 40, 70, 100 mm | h = 400 mm t = 36 mm to 55 mm ϕext = 260 mm |
| Investigation of the effect of longitudinal reinforcement | ||||||
| B | BK | 50 to 60 | 6 | 15 | μs = 1.0% to 6.0% s = 100 mm | h = 400, 800 mm t = 45 mm to 60 mm ϕext = 260 mm |
| BA | 25 to 40 | 12 | 26 | μs = 1.0% to 4.5% s = 100 mm | h = 400 mm t = 38 mm to 80 mm ϕext = 500 mm | |
| Investigation of the effect of longitudinal and transverse (spiral) reinforcement | ||||||
| C | C1 | 30 to 60 | 86 | 38 | μs = 1.0% to 6.0% μcir = 0.25% to 0.50% s = 100 mm | h = 400, 800 mm t = 35 mm to 60 mm ϕext = 260 mm |
| C2 | 42 | μs = 1.0% to 6.0% μcir = 0.5% to 1.0% s = 70 mm | ||||
| C3 | 38 | μs = 1.0% to 6.0% μcir = 1.0% to 1.25% s = 40 mm | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kliukas, R.; Lukoševičienė, O.; Jaras, A.; Jonaitis, B. The Mechanical Properties of Centrifuged Concrete in Reinforced Concrete Structures. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103570
Kliukas R, Lukoševičienė O, Jaras A, Jonaitis B. The Mechanical Properties of Centrifuged Concrete in Reinforced Concrete Structures. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103570
Chicago/Turabian StyleKliukas, Romualdas, Ona Lukoševičienė, Arūnas Jaras, and Bronius Jonaitis. 2020. "The Mechanical Properties of Centrifuged Concrete in Reinforced Concrete Structures" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103570
APA StyleKliukas, R., Lukoševičienė, O., Jaras, A., & Jonaitis, B. (2020). The Mechanical Properties of Centrifuged Concrete in Reinforced Concrete Structures. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3570. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103570




