Classification of Tactile and Motor Velocity-Evoked Hemodynamic Response in Primary Somatosensory and Motor Cortices as Measured by Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
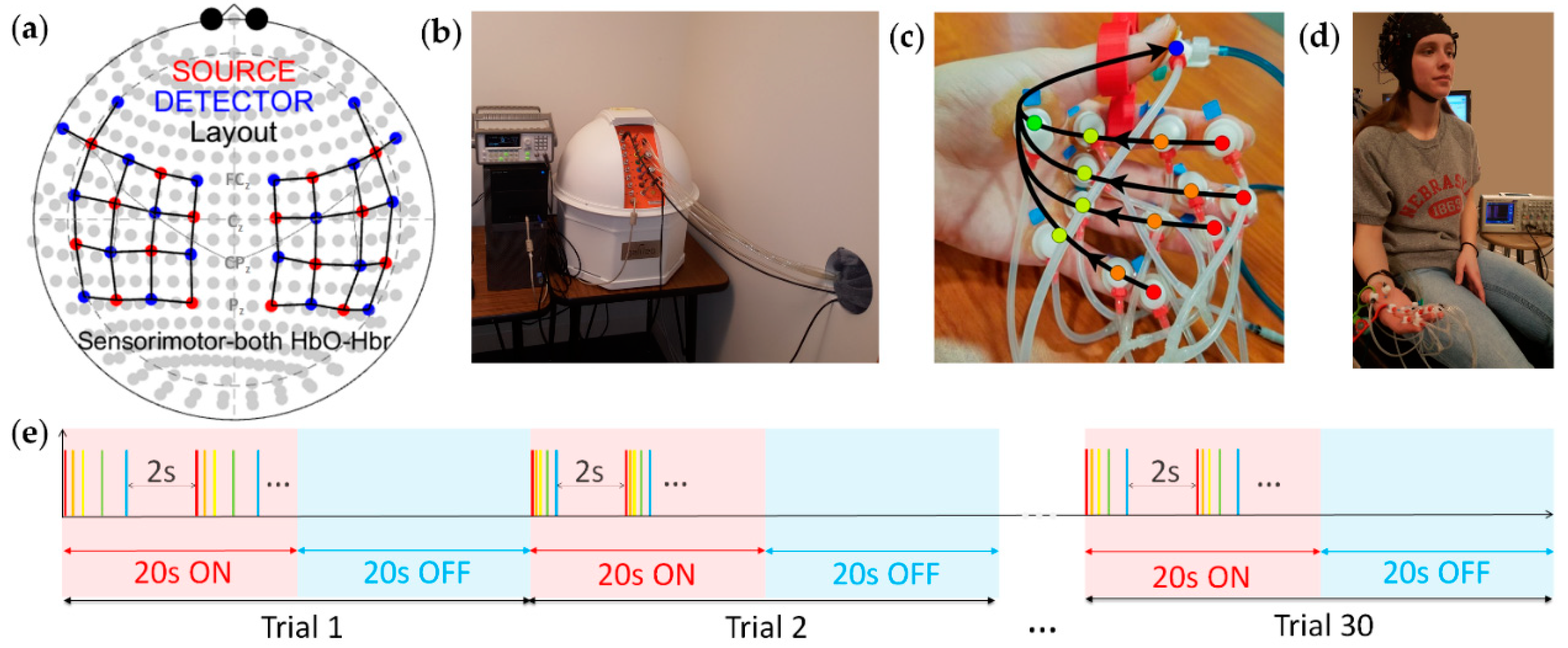
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Preprocessing
- BaselineCorrection() for removing DC-shift and motion correction which detects statistical outliers following an autoregressive integrative model fit of the data,
- OpticalDensity() for calculating , and
- BeerLambertLaw() for applying the modified Beer–Lambert law.
2.3.2. Channel Selection
2.3.3. Feature Extraction and Classification
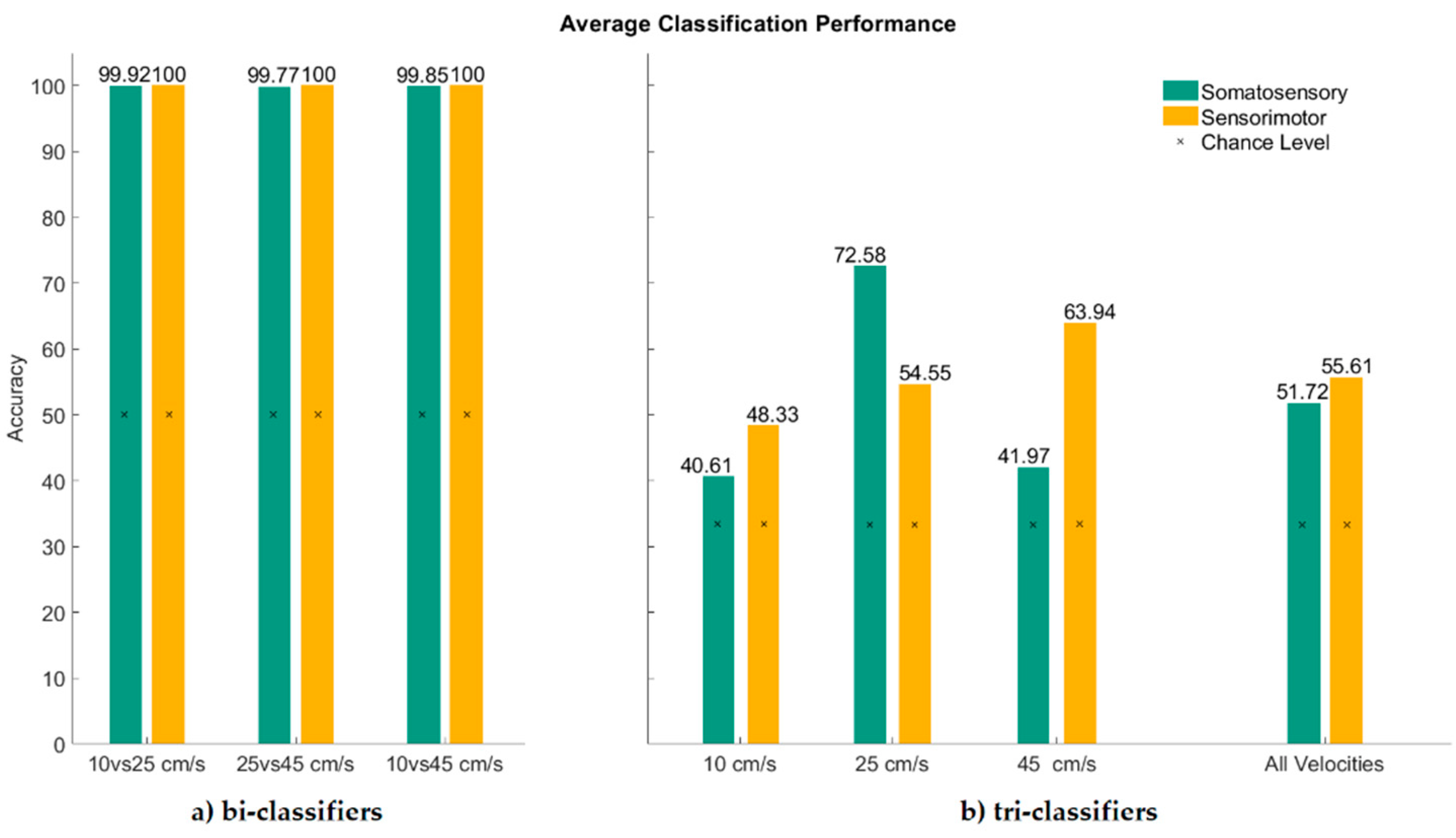
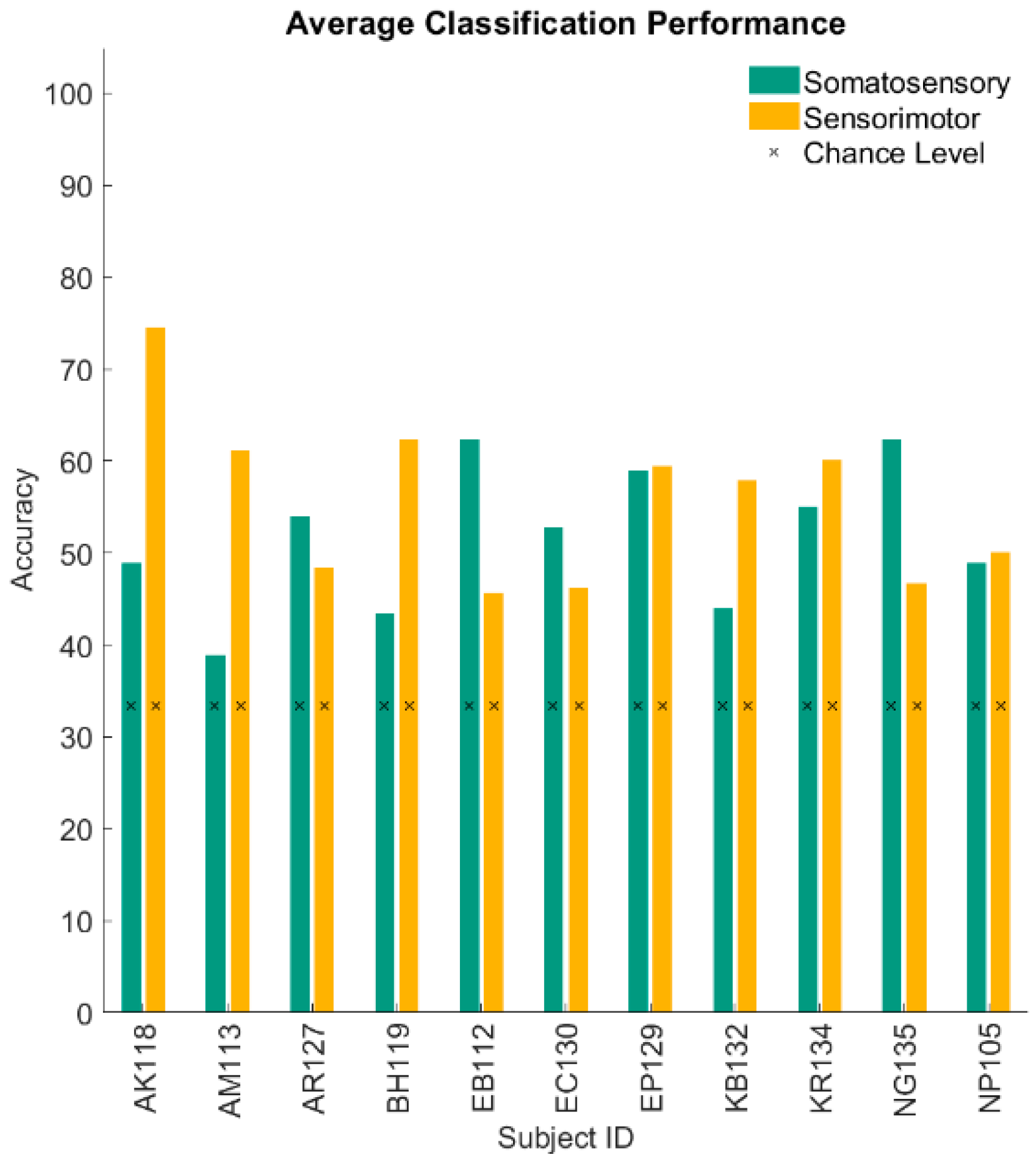
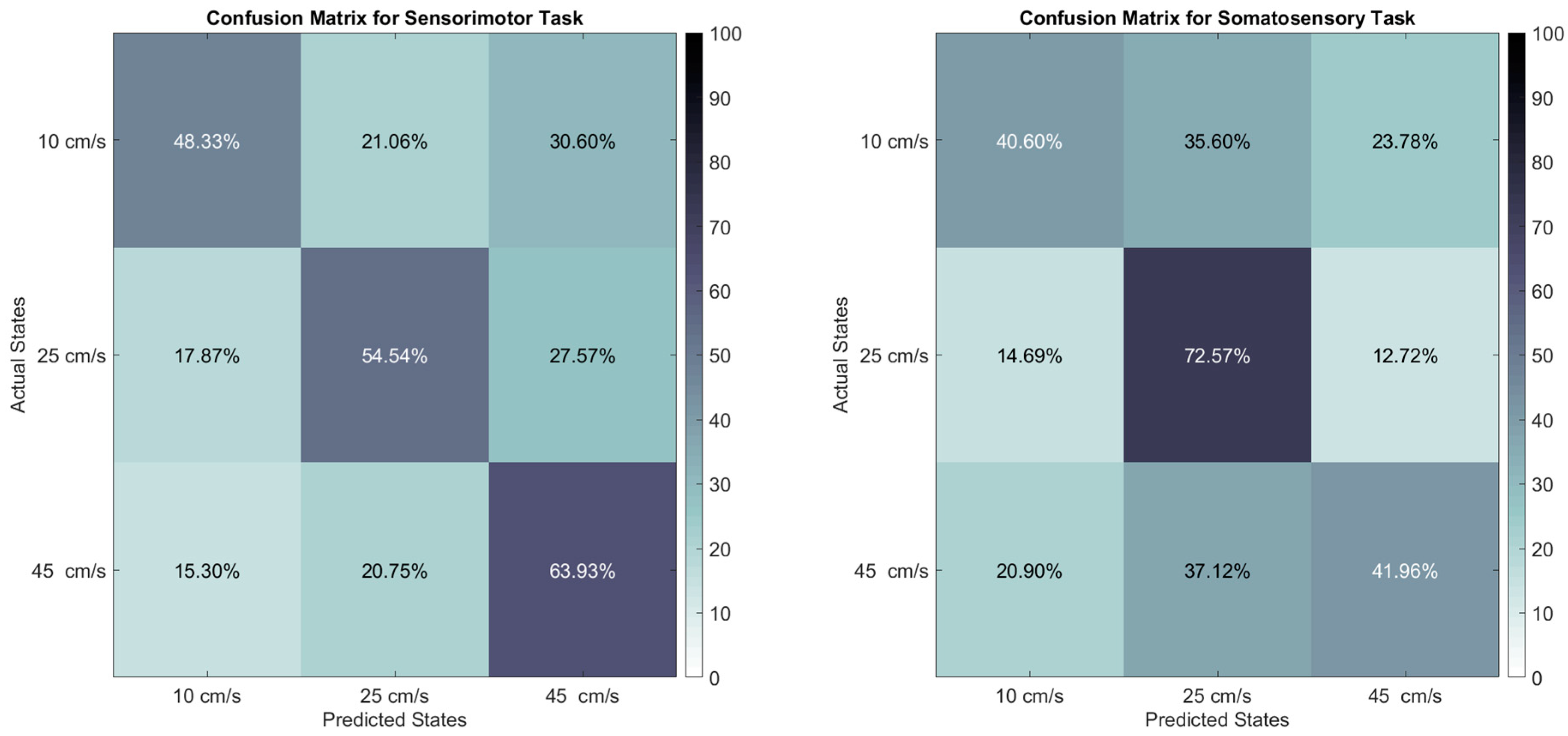
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamper, D.G.; Fischer, H.C.; Conrad, M.O.; Towles, J.D.; Rymer, W.Z.; Triandafilou, K.M. Finger-thumb coupling contributes to exaggerated thumb flexion in stroke survivors. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 111, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Cauraugh, J.H. Force control in chronic stroke. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 52, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, N.J.; Enders, L.R.; Motawar, B.; Kosmopoulos, M.L.; Fathi-Firoozabad, M. The extent of altered digit force direction correlates with clinical upper extremity impairment in chronic stroke survivors. J. Biomech. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.W.; Seo, H.J.; Cohen, L.G. Influence of electric somatosensory stimulation on paretic-hand function in chronic stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celnik, P.; Hummel, F.; Harris-Love, M.; Wolk, R.; Cohen, L.G. Somatosensory Stimulation Enhances the Effects of Training Functional Hand Tasks in Patients With Chronic Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos Conforto, A.; Nocelo Ferreiro, K.; Tomasi, C.; dos Santos, R.L.; Loureiro Moreira, V.; Nagahashi Marie, S.K.; Baltieri, S.C.; Scaff, M.; Cohen, L.G. Effects of Somatosensory Stimulation on Motor Function After Subacute Stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2010, 24, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleming, M.K.; Sorinola, I.O.; Roberts-Lewis, S.F.; Wolfe, C.D.; Wellwood, I.; Newham, D.J. The Effect of Combined Somatosensory Stimulation and Task-Specific Training on Upper Limb Function in Chronic Stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grant, V.M.; Gibson, A.; Shields, N. Somatosensory stimulation to improve hand and upper limb function after stroke—A systematic review with meta-analyses. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2018, 25, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaziani, E.; Couppé, C.; Siersma, V.; Søndergaard, M.; Christensen, H.; Magnusson, S.P. Electrical Somatosensory Stimulation in Early Rehabilitation of Arm Paresis After Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2018, 32, 899–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscia, M.; Wessel, M.J.; Chaudary, U.; Millán, J.D.R.; Micera, S.; Guggisberg, A.; Vuadens, P.; Donoghue, J.; Birbaumer, N.; Hummel, F.C. Neurotechnology-aided interventions for upper limb motor rehabilitation in severe chronic stroke. Brain 2019, 142, 2182–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lay, C.C.; Frostig, R.D. Complete protection from impending stroke following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in awake, behaving rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandla, A.; Le Teng Sherry, C.; Lim, F.; Chuan, C.K.; Liao, L.D.; Thakor, N.V. Peripheral sensory stimulation is neuroprotective in a rat photothrombotic ischemic stroke model. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume OCT, pp. 6086–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Feng, W.; Wang, P. A Systemic Review of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Stroke: Current Application and Future Directions. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, M.; Miyai, I. Review of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in neurorehabilitation. Neurophotonics 2016, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, M.; Hattori, N.; Hatakenaka, M.; Yagura, H.; Kawano, T.; Hino, T.; Miyai, I. Near-infrared spectroscopy-mediated neurofeedback enhances efficacy of motor imagery-based training in poststroke victims: A pilot study. Stroke 2013, 44, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soekadar, S.R.; Birbaumer, N.; Slutzky, M.W.; Cohen, L.G. Brain-machine interfaces in neurorehabilitation of stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 83, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villringer, A.; Planck, J.; Hock, C.; Schleinkofer, L.; Dirnagl, U. Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS): A new tool to study hemodynamic changes during activation of brain function in human adults. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 154, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, D.M.; Bolinger, L.; Li, H.; Kendrick, K.; Chance, B.; Wilson, J.R. Validation of near-infrared spectroscopy in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 77, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresima, V.; Ferrari, M. A Mini-Review on Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS): Where Do We Stand, and Where Should We Go? Photonics 2019, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V. A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application. Neuroimage 2012, 63, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, P.W.; Stewart, M.; Lewis, G.; Dujovny, M.; Ausman, J.I. Intracerebral penetration of infrared light: Technical note. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 76, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, G.; Maier, J.S.; Fabiani, M.; Mantulin, W.W.; Gratton, E. Feasibility of intracranial near-infrared optical scanning. Psychophysiology 1994, 31, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Bianco, S.; Martelli, F.; Zaccanti, G. Penetration depth of light re-emitted by a diffusive medium: Theoretical and experimental investigation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2002, 47, 4131–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Cui, X.; Bryant, D.M.; Glover, G.H.; Reiss, A.L. Inferring deep-brain activity from cortical activity using functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 1074–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Sibaii, F.; Custead, R.; Oh, H.; Barlow, S.M. Functional Connectivity Evoked by Orofacial Tactile Perception of Velocity. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, H.; Custead, R.; Wang, Y.; Barlow, S. Neural encoding of saltatory pneumotactile velocity in human glabrous hand. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Custead, R.; Oh, H.; Rosner, A.O.; Barlow, S. Adaptation of the cortical somatosensory evoked potential following pulsed pneumatic stimulation of the lower face in adults. Brain Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, L.; Barlow, S.; Popescu, M.; Popescu, A.; Auer, E.T. TAC-cell inputs to human hand and lip induce short-term adaptation of the primary somatosensory cortex. Brain Res. 2010, 1348, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hozan, M.; Greenwood, J.; Sullivan, M.; Barlow, S. Cerebral Hemodynamic Response Encodes the Velocity of Patterned Tactile Stimuli: An fNIRS Study. In Proceedings of the Society for Neuroscience 2019, Session 485—Touch: Transduction and Stimulus Encoding, Chicago, IL, USA, 19–23 October 2019; p. 485.19/L5. [Google Scholar]
- Hozan, M.; Greenwood, J.; Sullivan, M.; Barlow, S.M. An fNIRS study of sensorimotor cortical hemodynamics in hand motor tasks coupled with pneumotactile stimulation at different traverse velocities. In Proceedings of the Society for Neuroscience 2018, Session 671—Voluntary Movements: Finger and Grasp Control: Normal Human Behavior, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 November 2018; p. 671.10/LL3. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.; Hozan, M.; Sullivan, M.; Barlow, S.M. Cortical fNIRS hemodynamics during saltatory pneumotactile glabrous hand stimulation in neurotypical adults. In Proceedings of the Society for Neuroscience 2018, Session 392–Somatosensation: Thalamic and Cortical Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 November 2018; p. 392.13/BB4. [Google Scholar]
- Tak, S.; Ye, J.C. Statistical analysis of fNIRS data: A comprehensive review. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.A.; Mannan, M.M.N.; Jeong, M.Y. Cortical Signal Analysis and Advances in Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Signal: A Review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Bogdan, I.I.M.; Wang, S.; Dong, W.; Quan, W.; Dang, W.; Yu, X. Automatic schizophrenia discrimination on fNIRS by using PCA and SVM. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, BIBM 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K.K.; Gwak, J.; Park, C.M.; Song, J.I. Discrimination of Mental Workload Levels from Multi-Channel fNIRS Using Deep Leaning-Based Approaches. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 24392–24403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez Rojas, R.; Huang, X.; Ou, K.L. A Machine Learning Approach for the Identification of a Biomarker of Human Pain using fNIRS. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H. Regularized Discriminant Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 84, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankertz, B.; Tomioka, R.; Lemm, S.; Kawanabe, M.; Müller, K.R. Optimizing spatial filters for robust EEG single-trial analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIRScout fNIRS Neuroimaging | NIRx. Available online: https://nirx.net/nirscout (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Galileo Tactile Stimulator System—Brainbox. Available online: https://brainbox-neuro.com/catalogue/neuro-sensory/tactile-stimulation/galileo-tactile-stimulus-system/ (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Santosa, H.; Zhai, X.; Fishburn, F.; Huppert, T. The NIRS Brain AnalyzIR Toolbox. Algorithms 2018, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez Rojas, R.; Huang, X.; Hernandez-Juarez, J.; Ou, K.L. Physiological fluctuations show frequency-specific networks in fNIRS signals during resting state. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2550–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Gao, X. Common spatial pattern method for channel selection in motor imagery based brain-computer interface. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology—Proceedings, Shanghai, China, 31 August–3 September 2005; Volume 7, pp. 5392–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, D. Application of a common spatial pattern-based algorithm for an fNIRS-based motor imagery brain-computer interface. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 655, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.F.; Islam, S.M.R.; Rahman, M.A. Accuracy Improvement of fNIRS based Motor Imagery Movement Classification by Standardized Common Spatial Pattern. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information & Communication Technology (iCEEiCT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 13–15 September 2018; pp. 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakoolwilaiwan, T.; Lee, J.; Choi, J. Convolutional neural network for high-accuracy functional near- infrared spectroscopy in a brain–computer interface: Three-class classification of rest, right-, and left- hand motor execution. Neurophotonics 2017, 5, 011008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.S.; Naseer, N.; Kim, Y.H. Classification of prefrontal and motor cortex signals for three-class fNIRS-BCI. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 587, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, B.; Way, E.; Barlow, S.M.; Bashford, G.R. Real-Time Cerebral Hemodynamic Response to Tactile Somatosensory Stimulation. J. Neuroimaging 2018, 28, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, M.A.; Fantini, S.; Thompson, J.H.; Culver, J.P.; Boas, D.A. Hemodynamic evoked response of the sensorimotor cortex measured noninvasively with near-infrared optical imaging. Psychophysiology 2003, 40, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, T.H.; Liu, J.Z.; Saghal, V.; Brown, R.W.; Yue, G.H. Relationship between muscle output and functional MRI-measured brain activation. Exp. Brain Res. 2001, 140, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, I.; Osu, R.; Sato, M.A.; Ando, S.; Kawato, M.; Naito, E. Single-trial reconstruction of finger-pinch forces from human motor-cortical activation measured by near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Neuroimage 2009, 47, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
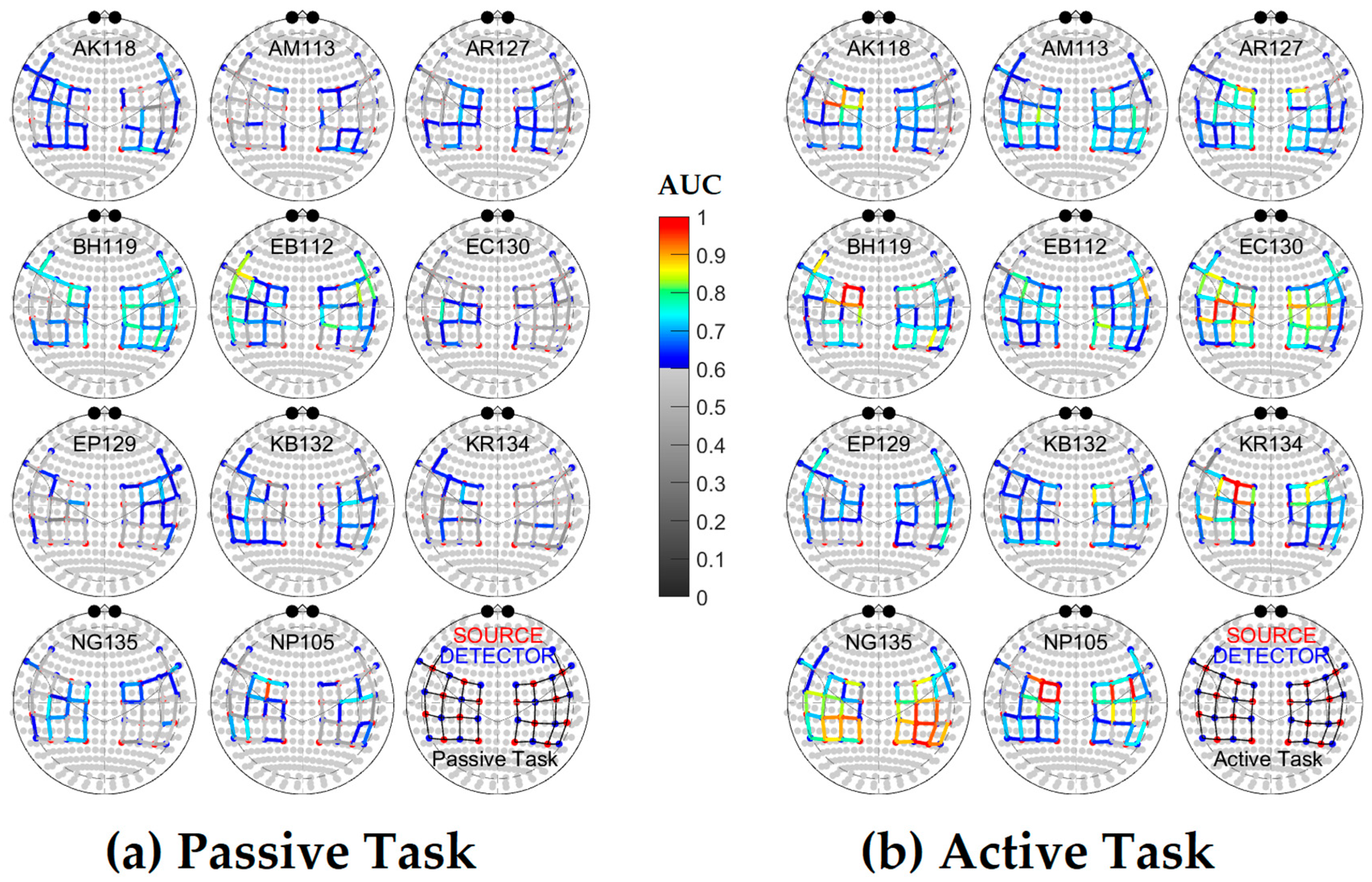
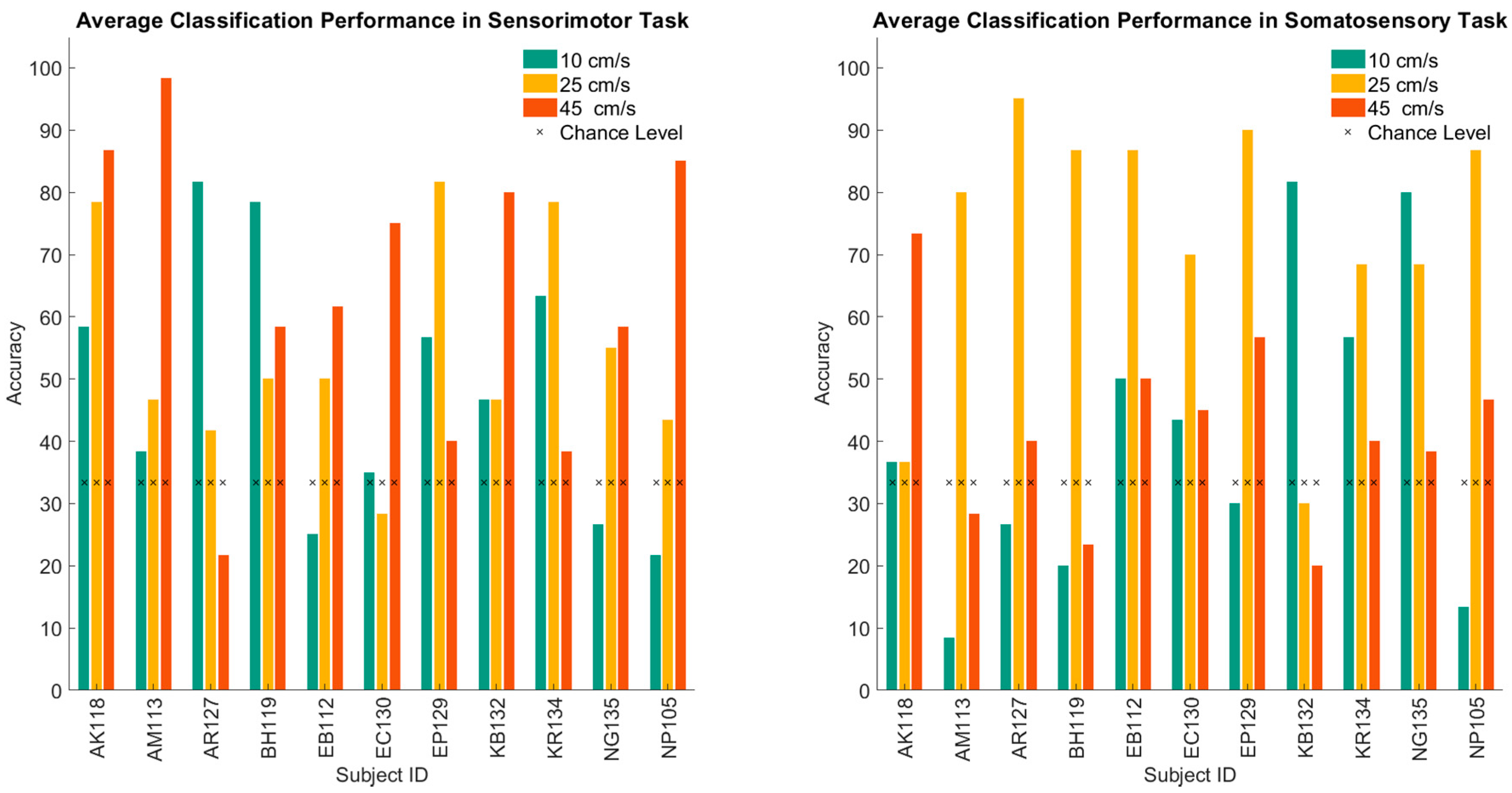
| AK118 | AM113 | AR127 | BH119 | EB112 | EC130 | EP129 | KB132 | KR134 | NG135 | NP105 | |
| Passive | 63.5% | 26.9% | 50.0% | 80.8% | 71.2% | 23.1% | 38.5% | 55.8% | 21.2% | 44.2% | 40.4% |
| Active | 59.6% | 86.5% | 73.1% | 73.1% | 86.5% | 94.2% | 63.5% | 73.1% | 67.3% | 88.5% | 82.7% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hozan, M.; Greenwood, J.; Sullivan, M.; Barlow, S. Classification of Tactile and Motor Velocity-Evoked Hemodynamic Response in Primary Somatosensory and Motor Cortices as Measured by Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103381
Hozan M, Greenwood J, Sullivan M, Barlow S. Classification of Tactile and Motor Velocity-Evoked Hemodynamic Response in Primary Somatosensory and Motor Cortices as Measured by Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103381
Chicago/Turabian StyleHozan, Mohsen, Jacob Greenwood, Michaela Sullivan, and Steven Barlow. 2020. "Classification of Tactile and Motor Velocity-Evoked Hemodynamic Response in Primary Somatosensory and Motor Cortices as Measured by Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103381
APA StyleHozan, M., Greenwood, J., Sullivan, M., & Barlow, S. (2020). Classification of Tactile and Motor Velocity-Evoked Hemodynamic Response in Primary Somatosensory and Motor Cortices as Measured by Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103381





