A 1D–2D Coupled Lattice Boltzmann Model for Shallow Water Flows in Large Scale River-Lake Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. 1D and 2D Shallow Water Submodels and Their Coupling Strategy
2.1. 1D Shallow Water Submodel
2.2. 2D Shallow Water Submodel
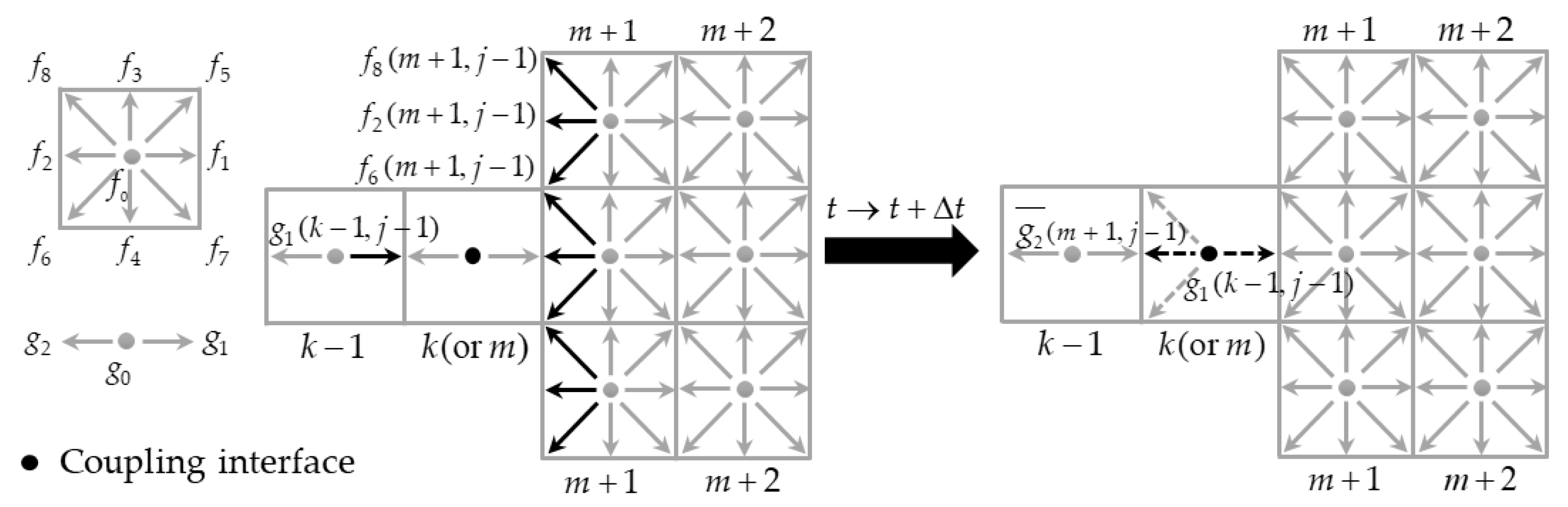
2.3. The Coupling Strategy of 1D and 2D Submodels
- (1)
- Calculate the three unknown distribution functions of the coupling interface;
- (2)
- Calculate the macroscopic parameters (water depth and velocity) of the coupling interface by the distribution functions solved in the first step;
- (3)
- Calculate the unknown distribution functions at the coupling boundaries of the 2D domain by the above calculated macroscopic parameters.
2.4. Stability Requirements
3. Numerical Experiments
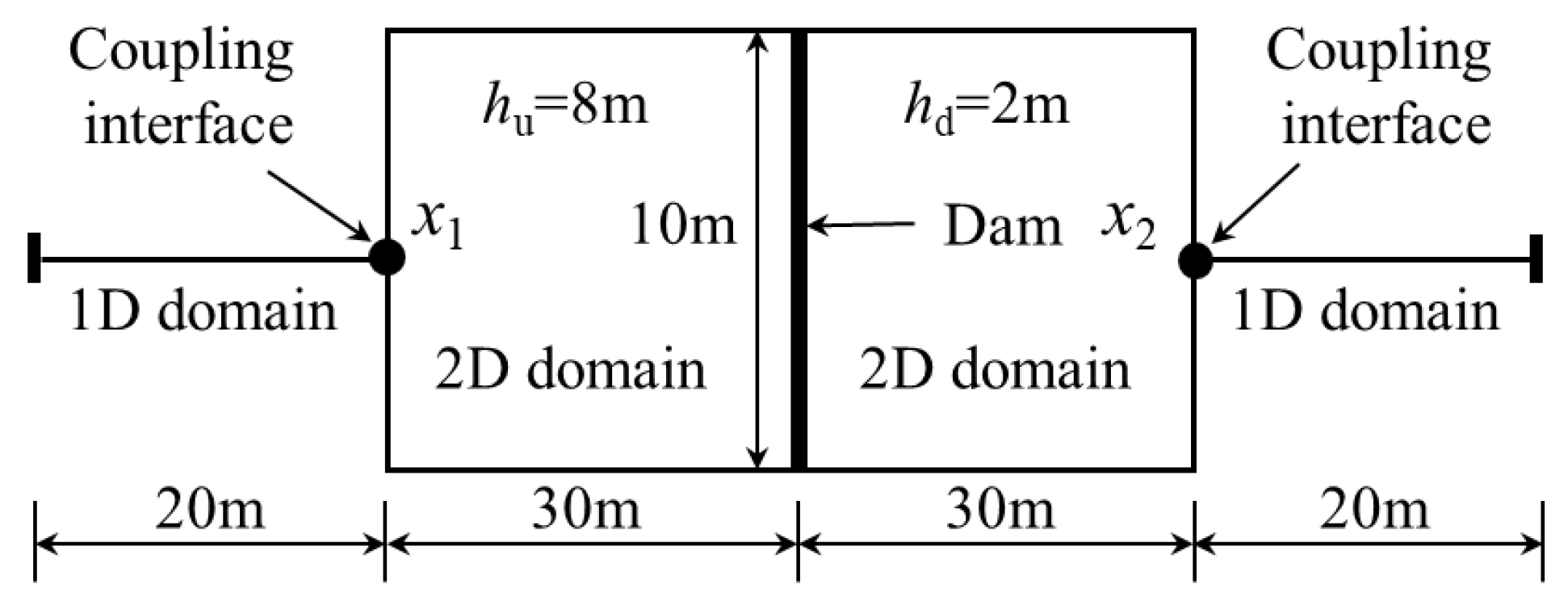
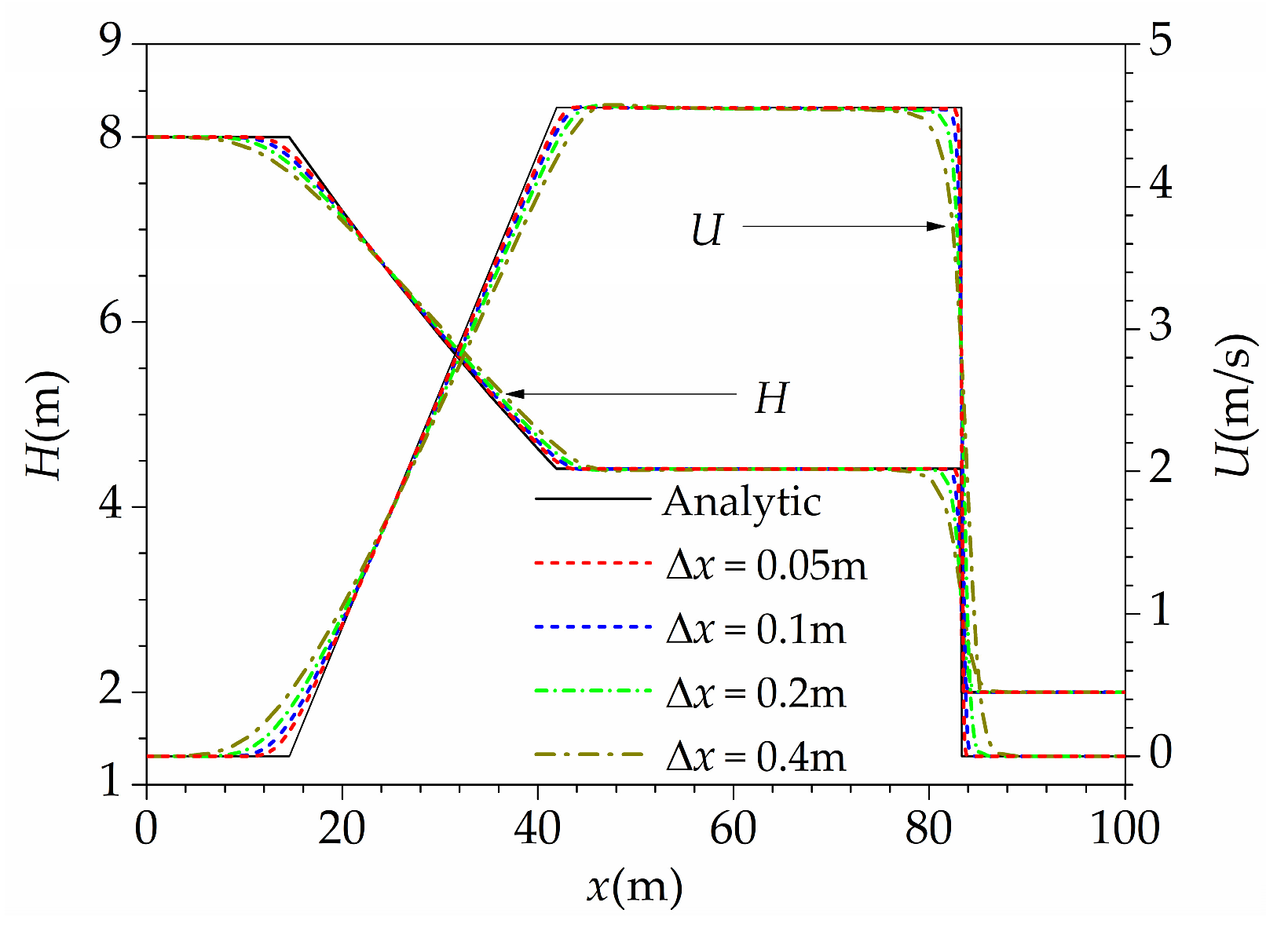
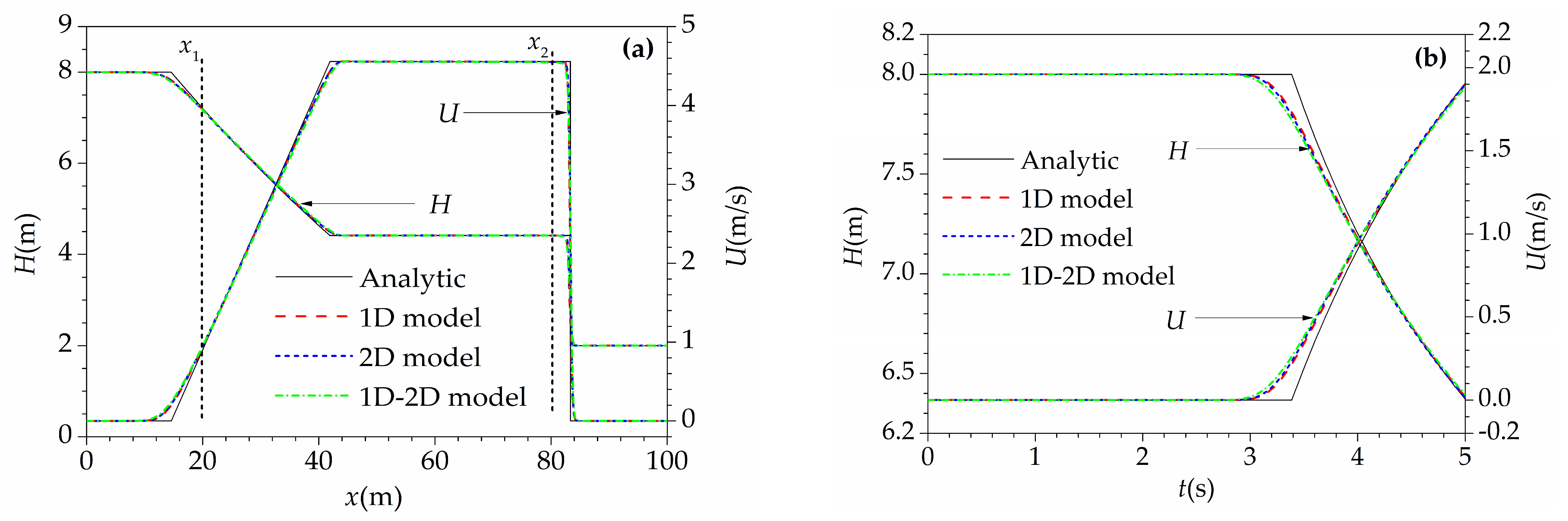
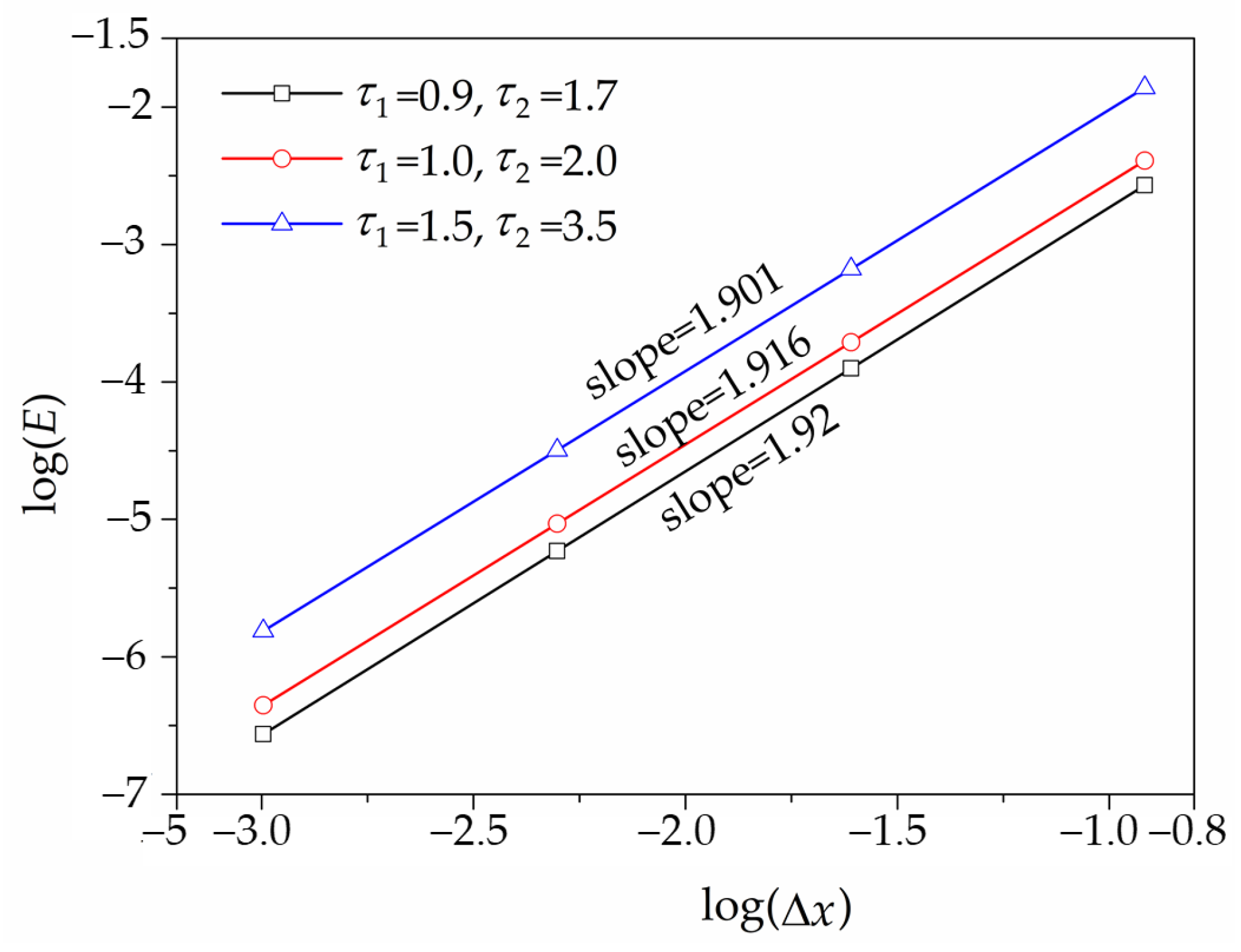
3.1. The Dam Break Flow
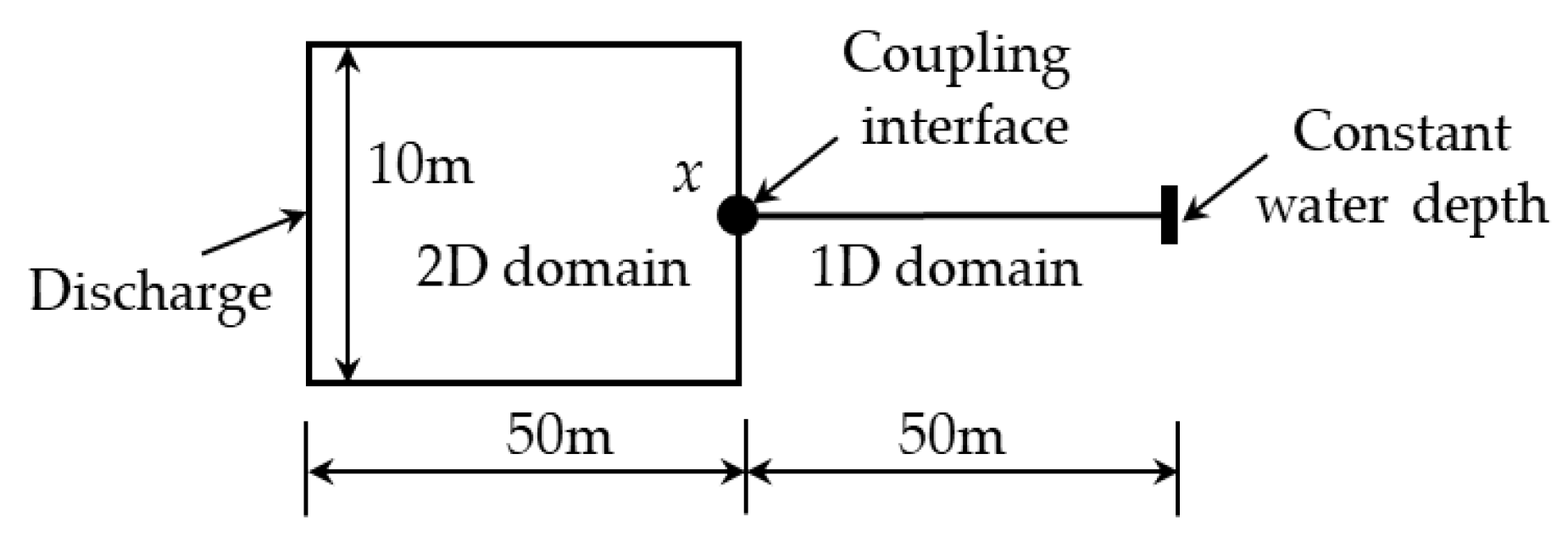
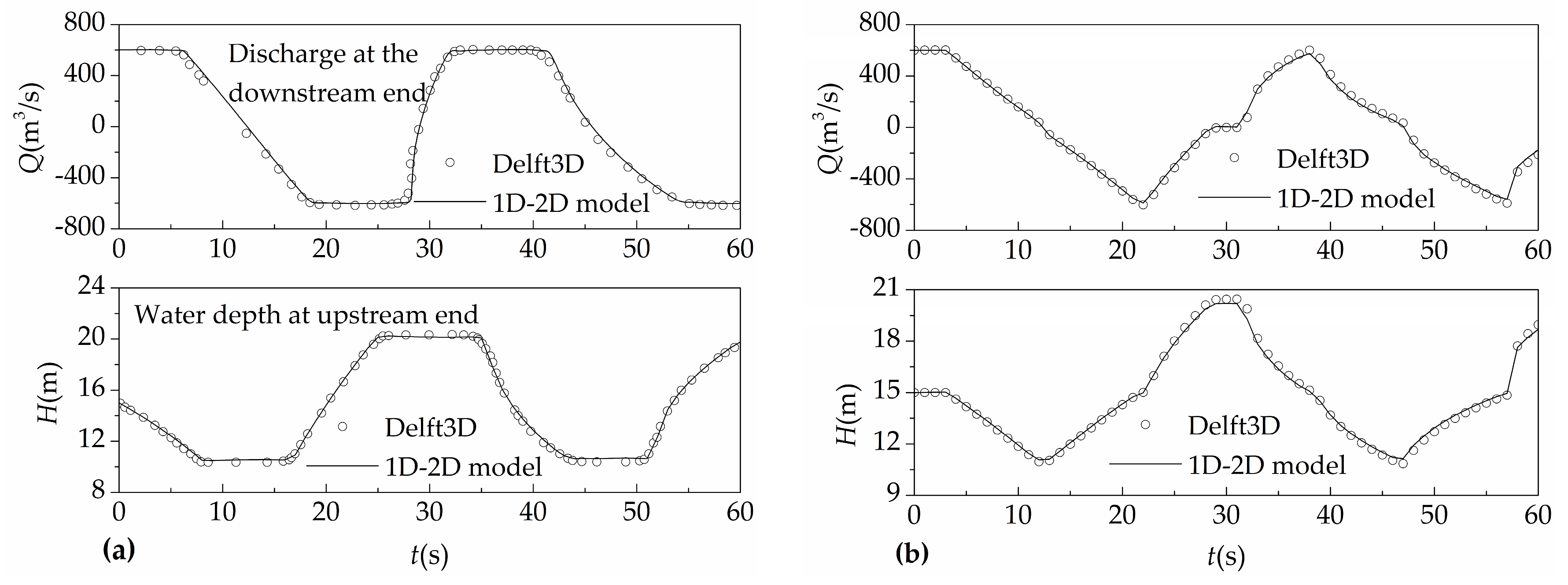
3.2. The Surge Waves in Tailrace Canal of a Hydropower Station
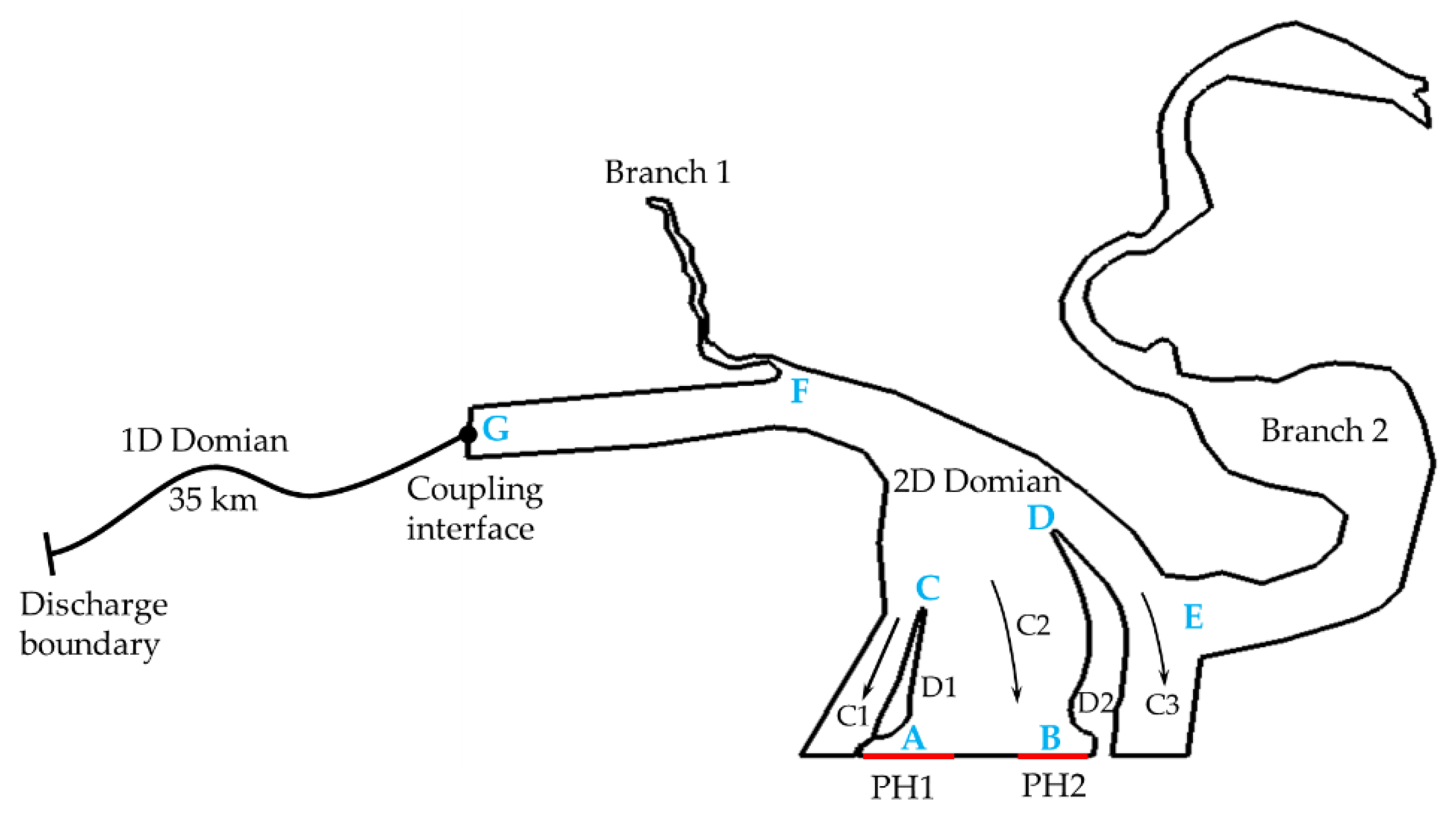
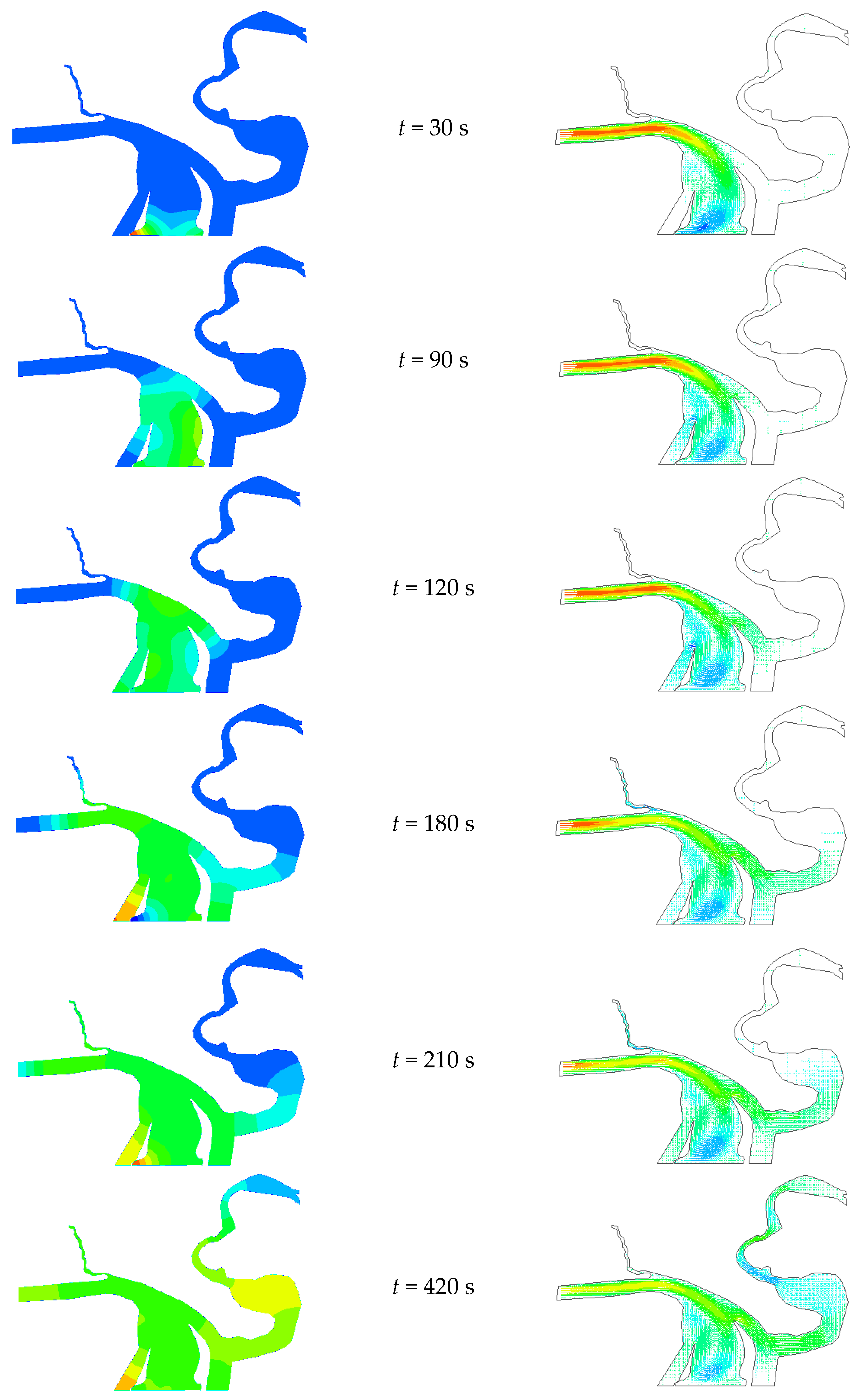
4. Simulation of Surge Waves in the Reservoir of a Run-of-River Hydropower Station
4.1. Computational Setup
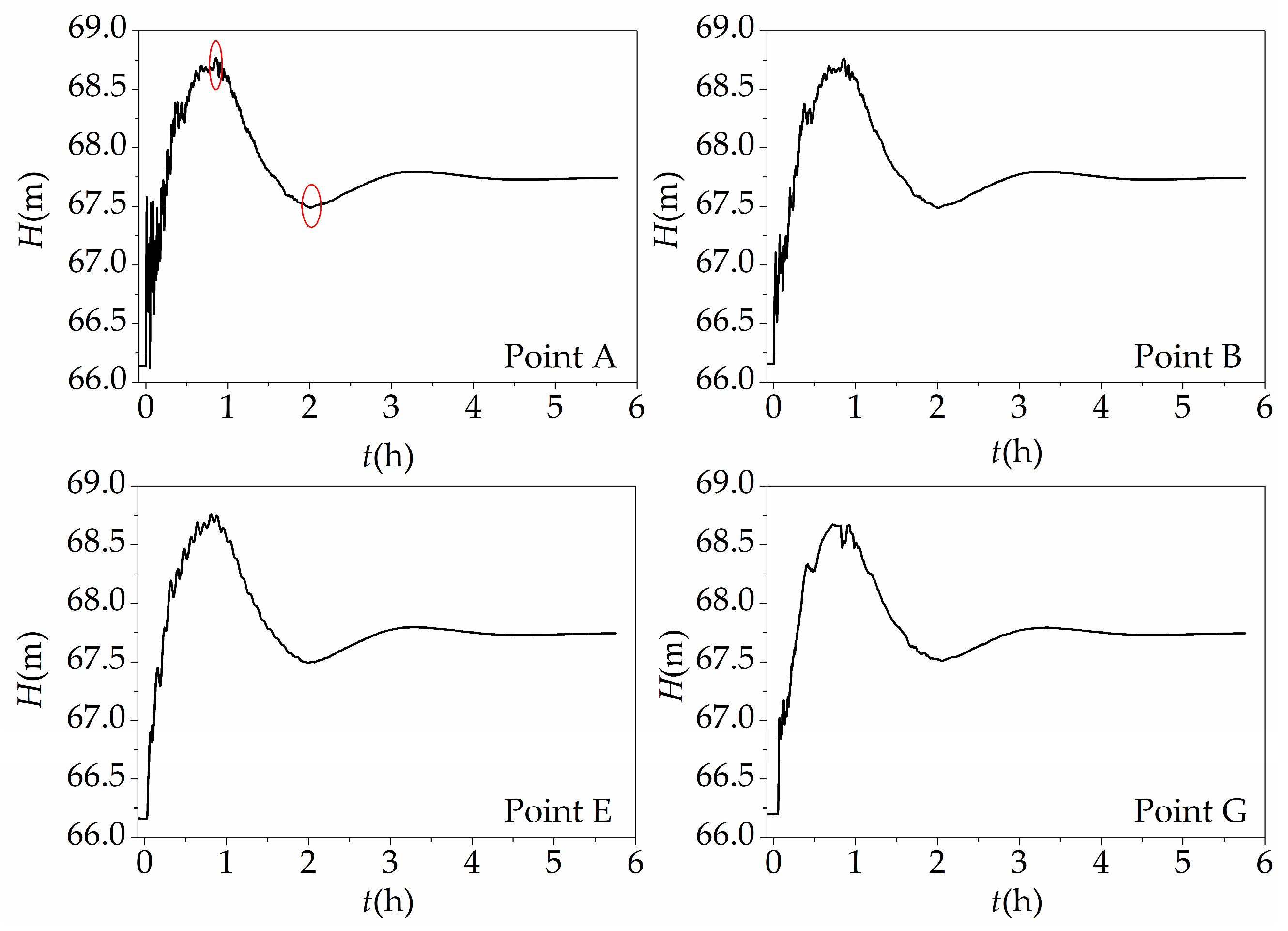
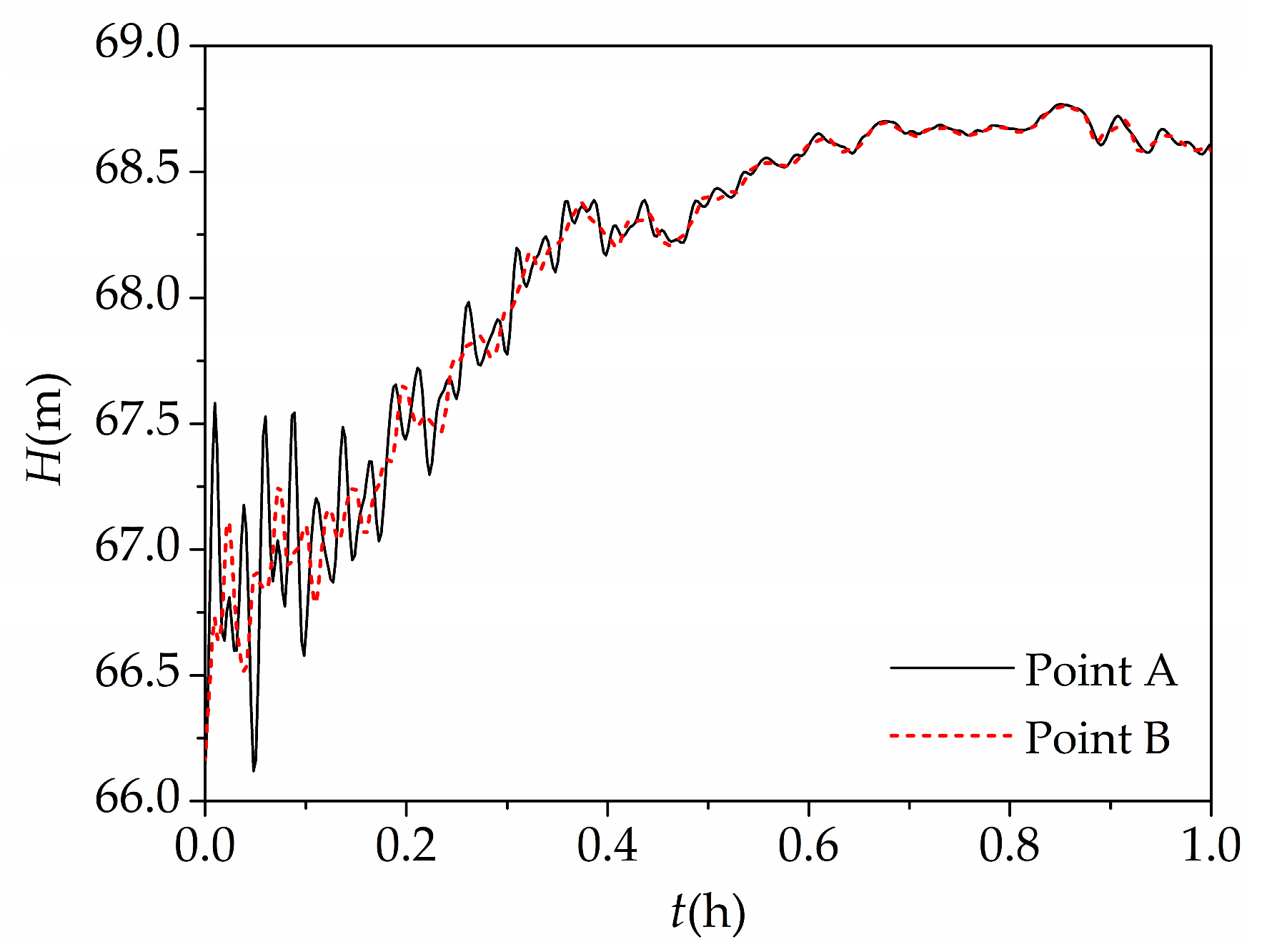
4.2. Simulation Results
4.3. Computational Efficiency Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adeogun, A.G.; Daramola, M.O.; Pathirana, A. Coupled 1D-2D hydrodynamic inundation model for sewer overflow: Influence of modeling parameters. Water Sci. 2015, 29, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. A coupled 1D-2D hydrodynamic model for flood simulation in flood detention basin. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 1303–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Hernández, M.; García-Navarro, P.; Burguete, J.; Brufau, P. A conservative strategy to couple 1D and 2D models for shallow water flow simulation. Comput. Fluids 2013, 81, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Diao, W. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of the open channel flow connecting two cascaded hydropower stations. J. Hydrodyn. 2016, 28, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Diao, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S. Three-Dimensional Numerical Method for Simulating Large-Scale Free Water Surface by Massive Parallel Computing on a GPU. Water 2019, 11, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, A.; Geier, M.; Lee, T. A mass-conserving lattice Boltzmann method with dynamic grid refinement for immiscible two-phase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2016, 315, 434–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Xu, W.; Luo, X. A Double-Distribution-Function Lattice Boltzmann Method for Bed-Load Sediment Transport. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2017, 9, 1750013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; Diao, W. GPU acceleration of FSI simulations by the immersed boundary-lattice Boltzmann coupling scheme. Comput. Math. Appl. 2016, 78, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y. Lattice Boltzmann model for two-dimensional shallow water flows realizing parallel computing on GPU. J. Hydrodyn. 2011, 26, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y. Application of the lattice boltzmann method-one dimensional dam breaker simulation. Mech. Eng. 2000, 22, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Suo, L. A lattice BGK lodel for simulating one-Dimensional unsteady open channel flows. Adv. Water Sci. 2000, 11, 362–367. [Google Scholar]
- Frandsen, J.B. A simple LBE wave runup model. Prog. Comput. Fluid Dyn. Int. J. 2008, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thang, P.; Chopard, B.; Lefèvre, L.; Ondo, D.A.; Mendes, E. Study of the 1D lattice Boltzmann shallow water equation and its coupling to build a canal network. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 229, 7373–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopard, B.; Pham, V.T.; Lefèvre, L. Asymmetric lattice Boltzmann model for shallow water flows. Comput. Fluids 2013, 88, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.G. A lattice Boltzmann model for the shallow water equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 2002, 191, 3527–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Suo, L. 2D open channel flow simulations by the lattice Boltzmann model. Adv. Water Sci. 2003, 14, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, G.J.; Burrows, R. Lattice Boltzmann model for shallow water flows in curved and meandering channels. Int. J. Comut. Fluid Dyn. 2009, 23, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q. Numerical analysis of the impact factors on the flow fields in a large shallow lake. Water 2019, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. Lattice Boltzmann method for the age concentration equation in shallow water. J. Comput. Phys. 2015, 299, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, D. 1D–2D Coupled Numerical Model for Shallow-Water Flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 138, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiry, S.; Sen, D.; Bates, P.D.; Yan, D. Application of the 1D-quasi 2D model tinflood for floodplain inundation prediction of the river thames. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestininzi, P.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Schumann, G.; Bates, P.D. Selecting the appropriate hydraulic model structure using low-resolution satellite imagery. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.; Monnier, J. Superposition of local zoom models and simultaneous calibration for 1D-2D shallow water flows. Math. Comput. Simul. 2009, 80, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Nieto, E.D.; Marin, J.; Monnier, J. Coupling superposed 1D and 2D shallow-water models: Source terms in finite volume schemes. Comput. Fluids 2010, 39, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinebach, G.; Rademacher, S.; Rentrop, P.; Schulz, M. Mechanisms of coupling in river flow simulation systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2004, 168, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Twigt, D.J.; De-Goede, E.D.; Zijl, F.; Schwanenberg, D.; Chiu, A.Y.W. Coupled 1D-3D hydrodynamic modelling, with application to the Pearl River Delta. Ocean. Dyn. 2009, 59, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Cheng, Y.G.; Yang, J.D.; Xia, L.S.; Lai, X. Simulation of the load rejection transient process of a francis turbine by using a 1D-3D coupling approach. J. Hydrodyn. 2014, 26, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bladé, E.; Gómez-Valentín, M.; Dolz, J.; Aragón-Hernández, J.L.; Corestein, G.; Sánchez-Juny, M. Integration of 1D and 2D finite volume schemes for computations of water flow in natural channels. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 42, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorimbert, Y.; Lätt, J.; Chopard, B. Coupling of lattice Boltzmann shallow water model with lattice Boltzmann free-surface model. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, D.; Variano, E.A.; Lin, J. Development and performance of a 1D–2D coupled shallow water model for large river and lake networks. J. Hydraul. Res. 2018, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zheng, C. Theory and Applications of Lattice Boltzmann Method; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009; ISBN 9787030235893. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. lattice Boltzmann Method: Theory and Application; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009; ISBN 9787030232724. [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg, I. Multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann. R. Soc. 2002, 360, 437–451. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Matthaeus, W.H. Recovery of the Navier-Stokes equations using a lattice-gas Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, 5339–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, J. Introducing unsteady non-uniform source terms into the lattice Boltzmann model. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2008, 56, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; He, X. On pressure and velocity flow boundary conditions and bounceback for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model. Phys. Fluids 1997, 9, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zheng, C.; Shi, B. Non-equilibrium extrapolation method for velocity and pressure boundary conditions in the lattice boltzmann method. Chin. Phys. 2002, 11, 366–374. [Google Scholar]
- Stoker, J.J. Water Waves; Pure and Applied Mathematics; Interscience Publisher: Geneva, Switzerland, 1957. [Google Scholar]
| Methods | x1 | x2 | ||||
| h (m) | AE (m) | RE (%) | h (m) | AE (m) | RE (%) | |
| Analytic | 7.203 | - | - | 4.414 | - | - |
| 1D model | 7.180 | 0.023 | 0.32 | 4.411 | 0.003 | 0.07 |
| 2D model | 7.170 | 0.033 | 0.46 | 4.410 | 0.004 | 0.09 |
| 1D–2D model | 7.169 | 0.034 | 0.47 | 4.414 | 0 | 0 |
| Methods | u (m/s) | AE (m/s) | RE (%) | u (m/s) | AE (m/s) | RE (%) |
| Analytic | 0.906 | - | - | 4.557 | - | - |
| 1D model | 0.938 | 0.032 | 3.53 | 4.551 | 0.006 | 0.13 |
| 2D model | 0.952 | 0.046 | 5.08 | 4.550 | 0.007 | 0.15 |
| 1D–2D model | 0.951 | 0.045 | 4.97 | 4.544 | 0.013 | 0.28 |
| Lattice Spacing (m) | 2D Grid | 1D Grid | Consumed Time (h) | Performance (MNUPS) | Speedup Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 17.28 | 400 300 | 2026 | 0.71 | 17.09 | - |
| = 8.64 | 800 600 | 4051 | 1.90 | 25.54 | 1.46 |
| = 4.32 | 1600 1200 | 8102 | 4.47 | 43.12 | 2.52 |
| = 2.16 | 320 2400 | 16204 | 15.42 | 49.92 | 2.92 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, W.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xia, L. A 1D–2D Coupled Lattice Boltzmann Model for Shallow Water Flows in Large Scale River-Lake Systems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010108
Meng W, Cheng Y, Wu J, Zhang C, Xia L. A 1D–2D Coupled Lattice Boltzmann Model for Shallow Water Flows in Large Scale River-Lake Systems. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(1):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010108
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Wanwan, Yongguang Cheng, Jiayang Wu, Chunze Zhang, and Linsheng Xia. 2020. "A 1D–2D Coupled Lattice Boltzmann Model for Shallow Water Flows in Large Scale River-Lake Systems" Applied Sciences 10, no. 1: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010108
APA StyleMeng, W., Cheng, Y., Wu, J., Zhang, C., & Xia, L. (2020). A 1D–2D Coupled Lattice Boltzmann Model for Shallow Water Flows in Large Scale River-Lake Systems. Applied Sciences, 10(1), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010108





