2. Research Methodology
In light of the lessons learnt from past PPP projects, this study developed an empirical survey to collect feedback from practitioners on the following aspects of risk management in Malaysian PPP projects. A series of structured questionnaires were conducted, targeting managers who had hands-on experience in managing PPP projects in Malaysia. The questionnaire of
Ke et al. (
2012) was selected as a basis for the structured questionnaire as presented in this paper, with their prior permission. The usage of the following aspects of the risk identification process in Malaysian PPP projects would be examined: The techniques and process for risk identification, factors limiting implementation of risk management, factors influencing a company’s project decision making, the importance of identifying the factors that have an impact on a company’s decision making and implementation of risk management, the preferred tools and techniques, and the process of risk identification in their companies.
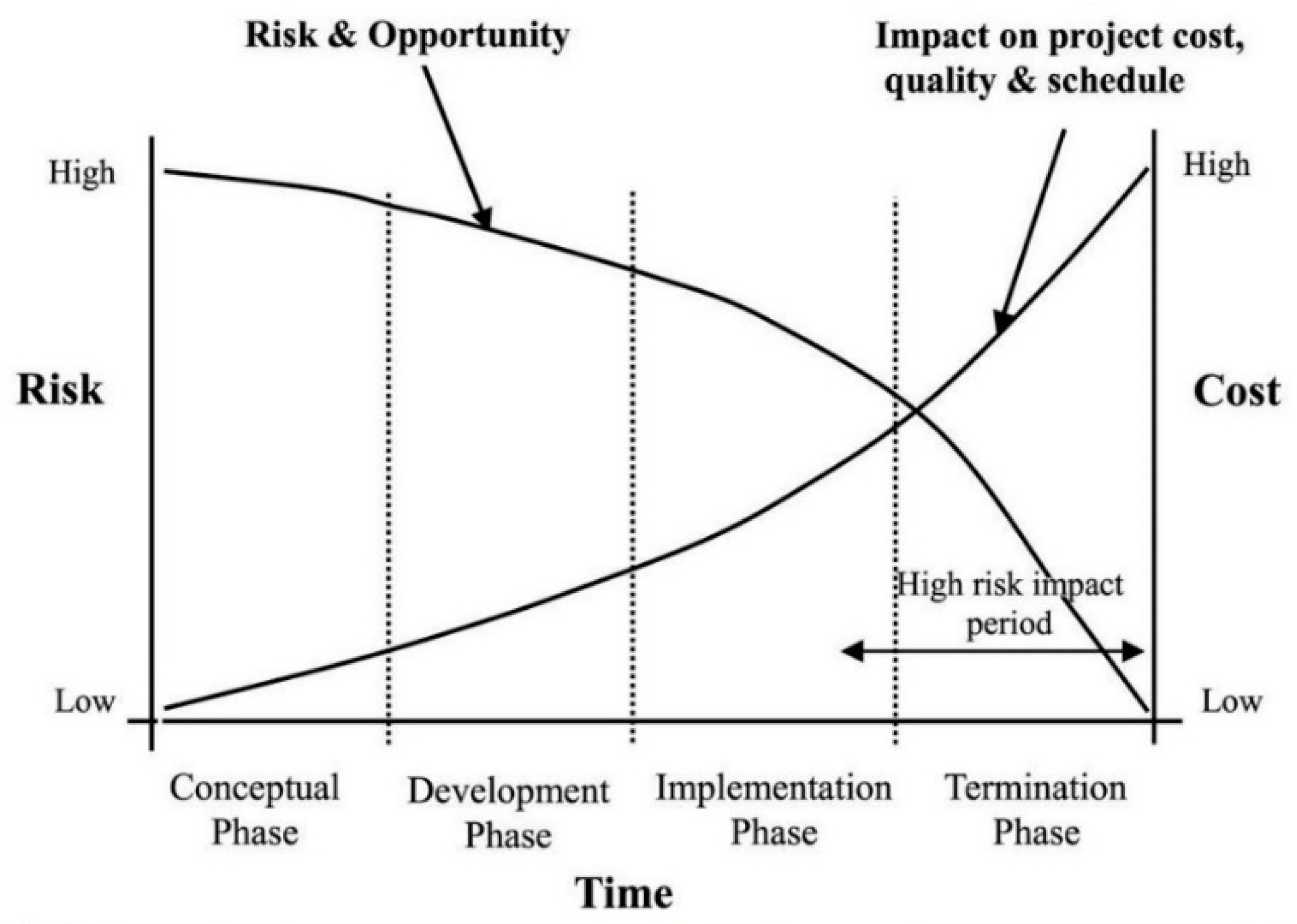
As shown in
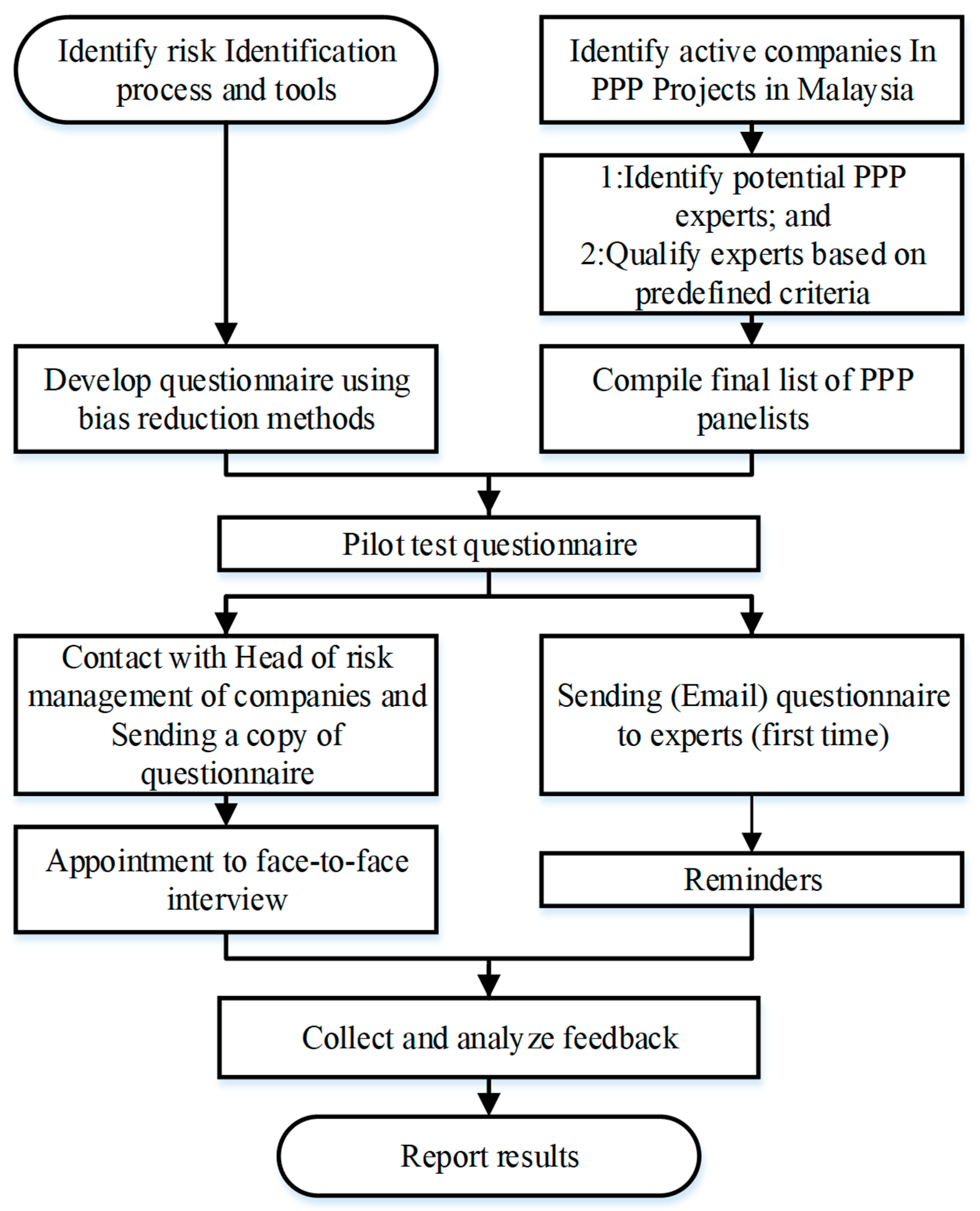
Figure 2, the research was conducted in a stage-by-stage process. First, a comprehensive analysis of previous research as a literature review was carried out to get in-depth knowledge on tools used in the risk identification process as well as knowledge on PPP. This step led to the development of a pilot study. At the same time, Malaysian companies engaged in PPP projects were identified. The companies were selected in consultation with the Public–Private Partnerships Unit (UKAS). It was believed that UKAS is the most prestigious source to identify Malaysian companies actively participating in PPP projects. This stage also led to the compilation of the final list of PPP experts.
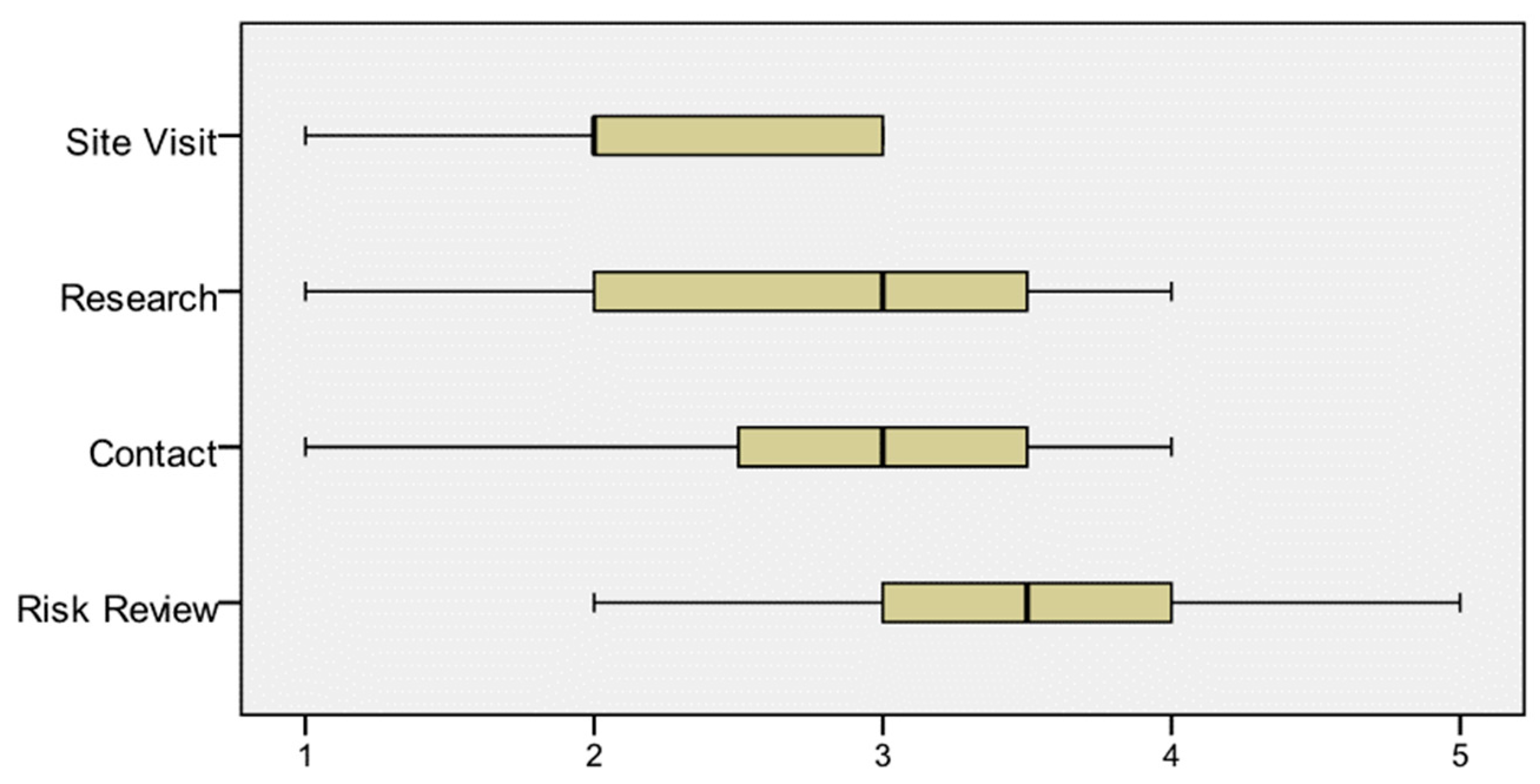
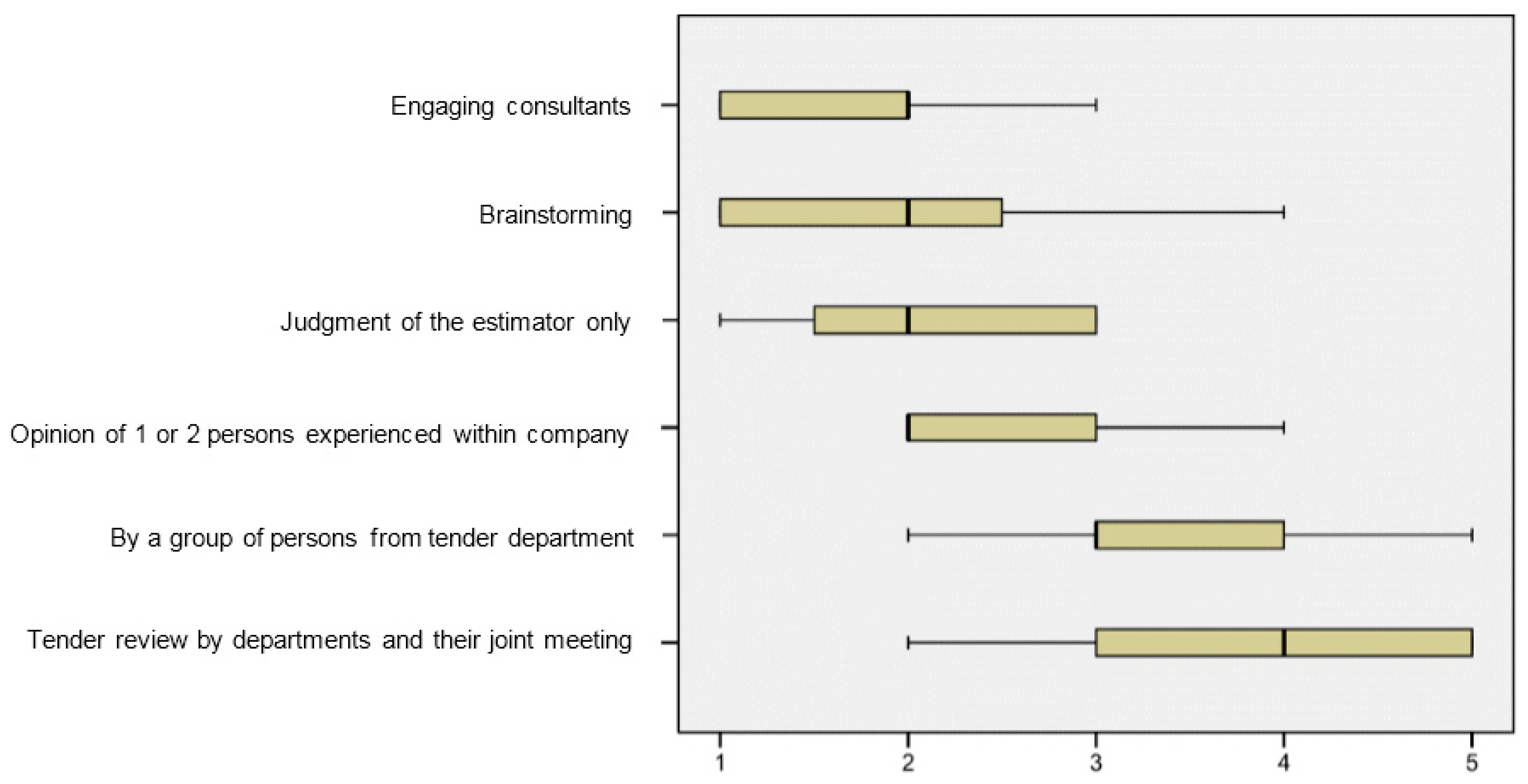
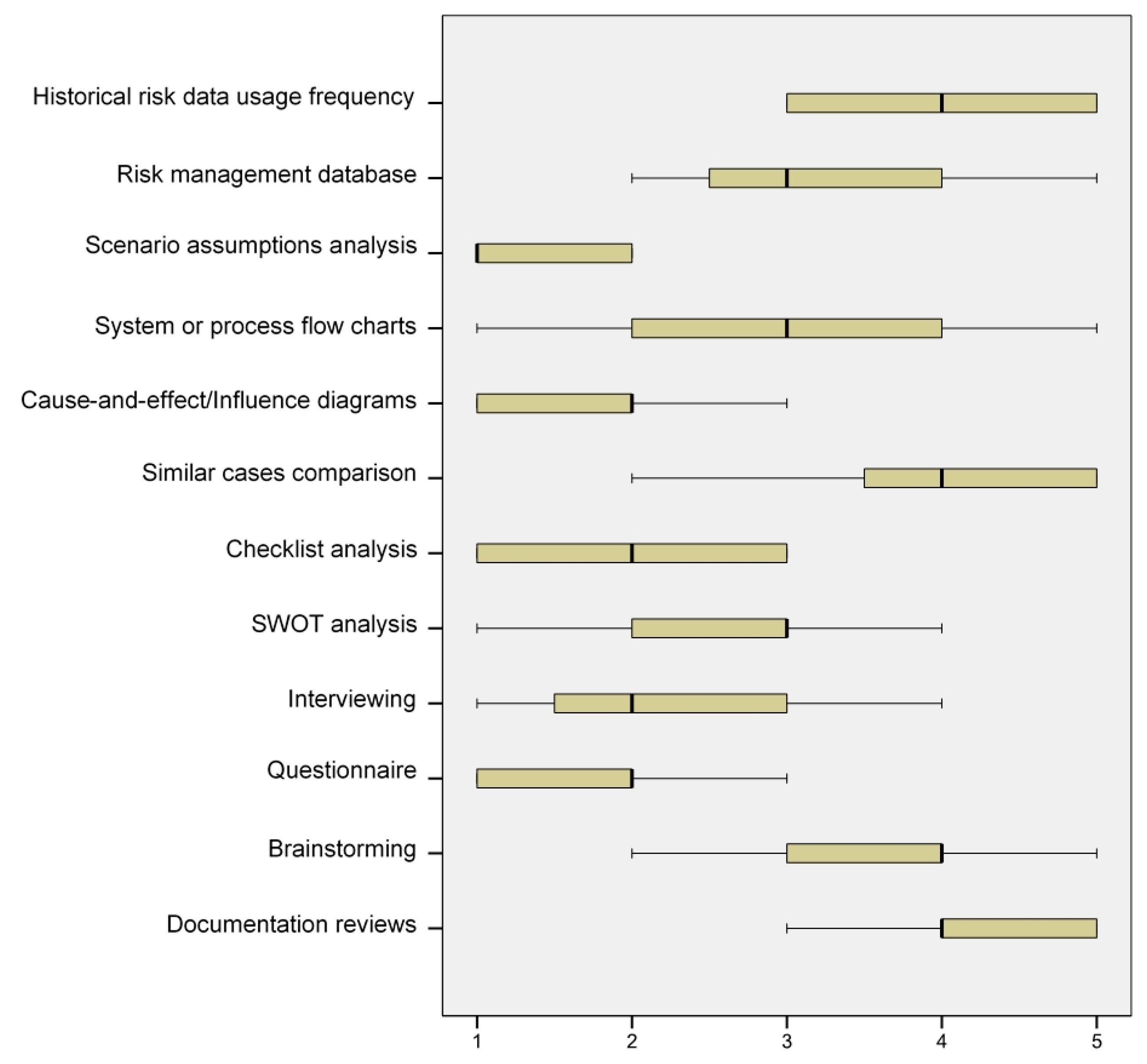
Before launching a main questionnaire survey, a pilot study was carried out to enhance the appropriateness of the survey. The field work started with a pilot study, including a meeting with construction professionals in a construction company actively participating in PPP projects. The company is specialised in residential and highway projects. It is based in Kuala Lumpur. Four managers attended the workshop: The operational manager, the financial manager, the risk and safety manager, and the contracting and tendering manager. It was an exploratory study for gaining better appreciation and understanding of the real risk analysis practice. Simultaneously, a pilot survey form was sent to ten experts of construction and PPP projects in Malaysia, and they were requested to vet the draft survey form and give their comments, including on the way the questions were set, the clarity of the questions, and the suitability of the options available for improvement of the draft survey questionnaire. The questionnaire was then modified based on the results of the pilot study. During this phase, the researchers conducted a consultation with our advisory group members about their priorities for the provision of a number of different formats for the questionnaire. Eventually, risk reviews, contact, research, and site visits were selected to investigate how risks are identified by the companies. In addition, a tender review by departments and their joint meeting, by a group of persons from the tender department, the opinion of 1 or 2 persons experienced within the company, judgement of the estimator only, and brainstorming and/or engaging consultants were selected as final items of company procedure for risk identification. Meanwhile, during the pilot survey, documentation reviews, brainstorming, questionnaires, interviewing, SWOT analysis, checklist analysis, similar cases comparison, cause-and-effect/influence diagrams, system or process flow charts, scenario assumptions analysis, risk management databases, and historical risk data usage frequency were approved by experts as risk identification tools used by the companies. Finally, the last version of the questionnaires was ready for distribution after modifications. In this study, the sample involved the private sector in PPP projects in Malaysia. The expert team included a member of a board of directors, a senior executive, a project manager, a technical director, a system engineer, and a quantity surveyor. Approximately 70 percent of them had over five years’ experience in PPP projects and were mostly at top management levels. Secondly, the questionnaire survey was executed to collect data regarding PPP projects in Malaysia and, finally, a comparative analysis of PPP project in Malaysia.
The mean score (MS) method was applied by
Chan and Kumaraswamy (
1996) to evaluate the relative importance of the causes of construction delays in Hong Kong. The MS method also has been used to analyse data by other researchers such as:
Xu et al. (
2010);
Islam et al. (
2018) and
Xiang et al. (
2018). A similar method was employed for data collected analysis in this study. In order to calculate the mean score for each factor, the five-point Likert scale was employed. Then, the ranking from most important to least important was determined. The mean score was calculated using the following formula:
where MS is mean score; f is frequency of each rating (1–5); s is a score given by expert based on a five-point scale from 1 to 5; and N is total number of respondents (N = 88).
Due to limitations in time and resources, the geographical scope of the study was limited to Malaysia. From the aspect of the amount of capital invested, Malaysia is one of the ten top countries in the implementation of PPP projects among developing countries; and Malaysia is the most active country in Southeast Asia in terms of PPP projects. However, based on the
World Bank Database (
2015), the percentage of cancelled PPP projects in Malaysia is 5 times higher than the global average. The private sector in Malaysia has been involved for so long in providing public facilities. It has existed since the mid-1980s, due to a major economic recession that badly affected the whole world and caused the government to be engaged in seeking help and assistance from the private sector for carrying out economic activities and their development (
Ismail and Rashid 2007).
The diversity of the states within Malaysia provided a rich source of data and information to the research. However, the major limitation of this study is the fact that, similar to other developing countries, only particular companies within Malaysia are able to implement PPP projects. Therefore, the sample size was limited to a few companies possessing the experience and knowledge of PPPs and actively participating in PPP projects (given by the Public–Private Partnerships Unit (UKAS)).
3. Survey Description
The collection of data is a very essential and complex step of any research. The manner of data collection depends on the question that the research intends to solve, along with the philosophical orientation of the researcher (
McCrae et al. 2011). Various tools and methodologies can be used for collecting data. The type of method one decides to choose depends on the objectives, research questions, and the approach one would follow while conducting research. In the case of the mixed-methods approach, the researcher would initiate the research using qualitative research tools to better understand the phenomenon and would then be able to propose a theory (
Hertz and Thomas 1983). Thereafter, the researcher would use quantitative tools to test the theory. Alternatively, the researcher could also survey the population and propose a hypothesis, then conduct interviews and case studies for validation of the hypothesis. Out of the numerous data collection tools that are available, conducting surveys (in form of questionnaires or interviews) and case studies are the most commonly used techniques in social science research.
The sample size and the representativeness of the sample should always be a key consideration. At the beginning, a researcher needs to define the population by setting up a sampling frame, which is a list of all cases that form the population (
Hoxley 2009). Ideally, the sampling frame should be a complete list of the population members. However, in practice, this may be impossible. In this research project, for instance, the sampling frame was a list of Malaysian construction companies actively participating in PPPs obtained from the UKAS database. Having experience in PPP projects was a key item to selecting a team of specialists.
Questionnaire Survey
The questionnaire included two sections in total. In section A, four questions were asked to get information about the type of PPP projects, type of role, and years of experience in the construction industry and PPP projects. These questions were to identify the background of the respondents and to certify their responses. Section B included the main questions about the techniques and process for risk identification, factors limiting the implementation of risk management, and factors influencing a company’s project decision making. The creation of the questionnaire was based on all previously published research papers and the information that was collected from the literature review about the risk identification stage in PPP projects. In this section, the experts were asked to convey their views regarding the importance of identifying the factors that have an impact on a company’s decision-making and implementation of risk management. Additionally, the respondents were asked to indicate the preferred tools and techniques and the process of risk identification in their companies.
As for B, the answers were presented in a 5-point Likert scale, i.e., 1 = very low, 2 = low, 3 = moderate, 4 = high, and 5 = very high. A five-point Likert scale can help interviewees to clarify their views of agreement or disagreement on the importance of different factors (
Burns et al. 2008;
Yuan et al. 2018). The use of 5-point Likert scales has been popular in construction management research, and they have also been successfully employed by several studies focusing on the identification and assessment of risks in construction projects (
Shrestha et al. 2017); thus, it was considered to be a trustworthy approach for collecting data for this study. Meanwhile, open-ended questions were employed for the last part of the questionnaires to gain more information based on the experts’ experience and understanding in this subject matter. These open-ended questions provided more freedom to respondents in sharing their knowledge and experience.
As a research tool, the questionnaire was used in order to gain expert views. In addition, the feedback collected from the questionnaire survey was analysed using various statistical methods by the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS). Prior to conducting the statistical analyses, the internal consistency and reliability of the factors was evaluated by Cronbach’s alpha (
McCrae et al. 2011) to ensure validity. The value of Cronbach’s alpha was calculated to be 0.832, indicating that a high level of uniformity among the survey responses was received. The value was greater than the threshold recommended by
Nunnally and Bernstein (
1978), who suggested that a reliability of 0.70 or higher should be sufficient in an early study on a construct’s prediction tests or hypothesised measures.
Content validity defines how representative and comprehensive the items were in presenting the hypothesis. It is assessed by examining the process that was used in generating the scale item (
Badri et al. 1995). As the questionnaire was designed based on a literature review and the opinions of interviewed experts, the content validity of the critical risk factors needs to be proven. It is believed that the items listed in the survey were highly comprehensive.
In this study, in-person consultation with the professionals and experts were chosen due to the fact that research on practical risk identification and risk management of PPP projects in Malaysia was found to be insufficient. Meanwhile, there are good numbers of practitioners and experts with hands-on experience in a specialised field. Participants were contacted by email for this research. The identity of the panellists chosen for the questionnaire analysis was undisclosed. The survey was launched in November and December 2014. The response rate to a questionnaire for the study was 44%. The percentage of experts is usually between the ranges of 40 to 77 percent. This statement can also be confirmed by
Lipnicka and Dado (
2013). The size of the sample was considered adequate for the purposes of data analysis when compared to other studies in the field of PPPs (
Yuan et al. 2018;
Ng et al. 2010).
5. Conclusions
The findings from the current study are impactful to risk management in PPP projects, with implications for both practice and academia, given the limited research studies of this nature. Some of the findings of the study are not unexpected, but the present results are significant in at least two major aspects. One of the issues emerging from the findings is that internal barriers were more important than external factors in limiting the implementation of risk management. This can be reflected in the absence of a risk management culture in the companies. Meanwhile, allocating and managing risks is one of the most important factors for achieving success in the implementation of PPP projects (
Valipour et al. 2015).
Although the brainstorming and questionnaire approaches use the experience of the experts as a collective group approach, the results showed that the review of documents, similar case comparisons and historical risk data usage frequency are the most frequently used risk identification techniques, while these techniques rely heavily on the insight and experience of over two experts within the company. Therefore, it is reasonable to use a combination of several risk identification tools, such as questionnaires and checklists, for PPP projects with high level of complexity, which should ensure that all external and internal risks within the project are identified.
Compared with another study about risk management practice in China’s PPP projects by
Ke et al. (
2012), it can be understood that similar identification tools are used by China’s companies. Another issue emerging from the findings is that, due to the low level of individual knowledge and experience of risk identification and management in PPPs in developing countries and also the unfamiliarity of most participants with risk identification tools, a database for risk identification can be a suitable alternative.
Based on the outcome of the survey, this study reports on assessing private partners’ risk identification approaches for PPP projects in Malaysia at the estimating stage and also evaluates their process of risk identification. The result shows that the most frequently applied risk identification procedure is group exercise, for instance, a tender review by departments and their joint meetings, as well as with a group of persons from the tender department. Historical information and previous experience play an undeniably important role in ensuring a smooth risk identification process. The majority of the previous research related to this field of study agreed that group exercise is always the best option for risk identification, regardless of any technique employed. This is because an individually conducted risk identification process may be not as effective as group exercise, since the experience and knowledge is limited.
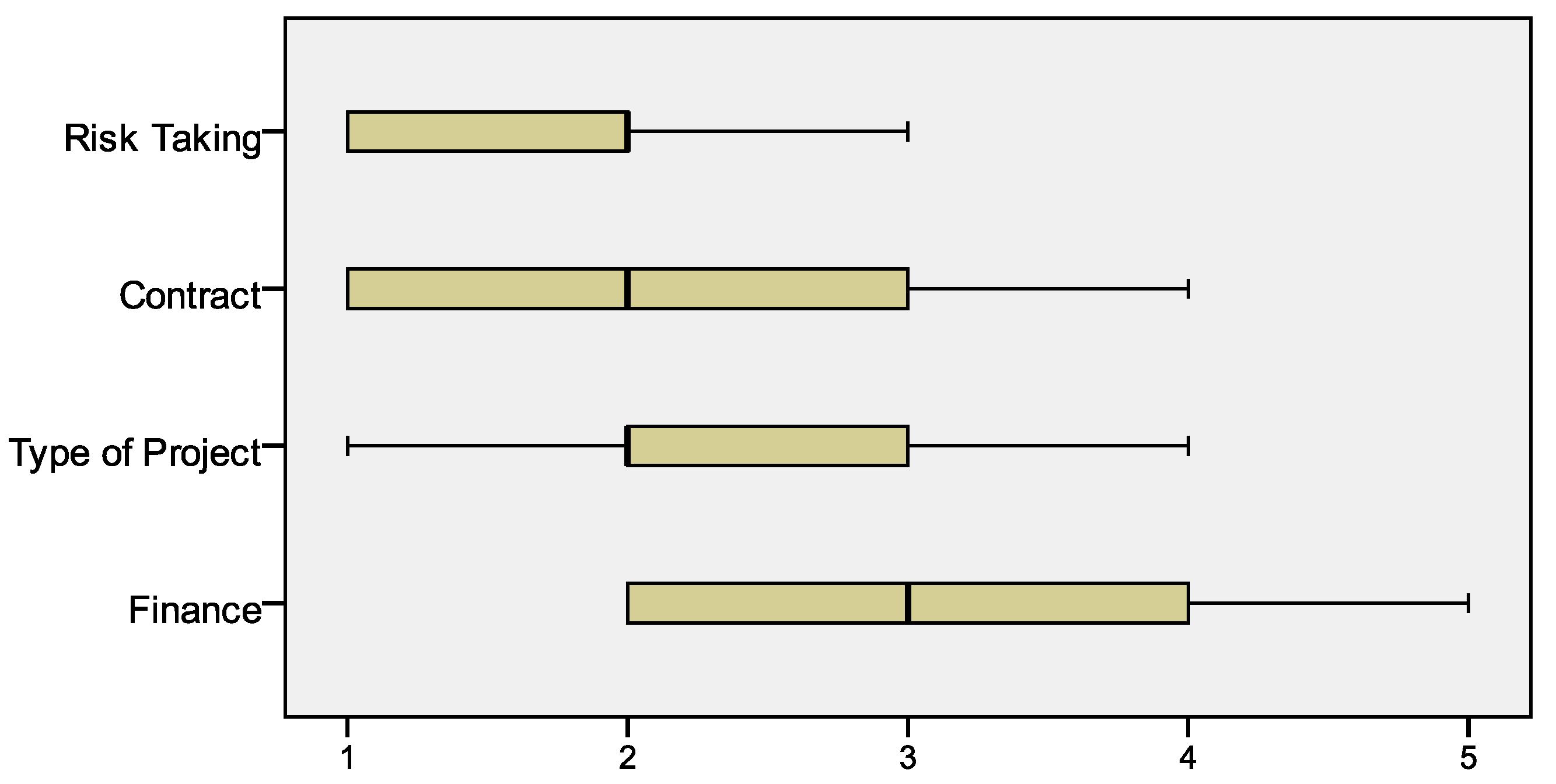
The study has explained that lack of time is the primary reason restraining risk management programmes in companies. Meanwhile, money is not listed as the most important factor. This may be due to the fact that in the construction business, production only starts after the client’s request. Connivance, an opportunity arising from a proper risk management programme, or lack of attention to the existing potential risks, may jeopardise the project objectives. Thus, the early development of a risk management plan during the initial stage of the project plays a significant role in helping the management to cater for major issues and keep the situation under control. Though it is not possible to generalise risk factors since they are unique to each different project, the findings in this study might contribute by helping both of public and private sectors to make decisions during the bidding, estimating, and tendering stages. Furthermore, it is also helpful in helping them to improve their risk management plan by considering the construction industry risk factors.