The Mediating Roles of Service Experience and Satisfaction: How Servicescape Influences Loyalty and Electronic Word-of-Mouth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Theoretical Foundation: An Integrated S-O-R, EDT, and Affective-Cognitive Framework
2.2. Servicescape as a Multidimensional Stimulus
- Space and Functionality: The layout, furniture arrangement, and facility design that affect comfort, privacy, and movement (Jin & Xiao, 2016).
- Signs and Symbols: Intentional design elements, branding, and “Instagrammable moments” that communicate value and encourage social sharing—a critical element in café environments where visual appeal drives digital marketing through user-generated content (Situmorang et al., 2018).
- Employees: Frontline staff whose demeanor, professionalism, and interactions directly shape the social atmosphere and perceived service quality (Ali et al., 2021).
2.3. Service Experience as Affective Organism
2.4. Customer Satisfaction as Cognitive Organism
2.5. The Loyalty-e-WOM Relationship
2.6. The Mediating Pathways
2.6.1. Customer Loyalty as Mediator
2.6.2. Service Experience as Mediator
2.6.3. Customer Satisfaction as Mediator
3. Materials and Methods
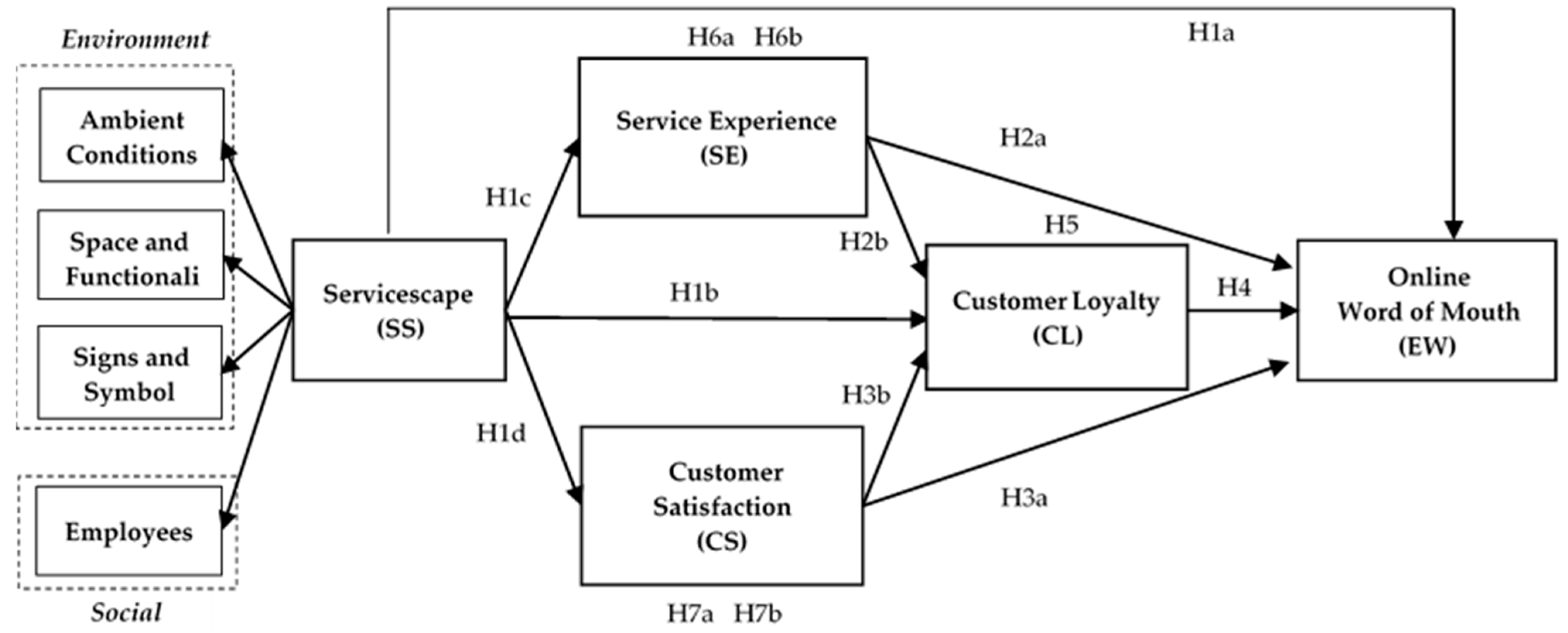
3.1. Research Design and Conceptual Framework
3.2. Population, Sample, and Data Collection
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Demographic of Customers
4.2. Reliability Testing
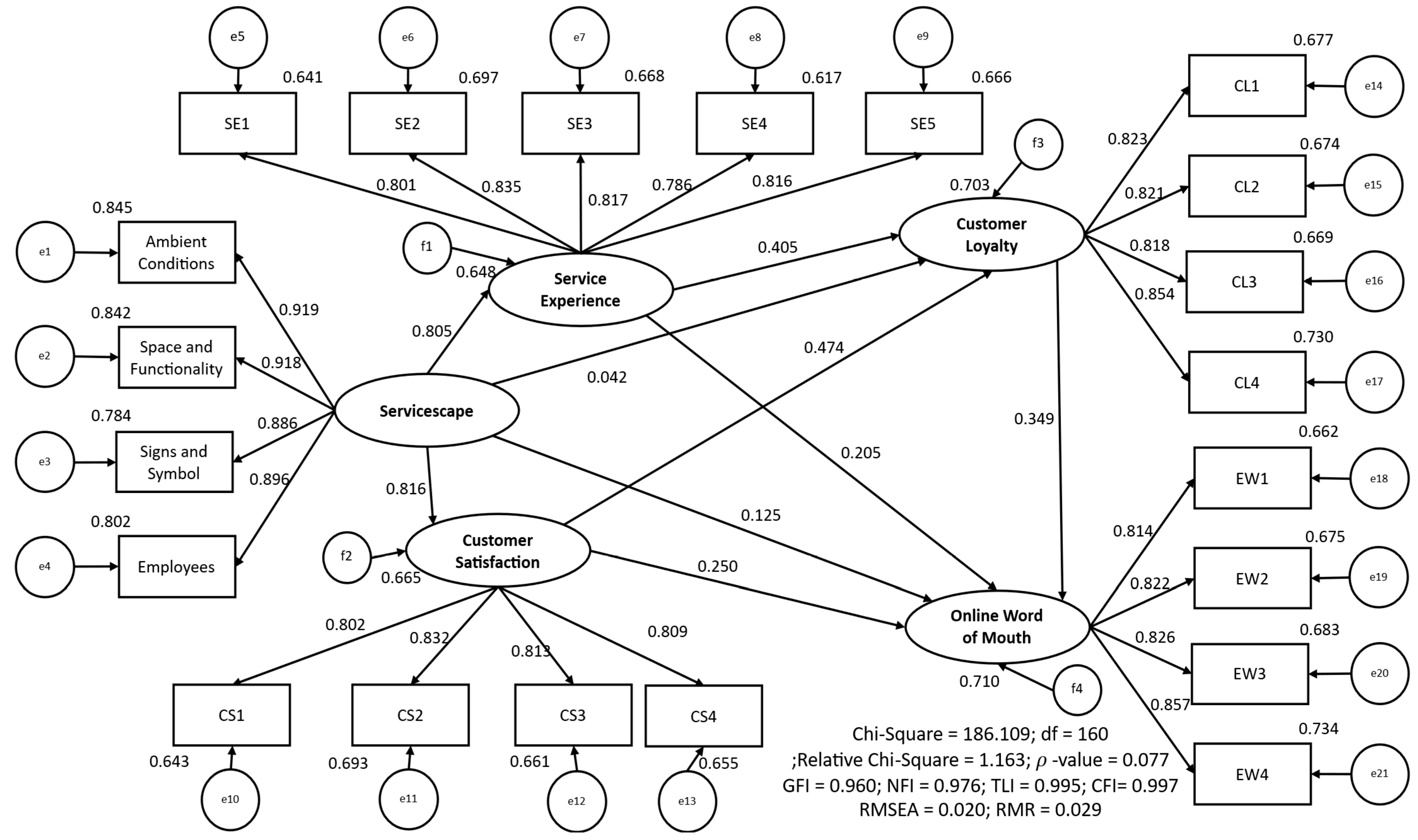
4.3. Structural Equation Modeling Analysis—Testing the Integrated S-O-R Framework
4.3.1. Stimulus to Organism Pathways: Dual Mechanisms Confirmed
4.3.2. Organism to Response Pathways: Distinct Behavioral Influences
4.3.3. Hypothesis Testing Summary: Direct Effects
4.3.4. Mediation Pattern Evidence
4.4. Mediation Analysis—Testing Indirect Pathways
4.4.1. Service Experience as Mediator: Affective Pathway Confirmed
4.4.2. Customer Satisfaction as Mediator: Cognitive Pathway Established
4.4.3. Loyalty as Mediator: Non-Significant Pathway
4.4.4. Total Indirect Effects and Mediation Patterns
5. Discussion
5.1. Reconciliation of Contradictory Empirical Evidence
5.2. Dual Pathways: Affective Versus Cognitive Mechanisms
5.3. Clarification of Behavioral Sequence and Mediation Patterns
5.4. Theoretical Focus on the Service Environment
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoretical Contributions
6.2. Practical Implications
- Dual-Pathway Design: Servicescape elements should address both affective and cognitive pathways. Atmospheric features (e.g., nature-themed designs, Instagrammable spots) primarily enhance service experience and stimulate digital sharing, while functional elements (e.g., layout efficiency, employee professionalism) more directly influence satisfaction evaluations. This distinction enables targeted resource allocation based on strategic objectives.
- Employee Development: Service staff should be trained to support both pathways simultaneously. Beyond functional competence, employees should develop interpersonal skills that create positive emotional experiences, as the social dimension of servicescape significantly influences both affective and cognitive responses.
- Strategic Monitoring: Service experience and customer satisfaction should be monitored as leading indicators of behavioral outcomes. Given their full mediation role, changes in these psychological states will manifest in loyalty and e-WOM, providing early signals for managerial intervention.
- Experience Integration: Environments should balance visual appeal with functional comfort to encourage both immediate sharing and sustained patronage. The finding that both pathways influence e-WOM suggests that aesthetically pleasing yet practically comfortable spaces optimize organic digital marketing through user-generated content.
6.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abidin, R., Yudistria, Y., & Ramli, A. (2025). The effect of customer experience, customer satisfaction and word of mouth on customer loyalty. Jurnal Ilmiah Manajemen Kesatuan, 13(2), 685–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M., Ting, D., Salim, L., & Rehman, M. (2021). Influence of servicescape on behavioural intentions through mediation and moderation effects: A study on Malaysia’s full-service restaurants. Cogent Business & Management, 8(1), 1924923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitner, M. J. (1992). Servicescapes: The impact of physical surroundings on customers and employees. Journal of Marketing, 56(2), 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datareportal. (2024). Digital 2024: Thailand. Kepios. Available online: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2024-thailand (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Dedeoglu, B. B., Bilgihan, A., Ye, B. H., Buonincontri, P., & Okumus, F. (2018). The impact of servicescape on hedonic value and behavioral intentions: The importance of previous experience. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 72, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginting, M. B., Lubis, A. N., & Sembiring, B. K. F. (2022). The influence of servicescape and brand image on consumer loyalty with consumer satisfaction as an intervening variable at The Coffee Crowd Medan. International Journal of Research and Review, 9(8), 483–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulertekin, S., & Genc, V. (2021). The effect of servicescape on revisit intention in restaurants: The mediating effect of brand familiarity. Journal of Tourism Leisure and Hospitality, 3(1), 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2019). Multivariate data analysis (8th ed.). Cengage Learning. [Google Scholar]
- Hennig-Thurau, T., Gwinner, K. P., Walsh, G., & Gremler, D. D. (2004). Electronic word-of-mouth via consumer-opinion platforms: What motivates consumers to articulate themselves on the Internet? Journal of Interactive Marketing, 18(1), 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6(1), 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthasang, C., Thiamjite, P., & Thongchan, S. (2022). Influence of servicescape on customer loyalty of coffee shop: Testing the role of customer satisfaction as mediation. Business Administration and Management Journal Review, 14(1), 106–125. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S., & Xiao, T. (2016). Brand personality, consumer satisfaction, and loyalty: A perspective from denim jeans brands. Family and Consumer Sciences Research Journal, 44(4), 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliana, J., Sihombing, S., & Antonio, F. (2025). Unveiling memorable tourism experiences effect on positive EWOM: Focus on the role of positive and negative emotion. Cogent Social Sciences, 11(1), 2557073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, P., Koloth, S., & Mekoth, N. (2016). Consumer satisfaction in retail stores: Theory and implications. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 40(6), 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandampully, J., Bilgihan, A., & Amer, S. M. (2023). Linking servicescape and experiencescape: Creating a collective focus for the service industry. Journal of Service Management, 34(2), 316–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazungu, I., & Kubenea, H. (2023). Customer satisfaction as a mediator of service facility and word of mouth in higher learning institutions. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education, 15(5), 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R. A., Racherla, P., & Bush, V. D. (2014). What we know and don’t know about online word-of-mouth: A review and synthesis of the literature. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 28(3), 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçan, M., & Yıldız, E. (2025). Mediator and regulatory effects of word of mouth on the effect of electronic servicescape on brand equity. Journal of Economics and Administrative Sciences, 26(1), 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-C., & Nakhata, C. (2019). The impact of electronic word-of-mouth on customer satisfaction. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 27(3), 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S., & Kim, D. Y. (2022). The impact of visual appeal of food and restaurant interior on willingness to pay and electronic word-of-mouth. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 105, 103278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, F., Clark, M., & Wilson, H. (2011). Customer experience quality: An exploration in business and consumer contexts using repertory grid technique. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 39(6), 846–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Line, N. D., Hanks, L., & Kim, W. G. (2018). An expanded servicescape framework as the driver of place attachment and word of mouth. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 42(3), 476–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., Hoffman, J. M., West, S. G., & Sheets, V. (2002). A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychological Methods, 7(1), 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabian, A., & Russell, J. A. (1974). An approach to environmental psychology. The MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, N., & Ueasangkomsate, P. (2023). The role of servicescape and social interaction affecting customer service experience in the coffee shop. Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Research in Asia, 29(1), 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, R. L. (1980). A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. Journal of Marketing Research, 17(4), 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R. L. (1996). Satisfaction: A behavioral perspective on the consumer. McGraw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, M.-Y., Chu, H.-C., Wang, S.-C., & Chen, Y.-M. (2013). Electronic word of mouth analysis for service experience. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(6), 1993–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1988). SERVQUAL: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perceptions of service quality. Journal of Retailing, 64(1), 12–40. [Google Scholar]
- Pine, B. J., II, & Gilmore, J. H. (2011). The experience economy: Updated edition. Harvard Business Review Press. [Google Scholar]
- Putra, R., Fauzi, A., & Lubis, A. N. (2020). The effect of servicescape on customer loyalty with customer satisfaction as an intervening variable at Killiney Coffee Shop Medan. International Journal of Research and Review, 7(10), 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Rini, E. S., Muchsin, S., & Dendy, D. (2021). Analysis of the effect of servicescape and service quality on customer satisfaction at post shop coffee Tofee in Bogor City. Aptisi Transactions on Technopreneurship, 4(1), 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, M., & Yuniarinto, S. (2023). The effect of customer experience on customer loyalty mediated by customer satisfaction and customer trust (Study on users of PLN mobile application at PLN UP3 Malang). Journal of Economics and Business Letters, 3(3), 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silanoi, T., Meeprom, S., & Jaratmetakul, P. (2022). Consumer experience co-creation in speciality coffee through social media sharing: Its antecedents and consequences. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences, 14(4), 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situmorang, S. H., Mulyono, H., & Azmi, A. (2018). Effect of servicescape and customer experience on social location marketing (case study at Caf, in Medan). In Proceedings of the 1st economics and business international conference 2017 (EBIC 2017) (p. 46). Atlantis Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suanchimplee, T., Ruanguttamanun, C., & Wongkhae, K. (2023). The effect of servicescape on eWOM intention for sustainable community-based tourism development: A case study of homestay in Thailand. Journal of Roi Kaensarn Academi, 8(12), 420–432. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, R. (2019). The moderating role of customer engagement experiences in customer satisfaction–loyalty relationship. European Journal of Marketing, 53(7), 1278–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walean, R., Lumawir, F., & Mandagi, D. (2025). The interplay of engagement rate, E-WOM, digital advertising and customer loyalty: Mediating role of brand trust. Journal of Economic, Bussines and Accounting, 8(5), 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P., Wu, L., Gao, L., & Mattila, A. (2025). The servicescape and its impact on consumer satisfaction: A meta-analysis. Psychology & Marketing, 42(3), 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y., & Kim, D. (2025). The effects of the physical environment of golf practice ranges on exercise flow and word-of-mouth intention: Focusing on the mediating role of exercise flow. Research in Dance and Physical Activity, 9(2), 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. (2022). Service trust and customer loyalty in China’s hotel services: The causal role of commitment. Sustainability, 14(13), 8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. (2020). Examining the role of emotion in online consumer reviews of various attributes in the surprise box shopping model. Decision Support Systems, 136, 113344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V. A., Berry, L. L., & Parasuraman, A. (1996). The behavioral consequences of service quality. Journal of Marketing, 60(2), 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T., & Zhao, X. (2020). The power of aesthetic: How restaurant interior design influences customer behavior. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 45, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Items | Details | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 101 | 24.05 |
| Female | 291 | 69.29 | |
| LGBTQIA+ | 28 | 6.67 | |
| Age | 20–29 Years | 201 | 47.86 |
| 30–39 Years | 116 | 27.62 | |
| 40–49 Years | 61 | 14.52 | |
| More than 50 Years | 42 | 10.00 | |
| Marital Status | Single | 271 | 64.52 |
| Marry | 130 | 30.95 | |
| Divorce | 19 | 4.52 | |
| Education | Primary education | 4 | 0.95 |
| Secondary education | 52 | 12.38 | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 317 | 75.48 | |
| Master’s degree | 25 | 5.95 | |
| Doctor of Philosophy | 8 | 1.90 | |
| Diploma | 14 | 3.33 | |
| Occupation | Student | 70 | 16.67 |
| Employee | 123 | 29.29 | |
| Civil servants/State enterprise employees | 90 | 21.43 | |
| Housekeeper/Househusband | 23 | 5.48 | |
| Private business/freelance/trading | 114 | 27.14 | |
| Monthly income | Less than 285 USD | 66 | 15.71 |
| 286–570 USD | 167 | 39.76 | |
| 571–857 USD | 86 | 20.48 | |
| More than 857 USD | 101 | 24.05 |
| Items | Details | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| On average, how many times per month do you visit a coffee shop? | 1–2 Time/month | 140 | 33.33 |
| 3–4 Time/month | 111 | 26.43 | |
| 5–6 Time/month | 63 | 15.00 | |
| More than 6 Time/month | 106 | 25.24 | |
| What time of day do you visit the coffee shop most often? | 5:00–8:59 a.m. | 32 | 7.62 |
| 9:00–12:00 a.m. | 125 | 29.76 | |
| 12:01–13:00 p.m. | 104 | 24.76 | |
| 13:01–16:00 p.m. | 134 | 31.90 | |
| After 16:00 p.m. | 25 | 5.95 | |
| How long do you spend in total at a coffee shop per visit? | Less than 30 min | 141 | 33.57 |
| 31 min–1 h | 162 | 38.57 | |
| 1–2 h | 89 | 21.19 | |
| More than 2 h | 28 | 6.67 | |
| The amount of money spent at a coffee shop per visit | Less than 2.85 USD/time | 127 | 30.24 |
| 2.86–8.57 USD/time | 225 | 53.57 | |
| 8.58–14.28 USD/time | 37 | 8.81 | |
| More than 14.28 USD/time | 31 | 7.38 |
| Constructs | Items | Factor Loading | CR | Cronbach’s Alpha | AVE | r2 | MSV | ASV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Servicescape | SS1: Ambient Conditions | 0.919 | 0.948 | 0.950 | 0.819 | 0.845 | 0.638 | 0.603 |
| SS2: Space and Functinionality | 0.918 | 0.842 | ||||||
| SS3: Signs and Symboe | 0.886 | 0.784 | ||||||
| SS4: Employees | 0.896 | 0.802 | ||||||
| Service Experience | SE1: Aappealing Design & Atmosphere | 0.801 | 0.906 | 0.906 | 0.658 | 0.641 | ||
| SE2: Relaxing Environment & Service | 0.835 | 0.697 | ||||||
| SE3: Perceived Value & Revisit Intention | 0.817 | 0.668 | ||||||
| SE4: Positive Social Media Sharing | 0.786 | 0.617 | ||||||
| SE5: Positive Social Interaction | 0.816 | 0.666 | ||||||
| Customer Satisfaction | CS1: Pleasant Ambiance | 0.802 | 0.887 | 0.887 | 0.663 | 0.643 | ||
| CS2: Functional Layout & Amenities | 0.832 | 0.693 | ||||||
| CS3: Clear Signage | 0.813 | 0.661 | ||||||
| CS4: Competent Staff | 0.809 | 0.655 | ||||||
| Customer Loyalty | CL1: Positive Service Experience | 0.823 | 0.898 | 0.900 | 0.687 | 0.677 | ||
| CL2: Revisit Intention | 0.821 | 0.674 | ||||||
| CL3: Price Insensitive Loyalty | 0.818 | 0.669 | ||||||
| CL4: First-Choice Advocacy | 0.854 | 0.730 | ||||||
| Online Word of Mouth | EW1: Positive Online Reviews | 0.814 | 0.898 | 0.895 | 0.689 | 0.662 | ||
| EW2: Online Brand Awareness | 0.822 | 0.675 | ||||||
| EW3: Visual Sharing Motivation | 0.826 | 0.683 | ||||||
| EW4: Influence by Online Content | 0.857 | 0.734 |
| Hypothesis | Paths | Path Coefficient | p-Value | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1a | Servicescape → Online Word of Mouth | 0.125 | 0.148 | Not Supported |
| H1b | Servicescape → Customer Loyalty | 0.042 | 0.638 | Not Supported |
| H1c | Servicescape → Service Experience | 0.805 *** | <0.001 | Supported |
| H1d | Servicescape → Customer Satisfaction | 0.816 *** | <0.001 | Supported |
| H2a | Service Experience → Online Word of Mouth | 0.205 ** | 0.004 | Supported |
| H2b | Service Experience → Customer Loyalty | 0.405 *** | <0.001 | Supported |
| H3a | Customer Satisfaction → Online Word of Mouth | 0.250 ** | 0.002 | Supported |
| H3b | Customer Satisfaction → Customer Loyalty | 0.474 *** | <0.001 | Supported |
| H4 | Customer Loyalty → Online Word of Mouth | 0.349 *** | <0.001 | Supported |
| Hypothesis | Paths | Path Coefficient | p-Value | Mediation | Relationship |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H5 | Servicescape → Customer Loyalty → Online Word of Mouth | 0.016 | 0.614 | No | Not Supported |
| H6a | Servicescape → Service Experience → Customer Loyalty | 0.348 *** | 0.000 | Full | Supported |
| H6b | Servicescape → Service Experience → Online Word of Mouth | 0.181 * | 0.022 | Full | Supported |
| H7a | Servicescape → Customer Satisfaction → Customer Loyalty | 0.413 *** | 0.000 | Full | Supported |
| H7b | Servicescape → Customer Satisfaction → Online Word of Mouth | 0.224 * | 0.013 | Full | Supported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wichitsathian, S.; Suvittawat, A. The Mediating Roles of Service Experience and Satisfaction: How Servicescape Influences Loyalty and Electronic Word-of-Mouth. Adm. Sci. 2025, 15, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15120485
Wichitsathian S, Suvittawat A. The Mediating Roles of Service Experience and Satisfaction: How Servicescape Influences Loyalty and Electronic Word-of-Mouth. Administrative Sciences. 2025; 15(12):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15120485
Chicago/Turabian StyleWichitsathian, Sareeya, and Adisak Suvittawat. 2025. "The Mediating Roles of Service Experience and Satisfaction: How Servicescape Influences Loyalty and Electronic Word-of-Mouth" Administrative Sciences 15, no. 12: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15120485
APA StyleWichitsathian, S., & Suvittawat, A. (2025). The Mediating Roles of Service Experience and Satisfaction: How Servicescape Influences Loyalty and Electronic Word-of-Mouth. Administrative Sciences, 15(12), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci15120485





