Abstract
This study aimed to study the association between organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation, perceived novelty, trust in the process, and the intention to apply, engage, and finish an artificial intelligence recruitment and selection process. It was also tested whether having already had the experience of having been involved in a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence moderated these relationships. The sample for this study consisted of 299 participants. The results indicate that organizational attractiveness and perceived novelty are positively and significantly associated with applying to, getting involved in, and completing the recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence for participants aged between 45 and 54. For participants aged between 35 and 44, trust in the process significantly affects their intention to apply to, get involved in, and complete the recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence. Intrinsic motivation did not prove to be a significant predictor of the intention to apply to, get involved in, and complete the recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence.
1. Introduction
We live in one of the most technologically relevant eras of modern times. Human Resources (HR) and its management must be open to the constant developments and changes occurring in Portugal and worldwide.
How technology, with artificial intelligence (AI), has swept through companies and HR departments has triggered a significant change in the processes and decision-making that directly affect people and, in the specific case of this dissertation, job applicants.
These changes bring with them the need to understand candidates’ perceptions when placed in a scenario where all or part of a decision that influences their future in an organization is now made by technologies based on or supported by AI (Al-Alawi et al. 2021). Some studies have identified the use of AI in recruitment and selection (R&S) processes as an asset (Pan et al. 2022).
In theory, candidates will benefit due to the greater ability of machines to identify the talent needed in the organization, conducting the process with transparency, fairness, and less bias and prejudice than traditional methods (Jain et al. 2021; Lee 2011; van Esch et al. 2019). On the other hand, other scholars have been reluctant about the preponderance of this technology and its interference in the person-to-person relationship (Delecraz et al. 2022), the way it will irreversibly affect the R&S market (Hmoud and Várallyai 2019), and the ethical issues latent in this whole topic (Tambe et al. 2019).
In all the studies on this subject, there is always one element that is at the centre of the process, and without it, it would make no sense: the candidate.
From here, we embarked on a novel and significant piece of research, in which we realized that, although this is a topic that has been in vogue and widely discussed in recent years, there are few studies that focus on how candidates perceive this type of process and how it relates to effective attraction, involvement, and completion in R&S processes with the help of AI technology.
Thus, the main objective of this study was to find out what the jobseeker’s perceptions are of a process of this type and what influence this has on the process itself, an idea that materialized in our starting question:
What are the reactions of jobseekers in Portugal to a recruitment and selection process that uses technology containing artificial intelligence?
This study also aimed to determine whether, due to the use of artificial intelligence in a recruitment and selection process, attractiveness, associated intrinsic rewards, perceived novelty, and trust positively influence a candidate’s intention to get involved and complete the process.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Artificial Intelligence
As no one individual can exclusively be identified as the inventor of AI, we must highlight those who are the concept’s forerunners and who have brought us to the state of the art where the term is today.
According to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD 2019), there is a broad consensus that the 1956 Dartmouth Summer Research Project may have been the birthplace of AI, as at this event, John McCarthy, Alan Newell, Arthur Samuel, Herbert Simon, and Marvin Minsky conceptualized the principles of AI.
First, Alan Turing published an article entitled Computing Machinery and Intelligence (Turing 1950). After that, research into this subject never stopped, although the initial ecstasy was halted by the overly optimistic prospects of the time, giving rise to what experts call the AI winter (Smith et al. 2006) until the mid-1970s. That winter was to end in the 1990s when data storage and processing capacity grew exponentially, so autonomous machines began to carry out tasks that had previously been considered quite complex (OECD 2019).
Chapman and Webster (2003) focused on how this phenomenon became increasingly present in HR practices, but its growth and preponderance were essentially focused on people.
Years later, Black and van Esch (2021) confirmed that this trend had materialized, and that AI applied to R&S intensifies the competitiveness of companies, bringing talent to them quickly and, above all, reaching passive candidates, those who are not actively looking for work but are available to be recruited if they can be reached.
This evolutionary phenomenon has been driven by the rapid evolution of AI for social, strategic, and financial reasons (Jain et al. 2021). From a broader point of view, this evolution is part of what we might call the fourth industrial revolution, with new concepts such as big data, robotics, the Internet of Things, algorithms, and digital platforms (Correio et al. 2021).
Chernov and Chernova (2019) warned us that this growth in computer technology would pose new challenges for current management systems, with the speed of “artificial thinking” constantly increasing. AI’s intelligence in perceiving, analyzing, and interacting with the environment leads it to constantly learn, which allows it to solve the most complex problems without any human interaction (Chui et al. 2016). Managers are then faced with their vision and decision-making capacity versus the “inhuman” capacity of the machine.
Various authors have studied the acceptance of artificial intelligence, including Gerlich (2023, 2024). This author concluded that the preference for using artificial intelligence is mainly due to its reliability compared with human reliability.
2.2. Artificial Intelligence in the Recruitment and Selection Process
2.2.1. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Recruitment and Selection Processes
Traditional methods of searching for candidates, such as mass media adverts and print advertising, are in apparent decline (Garg et al. 2021), and online recruitment sources, known as e-recruiting, have taken center stage.
Some researchers (Chernov and Chernova 2019; Coradini and Murini 2009; Jain et al. 2021) have discussed the idea that in a globalized world where change is constant, laws, organizations, technology, social trends, and diversity act as challenges that can alter candidate perceptions, forcing R&S to change.
In a study by Lee (2011), he created one of the first models to explain the benefits of integrating electronic recruitment. The researcher explained that, due to economic, social, technological, and cultural changes, modern organizations should strategically focus on managing technological recruitment, either because of the brutal reduction in process time or because of its return on investment (ROI). A six to one differential (ROI) had previously been pointed out in a study by Buckley et al. (2004). This research indicated that for every USD 1 spent on recruitment technology, we would get a return of USD 6.
Egorov et al. (2020), in a publication on the use of chatbots in HR, pointed out that the values that Buckley et al. (2004) used to show electronic recruitment to be the right way to invest in R&S could be much higher because the continuous learning of AI means that, in the future, an employee can, for example, ask a machine what the proper steps should be for them in a leadership training program and this, according to the authors, has an incalculable return, which led other researchers, such as Derous and de Fruyt (2016), to state that the integration of AI into HR is a logical and naturally evolving process.
In this vein, Derous and de Fruyt (2016) explained that AI is gradually restructuring R&S practices and processes, using technological tools that turn companies’ institutional websites and other digital platforms into major recruitment centers.
Screening and testing processes for potential candidates are now carried out online, and the option of interviewing/hiring employees is taken autonomously. If they are not the first choice, these autonomous platforms place the aligned profiles in massive databases, in a queuing logic, where, in the event of a need, all that is required is to ask the platform for a replacement, which quickly acts as a second line option for the market (Garg et al. 2021).
2.2.2. Candidates and the Recruitment and Selection Process Using Artificial Intelligence
Although there has been little research on the subject, specifically on the relationship between the process and the perceptions that give rise to candidates’ reactions to this type of process, the evidence that people are increasingly using technological means is strong. Souza and Cunha (2019) carried out a systematic literature review in which they postulated that the use of social networks could be very close to being considered a new addiction, with the main influence on young teenagers. In a few years, this generation will represent the greatest mass of workers at the start of their careers and will be confronted almost exclusively with R&S processes of the type we have mentioned.
From another perspective, Zha and Wu (2014) concluded that in digital marketing, adverts and other forms of advertising that appear to us automatically daily when we use our smartphones, and which are controlled by AI-enabled tools, are widely considered intrusive and ignored by consumers. Hence, the brands with which they are associated tend to be less considered (Miles and McCamey 2018).
Therefore, in this crucial research, we embarked on a journey to analyze, by means of a quantitative methodology, based on broad theoretical foundations, the possibility of candidates being attracted to processes, registering, engaging, and completing them. We aim to pinpoint factors that would be perceived by candidates and trigger reactions, which will lead us to draw conclusions that are materialized in the following points. Even if the R&S process with the help of AI is more efficient and effective than its predecessor, nothing guarantees that its real value is not limited by those perceptions that triggered reaction x or y to the process (van Esch and Mente 2018).
2.3. Attractiveness and Trust in a Recruitment and Selection Context Using Artificial Intelligence
2.3.1. Indirect Attractiveness Using Artificial Intelligence during Recruitment
Some of the studies carried out on this subject (Black and van Esch 2019; Ehrhart and Ziegert 2005; van Esch et al. 2021) corroborate the idea that candidates analyze and perceive not only the recruitment processes themselves, independently of the organizations, but also draw from them an objective perception of what the organization is versus what it demonstrates in terms of applicability.
Thus, candidates perceive the use or not of innovative technologies, such as AI and its direct or indirect applications (van Esch et al. 2019), to build an image of what will perhaps be the organizational nature of the company where they intend to make their contribution.
Therefore, when an organization uses AI in its R&S processes, this can give the candidate the perception that they are dealing with an innovative organization (Nikolaou et al. 2019) that is open to new realities.
Some articles (Langer et al. 2017; Meijerink and Keegan 2016) show that there is a relationship between the use of technology in the broad sense and an organization being perceived as more attractive by candidates. Pramod and Bharathi (2016) already studied the relationship between organizations that used social media to promote themselves and postulated that this made them more attractive to potential employee candidates.
Recent studies, such as van Esch and Black (2019)’s, tell us that the factors that influence the success of an R&S process, especially with new generations, are directly related to the engagement that is created and the use of technology that is seen as innovative (Ehrhart and Ziegert 2005).
In the specific case of AI, its widespread use in organizational platforms, assessment centers, and companies specializing in R&S is still relatively recent (Delecraz et al. 2022; Hmoud and Várallyai 2019; OECD 2019; Pan et al. 2022; van Esch et al. 2021) and, as we are dealing with sophisticated, innovative, and disruptive constructs, it is reasonable to expect that candidates, when they recognize its use, will subsequently have the same perception as the organizations involved.
This is the reasoning that leads us to formulate the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1:
In a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence, attractiveness positively and significantly affects the intention to apply and complete the process.
2.3.2. Intrinsic Motivation Using Artificial Intelligence during Recruitment
Intrinsic motivation can be defined as the impulse that drives us to perform an activity (Ryan and Deci 2000), in which it can be considered that the person has so much fun that the activity (work) in itself gives rise to a feeling of personal fulfilment and empowerment, increasing levels of trust in the organization, combined with a feeling of greater independence that promotes creativity, regardless of whether or not the results are expected (Black and van Esch 2019; van Esch et al. 2019, 2021).
For Venkatesh (2000), the anticipation of using a particular technology, considered new to users, was intrinsically motivating, so individuals’ perceptions of that technology increased the likelihood of using it. From the perspective of Martín-Núñez et al. (2023), the perceived learning of artificial intelligence is related to intrinsic motivation. Another study by Fidan and Gencel (2022) concluded that students who can interact with chatbots based on artificial intelligence have higher levels of intrinsic motivation than those who do not.
Deci and Ryan (2016) realized that the greater the anticipated intrinsic motivation, the more likely individuals were to get involved in the associated process.
This feeling of being able to be in an innovative and creative environment will increase intrinsic motivation, so an R&S process that uses AI technology should be perceived as innovative, rewarding, and likely to make candidates engage and complete the process. So, we arrive at our second hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2:
In a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence, intrinsic motivation has a positive and significant effect on the intention to apply and complete the process.
2.3.3. Perception of Novelty Using Artificial Intelligence during Recruitment
Some other facts discovered during the research have to do with whether novelty is a source of direct attractiveness. A classic theory (Deci and Ryan 1985) classified novelty as a particular type of intrinsic motivation, although more recent studies (Jeno et al. 2019; van Esch et al. 2021; van Esch and Black 2019) have informed us that engaging in activities that are novel to individuals can generate feelings of enthusiasm, creativity, and innovation. These studies have proven that an activity perceived as novel can be a powerful source of attraction and motivation.
Several studies in recent years have attempted to associate the factor of technological novelty and relate it directly to the use of technology. According to van Esch and Black (2019), the more the user of a given technology anticipates using a new one, the more likely they are to be interested and involved. Other studies corroborated this theory (Wells et al. 2010), which analyzed the risk of users using or not using something new versus an old method. The following hypothesis is therefore formulated:
Hypothesis 3:
In a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence, the perception of novelty positively and significantly affects the intention to apply and complete the process.
2.3.4. Trust in Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Recruitment Systems
So far, all the hypotheses have centered on the importance of novelty as a positive influence on the constructs that lead candidates to engage in and complete an R&S process.
For Pringle et al. (2016), the use of AI in its more general scope, in the face of a society thirsty for novelty, brings with it an incalculable number of consequences. Some will jeopardize the process, others will improve it considerably, because innovation, and this novelty in particular, can make some people trust the process and others anxious (Nikolaou et al. 2019).
As can be seen in the studies of some authors who have been cross-referencing the themes that govern this study (Chapman and Webster 2003; Deci and Ryan 2016; Hausknecht et al. 2004; Nikolaou et al. 2019; van Esch et al. 2021), trust as a reaction factor is not emphasized in most of the research in the area of R&S using technology, although in other areas it is considered preponderant.
Michael Gerlich is one of the authors who has studied trust in artificial intelligence. In one of his studies, he investigated trust in artificial intelligence compared with human beings (Gerlich 2024), concluding that there is a preference for artificial intelligence, mainly due to its impartiality and accuracy in contrast to low human reliability. In another study, whose participants were academics from the United States, Gerlich (2023) concluded that trust, breadth of application, and perceived vulnerability influence public opinion, which can regard artificial intelligence as a blessing or a disgrace for humanity.
This study aims to directly analyze candidates’ trust in an R&S process in which AI is used. However, it has the challenge of entering a relatively new reality where data on whether candidates trust this type of process are limited and often held by the companies that build the AI tools (Avelar et al. 2021; Nawaz 2020).
Another relevant study was carried out by Prahl and van Swol (2017) on recent university graduates in the USA who, when faced with a surgical situation and having to decide the point of view of operating theatre management, did not show a preferential choice for counselling between a human expert and an AI. This opinion was then tested in another variable, where participants were told that the AI had already made a mistake in the past in an identical situation. The research postulated that, with this small change, the participants radically changed their opinion, totally in favor of the human side.
In the opposite direction, Logg et al. (2018), confronted with all the literature against and in favor of logical algorithms, which give rise to AI “thinking”, carried out a study in which they put groups of participants in a position to choose between a human and an algorithm when advising on a highly important decision. Surprisingly, they found results that indicated there was no aversion on the part of people to “machine” decisions, just as this study indicates that, over time, people tend to follow the algorithm’s recommendation, even when faced with alternative advice from highly credentialled human experts.
In line with this reasoning, Xu et al. (2020) carried out a study in the banking sector to see whether customers preferred to be served by a human operator or by an autonomous AI system and concluded that, for what were considered more basic tasks, customers preferred to use AI because it is faster, more dynamic, and offers a wider range of solutions to solve the problem. On the other hand, when faced with tasks that were becoming more complex and individualized, customers preferred solving their problem through a human.
Because the name of this technology (AI) contains the word “intelligence,” which tends to be seen as an exclusively human characteristic, it seems somewhat reasonable to expect that in an R&S process, there will be people who can trust this technology associated with the process and others who are reluctant to use it.
However, this literature review does not necessarily confirm that candidates will trust an R&S process because it contains AI technologies, but rather the likelihood that this increase in trust will lead to greater involvement and therefore a higher rate of completion of the R&S process. So, we arrive at our fourth hypothesis:
Hypothesis 4:
In a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence, trust in the process positively and significantly affects the intention to apply and complete the process.
The following research model summarizes the hypotheses formulated in this study (Figure 1).
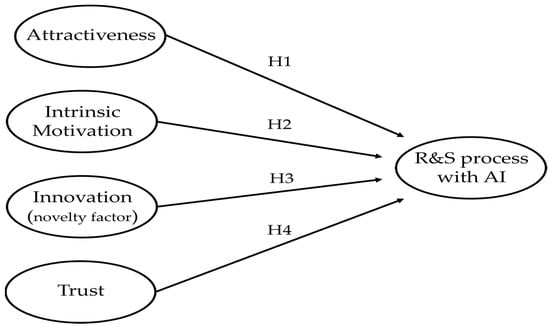
Figure 1.
Research Model.
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Collection Procedure
This study was aimed at Portuguese citizens of working age. The participants were selected through a non-probabilistic process of convenience, which, according to Marôco and Bispo (2003), means that some of the participants were selected purely accidentally, thus facilitating data collection.
The questionnaire was posted on the Google Forms platform and circulated on social and professional networks, Facebook, LinkedIn, WhatsApp, and email. At the beginning of the questionnaire, all the information about the purpose of the study was given and it was stated that the confidentiality of the answers would be guaranteed. Participants were also informed that their data would never be known, as it would only be processed as a whole. After reading the informed consent form, the participants had to answer a question about their willingness to participate in the study. If they agreed to participate in the study, they were directed to the questionnaire in the next section. If they did not agree to participate, they were directed to the end of the form. In addition to the scale used in this study, the questionnaire consisted of three sociodemographic questions (age, gender, and academic qualifications) and a question asking whether the individuals had a clear idea of having gone through a similar process in their personal experience. The data were collected between January and March 2023.
3.2. Participants
The sample for this study consisted of 299 participants aged between 19 and 70 (M = 44.44; SD = 11.92). The age of participants was transformed into age groups, and four groups were formed: up to 35 years old, 35 to 45 years old, 45 to 54 years old, and over 54 years old. Of these participants, 171 (57.2%) were female and 128 (42.8%) males. In terms of educational qualifications, 55 (18.4%) had a 12th-grade degree or less, 143 (47.8%) had a bachelor’s degree, and 101 (33.8%) had a master’s degree or higher. When asked if they had ever been in a recruitment and selection process in which AI-containing technologies were used, 53 (17.7%) said they did not know, 218 (72.9%) said no, and 28 (9.4%) said yes.
3.3. Instrument
To measure the variables under study, we used the instrument developed by van Esch et al. (2021), adapted for this study since the “anxiety” dimension was not used. This instrument is composed of six subscales: application process, organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation, innovation, confidence in the process, and anxiety. The anxiety subscale was not used in this study, as mentioned above. All the items in this instrument were classified on a Likert scale (from 1 “Strongly Disagree” to 7 “Strongly Agree”). The five subscales are made up as follows: the application process is made up of 5 items (e.g., “how likely am I to contact a company to find out more about a job vacancy if I know that artificial intelligence is used in the recruitment and selection process?”); organizational attractiveness is made up of 3 items (e.g., “I feel inspired by organizations that use new technologies such as artificial intelligence”); intrinsic motivation is made up of 5 items (e.g., “applying for a job using artificial intelligence would give me valuable feelings of personal fulfilment”); innovation is made up of 4 items (e.g., “using artificial intelligence platforms to apply for jobs offers me new experiences”); and trust in the process is made up of two items (e.g., “using artificial intelligence to apply for a job seems safe to me”).
An exploratory factor analysis was initially carried out to test validity. A KMO of 0.91 was obtained, and Bartlett’s test proved to be significant (p < 0.001), which indicates that the data come from a multivariate population (Pestana and Gageiro 2003). This instrument comprises five dimensions that explain 79.78 per cent of its total variability.
A five-factor confirmatory factor analysis was then carried out. The fit indices obtained were adequate (χ2/gl = 2.06; GFI = 0.91; CFI = 0.97; TLI = 0.96; RMSEA = 0.059; SRMR = 0.136), confirming the five factors’ existence. Composite reliability varied between 0.88 (innovation) and 0.94 (trust), which indicates that all the dimensions had good composite reliability. Good convergent validity values were also obtained for all the dimensions, with AVE values ranging from 0.64 (innovation) to 0.89 (trust). The AVE square root values were higher than the correlation values between the respective factors, which indicates the existence of discriminant validity. As for internal consistency, Cronbach’s alpha was 0.90 for the application process using AI, 0.92 for organizational attractiveness, 0.93 for intrinsic motivation to apply, 0.89 for innovation, and 0.94 for trust in the process.
As for the sensitivity of the items, all of them had responses at all points, none of them had the median leaning against one of the extremes, and their absolute values of asymmetry and kurtosis were below 3 and 7, respectively, which indicates that they did not grossly violate normality (Kline 1998).
3.4. Data Analysis Procedure
Once the data had been collected on Google Forms, it was imported into SPSS Statistics software 29 (SPSS; IBM Corp 2021). The first step was to test the metric qualities of the instruments used in this study. To validate the scale, exploratory factor analysis was first carried out, the aim of which is to discover and analyze the structure of a set of interrelated variables to construct a measurement scale for (intrinsic) factors that, in some way, control the original variables (Marôco 2021). The KMO (Keiser-Meyer-Olkin) value should be greater than 0.70 and the Bartlett’s test should be significant, thus indicating that the data come from a normal multivariate population (Pestana and Gageiro 2003). Two confirmatory factor analyses were then carried out using AMOS Graphics software 29 (SPSS; IBM Corp 2021), with one and five factors, to confirm the factor structure of this instrument (Arbuckle 2008). The maximum likelihood estimation method and the covariance matrix were used (Russell 2002). The recommendations set out by Hu and Bentler (1999) were followed, combining the six fit indices: chi-square ratio/degrees of freedom (χ2/gl); Tucker–Lewis Index (TLI); Goodness-of-fit Index (GFI); Comparative, et al. (CFI); Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA); and Root Mean Square Residual (RMSR). For chi-square, a value ≤ 5 was considered acceptable. For CFI, TLI, and GFI, values above 0.90 were considered acceptable. For RMSEA, values below 0.08 were acceptable (Wright and Bonett 2002). Finally, concerning RMSR, the lower the value, the better the fit (Hu and Bentler 1999). To establish good construct validity, good convergent validity, and good discriminant validity and to check the risks associated with common variance methods, it was essential to obtain a good fit for the measurement model (Podsakoff et al. 2003).
Next, internal consistency was tested by calculating Cronbach’s Alpha, the value of which should vary between “0” and “1” and should not be negative (Hill and Hill 2002). In organizational studies, Cronbach’s Alpha greater than 0.70 was considered an appropriate value (Bryman and Cramer 2003).
The items’ sensitivity was tested by calculating the median, minimum, maximum, asymmetry, and kurtosis. The items’ medians should not touch any of the extremes; they should have responses at all points, and the absolute values of skewness and kurtosis should be below 3 and 7, respectively (Kline 1998).
The association between the variables under study was analyzed using Pearson’s correlations. To test the effect of sociodemographic variables on the variables under study, parametric t-student tests for independent samples and One-Way ANOVA were used. Path analysis was used to test the hypotheses formulated in this study, carrying out multi-group analyses according to age group.
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics for the Variables under Study
To understand the position of the answers given by the participants in this research, descriptive statistics were carried out on the variables under study.
Firstly, as Figure 2 shows, regardless of the theoretical basis of van Esch and his team, our research and all the information circulating on the subject, whether in the form of published scientific knowledge such as Al-Alawi et al. (2021), Garg et al. (2021), Hmoud and Várallyai (2019), Nawaz (2020), Nikolaou et al. (2019), Pan et al. (2022), Pramod and Bharathi (2016), Soares et al. (2020), Tambe et al. (2019), and van Esch et al. (2020), as well as in the varied news stories that have appeared on the subject in the national and international media, which show us the exponential growth of this type of technology, the overwhelming majority of participants say that they have either never taken part in a process of this type (73.2%) or do not know whether they have or not (17.4%).
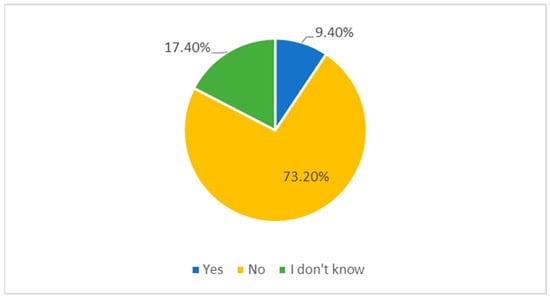
Figure 2.
Participation in the R&S process with previous knowledge of using AI.
According to Table 1, the variables themselves, the intention to apply to, get involved in, and finish the AI-enabled R&S process, organizational attractiveness, perceived innovation, and trust in the process are significantly above the central point (4) of the scale.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics for the variables under study.
These results indicate that the participants in this study have a high intention to apply to, get involved in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology, a high perception of organizational attractiveness, innovation, and trust in the process. An intrinsic motivation to apply does not differ significantly from the centre point of the scale (4).
4.2. Effect of Sociodemographic Variables on the Variables under Study
Next, we tested the effect of sociodemographic variables on the variables under study, using the parametric Student’s t-test for independent samples and One-Way ANOVA after testing the assumptions of normality and homogeneity of variances.
As Figure 3 shows, male participants have a higher perception of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology, organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation to apply, innovation, and trust in the process than female participants.
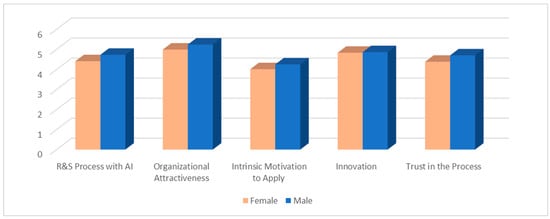
Figure 3.
Distribution of the variables under study according to gender.
Regarding academic qualifications, as Figure 4 shows, participants with a master’s degree or higher have a higher perception of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology and organizational attractiveness but a lower perception of intrinsic motivation to apply, innovation, and trust in the process.
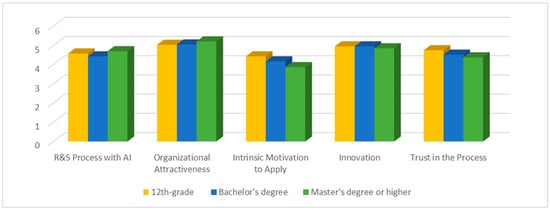
Figure 4.
Distribution of the variables under study according to academic qualifications.
Participants with a 12th-grade degree or less have a higher perception of intrinsic motivation to apply and trust in the process. Participants with a bachelor’s degree have a higher perception of innovation but a lower perception of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology.
As shown in Figure 5, the participants’ age has already been transformed into the age ranges explained above. In the over-54 age group, there is a greater perception of organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation to apply, innovation, and trust in the process.

Figure 5.
Distribution of the variables under study according to age range.
On the other hand, those aged between 45 and 54 have the lowest perception of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology, organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation to apply, and trust in the process. The participants with the highest perception of the AI-enabled R&S process are those aged between 35 and 45.
4.3. Analysing Correlations between Variables
To study the direction and intensity of the association between the variables under study, Pearson’s correlations were used, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Results of Pearson’s correlations.
The results show that the AI-enabled R&S process is positively and significantly associated with organizational attractiveness (r = 0.25; p < 0.001), intrinsic motivation to apply (r = 0.26; p < 0.001), perceived novelty (r = 0.29; p < 0.001), and trust in the process (r = 0.32; p < 0.001) (Table 2).
The higher the perception of organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation to apply, innovation, and trust in the process, the greater the intention to apply to, get involved in, and finish the R&S process with AI-enabled technology.
4.4. Test of the Hypotheses
After analyzing and describing the results above regarding the evaluation of metric qualities, the relationships between variables, and the impact of sociodemographic variables on the variables under study, we then proceeded to study the research hypotheses that had been identified. Path analysis was used to test the hypotheses formulated in this study, carrying out multi-group analyses according to age group.
About Hypothesis 1 (“In a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence, attractiveness positively and significantly affects the intention to apply and complete the process.”), the results show that, for participants aged between 45 and 54, organizational attractiveness has a positive and significant effect on the intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology (β = 0.345, p = 0.010) (Table 3). The model explains 41.1 per cent of the variability in intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology.

Table 3.
Path Analysis results by age group.
This hypothesis was partially supported.
In turn, concerning Hypothesis 2 (“In a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence, intrinsic motivation has a positive and significant effect on the intention to apply and complete the process.”), the results show that intrinsic motivation does not significantly affect the intention to apply to, engage in, and complete the R&S process with AI-enabled technology (Table 3).
This hypothesis was not supported.
As for Hypothesis 3 (“In a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence, the perception of novelty positively and significantly affects the intention to apply and complete the process.”), the results show that, for participants aged between 45 and 54, innovation has a positive and significant effect on the intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology (β = 0.332, p = 0.030) (Table 3). The model explains 41.1% of the variability in intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology.
This hypothesis was partially supported.
Finally, about Hypothesis 4 (“In a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence, trust in the process positively and significantly affects the intention to apply and complete the process.”), the results show that, for participants aged between 35 and 44, trust in the process has a positive and significant effect on the intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology (β = 0.443, p = 0.015) (Table 3). The model explains 13.8 per cent of the variability in intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology.
This hypothesis was partially supported.
5. Discussion
This study aimed to investigate the association between organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation, perceived novelty, trust in the process, and the intention to apply for, participate in, and complete an artificial intelligence recruitment and selection process.
Next, we will discuss the research hypotheses. As expected, Hypothesis 1 was confirmed since, for participants aged between 45 and 54, attractiveness positively and significantly affects the intention to apply for and complete the recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence. The results indicated that organizational attractiveness is crucial in determining candidates’ intention to engage in the R&S process with AI. The more candidates perceive the organization as attractive due to the adoption of this technology, the greater their intention to apply to, get involved in, and complete the process. These results are in line with the literature, which states that the factors that influence the success of a recruitment and selection process, especially for the younger generations, are directly related to the engagement that is created using technology since this use of technology is seen as innovative (Ehrhart and Ziegert 2005; van Esch and Black 2019).
Secondly, and as expected, Hypothesis 2 did not confirm that intrinsic motivation positively and significantly affects the intention to apply and complete the recruitment process using artificial intelligence. Intrinsic motivation did not prove to have a substantial impact on candidates’ intentions. These results run counter to the literature. According to Venkatesh (2000), the anticipation of using a particular technology that users consider new is intrinsically motivating, and the greater the anticipated intrinsic motivation, the more likely participants are to engage in the associated process (Deci and Ryan 2016). This may be because intrinsic motivation is strongly correlated with the other independent variables despite the fact that there were no multicollinearity problems. Thirdly, and as expected, Hypothesis 3 confirmed that, for participants aged between 45 and 54, in a recruitment process using artificial intelligence, innovation has a positive and significant effect on the intention and completion of the process. Innovation also proved to be a crucial factor in candidates’ intentions. This suggests that the perceived novelty associated with AI-enabled technology plays a more prominent role in candidate motivation in contexts where this perception is more pronounced. These results are also in line with what the literature tells us. In the view of van Esch and Black (2019), when the user of a particular technology foresees the possibility of using a new technology, they are likely to become interested in it and get involved. In this sense, candidates can perceive the use of AI in the recruitment and selection process as a novelty (Soares et al. 2020).
Finally, and as expected, Hypothesis 4 confirmed that in a recruitment process using artificial intelligence, for participants aged between 35 and 44, trust in the process has a positive and significant effect on the intention and conclusion of the process. Trust in the process positively and significantly impacted candidates’ intentions, suggesting that it plays a vital role in candidates’ decisions. These results are in line with some studies and against other studies carried out previously. In a study carried out in the banking sector by Xu et al. (2020), which aimed to study whether customers preferred to be served by a human operator or an autonomous AI system, they concluded that when the tasks were more basic, customers preferred to use AI because it was faster, more dynamic, and offered a wider range of solutions for solving the problem. However, when the task was more complex and individualized, they preferred their problem to be solved by a human being.
It should be noted that contrary to expectations, for younger participants aged up to 35, organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation, innovation, and trust in the process did not significantly affect the intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology.
Despite the many reports in the national and international media on the subject, which indicate the exponential growth of this type of technology, most of the participants in this study say they have never taken part in a process of this type or do not know whether they have.
5.1. Limitations and Future Studies
This study has some limitations. The first limitation is the data collection process, which was non-probabilistic, intentional, and of the snowball type. Another limitation is that a closed-ended questionnaire was used, which may have biased the participants’ responses. The fact that it was a cross-sectional study can be considered another limitation since no causal relationships can be established.
Finally, another limitation was the low percentage of participants who revealed they had participated in a recruitment and selection process using artificial intelligence.
This research opens a path for organizations to develop their perceptions and apply what this theoretical framework indicates in practice.
The way forward will be to build real scenarios where organizations can understand candidates’ real perceptions, their reactions based on these perceptions, and, most importantly, the reliability factor that requires experience; only after use will people’s opinions normally reach the next stage.
In the future, other academic or organizational researchers can improve the development of the research framework by applying experimental studies, where the idea is to compare groups with actual experience in these processes with others who only know traditional R&S.
In the future, with an expanded theoretical framework and after many practical tests, we may be able to arrive at a framework of perceptions that trigger reactions in people when confronted with R&S processes with AI-enabled technology and that are distributed across various cultural and personal factors. Thus, “intelligent” technology may become closer to us and understanding us, with all the good and bad that this has to offer.
5.2. Practical Implications
Organizations today are more than just places where individuals apply their knowledge in exchange for a salary at the end of the month. The development of Human Capital brought into organizations makes them competitive and differentiated; it is the real leverage between the past and the present. As such, we are increasingly seeing an attempt to increase the attractiveness of workers and make quick, correct, and consistent choices.
Now, the path seems to be defined by the modernization and increase in technologies within organizations, a phenomenon that has no central area; quite the contrary, it covers all sectors of the company. That is why HR, as the area responsible for the Human Capital that enters, stays, and leaves the company, is an area where this type of integration between technology and processes is increasingly being seen.
Concerning the process chosen as the centerpiece of this dissertation, R&S, in this case, is always related to AI; its usefulness today is undeniable. In very recent studies such as that by Jain et al. (2023), the integration of AI is seen as inevitable and facilitating due to its extreme usefulness, for example, in R&S activities where information is processed in such high volumes, which any human being would take weeks to conclude, while these tools can perform this task in a few minutes, not resting and only producing final outputs where the input of a human element in the process can be differentiating.
According to recent forecasts by the consultancy IDC, in its study, Futurescape: Worldwide Artificial Intelligence and Automation 2023 Predictions (IDC 2023), by the end of 2022, companies worldwide will have invested an average of 110 billion euros in pure AI solutions or development. Analyzing the period from 2021 to 2026, the consultancy expects this expenditure to rise to 280 billion euros, giving us an annual growth rate of around 27 per cent. To give you an idea of the scale, the same consultancy describes in its forecast study that, if these figures are confirmed, we are looking at a growth rate of around four times more than everything invested in IT worldwide.
So, we are facing a train that seems unstoppable. Although much of the potential of AI in the R&S process is yet to be developed, we know in advance that people will continue to be needed. No company will prioritize a strategy that leads them to find the “wrong people” when they have more and more tools at their disposal that seem to have manifestly superior results in terms of cost/results, and that to use them successfully, it will be enough to know how to bring people and technology together.
There are many ethical standards and doubts about what the future holds, but as the future has always been uncertain, it will continue to be.
6. Conclusions
General and specific literature was used as a starting point for this research to understand the most characteristic perceptions of a candidate faced with an R&S process using artificial intelligence.
It can be concluded that for younger participants, aged up to 35, and older participants, aged over 54, organizational attractiveness, intrinsic motivation, innovation, and trust in the process do not have a significant effect on the intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology. For participants aged between 35 and 44, only the effect of trust in the process was significant. Finally, for participants aged between 45 and 54, organizational attractiveness and innovation are relevant to boosting the intention to apply to, engage in, and reach the end of the R&S process with AI-enabled technology.
In this study, trust in the process proved to be relevant for participants aged between 35 and 44. It should also be noted that this is the strongest of the significant associations with the intention to apply to, engage in, and complete the R&S process with AI-enabled technology. This result could be related to other large-scale studies of cultural patterns, such as Hofstede or the Globe Project, and how much our society depends on uncertainty aversion (security) values.
Today, if an organization optimizes processes by investing in technologies that contain or are AI-enabled, it will have to meet the most common perceptions, but that will not be enough. Suppose the process aims to attract, recruit, select, and retain people so that they reach the end of the process. In that case, there will have to be an effective transfer of trust on the part of organizations, which will bring all perceptions into line, in the sense that there will be a positive reaction to the R&S process with AI-enabled technology, which was the aim of the study by van Esch et al. (2021) and which is reinforced by this research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.L. and I.D.; methodology, N.L. and I.D.; software, A.M.; validation, N.L., I.D. and A.M.; formal analysis, A.M.; investigation, N.L. and I.D.; resources, N.L.; data curation, A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, N.L. and I.D.; writing—review and editing, N.L., I.D. and A.M.; visualization, N.L. and I.D.; supervision, I.D.; project administration, N.L. and I.D.; funding acquisition, A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, as all participants (before answering the questionnaire) needed to read the informed consent. After reading the informed consent, they had to answer a question as to whether they agreed to answer the questionnaire. Only if they agreed could they complete the questionnaire. If they disagreed, they could not do so. The participants were informed about the study’s purpose and the confidentiality of the results since the individual results would never be known and would only be analyzed as a whole.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available because in their informed consent, participants were informed that the data were confidential and that individual responses would never be known, as data analysis would be of all participants combined.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Al-Alawi, Adel Ismail, Misbah Naureen, Ebtesam Ismaeel Alalawi, and Ahmed Addulla Naser Al-Hadad. 2021. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Recruitment Process Decision-Making. Paper presented at the 2021 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Application, DASA 2021, Sakheer, Bahrain, December 7–8; pp. 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuckle, James L. 2008. AMOS 17 User’s Guide. Chicago: SPSS Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Avelar, Cátia Fábiola Parreira de, Yuri Matsumoto Silva, and Hugo Lacerda Saraiva. 2021. Tecnologia Aplicada ao Recrutamento e Seleção: Mudanças Divulgadas e Resultados Percebidos no Uso de Soluções Oferecidas por HR TECHS Brasileiras. Gestão & Sociedade 15: 4620–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, Stewart, and Patrick van Esch. 2019. AI-enabled recruiting: What is it and how should a manager use it? Business Horizons 63: 215–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, Stewart, and Patrick van Esch. 2021. AI-enabled recruiting in the war for talent. Business Horizons 64: 513–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryman, Alan, and Duncan Cramer. 2003. Análise de dados em ciências sociais. Introdução às técnicas utilizando o SPSS para windows, 3rd ed. Oeiras: Celta. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, Patrick, Kathleen Minette, Dennis Joy, and Jeff Michaels. 2004. The use of an automated employment recruiting and screening system for temporary professional employees: A case study. Human Resource Management 43: 233–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, Derek S., and Jane Webster. 2003. The use of technologies in the recruiting, screening, and selection processes for job candidates. International Journal of Selection and Assessment 11: 113–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, Alexei, and Victoria A. Chernova. 2019. Artificial Intelligence in Management: Challenges and Opportunities. Paper presented at the 38th International Scientific Conference on Economic and Social Development, Rabat, Morocco, March 21–22; pp. 21–22. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332082521 (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Chui, Michael, James Manyika, and Mehdi Miremadi. 2016. Four fundamentals of workplace automation. In McKinsey Quarterly. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/four-fundamentals-of-workplace-automation (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Coradini, Joziane Rizetti, and Lizandra Taschetto Murini. 2009. Recrutamento e Seleção de Pessoal: Como Agregar Talentos à Empresa. Disciplinarum Scientia 5: 55–78. [Google Scholar]
- Correio, Lucelia, Jusirmar Correio, and Claudemir Correio. 2021. A Quarta Revolução Industrial: Desafios e Características da Gestão de Pessoa 4.0. Administração de Empresas Em Revista 1: 279–302. [Google Scholar]
- Deci, Edward L., and Richard M. Ryan. 1985. Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in Human Behavior. New York: Plenum Press. [Google Scholar]
- Deci, Edward L., and Richard M. Ryan. 2016. Optimizing Students’ Motivation in the Era of Testing and Pressure: A Self-Determination Theory Perspective. In Building Autonomous Learners. Singapore: Springer, pp. 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delecraz, Sebastian, Loukman Eltarra, Martin Becuwea, Henri Bouxina, Nicolas Boutina, and Olivier Oullier. 2022. Responsible Artificial Intelligence in Human Resources Technology: An innovative inclusive and fair by design matching algorithm for job recruitment purposes. Journal of Responsible Technology 11: 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derous, Eva, and Filip de Fruyt. 2016. Developments in Recruitment and Selection Research. International Journal of Selection and Assessment 24: 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, Evgeniy E., Tatyana E. Lebedeva, Maria P. Prokhorova, Tatyana N. Tsapina, and Anzhelika A. Shkunova. 2020. Opportunities and Prospects of Using Chatbots in HR. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems 129: 782–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhart, Karen Holcombe, and Jonathan C. Ziegert. 2005. Why are individuals attracted to organizations? Journal of Management 31: 901–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, Mustafa, and Nurgun Gencel. 2022. Supporting the Instructional Videos With Chatbot and Peer Feedback Mechanisms in Online Learning: The Effects on Learning Performance and Intrinsic Motivation. Journal of Educational Computing Research 60: 1716–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, Ashima, Sweta Gaur, and Preeti Sharma. 2021. A Review Paper: Role of Artificial Intelligence in Recruitment Process. ANWESH: International Journal of Management & Information Technology 6: 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich, Michael. 2023. Perceptions and Acceptance of Artificial Intelligence: A Multi-Dimensional Study. Social Sciences 12: 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, Michael. 2024. Exploring Motivators for Trust in the Dichotomy of Human—AI Trust Dynamics. Social Sciences 13: 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausknecht, John P., David V. Day, and Scott C. Thomas. 2004. Applicant Reactions to Selection Procedures: An Updated Model and Meta-Analysis. Personnel Psychology 57: 639–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, Manuela, and Andrew Hill. 2002. Investigação por Questionário, 2nd ed. Lisboa: Edições Sílabo. [Google Scholar]
- Hmoud, Bilal, and Lászlo Várallyai. 2019. Will Artificial Intelligence Take Over Humanresources Recruitment and Selection? Network Intelligence Studies 7: 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Li-tze, and Peter M. Bentler. 1999. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling 6: 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, Eti, Taruna Chopra, and S.K. Sharma. 2023. Reinventing Human Resource Management in the Era of Artificial Intelligence. Paper presented at the International Conference on Application of AI and Statistical Decision Making for the Business World, ICASDMBW 2022, Delhi, India, December 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, María Luisa Villasano, Héctor Cuellar Hernández, Rosa Alejandra Reyes Rizo, and Helga Elena Roesner García. 2021. Repercusión de la inteligencia artificial en el ámbito de la gestión del talento humano en las organizaciones. Revista RELAYN—Micro Y Pequeñas Empresas En Latinoamérica 5: 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeno, Lucas Matias, Vigdis Vandvik, Sigrunn Eliassen, and John Arvid Grytnes. 2019. Testing the novelty effect of an m-learning tool on internalization and achievement: A Self-Determination Theory approach. Computers and Education 128: 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, Rex B. 1998. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. New York: Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, Markus, Cornelius König, and Kevin Krause. 2017. Examining digital interviews for personnel selection: Applicant reactions and interviewer ratings. International Journal of Selection and Assessment 25: 371–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, In. 2011. Modeling the benefit of e-recruiting process integration. Decision Support Systems 51: 230–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logg, Jennifer M., Julia A. Minson, and Don A. Moore. 2018. Algorithm Appreciation: People Prefer Algorithmic To Human Judgment. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 151: 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marôco, João. 2021. Análise estatística com o SPSS Statistics, 8th ed. Pêro Pinheiro: ReportNumber. [Google Scholar]
- Marôco, João, and Regina Bispo. 2003. Estatística aplicada às ciências sociais e humanas. Lisboa: Climepsi Editores. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Núñez, José Luís, Anil Yasin Ar, Rodrigo Pérez Fernández, Asad Abbas, and Danica Radovanović. 2023. Does intrinsic motivation mediate perceived artificial intelligence (AI) learning and computational thinking of students during the COVID-19 pandemic? Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence 4: 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijerink, Jeroen, and Anne Keegan. 2016. Conceptualizing human resource management in the gig economy: Toward a platform ecosystem perspective. Journal of Managerial Psychology 34: 214–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, Sandra Jeanquart, and Randy McCamey. 2018. The candidate experience: Is it damaging your employer brand? Business Horizons 61: 755–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Nishad. 2020. Artificial Intelligence Aplications For Face Recognition in Recruitment Process. Journal of Management Information & Decision Sciences 23: 499–509. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaou, Ioannis, Konstantina Georgiou, Talya N. Bauer, and Donald M. Truxillo. 2019. Applicant reactions in employee recruitment and selection: The role of technology. In The Cambridge Handbook of Technology and Employee Behavior. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 100–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. 2019. Artificial Intelligence in Society. Paris: OECD Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Yuan, Fabian Froese, Ni Liu, Hu Yunyang, and Maolin Ye. 2022. The adoption of artificial intelligence in employee recruitment: The influence of contextual factors. International Journal of Human Resource Management 33: 1125–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, Maria Helena, and João Nunes Gageiro. 2003. Análise de dados para ciências sociais: A complemen- taridade de SPSS, 3rd ed. Lisboa: Edições Silabo. [Google Scholar]
- Podsakoff, Phillip M., Scott B. MacKenzie, Jeong Y. Lee, and Nathan P. Podsakoff. 2003. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology 88: 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahl, Andrew, and Lyn van Swol. 2017. Understanding algorithm aversion: When is advice from automation discounted? Journal of Forecasting 36: 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramod, Dhanya, and S. Vijayakumar Bharathi. 2016. Social media impact on the recruitment and selection process in the information technology, industry. International Journal of Human Capital and Information Technology Professionals 7: 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, Ramona, Katina Michael, and M. G. Michael. 2016. Unintended Consequences of Living with AI: The Paradox of Technological Potential? Part II [Guest Editorial]. Technology and Society Magazine 35: 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, Daniel W. 2002. In Search of Underlying Dimensions: The Use (and Abuse) of Factor Analysis in Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 28: 1629–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, Ruchard M., and Edward L. Deci. 2000. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations: Classic Definitions and New Directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology 25: 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Christopher, Brian McGuire, Ting Huang, and Gary Yang. 2006. The History of Artificial Intelligence. Seattle: University of Washington, December, Available online: https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/csep590/06au/projects/history-ai.pdf (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Soares, Simarly Maria, Simone Gelmini, Gisela Demo, and Ana Carolina Rezende Costa. 2020. Recrutamento e Seleção: O que diz a produção nacional de primeira linha? Revista Pretexto 21: 111–28. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, Karlla, and Mónica Ximenes Carneiro da Cunha. 2019. Impactos do uso das redes sociais virtuais na saúde mental dos adolescentes: Uma revisão sistemática da literatura. Revista Educação, Psicologia e Interfaces 3: 204–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, Prasanna, Peter Cappelli, and Valery Yakubovich. 2019. Artificial intelligence in human resources management: Challenges and A path forward. California Management Review 61: 15–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turing, Alan M. 1950. Computing Machinery and Intelligence. Mind LIX: 433–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Esch, Patrick, and Margaret Mente. 2018. Marketing video-enabled social media as part of your e-recruitment strategy: Stop trying to be trendy. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 44: 266–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Esch, Patrick, and Stewart Black. 2019. Factors that influence new generation candidates to engage with and complete digital, AI-enabled recruiting. Business Horizons 62: 729–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Esch, Patrick, Stewart Black, and Denni Arli. 2021. Job candidates’ reactions to AI-Enabled job application processes. AI and Ethics 1: 119–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Esch, Patrick, Stewart Black, and Joseph Ferolie. 2019. Marketing AI recruitment: The next phase in job application and selection. Computers in Human Behavior 90: 215–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Esch, Patrick, Stewart Black, Drew Franklin, and Mark Harder. 2020. Al-enabled biometrics in recruiting: Insights from marketers for managers. Australasian Marketing Journal 29: 225–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, Viswanath. 2000. Determinants of Perceived Ease of Use: Integrating Control, Intrinsic Motivation, and Emotion into the Technology Acceptance Model. Information Systems Research 11: 342–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, John D., Damon E. Campbell, Joseph S. Valacich, and Mauricio Featherman. 2010. The Effect of Perceived Novelty on the Adoption of Information Technology Innovations: A Risk/Reward Perspective. Decision Sciences 41: 813–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, Thomas A., and Douglas G. Bonett. 2002. The moderating effects of employee tenure on the relation between organizational commitment and job performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology 87: 1183–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Yingzi, Chih-Hui Shieh, Patrick van Esch, and I-Ling Ling. 2020. AI customer service: Task complexity, problem-solving ability, and usage intention. Australasian Marketing Journal 28: 189–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Wei, and H. Denis Wu. 2014. The Impact of On-line Disruptive Ads on Users’ Comprehension, Evaluation of Site Credibility, and Sentiment of Intrusiveness. American Communication Journal 16: 15–28. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).