The Impact of Green Human Resource Management Practices on Employees, Clients, and Organizational Performance: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Employee green attitudes and perceptions.
- (2)
- Employee green satisfaction.
- (3)
- Employee green behavior.
- (4)
- Client green satisfaction.
- (5)
- Organizational green performance.
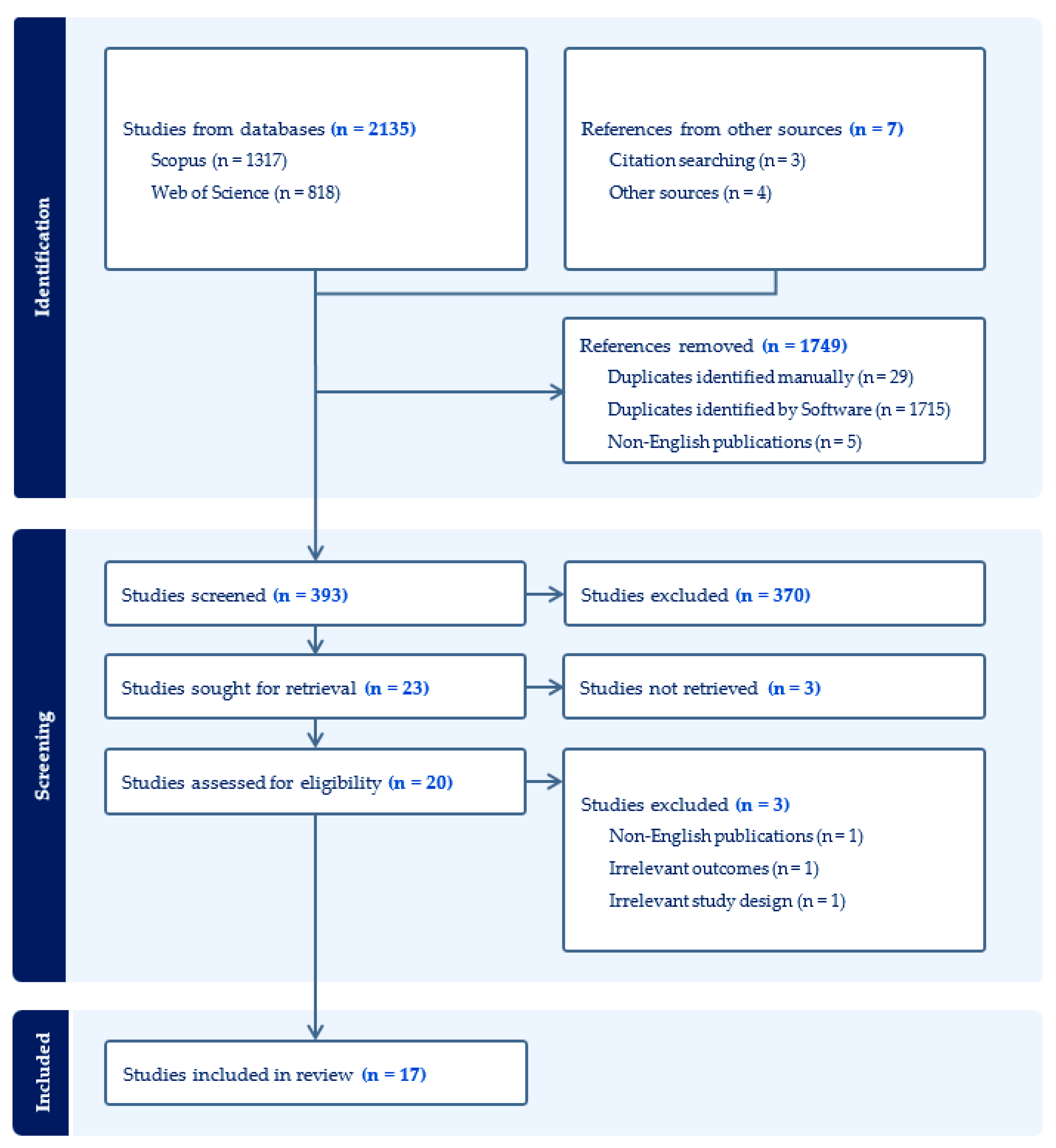
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Data Extraction and Synthesis
2.6. Theoretical Base of This Review
2.7. Definitions
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Main Findings
4.2. Academic, Managerial and Policy Implications
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelhamied, Hany Hosny, Ahmed Mohamed Elbaz, Bassam Samir Al-Romeedy, and Tamer Mohamed Amer. 2023. Linking Green Human Resource Practices and Sustainable Performance: The Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction and Green Motivation. Sustainability 15: 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, Priyanka, and Tanuja Agarwala. 2023. Relationship of Green Human Resource Management with Environmental Performance: Mediating Effect of Green Organizational Culture. Benchmarking 30: 2351–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Shoeb. 2015. Green Human Resource Management: Policies and Practices. Cogent Business & Management 2: 1030817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albloush, Ahmad, Malek Alharafsheh, Rami Hanandeh, Ala Albawwat, and Mahmood Abu Shareah. 2022. Human Capital as a Mediating Factor in the Effects of Green Human Resource Management Practices on Organizational Performance. International Journal of Sustainable Development and Planning 17: 981–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Muhammad, and Muhammad Hassan. 2023. Green Management Practices and Trust for Green Behavioral Intentions and Mediation of Ethical Leadership. An Attribution Theory Perspective in Tourism. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 35: 3193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Swidi, Abdullah Kaid, Hamid Gelaidan, and Redhwan Mohammed Saleh. 2021. The Joint Impact of Green Human Resource Management, Leadership and Organizational Culture on Employees’ Green Behaviour and Organisational Environmental Performance. Journal of Cleaner Production 316: 128112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutha, Namboodiri, and Ramani Geetha. 2023. Green Employee Empowerment for Environmental Organization Citizenship Behavior: A Moderated Parallel Mediation Model. Current Psychology 43: 5685–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, Eileen. 2000. Manufacturing Advantage: Why High-Performance Work Systems Pay Off. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, Muhammad, Ghulam Abid, Francoise Contreras, Natasha Saman Elahi, and Saira Ahmed. 2022. Greening the Hospitality Sector: Employees’ Environmental and Job Attitudes Predict Ecological Behavior and Satisfaction. International Journal of Hospitality Management 102: 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykal, Elif, Ayşe Öykü Yılmaz, and Seray Kayra Koktekin. 2023. Impact of Green Human Resources Management on Job Satisfaction. In Economic Development and the Environmental Ecosystem: The Role of Energy Policy in Economic Growth. Edited by Hasan Dincer and Serhat Yüksel. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, pp. 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevene, Paula, and Ilaria Buonomo. 2020. Green Human Resource Management: An Evidence-Based Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 12: 5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandis, Susan, John Rice, and Stephanie Schleimer. 2017. Dynamic workplace interactions for improving patient safety climate. Journal of Health Organization and Management 31: 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahyadi, Afriyadi, Diah Natalisa, József Poór, Badia Perizade, and Katalin Szabó. 2023. Predicting the Relationship between Green Transformational Leadership, Green Human Resource Management Practices, and Employees’ Green Behavior. Administrative Sciences 13: 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Silu, Wanxing Jiang, Xin Li, and Han Gao. 2021. Effect of Employees’ Perceived Green Hrm on Their Workplace Green Behaviors in Oil and Mining Industries: Based on Cognitive-Affective System Theory. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18: 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Baroudi, Sabrine, Wenjing Cai, Svetlana Khapova, and Yang Jiang. 2023. Green Human Resource Management and Team Performance in Hotels: The Role of Green Team Behaviors. International Journal of Hospitality Management 110: 103436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, Ibrahim, Alaa Azazz, Chokri Kooli, Ali Saleh Alshebami, Mohammad Zeina, and Sameh Fayyad. 2023. Green Human Resource Management and Brand Citizenship Behavior in the Hotel Industry: Mediation of Organizational Pride and Individual Green Values as a Moderator. Administrative Sciences 13: 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, Shaha. 2023. Green Human Resource Management—A Synthesis. Sustainability 15: 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrukh, Muhammad, Nabeel Ansari, Ali Raza, Yihua Wu, and Hong Wang. 2022. Fostering Employee’s pro-Environmental Behavior through Green Transformational Leadership, Green Human Resource Management and Environmental Knowledge. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 179: 121643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, Luis Miguel, José Pedro Domingues, and Alina Mihaela Dima. 2020. Mapping the Sustainable Development Goals Relationships. Sustainability 12: 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, Carla, and Pietra Pieta. 2022. The Impact of Green Human Resource Management on Organizational Citizenship Behaviors: The Mediating Role of Organizational Identification and Job Satisfaction. Sustainability 14: 7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavan, Thomas, Irfan Ullah, Fergal O‘Brien, and Yasir Hayat Mughal. 2023. Employee Perceptions of Individual Green HRM Practices and Voluntary Green Work Behaviour: A Signalling Theory Perspective. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources 61: 32–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, Zahid, Khwaja Fareed, Ikram Ullah Khan, Tahir Islam, Zaryab Sheikh, and Rana Muhammad Naeem. 2019. Do Green HRM Practices Influence Employees’ Environmental Performance? International Journal of Manpower 41: 1061–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Ali Junaid, Waseem Ul Hameed, Jawad Iqbal, Ashfaq Ahmad Shah, Muhammad Atiq Ur Rehman Tariq, and Furrukh Bashir. 2022. Green HRM and Employee Efficiency: The Mediating Role of Employee Motivation in Emerging Small Businesses. Frontiers in Environmental Science 10: 1044629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Filho, Walter, Laís Viera Trevisan, Izabela Simon Rampasso, Rosley Anholon, Maria Alzira Pimenta Dinis, Luciana Londero Brandli, Javier Sierra, Amanda Lange Salvia, Rudi Pretorius, Melanie Nicolau, and et al. 2023. When the Alarm Bells Ring: Why the UN Sustainable Development Goals May Not Be Achieved by 2030. Journal of Cleaner Production 407: 137108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Wei, Alaa Amin Abdalla, Tamara Mohammad, Osama Khassawneh, and Mahwish Parveen. 2023. Towards Examining the Link Between Green HRM Practices and Employee Green In-Role Behavior: Spiritual Leadership as a Moderator. Psychology Research and Behavior Management 16: 383–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Tung-Shan, John Rice, and Nigel Martin. 2011. The role of the market in transforming training and knowledge to superior performance: Evidence from the Australian manufacturing sector. The International Journal of Human Resource Management 22: 376–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Xiao, and Kuen-Lin Lin. 2020. Green Organizational Culture, Corporate Social Responsibility Implementation, and Food Safety. Frontiers in Psychology 11: 585435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, Fatima, Muhammad Mustafa Raziq, Mumtaz Ali Memon, Adeel Tariq, and John Lewis Rice. 2023. Transformational leadership, job engagement, and championing behavior: Assessing the mediating role of role clarity. European Business Review 35: 941–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, Nigel, John Rice, and Sumit Lodhia. 2014. Sustainable development planning: A case of public participation using online forums. Sustainable Development 22: 265–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, Hiba, and Ayham Jaaron. 2017. Assessing Green Human Resources Management Practices in Palestinian Manufacturing Context: An Empirical Study. Journal of Cleaner Production 143: 474–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, Leonard Emmanuel, Shalini Shukla, and Hera Fatima Iqbal. 2023. Green Human Resource Management Practices and Employee Innovative Behaviour: Reflection from Ghana. IIMBG Journal of Sustainable Business and Innovation 1: 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, Matumona, and Yinfei Chen. 2022. Impact of Green Human Resource Management on Organizational Reputation and Attractiveness: The Mediated-Moderated Model. Frontiers in Environmental Science 10: 962531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, Sharifa, and Mohammed Othman. 2020. The Impact of Green Human Resource Management Practices on Sustainable Performance in Healthcare Organisations: A Conceptual Framework. Journal of Cleaner Production 243: 118595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, Sidra, Hummaira Qudsia, Yousaf Muneeb Ahmed, and Sumaira Rehman. 2022. Effects of Green Human Resource Management on Green Innovation through Green Human Capital, Environmental Knowledge, and Managerial Environmental Concern. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management 52: 141–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, Michael, and Charles Oppenheim. 2007. Comparing Alternatives to the Web of Science for Coverage of the Social Sciences’ Literature. Journal of Informetrics 1: 161–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Nhat, Tan Vo-Thanh, Zuzana Tučková, and Thuy Vo. 2020. The Role of Green Human Resource Management in Driving Hotel’s Environmental Performance: Interaction and Mediation Analysis. International Journal of Hospitality Management 88: 102392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawashdeh, Adnan. 2018. The Impact of Green Human Resource Management on Organizational Environmental Performance in Jordanian Health Service Organizations. Management Science Letters 8: 1049–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Shuang, Guiyao Tang, and Susan Jackson. 2018. Green Human Resource Management Research in Emergence: A Review and Future Directions. Asia Pacific Journal of Management 35: 769–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Zhengyu, and Rana Yassir Hussain. 2022. A Mediated–Moderated Model for Green Human Resource Management: An Employee Perspective. Frontiers in Environmental Science 10: 973692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, Bilal, Bilal Afsar, Shakir Hafeez, Imran Khan, Muhammad Tahir, and Muhammad Asim Afridi. 2019. Promoting Employee’s Proenvironmental Behavior through Green Human Resource Management Practices. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management 26: 424–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaei, Azadeh, Mehran Nejati, and Yusmani Mohd Yusoff. 2020. Green Human Resource Management: A Two-Study Investigation of Antecedents and Outcomes. International Journal of Manpower 41: 1041–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, Muhammad, Roman Zámečník, Zuhair Abbas, Mohsin Javed, and Asad Ur Rehman. 2021. Green Human Resource Management and Green Human Capital: A Systematic Literature Review. Paper presented at the International Scientific Conference: Contemporary Issues in Business, Management and Economics Engineering, Vilnius, Lithuania, May 13–14; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Muhammad-Shoaib-101/publication/351569814_GREEN_HUMAN_RESOURCE_MANAGEMENT_AND_GREEN_HUMAN_CAPITAL_A_SYSTEMATIC_LITERATURE_REVIEW/links/60a0c956299bf147699f587b/GREEN-HUMAN-RESOURCE-MANAGEMENT-AND-GREEN-HUMAN-CAPITAL-A-SYSTEMATIC-LITERATURE-REVIEW.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Tirno, Rabbir Rashedin, Nafiza Islam, and Kamrunnahar Happy. 2023. Green HRM and Ecofriendly Behavior of Employees: Relevance of Proecological Climate and Environmental Knowledge. Heliyon 9: e14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranfield, David, David Denyer, and Palminder Smart. 2003. Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. British Journal of Management 14: 207–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, Luu. 2022. Promoting Employee Green Behavior in the Chinese and Vietnamese Hospitality Contexts: The Roles of Green Human Resource Management Practices and Responsible Leadership. International Journal of Hospitality Management 105: 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Kuei Y., Chuan C. Chou, and Jerry C.-Y. Lai. 2019. A Structural Model of Total Quality Management, Work Values, Job Satisfaction and Patient-Safety-Culture Attitude among Nurses. Journal of Nursing Management 27: 225–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikhamn, Wajda. 2019. Innovation, Sustainable HRM and Customer Satisfaction. International Journal of Hospitality Management 76: 102–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, Geoffrey, and Frank Horwitz. 2015. Theories and Institutional Approaches to HRM and Employment Relations in Selected Emerging Markets. In Handbook of Human Resource Management in Emerging Markets. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing, pp. 19–41. Available online: https://china.elgaronline.com/edcollchap/edcoll/9781781955000/9781781955000.00009.xml (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Xiao, Yunxia, Rabia Younus, Wizra Saeed, Junaid Ul Haq, and Xiuwen Li. 2022. Is There a Link Between Green Human Resource Management and Consumer Buying Behavior? The Moderating Role of Employee Diffidence. Frontiers in Psychology 13: 800936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, Ahmed, Ayham Jaaron, and Abdul Talib Bon. 2018. The Impact of Green Human Resource Management and Green Supply Chain Management Practices on Sustainable Performance: An Empirical Study. Journal of Cleaner Production 204: 965–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Shanshan, Xiande Zhao, and Zhiqiang Wang. 2019. Effects of Proactive Environmental Strategy on Environmental Performance: Mediation and Moderation Analyses. Journal of Cleaner Production 235: 1438–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors (Year) | Country | Aim of Study | Study Design | Population Description | Data Collection Method | Number of Participants |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
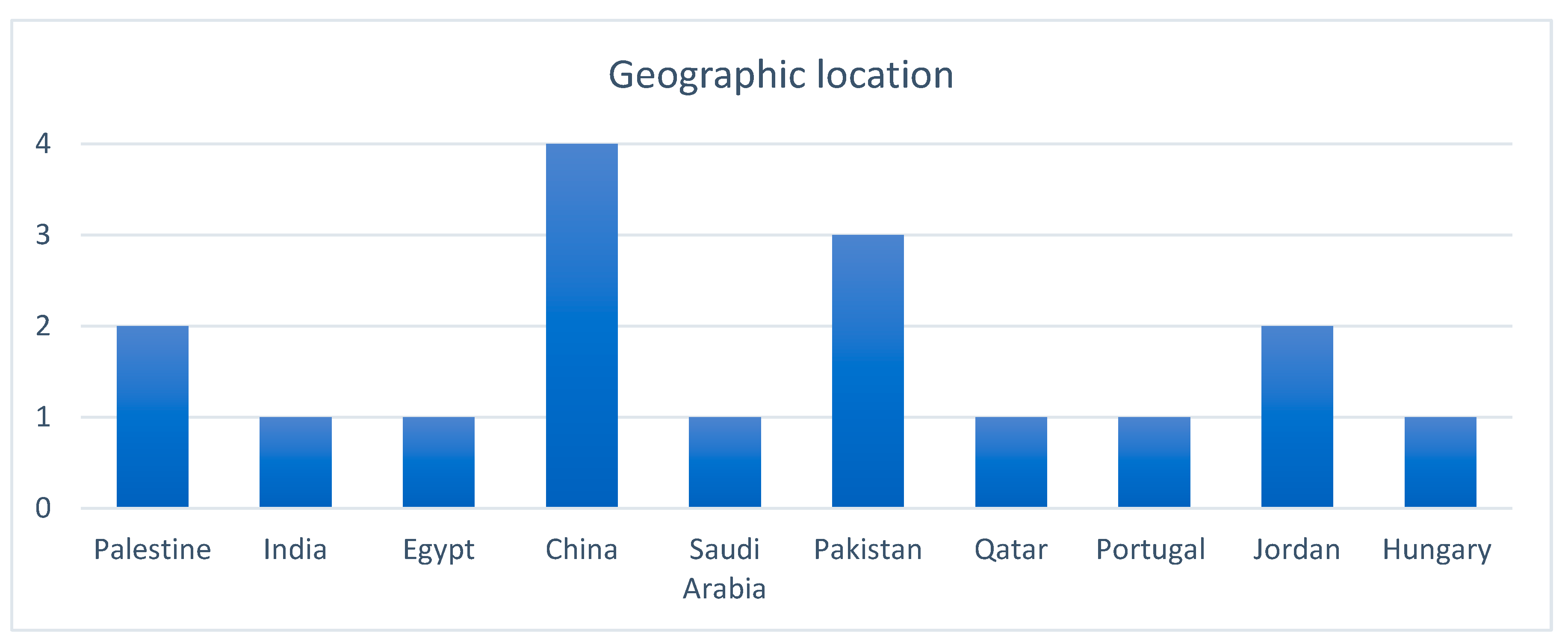
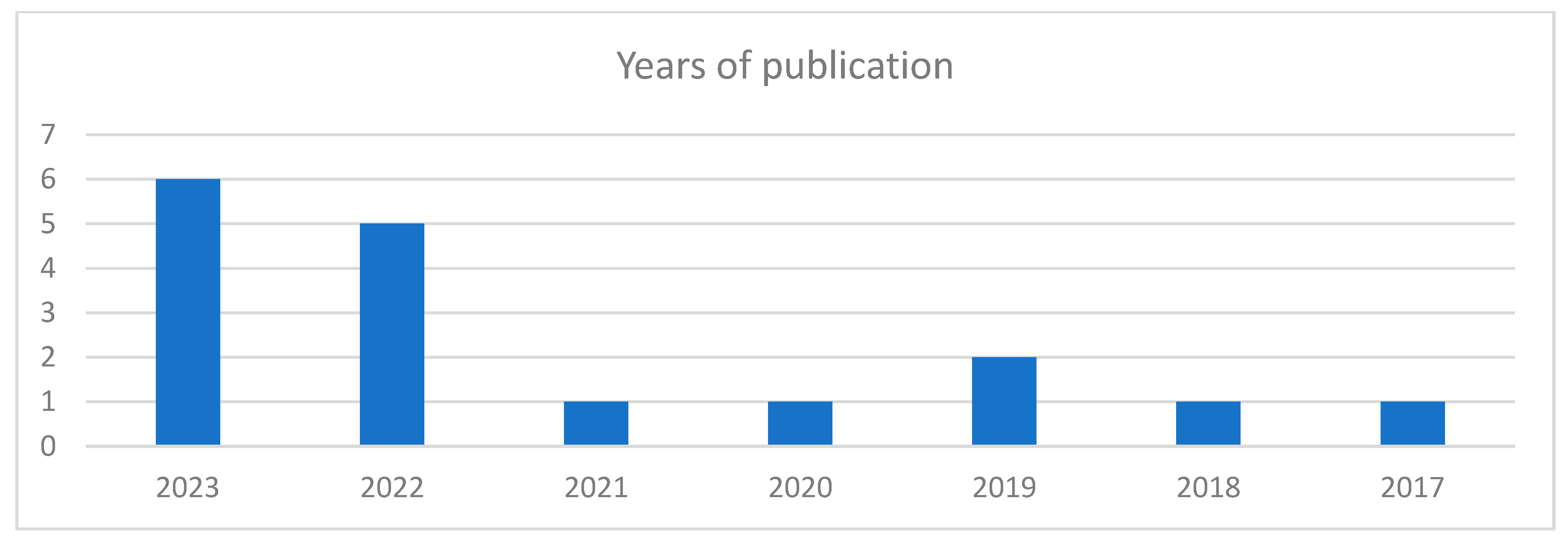
| Ali and Hassan (2023) | Egypt | To assess nurse managers’ perception about G-HRM practices. | Cross-sectional | Nurse managers in five University Hospitals | Paper-based questionnaire | 95 |
| Cahyadi et al. (2023) | Hungary | To examine relationship between G-HRM policies and employees’ behavior | Cross-sectional | Prospective employees in business sector | E-Survey | 252 |
| El Baroudi et al. (2023) | China | To examine the role of G-HRM on employee green behavior and overall organizational performance | Cross-sectional | Team members working in 4 hospitality and tourism settings | Paper-based questionnaire | 277 |
| Elshaer et al. (2023) | Saudi Arabia | To examine the relationship between G-HRM and organizational performance and how employee pro-environmental behavior may moderate this relationship. | Cross-sectional | Employees at managerial level in small- and medium-sized hotels and travel agencies | Paper-based questionnaire | 304 |
| Li et al. (2023) | China | To examine the effect of G-HRM practices on an employees’ green behavior. | Cross-sectional | Employees working in Chinese Multinational Corporation | Paper-based questionnaire | 374 |
| Mensah et al. (2023) | India | To investigate the relationship between G-HRM practices and employee green behavior in the hospital settings. | Cross-sectional | Human resource and administrative managers at Korle Bu Teaching Hospital | Paper-based questionnaire | 264 |
| Albloush et al. (2022) | Jordan | To determine the effect of G-HRM policies on organizational performance | Cross-sectional | Employees in public institutions | E-survey | 275 |
| Arshad et al. (2022) | Pakistan | To examine the impact of G-HRM policies on employees’ attitudes, satisfaction, and behavior. | Cross-sectional | Employees in the hospitality sector | Paper-based questionnaire | 508 |
| Freire and Pieta (2022) | Portugal | To analyze the impact of G-HRM on organizational behavior through the mediating role of organizational identification and job satisfaction | Cross-sectional | Employees in industrial companies | E-Survey | 120 |
| Ren and Hussain (2022) | Pakistan | Explores the direct and indirect effects of G-HRM on the environmental performance. | Cross-sectional | Employees in manufacturing companies. | E-survey | 306 |
| Xiao et al. (2022) | China | The study focuses on investigating the moderating role of G-HRM on consumer behavior and Employee Performance. | Cross-sectional | Frontline employees of the hospitality sector. | Paper-based questionnaire | 210 |
| Al-Swidi et al. (2021) | Qatar | To examine the effects of G-HRM culture on employees’ behavior | Cross-sectional | Employees in public and private sector | Paper-based questionnaire | 632 |
| Mousa and Othman (2020) | Palestine | To assess the level of implementation of G-HRM practices in healthcare sector and their impact on sustainable performance. | Mixed Methods | HR experts from the healthcare sector | Interview | 69 |
| Hameed et al. (2019) | Pakistan | To test the role of G-HRM practices on employee green behavior and to investigates the moderating effect of individual green values. | Cross-sectional | Employees and their supervisors in a large manufacturing company | Paper-based questionnaire | 365 |
| Zhang et al. (2019) | China | To examine the influence of five types of G-HRM practices (employee life cycle, rewards, education and training, employee empowerment, and manager involvement) on employee green behavior in the workplace. | Cross-sectional | Employees in different industrial settings. | Paper-based questionnaire | 145 |
| Rawashdeh (2018) | Jordan | To explore the relationship between G-HRM practices and environmental performance in Jordanian health service organization | Cross-sectional | Hospital managers | E-Survey | 91 |
| Masri and Jaaron (2017) | Palestine | To examine the effect of G-HRM practices on Environmental Performance | Mixed Methods | Organizations operating in manufacturing sectors | Interview | 110 |
| Authors (Year) | Setting | Study Outcomes | Main Findings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Employee Attitude | Employee Satisfaction | Employee Behavior | Client Satisfaction | Organizational Performance | |||
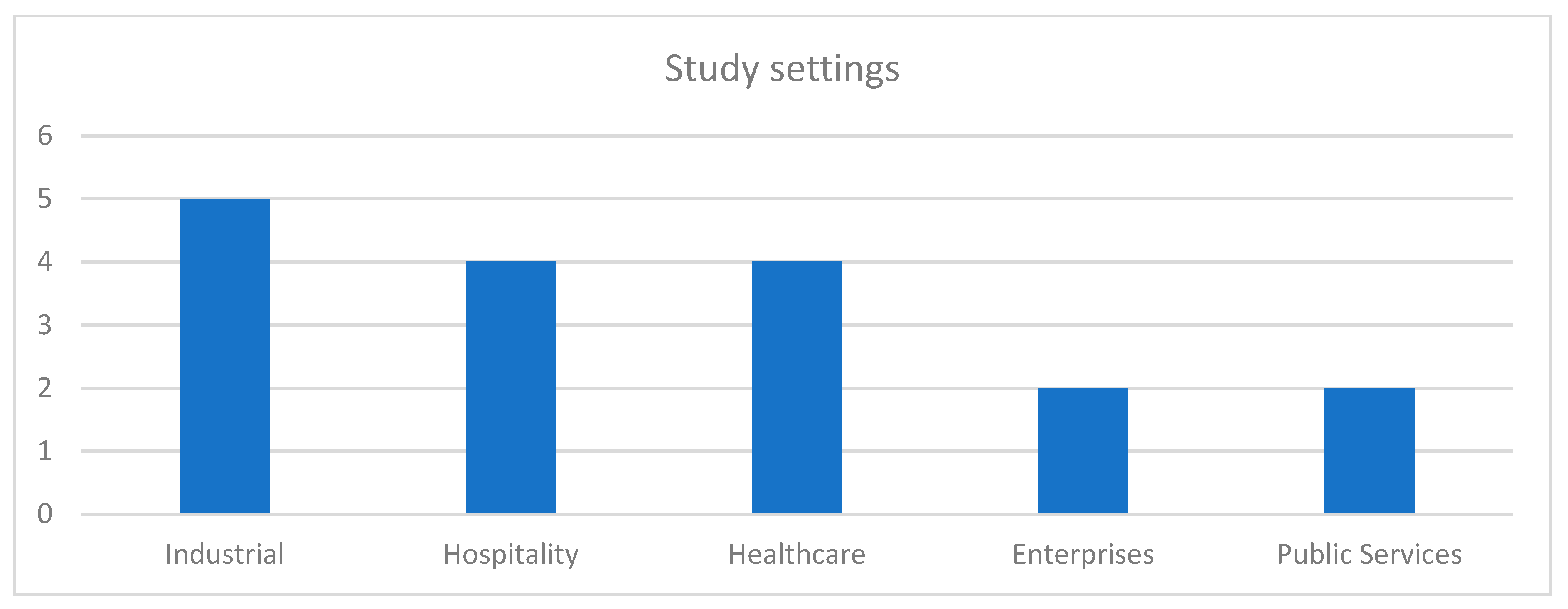
| Ali and Hassan (2023) | Healthcare | √ | - | - | - | - | A statistically significant positive correlation exists between G-HRM Practices and employees’ work values. |
| Cahyadi et al. (2023) | Enterprises | - | - | √ | - | - | G-HRM practices positively influence employees’ green behavior. G-HRM practices mediate the relationship between green transformational leadership and employees’ green behavior. |
| El Baroudi et al. (2023) | Hospitality and Tourism | √ | - | √ | - | √ | Green employee behaviors mediate the relationship between employee attitudes and perceptions of G-HRM and nongreen performance. |
| Elshaer et al. (2023) | Hospitality and Tourism | - | - | √ | - | √ | G-HRM practices can improve environmental, economic, and social performance, and these relationships can be strengthened through the moderating effects of employees’ pro-environmental behavior. |
| Li et al. (2023) | Industry | - | - | √ | - | - | G-HRM practices have a positive effect on employees’ green behavior. Psychological green climate mediates the relation between G-HRM practices and employee in-role green behavior. |
| Mensah et al. (2023) | Healthcare | - | - | √ | - | - | Green training, green hiring, and green compensation were significant predictors of innovative work behavior among employees. |
| Albloush et al. (2022) | Public Services | - | - | - | - | √ | A significant association between G-HRM (green rewards, compensation, and training) and organizational performance. Human Capital mediates the link between G-HRM and Organizational Performance. |
| Arshad et al. (2022) | Hospitality and Tourism | √ | √ | √ | - | - | Employee environmental attitudes encourage employees’ ecological behavior and satisfaction with the organization. |
| Freire and Pieta (2022) | Industry | - | √ | - | - | √ | There is a mediation effect of job satisfaction on the relationship between G-HRM and its impact on organizational citizenship behavior. |
| Ren and Hussain (2022) | Industry | - | - | √ | - | √ | A positive and significant effect of G-HRM on employee and organizational environmental performance. There is a partial mediation of employee environmental performance. |
| Xiao et al. (2022) | Hospitality and Tourism | - | - | √ | √ | - | G-HRM, aka G-HRM, directly impacts consumer behavior. Diffidence moderates the relationship between G-HRM and employee performance and employee eco-friendly behavior. |
| Al-Swidi et al. (2021) | Public Services | - | - | √ | - | √ | A significant effect of G-HRM practices on green organizational culture. G-HRM practices has a significant positive relationship with employees’ behavior and organizational performance. |
| Mousa and Othman (2020) | Healthcare | - | - | - | - | √ | G-HRM practices had a positive influence on sustainable performance |
| Hameed et al. (2019) | Industry | √ | - | √ | - | - | G-HRM has a significant indirect effect on employee organizational citizenship behavior toward environment through green employee empowerment. The individual green values moderated this relationship. |
| Zhang et al. (2019) | Enterprises | - | - | √ | - | - | G-HRM practices (employee life cycle, education and training, employee empowerment, and manager involvement) all had significant positive effect on the employees in-role and extra-role green behavior. |
| Rawashdeh (2018) | Healthcare | - | - | - | - | √ | A positive significant correlation between G-HMR practices (recruitment and selection, training, and development) and organizational performance. |
| Masri and Jaaron (2017) | Industry | - | - | - | - | √ | A positive significant correlation between the G-HRM practices (recruitment and selection, training and development, performance management and appraisal, reward and compensation, employee empowerment and participation, and green management) and environmental performance. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlKetbi, A.; Rice, J. The Impact of Green Human Resource Management Practices on Employees, Clients, and Organizational Performance: A Literature Review. Adm. Sci. 2024, 14, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14040078
AlKetbi A, Rice J. The Impact of Green Human Resource Management Practices on Employees, Clients, and Organizational Performance: A Literature Review. Administrative Sciences. 2024; 14(4):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14040078
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlKetbi, Aisha, and John Rice. 2024. "The Impact of Green Human Resource Management Practices on Employees, Clients, and Organizational Performance: A Literature Review" Administrative Sciences 14, no. 4: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14040078
APA StyleAlKetbi, A., & Rice, J. (2024). The Impact of Green Human Resource Management Practices on Employees, Clients, and Organizational Performance: A Literature Review. Administrative Sciences, 14(4), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14040078






