A Longitudinal Investigation of the Changes in Work Motivation and Employees’ Psychological Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
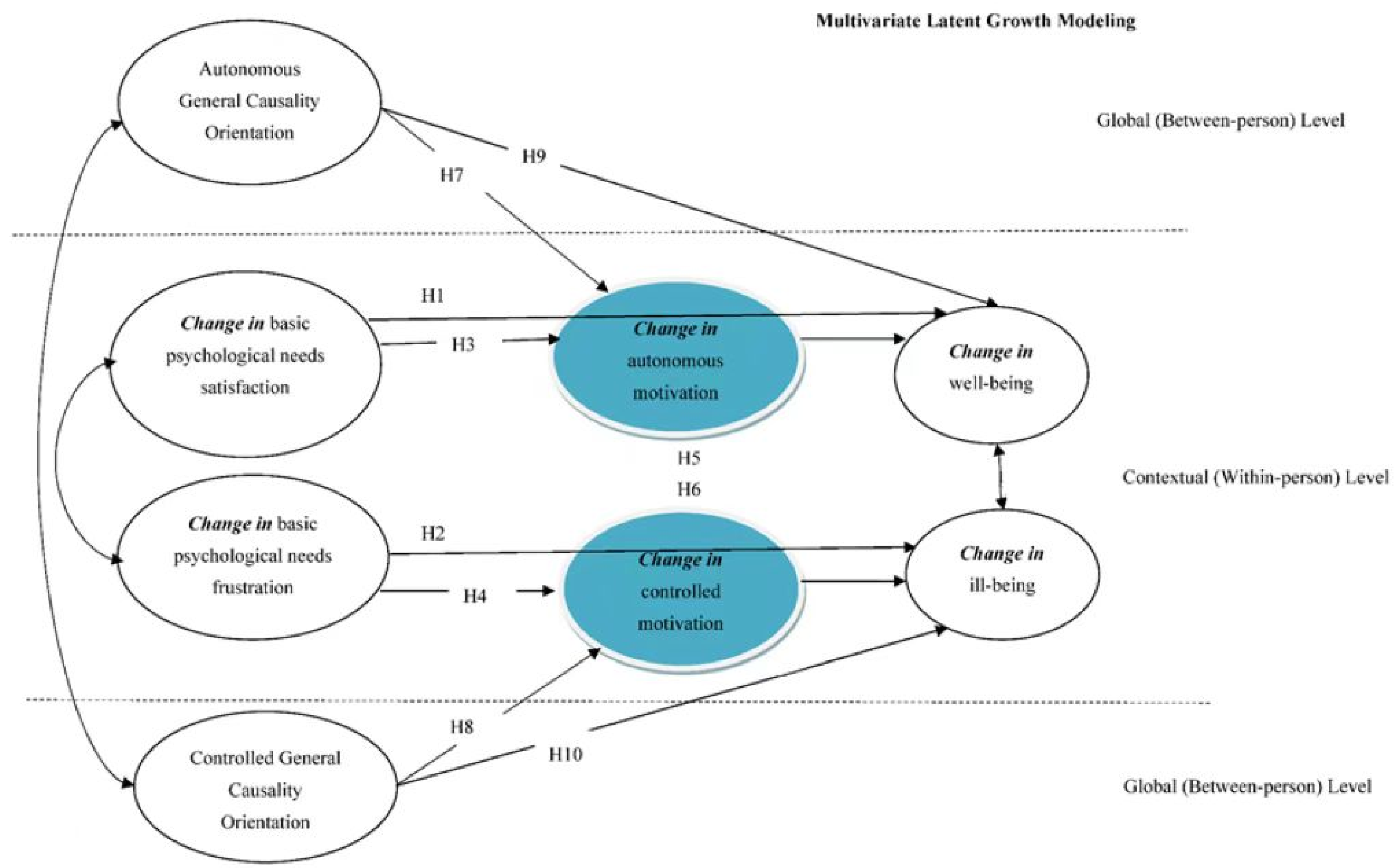
Theoretical Framework and Research Hypotheses
2. Methods
2.1. Procedures
2.2. Samples
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Simple Correlations
3.2. Measurement Invariance
3.3. Multivariate Latent Growth Curve Modelling
4. Discussions, Limitations, and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adie, James W., Joan L. Duda, and Nikos Ntoumanis. 2008. Autonomy support, basic need satisfaction and the optimal functioning of adult male and female sport participants: A test of basic needs theory. Motivation and Emotion 32: 189–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adie, James W., Joan L. Duda, and Nikos Ntoumanis. 2012. Perceived coach-autonomy support, basic need satisfaction and the well-and ill-being of elite youth soccer players: A longitudinal investigation. Psychology of Sport and Exercise 13: 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baard, Paul P., Edward L. Deci, and Richard M. Ryan. 2004. Intrinsic need satisfaction: A motivational basis of performance and well-being in two work settings. Journal of Applied Social Psychology 34: 2045–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, Albert. 1991. Social cognitive theory of self-regulation. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 50: 248–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, Albert. 2001. Social cognitive theory: An agentic perspective. Annual Review of Psychology 52: 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomew, Kimberley Jane, Nikos Ntoumanis, Richard M. Ryan, Jos A. Bosch, and Cecilie Thøgersen-Ntoumani. 2011. Self-determination theory and diminished functioning: The role of interpersonal control and psychological need thwarting. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin 37: 1459–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, Roy F., and Mark R. Leary. 1995. The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychological Bulletin 117: 497–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidee, Jemima, Tim Vantilborgh, Roland Pepermans, Yannick Griep, and Joeri Hofmans. 2016. Temporal dynamics of need satisfaction and need frustration. Two sides of the same coin? European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology 25: 900–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boezeman, Edwin J., and Naomi Ellemers. 2009. Intrinsic need satisfaction and the job attitudes of volunteers versus employees working in a charitable volunteer organization. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology 82: 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brislin, Richard. W. 1980. Translation and content analysis of oral and written materials. In Handbook of Cross-Cultural Psychology: Methodology. Edited by Harry. C. Triandis and Water Lonner. Boston: Allyn & Bacon, vol. 2, pp. 389–444. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, David, and Neal Schmitt. 2000. Interindividual differences in intraindividual changes in proactivity during organizational entry: A latent growth modeling approach to understanding newcomer adaptation. Journal of Applied Psychology 85: 190–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Beiwen, Maarten Vansteenkiste, Wim Beyers, Liesbet Boone, Edward L. Deci, J Van der Kaap-Deeder, Bart Duriez, Willy Lens, Lennia Matos, Athanasios Mouratidis, and et al. 2015. Basic psychological need satisfaction, need frustration, and need strength across four cultures. Motivation and Emotion 39: 216–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirkov, Valert, Richard M. Ryan, Youngmee Kim, and Ulas Kaplan. 2003. Differentiating autonomy from individualism and independence: A self-determination theory perspective on internalization of cultural orientations and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 84: 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csikszentmihalyi, Mihaly. 1988. Society, Culture, and Person: A Systems View of Creativity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- DeCharms, Richard. 1968. Personal Causation. New York: Academic Press. [Google Scholar]
- Deci, Edward L., and Richard M. Ryan. 1985a. Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in Human Behavior. New York: Springer Science & Business Media. [Google Scholar]
- Deci, Edward L., and Richard M. Ryan. 1985b. The general causality orientations scale: Self-determination in personality. Journal of Research in Personality 19: 109–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, Edward L., and Richard M. Ryan. 2000. The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior. Psychological Inquiry 11: 227–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, Edward L., and Richard M. Ryan. 2008a. Facilitating optimal motivation and psychological well-being across life’s domains. Canadian Psychology/Psychologie Canadienne 49: 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, Edward L., and Richard M. Ryan. 2008b. Self-determination theory: A macro theory of human motivation, development, and health. Canadian Psychology/Psychologie Canadienne 49: 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, Edward L, Richard M. Ryan, Marylène Gagné, Dean R. Leone, Julian Usunov, and Boyanka P. Kornazheva. 2001. Need satisfaction, motivation, and well-being in the work organizations of a former eastern bloc country: A cross-cultural study of self-determination. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 27: 930–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernet, Claude, David Litalien, Alexandre J. Morin, Stéphanie Austin, Marylène Gagné, Mélanie Lavoie-Tremblay, and Jacques Forest. 2020. On the temporal stability of self-determined work motivation profiles: A latent transition analysis. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology 29: 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, Marylène. 2003. Autonomy support and need satisfaction in the motivation and well-being of gymnasts. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology 15: 372–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, Marylène, and Devasheesh Bhave. 2011. Autonomy in the workplace: An essential ingredient to employee engagement and well-being in every culture. In Human Autonomy in Cross-Cultural Context. New York: Springer, pp. 163–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, Marylène, and Edward. L. Deci. 2005. Self-determination theory and work motivation. Journal of Organizational Behavior 26: 331–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, Marylène, Jacques Forest, Maarten Vansteenkiste, Laurence Crevier-Braud, Anja Van den Broeck, Ann Kristin Aspeli, Jenny Bellerose, Charles Benabou, Emenuela Chemolli, Stefan Tomas Güntert, and et al. 2015. The Multidimensional Work Motivation Scale: Validation evidence in seven languages and nine countries. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology 24: 178–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, Nicholas, Evelyne Fouquereau, Jacques Forest, Paul Brunault, and Philippe Colombat. 2012. The impact of organizational factors on psychological needs and their relations with well-being. Journal of Business and Psychology 27: 437–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, Jodi S., and Terry C. Blum. 1996. Assessing the non-random sampling effects of subject attrition in longitudinal research. Journal of Management 22: 627–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guastello, Stephen J., David E. Marra, Julian Castro, Marybeth Gomez, and Claire Perna. 2017. Performance and participation dynamics in an emergency response simulation. Nonlinear Dynamics, Psychology, and Life Sciences 21: 217–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guastello, Stephen J., Matthijs Koopmans, and David Pincus, eds. 2008. Chaos and Complexity in Psychology: The Theory of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Guay, Frédéric, Geneviève A. Mageau, and Richard J. Vallerand. 2003. On the hierarchical structure of self-determined motivation: A test of top-down, bottom-up, reciprocal, and horizontal effects. Personality & Social Psychology Bulletin 29: 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogenelst, Koen, Roos Schelvis, Tanja Krone, Marylène Gagné, Matti T. Heino, Keegan Knittle, and Nelli Hankonen. 2020. A Within-Person Approach to the Relation between Quality of Task Motivation, Performance and Job Satisfaction in Everyday Working Life. Available online: psyarxiv.com (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Hooper, Daire, Joseph Coughlan, and Michael R. Mullen. 2008. Structural equation modeling: Guidelines for determining model fit. Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods 6: 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Koestner, Richard, and Miron Zuckerman. 1994. Causality orientations, failure, and achievement. Journal of Personality 62: 321–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, Bethany M., Ann E. C. Hooper, Renee E. Magnan, and Angela D. Bryan. 2011. A longitudinal diary study of the effects of causality orientations on exercise-related affect. Self and Identity 10: 363–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, Charles E., Robert J. Vandenberg, and Robin M. Self. 2000. Latent growth models of individual change: The case of newcomer adjustment. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 83: 107–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonky, E., and J. M. Reihman. 1990. Self-Regulation and Moral Reasoning as Mediators of Moral Behavior, Unpublished manuscript. Oswego, NY, USA: Department of Psychology, the State University of New York at Oswego.
- Martela, Frank, and Kennon M. Sheldon. 2019. Clarifying the concept of well-being: Psychological needs satisfaction as the common core connecting eudaimonic and subjective well-being. Review of General Psychology 23: 458–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdams, Dan P., and Jennifer L. Pals. 2006. A new Big Five: Fundamental principles for an integrative science of personality. American Psychologist 61: 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milyavskaya, Marina, and Richard Koestner. 2011. Psychological needs, motivation, and well-being: A test of self-determination theory across multiple domains. Personality and Individual Differences 50: 387–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthén, Begnt. 2002. Beyond SEM: General latent variable modeling. Behaviormetrika 29: 81117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthén, Linda K., and Begnt O. Muthén. 2012. Mplus Version 7 User’s Guide. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, José, and Carlos Arrieta. 2010. Chaos in human behavior: The case of work motivation. The Spanish Journal of Psychology 13: 244–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, José, Rita Rueff-Lopes, and Ramón Rico. 2020. New nonlinear and dynamic avenues for the study of work and organizational psychology: An introduction to the special issue. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology 29: 477–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Takuma, and Takashi Suzuki. 2016. Basic psychological need satisfaction and frustration in Japan: Controlling for the big five personality traits. Japanese Psychological Research 58: 320–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinder, Craig C., ed. 2008. Work Motivation in Organizational Behavior, 2nd ed. New York: Psychology Press, Taylor & Francis Group. [Google Scholar]
- Ployhart, Robert E., and Robert J. Vandenberg. 2010. Longitudinal research: The theory, design, and analysis of change. Journal of Management 36: 94–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raedeke, Thomas D., and Alan L. Smith. 2001. Development and preliminary validation of an athlete burnout measure. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology 23: 281–306. [Google Scholar]
- Reinboth, Michael, and Joan L. Duda. 2006. Perceived motivational climate, need satisfaction and indices of well-being in team sports: A longitudinal perspective. Psychology of Sport and Exercise 7: 269–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, Harry T., Kennon M. Sheldon, Shelly L. Gable, Joseph Roscoe, and Richard M. Ryan. 2000. Daily well-being: The role of autonomy, competence, and relatedness. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 26: 419–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, Richard M., and Edward L. Deci. 2000. Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist 55: 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, Richard M., and Edward L. Deci. 2001. On happiness and human potentials: A review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Annual Review of Psychology 52: 141–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, Richard M., and Edward L. Deci. 2017. Self-Determination Theory: Basic Psychological Needs in Motivation, Development, and Wellness. New York: Guilford Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Schaufeli, Wilmar B., Arnold B. Bakker, and Marisa Salanova. 2006. The measurement of work engagement with a short questionnaire a cross-national study. Educational and Psychological Measurement 66: 701–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, Abbie J., and Michael S. Cole. 2015. Time in individual-level organizational studies: What is it, how is it used, and why isn’t it exploited more often? Annual Review of Organizational. Psychology and Organizational Behavior 2: 237–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Alison, Nikolaos Ntoumanis, and Joan L. Duda. 2007. Goal striving, goal attainment, and well-being: Adapting and testing the self-concordance model in sport. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology 29: 763–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, Pual E. 1986. Perceived control by employees: A meta-analysis of studies concerning autonomy and participation at work. Human Relations 39: 1005–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standage, Martyn, Joan L. Duda, and Nikos Ntoumanis. 2006. Students’ motivational processes and their relationship to teacher ratings in school physical education: A self-determination theory approach. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 77: 100–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taris, Toon W., Raija Kalimo, and William B. Schaufeli. 2002. Inequity at work: Its measurement and association with worker health. Work & Stress 16: 287–301. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, Cynthia A., and David J. Prottas. 2006. Relationships among organizational family support, job autonomy, perceived control, and employee well-being. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology 11: 100–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallerand, Robert J. 1997. Toward a hierarchical model of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology 29: 271–360. [Google Scholar]
- Vallerand, Robert J., and Catherine F. Ratelle. 2002. Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation: A hierarchical model. Handbook of Self-Determination Research 128: 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broeck, Anja, Maarten Vansteenkiste, Hans Witte, Bart Soenens, and Willy Lens. 2010. Capturing autonomy, competence, and relatedness at work: Construction and initial validation of the Work-related Basic Need Satisfaction scale. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology 83: 981–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Voorhis, Carmen W., and Bestsy L. Morgan. 2007. Understanding power and rules of thumb for determining sample sizes. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology 3: 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, Maarten, and Richard M. Ryan. 2013. On psychological growth and vulnerability: Basic psychological need satisfaction and need frustration as a unifying principle. Journal of Psychotherapy Integration 23: 263–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, Maarten, Richard M. Ryan, and Bart Soenens. 2020. Basic psychological need theory: Advancements, critical themes, and future directions. Motivation and Emotion 44: 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Soest, Tilmann, and Knut A. Hagtvet. 2011. Mediation analysis in a latent growth curve modeling framework. Structural Equation Modelling 18: 289–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Zheni, and Marylène Gagné. 2013. Mapping the moment-to-moment motivation and well-being at work: A mixed-method and multi-level investigation. Paper presented at the 5th International Conference on Self-determination Theory, Rochester, NY, USA, June 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, Geoffrey C., Virginia M. Grow, Zachary R. Freedman, Richard M. Ryan, and Edward L. Deci. 1996. Motivational predictors of weight loss and weight-loss maintenance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 70: 115–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Variables | Min. | Max. | Mean | SD | Variance | Skewness | Kurtosis | Independent t-Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stat | Std. Err. | Stat | Std. Err. | T1 vs. T2 | T1 vs. T3 | T2 vs. T3 | ||||||||
| Basic Needs Satisfaction | Autonomy | T1 | 3 | 7 | 4.31 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.15 | 0.23 | −0.20 | 0.46 | A | A | A |
| T2 | 3 | 7 | 4.41 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 0.38 | 0.23 | 0.95 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 2 | 7 | 4.38 | 0.76 | 0.57 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 1.31 | 0.46 | |||||
| Competence | T1 | 3 | 7 | 5.44 | 0.86 | 0.74 | −0.34 | 0.23 | −0.29 | 0.46 | A | A | A | |
| T2 | 4 | 7 | 5.24 | 0.82 | 0.66 | −0.02 | 0.23 | −0.67 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 4 | 7 | 5.27 | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.02 | 0.23 | −0.88 | 0.46 | |||||
| Relatedness | T1 | 3 | 7 | 4.96 | 0.63 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.62 | 0.46 | B | B | A | |
| T2 | 4 | 6 | 4.80 | 0.54 | 0.29 | −0.15 | 0.23 | −0.53 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 3 | 6 | 4.78 | 0.58 | 0.34 | −0.24 | 0.23 | −0.32 | 0.46 | |||||
| Basic Needs Frustration | Autonomy | T1 | 1 | 7 | 3.54 | 1.12 | 1.26 | −0.07 | 0.23 | 0.34 | 0.46 | A | A | A |
| T2 | 1 | 6 | 3.59 | 1.07 | 1.14 | −0.40 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 1 | 6 | 3.45 | 1.08 | 1.17 | −0.27 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.46 | |||||
| Competence | T1 | 1 | 7 | 4.24 | 1.06 | 1.13 | −0.48 | 0.23 | 1.02 | 0.46 | B | B | A | |
| T2 | 1 | 6 | 3.93 | 0.86 | 0.75 | −0.45 | 0.23 | 0.79 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 2 | 6 | 3.78 | 0.98 | 0.95 | −0.04 | 0.23 | −0.31 | 0.46 | |||||
| Relatedness | T1 | 1 | 7 | 2.93 | 1.09 | 1.19 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 1.15 | 0.46 | A | A | A | |
| T2 | 1 | 6 | 2.92 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 0.23 | −0.09 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 1 | 7 | 2.67 | 1.03 | 1.07 | 1.11 | 0.23 | −0.31 | 0.46 | |||||
| Motivation at Work | Autonomous Motivation | T1 | 1 | 7 | 4.77 | 1.01 | 1.03 | −0.92 | 0.23 | 2.83 | 0.46 | A | A | A |
| T2 | 2 | 7 | 4.76 | 0.80 | 0.64 | −0.09 | 0.23 | 0.58 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 1 | 7 | 4.77 | 1.02 | 1.04 | −0.07 | 0.23 | 1.28 | 0.46 | |||||
| Controlled Motivation | T1 | 1 | 7 | 4.27 | 0.96 | 0.92 | −0.82 | 0.23 | 1.78 | 0.46 | A | A | A | |
| T2 | 1 | 7 | 4.39 | 0.96 | 0.92 | −0.47 | 0.23 | 1.36 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 1 | 6 | 4.25 | 0.99 | 0.99 | −0.29 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 0.46 | |||||
| Well-being | Work Engagement | T1 | 2 | 7 | 5.02 | 1.06 | 1.13 | −0.20 | 0.23 | −0.41 | 0.46 | A | A | A |
| T2 | 2 | 7 | 4.99 | 0.99 | 0.98 | −0.29 | 0.23 | −0.01 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 2 | 7 | 5.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 0.08 | 0.23 | −0.46 | 0.46 | |||||
| Ill-being | Physical and Psychological Exhaustion | T1 | 1 | 5 | 2.44 | 0.52 | 0.25 | −0.09 | 0.23 | −0.98 | 0.46 | A | A | A |
| T2 | 1 | 4 | 2.38 | 0.50 | 0.25 | −0.15 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.46 | |||||
| T3 | 1 | 5 | 2.37 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.84 | 0.46 | |||||
| GCO | Autonomous | T1 | 2 | 6 | 3.61 | 0.72 | 0.51 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.61 | 0.47 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Controlled | T1 | 3 | 7 | 4.83 | 0.78 | 0.62 | −0.14 | 0.24 | −0.12 | 0.47 | ||||
| Impersonal | T1 | 3 | 7 | 4.34 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 0.45 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.47 | ||||
| Scale | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Basic Needs Satisfaction | A | T1 | 0.97 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | T2 | 0.59 ** | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | T3 | 0.48 ** | 0.67 ** | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | C | T1 | 0.29 * | 0.24 * | 0.28 ** | 0.97 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | T2 | 0.15 | 0.40 ** | 0.36 ** | 0.49 ** | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | T3 | 0.21 * | 0.29 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.59 ** | 0.83 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | R | T1 | 0.28 ** | 0.29 ** | 0.23 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | T2 | 0.19 * | 0.36 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.30 ** | 0.36 ** | 0.35 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.78 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | T3 | 0.21 * | 0.36 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.20 ** | 0.17 | 0.33 ** | 0.37 ** | 0.55 ** | 0.70 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Basic Needs Frustration | A | T1 | −0.58 ** | −0.46 ** | −0.35 ** | −0.25 ** | −0.33 ** | −0.27 ** | −0.23 * | −0.19 * | −0.22 * | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | T2 | −0.47 ** | −0.60 ** | −0.54 ** | −0.13 | −0.24 ** | −0.12 | −0.31 ** | −0.25 ** | −0.24 * | 0.51 ** | 0.86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | T3 | −0.42 ** | −0.47 ** | −0.67 ** | −0.22 * | −0.23 ** | −0.30 ** | −0.14 | −0.17 | −0.24 * | 0.45 ** | 0.62 ** | 0.88 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | C | T1 | −0.40 ** | −0.25 ** | −0.21 * | −0.13 | −0.08 | −0.01 | −0.04 | −0.15 | −0.03 | 0.48 ** | 0.21 * | 0.24 * | 0.94 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | T2 | −0.34 ** | −0.36 ** | −0.33 ** | −0.29 ** | −0.18 | −0.11 | −0.10 | −0.06 | −0.04 | 0.35 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.86 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | T3 | −0.22 * | −0.29 ** | −0.43 ** | −0.21 * | −0.23 * | −0.29 ** | 0.07 | −0.03 | −0.11 | 0.24 * | 0.36 ** | 0.59 ** | 0.22 * | 0.42 ** | 0.75 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | R | T1 | −0.41 ** | −0.36 ** | −0.38 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.20 * | −0.32 ** | −0.23 * | −0.38 ** | −0.30 * | 0.55 ** | 0.27 ** | 0.28 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.24 * | 0.94 | |||||||||||||||||
| 17 | T2 | −23 * | −0.26 ** | −0.25 ** | −0.16 | −0.10 | −0.13 | −0.06 | −0.21 * | −0.19 | 0.25 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.31 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.34 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||
| 18 | T3 | −0.15 | −0.13 | −0.23 ** | −0.12 | 0.06 | −0.28 ** | −0.03 | −0.15 | −0.19 * | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.39 ** | 0.20 ** | 0.19 | 0.32 ** | 0.36 ** | 0.54 ** | 0.87 | ||||||||||||||||
| 19 | Motivation at Work | AM | T1 | 0.23 * | 0.22 * | 0.26 ** | 0.31 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.33 ** | 0.21 * | 0.32 ** | 0.24 * | −0.30 ** | −0.18 | −0.17 | −0.03 | −0.08 | −0.11 | −0.32 ** | −0.02 | −0.02 | 0.97 | |||||||||||||
| 20 | T2 | 0.21 * | 0.34 ** | 0.29 ** | 0.23 * | 0.32 ** | 0.24 ** | 0.16 | 0.21 * | 0.25 ** | −0.22 * | −0.19 * | −0.17 | 0.09 | −0.05 | −0.21 * | −0.08 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.37 ** | 0.81 | ||||||||||||||
| 21 | T3 | 0.23 * | 0.21 * | 0.32 ** | 0.25 * | 0.40 ** | 0.59 ** | 0.22 * | 0.22 * | 0.40 ** | −0.44 ** | −0.13 | −0.32 ** | −0.15 | −0.16 | −0.23 * | −0.30 ** | −0.04 | −0.20 * | 0.43 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.94 | |||||||||||||
| 22 | CM | T1 | −0.21 * | −0.14 | −0.07 | −0.01 | 0.11 | 0.22 * | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.21 * | 0.19 | 0.06 | 0.28 ** | 0.10 | 0.40 ** | 0.23 * | 0.35 ** | 0.97 | |||||||||||
| 23 | T2 | −0.17 | −0.04 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.13 | −0.03 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.19 * | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.21 * | 0.17 | 0.25 ** | 0.50 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.49 ** | 0.93 | |||||||||||
| 24 | T3 | −0.10 | −0.12 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.25 ** | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.08 | −0.06 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.14 | −0.05 | 0.22 * | 0.04 | 0.32 ** | 0.29 ** | 0.51 ** | 0.62 ** | 0.60 ** | 0.91 | ||||||||||
| 25 | Well-being | WE | T1 | 0.43 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.22 ** | 0.25 ** | 0.31 ** | 0.22 * | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.26 ** | −0.41 ** | −0.24 * | −0.26 ** | 0.18 | −0.25 ** | −0.12 | −0.15 | −0.18 | −0.12 | 0.27 ** | 0.38 ** | 0.29 ** | −0.02 | 0.21 * | −0.01 | 0.98 | |||||||
| 26 | T2 | 0.30 ** | 0.44 ** | 0.25 ** | 0.20 * | 0.31 ** | 0.25 ** | 0.12 | 0.21 * | 0.22 * | −0.37 ** | −0.26 ** | −0.21 * | 0.04 | −0.18 | −0.18 | −0.11 | −0.03 | −0.02 | 0.35 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.12 | 0.37 ** | 0.11 | 0.75 ** | 0.96 | ||||||||
| 27 | T3 | 0.26 ** | 0.39 ** | 0.28 ** | 0.26 ** | 0.39 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.29 ** | 0.24 * | 0.30 ** | −0.43 ** | −0.29 ** | −0.26 ** | 0.08 | −0.22 * | −0.19 * | −0.17 | −0.19 | −0.16 | 0.29 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.53 ** | 0.04 | 0.24 * | 0.13 | 0.67 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.97 | |||||||
| 28 | Ill-being | ABQ | T1 | −0.62 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.34 ** | −0.34 ** | −0.35 ** | −0.28 ** | −0.24 * | −0.20 * | −0.28 ** | 0.62 ** | 0.41 ** | 0.31 ** | 0.39 * | 0.31 ** | 0.19 * | 0.36 ** | 0.29 ** | 0.17 | −0.25 ** | −0.19 * | −0.31 ** | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.04 | −0.53 ** | −0.40 ** | −0.34 ** | 0.99 | ||||
| 29 | T2 | −0.35 ** | −0.50 ** | −0.43 ** | −0.30 ** | −0.37 ** | −0.30 ** | −0.19 * | −0.16 | −0.29 ** | 0.35 ** | 0.49 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.08 | 0.37 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.15 | 0.27 ** | 0.06 | −0.27 ** | −0.38 ** | −25 ** | −0.07 | −0.20 * | 0.03 | −0.48 ** | −0.55 ** | −0.50 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.90 | |||||
| 30 | T3 | −0.24 ** | −0.37 ** | −0.42 ** | −0.19 ** | −0.30 ** | −0.48 ** | −0.15 | −0.19 * | −0.38 ** | 0.36 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.53 ** | 0.17 | 0.30 ** | 0.56 ** | 0.26 ** | 0.31 ** | 0.39 ** | −0.18 | −0.32 ** | −0.51 ** | −0.12 | −0.13 | −0.11 | −0.35 ** | −0.40 ** | −0.48 ** | 0.42 ** | 0.62 ** | 0.92 | ||||
| 31 | GCO | AUT | T1 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.27 ** | 0.21 * | 0.26 ** | 0.30 ** | −0.09 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.07 | −0.26 * | 0.01 | −0.07 | −0.07 | 0.20 * | 0.34 ** | 0.27 ** | 0.29 ** | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.21 * | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.00 | −0.17 | 0.78 | |
| 32 | CON | T1 | −0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.26 ** | 0.20 * | 0.30 ** | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.22 * | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 05 | −0.07 | −0.20 * | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.26 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.33 ** | 0.24 | 0.28 ** | 0.18 | 0.30 ** | 0.28 ** | −0.18 | 0.20 * | −0.31 ** | 0.46 ** | 0.75 | |
| Model Fit Index | χ2 | df | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Work Motivation | Autonomous Motivation | 547.56 | 30 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.09 | 0.13 |
| Controlled Motivation | 1348.62 | 135 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.06 | 0.10 | |
| Needs Satisfaction | Autonomy | 312.03 | 18 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| Competence | 219.73 | 18 | 0.996 | 0.997 | 0.02 | 0.09 | |
| Relatedness | 347.70 | 18 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.08 | 0.08 | |
| Needs Frustration | Autonomy | 296.51 | 45 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.04 | 0.08 |
| Competence | 245.48 | 18 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.10 | |
| Relatedness | 260.25 | 45 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.06 | 0.10 | |
| Well-being | Work Engagement | 3993.11 | 408 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| Ill-being | ABQ | 2090.22 | 315 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.08 | 0.10 |
| Autonomy Need | Competence Need | Relatedness Need | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | S.E. | p | Estimate | S.E. | p | Estimate | S.E. | p | |
| Mean Levels | |||||||||
| Intercept Needs_S | 4.43 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | 5.50 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | 4.94 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Needs_F | 3.66 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 4.17 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 3.01 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 |
| Intercept well | 5.02 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 4.97 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 4.97 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Ill | 2.39 ** | 0.05 | 0.000 | 2.38 ** | 0.06 | 0.000 | 2.38 ** | 0.06 | 0.000 |
| Slope Well | −0.004 | 0.04 | 0.93 | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.92 | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.86 |
| Slope Ill | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.12 | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.13 | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.13 |
| Slope Needs_S | 0.007 | 0.07 | 0.92 | −0.05 | 0.07 | 0.46 | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.40 |
| Slope Needs_F | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.64 | −0.11 | 0.07 | 0.11 | −0.08 | 0.06 | 0.22 |
| Variances | |||||||||
| Intercept Needs_S | 0.40 ** | 0.07 | 0.000 | 0.38 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | 0.16 * | 0.04 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Needs_F | 0.69 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 | 0.43 * | 0.09 | 0.000 | 0.48 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Well | 0.74 ** | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.77 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 | 0.76 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Ill | 0.15 ** | 0.03 | 0.000 | 0.15 ** | 0.03 | 0.000 | 0.13 ** | 0.03 | 0.000 |
| Slope Well | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.13 | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.41 |
| Slope Ill | −0.05 ** | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.04 * | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.04 * | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Slope Needs_S | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.36 | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.64 |
| Slope Needs_F | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.51 | −0.03 | 0.03 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.18 |
| Correlations | |||||||||
Intercept Needs_S  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | −0.84 ** | 0.07 | 0.000 | −0.40 * | 0.12 | 0.001 | −0.14 * | 0.04 | 0.002 |
Intercept Needs_S  Intercept ill Intercept ill | −0.72 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | −0.58 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | −0.07 * | 0.02 | 0.001 |
Intercept Well  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | −0.48 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | −0.28 ** | 0.11 | 0.009 | −0.12 | 0.08 | 0.115 |
Intercept Well  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | 0.56 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 0.45 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 0.14 * | 0.05 | 0.005 |
Intercept ill  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | 0.79 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 0.56 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 | 0.16 ** | 0.04 | 0.000 |
Slope ill  Slope Well Slope Well | −0.68 ** | 0.14 | 0.000 | −0.63 * | 0.19 | 0.001 | −0.02 | 0.01 | 0.119 |
| Coefficients | |||||||||
Intercept Needs_S  Slope Well Slope Well | −0.51 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 | −0.11 | 0.19 | 0.57 | −1.28 | 0.88 | 0.15 |
Intercept Needs_F  Slope Ill Slope Ill | −0.37 ** | 0.12 | 0.002 | −0.53 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 | −0.67 | 0.67 | 0.33 |
Intercept Well  Slope Needs_S Slope Needs_S | −0.29 * | 0.13 | 0.020 | −0.17 | 0.15 | 0.27 | −0.64 | 1.28 | 0.62 |
Intercept Ill  Slope Needs_F Slope Needs_F | −0.49 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | −0.28 * | 0.13 | 0.03 | −0.46 * | 0.25 | 0.05 |
Slope Needs_S  Slope Well (H1) Slope Well (H1) | 0.90 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 1.09 ** | 0.29 | 0.000 | 0.82 | 0.58 | 0.16 |
Slope Needs_F  Slope Ill (H2) Slope Ill (H2) | 0.94 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | 1.09 ** | 0.11 | 0.45 | 1.24 * | 0.49 | 0.01 |
| Autonomy Need | Competence Need | Relatedness Need | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | S.E. | p | Estimate | S.E. | p | Estimate | S.E. | p | |
| Mean Levels | |||||||||
| Intercept Needs_S | 4.43 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | 5.50 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | 4.96 ** | 0.06 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Needs_F | 3.72 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 4.26 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 3.02 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Auto_M | 4.87 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 4.87 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 4.86 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 |
| Slope Auto_M | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.54 | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.57 | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.60 |
| Intercept Contr_M | 4.37 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 4.36 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 4.36 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 |
| Slope Contr_M | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.51 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.54 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.57 |
| Slope Needs_S | −0.00 | 0.05 | 0.93 | −0.02 | 0.06 | 0.71 | −0.02 | 0.06 | 0.72 |
| Slope Needs_F | −0.09 | 0.06 | 0.12 | −0.21 * | 0.06 | 0.001 | −0.04 | 0.17 | 0.81 |
| Variances | |||||||||
| Intercept Needs_S | 0.41 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 0.42 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 0.16 * | 0.05 | 0.002 |
| Intercept Needs_F | 0.66 ** | 0.13 | 0.000 | 0.34 * | 0.10 | 0.001 | 0.66 * | 0.19 | 0.001 |
| Intercept Auto_M | 0.31 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.41 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 0.38 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Contr_M | 0.30 * | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.41 * | 0.15 | 0.008 | 0.55 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 |
| Slope Auto_M | −0.06 | 0.10 | 0.54 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.41 |
| Slope Contr_M | −0.13 | 0.08 | 0.10 | −0.04 | 0.06 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.97 |
| Slope Needs_S | 0.06 * | 0.03 | 0.03 | −0.001 | 0.04 | 0.98 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.67 |
| Slope Needs_F | 0.11 * | 0.05 | 0.03 | −0.007 | 0.05 | 0.87 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| Correlations | |||||||||
Intercept Needs_S  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | −0.51 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 | −0.13 | 0.07 | 0.06 | −0.63 * | 0.20 | 0.002 |
Intercept Needs_F  Intercept Auto_M Intercept Auto_M | −0.17 | 0.09 | 0.10 | −0.09 | 0.08 | 0.27 | −0.42 * | 0.17 | 0.017 |
Intercept Auto_M  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | 0.20 * | 0.07 | 0.007 | 0.29 ** | 0.09 | 0.001 | 0.56 ** | 0.16 | 0.000 |
Intercept Auto_M  Intercept Contr_M Intercept Contr_M | 0.40 ** | 0.05 | 0.000 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.48 * | 0.16 | 0.003 |
Intercept Needs_F  Intercept Contr_M Intercept Contr_M | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.17 * | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.19 |
Slope Needs_S  Slope Needs_F Slope Needs_F | −0.07 * | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.62 | 0.41 | 1.24 | 0.74 |
Slope Auto_M  Slope Contr_M Slope Contr_M | −0.01 | 0.03 | 0.67 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.72 | −6.51 | 92.63 | 0.94 |
Intercept Needs_F  Slope Auto_M Slope Auto_M | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.17 | −0.003 | 0.04 | 0.94 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.91 |
Intercept Needs_S  Slope Contr_M Slope Contr_M | −0.08 | 0.06 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.72 | −0.09 | −0.24 | 0.81 |
Intercept Needs_S  Slope Auto_M Slope Auto_M | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.21 | 4.19 | 59.02 | 0.97 |
Intercept Needs_F  Slope Contr_M Slope Contr_M | 0.08 * | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.13 | −2.84 | 39.37 | 0.34 |
| Coefficients | |||||||||
Slope Needs_S  Slope Auto_M (H3) Slope Auto_M (H3) | 0.09 | 0.34 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 0.53 | 0.07 † | 0.82 | 0.38 | 0.22 |
Slope Needs_F  Slope Contr_M (H4) Slope Contr_M (H4) | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.44 | −0.40 | 0.53 | 0.45 | 0.14 | 1.92 | 0.94 |
| Autonomy Need | Competence Need | Relatedness Need | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | S.E. | p | Estimate | S.E. | p | Estimate | S.E. | p | |
| Mean Levels | |||||||||
| Intercept Needs_S | 4.41 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 5.50 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | 4.96 ** | 0.06 | 0.000 |
| Slope Needs_S | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.98 | −0.05 | 0.07 | 0.46 | −0.05 | 0.04 | 0.18 |
| Intercept Needs_F | 3.72 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 4.25 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 3.05 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Slope Needs_F | −0.09 | 0.06 | 0.11 | −0.19 | 0.06 | 0.11 | −0.14 * | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| Intercept Auto_M | 4.86 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 4.86 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 4.85 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Contr_M | 4.36 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 4.35 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 4.35 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Well | 5.00 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 5.00 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 5.01 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Ill | 2.43 ** | 0.05 | 0.000 | 2.44 ** | 0.05 | 0.000 | 2.44 ** | 0.05 | 0.000 |
| Slope Auto_M | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.88 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.45 |
| Slope Contr_M | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.99 | −0.01 | 0.06 | 0.87 |
| Slope Well | −0.06 | 0.17 | 0.72 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.61 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.64 |
| Slope Ill | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.29 |
| Variances | |||||||||
| Intercept Needs_S | 0.58 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 0.40 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 0.16 ** | 0.05 | 0.001 |
| Intercept Needs_F | 0.77 ** | 0.14 | 0.000 | 0.49 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 | 0.50 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Auto_M | 0.44 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 0.42 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 0.38 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Intercept Contr_M | 0.59 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 0.57 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 | 0.57 ** | 0.11 | 0.000 |
| Intercept well | 0.82 ** | 0.13 | 0.000 | 0.79 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 | 0.77 ** | 0.12 | 0.000 |
| Intercept ill | 0.22 ** | 0.04 | 0.000 | 0.19 ** | 0.03 | 0.000 | 0.18 ** | 0.04 | 0.000 |
| Slope Needs_S | 0.10 * | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.09 * | 0.04 | 0.016 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.24 |
| Slope Needs_F | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.15 |
| Slope Auto_M | −0.02 | 0.03 | 0.56 | −0.03 | 0.03 | 0.44 | −0.02 | 0.04 | 0.54 |
| Slope Contr_M | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.41 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.26 |
| Slope well | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.65 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.83 |
| Slope ill | −0.02 | 0.03 | 0.47 | −0.05 | 0.04 | 0.17 | −0.00 | 0.02 | 0.92 |
| Correlations | |||||||||
Slope Needs_S  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | −0.12 * | 0.05 | 0.01 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.40 | 0.002 | 0.02 | 0.92 |
Intercept Needs_F  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | −0.54 ** | 0.11 | 0.001 | −0.22 * | 0.07 | 0.002 | 0.11 * | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Intercept Needs_F  Slope Needs_S Slope Needs_S | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.40 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.78 |
Slope Needs_F  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | 0.08 * | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.26 |
Slope Needs_F  Slope Needs_S Slope Needs_S | −0.05 * | 0.03 | 0.03 | −0.05 | 0.03 | 0.06 | −0.03 | 0.02 | 0.10 |
Slope Needs_F  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | −0.09 | 0.05 | 0.10 | −0.10 | 0.07 | 0.14 | −0.02 | 0.04 | 0.57 |
Intercept Auto_M  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | 0.19 * | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.27 ** | 0.07 | 0.000 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
Intercept Auto_M  Slope Needs_S Slope Needs_S | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.59 | −0.01 | 0.04 | 0.86 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.85 |
Intercept Auto_M  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | −0.24 * | 0.08 | 0.003 | −0.14 * | 0.06 | 0.03 | −0.02 | 0.07 | 0.82 |
Intercept Auto_M  Slope Needs_F Slope Needs_F | −0.02 | 0.03 | 0.42 | −0.03 | 0.03 | 0.91 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.75 |
Intercept Contr_M  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | −0.20 * | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.80 |
Intercept Contr_M  Slope Needs_S Slope Needs_S | 0.11 * | 0.04 | 0.008 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.27 |
Intercept Contr_M  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | 0.19 * | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.20 * | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.21 * | 0.08 | 0.01 |
Intercept Contr_M  Slope Needs_F Slope Needs_F | −0.07 * | 0.03 | 0.03 | −0.08 * | 0.04 | 0.05 | −0.06 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
Intercept Contr_M  Intercept Auto_M Intercept Auto_M | 0.29 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 | 0.25 ** | 0.08 | 0.001 | 0.25 ** | 0.08 | 0.001 |
Intercept well  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | 0.40 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | 0.25 * | 0.08 | 0.002 | 0.12 * | 0.05 | 0.02 |
Intercept well  Slope Needs_S Slope Needs_S | −0.10 * | 0.05 | 0.03 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.65 |
Intercept well  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | −0.39 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 | −0.18 * | 0.08 | 0.02 | −0.11 | 0.08 | 0.18 |
Intercept well  Slope Needs_F Slope Needs_F | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.33 | −0.001 | 0.03 | 0.96 | −0.002 | 0.03 | 0.95 |
Intercept well  Intercept Auto_M Intercept Auto_M | 0.36 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 0.39 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 | 0.36 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 |
Intercept well  Intercept Contr_M Intercept Contr_M | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
Intercept ill  Intercept Needs_S Intercept Needs_S | −0.27 ** | 0.05 | 0.000 | −0.15 ** | 0.04 | 0.000 | −0.07 * | 0.03 | 0.01 |
Intercept ill  Slope Needs_S Slope Needs_S | 0.07 * | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.35 | −0.004 | 0.01 | 0.76 |
Intercept ill  Intercept Needs_F Intercept Needs_F | 0.30 ** | 0.06 | 0.000 | 0.19 ** | 0.05 | 0.000 | 0.16 * | 0.05 | 0.002 |
Intercept ill  Slope Needs_F Slope Needs_F | −0.06 | 0.03 | 0.053 | −0.04 | 0.02 | 0.11 | −0.04 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
Intercept ill  Intercept Auto_M Intercept Auto_M | −0.13 * | 0.04 | 0.002 | −0.15 ** | 0.04 | 0.000 | −0.14 ** | 0.04 | 0.001 |
Intercept ill  Intercept Contr_M Intercept Contr_M | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.54 | 0.006 | 0.04 | 0.90 |
Intercept ill  Intercept Well Intercept Well | −0.26 ** | 0.06 | 0.000 | −0.21 ** | 0.05 | 0.000 | −0.20 ** | 0.05 | 0.001 |
| Coefficients | |||||||||
Slope Needs_S  Slope Auto_M (H5a’) Slope Auto_M (H5a’) | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.56 | 0.69 * | 0.27 | 0.01 | 1.54 † | 0.80 | 0.06 |
Slope Needs_S  Slope Well (H5c’) Slope Well (H5c’) | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.31 | 0.97 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 2.55 | 4.03 | 0.53 |
Slope Auto_M  Slope Well (H5b’) Slope Well (H5b’) | −2.21 | 4.13 | 0.59 | −0.44 | 1.01 | 0.66 | −1.45 | 2.64 | 0.58 |
Slope Needs_F  Slope Contr_M (H6a’) Slope Contr_M (H6a’) | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.51 | 0.06 | 0.27 | 0.83 |
Slope Needs_F  Slope ill (H6c’) Slope ill (H6c’) | 0.90 * | 0.39 | 0.02 | 0.94 * | 0.41 | 0.02 | 0.84 * | 0.42 | 0.05 |
Slope Contr_M  Slope ill (H6b’) Slope ill (H6b’) | 0.18 | 0.53 | 0.74 | 0.14 | 0.35 | 0.70 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.45 |
| Parameter Estimate | S.E. | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Levels | |||
| Intercept Auto_M | 3.70 ** | 0.53 | 0.000 |
| Slope Auto_M | −0.22 | 0.33 | 0.52 |
| Intercept Contr_M | 3.31 ** | 0.46 | 0.000 |
| Slope Contr_M | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.64 |
| Auto_GC | 4.89 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 |
| Contr_GC | 4.41 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 |
| Variances | |||
| Intercept Auto_M | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.35 |
| Slope Auto_M | −0.13 | 0.10 | 0.21 |
| Intercept Contr_M | 0.28 | 0.15 | 0.06 |
| Slope Contr_M | −0.08 | 0.08 | 0.34 |
| Auto_GC | 0.76 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Contr_GC | 0.71 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Correlations | |||
Intercept Auto_M  Intercept Contr_M Intercept Contr_M | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.74 |
Slope Auto_M  Slope Contr_M Slope Contr_M | −0.07 | 0.07 | 0.14 |
Intercept Auto_M  Slope Auto_M Slope Auto_M | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.22 |
Intercept Contr_M  Slope Auto_M Slope Auto_M | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.24 |
Intercept Auto_M  Slope Contr_M Slope Contr_M | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.14 |
Intercept Contr_M  Slope Contr_M Slope Contr_M | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.11 |
| Coefficients | |||
Auto_GC  Slope Auto_M (H7) Slope Auto_M (H7) | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.57 |
Auto_GC  Intercept Auto_M Intercept Auto_M | 0.24 * | 0.11 | 0.03 |
Contr_GC  Slope Contr_M (H8) Slope Contr_M (H8) | −0.03 | 0.05 | 0.55 |
Contr_GC  Intercept Contr_M Intercept Contr_M | 0.24 * | 0.10 | 0.02 |
| Parameter Estimate | S.E. | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Levels | |||
| Intercept well | 3.93 ** | 0.49 | 0.000 |
| Slope well | −0.005 | 0.23 | 0.98 |
| Intercept ill | 2.64 ** | 0.22 | 0.000 |
| Slope ill | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.42 |
| Auto_GC | 4.89 ** | 0.09 | 0.000 |
| Contr_GC | 4.41 ** | 0.08 | 0.000 |
| Variances | |||
| Intercept well | 0.82 ** | 0.16 | 0.000 |
| Slope well | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.61 |
| Intercept ill | 0.16 ** | 0.04 | 0.000 |
| Slope ill | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.08 |
| Auto_GC | 0.76 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Contr_GC | 0.71 ** | 0.10 | 0.000 |
| Correlations | |||
Intercept well  Intercept ill Intercept ill | −0.25 ** | 0.06 | 0.000 |
Slope well  Slope ill Slope ill | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.26 |
Intercept well  Slope well Slope well | −0.06 | 0.08 | 0.43 |
Intercept ill  Slope well Slope well | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.26 |
Intercept well  Slope ill Slope ill | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.32 |
Intercept ill  Slope ill Slope ill | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.30 |
| Coefficients | |||
Auto_GC  Slope well (H9) Slope well (H9) | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.35 |
Auto_GC  Intercept well Intercept well | 0.22 * | 0.10 | 0.03 |
Contr_GC  Slope ill (H10) Slope ill (H10) | −0.05 | 0.05 | 0.27 |
Contr_GC  Intercept ill Intercept ill | −0.05 | 0.05 | 0.35 |
| Summary of Fit Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Types | Basic Needs | CFI | TLI | RMSEA | SRMR |
| Direct Path Model I (Needs to Well/Ill-being) | Autonomy | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Relatedness | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.03 | 0.05 | |
| Competence | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.05 | 0.03 | |
| Direct Path Model II (Needs to Motivation) | Autonomy | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Relatedness | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 0.03 | |
| Competence | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| Indirect Path Model (Needs to Well/Ill-being via Motivation) | Autonomy | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| Relatedness | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 0.05 | |
| Competence | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.04 | 0.02 | |
| Cross-Level Change Model | GCOs to Needs | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| GCOs to Motivation | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.07 | 0.07 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Panaccio, A. A Longitudinal Investigation of the Changes in Work Motivation and Employees’ Psychological Health. Adm. Sci. 2022, 12, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci12040193
Wang Z, Panaccio A. A Longitudinal Investigation of the Changes in Work Motivation and Employees’ Psychological Health. Administrative Sciences. 2022; 12(4):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci12040193
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zheni, and Alexandra Panaccio. 2022. "A Longitudinal Investigation of the Changes in Work Motivation and Employees’ Psychological Health" Administrative Sciences 12, no. 4: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci12040193
APA StyleWang, Z., & Panaccio, A. (2022). A Longitudinal Investigation of the Changes in Work Motivation and Employees’ Psychological Health. Administrative Sciences, 12(4), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci12040193





