Abstract
This systematic literature review investigates whether corporate sustainability (CS), according to the triple bottom line concept (TBL), is implemented in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and further identifies associated drivers. Building on upper echelon theory (UET) and the Schwartz value system (SVS) this study aims to analyze and contextualize extant empirical research. We developed a PRISMA-based framework to select relevant studies systematically. Based on an initial sample of 1249 articles between 2000 and 2020, we provide critical analysis of 31 best practice, peer-reviewed journal articles. Our findings suggest seven specifications of CS in SMEs that are driven by either internal or external motivations. Our review reveals that, overwhelmingly, SMEs engage in CS but fail to report it (“green blushing”). Furthermore, we find that the top managers of SMEs are a huge driver of CS. Oftentimes, they are even pioneers of good social and environmental practices. Finally, we identify four value dimensions (benevolence, achievement, power, and conformity values) according to the dimensions of the SVS that drive SMEs’ top managers’ engagement in CS. We contribute to the current state of research by conducting the first literature review that exclusively investigates how SMEs’ executives influence the enterprise’s commitment towards CS, based on the UET and the SVS. Thereby, we discuss implications and provide valuable recommendations for researchers, practitioners, and regulators alike.
1. Introduction
Corporate sustainability (CS) attracts a significant amount of attention in academic research as well as in business practice (Lueg et al. 2015). Despite recent research mostly focused on large multinational corporations (Jamali et al. 2009; Muheki et al. 2014; Spence 2007) research on small and medium enterprises (SMEs) has gained further momentum (Baden et al. 2011; Fassin et al. 2011). Although there has been a notable increase in SME-related CS studies, research in this area is still needed (Berk 2017). SMEs have only a limited individual impact. However, the overall SME business sector is globally important in economic, environmental, and social terms (Jenkins 2004; Kechiche and Soparnot 2012). SMEs represent 99 percent of all businesses in the European Union (EU) and employ nearly 70 percent of the workforce (European Commission 2003). Due to their heterogeneity and specific characteristics, “SMEs are not just smaller versions of larger-scale business” but needed to be considered separately in terms of implementing and developing CS (Kechiche and Soparnot 2012, p. 97; Jenkins 2004). SMEs possess several limitations due to their size, such as resource scarcity, financial restrictions, and lack of formalized planning (Del Brío and Junquera 2003; Klewitz and Hansen 2014). However, they benefit from less formal structures, fewer procedural hurdles, and the control of top executives (Longenecker et al. 2006; Fassin 2008; Jenkins 2004; Spence 2007). While large enterprises engage in sophisticated CS-reporting most SMEs currently do not, leading to the fallacy that SMEs do not engage in CS at all. The purpose of this literature review is to identify, analyze, and synthesize evidence to answer the two research questions:
RQ1: How do SMEs’ top managers perceive and implement CS?
RQ2: Which values drive SMEs’ top managers to engage in CS?
Based on an initial sample of 1249 articles, we conduct a systematic literature review of 31 key journal articles from 2000 to 2020. At present, no coherent theory exists about the drivers of CS in SMEs (Lepoutre and Heene 2006). Due to the difficulty of integrating the heterogenic field of SMEs in one general theoretical framework most extant theories only fit the context of large corporations (Lepoutre and Heene 2006; Johnson et al. 2001). However, research indicated that the perceptions of SME top managers are an important driver towards CS. Thus, this study builds on the upper echelon theory (UET) by Hambrick and Mason (1984) and the Schwartz value system (SVS) by Schwartz (2012). By adopting those theoretical frameworks to the specific characteristics of SMEs, the study provides useful insights in understanding how SME executives think and make strategic choices. Furthermore, the adoption of the UET should enrich the extant literature, which primarily focused on stakeholder or institutional theoretical explanations by investigating why SMEs’ top managers adopt CS. For defining CS, we build on the study of Lueg and Radlach (2016) which refers to CS as a concept of stakeholder management equally comprising economic, environmental, and social aspects. The literature argues that enterprises that use the triple bottom line (TBL) concept of CS voluntarily deal with social, economic, and environmental issues (people, profit, and planet), remain sustainable and survive in the long run (Van Marrewijk and Were 2003; Masud et al. 2019). In this systematic literature review, we use CS as an umbrella term, while referring to “any concept that addresses the three dimensions of ecological integrity, social responsibility and economic prosperity” (Lueg and Radlach 2016, p. 2).
We identified that SMEs engage in CS in seven different ways, driven by either internal motivations (e.g., (1) enterprise values and identity, (2) relationship with the local community, (3) business actions, (4) CS-reporting, (5) collaborations) or external motivations (e.g., (6) stakeholder pressure, (7) compliance with laws and regulations). Our results show that most SMEs engage in CS, although just a rare amount reports on it. This phenomenon is called green blushing, which is the opposite of greenwashing behavior, and could be reasoned by the missing regulatory obligation for SMEs to disclose on CS (Lueg and Lueg 2020). Moreover, we found that oftentimes the top managers are both driver and implementer of CS, as they exhibit their values and beliefs through the exercise of their decision-making power (Jenkins 2006). Accordingly, we identified major value dimensions of SME top managers (benevolence, achievement, power, and conformity values) that mostly drive CS. Our literature review contributes to calls for research by academics, regulators, and practitioners, to further investigate the development of CS in SMEs (Berk 2017). Moreover, our findings contribute to social interest as well as the management literature by deriving recommendations and practical implications. First, we recommend policymakers to develop a sustainable legal framework for SMEs to further increase the commitment of SMEs towards CS. Second, we recommend SMEs’ top managers to voluntarily report on their social and environmental engagement and/or at least promote those actions more intensively
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Domain Theories: Greenblushing and Corporate Sustainability in SMEs
According to the definition of the EU recommendation (2003), SMEs employ less than 250 people and either have an annual turnover of a maximum of 50 million Euro or a maximum balance sheet total of 43 million Euro. Additionally, we include articles that fall within the scope of commonly accepted definitions. Although most research refers simply to the use of quantitative measures for defining SMEs, we argue that SMEs are not just smaller versions of larger enterprises (Saeed and Ziaulhaq 2019). Apart from differences in size, SMEs usually vary from larger enterprises regarding their resources and capabilities (Lepoutre and Heene 2006) stakeholder relation (Fisher et al. 2009) as well as organizational structure (Apospori et al. 2012).
Due to the specific characteristics, SMEs and large corporations are inherently different (Baumann-Pauly et al. 2013), hence currently applied CS strategies of large corporations cannot be likewise transferred to SMEs (Fassin 2008). One relevant aspect, for instance, is CS-reporting, which is an enterprise’s systematic disclosure of information on its sustainability performance. Large enterprises are forced by regulations to disclose on CS, whereas SMEs are not, and currently, existing reporting standards do not fit the context of SMEs. Accordingly, just a rare amount of SMEs report on their social and environmental actions which leads to the fallacy that SMEs “have not taken up their social responsibility”, justified by the idea that enterprises that do not report on CS simply do not engage in CS (Fassin 2008, p. 368). However, existing research indicates that SMEs engage in CS (Nielsen et al. 2019, 2021; Lueg et al. 2016). Most SMEs particularly perceive CS as a social responsibility and show a great sensitivity towards two stakeholder groups—the local community surrounding them and their employees (Kechiche and Soparnot 2012). In particular, top executives have “strong local attachments […] generally with the region where they are based” (Kechiche and Soparnot 2012, p. 99). Therefore, most SMEs are strongly connected to their social community and support these with sponsoring or charitable events (CROCIS-CCIP 2007). Additionally, the well-treatment of employees is a key characteristic of SMEs (Hammann et al. 2009) due to the more direct and intense relation between SME executives and their employees (Torrès 2003). However, although existing literature indicated that SMEs engage in CS, several studies showed that most SMEs do not comprehend or use the term “CS” even when interacting in CS (Berk 2017; Giovanna and Lucio 2012) and oftentimes perceive the term CS as unattractive and off-putting (Grayson and Dodd 2007). Arguing that most SME executives do not view CS as an external but rather as “an integral part of the way they manage their firm” (Jenkins 2009; Kechiche and Soparnot 2012, p. 98). Based on existing literature we assume that most SMEs engage in CS, however, they do not promote such activities as well as not report on them in contrast to large enterprises (green blushing vs. greenwashing behavior).
2.2. Meta Theories: Upper Echelons and the Schwartz Value System
The UET by Hambrick and Mason (1984) argues that managers’ personal as well as cognitive characteristics, based on bounded rationality, influence strategic choices and organizational outcomes. The seminal paper of Hambrick and Mason (1984) advocates the assessment of the top managers’ impact by analyzing their demographic characteristics, such as age and education. Those demographic variables should proxy for more complex psychological constructs, such as managerial values, beliefs, perception, and cognition, which are classified as being unobservable (Hambrick and Mason 1984). Additionally, several developments of the theory further suggest examining personality traits, such as narcissism, charisma, or hubris, as well as the influence of moderators (e.g., discretion and executive job demands) on enterprises’ strategic choices (Hambrick 2007; Hambrick and Finkelstein 1987). The general UET research is usually applied in the context of large corporations with hired executives (Saeed and Ziaulhaq 2019). A significant number of studies focused exclusively on large corporations for investigating the impact of executive characteristics, e.g., risk perception (Borisov and Lueg 2012; Lueg and Borisov 2014; Lueg and Knapik 2016) on various organizational outcomes. Particularly, studies predominantly focused either on the top managers or the top management teams of an enterprise, arguing that those have a significant influence on strategic choices, organizational culture, and organizational outcomes (e.g., Burkert and Lueg 2013; Andersen and Lueg 2017). At present, research on SMEs based on UET is limited (Acar 2016). Few studies analyzed SMEs’ top managers’ influence on different organizational outcomes, such as export performance, organizational ambidexterity, innovation, internalization, market orientation, and performance, by using UET (e.g., Acar 2016; Cao et al. 2010; Davis et al. 2010; Saeed and Ziaulhaq 2019). However, no study examined the impact of top executives in the context of CS as an organizational outcome of SMEs. Previous research relating to SMEs’ environmental and social engagement builds on either institutional theory or stakeholder theory (e.g., Jenkins 2006; Murillo and Lozano 2006). However, we expect that the perceptions and beliefs of the top executives have a huge impact on the presence and implementation of CS in SMEs. Thus, our research aims to contribute to the call for research by adopting a UET perspective in an SME setting for investigating CS (Spence 2016).
Accordingly, the UET by Hambrick and Mason (1984) is an appropriate framing for our literature review. We elaborate the specifics of UET research in SMEs in the following: our research considers SMEs that are mostly managed by the owners themselves. Those are expected to have a different mindset due to their dual functioning as managers and shareholders (Fassin et al. 2011; Saeed and Ziaulhaq 2019). Furthermore, Azam and Abdullah (2015, p. 132) argue that owners’ and managers’ decision-making capacity varies as well as “the authority of leadership usually kept for the owners”. However, for our investigation, we cannot guarantee that the owner is an active manager because SMEs are not just startups where the founder/owner is the manager, therefore, we refer to “top managers” as an umbrella term covering the scope of SME hired executives as well as owners. Existing research has compared hired executives of large corporations to executives of SMEs, resulting in fundamental differences regarding the psychologies of both leaders (Hannafey 2003). SME executives are usually long-term oriented, following an approach of satisficing behavior. They are driven by the need for achievement instead of financial rewards as a prime motivator, thus heighten the propensity of CS (Morris et al. 2002). Moreover, executives in SMEs are oftentimes associated with problems of bounded rationality (Nooteboom 1994; Simon 1982) due to less functional areas in employees, less functional specialization, and expertise (Verhees and Meulenberg 2004) as well as the dominance of the top manager. Lastly, the impact of SMEs’ executives is particularly emphasized due to the resource scrutiny and the specialized organizational structure of SMEs, as SMEs tend to be less hierarchical and fewer restricted by organizational inertia. Furthermore, top managers of SMEs are frequently responsible for a broad range of strategic and operational functions (Lubatkin et al. 2006). As SMEs executives participate more directly in the day-to-day implementation of strategies this leads to a greater opportunity of directly influencing organizational outcomes (Cao et al. 2010; Lubatkin et al. 2006). Additionally, the personal contact between top managers and employees must be highlighted, as a closer relationship, informal working relations, and smaller gaps between various interfaces within the enterprises exist (Torrès 2000). Thus, we argue that the adoption of UET in an SME context could be especially appropriate for investigating how executives impact CS in SMEs.
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Framework
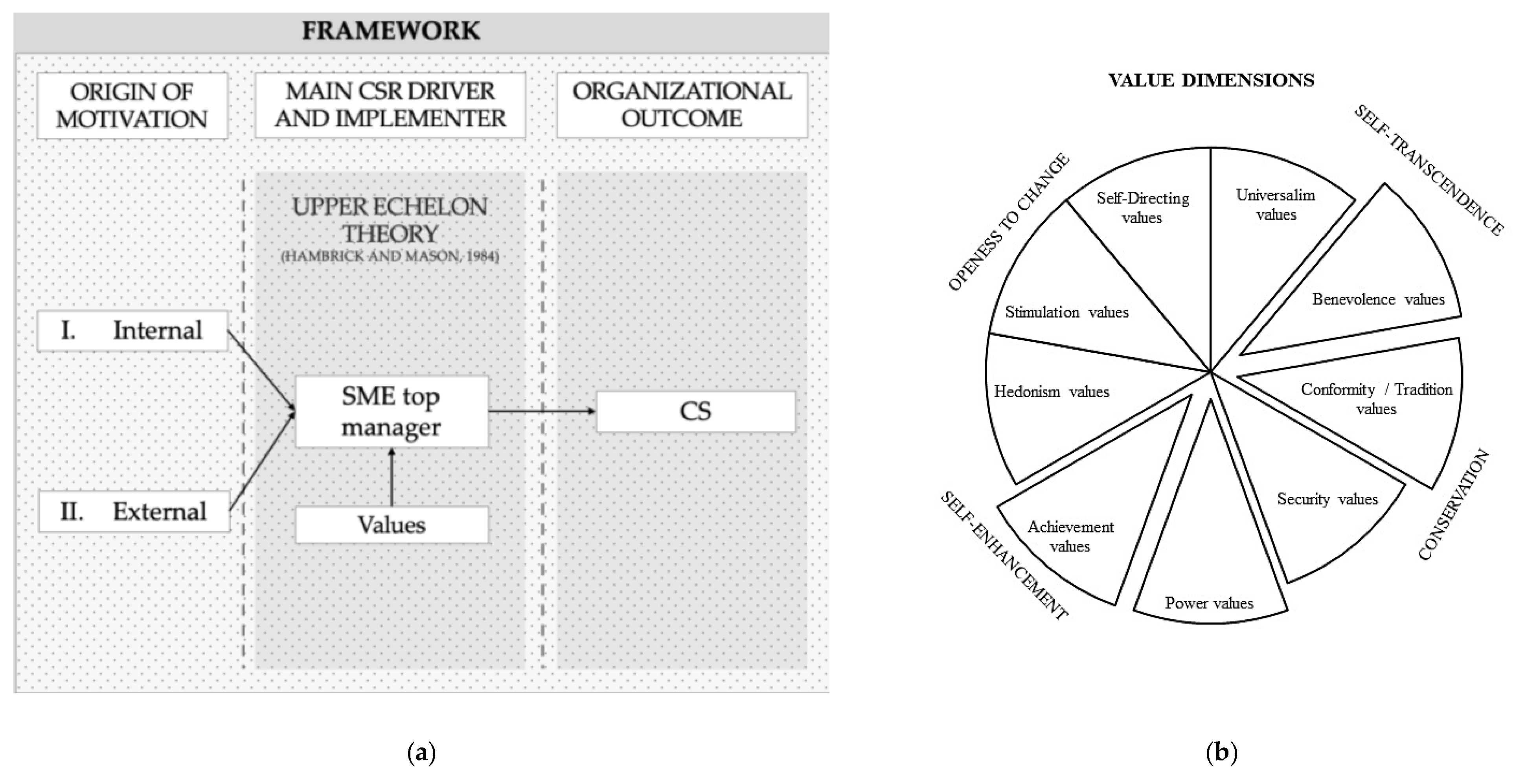
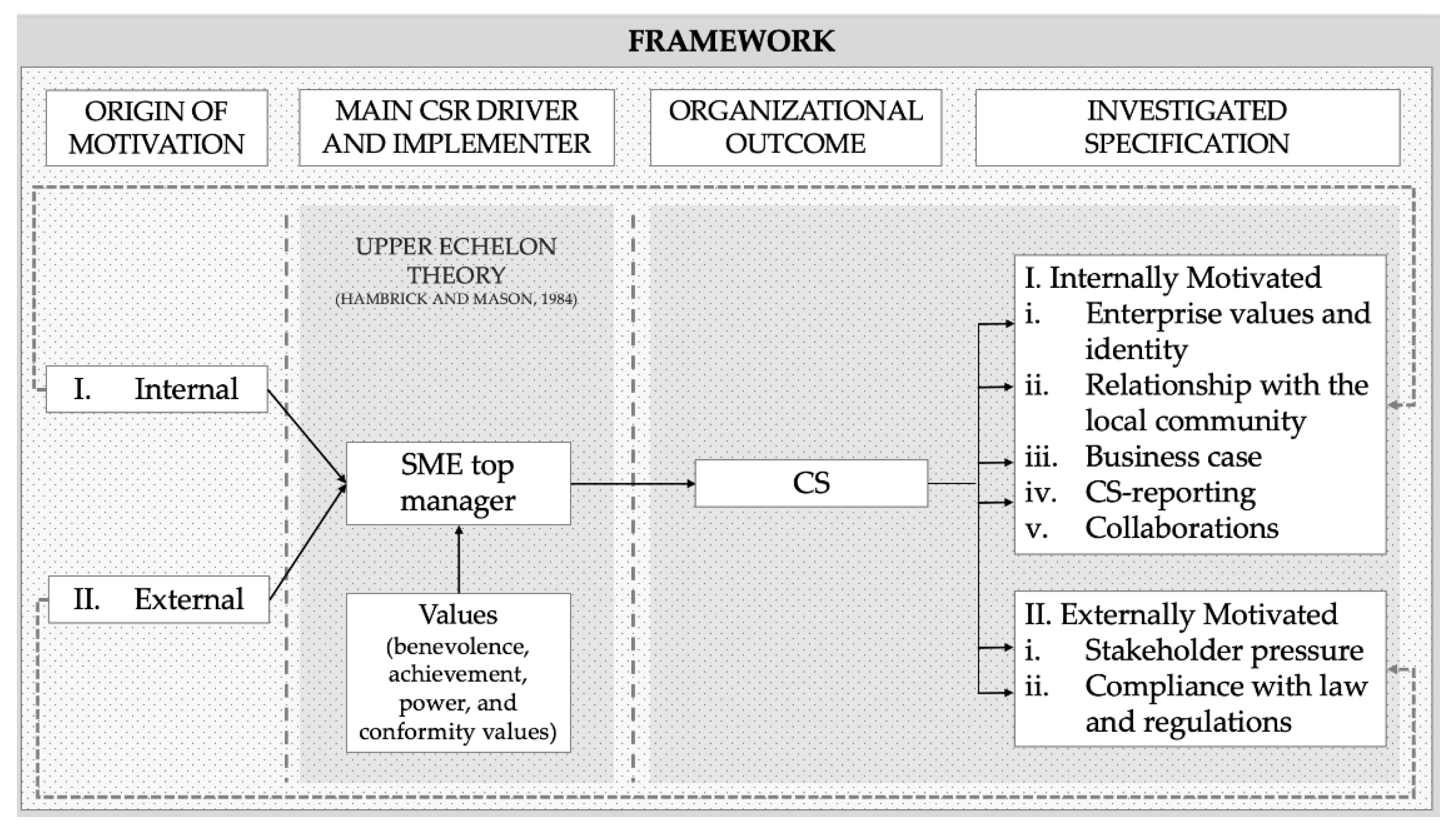
We developed a research framework in line with our theoretical foundation, aiming to answer our first research question: how do SMEs’ top managers perceive and implement CS? Thus, we investigate the CS of SMEs as an organizational outcome, which is driven and implemented by the SMEs’ executives (see Figure 1). We expect various specifications of CS originating either from the internal motivation of SMEs’ executives or external motivation. To answer our second research question: which values drive SMEs’ top managers to engage in CS? we intend to particularly examine how CS is perceived by top managers, assuming that their attitude towards CS is affected by their values. To investigate the drivers of executives engaging in CS, we analyze their values by adopting the SVS. Building on the different dimensions of the SVS framework enables a classification of several value domains based on a systematic psychological classification of values (Schwartz 2012; Schwartz and Bilsky 1987). This approach has successfully been applied in previous works on environmental engagement as well as enterprise social responsibility (Mirosa et al. 2013; Onkila 2009). Furthermore, it has been used in the context of SMEs environmental engagement by Schaefer et al. (2020) likewise. The SVS framework consists of ten value dimensions. We allocated our findings, of both internal and external motivated CS, to the value dimensions by Schwartz (2012).
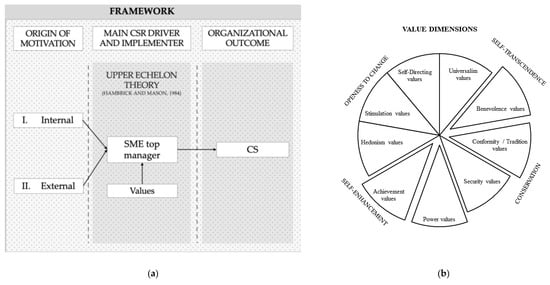
Figure 1.
Research framework. (a) Own depiction according to Dacin et al. (2010) and Colovic et al. (2019). (b) Own depiction according to Schwartz (2012) and Schwartz and Bilsky (1987).
3.2. Sample Selection
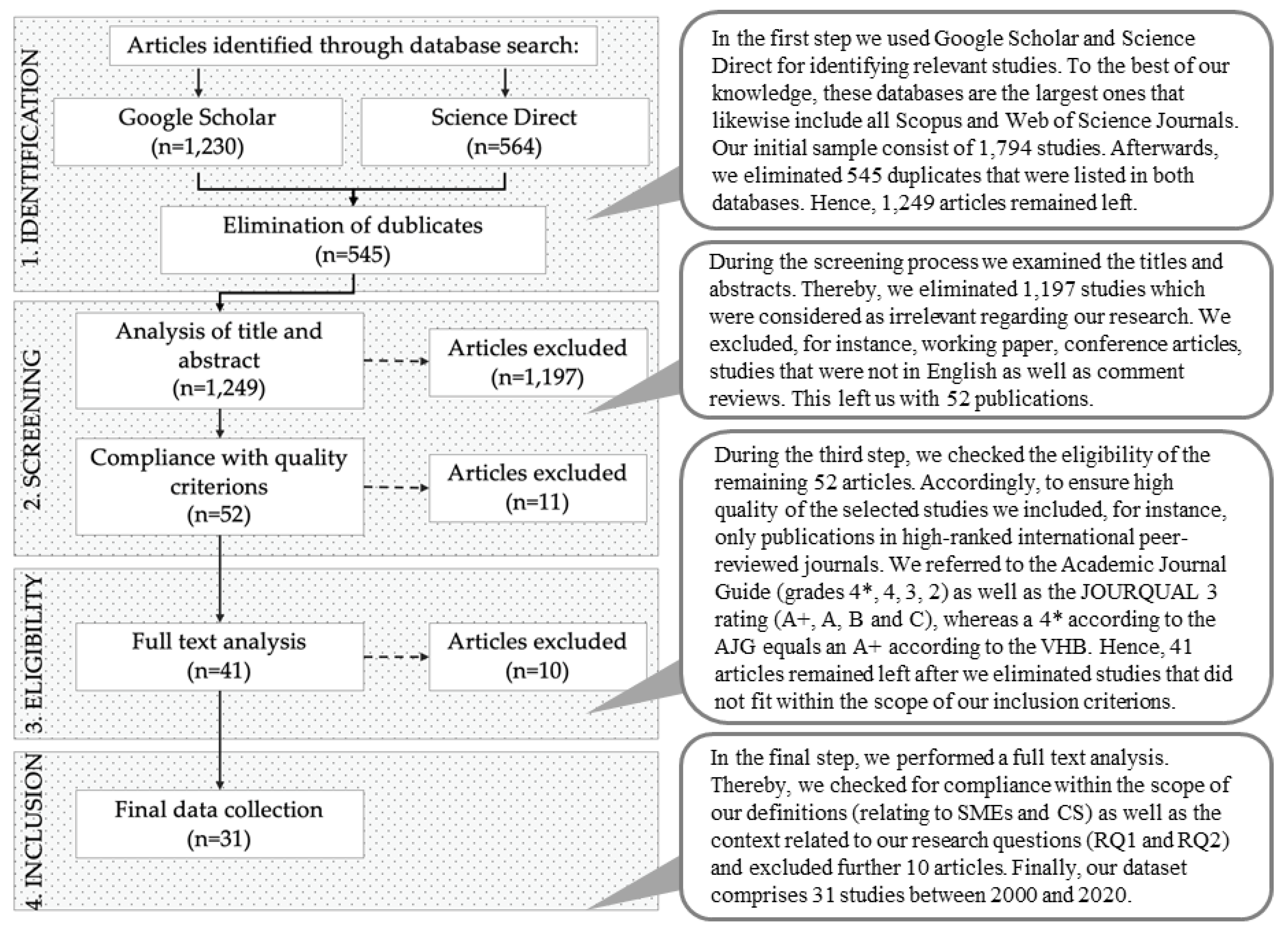
To conduct our systematic literature review we applied a multistep search approach for identifying relevant publications following the PRISMA framework (Denyer and Tranfield 2008; Moher et al. 2009). Thereby, we aim to present a comprehensive picture of the current state of research regarding CS and its drivers in SMEs. We followed common practices in this field (Albertsen and Lueg 2014; Lueg and Carvalho e Silva 2013; Lueg and Julner 2014; Lueg and Schäffer 2010; Lueg and Vu 2015; Toft and Lueg 2015; Rahman et al. 2020).
First, we searched international databases (Google Scholar, ScienceDirect) to select relevant studies. We identified the following keywords: “SME”, “SMEs CEO”, “SME top manager”, “SME executive”, “corporate sustainability” “CSR”, “small business social responsibility”, “small business”, “entrepreneurship”, “responsibility”, “sustainability”, “triple bottom line concept” “SVS” and “Schwartz value system”. As we intended to provide a detailed overview of the current state of research, the limitation to a specific timeframe, region, or research design was deemed not appropriate. Accordingly, the initial sample consists of 1794 studies. Afterward, we eliminated 545 duplicates, giving us our overall sample of 1249 sources.
Secondly, we examined the titles and abstracts. We eliminated 1197 studies, which were considered irrelevant regarding our research question. This left us with 52 publications.
In a third step, we defined several criteria to ensure a high quality of the selected studies. In this regard, we included only publications in high-ranked international peer-reviewed journals. Thereby, we refer to the Academic Journal Guide (grades 4*, 4, 3, 2) (AJG 2018) and complemented it according to the VHB-JOURQUAL 3 rating (A+, A, B, and C) (VHB 2020). A total of 41 articles remained after eliminating the ones that did not meet our inclusion criteria.
Finally, we performed a full-text analysis. We accepted a broader definition of SMEs as described above since we had a multi-country sample where researchers adjusted the definitions of SMEs to their local contexts (Lepoutre and Heene 2006). This approach allowed us to increase the possibility of generalizable findings across different SME-related enterprises. Furthermore, we checked for compliance with the scope of our definitions as well as the context related to our research question. After excluding unsuitable articles, our dataset comprises 31 studies between 2000 and 2020. The process of our data collection is presented in Figure 2.
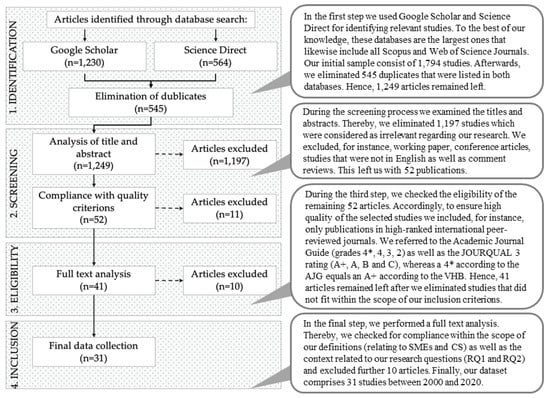
Figure 2.
Selection process. Note: own depiction according to the PRISMA framework (Moher et al. 2009).
4. Findings
4.1. Bibliometric Analysis
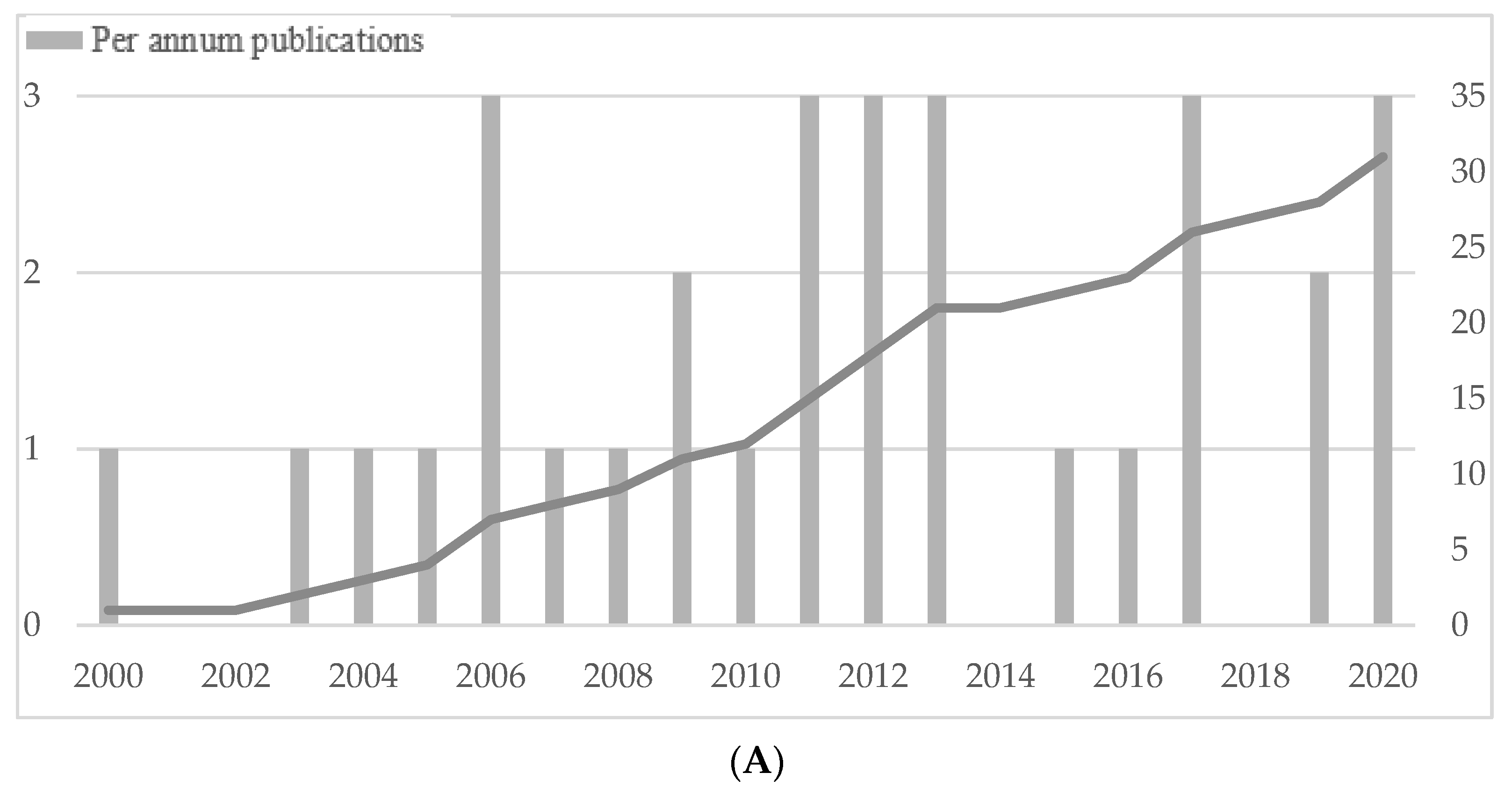
We analyzed a sample of 31 studies. Figure 3A depicts the number of published journal articles per annum as well as a cumulative figure. The studies considered in our analysis have been published within a timeframe beginning in 2000 and ending in 2020. Overall, we investigated a volatile distribution, with a maximum of three new articles within one year. Moreover, Panel A shows that research is frequently conducted since 2000. In 2020, already three articles have been published during the first half of the year with an increasing tendency, indicating the relevance of the topic.
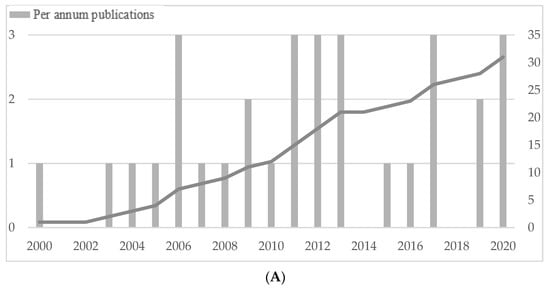
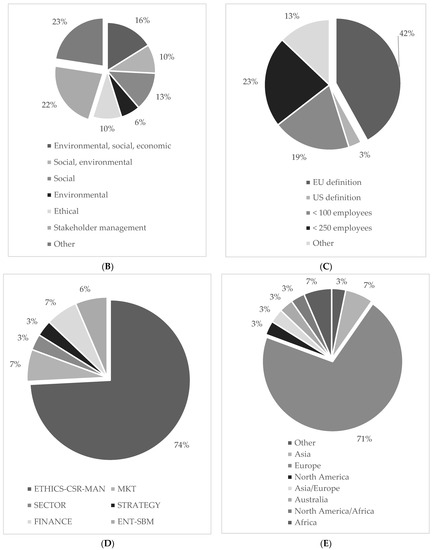
Figure 3.
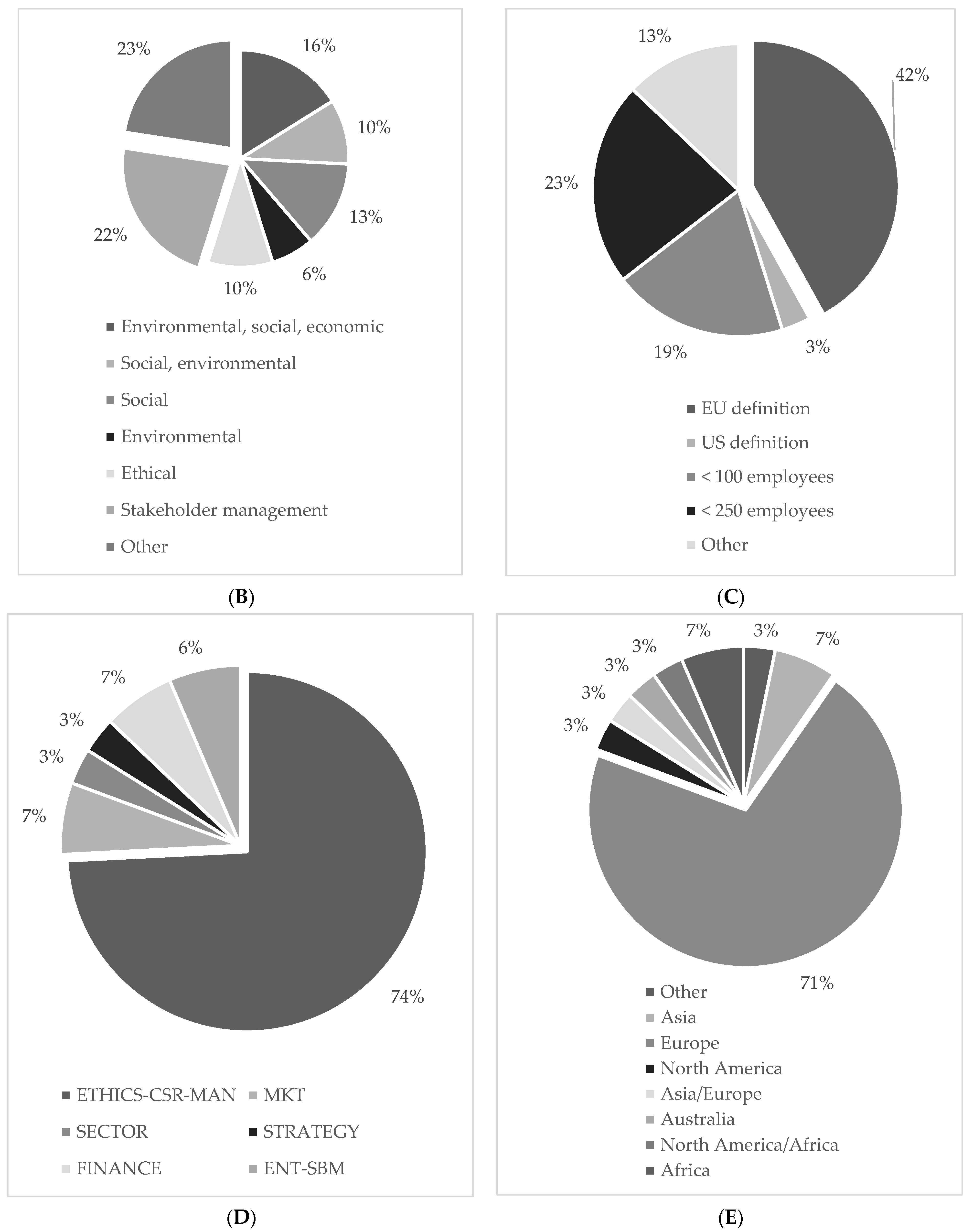
Descriptive statistics. (A) Distribution of sampled publications over years. (B) CS definitions. (C) SME definitions. (D) Distribution of sampled publications per research field. Note: Marketing (MKT), Management (MAN), Entrepreneurship and Small business management (ENT-SBM). (E) Distribution of sampled publications by geographic regions.
Figure 3B refers to CS definitions, which were used by the studies while investigating the SME top executives’ impact on sustainability practices. We differentiated seven categories. Approximately 23% of the sampled studies refer to CS using the TBL approach of equally integrating social, environmental, and economic practices The relevance of managing stakeholders was underlined by 22% of the studies that analyzed CS in that specific context. As mentioned above, different stakeholder groups, such as employees and local communities play a huge role in SMEs. Moreover, either social (13%) or environmental (6%) aspects were separately considered as well as the combination of both (10%). Finally, the importance of ethics (10%) was taken into consideration, as many SME executives are driven by values.
Figure 3C shows the definitions of SMEs used by the sampled studies. We note that most commonly studies refer to the EU-definition (42%) or apply quantitative specifications relating to the number of employees. Approximately 23% of the sampled studies used a definition of fewer than 250 employees while 19% refer to a measure of fewer than 100 employees. Only one study applies the US definition (3%).
Figure 3D depicts the distribution of articles by the research field. We identified six categories with respect to the Academic Journal Guide (AJG 2018). Most of the studies (74%) refer to the ethics–CS–management field. Moreover, finance and marketing disciplines include 7% of the sampled studies, respectively. Surprisingly, only two studies (6%) were published in entrepreneurship–small business management journals. Finally, approximately 3% of the studies have been published in either strategy or sector studies (e.g., Journal of Cleaner Production).
Figure 3E illustrates the distribution of studies by geographic regions. A total of 71% of our sampled studies were conducted in Europe, following by Asia and Africa with 7%, respectively. Few studies were undertaken in an Australian (3%) and North American (3%) setting. Furthermore, we found multicontinental studies, which refer to North America/Africa (3%) and Asia/Europe (3%).
4.2. Content Analysis
Overall, we identify that CS, as organizational outcomes, originate from either internal motivation (see Figure 4, e.g., (1) enterprise values and identity, (2) relationship with the local community, (3) business actions, (4) CS-reporting, and (5) collaborations) or external motivation (e.g., (6) stakeholder pressure, (7) compliance with laws and regulations). Studies are structured according to motivation in Table 1. Furthermore, we identify four major value dimensions that drive SMEs’ top managers’ CS engagement: benevolence, achievement, power, and conformity values.
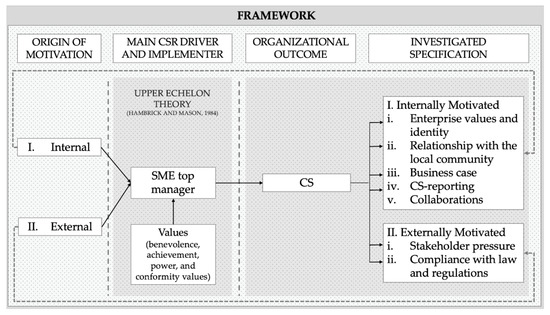
Figure 4.
Research framework including the findings. Note: own depiction used according to Dacin et al. (2010) and Colovic et al. (2019).

Table 1.
Studies structured by discussed motives for CS and methodology.
4.2.1. Enterprise Values and Identity
Inherent motives represent one crucial factor of enterprises’ engagement in CS, arguing that profit is not always the metric to measure an enterprise. Recent literature evidenced that such a mindset could be especially investigated in the context of SMEs (Fitjar 2011; Longo et al. 2005; Spence and Lozano 2000) as oftentimes, the executives of SMEs are both the driver as well as the implementer of enterprise values. Colovic et al. (2019) and Jenkins (2006) state that top managers of SMEs have a greater possibility to express their values regarding enterprise decisions compared to larger enterprises’ top executives. Several studies investigate that surveyed SMEs’ executives perceive CS as important and necessary to engage in related activities (Fassin et al. 2011; Jenkins 2006; Nkiko 2013; Lamberti and Noci 2012; Lenssen et al. 2007; Spence et al. 2003). Furthermore, previous studies examine that even though few SMEs’ top managers do not have a clear understanding of various CS-related definitions, they intrinsically act responsibly (Baumann-Pauly et al. 2013; Demuijnck and Ngnodjom 2013; Fassin et al. 2011). Most SMEs view their employees as the key stakeholders, which is especially underlined by their engagement in sustainability initiatives. Accordingly, interviewed SMEs’ executives highlighted that job creation and employee satisfaction are the main responsibilities for most top managers (Fassin et al. 2011). Aragón et al. (2016) mention that some SMEs’ top managers stated to further employ their workers even when their enterprises gained losses and having difficult times. In addition, they find that several SMEs’ top managers integrated their employees into decision-making processes to achieve a higher commitment and a mutual culture with joint values (Aragón et al. 2016). Following the same reasoning, some executives offer employee profit participation, for instance (Aragón et al. 2016). Moreover, Demuijnck and Ngnodjom (2013) identify that particularly safety and security on the workspaces are significantly relevant for SMEs’ top executives. The study of Demuijnck and Ngnodjom (2013), for instance, highlights the great importance of employee well-being for many SMEs’ top managers. The study undertaken in an African setting shows that SMEs’ executives offer their employees vaccinations and HIV information supplementary to fair payment. Colovic et al. (2019); Ciliberti et al. (2008); and Eweje (2020) equally emphasize SMEs’ top managers’ pronounced social and environmental engagement as they find moral reasons and personal values were both the main drivers of responsible behavior for most SMEs’ executives.
4.2.2. Relationship with the Local Community
Usually, SMEs have a closer connection to their local community, resulting in more intensive interactions. Due to their relationship, e.g., living in the same neighborhood, many SMEs’ top managers feel responsible for their local fellowship resulting in intrinsic motivation to engage in CS (Fitjar 2011; Russo and Tencati 2009; Ciliberti et al. 2008; Eweje 2020; Lamberti and Noci 2012; Lenssen et al. 2007; Longo et al. 2005). Furthermore, Nkiko (2013) finds that the own experiences of executives of SMEs represent another internal motivation for engaging in local community activities. To consider local or regional needs, many enterprises support non-governmental organizations, local sports clubs as well as local farmers (Aragón et al. 2016; Fraj-Andrés et al. 2012; Colovic et al. 2019; Spence et al. 2003). Aragón et al. (2016) especially highlight the importance for SMEs’ top managers to have a well-maintained relationship with the local community, which could additionally enhance the enterprise’s reputation. Some SMEs have specific budgets, that are exclusively utilized for the local needs (Murillo and Lozano 2006; von Weltzien Høivik and Melé 2009), while others operate on an ad hoc basis (Jenkins 2006).
4.2.3. Business Case
Underlining the assumption of an enterprise’s overall market- and profit-orientation, SMEs’ adaption of CS could be additionally explained by economic motives (Bouzzine and Lueg 2020; Fraj-Andrés et al. 2012; Lueg et al. 2019). In this regard, Murillo and Lozano (2006) analyzed SMEs in a French and Spanish setting. They argue that most CS conducted resulted in an enhanced enterprise’s market position, and could be reasoned by the competitive advantage gained through differentiation. Colovic et al. (2019) analyzed a French wine producer and likewise state that CS is used for differentiation purposes to gain a competitive advantage. Moreover, studies find that engaging in social and environmental activities could enhance the enterprise’s reputation, leading to a potentially increased financial performance in the long run (Aragón et al. 2016), thus, arguing that SMEs’ executives oftentimes get involved in philanthropic activities for business motives alike. The importance of the enterprise’s reputation is further confirmed by Fitjar (2011) who finds that CS could lead to higher product prices due to fair-trade labeling, for instance. Additionally, an analysis by Rekik and Bergeron (2017) find that green practices were associated with enterprises’ financial performance indicating that CS originate in business motives. However, Jenkins (2006) indicates that except for some actual and effective monetary advantages, most CS of SMEs are intangible, such as improved public image, and thus, indirectly affect the financial performance.
4.2.4. CS-Reporting
Recent literature shows that SMEs perceive the relevance of CS-reporting differently, compared to larger enterprises. SMEs’ executives state that it is burdensome to create a report that consumes an excessive amount of time and money and requires a huge number of personnel resources (Baumann-Pauly et al. 2013). Moreover, they underline that the non-reporting on CS does not lead to non-engagement in sustainable actions. Research shows that SMEs limited resources are used to actively perform CS and not being wasted to extensive reports following the green-washing philosophy of larger enterprises (Baumann-Pauly et al. 2013; Russo and Tencati 2009). Murillo and Lozano (2006) find that most SMEs’ top managers prefer doing CS instead of promoting and reporting it. This awareness of SMEs’ top executives is equally confirmed by Jenkins (2006) who argues that most SMEs are not comfortable with labeling and promoting their CS. They perceive reporting as a public relations activity, which is usually utilized by large enterprises. However, the awareness about informational access is still present as SMEs belonging to the supply chain of large enterprises, oftentimes receive requests for information, which is usually provided in CS reports, for instance (Baumann-Pauly et al. 2013). Hence, several executives call for the formalization of CS practices (Meyer et al. 2017). They require greater visibility of sustainable practices by voluntarily publishing well-documented reports thus, satisfying stakeholder needs (Meyer et al. 2017). Few executives even suggest obliging SMEs to report on CS, as they perceive social and environmental issues as important as financial information that had to be reported (Preuss and Perschke 2010; Russo and Tencati 2009; von Weltzien Høivik and Melé 2009).
4.2.5. Collaborations
Baumann-Pauly et al. (2013) and Spence et al. (2003) find that several top managers of SMEs engage in CS through external collaborations. Furthermore, they state that all SMEs investigated engaged in external collaborations to solve CS problems. Surprisingly, none of the executives mentioned a lack of labor or financial resources, which could hinder CS practices. They highlight that the synergy of collective actions was more effective than the individual engagement into CS. Mutual participation in sustainability platforms, e.g., Fair Wear Foundation, helps to expand the awareness on CS-related issues (Baumann-Pauly et al. 2013). Moreover, Meyer et al. (2017) prove the importance of cooperations by investigating a French sample of SMEs. Due to external collaborations, SMEs were trained not only to implement and maintain but also to report CS. Upon request of top managers, consultants guided them to implement sustainable practices, quality management, and long-term oriented business (Lueg 2009). Some SMEs cooperate with organizations that provide necessary data about a contractual partner, for instance, resulting in financial support for suppliers that ensure fair work conditions (von Weltzien Høivik and Melé 2009). Moreover, the study of von Weltzien Høivik and Shankar (2011) emphasizes that synergies through external collaborations enable superior negotiation power and an enhanced enterprise reputation.
4.2.6. Stakeholder Pressure
SMEs are especially dependent on their reputation as their business usually depends on few stakeholders, and their actions tend to be closely observed by the public (Lenssen et al. 2007; Spence and Lozano 2000). Thus, SMEs must ensure that the stakeholders positively perceive their actions (Lähdesmäki et al. 2019). Compared to large enterprises, where the stakeholders are rather anonymous, SMEs usually have tied contacts with their interest groups. As mentioned, community peers from the neighborhood, employees, or clients can directly impact SMEs’ executive decisions. Aragón et al. (2016) analyzed a Spanish sample and reveal that enterprises were forced by their biggest customers to change their production in line with CS issues. Furthermore, similar studies find that SMEs of other industries were guided by their stakeholder to engage in CS activities (Fitjar 2011; Meyer et al. 2017).
4.2.7. Compliance with Law and Regulations
Most SMEs’ executives mentioned legal requirements as one of the most important motives of implementing CS (Fraj-Andrés et al. 2012; Ciliberti et al. 2008; Eweje 2020; Longo et al. 2005; Spence and Lozano 2000). Colovic et al. (2019) find that SMEs implemented various quality management tools according to environmental standards because they were obligated by regulatory requirements. von Weltzien Høivik and Melé (2009) argue that many SMEs conduct transparent documentation of actions regarding each party of the supply chain to fulfill CS-related requirements. However, most SMEs are currently not subject to regulatory standards concerning CS, resulting in the possibility of opportunistic management behavior and non-sustainable actions (Demuijnck and Ngnodjom 2013; Nkiko 2013). Although, top managers are aware of potentially harmful actions some executives stated to continue until they will be forced to make changes (Nkiko 2013). These findings indicate that a legislative framework could encourage the development of sustainable enterprises. Thereby, social grievances, e.g., child labor, underpayment, and exploitation of nature, could be eliminated as shown by Preuss and Perschke (2010).
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Synthesis of the Findings
The findings section categorized the CS practices of the SMEs in relation to the role of their executives. In the synthesis section, we offer a categorization by the motives that led to implementing the CS practices. This offers the advantage to cluster SMEs according to the values that their top managers enact. We thereby achieve the goal of this review to link CS in SMEs with the values of their top executives. The SVS serves as a basis and offers three distinct (but possibly parallel) motives for SME executives to implement CS.
5.1.1. Benevolence and Power Values: Identity, Local Community and Collaborations
Top managers who engage in CS relating to enterprise values and identitys, as well as relationships with the local community, are usually influenced by benevolence values. Hence, they are especially concerned about the welfare of other people belonging to their community (Schwartz 1994). Top managers in this category frequently support their local community, care about their employee’s satisfaction and welfare. Most investigated market values are responsibility, helpfulness, loyalty, reliability, and working for other people’s welfare, for instance (Ralston et al. 2011; Schaefer et al. 2020). Moreover, we argue that engagement in the category enterprise values and identity refers to top managers influenced by achievement values that include the following marker values: having an impact, success, achieving goals. Managers who are influenced by achievement values feel influential and capable, oftentimes striving for being the leading pioneers towards CS. They usually do not perceive CS as an extrinsic motivation to ensure compliant behavior or a tool for improving their financial performance. In contrast, those top managers talked about their intrinsic motivation of implementing CS in their enterprise, thereby making a difference and set an example (Schaefer et al. 2020). Moreover, SMEs’ top managers who accept the global sustainability challenges, seek to reduce their ecological footprint, and be sustainable via external collaborations refer to achievement values alike. Associated executives aim to be influential, have an impact, comply with prevailing cultural standards, and demonstrate competence (Ralston et al. 2011; Schaefer et al. 2020). To be more efficient and competent regarding the implementation of CS executives cooperate with other organizations (Meyer et al. 2017).
5.1.2. Power Values: Business Case and Reporting
SMEs’ executives who engaged in CS for the business case (e.g., gaining a competitive advantage; differentiation; reputation building) belong to the power value dimension. Power values are viewed as a part of top managers’ self-enhancement and are usually associated with the striving for social status, prestige, and control over people as well as resources (Schwartz 1994). The dominant values of this category are wealth, money, social power, public image, and dominant leadership (Ralston et al. 2011; Schaefer et al. 2020). The best example of the power values is provided by the study of Eweje (2020, p. 4) where SMEs executive describes top managers as a “king of your own domain”. These top managers oftentimes engage in CS to save costs or differentiate from others aiming to get a superior position compared to their competitors. For instance, some SMEs’ top managers perceive CS as a distinct and a selling point (Colovic et al. 2019), resulting in their awareness of a “better position than those [companies] who have only recently decided to show a responsible image” (Fraj-Andrés et al. 2012, p. 275). SME’s sustainability initiatives, such as implementing ISO standards, supporting tree planting, and publishing environmental reports influence SME executives’ public image (e.g., Eweje 2020).
Power values are partially associated with greenwashing behavior, which describes the reporting on environmental and social issues without really engaging in those. However, since SMEs oftentimes do not report on CS, greenwashing is usually a phenomenon of larger enterprises (Baumann-Pauly et al. 2013; Russo and Tencati 2009).
5.1.3. Conformity Values: Stakeholder Pressure and Compliance
SMEs’ top managers who engage in CS due to external motivations (e.g., industry regulations, or supply chain pressure) belong to the conformity value dimension. Conformity values are associated with the restraint of actions that are likely to violate social expectations or norms (Schwartz 2012). SMEs’ executives comply with law and regulations and implement sustainable practices due to customer pressure because they are aware that violating such requirements could heavily harm their enterprises (Colovic et al. 2019). Moreover, several SMEs’ top managers underline that they “act responsibly to mitigate adverse industry and product effects by going beyond the legal requirements” (Colovic et al. 2019, p. 797). Although compared to the global multinational entities, SMEs’ visibility is less, yet several industries, such as textile and alcoholic beverages, are subject to media scrutiny. For instance, the Norwegian apparel SME needs to deal with its supply chain management and to respond to the customers’ critique regarding poor working conditions (Fitjar 2011). As a result, the conformity value was a main driver for the implementation of ‘Codes of Conduct’ in this SME. In this regard, SMEs’ dependence on external parties plays a major role (Ralston et al. 2011).
5.2. Contribution to Theory and Practice
Our study contributes to research and practice. We are the first to offer researchers an exclusive analysis of top managers’ roles in SMEs when implementing CS. Moreover, we were the first who adopted the UET by Hambrick and Mason (1984) and additionally applied the SVS by Schwartz (2012). By investigating the key role of executives’ values for the implementation of CS in SMEs, our analysis provides robust results and highlights the importance of top managers’ values. Relating to our first research question How do SMEs’ top managers perceive and implement CS?; we based our research on the UET (Hambrick and Mason 1984) and find that SMEs’ top managers engage differently in CS. Thereby, we identify seven categories related to CS that were either driven by internal motivations (e.g., (1) enterprise values and identity, (2) relationship with the local community, (3) business actions, (4) CS-reporting, and (5) collaborations) or external motivations (e.g., (6) stakeholder pressure, and (7) compliance with laws and regulations). Furthermore, intended to answer our second research question; which values drive SMEs’ top managers to engage in CS? we build on the SVS (Schwartz 2012) and identify four major value dimensions of SME top managers (e.g., benevolence, achievement, power, and conformity values) that mostly drive CS.
Additionally, we offer some practical implications. Previous literature argued that the public does not take prominent note of CS in SMEs. However, our findings indicate that many SMEs engage in CS but fail to report it as prominently as large enterprises (green blushing). Most executives of SMEs view CS as an integral part of their business model (Jenkins 2009; Kechiche and Soparnot 2012). Yet, SMEs are not comfortable with promoting their CS. We identify substantial upside potential in voluntarily reporting on CS, either as a comprehensive practice (i.e., a CS report) or by at least promoting selected CS practices. SMEs might benefit from the positive impacts of CS, such as the enterprise’s reputation or enhanced financial performance in the long run.
With respect to public policy, our findings indicate that SMEs currently engage in diverse CS practices. First, regulators might systematically underestimate the notable amount of CS practices in SMEs. Second, some top managers argued that undertaken costly investments into CS practices would lead to a competitive disadvantage (Fraj-Andrés et al. 2012). Regulators could level the playing field by obliging their competitors to achieve a basic level as well (Fraj-Andrés et al. 2012).
5.3. Future Research Agenda and Critical Reflection
Our research indicated that the executives of SMEs driver are often the pioneers of good social and environmental practices (Fraj-Andrés et al. 2012). The categorization of CS practices related to the different value dimensions allows us to identify the most important executive characteristics that should be used to proxy for top managers’ values and believes. We argue that in line with the four value dimensions (achievement, benevolence, power, and conformity values) an investigation of the executives’ educational background, experience, power, or tenure could be relevant proxies for future research endeavors. Future studies should build on behavioral research designs, by investigating the mental models, beliefs, and values of executives. By using a UET framework, studies could examine the mindset of SMEs’ top managers regarding the integration and implementation of CS. Researchers argued that different socio-economic factors are potentially heavily affecting CS in SMEs (Morros 2016). Based on future research findings, new ways of further accelerating CS in SMEs could be developed. Additional investigations could help standard setters to process new models of CS integration as well as regulatory requirements specifically for SMEs.
Future research could also analyze the impact of corporate governance-related variables on CS in an SME setting (e.g., industry regulation and legal enforcement). Recent research regarding SMEs indicated that the manager’s cognition in relation to CS is additionally dependent on external circumstances (Fassin et al. 2015). We recommend investigating the executive’s discretion in the context of CS. Additionally, existing literature shows that large enterprises with a top manager insider perform better than those with an executive appointed from outside the enterprise (Rhim et al. 2006). Previous research recognized ownership as one of the main sources of power (Finkelstein 1992; Onali et al. 2016). Thus, an investigation of executive ownership or origin (internal vs. external) could be fruitful avenues for further research endeavors. These variables are especially relevant as SMEs are frequently managed by managing owners.
Finally, we qualify our research in the light of its limitations and critically reflect on the main caveats of our work. First, considering the subjectivity of our selection and scanning process, we might not have captured all relevant studies. Thus, we cannot guarantee comprehensiveness as regards the selection of literature. Second, we limited our study to several inclusion criteria of two independent journal ratings. Hence, our selection is restricted to the qualitative evaluation of those ratings. Third, the sample size is rather small, however, it is reasoned by the constrained availability of relevant studies as research in this field is in its infancy. Lastly, our work did not explicitly capture the differences between manager owners and hired executives on CS.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K., P.T., and R.L.; methodology, J.K., P.T. and R.L.; software, J.K., P.T. and R.L.; validation, R.L.; formal analysis, J.K. and P.T.; investigation, J.K. and P.T.; resources, J.K., P.T. and R.L.; data curation, J.K. and P.T.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K. and P.T.; writing—review and editing, J.K., P.T. and R.L.; visualization, J.K., P.T. and R.L.; supervision, R.L.; project administration, R.L.; funding acquisition, n/a. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No original data produced.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Acar, F. Pinar. 2016. The effects of top management team composition on SME export performance: An upper echelons perspective. Central European Journal of Operations Research 24: 833–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Noor Hazlina, and T. Ramayah. 2012. Does the notion of ‘doing well by doing good’ prevail among entrepreneurial ventures in a developing nation? Journal of Business Ethics 106: 479–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AJG (Academic Journal Guide). 2018. Academic Journal Guide—Methodology. Available online: https://charteredabs.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/AJG2018-Methodology.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Albertsen, Oana, and Rainer Lueg. 2014. The Balanced Scorecard’s missing link to compensation: A literature review and an agenda for future research. Journal of Accounting and Organizational Change 10: 431–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, Christian Vium, and Rainer Lueg. 2017. Management Control Systems, culture and upper echelons—A systematic literature review on their interactions. Corporate Ownership and Control 14: 312–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apospori, Eleni, Konstantinos G. Zografos, and Solon Magrizos. 2012. SME corporate social responsibility and competitiveness: A literature review. International Journal of Technology Management 58: 10–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, Cristina, Lorea Narvaiza, and Maite Altuna. 2016. Why and how does social responsibility differ among SMEs? A social capital systemic approach. Journal of Business Ethics 138: 365–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S. M. Ferdous, and Moha A. Abdullah. 2015. Differential roles between owner and manager in financial practice contribute to business success: An analysis on Malaysian small business. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies 4: 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baden, D., I. Harwood, and D. Woodward. 2011. The effects of procurement policies on downstream CSR activity: Content analytic insights into the views and actions of SME owner–manager. International Small Business Journal 29: 259–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann-Pauly, Dorothée, Christopher Wickert, Laura J. Spence, and Andreas Georg Scherer. 2013. Organizing corporate social responsibility in small and large firms: Size matters. Journal of Business Ethics 115: 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, Abigail. 2017. Small Business Social Responsibility—More than Size. The Journal of Corporate Citizenship 67: 12–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, Boris, and Rainer Lueg. 2012. Are you sure about what you mean by ‘uncertainty’? The actor’s perspective vs. the institutional perspective. Proceedings of Pragmatic Constructivism 2: 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzzine, Yassin Denis, and Rainer Lueg. 2020. The contagion effect of environmental violations: The case of Dieselgate in Germany. Business Strategy and the Environment 29: 3187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkert, Michael, and Rainer Lueg. 2013. Differences in the sophistication of Value-based Management—The role of top executives. Management Accounting Research 24: 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, Jeffrey M., and Joohyung Park. 2017. Extending the resource-based view: Effects of strategic orientation toward community on small business performance. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 34: 302–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Qing, Zeki Simsek, and Hongping Zhang. 2010. Modelling the Joint Impact of the CEO and the TMT on Organizational Ambidexterity. Journal of Management Studies 47: 1272–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciliberti, Francesco, Pierpaolo Pontrandolfo, and Barbara Scozzi. 2008. Investigating corporate social responsibility in supply chains: A SME perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production 16: 1579–88. [Google Scholar]
- Colovic, Ana, Sandrine Henneron, Maik Huettinger, and Ruta Kazlauskaite. 2019. Corporate social responsibility and SMEs. European Business Review 17: 523–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CROCIS-CCIP. 2007. Le Développement Durable dans les PME-PMI de la Région Parisienne. Baromètre. Available online: http://www.crocis.ccip.fr (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Dacin, M. Tina, Kamal Munir, and Paul Tracey. 2010. Formal dining at cambridge colleges: Linking ritual performance and institutional maintenance. Academy of Management Journal 53: 1393–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, Peter S., Emin Babakus, Paula Danskin Englis, and Tim Pett. 2010. The Influence of CEO Gender on Market Orientation and Performance in Service Small and Medium-Sized Service Businesses. Journal of Small Business Management 48: 475–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brìo, Jesùs Angel, and Beatriz Junquera. 2003. A review of the literature on environmental innovation management in SMEs: Implications for public policies. Technovation 23: 939–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuijnck, Geert, and Hubert Ngnodjom. 2013. Responsibility and informal CSR in formal Cameroonian SMEs. Journal of Business Ethics 112: 653–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denyer, David, and David Tranfield. 2008. Producing a systematic review. In The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods. Edited by D. Buchanan and A. Bryman. London: Sage, pp. 671–89. [Google Scholar]
- Enderle, Georges. 2004. Global competition and corporate responsibilities of small and medium sized enterprises. Business Ethics: A European View 13: 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. 2003. Observatory of European SMEs: Report 2003, SMEs in Europe 2003. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities. [Google Scholar]
- Eweje, Gabriel. 2020. Proactive environmental and social strategies in a small-to medium-sized company: A case study of a Japanese SME. Business Strategy and the Environment 29: 2927–38. [Google Scholar]
- Fassin, Yves. 2008. SMEs and the fallacy of formalizing CSR. Business Ethics: A European Review 17: 364–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassin, Yves, Annick Van Rossem, and Marc Buelens. 2011. Small-business owner-managers’ perceptions of business ethics and CSR-related concepts. Journal of Business Ethics 98: 425–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassin, Yves, Andrea Werner, Annick Van Rossem, Silvana Signori, Elisabet Garriga, Heidi von Weltzien Hoivik, and Hans-Jörg Schlierer. 2015. CSR and related terms in SME owner–managers’ mental models in six European countries: National context matters. Journal of Business Ethics 128: 433–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, Sydney. 1992. Power in top management teams: Dimensions, measurement, and validation. Academy of Management Journal 35: 505–38. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, Kyla, Jessica Geenen, Marie Jurcevic, Katya McClintock, and Glynn Davis. 2009. Applying asset-based community development as a strategy for CSR: A Canadian perspective on a win–win for stakeholders and SMEs. Business Ethics: A European Review 18: 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitjar, Rune Dahl. 2011. Little big firms? Corporate social responsibility in small businesses that do not compete against big ones. Business Ethics: A European Review 20: 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraj-Andrés, Elena, M. Eugenia López-Pérez, Iguácel Melero-Polo, and Rosario Vázquez-Carrasco. 2012. Company image and corporate social responsibility: Reflecting with SMEs’ managers. Marketing Intelligence & Planning 30: 266–80. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanna, Campopiano, and Cassia Lucio. 2012. Corporate social responsibility: A survey among SMEs in Bergamo. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 62: 325–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graafland, Johan, and Bert Van de Ven. 2006. Strategic and moral motivation for corporate social responsibility. Journal of Corporate Citizenship 22: 111–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, David, and Tom Dodd. 2007. Small Is Sustainable (and Beautiful): Encouraging European Smaller Enterprises to be Sustainable. Cranfield: Doughty Centre for Corporate Responsibility, Cranfield University. [Google Scholar]
- Hambrick, Donald C. 2007. Upper echelons theory: An update. Academy of Management Review 32: 334–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrick, Donald C., and Sydney Finkelstein. 1987. Managerial discretion: A bridge between two polar views on organizations. In Research in Organizational Behavior. Edited by B. M. Staw and L. L. Cummings. Greenwich: JAI Press, vol. 9, pp. 369–406. [Google Scholar]
- Hambrick, Donald C., and Phyllis A. Mason. 1984. Upper echelons: The organization as a reflection of its top managers. Academy of Management Review 9: 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammann, Eva-Maria, Andre Habisch, and Harald Pechlaner. 2009. Values that create value: Socially responsible business practices in SMEs—Empirical evidence from German companies. Business Ethics: A European Review 18: 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannafey, Francis T. 2003. Entrepreneurship and Ethics: A Literature Review. Journal of Business Ethics 46: 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, Dima, Mona Zanhour, and Tamar Keshishian. 2009. Peculiar strengths and relational attributes of SMEs in the context of CSR. Journal of Business Ethics 87: 355–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, Heledd. 2004. A critique of conventional CSR theory: An SME perspective. Journal of General Management 29: 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, Heledd. 2006. Small business champions for corporate social responsibility. Journal of Business Ethics 67: 241–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, Heledd. 2009. A ‘business opportunity’ model of corporate social responsibility for small- and medium-sized enterprises. Business Ethics: A European Review 18: 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, Phil, James Curran, Joanne Duberley, and Robert A. Blackburn. 2001. Researching the Small Enterprise. London: Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Kechiche, Amina, and Richard Soparnot. 2012. CSR within SMEs: Literature review. International Business Research 5: 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefhaber, Eva, Kathryn Pavlovich, and Katharina Spraul. 2020. Sustainability-Related Identities and the Institutional Environment: The Case of New Zealand Owner–Managers of Small-and Medium-Sized Hospitality Businesses. Journal of Business Ethics 163: 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Klewitz, Johanna, and Erik G. Hansen. 2014. Sustainability-oriented innovation of SMEs: A systematic review. Journal of Cleaner Production 65: 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähdesmäki, Merja, Marjo Siltaoja, and Laura J. Spence. 2019. Stakeholder salience for small businesses: A social proximity perspective. Journal of Business Ethics 158: 373–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, Lucio, and Giuliano Noci. 2012. The relationship between CSR and corporate strategy in medium-sized companies: Evidence from Italy. Business Ethics: A European Review 21: 402–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lenssen, Gilbert, Francesco Perrini, Antonio Tencati, Peter Lacy, and Lorraine Sweeney. 2007. Corporate social responsibility in Ireland: Barriers and opportunities experienced by SMEs when undertaking CSR. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society 7: 516–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lepoutre, Jan, and Aimé Heene. 2006. Investigating the impact of firm size on small business social responsibility: A critical review. Journal of Business Ethics 67: 257–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longenecker, Justin G., Carlos W. Moore, J. William Petty, Leslie E. Palich, and Joseph A. McKinney. 2006. Ethical attitudes in small businesses and large corporations: Theory and empirical findings from a tracking study spanning three decades. Journal of Small Business Management 44: 167–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, Mariolina, Matteo Mura, and Alessandra Bonoli. 2005. Corporate social responsibility and corporate performance: The case of Italian SMEs. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society 32: 646–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lubatkin, Michael H., Zeki Simsek, Yan Ling, and John F. Veiga. 2006. Ambidexterity and performance in small- to medium-sized firms: The pivotal role of TMT behavioral integration. Journal of Management 32: 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Rainer. 2009. Führt der Einsatz externer Berater zur Überimplementierung innovativer Steuerungsinstrumente? Zeitschrift der Unternehmensberatung 4: 249–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lueg, Rainer, and Boris Genadiev Borisov. 2014. Archival or perceived measures of environmental uncertainty? Conceptualization and new empirical evidence. European Management Journal 32: 658–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Rainer, and Ana Carvalho e Silva. 2013. When one size does not fit all: A literature review on the modifications of the balanced scorecard. Problems and Perspectives in Management 11: 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lueg, Rainer, and Pernille Julner. 2014. How are Strategy Maps linked to strategic and organizational change? A review of the empirical literature on the Balanced Scorecard. Corporate Ownership & Control 11: 439–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lueg, Rainer, and Magdalena Knapik. 2016. Risk management with management control systems: A pragmatic constructivist perspective. Corporate Ownership and Control Journal 13: 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Klarissa, and Rainer Lueg. 2020. Detecting green-washing or substantial organizational communication: A model for testing two-way interaction between risk and sustainability reporting. Sustainability 12: 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Rainer, and Ronny Radlach. 2016. Managing sustainable development with management control systems: A literature review. European Management Journal 34: 158–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Rainer, and Utz Schäffer. 2010. Assessing empirical research on Value-based Management: Guidelines for improved hypothesis testing. Journal für Betriebswirtschaft 60: 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Rainer, and Louisa Vu. 2015. Success factors in Balanced Scorecard implementations—A literature review. Management Revue: Socio-Economic Studies 26: 306–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Rainer, Maria Medelby Pedersen, and Søren Nørregaard Clemmensen. 2015. The role of corporate sustainability in a low-cost business model—A case study in the Scandinavian fashion industry. Business Strategy and the Environment 24: 344–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Klarissa, Rainer Lueg, Karina Andersen, and Veronica Dancianu. 2016. Integrated reporting with CSR practices: A pragmatic constructivist case study in a Danish cultural setting. Corporate Communications: An International Journal 21: 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueg, Klarissa, Boris Krastev, and Rainer Lueg. 2019. Bidirectional effects between sustainability disclosure and risk—A disaggregate analysis of listed companies in South Africa. Journal of Cleaner Production 229: 268–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, Md. Abdul Kaium, Md. Harun Ur Rashid, Tehmina Khan, Seong Mi Bae, and Jong Dae Kim. 2019. Organizational Strategy and Corporate Social Responsibility: The Mediating Effect of Triple Bottom Line. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16: 4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Maryline, Sébastien Narjoud, and Julien Granata. 2017. When collective action drives corporate social responsibility implementation in small and medium-sized enterprises: The case of a network of French winemaking cooperatives. International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Small Business 32: 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirosa, Miranda, Rob Lawson, and Daniel Gnoth. 2013. Linking personal values to energyefficient behaviors in the home. Environment & Behavior 45: 455–75. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, David, Alessandro Liberati, Jennifer Tetzlaff, and Douglas G. Altman. 2009. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Medicine 6: e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, Michael H., Minet Schindehutte, John Walton, and Jeffrey Allen. 2002. The ethical context of entrepreneurship: Proposing and testing a development framework. Journal of Business Ethics 40: 331–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morros, Jordi. 2016. The integrated reporting: A presentation of the current state of art and aspects of integrated reporting that needed further development. Intangible Capital 12: 336–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muheki, Mark K., Klarissa Lueg, Rainer Lueg, and Christian Schmaltz. 2014. How business reporting changed during the financial crisis: A comparative case study of two large U.S. banks. Problems and Perspectives in Management 12: 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo, David, and Josep M. Lozano. 2006. SMEs and CSR: An approach to CSR in their own words. Journal of Business Ethics 67: 227–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, Janni Grouleff, Rainer Lueg, and Dennis van Liempd. 2019. Managing Multiple Logics: The Role of Performance Measurement Systems in Social Enterprises. Sustainability 11: 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, Janni Grouleff, Rainer Lueg, and Dennis Van Liempd. 2021. Challenges and boundaries in implementing social return on investment: An inquiry into its situational appropriateness. Nonprofit Management and Leadership 31: 413–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkiko, Cedric Marvin. 2013. SME owner–managers as key drivers of corporate social responsibility in Uganda. International Journal of Business Governance and Ethics 8: 376–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooteboom, Bart. 1994. Innovation and Diffusion in Small Firms: Theory and Evidence. Small Business Economics 6: 327–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onali, Enrico, Ramilya Galiakhmetova, Philip Molyneux, and Giuseppe Torluccio. 2016. CEO power, government monitoring, and bank dividends. Journal of Financial Intermediation 27: 89–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onkila, Tiina Johanna. 2009. Corporate argumentation for acceptability: Reflections of environmental values and stakeholder relations in corporate environmental statements. Journal of Business Ethics 87: 285–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, Lutz, and Jack Perschke. 2010. Slipstreaming the larger boats: Social responsibility in medium-sized businesses. Journal of Business Ethics 92: 531–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Mahfuzur, Che Ruhana Isa, Teng-Tsai Tu, Moniruzzaman Sarker, and Md Abdul Kaium Masud. 2020. A bibliometric analysis of socially responsible investment sukuk literature. Asian Journal of Sustainability and Social Responsibility 5: 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, David A., Carolyn P. Egri, Emmanuelle Reynaud, Narasimhan Srinivasan, Olivier Furrer, David Brock, Ruth Alas, Florian Wangenheim, Fidel León Darder, Christine Kuo, and et al. 2011. A twenty-first century assessment of values across the global workforce. Journal of Business Ethics 104: 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, Lilia, and Francois Bergeron. 2017. Green Practice Motivators and Performance in SMEs: A Qualitative Comparative Analysis. Journal of Small Business Strategy 27: 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rhim, Jong C., Joy V. Peluchette, and Inam Song. 2006. Stock market reactions and firm performance surrounding CEO succession: Antecedents of succession and successor origin. American Journal of Business 21: 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, Angeloantonio, and Antonio Tencati. 2009. Formal vs. informal CSR strategies: Evidence from Italian micro, small, medium-sized, and large firms. Journal of Business Ethics 85: 339–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, Abubakr, and Hafiz Muhammad Ziaulhaq. 2019. The Impact of CEO Characteristics on the Internationalization of SMEs: Evidence from the UK. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences 36: 322–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, Anja, Sarah Williams, and Richard Blundel. 2020. Individual Values and SME Environmental Engagement. Business & Society 59: 642–75. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, Shalom H. 1994. Are there universal aspects in the structure and contents of human values? Journal of Social Issues 50: 19–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, Shalom H. 2012. An Overview of the Schwartz Theory of Basic Values. Online Readings in Psychology and Culture 2: 2307-0919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, Shalom H., and Wolfgang Bilsky. 1987. Toward a universal psychological structure of human values. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 53: 550–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, Herbert Alexander. 1982. Models of Bounded Rationality. In Behavioral Economics and Business Organizations. Cambridge: MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Spence, Laura J. 2007. CSR and small business in a European policy context: The five “C”s of CSR and small business research agenda 2007. Business and Society Review 112: 533–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, Laura J. 2016. Small business social responsibility: Expanding core CSR theory. Business and Society 55: 23–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, Laura J., and José Félix Lozano. 2000. Communicating about ethics with small firms: Experiences from the UK and Spain. Journal of Business Ethics 27: 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, Laura J., René Schmidpeter, and André Habisch. 2003. Assessing social capital: Small and medium sized enterprises in Germany and the UK. Journal of Business Ethics 47: 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toft, Jon, and Rainer Lueg. 2015. Does EVA beat earnings? A literature review of the evidence since Biddle et al. (1997). Corporate Ownership and Control 12: 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, Olivier. 2000. Du rôle et de l’importance de la proximité dans la spécificité de gestion des PME. Paper presented at 5ème Congrès International Francophone PME (CIFPME), Lille, France, October 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Torrès, Olivier. 2003. Petitesse des entreprises et grossissement des effets de proximité. Revue Française de Gestion 144: 119–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Marrewijk, Marcel, and Marco Werre. 2003. Multiple levels of corporate sustainability. Journal of Business Ethics 44: 107–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhees, Frans J. H. M., and Matthew T. G. Meulenberg. 2004. Market Orientation, Innovativeness, Product Innovation, and Performance in Small Firms. Journal of Small Business Management 42: 134–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VHB (Verband der Hochschullehrer für Betriebswirtschaft). 2020. JOURQUAL3: Methode. Available online: https://vhbonline.org/en/vhb4you/vhb-jourqual/vhb-jourqual-3/complete-list (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- von Weltzien Hoivik, Heidi, and Domènec Melé. 2009. Can an SME become a global corporate citizen? Evidence from a case study. Journal of Business Ethics 88: 551–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Weltzien Høivik, Heidi, and Deepthi Shankar. 2011. How can SMEs in a cluster respond to global demands for corporate responsibility? Journal of Business Ethics 101: 175–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).