What Is Worth Knowing in Interventional Practices about Medical Staff Radiation Exposure Monitoring: A Review of Recent Outcomes of EURADOS Working Group 12
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Simulation of the Scattered Radiation Field and the Operator Doses
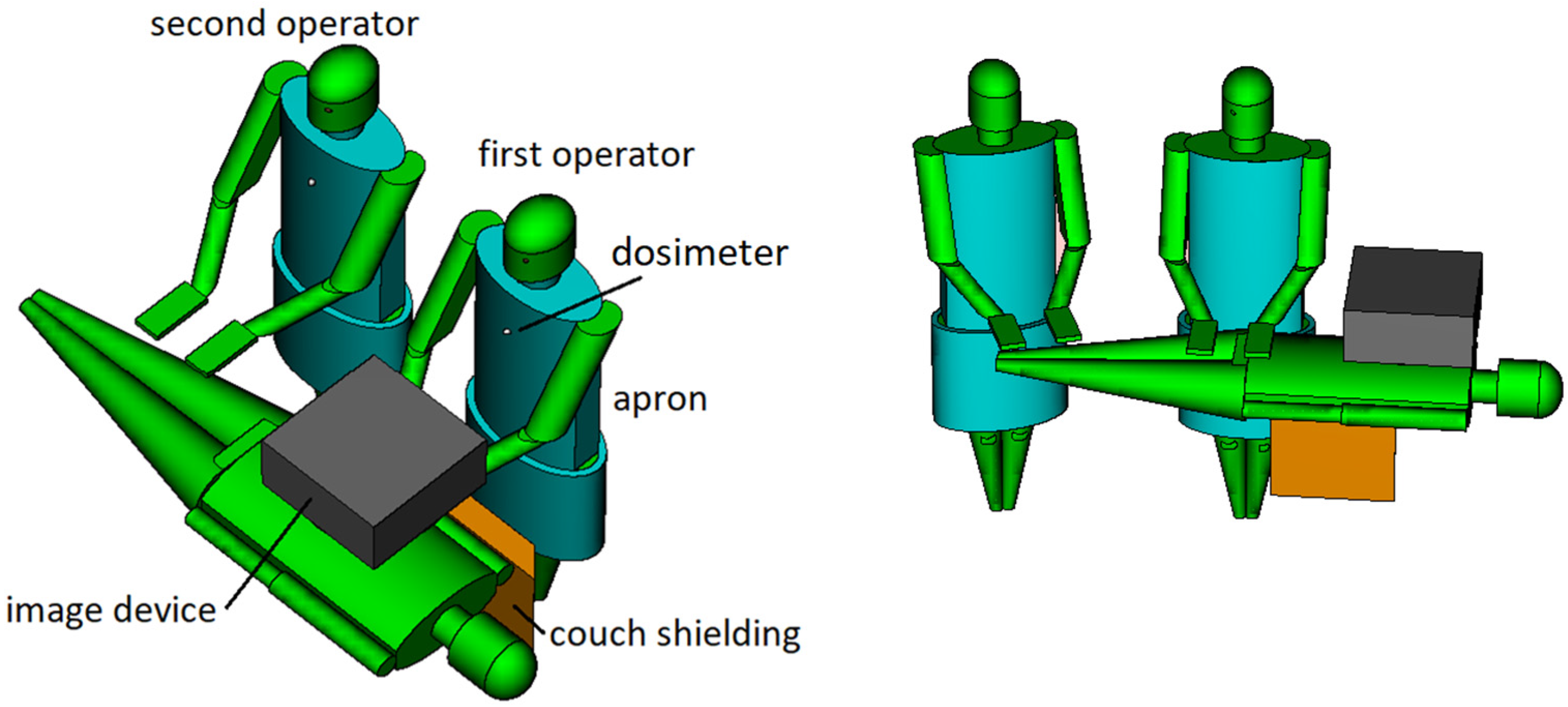
2.1. Interventional Theater Modelling
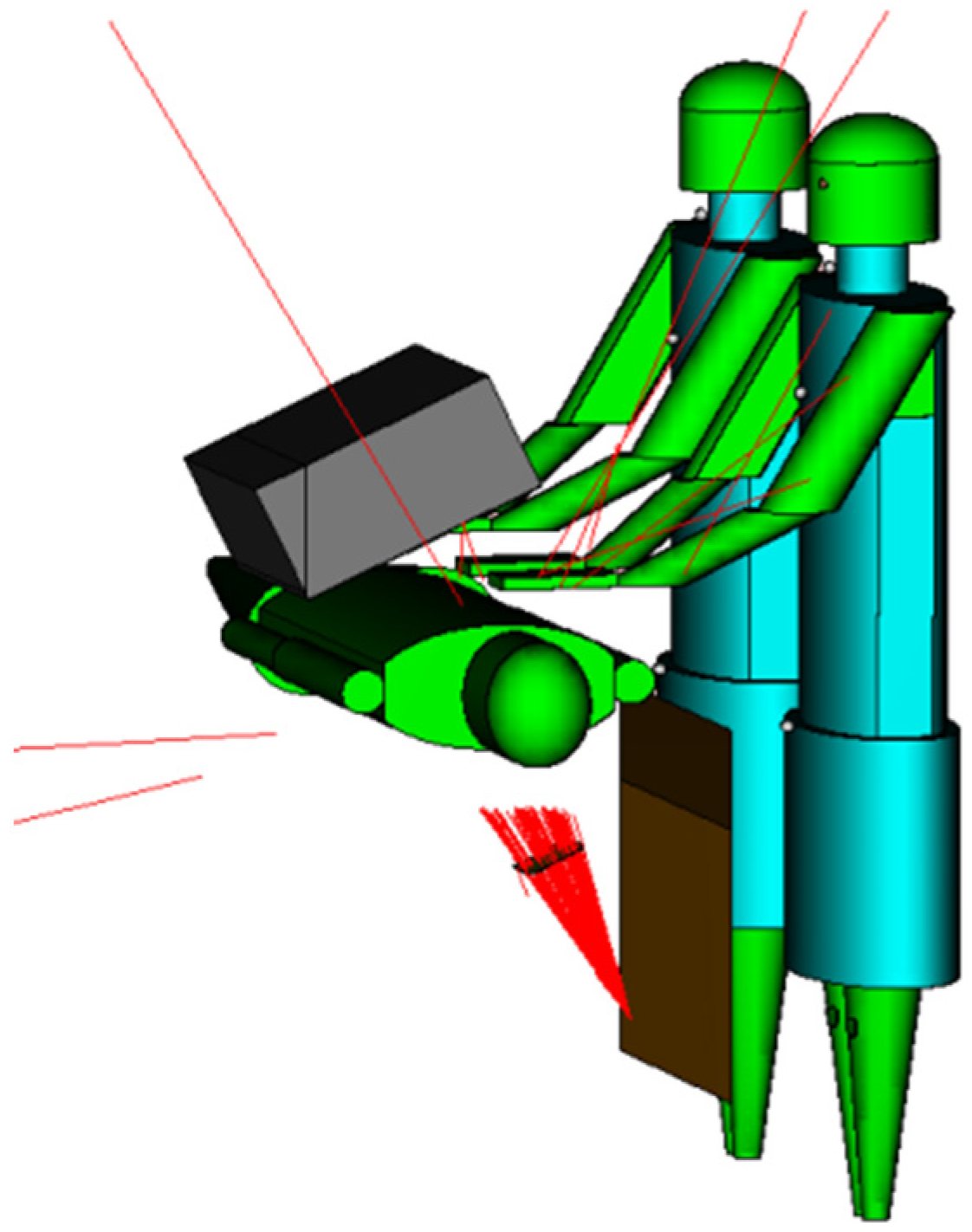
2.2. Scattering Field Evaluation and Operator’s Whole Body Exposure
2.3. Exposure of the Operator’s Head and Eye Lens
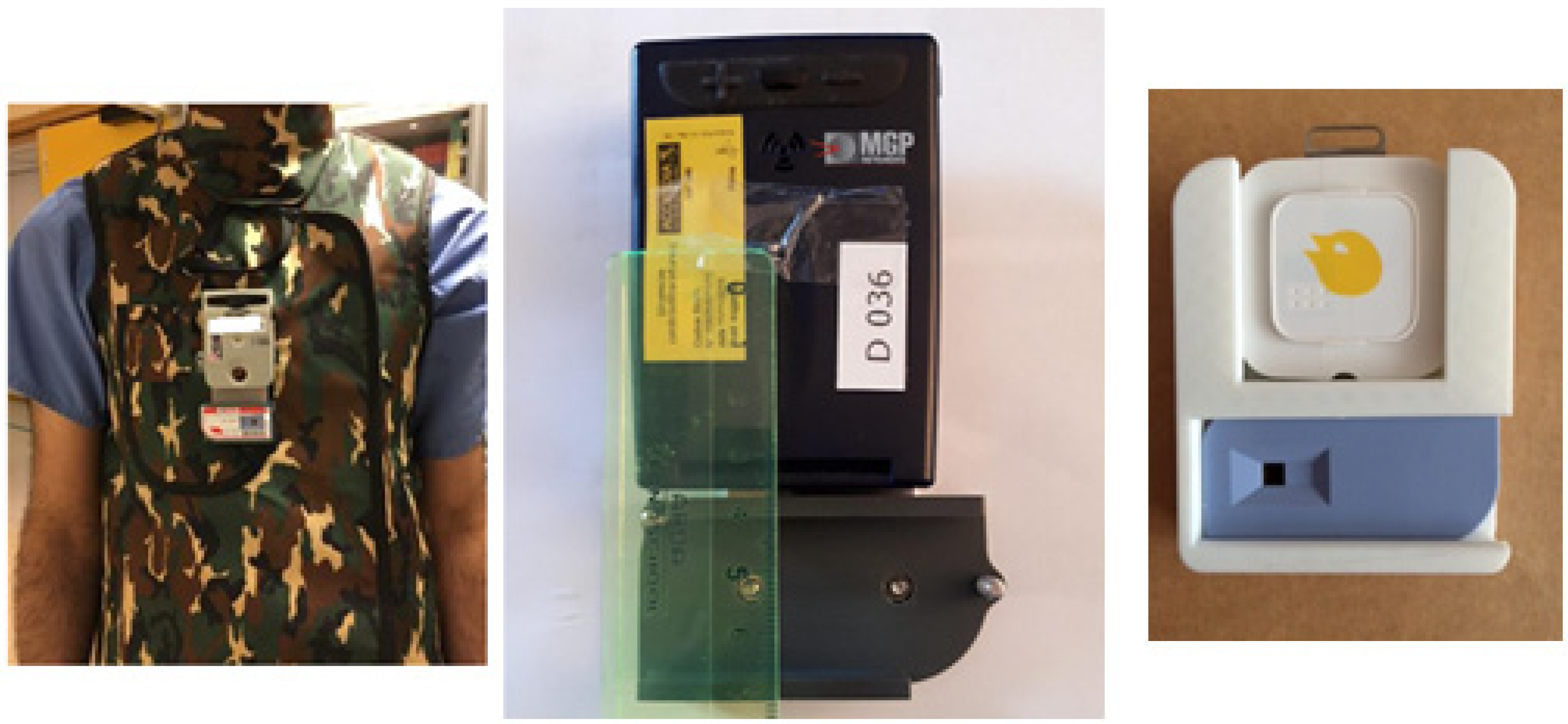
3. Testing Active Personal Dosimeters in Interventional Practices
3.1. APD Response in Continuous and Pulsed X-ray Field
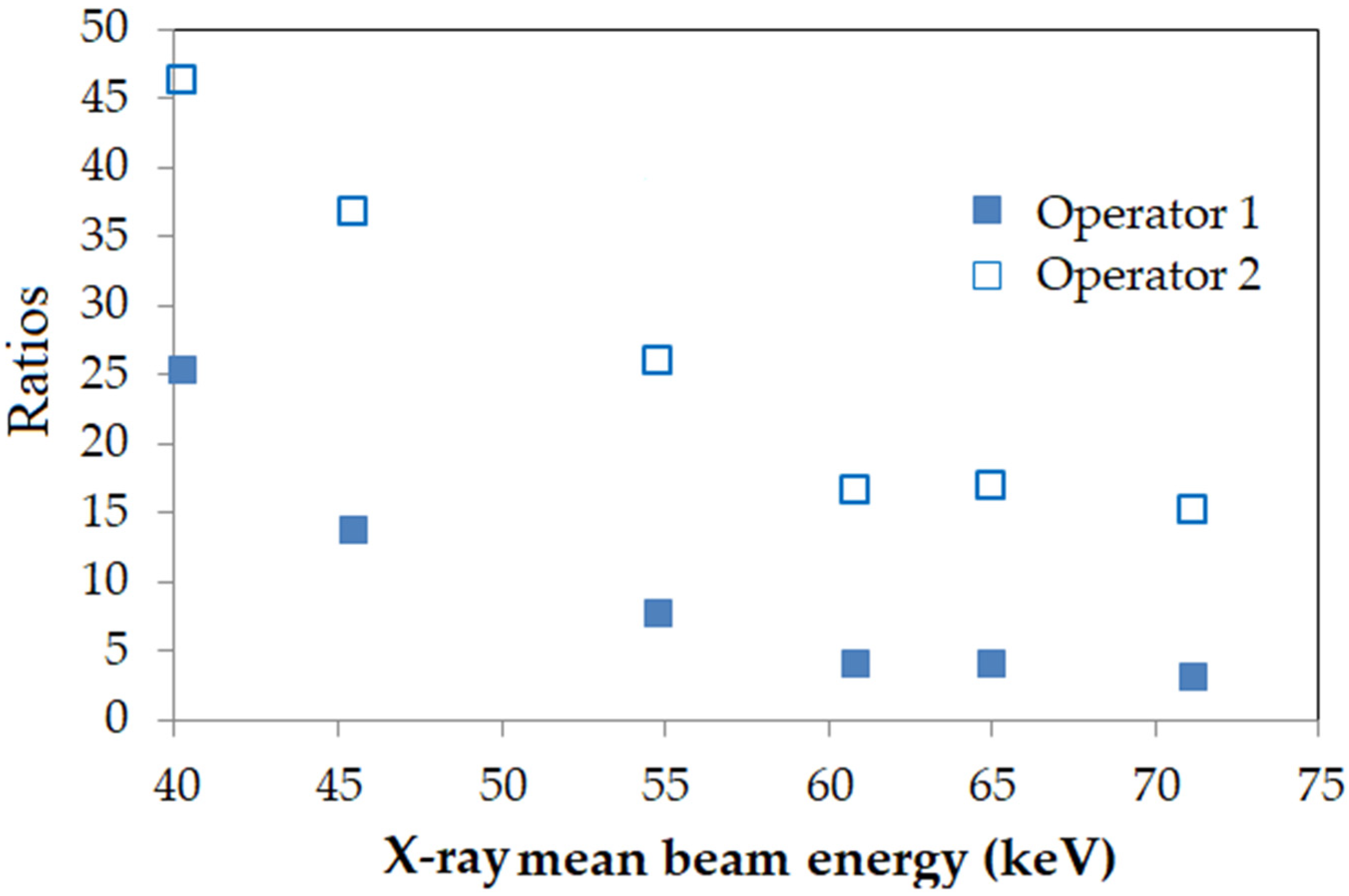
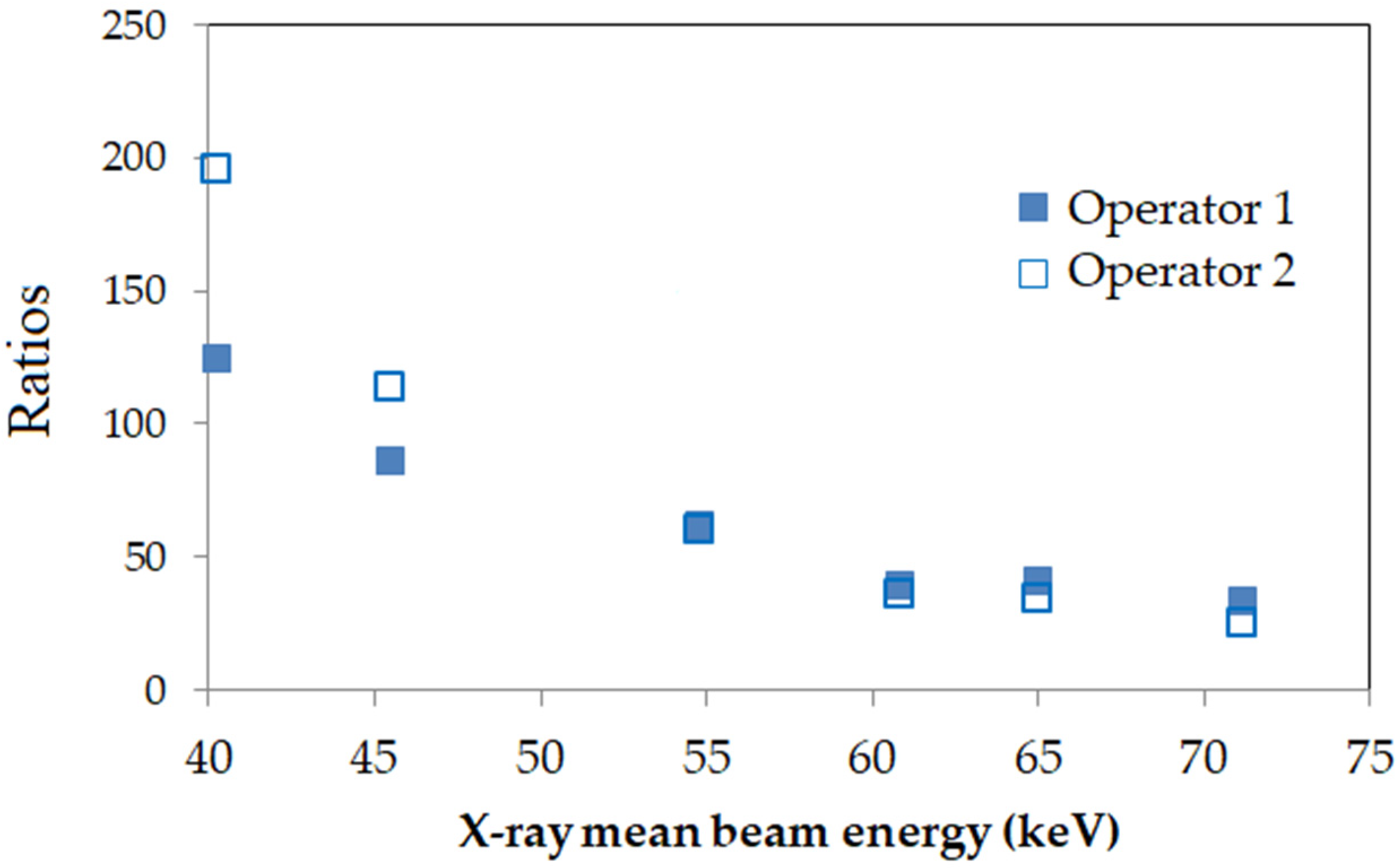
3.2. Effect of the Protective Apron on a Dosimeter’s Response
3.3. Comparison of the Responses of Active and Passive Dosimeters in the Hospital
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Covens, P.; Berus, D.; Buls, N.; Clerinx, P.; Vanhavere, F. Personal dose monitoring in hospitals: Global assessment, critical applications and future needs. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2007, 124, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.J. A review of radiology staff doses and dose monitoring requirements. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2009, 136, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovani, R.; Rodella, C.A. Staff dosimetry in interventional cardiology. Rad. Prot. Dosim. 2001, 94, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukorava, C.; Carinou, E.; Ferrari, P.; Krim, S.; Struelens, L. Study of the parameters affecting operator doses in interventional radiology using Monte Carlo simulations. Rad. Meas. 2011, 46, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESR. European Society of Radiology (ESR) and Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE). Interventional Radiology in European Radiology Departments: A Joint Survey from the European Society of Radiology (ESR) and the Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE). Insights into Imaging; 10:16. 2019. Available online: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13244-019-0698-6 (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- On behalf of the ICRP; Cousins, C.; Miller, D.L.; Bernardi, G.; Rehani, M.M.; Schofield, P.; Vañó, E.; Einstein, A.J.; Geiger, B.; Heintz, P.; et al. International Commission on Radiological Protection: Radiological protection in cardiology. Ann. ICRP 2013, 42, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vañó, E.; González, L.; Guibelalde, E.; Fernández, J.M.; Ten, J.I. Radiation exposure to medical staff in interventional and cardiac radiology. Brit. J. Radiol. 1998, 71, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadille, L.; Carinou, E.; Brodecki, M.; Domienik, K.; Jankowskic, J.; Koukorava, C.; Krim, S.; Nikodemova, D.; Ruiz-Lopez, N.; Sans-Merce, M.; et al. Staff eye lens and extremity exposure in interventional cardiology: Results of the ORAMED project. Rad. Meas. 2011, 46, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikodemová, D.; Brodecki, M.; Carinou, E.; Domienik, K.; Donadille, L.; Koukorava, C.; Krim, S.; Ruiz-López, N.; Sans-Merce, M.; Struelens, L.; et al. Staff extremity doses in interventional radiology. Results of the ORAMED measurement campaign. Rad. Meas. 2011, 46, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerinx, P.; Buls, N.; Bosmans, H.; de Mey, J. Double dosimetry algorithm for workers in interventional radiology. Rad. Prot. Dosim. 2008, 129, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, R.; Foti, C.; Malisan, M.R. Staff dosimetry protocols in interventional radiology. Rad. Prot. Dosim 2001, 94, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. The 2007 recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Ann. ICRP 2007, 103, 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Statement on tissue reactions/early and late effects of radiation in normal tissues and organs threshold doses for tissue reactions in a radiation protection context. Ann. ICRP 2012, 41, 1–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council Directive 2013/59/Euratom of 5 December 2013 Laying down Basic Safety Standards for Protection against the Dangers Arising from Exposure to Ionising Radiation, and Repealing Directives. 89/618/Euratom, 90/641/Euratom, 96/29/Euratom, 97/43/Euratom and 2003/122/Euratom. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2013/59/oj (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Carinou, E.; Ferrari, P.; Ciraj Bjelac, O.; Ginjaume, M.; Sans Merce., M.; O’Connor, U. Eye lens monitoring for interventional radiology personnel: Dosemeters, calibration and practical aspects of Hp(3) monitoring. A 2015 review. J. Radiol. Prot. 2015, 35, R17–R34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciraj Bjelac, O.; Carinou, E.; Ferrari, P.; Ginjaume, M.; Sans Merce, M.; O’Connor, U. Occupational Exposure of the Eye Lens in Interventional Procedures: How to Assess and Manage Radiation Dose. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2016, 3, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Lombardo, P.; Vanhavere, F.; Seret, A.; Phillips, C.; Covens, P. First steps towards online personal dosimetry using computational methods in interventional radiology: Operator’s position tracking and simulation input generation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 171, 108702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, Y.; Chida, K.; Kobayashi, R.; Kaga, R.; Zuguchi, M. Fundamental study of a real-time occupational dosimetry system for interventional radiology staff. J. Radiol. Prot. 2014, 34, N65–N71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vañó, E.; Fernandez, J.M.; Sanchez, R. Occupational dosimetry in real time. Benefits for interventional radiology Rad. Meas. 2011, 46, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Vañó, E.; Sanchez., R.; Fernandez, J.M. Strategies to optimise occupational radiation protection in interventional cardiology using simultaneous registration of patient and staff doses. J. Radiol. Prot. 2018, 38, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelowitz, D.B. (Ed.) MCNPX User’s Manual; LA-CP-05-0369; Los Alamos Laboratoty: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pelowitz, D.B. (Ed.) MCNP6 User’s Manual; Version 1.0, s LA-CP-13-00634; Los Alamos Laboratoty: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, P.; Becker, F.; Carinou, E.; Chumak, V.; Farah, J.; Jovanovic, Z.; Krstic, D.; Morgun, A.; Principi, S.; Teles, P. Monte Carlo study of the scattered radiation field near the eyes of the operator in interventional procedures. J. Radiol. Prot. 2016, 36, 902–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements. ICRU Report 57 Conversion Coefficients for Use in Radiological Protection against External Radiation; Oxford University Press: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- IPEM. Catalogue of Diagnostic X ray and Other Spectra; Scientific Report Series No.78; IPEM: York, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ginjaume, M.; Vanhavere, F.; Carinou, E.; Gualdrini, G.; Clairand, I.; Sans-Merce, M. (Eds.) International Workshop on Optimization of Radiation Protection of Medical Staff. ORAMED Rad. Meas. 2011, 46, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, P.; Becker, F.; Jovanovic, Z.; Khan, S.; Bakhanova, E.; Principi, S.; Krstic, D.; Pierotti, L.; Mariotti, F.; Faj, D. Simulation of Hp(10) and effective dose received by the medical staff in interventional radiology procedures. J. Radiol. Prot. 2019, 39, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, M.; Carbonez., P.; Krauss, M.; Verdun, F.R.; Damet, J. Characterisation and mapping of scattered radiation fields in interventional radiology theatres. Sci. Rep. 2020, 30, 18754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyton, F.; Nogueira, M.S.; Gubolino, L.A.; Pivetta, M.R.; Ubeda, C. Correlation between scatter radiation dose at height of operator’s eye and dose to patient for different angiographic projections. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2016, 117, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.P.; Miller, D.L.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Balter, S.; Kleinerman, R.A.; Ostroumova, W.; Simon, S.L.; Linet, M.S. Occupational radiation doses to operator performing fluoroscopically-guided procedures. Health Phys. 2012, 103, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements Use of Personal Monitors to Estimate Effective Dose Equivalent to Workers for External Exposure to Low-LET Radiation. Bethesda, MDNCRP NCRP Report No. 122. 1995. Available online: https://ncrponline.org/shop/reports/report-no-122-use-of-personal-monitors-to-estimate-effective-dose-equivalent-and-effective-dose-to-workers-for-external-exposure-to-low-let-radiation-1995/ (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- McEwan, A.C. Assessment of occupational exposure in New Zealand from personal monitoring records. Radiat. Prot. Australas. 2000, 17, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvinen, H.; Buls, N.; Clerinx, P.; Jansen, J.; Miljanic, S.; Nikodemova, D.; Ranogajec-Komor, M.; d’Errico, F. Overview of double dosimetry procedures for the determination of the effective dose to the interventional radiology staff. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2008, 129, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domienik, J.; Brodecki, M. The effectiveness of lead glasses in reducing the doses to eye lenses during cardiac implantation procedures performed using x-ray tubes above the patient table. J. Radiol. Prot. 2016, 36, N19–N25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Roojien, B.D.; de Haan, M.W.; Das, M.; Arnoldusse, C.W.K.P.; de Graaf, R.; van Zwam, W.H.; Backes, W.H.; Jeuken, C.R.L.P.N. Efficacy of Radiation Safety Glasses in Interventional Radiology Cardio. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 37, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.J.; Magee, J.S.; Sandblom, V.; Almén, A.; Lundh, C. Eye dosimetry and protective eyewear for interventional clinicians. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 165, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominiek, J.; Brodecki, M.; Carinou, E.; Donadille, L.; Jankowski, J.; Koukorava, C.; Krim, S.; Nikodemova, D.; Ruiz-Lopez, N.; Sans-Merce, M.; et al. Extremity and eye lens doses in interventional radiology and cardiology procedures: First results of the ORAMED project. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2011, 144, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailer, A.M.; Vergoossen, L.; Paulis, L.; van Zwam, W.H.; Das, M.; Wildberger, J.E.; Jeukens, C.R. Personalized Feedback on Staff Dose in Fluoroscopy-Guided Interventions: A New Era in Radiation Dose Monitoring. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picano, E.; Vano, E.; Domenici, L.; Bottai, M.; Thierry-Chef, I. Cancer and non-cancer brain and eye effects of chronic low-dose ionizing radiation exposure. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roguin, A.; Goldstein, J.; Bar, O.; Goldestein, J.A. Brain and neck tumours among physicians performing interventional procedures. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 1368–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, R.R.; Ang, L.; Bahadorani, J.; Naghi, J.; Dominguez, A.; Palakodeti, V.; Tsimikas, S.; Patel, M.P.; Mahmud, E. Invasive Cardiologists are exposed to greater left sided cranial radiation: The Brain study. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 8, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kithara, C.M.; Linet, M.S.; Balter, S.; Miller, D.L.; Rajaraman, P.; Cahoon, E.K.; Velazquez-Kronen, R.; Simon, S.L.; Little, M.P.; Doody, M.M.; et al. Occupational radiation exposure and deaths from malignant intracranial neoplasms of the brain and CNS in U.S. radiologic technologists, 1983–2012. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, P.; Jovanovic, Z.; Bakhanova, E.; Becker, F.; Krstic, D.; Jansen, J.; Principi, S.; Teles, P.; Clairand, I.; Knezevic, Ž. Absorbed dose in the operator’s brain in interventional radiology practices: Evaluation through KAP value conversion factors. Phys. Med. 2020, 76, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, L.E.; Riggs, M.W.; Bourland, P.D. Radiation exposure during cardiology fellowship training. Health Phys. 1997, 73, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, S.; Monzen, H.; Tamura, M.; Kosaka, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Nishimura, Y. Estimating radiation exposure of the brain of a physician with a protective flap in interventional radiology: A phantom study. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE EN ISO 4037-3; 2021 Radiological Protection–X and Gamma Reference Radiation for Calibrating Dosemeters and Doserate Meters and for Determining Their Response as a Function of Photon Energy–Part 3: Calibration of Area and Personal Dosemeters and the Measurement of Their Response as a Function of Energy and Angle of Incidence (ISO 4037-3:2019). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/66874.html (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- IEC 61267:2005; Medical Diagnostic X-ray Equipment—Radiation Conditions for use in the Determination of Characteristics. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/5079 (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Hupe, O.; Friedrich, S.; Vanhavere, F.; Marcin, B. Determining the dose rate dependence of different active personal dosemeters in standardized pulsed and continuous radiation fields. Rad. Prot. Dosim. 2019, 187, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Electrotechnical Commission. Radiation Protection Instrumentation–Dosemeters for Pulsed Fields of Ionizing Radiation. International Draft Technical Specification IEC/DTS 63050, Community Draft. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/preview/info_iects63050%7Bed1.0%7Den.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Ginjaume, M.; Carinou, E.; Marcin, B.; Clairand, I.; Domienik-Andrzejewska, J.; Exner, L.; Ferrari, P.; Jovanović, Z.; Krstic, D.; Principi, S.; et al. Effect of the radiation protective apron on the response of active and passive personal dosemeters used in interventional radiology and cardiology. J. Radiol. Prot. 2019, 39, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhavere, F.; Carinou, E.; Clairand, I.; Ciraj-Bjela, O.; De Monte, F.; Domienik-Andrzejewska, J.; Ferrari, P.; Ginjaume, M.; Hrsak, H.; Hupe, O.; et al. The use of active personal dosemeters in interventional workplaces in hospitals: Comparison between active and passive dosemeters worn simultaneously by medical staff. Rad. Prot. Dosim. 2020, 188, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, U.; Carinou, E.; Clairand, I.; Ciraj-Bjelac, O.; De Monte, F.; Domienik-Andrzejewska, J.; Ferrari, P.; Ginjaume, M.; Hršak, H.; Hupe, O.; et al. Recommendations for the use of active personal dosemeters (APDs) in interventional workplaces in hospitals. Phys. Med. 2021, 87, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeder, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Wolber, T.; Ammann, P.; Roelli, H.; Rohner, F.; Rickli, H. Impact of a Lead Glass Screen on Scatter Radiation to Eyes and Hands in Interventional Cardiologists. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2006, 67, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.J. Eye lens dosimetry for fluoroscopically guided clinical procedures: Practical approaches to protection and dose monitoring. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2016, 169, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrari, P.; Ginjaume, M.; Hupe, O.; O’Connor, U.; Vanhavere, F.; Bakhanova, E.; Becker, F.; Campani, L.; Carinou, E.; Clairand, I.; et al. What Is Worth Knowing in Interventional Practices about Medical Staff Radiation Exposure Monitoring: A Review of Recent Outcomes of EURADOS Working Group 12. Environments 2022, 9, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9040053
Ferrari P, Ginjaume M, Hupe O, O’Connor U, Vanhavere F, Bakhanova E, Becker F, Campani L, Carinou E, Clairand I, et al. What Is Worth Knowing in Interventional Practices about Medical Staff Radiation Exposure Monitoring: A Review of Recent Outcomes of EURADOS Working Group 12. Environments. 2022; 9(4):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9040053
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrari, Paolo, Mercè Ginjaume, Oliver Hupe, Una O’Connor, Filip Vanhavere, Elena Bakhanova, Frank Becker, Lorenzo Campani, Eleftheria Carinou, Isabelle Clairand, and et al. 2022. "What Is Worth Knowing in Interventional Practices about Medical Staff Radiation Exposure Monitoring: A Review of Recent Outcomes of EURADOS Working Group 12" Environments 9, no. 4: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9040053
APA StyleFerrari, P., Ginjaume, M., Hupe, O., O’Connor, U., Vanhavere, F., Bakhanova, E., Becker, F., Campani, L., Carinou, E., Clairand, I., Faj, D., Jansen, J., Jovanović, Z., Knežević, Ž., Krstić, D., Mariotti, F., Sans-Merce, M., Teles, P., & Živković, M. (2022). What Is Worth Knowing in Interventional Practices about Medical Staff Radiation Exposure Monitoring: A Review of Recent Outcomes of EURADOS Working Group 12. Environments, 9(4), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9040053





