High-Solid Anaerobic Digestion: Reviewing Strategies for Increasing Reactor Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Effect of Organic Loading on Digestion Performance
3. Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion (SS-AD)
3.1. Operating Conditions and Leachate Bed Configuration
3.2. Commercial Technologies for SS-AD
4. The Effect of Adsorbents and Materials in Accelerating Anaerobic Degradation
5. Temperature and Digestion Performance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehta, N.; Shah, K.J.; Lin, Y.I.; Sun, Y.; Pan, S.Y. Advances in Circular Bioeconomy Technologies: From Agricultural Wastewater to Value-Added Resources. Environments 2021, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.; Visvanathan, C. Management strategies for anaerobic digestate of organic fraction of municipal solid waste: Current status and future prospects. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S1), 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pastorelli, R.; Valboa, G.; Lagomarsino, A.; Fabiani, A.; Simoncini, S.; Zaghi, M.; Vignozzi, N. Recycling Biogas Digestate from Energy Crops: Effects on Soil Properties and Crop Productivity. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, S.; Ehimen, E.; Pillai, S.C.; Power, N.; Lyons, G.A.; Bartlett, J. An Investigation of the Potential Adoption of Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Production in Irish Farms. Environments 2021, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.M.; Tian, J.; Güngör-Demirci, G.; Phelan, P.; Villalobos, J.R.; Milcarek, R.J. Techno-Economic Assessment of CHP Systems in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environments 2020, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Xu, F.; Li, Y. Solid-state anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass: Recent progress and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Cheng, Y. Influencing mechanism of high solids concentration on anaerobic mono-digestion of sewage sludge without agitation. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y.C.; Liu, C. Influence of solids concentration on diffusion behavior in sewage sludge and its digestate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 152, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaemngoen, A.; Saritpongteeraka, K.; Leu, S.Y.; Phuttaro, C.; Sawatdeenarunat, C.; Chaiprapat, S. Anaerobic Digestion of Napier Grass (Pennisetum purpureum) in Two-Phase Dry Digestion System Versus Wet Digestion System. BioEnergy Res. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Gai, X.; Dong, B. Rheology evolution of sludge through high-solid anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 174, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Haward, S.J.; Wu, Z.; Dai, X.; Tao, W.; Li, Z. Evolution of rheological characteristics of high-solid municipal sludge during anaerobic digestion. Appl. Rheol. 2016, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, J.; Xiang, S.; Huang, Z.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y. Nutrient removal from digested swine wastewater by combining ammonia stripping with struvite precipitation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6725–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.D.; Lim, D.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Baek, U.I.; Chung, E.G.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.K. Struvite Precipitation for Sustainable Recovery of Nitrogen and Phosphorus from Anaerobic Digestion Effluents of Swine Manure. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Li, B.; Patel, K.; Wang, L.B. A review of the processes, parameters, and optimization of anaerobic digestion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wainaina, S.; Lukitawesa, M.K.A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Bioengineering of anaerobic digestion for volatile fatty acids, hydrogen or methane production: A critical review. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anukam, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Naqvi, M.; Granström, K. A review of the chemistry of anaerobic digestion: Methods of accelerating and optimizing process efficiency. Processes 2019, 7, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldin, S.; Nakhla, G.; Ray, M.B. Modeling the influence of particulate protein size on hydrolysis in anaerobic digestion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10843–10849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevillano, C.A.; Pesantes, A.A.; Peña Carpio, E.; Martínez, E.J.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic Digestion for Producing Renewable Energy—The Evolution of This Technology in a New Uncertain Scenario. Entropy 2021, 23, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.B.; Passos, F.; Chernicharo, C.A.; de Souza, C.L. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Effect of the Organic Load Variation in a Demo-Scale System. Waste Biomass Valoris. 2021, 12, 4407–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, L.; Pauss, A.; Ribeiro, T. Solid anaerobic digestion: State-of-art, scientific and technological hurdles. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gong, H.; Dai, X. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: Achievements and perspectives. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Li, H.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, N.; Li, C.; Yang, Y. Process performance of high-solids batch anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 2652–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, J.; Martinez, E.J.; Rosas, J.G.; Fernández, R.A.; López, R.; Gómez, X. Co-Digestion of swine manure and crude glycerine: Increasing glycerine ratio results in preferential degradation of labile compounds. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellacuriaga, M.; García-Cascallana, J.; Gómez, X. Biogas Production from Organic Wastes: Integrating Concepts of Circular Economy. Fuels 2021, 2, 144–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziganshin, A.M.; Schmidt, T.; Scholwin, F.; Il’Inskaya, O.N.; Harms, H.; Kleinsteuber, S. Bacteria and archaea involved in anaerobic digestion of distillers grains with solubles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 89, 2039–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, S.G.; Gabris, C.; Einfalt, D.; Wemheuer, B.; Kazda, M.; Bengelsdorf, F.R. Different response of bacteria, archaea and fungi to process parameters in nine full-scale anaerobic digesters. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1210–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Otero, M.; Morán, A. Anaerobic digestion of solid slaughterhouse waste (SHW) at laboratory scale: Influence of co-digestion with the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW). Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 40, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Dong, B.; Wu, B.; Dai, X. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge under mesophilic conditions: Feasibility study. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 104, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Morán, A.; Otero, M.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic co-digestion of poultry blood with OFMSW: FTIR and TG–DTG study of process stabilization. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowski, S.; Domański, J.; Weatherley, L. Anaerobic co-digestion of swine and poultry manure with municipal sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggi-Varaldo, H.M.; Rodriguez-Vazquez, R.; Fernandez-Villagomez, G.; Esparza-Garcia, F. Inhibition of mesophilic solid-substrate anaerobic digestion by ammonia nitrogen. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 47, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanapan, C.; Sinchai, L.; Suksaroj, T.T.; Kantachote, D.; Ounsaneha, W. Biogas production by co-digestion of canteen food waste and domestic wastewater under organic loading rate and temperature optimization. Environments 2019, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.; Song, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, T. The effects of initial substrate concentration, C/N ratio, and temperature on solid-state anaerobic digestion from composting rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 177, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinuevo-Salces, B.; García-González, M.C.; González-Fernández, C.; Cuetos, M.J.; Morán, A.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic co-digestion of livestock wastes with vegetable processing wastes: A statistical analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9479–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habagil, M.; Keucken, A.; Horváth, I.S. Biogas production from food residues—The role of trace metals and co-digestion with primary sludge. Environments 2020, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Poquet, V.; Papirio, S.; Trably, E.; Rintala, J.; Escudié, R.; Esposito, G. High-solids anaerobic digestion requires a trade-off between total solids, inoculum-to-substrate ratio and ammonia inhibition. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 7011–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, M.; Yaguchi, J. High-solids thermophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: Effect of ammonia concentration. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadh, P.K.; Duhan, S.; Duhan, J.S. Agro-industrial wastes and their utilization using solid state fermentation: A review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2018, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melnichuk, N.; Braia, M.J.; Anselmi, P.A.; Meini, M.R.; Romanini, D. Valorization of two agroindustrial wastes to produce alpha-amylase enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae by solid-state fermentation. Waste Manag. 2020, 106, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Gea, T.; Sánchez, A.; Font, X. Agro-wastes and Inert Materials as Supports for the Production of Biosurfactants by Solid-state Fermentation. Waste Biomass Valoris. 2021, 12, 1963–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, N.A.; Barrena, R.; Komilis, D.; Sánchez, A. Solid-state fermentation as a novel paradigm for organic waste valorization: A review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourkhanali, K.; Khayati, G.; Mizani, F.; Raouf, F. Isolation, identification and optimization of enhanced production of laccase from Galactomyces geotrichum under solid-state fermentation. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaný, O.; Klempová, T.; Shapaval, V.; Zimmermann, B.; Kohler, A.; Čertík, M. Biotransformation of animal Fat-by products into ARA-enriched fermented bioproducts by solid-state fermentation of mortierella alpina. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Dekker, S.; Kyriakopoulou, K.; Boom, R.M.; Smid, E.J.; Schutyser, M.A. Enhanced nutritional value of chickpea protein concentrate by dry separation and solid state fermentation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 59, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi-Banji, A.A.; Rahman, S.; Sunoj, S.; Igathinathane, C. Impact of corn stover particle size and C/N ratio on reactor performance in solid-state anaerobic co-digestion with dairy manure. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2020, 70, 436–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilford, N.G.; Lee, H.P.; Kanger, K.; Meyer, T.; Edwards, E.A. Solid-state anaerobic digestion of mixed organic waste: The synergistic effect of food waste addition on the destruction of paper and cardboard. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12677–12687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzolla, D.; Di Maria, F.; Zadra, C.; Massaccesi, L.; Sordi, A.; Gigliotti, G. Optimization of solid-state anaerobic digestion through the percolate recirculation. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 96, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wen, Z. Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion for Waste Management and Biogas Production. In Solid State Fermentation. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Steudler, S., Werner, A., Cheng, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 169, pp. 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, T.; Mei, Z.; Li, J.; Qiu, K.; Ge, Y. Dry anaerobic digestion technologies for agricultural straw and acceptability in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degueurce, A.; Trémier, A.; Peu, P. Dynamic effect of leachate recirculation on batch mode solid state anaerobic digestion: Influence of recirculated volume, leachate to substrate ratio and recirculation periodicity. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedwitschka, H.; Gallegos, D.; Tietze, M.; Reinhold, J.; Jenson, E.; Liebetrau, J.; Nelles, M. Effect of Substrate Characteristics and Process Fluid Percolation on Dry Anaerobic Digestion Processes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2020, 43, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Stiverson, J.A.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y. Reactor performance and microbial community dynamics during solid-state anaerobic digestion of corn stover at mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Nelles, M.; Stinner, W.; Li, Y. Effects of percolate recirculation on dry anaerobic co-digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and corn straw. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 12183–12191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Kong, X.; Dong, P.; Zhen, F.; Sun, Y. Leachate recirculation effects on solid-state anaerobic digestion of Pennisetum hybrid and microbial community analysis. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y. Effect of Leachate Spraying Intensity on High-Solid Anaerobic Digestion of Corn Stover and Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. Waste Biomass Valoris. 2020, 11, 3293–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizami, A.S.; Thamsiriroj, T.; Singh, A.; Murphy, J.D. Role of leaching and hydrolysis in a two-phase grass digestion system. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4549–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Lam, H.P.; Karthikeyan, O.P.; Wong, J.W.C. Optimization of food waste hydrolysis in leach bed coupled with methanogenic reactor: Effect of pH and bulking agent. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3702–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, A.; Limonti, C.; Curcio, G.M.; Calabrò, V. Biogas generation through anaerobic digestion of compost leachate in semi-continuous completely stirred tank reactors. Processes 2019, 7, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.Y.; Liao, B. Anaerobic co-digestion of vegetable and fruit market waste in LBR+ CSTR two-stage process for waste reduction and biogas production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, P.; Goyette, B.; Rahaman, M.; Rajagopal, R. Processing High-Solid and High-Ammonia Rich Manures in a Two-Stage (Liquid-Solid) Low-Temperature Anaerobic Digestion Process: Start-Up and Operating Strategies. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, S.; Torrijos, M.; Vives, G.; Esposito, G.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Steyer, J.P.; Escudié, R. Leachate flush strategies for managing volatile fatty acids accumulation in leach-bed reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chynoweth, D.P.; Bosch, G.; Earle, J.F.K.; Legrand, R.; Liu, K. A novel process for anaerobic composting of municipal solid waste. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1991, 28, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, S.; Chynoweth, D.P.; Clarke, W.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Rudolph, V. Degradation of unsorted municipal solid waste by a leach-bed process. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 69, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusch, S.; Oechsner, H.; Jungbluth, T. Biogas production with horse dung in solid-phase digestion systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1280–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez, X.; Diaz, M.C.; Cooper, M.; Blanco, D.; Morán, A.; Snape, C.E. Study of biological stabilization processes of cattle and poultry manure by thermogravimetric analysis and 13C NMR. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeken, A.H.M.; Hamelers, B.V.M. Effect of substrate-seed mixing and leachate recirculation on solid state digestion of biowaste. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 41, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Bekon Process. Available online: https://www.bekon.eu/en/technology/ (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Available online: http://www.gicon-engineering.com/en/gicon-biogas-technologies/the-gicon-process.html (accessed on 22 April 2021).
- BIOFerm™ Dry Fermentation Digester. Available online: https://www.biofermenergy.com/ext-dry-fermentation#:~:text=Our%20BIOFerm%E2%84%A2%20Dry%20Fermentation,any%20kind%20of%20organic%20waste (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Dranco Process. Available online: https://www.ows.be/es/household_waste/dranco-3/ (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Valorga’s Anaerobic Digestion Process. Available online: http://www.valorgainternational.fr/en/mpg3-128079--VALORGA-S-ANAEROBIC-DIGESTION-PROCESS.html (accessed on 8 May 2021).
- Elsharkawy, K.; Elsamadony, M.; Afify, H. Comparative analysis of common full scale reactors for dry anaerobic digestion process. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 83, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompogas® Anaerobic Digestion. Available online: https://www.hz-inova.com/renewable-gas/anaerobic-digestion/ (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Rocamora, I.; Wagland, S.T.; Villa, R.; Simpson, E.W.; Fernández, O.; Bajón-Fernández, Y. Dry anaerobic digestion of organic waste: A review of operational parameters and their impact on process performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaee, F.; Mokhtarani, N.; Niavol, K.P. Solid-state anaerobic co-digestion of organic fraction of municipal waste and sawdust: Impact of co-digestion ratio, inoculum-to-substrate ratio, and total solids. Biodegradation 2021, 32, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, C.; Liu, G.; He, Y.; Liu, X. Biogas production from co-digestion of corn stover and chicken manure under anaerobic wet, hemi-solid, and solid state conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holliger, C.; de Laclos, H.F.; Hack, G. Methane production of full-scale anaerobic digestion plants calculated from substrate’s biomethane potentials compares well with the one measured on-site. Front. Energy Res. 2017, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yang, G.; Li, F.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Response surface optimization of methane potentials in anaerobic co-digestion of multiple substrates: Dairy, chicken manure and wheat straw. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Lee, S.; Jo, H.; Jeong, J.; Mulbry, W.; Rhaman, S.; Ahn, H. Solid-state anaerobic digestion of dairy manure from a sawdust-bedded pack barn: Moisture responses. Energies 2018, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A. Solid-state fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 13, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, C.; Crolla, A.; Kinsley, C.; McBean, E. Anaerobic digestion of poultry manure: Process optimization employing struvite precipitation and novel digestion technologies. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demirbas, A.; Ozturk, T. Anaerobic digestion of agricultural solid residues. Int. J. Green Energy 2005, 1, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, F.; Yang, H.; Zhi, S.; Liu, G. Anaerobic digestion performance of sweet potato vine and animal manure under wet, semi-dry, and dry conditions. AMB Expr. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhesh, M.J.; Rao, P.V. Synergistic effect in anaerobic co-digestion of rice straw and dairy manure-a batch kinetic study. Energy Source Part A 2019, 41, 2145–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, O.; Akyol, Ç.; Ozbayram, E.G.; Tutal, B.; Ince, B. Enhancing methane production from anaerobic co-digestion of cow manure and barley: Link between process parameters and microbial community dynamics. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, 13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Qi, G.; Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J.; Yamashiro, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Umetsu, K. Anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure and Japanese knotweed (Fallopia japonica) under thermophilic condition: Optimal ratio for biochemical methane production. Anim. Sci. J. 2021, 92, e13523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardi, M.J.; Rad, H.A. Simultaneous synergistic effects of addition of agro-based adsorbent on anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and sewage sludge. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achi, C.G.; Hassanein, A.; Lansing, S. Enhanced biogas production of cassava wastewater using zeolite and biochar additives and manure co-digestion. Energies 2020, 13, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arias, J.G.; Sánchez, M.E.; Gómez, X. Enhancing anaerobic digestion: The effect of carbon conductive materials. C J. Carbon Res. 2018, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, X.C. Sawdust-derived biochar much mitigates VFAs accumulation and improves microbial activities to enhance methane production in thermophilic anaerobic digestion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Herrmann, C.; Maja, W.; Borja, R. Effect of organic loading rate on the anaerobic digestion of swine waste with biochar addition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Patel, A.; Datta, M. Effects of adsorbents on anaerobic digestion of water hyacinth-cattle dung. Bioresour. Technol. 1992, 40, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milán, Z.; Sánchez, E.; Weiland, P.; Borja, R.; Martın, A.; Ilangovan, K. Influence of different natural zeolite concentrations on the anaerobic digestion of piggery waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 80, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, B.; Biswas, S.; Rabbi, M.S. Biogas from mesophilic anaerobic digestion of cow dung using silica gel as catalyst. Procedia Eng. 2015, 105, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatima, B.; Liaquat, R.; Farooq, U.; Jamal, A.; Ali, M.I.; Liu, F.J.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Urynowicz, M.; Huang, Z. Enhanced biogas production at mesophilic and thermophilic temperatures from a slaughterhouse waste with zeolite as ammonia adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petracchini, F.; Liotta, F.; Paolini, V.; Perilli, M.; Cerioni, D.; Gallucci, F.; Carnevale, M.; Bencini, A. A novel pilot scale mul-tistage semidry anaerobic digestion reactor to treat food waste and cow manure. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Fazzino, F.; Limonti, C.; Siciliano, A. Enhancement of Anaerobic Digestion of Waste-Activated Sludge by Conductive Materials under High Volatile Fatty Acids-to-Alkalinity Ratios. Water 2021, 13, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Martinez, E.J.; Moreno, R.; Gonzalez, R.; Otero, M.; Gomez, X. Enhancing anaerobic digestion of poultry blood using activated carbon. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastyar, W.; Azizi, S.M.M.; Meshref, M.N.; Dhar, B.R. Powdered activated carbon amendment in percolate tank enhances high-solids anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 151, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Role and potential of direct interspecies electron transfer in anaerobic digestion. Energies 2018, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Si, B.; Watson, J.; Zhang, Y. Accelerating anaerobic digestion for methane production: Potential role of direct interspecies electron transfer. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo, M.; Viñas, M.; Bonmatí, A. Anaerobic digestion and electromethanogenic microbial electrolysis cell integrated system: Increased stability and recovery of ammonia and methane. Renew. Energy 2018, 120, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arenas, C.B.; Meredith, W.; Snape, C.E.; Gómez, X.; González, J.F.; Martinez, E.J. Effect of char addition on anaerobic digestion of animal by-products: Evaluating biogas production and process performance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24387–24399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Mao, F.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Tong, Y.W.; Peng, Y. Biochar enhanced high-solid mesophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste: Cell viability and methanogenic pathways. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, N.; Liu, Y. Impacts of conductive materials on microbial community during syntrophic propionate oxidization for biomethane recovery. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, E.M.; Samer, M. Biostimulation of anaerobic digestion using nanomaterials for increasing biogas production. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Hafeez, F.Y.; Zafar, Y.; Majeed, S.; Leng, X.; Zhao, S.; Saif, I.; Malik, K.; Li, X. A review on nanoparticles as boon for biogas producers—Nano fuels and biosensing monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Regulating secretion of extracellular polymeric substances through dosing magnetite and zerovalent iron nanoparticles to affect anaerobic digestion mode. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9655–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.A.; RuiZhe, F.; Shi, Y.; Khan, S.Z.; Mushtaq, K. Nanoparticles augmentation on biogas yield from microalgal biomass anaerobic digestion. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 14202–14213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.S.; Hassaneen, F.Y.; Faisal, Y.; Mansour, M.S.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Abo-Elfadl, S.; Salem, H.G.; Allam, N.K. Effect of Ni-Ferrite and Ni-Co-Ferrite nanostructures on biogas production from anaerobic digestion. Fuel 2019, 254, 115673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.A.; Pantaleo, A.; Tedone, L.; Elkatory, M.R.; Ali, R.M.; Nemr, A.E.; Mastro, G.D. Enhancement of biogas production via green ZnO nanoparticles: Experimental results of selected herbaceous crops. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2021, 208, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosser, A.; Grobelak, A.; Rorat, A.; Courtois, P.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Lemière, S.; Guyoneaud, R.; Attard, E.; Celary, P. Effects of silver nanoparticles on performance of anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge and associated microbial communities. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniamerian, H.; Isfahani, P.G.; Tsapekos, P.; Alvarado-Morales, M.; Shahrokhi, M.; Vossoughi, M.; Angelidaki, I. Application of nano-structured materials in anaerobic digestion: Current status and perspectives. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; He, P.; Wang, Y.; Shao, L.; Lü, F. Effects and optimization of the use of biochar in anaerobic digestion of food wastes. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linville, J.L.; Shen, Y.; de Leon, P.A.I.; Schoene, R.P.; Urgun-Demirtas, M. In-situ biogas upgrading during anaerobic digestion of food waste amended with walnut shell biochar at bench scale. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Liao, Y.; Cho, E.; Ko, J.H. Effects of biochar addition on the anaerobic digestion of carbohydrate-rich, protein-rich, and lipid-rich substrates. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2020, 70, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, E.J.; Rosas, J.G.; Sotres, A.; Moran, A.; Cara, J.; Sánchez, M.E.; Gómez, X. Codigestion of sludge and citrus peel wastes: Evaluating the effect of biochar addition on microbial communities. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 137, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Świechowski, K.; Manczarski, P.; Koziel, J.A.; Białowiec, A. The effect of biochar addition on the biogas production kinetics from the anaerobic digestion of brewers’ spent grain. Energies 2019, 12, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambaye, T.G.; Rene, E.R.; Dupont, C.; Wongrod, S.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Anaerobic digestion of fruit waste mixed with sewage sludge digestate biochar: Influence on biomethane production. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lü, C.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, N.; Yuan, H. Redox-Active Biochar and Conductive Graphite Stimulate Methanogenic Metabolism in Anaerobic Digestion of Waste-Activated Sludge: Beyond Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12626–12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Usman, M.; Tsang, D.C.; O-Thong, S.; Angelidaki, I.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Luo, G. Hydrochar-Facilitated anaerobic digestion: Evidence for direct interspecies electron transfer mediated through surface oxygen-containing functional groups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5755–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milán, Z.; Villa, P.; Sánchez, E.; Montalvo, S.; Borja, R.; Ilangovan, K.; Briones, R. Effect of natural and modified zeolite addition on anaerobic digestion of piggery waste. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Shi, D.; Chai, H.; Li, L.; Ai, H.; He, Q. Enhancement of performance and stability of anaerobic co-digestion of waste activated sludge and kitchen waste by using bentonite. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Zheng, H.; Hu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Stanislaus, M.S.; Li, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. Enhanced bio-methane production from ammonium-rich waste using eggshell-and lignite-modified zeolite (ELMZ) as a bio-adsorbent during anaerobic digestion. Process. Biochem. 2019, 81, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Fazzino, F.; Folino, A.; Paone, E.; Komilis, D. Semi-continuous anaerobic digestion of orange peel waste: Effect of activated carbon addition and alkaline pretreatment on the process. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Qin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Han, B.; Ren, J. Simultaneous addition of zero-valent iron and activated carbon on enhanced mesophilic anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22371–22381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.; Madamwar, D. Anaerobic digestion of a mixture of cheese whey, poultry waste and cattle dung: A study of the use of adsorbents to improve digester performance. Environ. Pollut. 1994, 86, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, G.; Khater, D.; Odeh, F.; Shatanawi, K.; Halalsheh, M.; Arafah, M.; van Lier, J.B. Impact of Nanoscale Magnetite and Zero Valent Iron on the Batch-Wise Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Waste-Activated Sludge. Water 2020, 12, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsalam, E.; Samer, M.; Attia, Y.A.; Abdel-Hadi, M.A.; Hassan, H.E.; Badr, Y. Effects of Co and Ni nanoparticles on biogas and methane production from anaerobic digestion of slurry. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 141, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.A.; Feng, R.; Malik, A.; Khan, S.Z.; Shi, Y.; Bhutta, A.J.; Shah, A.H. Combining microwave pretreatment with iron oxide nanoparticles enhanced biogas and hydrogen yield from green algae. Processes 2019, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushal, R.; Baitha, R. Biogas and methane yield enhancement using graphene oxide nanoparticles and Ca (OH)2 pre-treatment in anaerobic digestion. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2021, 42, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, E.; Barrena, R.; García, A.; González, E.; Delgado, L.; Busquets-Fité, M.; Font, X.; Arbiol, J.; Glatzel, P.; Kvashnina, K.; et al. Programmed iron oxide nanoparticles disintegration in anaerobic digesters boosts biogas production. Small 2014, 10, 2801–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelwahab, T.A.M.; Mohanty, M.K.; Sahoo, P.K.; Behera, D. Impact of iron nanoparticles on biogas production and effluent chemical composition from anaerobic digestion of cattle manure. Biomass Convers. Bior. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, M.; Andriamanohiarisoamanana, F.J.; Ahmed, M.M.; Kotb, S.; Yamashiro, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Umetsu, K. Impacts of iron oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on biogas production: Hydrogen sulfide mitigation, process stability, and prospective challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Mahar, R.B.; Soomro, R.A.; Sherazi, S.T.H. Fe3O4 nanoparticles facilitated anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste for enhancement of methane production. Energy Source Part A 2017, 39, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Li, J.; Ma, W.; Qian, F. Clarifying the synergetic effect of magnetite nanoparticles in the methane production process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babalola, M.A. Application of GIS-Based Multi-Criteria Decision technique in exploration of suitable site options for anaerobic digestion of food and biodegradable waste in Oita City, Japan. Environments 2018, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borja, R.; González, E.; Raposo, F.; Millán, F.; Martín, A. Kinetic analysis of the psychrophilic anaerobic digestion of wastewater derived from the production of proteins from extracted sunflower flour. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4628–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; Lu, X. Influence of temperature on biogas production efficiency and microbial community in a two-phase anaerobic digestion system. Water 2019, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Huang, W.; Jiang, M.; Xu, C.; Fan, G.; Yan, J.; Chai, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Challenges of anaerobic digestion in China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Solid-phase methane fermentation of solid wastes. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1985, 107, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P. Assessment of Batch and Semi-continuous Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste at Psychrophilic Range at Different Food Waste to Inoculum Ratios and Organic Loading Rates. Waste Biomass Valoris. 2019, 10, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.; Cordero, C.; Tapia, X.; Muñoz, L.; Candia, O. Assessment of anaerobic digestion of food waste at psychrophilic conditions and effluent post-treatment by microalgae cultivation. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2020, 22, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, D.I.; Gilbert, Y.; Saady, N.M.C.; Liu, C. Low-temperature anaerobic digestion of swine manure in a plug-flow reactor. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Bellavance, D.; Rahaman, M.S. Psychrophilic anaerobic digestion of semi-dry mixed municipal food waste: For North American context. Process. Saf. Environ. 2017, 105, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, D.I.; Saady, N.M.C. Dry anaerobic digestion of high solids content dairy manure at high organic loading rates in psychrophilic sequence batch reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4521–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes-Estévez, J.; Zafra, G.; Martí-Herrero, J.; Pelaz, G.; Morán, A.; Puentes, A.; Gómez, C.; Castro, L.; Escalante Hernández, H. Psychrophilic Full Scale Tubular Digester Operating over Eight Years: Complete Performance Evaluation and Microbiological Population. Energies 2021, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yan, F.; Li, X.; Piao, R.; Wang, W.; Cui, Z. Impact of Organic Loading Rate on Performance and Methanogenic Microbial Communities of a Fixed-Bed Anaerobic Reactor at 4 °C. Water 2020, 12, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmasoumi, S.; Ebrahimi, S.; Saray, R.K. Enhancement of biogas production from sewage sludge in a wastewater treatment plant: Evaluation of pretreatment techniques and co-digestion under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Energy 2018, 157, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, G.K.; Bhattarai, S.; Kim, S.H.; Chen, L. Effect of feed to microbe ratios on anaerobic digestion of Chinese cabbage waste under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions: Biogas potential and kinetic study. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Jensen, P.D.; Batstone, D.J. Relative kinetics of anaerobic digestion under thermophilic and mesophilic conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, A.; Bolzonella, D.; Pavan, P.; Cavinato, C.; Cecchi, F. Co-digestion of livestock effluents, energy crops and agro-waste: Feeding and process optimization in mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.J.; Chickering, G.W.; Townsend, T.G.; Pullammanappallil, P. Effects of temperature and particle size on the biochemical methane potential of municipal solid waste components. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryue, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.; McCartney, D.; Dhar, B.R. Comparative effects of GAC addition on methane productivity and microbial community in mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 146, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Hussain, A.; Dubey, S.K. Methane formation from food waste by anaerobic digestion. Biomass Convers. Bior. 2016, 6, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, E.J.; Gil, M.V.; Fernandez, C.; Rosas, J.G.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic codigestion of sludge: Addition of butcher’s fat waste as a cosubstrate for increasing biogas production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Blanco, D.; Fierro, J.; Martínez, E.J.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge with cheese whey under thermophilic and mesophilic conditions. Int. J. Energy Eng. 2014, 4, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, X.; Blanco, D.; Lobato, A.; Calleja, A.; Martínez-Núñez, F.; Martin-Villacorta, J. Digestion of cattle manure under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions: Characterization of organic matter applying thermal analysis and 1 H NMR. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieślik, M.; Dach, J.; Lewicki, A.; Smurzyńska, A.; Janczak, D.; Pawlicka-Kaczorowska, J.; Boniecki, P.; Cyplik, P.; Czekała, W.; Jóźwiakowski, K. Methane fermentation of the maize straw silage under meso-and thermophilic conditions. Energy 2016, 115, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-González, I.; Moreno, G.; Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Sánchez, A.; Quijano, G.; Buitrón, G. From mesophilic to thermophilic conditions: One-step temperature increase improves the methane production of a granular sludge treating agroindustrial effluents. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 40, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Champagne, P.; Anderson, B.C. Biogas production performance of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion with fat, oil, and grease in semi-continuous flow digesters: Effects of temperature, hydraulic retention time, and organic loading rate. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labatut, R.A.; Angenent, L.T.; Scott, N.R. Conventional mesophilic vs. thermophilic anaerobic digestion: A trade-off between performance and stability? Water Res. 2014, 53, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreeyessus, G.D.; Jenicek, P. Thermophilic versus mesophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: A comparative review. Bioengineering 2016, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Novak, J.T. Digestion performance of various combinations of thermophilic and mesophilic sludge digestion systems. Water Environ. Res. 2011, 83, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, B.; Petersen, G. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion and pasteurisation. Practical experience from Danish wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, J.; Smet, D.; Klok, J.; Colsen, J.; Angenent, L.T.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Thermophilic sludge digestion improves energy balance and nutrient recovery potential in full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.J.; Chesshire, M.; Stringfellow, A. A pilot-scale comparison of mesophilic and thermophilic digestion of source segregated domestic food waste. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestre, G.; Fernández, B.; Bonmatí, A. Addition of crude glycerine as strategy to balance the C/N ratio on sewage sludge thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Qin, W.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Wen, X. Long-term performance and microbial community characteristics of pilot-scale anaerobic reactors for thermal hydrolyzed sludge digestion under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenigün, O.; Demirel, B. Ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion: A review. Process. Biochem. 2013, 48, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinas, S.; Euverink, G.J.W. Effect of Temperature and Organic Load on the Performance of Anaerobic Bioreactors Treating Grasses. Environments 2020, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrin, J.; Antle, S.; Bryant, M.; Berry, Z.; Lovanh, N. Evaluation of Microaeration and Sound to Increase Biogas Production from Poultry Litter. Environments 2020, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrin, J.; Lovanh, N. Aeration to improve biogas production by recalcitrant feedstock. Environments 2019, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacab, F.C.; Gamboa, E.E.; Espinoza, J.E.R.; Leal-Bautista, R.M.; Tussell, R.T.; Maldonado, J.D.; Canto Canché, B.; Alzate-Gaviria, L. Two Phase Anaerobic Digestion System of Municipal Solid Waste by Utilizing Microaeration and Granular Activated Carbon. Energies 2020, 13, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; He, C.; Li, G.; Ding, P.; Lan, M.; Gao, Z.; Jiao, Y. Biological pretreatment of corn straw for enhancing degradation efficiency and biogas production. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Hua, D.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, G. Effect of microaerobic microbial pretreatment on anaerobic digestion of a lignocellulosic substrate under controlled pH conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, W.; Qi, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Z. Review on microaeration-based anaerobic digestion: State of the art, challenges, and prospectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Kopsell, D.E.; Kottke, A.M.; Johnson, M.Q. Development of a cartridge design anaerobic digestion system for lignocellulosic biomass. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 160, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Moran, T.; Han, A. Comparison of Operating Methods in Cartridge Anaerobic Digestion of Corn Stover. Bioenergy Res. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
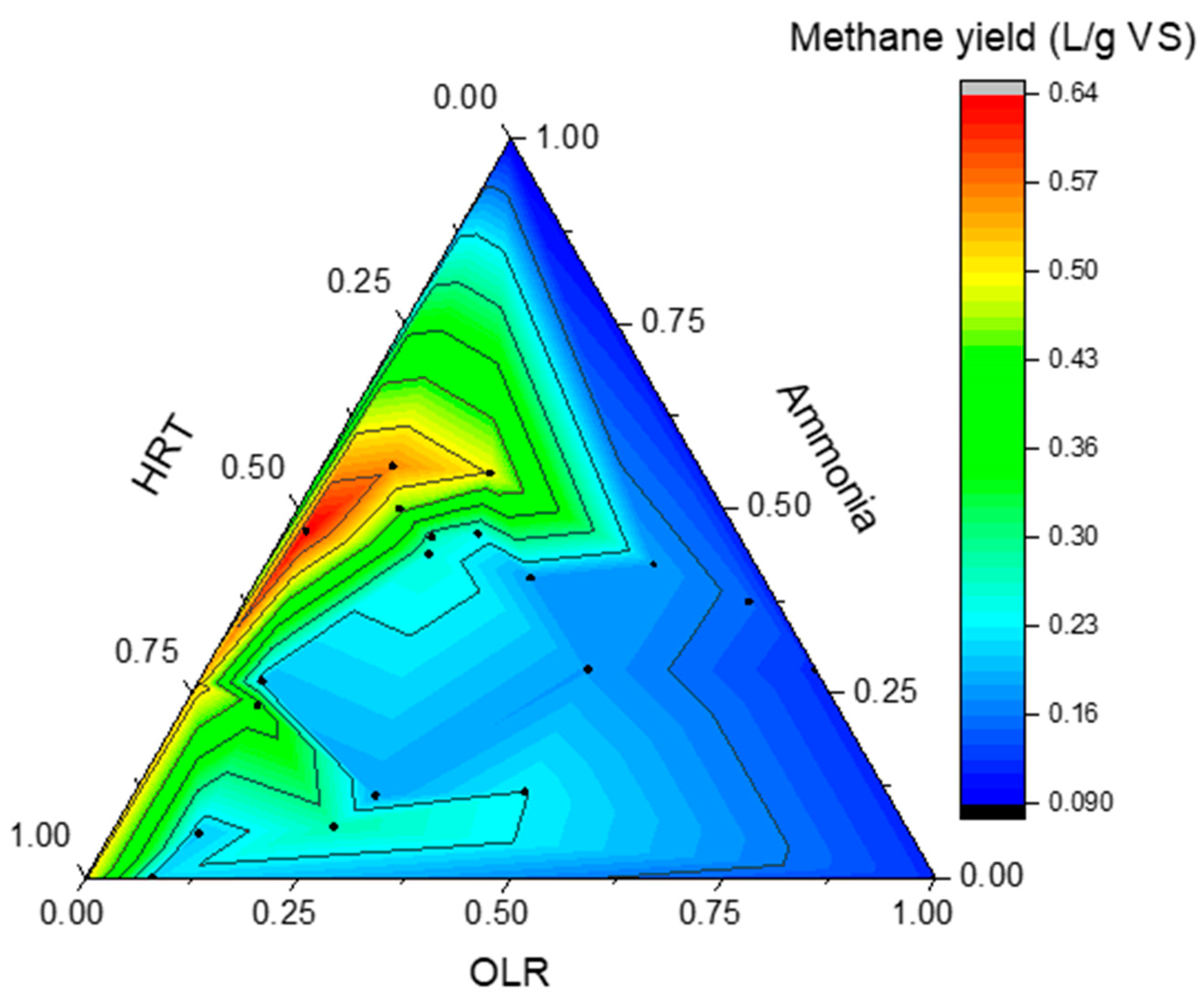


| Substrate | OLR (g VS/Lr d) | Ammonia (TAN) (mg/L) | HRT (d) | Methane Yield (L/g VS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slaughterhouse waste and food wastes [27] | 0.9 | 2143 | 50 | 0.53 |
| 1.16 | 3022 | 36 | 0.64 | |
| 1.7 | 3210 | 25 | 0.56 | |
| 1.85 | 2106 | 50 | 0.4 | |
| 2.56 | 3830 | 36 | 0.45 | |
| 3.7 | 4099 | 25 | 0.5 | |
| High-solid digestion of sewage sludge [28] 1 | 3.0 | 3250 | 30 | 0.27 |
| 3.5 | 3176 | 25 | 0.24 | |
| 4.0 | 2635 | 20 | 0.18 | |
| 4.5 | 1968 | 17 | 0.18 | |
| 5.0 | 2585 | 10.5 | 0.18 | |
| 7.0 | 2596 | 6 | 0.15 | |
| 8.5 | 2255 | 4 | 0.12 | |
| 3.0 | 3054 | 30 | 0.25 | |
| Blood and food wastes [29] | 1.5 | 1921 | 36 | 0.2 2 |
| Swine and poultry manure co-digestion with sewage sludge [30] | 1.27 | 1066 | 30 | 0.21 2 |
| 1.91 | 1174 | 20 | 0.27 2 | |
| 1.43 | 1189 | 30 | 0.20 2 | |
| 2.15 | 1261 | 20 | 0.18 2 | |
| 2.86 | 1264 | 15 | 0.23 2 |
| Supplement | Substrate | Benefits | Biogas Yield Increase | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon conductive materials | ||||
| Biochar | Food wastes | Reduce digestion lag phase | 33–275% | [114] |
| Increase process’s alkalinity, CO2 removal | 77.5–98.1% (methane yield) | [115] | ||
| Food waste components | Reduce digestion lag phase | 4.74 times higher | [116] | |
| Citrus wastes | Reduce digestion lag phase, favored co-culture formation | 56% | [117] | |
| Animal carcasses | Faster degradation of lipids and proteins | 24% | [103] | |
| Brewer’s spent grain | No enhancement clear | High variability in results | [118] | |
| Fruit wastes | Reduced VFA formation | 13–27% | [119] | |
| Waste-activated sludge | Enhancement of acetoclastic pathway | 46.9% | [120] | |
| Hydrochar | glucose | Enhanced hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis | 15–29% | [121] |
| Graphite | Waste-activated sludge | Enhancement of acetoclastic pathway | 38.3% | [120] |
| Adsorbents | ||||
| Biochar + zeolite | Cassava wastewater + livestock manure | Reduce digestion lag phase | No enhancement clear | [88] |
| Mg-zeolite, Co-zeolite, Ni-zeolite | Piggery waste | Increased biodegradability | 8.5 times higher (Mg-zeolite), 4.4 (Co-zeolite), 2.8 (Ni-zeolite) | [122] |
| Zeolite | poultry slaughterhouse waste | Reduce ammonia concentration in digesters | 15% | [95] |
| Bentonite | Waste activated sludge + kitchen waste | Reduce digestion lag phase | Two–threefold increase | [123] |
| Eggshell and lignite-modified zeolite (ELMZ) | Synthetic media evaluating high-ammonia conditions | Increase degradation rate | 7-fold higher when compared with natural zeolite system | [124] |
| Granular activated carbon (GAC) | Orange peel wastes | Good process stability | 65% | [125] |
| Sorghum-based activated carbon | Food waste + sewage sludge | Ammonia and TVFA concentrations were reduced | 35% | [87] |
| Zero-valent iron (ZVI) + activated carbon | Waste-activated sludge | Increase in methane content, greater removal of organics | 37.6% | [126] |
| Aluminum powder, pectin, gelatin, silica gel, bentonite, powdered activated charcoal | Cattle dung, poultry waste, cheese whey (2:1:3, w/w dry weight basis) | Adsorbents provide a site for anaerobic reaction to take place; 17% greater methane content | Twofold gas enhancement | [127] |
| Addition of nanoparticles | ||||
| Zero-valent iron (ZVI) Fe3O4 nanoparticles | Food waste and waste activated sludge | Higher biodegradability | 50% with Fe3O4 No significant effect with ZVI | [128] |
| Co, Ni nanoparticles | Animal manure | Reduce lag phase and degradation time | 1.64–1.74 times increase | [129] |
| Metal oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4, MgO) and Ni, Co nanoparticles | Microalgal biomass | Increase in biogas production rate | 8–28% | [109] |
| Fe3O4 nanoparticle + microwave pretreatment | Green algae (Enteromorpha) | Increase in biogas production rate | 54% 1 | [130] |
| Graphene oxide nanoparticles | Pre-treated slurry mixed with wheat straw | Increase in volumetric production at 40 days HRT | 1.74–2.54 times increase | [131] |
| Substrate | Methane Yield (L CH4/g VS) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesophilic | Thermophilic | ||
| Cow manure | 0.120 | 0.120 | [152] |
| Maize silage | 0.400 | 0.550 | [152] |
| Newspaper | 0.046–0.061 | 0.077 | [153] |
| Food wastes (F/M = 3) 1 | 0.114 2 | 0.700 | [154] |
| Food wastes (F/M = 0.25–1) 1 | 0.480–0.530 | 0.650–0.740 | [155] |
| Chinese cabbage waste (F/M = 0.5–2.0) 2 | 0.591–0.677 | 0.434–0.639 | [150] |
| Poultry slaughterhouse waste (intestine content) | 0.610 | 0.675 | [94] |
| Poultry feathers 2 | 0.200 | 0.276 | [156] |
| Sewage sludge + fat 2 | 0.680 | 0.490 | [156] |
| Cheese whey | 0.304 | 0.160 | [157] |
| Cattle manure | 0.234 | 0.159 | [158] |
| Maize straw silage 2 | 0.105 | 0.114 | [159] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ellacuriaga, M.; Cascallana, J.G.; González, R.; Gómez, X. High-Solid Anaerobic Digestion: Reviewing Strategies for Increasing Reactor Performance. Environments 2021, 8, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8080080
Ellacuriaga M, Cascallana JG, González R, Gómez X. High-Solid Anaerobic Digestion: Reviewing Strategies for Increasing Reactor Performance. Environments. 2021; 8(8):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8080080
Chicago/Turabian StyleEllacuriaga, Marcos, José García Cascallana, Rubén González, and Xiomar Gómez. 2021. "High-Solid Anaerobic Digestion: Reviewing Strategies for Increasing Reactor Performance" Environments 8, no. 8: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8080080
APA StyleEllacuriaga, M., Cascallana, J. G., González, R., & Gómez, X. (2021). High-Solid Anaerobic Digestion: Reviewing Strategies for Increasing Reactor Performance. Environments, 8(8), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8080080







