Abstract
Gas transport parameters such as gas diffusivity (Dp/D0), air permeability (ka), and their dependency on void space (air-filled porosity, ε) in a waste body govern convective air and gas diffusion at solid waste dumpsites and surface emission of various gases generated by microbial processes under aerobic and anaerobic decompositions. In this study, Dp/D0(ε) and ka(ε) were measured on dumping solid waste in Japan such as incinerated bottom ash and unburnable mixed waste as well as a buried waste sample (dumped for 20 years). Sieved samples with variable adjusted moistures were compacted by a standard proctor method and used for a series of laboratory tests for measuring compressibility, saturated hydraulic conductivity, and gas transport parameters. Results showed that incinerated bottom ash and unburnable mixed waste did not give the maximum dry density and optimum moisture content. Measured compressibility and saturated hydraulic conductivity of tested samples varied widely depending on the types of materials. Based on the previously proposed Dp/D0(ε) models, the diffusion-based tortuosity (T) was analyzed and unique power functional relations were found in T(ε) and could contribute to evaluating the gas diffusion process in the waste body compacted at different moisture conditions.
1. Introduction
Solid waste disposal has always remained a crucial part of the waste management system. Due to the scarcity of landfills, it is essential to consider landfill facilities’ optimization and how ecofriendly they are. For volume reduction, burnable waste is usually incinerated and unburnable waste shredded before dumping at landfill sites in Japan [1,2]. In contrast, in developing countries, without segregation waste is directly sent to the landfill site, consisting of heterogeneous materials [3,4]. The decomposition of the dumped solid waste produces various types of organic and inorganic gases such as methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), aromatic carbons, nonmethane hydrocarbons, and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) [5,6,7,8]. It is also well known that waste landfills dumped with organic-rich waste are a significant source of anthropogenic methane emission resulting from the microbial degradation of organic matter in a waste body [9]. The microbial degradation changes aerobic to anaerobic degradation over a specific time depending upon the landfill operation due to the reduction of void spaces [10,11,12].
To understand the gas emission from waste dumping sites and to reduce the harmful gas generation, it is essential to evaluate the gas transport process in the waste body as well as the landfill cover soil and to maintain the proper air movement in the waste body [10,13]. The gas transport processes in the waste body and emission of landfill gases are controlled by many factors such as packing of dumped waste (i.e., compaction), moisture and void space, degree of biodegradation, the thickness of landfill cover soil, and the design of dumpsite facility [14,15]. In particular, gas transport parameters of gas diffusivity (Dp/D0: the ratio of gas diffusion coefficient, Dp, to gas diffusion in free air, D0) and air permeability (ka) and their dependency on void space (air-filled porosity, ε) in the waste body govern convective air and gas diffusion at solid waste dumpsites. However, only limited information on gas diffusivity and air permeability for compacted dumped waste are available.
Therefore, this research aims to measure the gas transport parameters, Dp/D0 and ka, for compacted typical dumping solid waste such as incinerated bottom ash and unburnable mixed waste (after shredded) and to characterize their dependency of ε [= air-filled volume (cm3)/total volume (cm3)]. Besides, a buried waste sample (dumped for 20 years) taken from a waste dumping site was used as a testing material as well as literature data of a landfill cover soil [13] for evaluating the pore tortuosity characteristics based on the previously proposed Dp/D0 models.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Waste Materials
In this research, three different types of waste brought to an engineered waste landfill in Saitama prefecture, Japan, were used: incinerated bottom ash from municipal solid waste and two types of unburnable mixed waste [hereafter labeled as unburnable mixed waste (1) and (2)]. Besides, buried waste was taken from a post-closure industrial waste landfill site in Saitama Prefecture, Japan. The buried waste was taken around 2 m below ground surface and was dumped for 20 years, according to the landfill record. Photos of samples are shown in Figure 1.
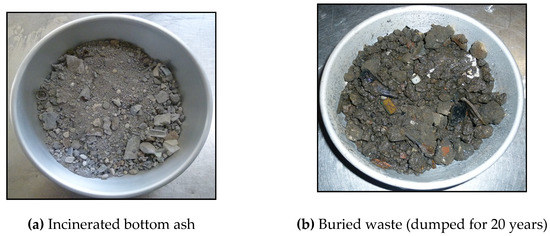
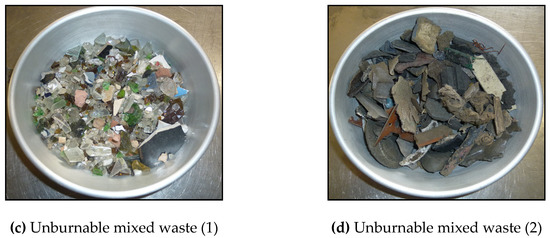
Figure 1.
Photos of tested samples. (a) Incinerated bottom ash, (b) buried waste (dumped for 20 years), (c) unburnable mixed waste (1), and (d) unburnable mixed waste (2).
2.2. Physical and Chemical Properties, Waste Composition
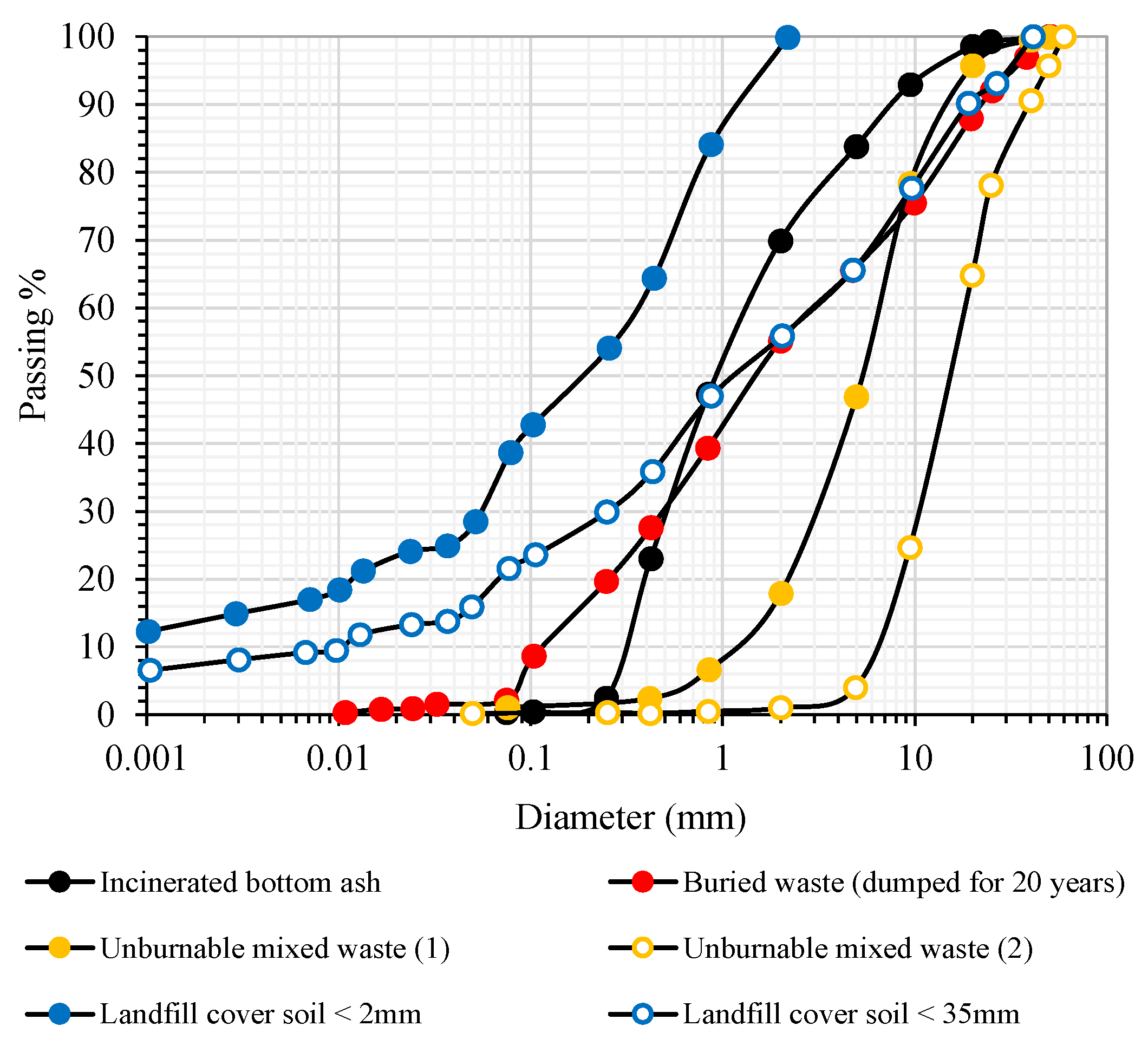
Basic physical and chemical properties of the tested samples were determined following American Standards for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and Japan Industrial Standards (JIS) and were presented in Table 1. According to Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) textural classification, incinerated bottom ash and buried waste (dumped for 20 years) belonged to coarse grained sand, while unburnable mixed waste (1) and (2) belonged to coarse grained gravel. Size distributions of the tested samples were shown in Figure 2 together with the reported particle size distributions of a landfill cover soil, <2 mm and <35 mm, taken from the same engineered landfill in Saitama Prefecture [13].

Table 1.
Physical and chemical properties for the tested samples and landfill cover soil.
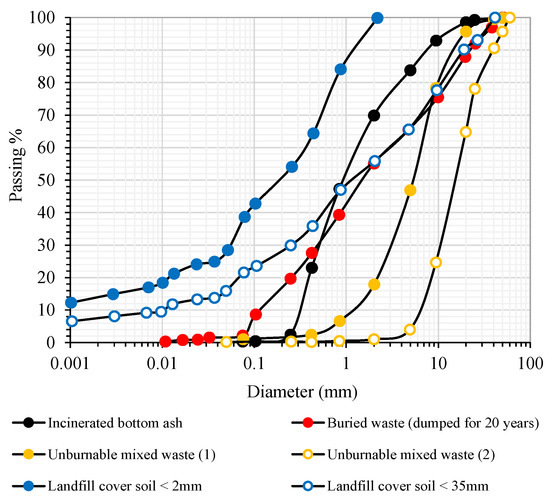
Figure 2.
Size distribution of tested samples and landfill cover soil.
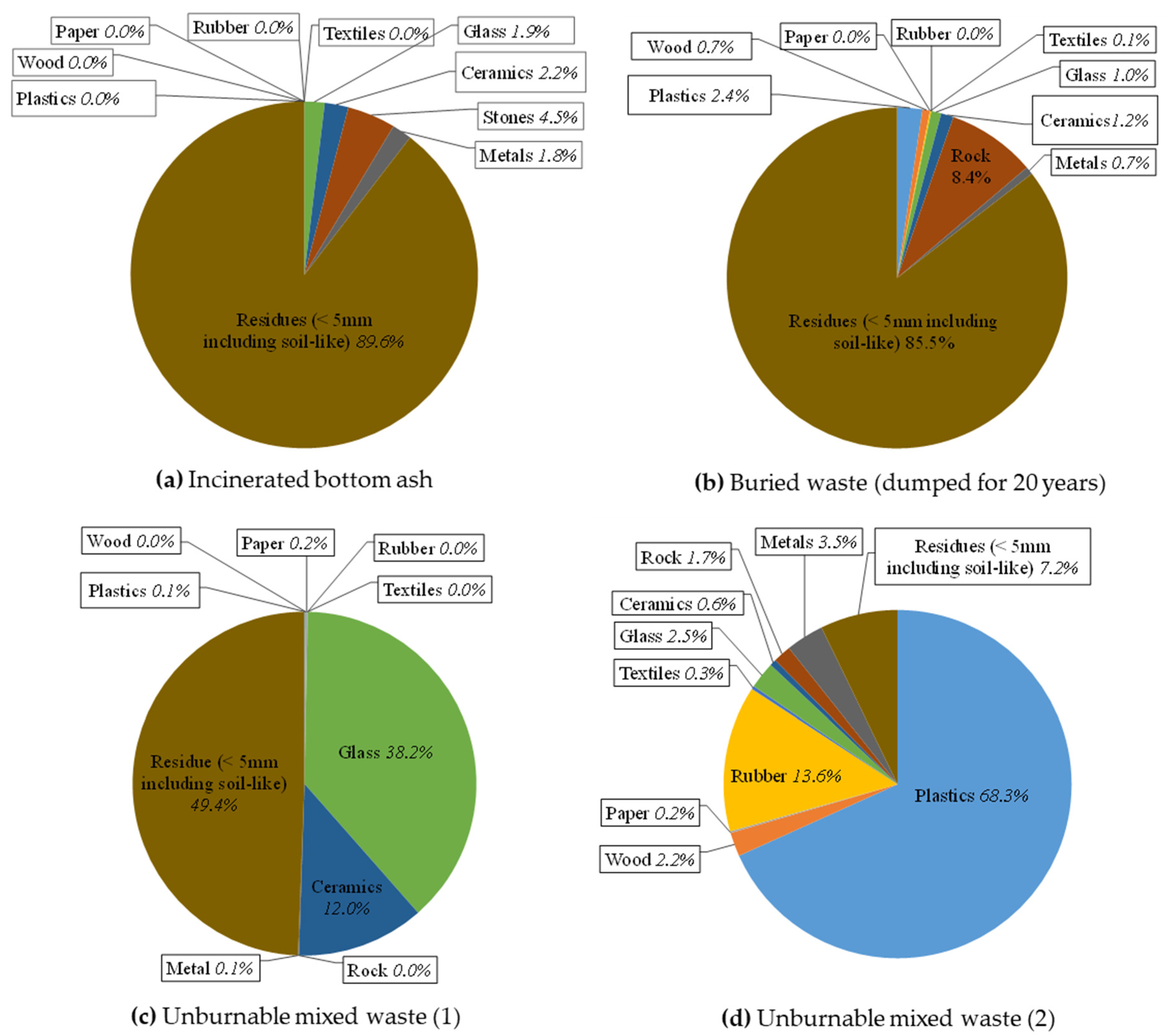
Incinerated bottom ash and buried waste consisted mainly of the size fraction with <5 mm. Measured pH values showed that incinerated bottom ash (pH = 11.1) and buried waste (pH = 8.8) were alkaline, while unburnable mixed waste (1) and (2) (pH = 7.2, 7.8) including landfill cover soil (pH = 5.6) were neutral. Measured loss on ignition (LOI) showed the highest value (81%) for unburnable mixed waste (2) due to the presence of the rubber and plastic types fraction (see, Figure 3).
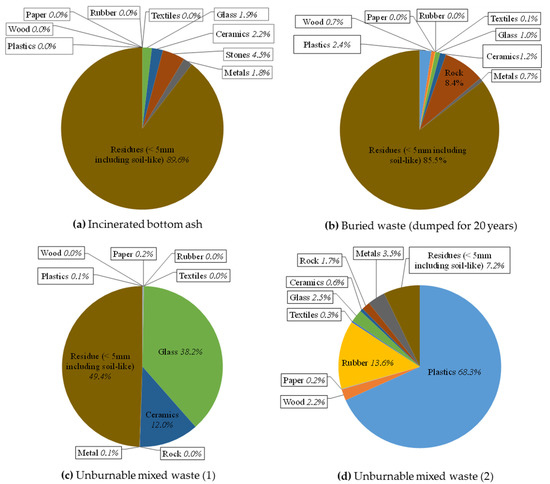
Figure 3.
Composition of tested samples. (a) Incinerated bottom ash, (b) buried waste (dumped for 20 years), (c) unburnable mixed waste (1), and (d) unburnable mixed waste (2).
After air-drying the tested samples, the waste composition for each tested sample was determined using around 2–3 kg air-dried mass, and the results are shown in Figure 3. Incinerated bottom ash and buried waste consisted mainly of residues (<5 mm) including a soil-like material (see also Figure 2). Unburnable mixed waste (1) contained around 50% of glass and ceramics; on the other hand, unburnable mixed waste (2) contained high amounts of plastic and rubber (see also Figure 1).
2.3. Measurements of Compaction Property, Compressibility, Hydraulic Conductivity, and Gas Transport Parameters
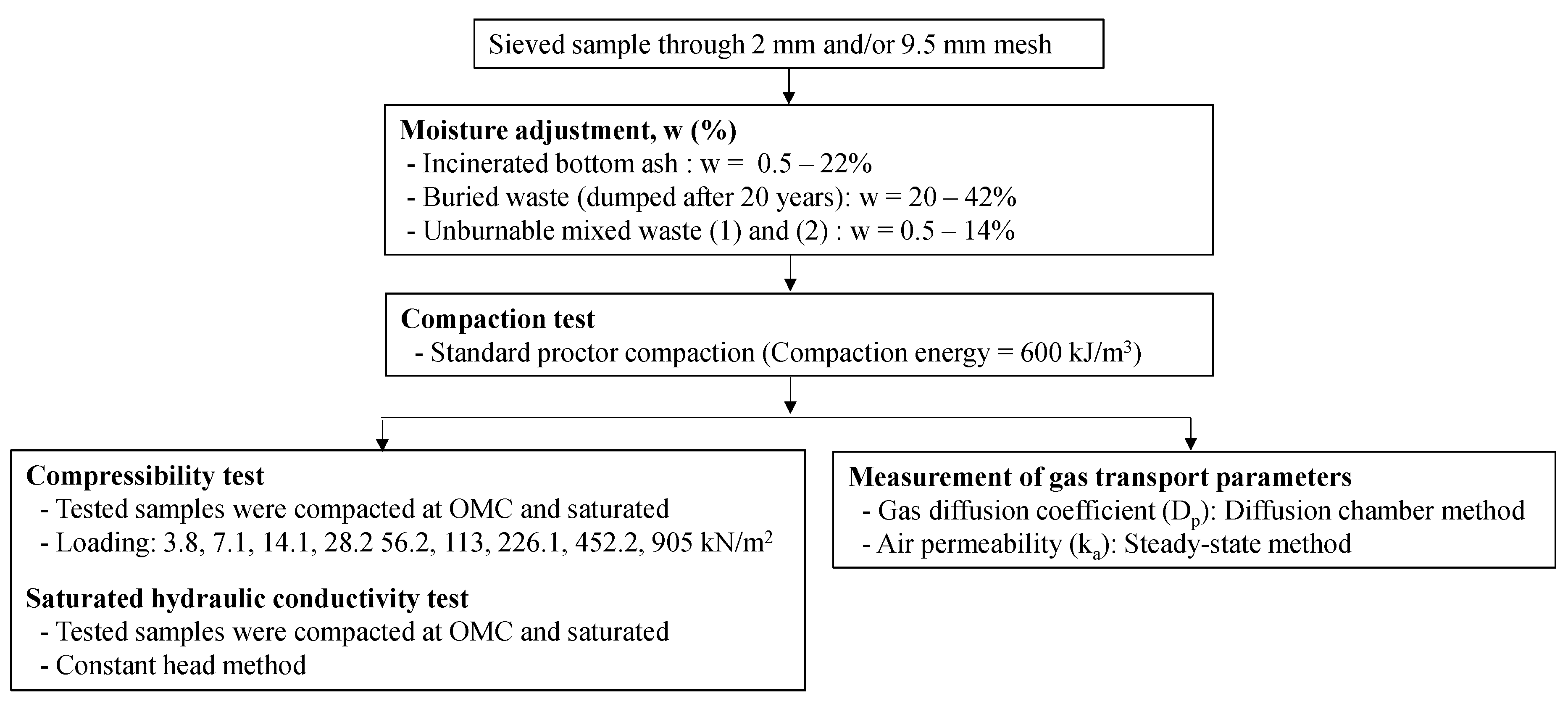
A series of laboratory tests were carried out to determine compaction property, compressibility, hydraulic conductivity, and gas transport parameters. A chart of sample preparation, treatment, and subsequent measurements is shown in Figure 4. First, the samples were sieved with <2 mm and/or <9.5 mm, and adjusted moisture contents. Then, the samples were used for the compaction tests following a standard Proctor method [16] and determined the maximum dry density (ρdmax) and optimum moisture content (OMC). In the compaction test, the samples were packed into three layers in a mold with an internal diameter of 12.75 cm and height of 10 cm with a rammer of 2.5 kg dropping at the height of 30.5 cm with 27 blows. After the compaction test, the compacted samples at OMC were saturated and used to measure the compressibility (Cc) at different loading conditions from 3.8 to 905 kPa and to measure the saturated hydraulic conductivity (ks in m/s) with a constant head method.
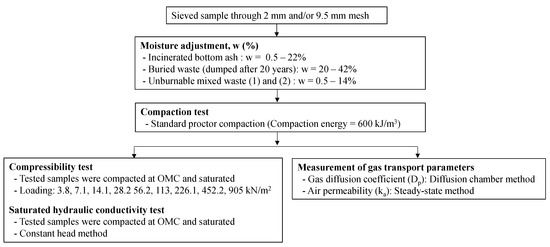
Figure 4.
Chart of sample preparation, treatment, and subsequent measurements. w= water content, OMC: optimum moisture content.
The compacted samples with different moisture conditions packed in a mold with an inner diameter of 15 cm and a height of 12 cm were used for measuring the gas transport parameters, Dp/D0 and ka. A gas diffusion chamber was used to measure Dp/D0 at room temperature at 20 °C, and oxygen was used as a tracer gas [17]. The diffusion chamber was first flushed with 100% N2, after which the upper end of the testing sample was exposed to the atmosphere. Oxygen was measured in the diffusion chamber with an oxygen electrode. Change of oxygen was measured as a function of time in the diffusion chamber, and the Dp (cm2/s) was calculated by applying Fick’s law. The gas diffusion of oxygen in free air (D0) at 20 °C of 0.20 (cm2/s) was used in this research. The ka (μm2) was measured at room temperature at 20 °C using a steady-state method [18]. A constant, small air pressure difference (to maintain laminar steady airflow without the redistribution of water inside the sample) was applied to the samples, and the airflow rate was measured. The ka was calculated based on Darcy’s law using air density and viscosity. Then, the measured Dp/D0 and ka values were plotted against measured air-filled porosity (ε). It was noted that the ε values for compacted samples were calculated using dry bulk density and water content of tested samples in this study, indicating that the ε values did not represent connected open pores, but a total volume of air-filled pores in the samples. Additionally, the compaction property, compressibility, and hydraulic conductivity for unburnable mixed waste (1) and (2) were measured but, the Dp/D0 and ka values for these samples could not be determined because a gap between the compacted sample and surrounding mold caused the inaccuracy of measured values.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compaction, Compressibility, and Hydraulic Properties
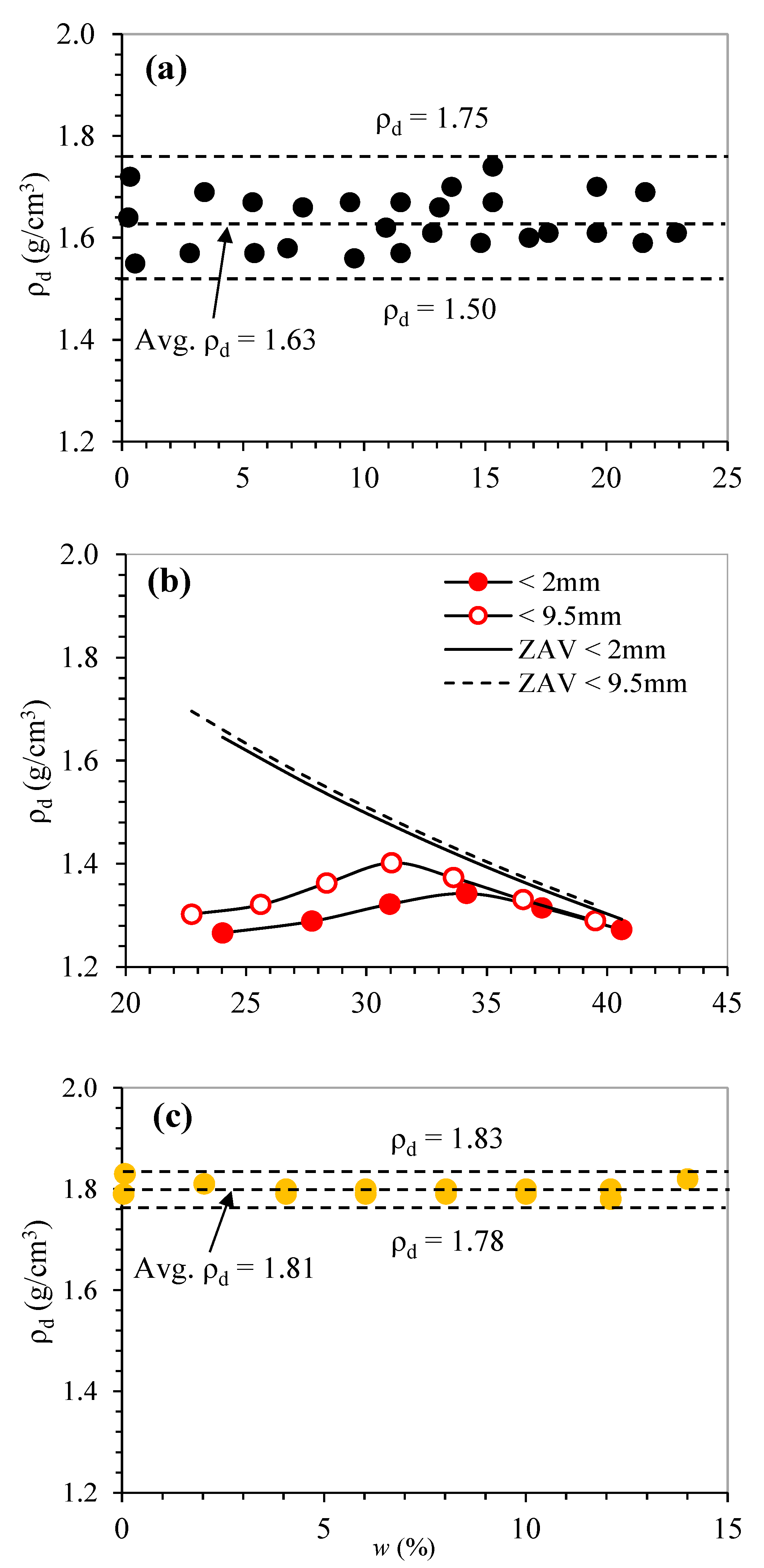
Measured compaction curves of the tested samples are shown in Figure 5. Incinerated bottom ash (Figure 5a) and unburnable mixed waste (1) (Figure 5c), and unburnable mixed waste (2) (not shown) were independent of initial moisture condition and did not show any clear peak (i.e., the maximum dry density, ρdmax) in the compaction curves. Similar results were reported in many kinds of literature, especially for the tested results from cohesionless solid waste materials and industrial by-products, which did not show the clear peak in the compaction curves: incinerated bottom ash [19,20], recycled concrete and clay bricks [21], glass types materials [22], and slag bottom ash [23]. On the other hand, buried waste (dumped for 20 years) (Figure 5b) as well as landfill cover soil (data not shown. See Figure 3 in [13]) showed a clear peak and gave ρdmax and optimum moisture content (OMC) in the compaction curve.
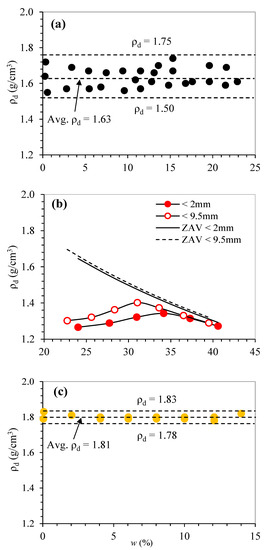
Figure 5.
Compaction curves for tested samples. (a) Incinerated bottom ash, (b) buried waste (dumped for 20 years), and (c) unburnable mixed waste (1). Note that the ρd values for unburnable mixed waste (2) became almost constant ρd = 0.62 g/cm3 irrespective of moisture content.
The measured values of ρdmax and OMC were summarized in Table 2 with some reported literature values. Generally, the ρdmax values depending on the material properties such as specific gravity (Gs) and composition, lower Gs materials gave lower ρdmax values. This can be found typically for the unburnable mixed waste (1) rich in plastic and vinyl in this study and dumped municipal solid waste (MSW) rich in organic materials [24]. Besides, it can be found that the materials with coarser fraction showed higher ρdmax and lower OMC compared to the materials with finer fraction (e.g., buried waste in this study and landfill cover soil [13]).

Table 2.
Summary of compaction, compressibility, hydraulic parameters for the tested samples and references.
Measured values of compressibility (Cc) and saturated hydraulic conductivity (ks) are summarized in Table 2. Among tested samples in this study, unburnable mixed waste (2) showed the highest Cc (=0.23). This was probably due to the unburnable mixed waste (2), which was rich in easily compressible materials such as plastic, vinyl, and rubber (Figure 3d). On the other hand, the unburnable mixed waste (1) rich in glass and ceramics gave the lowest Cc (=0.013) due to the non-compressible nature of those materials. Compared to the reported Cc values of dumped and fresh MSW [24,25,26,27,28], the measured Cc values of incinerated bottom ash and buried waste in this study became approximately one order smaller.
Measured ks values for unburnable mixed waste (1) and (2) were in the order of 10−4 m/s and became higher than those for other materials including dumped and fresh MSW. This indicated clearly that the waste body consisted of an unburnable mixed waste of plastic, glasses, ceramics, which became more water permeable, contrary to other dumped industrial by-products of incinerated bottom ash (10−6 m/s), MSW (10−8~10−4 m/s) and buried waste with high fine residue (10−8 m/s). It was noted that ks values in the dumped waste body change widely with the stress level, density due to the overburden, and strata of dumped waste in the landfill site [27,29]. Besides, the decomposition of biodegradable materials highly affected compressibility and water permeability [26]. These factors should be considered to examine the mechanical behaviors (e.g., settlement, consolidation) and mass transport processes in the waste body.
3.2. Gas Transport Parameters and Pore Tortuosity Characteristics
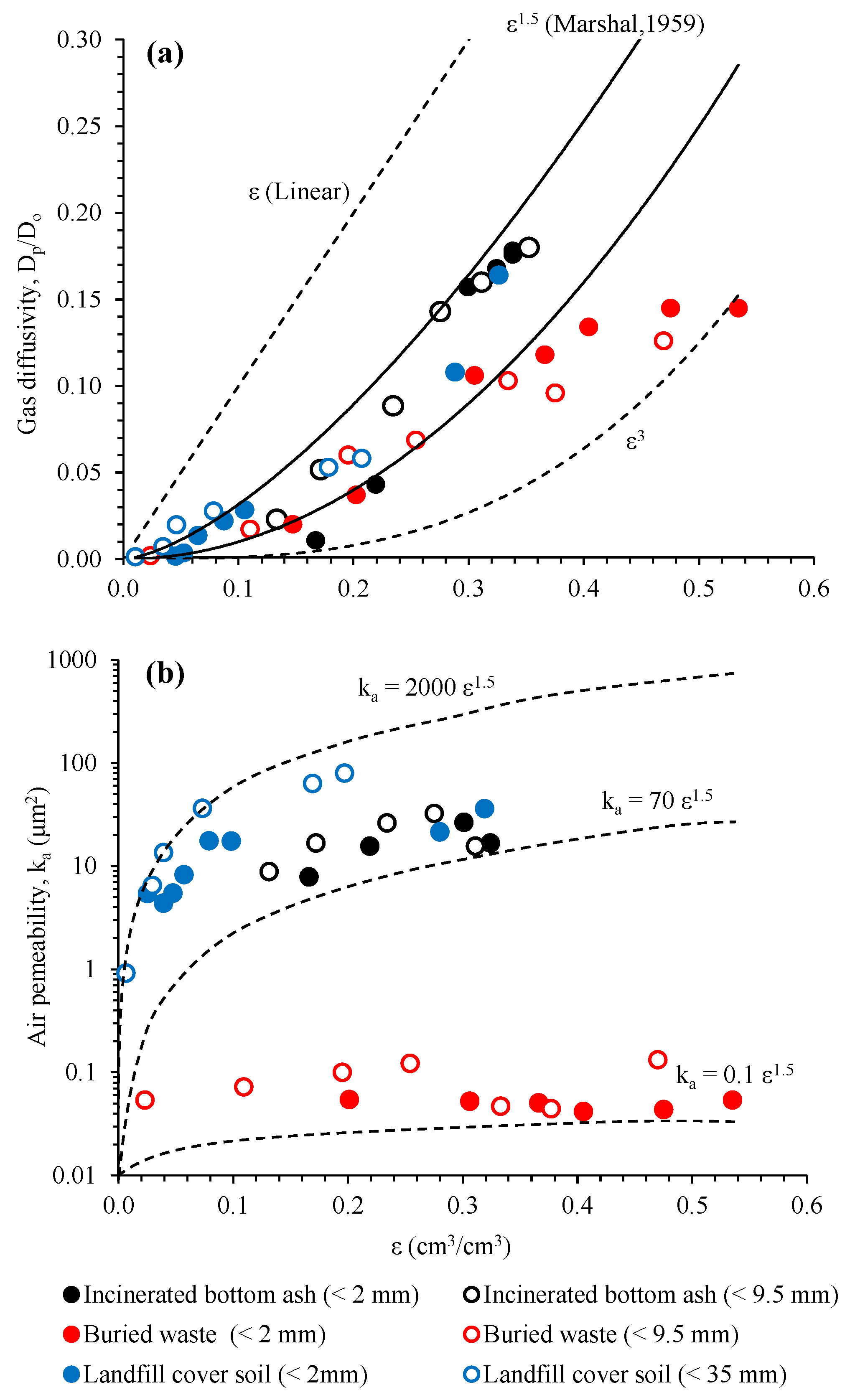
Measured gas diffusivity (Dp/D0) of the tested samples was shown as a function of air-filled porosity (ε) in Figure 6a. For incinerated bottom ash (<2 mm and <9.5 mm) and a landfill cover soil (<2 mm and <35 mm) [13], the Dp/D0 increased with increasing of ε and the data mostly ranged in power-law Dp/D0(ε) models of Buckingham (1904) [30] and Marshall (1959) [31]. On the other hand, the Dp/D0 values of buried waste (<2 mm and <9.5 mm) gave an increment at ε = 0~0.3, however, the Dp/D0 became almost constant at ε > 0.3 and the data ranged between Buckingham model (ε2) and Dp/D0 = ε3. Measured air permeability (ka) of the tested samples were shown as a function of ε in Figure 6b. In Figure 6b, an empirical power functional ka model with b = 1.5 (Marshal’s tortuosity factor [31]) was adopted to capture the range of measured values [13]. Contrary to the relations of Dp/D0(ε) (Figure 6a), the ka values for tested samples did not show a clear increment with increasing of ε. Especially, the measured ka of buried waste (<2 mm and <9.5 mm) became almost constant irrespective of ε values. The measured ka(ε) for incineration ash (<2 mm and <9.5 mm) and landfill cover soil (<2 mm and <35 mm) mostly ranged between 2000ε1.5 and 70ε1.5.
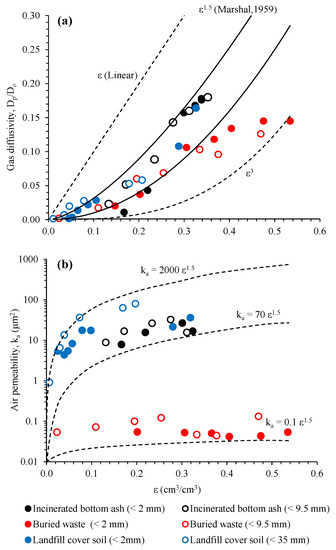
Figure 6.
(a) Gas diffusivity, Dp/D0, as a function of air-filled porosity, ε (b) Air permeability, ka, as a function of ε for incinerated bottom ash, buried waste, and landfill cover soil [13].
It was reported that the compaction effort and packed density highly affected Dp/D0(ε) and ka(ε) of geomaterials and soils [10,13,32]. The particle rearrangement and water blockage due to the compaction change the pore structural network in the compacted samples, causing the change of pore structural parameters such as pore size distribution, pore tortuosity and connectivity [33]. In this study, two empirical indices for characterizing the change of pore structural parameters induced by the compaction were used to understand the pore tortuosity and connectivity based on the measured Dp/D0 values. One was the so-called pore connectivity-tortuosity factor, Xg, in the Buckingham model [30]:
The other one was called the pore tortuosity factor, T, in the tortuosity-based Dp/D0 model proposed by Moldrup et al. (2001) [34]:
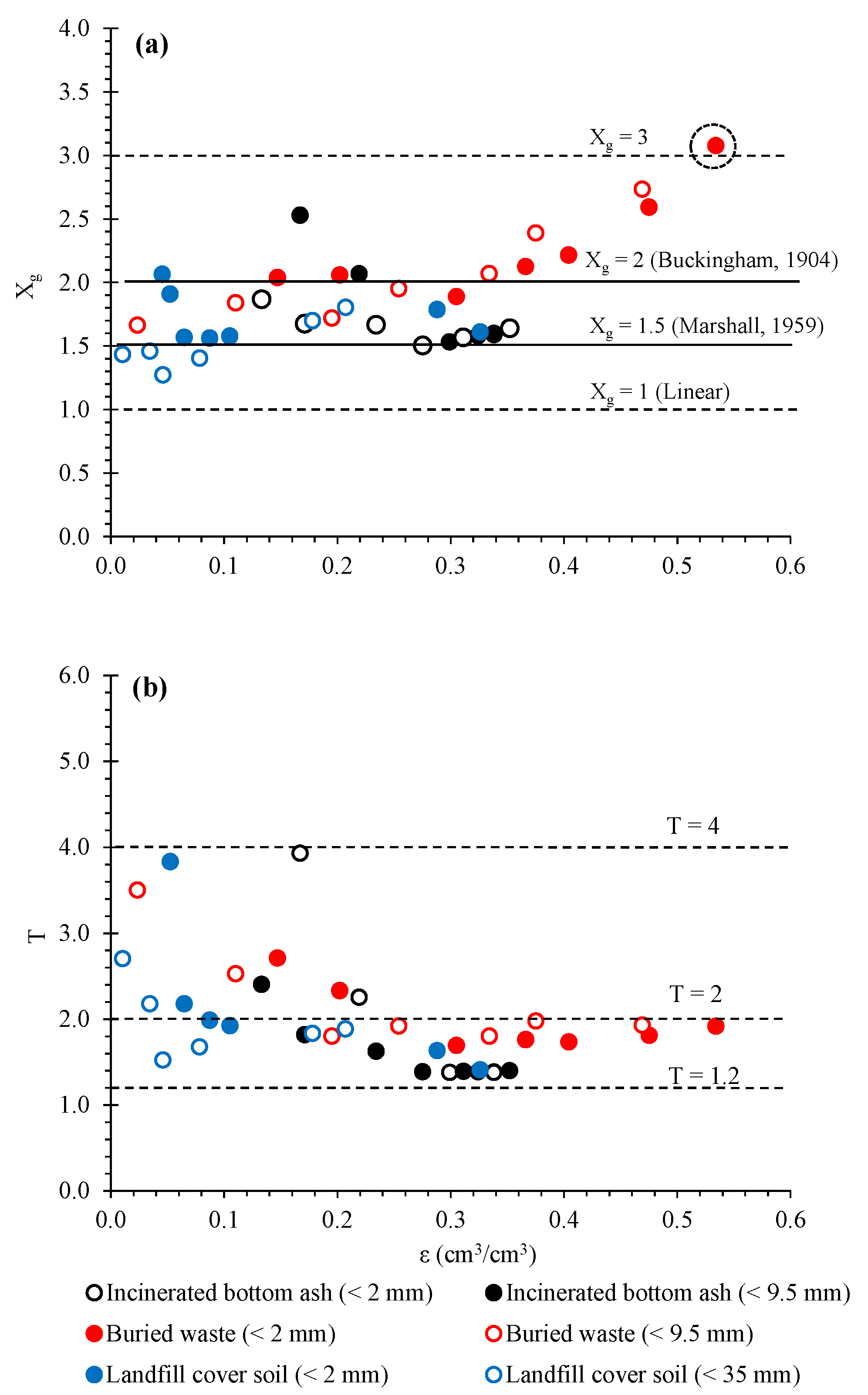
The Xg and T values were plotted as a function of ε, as shown in Figure 7. For tested samples including landfill soil, the Xg values ranged mostly between 1 to 3. The Xg values incinerated bottom ash (<2 mm and <9.5 mm) and landfill cover soil (<2 mm and <35 mm) did not show any significant increment in Xg(ε). For the buried waste (<2 mm and <9.5 mm); however, the Xg values increased with an increase of ε at ε > 0.3 and reached Xg 3. This increment in Xg corresponds to no significant increase in Dp/D0(ε) at ε > 0.3 in Figure 6a, indicating that the compaction of buried waste at the dry condition (high ε) caused more tortuous-connected pores compared to the compacted samples at the wet condition (low ε). On the other hand, the T values decreased with the increase of ε for all tested samples up to around ε = 0.3, including a landfill cover soil shown in Figure 7b, and ranged between 1.2 to 4. At ε > 0.3, the T values became constant irrespective of ε. This strongly suggests that the pore tortuosity of samples depends on the moisture condition at the compaction and the pore network became less tortuous (smaller T) for the samples compacted at the drier condition.
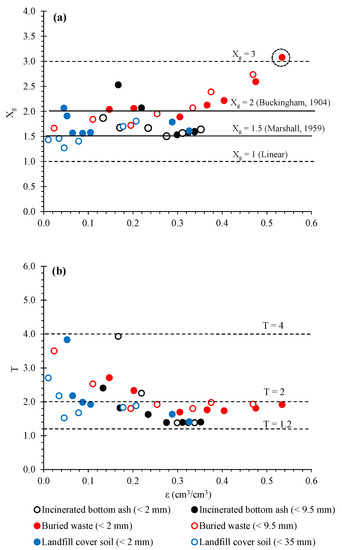
Figure 7.
(a) Pore connectivity-tortuosity factor, Xg, and (b) Diffusion-based tortuosity, T, as a function of air-filled porosity, ε.
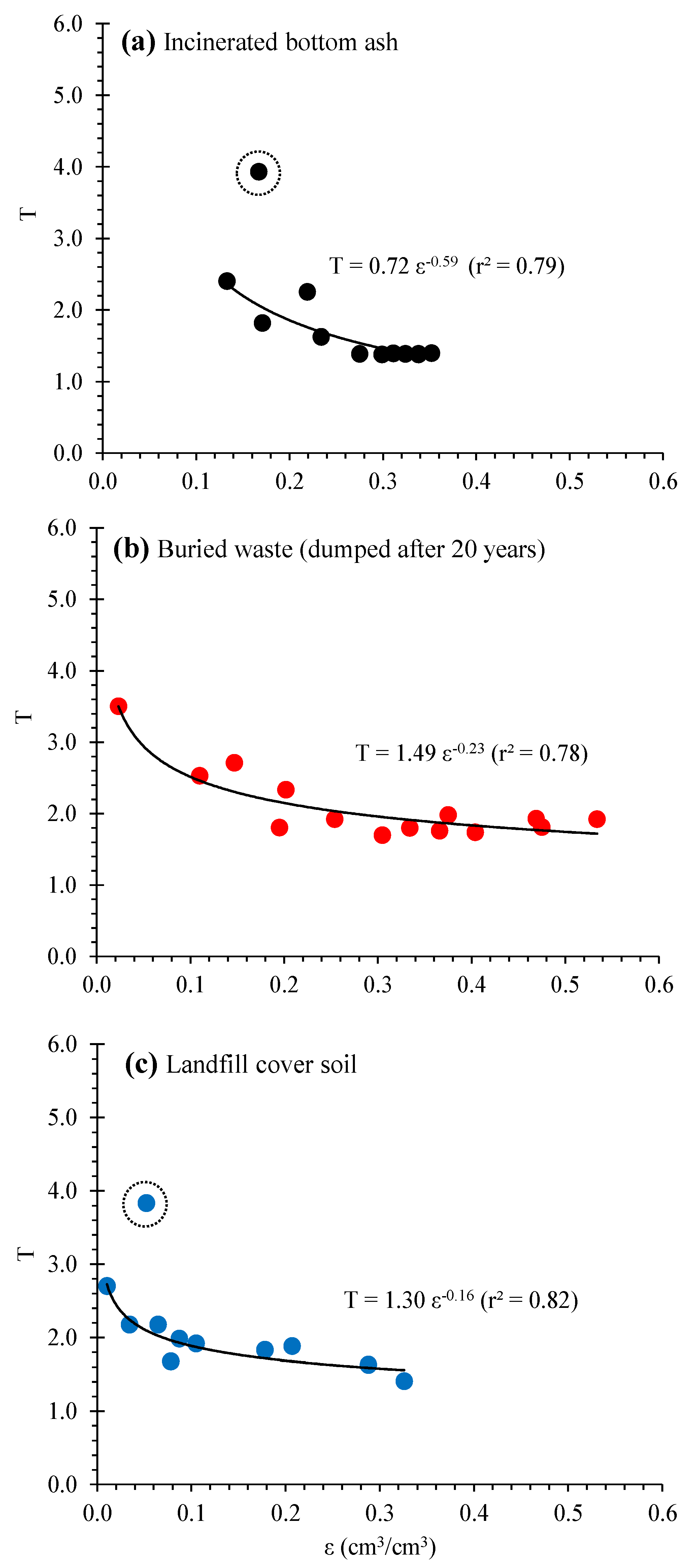
Finally, the relations of T and ε were fitted with a power function, as shown in Figure 8. Except for some irregular plots in Figure 8a,c, the power function well fitted the T(ε) relations with high r2 values. The fitted T(ε) relations can be directly combined with Equation (2) and be applicable to estimate Dp/D0(ε) for compacted tested samples [e.g., Dp/D0 = ε(0.72e0.59)−2] for incinerated bottom ash). This approach could evaluate the gas diffusion process of compacted dumped materials in landfill sites’ waste bodies.
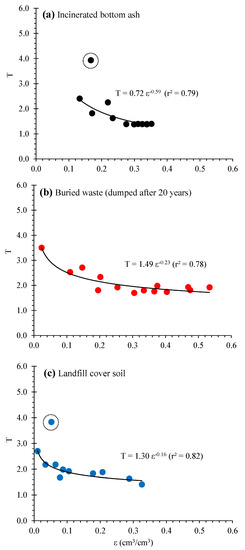
Figure 8.
Fitted power functional correlations between T and ε: (a) incinerated bottom ash, (b) buried waste, and (c) landfill cover soil. Note that measured plots surrounding by dotted circles were omitted to determine the regression curves.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the compaction property, compressibility, hydraulic property, and gas transport parameters for compacted waste samples at different moisture conditions by a series of laboratory experiments. It can be concluded that the measured indices for characterizing compaction property, compressibility, and hydraulic property depended highly on the types of waste (waste composition) and varied widely depending on the waste composition. The measured gas diffusivity and air permeability for incinerated bottom ash and landfill cover soil became higher than those of buried waste. Based on the analysis of the pore structural indices, it can be shown that the pore tortuosity of samples depended on the moisture condition at the compaction and the pore network became less tortuous for the samples compacted at the drier condition. Besides, unique power functional relations were found between pore tortuosity and air-filled porosity for the compacted samples. Further studies are needed to examine the scale-up of testing samples (i.e., representative volume size). Especially, the rearrangement of coarser fraction in unburnable waste under compaction process would be dependent on the mold size and the formation of pore networks that affects the gas transport parameters varies depending on the sample size. Additionally, it is essential to apply the measured transport parameters for investigating the gas exchange process and gas transport characteristics in the waste body, fully considering the microbial activities, heterogeneity/variety of dumped waste materials, and repeated wet and dry cycles.
Author Contributions
Investigation, H.L.D.N.; resources, Y.I.; supervision, K.K.; writing—original draft, M.R.I. All authors had contributed to the experimental and analysis work jointly. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by JST-JICA Science (SATREPS) project and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (No. JPMJSA1701).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this research is available on request from the corresponding author. The data cannot be disclosed due to the security concerns of the project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare having no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ministry of the Environment in Japan. Report on the Management and Disposal of Industrial Waste in Japan; Ministry of the Environment in Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2020. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/recycle/waste/sangyo.html (accessed on 6 December 2020). (In Japanese)
- Ministry of the Environment in Japan. Report on the Investigation of Actual Condition of Municipal Solid Waste Treatment in Japan; Ministry of the Environment in Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2020. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/recycle/waste_tech/ippan/index.html (accessed on 6 December 2020). (In Japanese)
- Dixon, N.; Jones, D.R.V.J. Engineering properties of municipal solid waste. Geotext. Geomembr. 2005, 23, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madon, I.; Drev, D.; Likar, J. Long-term risk assessments comparing environmental performance of different types of sanitary landfills. Waste Manag. 2019, 96, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogner, J.E.; Spokas, K.A.; Burton, E.; Sweeney, R.; Corona, V. Landfills as atmospheric methane sources and sinks. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 4119–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, B.; Anderson, E.P.; Walker, B.L.; Burrows, D.B. Characterization of landfill gas composition at the fresh kills municipal solid waste landfill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2233–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfearn, A.; Roberts, R.D.; Dockerty, J.C.; May, M.; Hughes, S.H. Predictive health risk assessment for landfill gas. CIWM Scientific & Technical Review. Waste Manag. 2002, 12, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.K.; Shon, Z.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, J.-K. Monitoring of atmospheric reduced sulfur compounds and their oxidation in two coastal landfill areas. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, V.C.J.W.; Gebert, J. Effect of compaction and soil moisture on the effective permeability of sands for use in methane oxidation systems. Waste Manag. 2020, 107, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, S.; Moldrup, P.; Kawamoto, K.; Wickramarachchi, P.N.; Nagamori, M.; Komatsu, T. Extreme compaction effects on gas transport parameters and estimated climate gas exchange for a landfill final cover soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Scheutz, C.; Kjeldsen, P. Trace gas emissions from municipal solid waste landfills: A review. Waste Manag. 2020, 119, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Fan, C.; He, W.; Deng, J.; Yin, H. Sulfur-containing amino acid methionine as the precursor of volatile organic sulfur compounds in algea-induced black bloom. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramarachchi, P.; Kawamoto, K.; Hamamoto, S.; Nagamori, M.; Moldrup, P.; Komatsu, T. Effects of dry bulk density and particle size fraction on gas transport parameters in variably saturated landfill cover soil. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2464–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Hettiarachchi, H.; Parakalla, N.S.; Gangathulasi, J.; Bogner, J.E. Geotechnical properties of fresh municipal solid waste at orchard hills landfill, USA. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Yesiller, N.; Stockhausen, S.A.V.; Wong, W.W. Compaction characteristics of municipal solid waste. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2010, 136, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM D698-12e2 (2012): Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction Characteristics of Soil Using Standard Effort (12 400 ft-lbf/ft3 (600 kN-m/m3)); ASTM International: West Consthohohcken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rolston, D.E.; Moldrup, P. Gas diffusivity. In Methods of Soil Analysis; SSSA Book Series 5; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; Part 4; pp. 1113–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, B.C.; Schjønning, P. Air permeability. In Methods of Soil Analysis; SSSA Book Series 5; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; Part 4; pp. 1141–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.H. The Use of Bottom Ash in Highway Embankments, Subgrades, and Subbases; Indiana Department of Transportation and Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.R.; Hashimoto, K.; Tachibana, S.; Kawamoto, K. Geotechnical properties of sludge blended with crushed concrete and incineration ash. Int. J. Geomate 2019, 16, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.R.; Kawamoto, K.; Uchimura, T.; Dung, N.T.; Ton, T.K.; Tuan, N.V.; Giang, N.H. Compaction characteristics and CBR of sludge blended with recycled clay bricks for road subgrade application. Int. J. Geomate 2020, 19, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disfani, M.M.; Arulrajah, A.; Bo, M.W.; Hankour, R. Recycled crushed glass in road work applications. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, Y.B.; Seals, R.K.; Puppala, A.J. Engineering and Compaction Characteristics of Boiler Slag; Landva, A., Knowles, G.D., Eds.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 123–141. [Google Scholar]
- Gabr, M.A.; Valero, S.N. Geotechnical properties of municipal solid waste. Geotech. Test. J. 1995, 18, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, O.M.; Carvalho, M.F. Shear strength and consolidation properties of municipal solid waste. In Proceedings of the International Workshop, Hydro-Physico-Mechanics of Landfills, LIRIGM, Grenoble, France, 21–22 March 2005; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Zhan, T.L.T.; Wei, H.Y.; Ke, H. Aging and compressibility of municipal solid wastes. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bareither, C.A.; Breitmeyer, R.J.; Benson, C.H.; Barlaz, M.A.; Edil, T.B. Deer track bioreactor experiment: Field-scale evaluation of municipal solid waste bioreactor performance. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2012, 138, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Hettiarachchi, H.; Parakalla, N.; Gangathulasi, J.; Bogner, J. Hydraulic conductivity of municipal solid waste in landfills. Int. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleiker, D.E.; Farquhar, G.; McBean, E. Landfill settlement and the impact on site capacity and refuse hydraulic conductivity. Waste Manag. Res. 1995, 13, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, E. Contributions to Our Knowledge of the Aeration of Soils; Bulletin Series No. 25; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Bureau of Soils, Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1904; pp. 1–52.
- Marshall, T.J. The diffusion of gases through porous media. J. Soil Sci. 1959, 10, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepagoda, T.K.K.C.; Moldrup, P.; Schjønning, P.; Kawamoto, K.; Kpmatsu, T.; Jonge, W.D. Generalized density-corrected model for gas diffusivity in variably saturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniya, A.; Kawamoto, K.; Hamamoto, S.; Sakaki, T.; Saito, T.; Müller, K.; Moldrup, P.; Komatsu, T. Linking pore network structure derived by micro-focus X-ray CT to mass transport parameters in differently compacted loamy soils. Soil Res. 2019, 57, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldrup, P.; Olesen, T.; Komatsu, T.; Schjonning, P.; Rolston, D.E. Tortuosity, diffusivity, and permeability in the soil liquid and gaseous phases. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).