Abstract
Mercury bioavailability was assessed by exposing the dipteran Chironomus riparius for the whole life cycle to legacy-contaminated fluvial sediments (0.038–0.285 mg Hg kg−1 d.w.) and analyzing tissue concentrations in larvae at different exposure times (7, 11, and 16 days) and in adults. In the same experiment, diffusive gradients in thin-film passive samplers (DGTs), both piston- and probe-shaped, were co-deployed in the same sediments and retrieved at the same times as the organisms. To compare the two approaches, results showed a good agreement between accumulation kinetics of C. riparius and DGTs, both approximating an apparent steady-state. A strong correlation was found between values in tissues and in both types of DGTs (r between 0.74 and 0.99). Concentrations in mature larvae (19–140 µg kg−1 w.w.), which may represent a basal level of the aquatic food web, exceeded the European Environmental Quality Standard for biota (20 µg kg−1 w.w.), which aims at protecting the top predators from secondary poisoning. Body burdens in larvae and in adults were similar, showing negligible decontamination during metamorphosis and proving an efficient mercury transfer from sediments to terrestrial food webs.
1. Introduction
Mercury is considered a contaminant of concern, due to wide distribution in both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and to high bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential [1,2]. Freshwater sediments are often characterized by accumulation of mercury deriving from anthropic inputs. Different chemical forms, i.e., inorganic as well as organic species, can be found depending on local biogeochemical conditions, such as redox potential, temperature, and total organic carbon content [3]. Methylmercury is the most bioavailable and toxic species, and it is mostly formed by bacteria in anoxic conditions in the presence of sulfide [4,5]. Thus, the sediment compartment is a suitable site for methylation and can be a significant source of the contaminant for the water column and for aquatic biota [2]. For this reason, the evaluation of lability of mercury from sediments is needed in a risk assessment perspective, to determine the extent at which the contaminant is bioavailable.
Previous studies demonstrated that benthic invertebrates actively contribute of the transfer of sediment-bound mercury to the food chains. Sediment bioturbation as well as ingestion are both effective mechanisms determining mercury release from the solid compartment to the water column and to biota [5,6]. Aquatic insects were proved to be characterized by significant concentrations of mercury and methylmercury [7,8]. These organisms, among which is the well-known test organism Chironomus riparius, are prey for other invertebrates and for fish, so they are involved in mercury biomagnification along the trophic chains. Moreover, these insects develop into terrestrial adults, which may transport mercury from the aquatic to the terrestrial environment, potentially exerting harmful effect on insectivorous predators such as birds and bats [9,10,11,12].
When exposed to contaminated sediments, benthic invertebrates generally show rapid bioaccumulation, which depends on the equilibrium between uptake and elimination [5,13]. The net uptake may depend on sediment characters such as organic matter content, oxygenation, and acid-volatile sulfide (AVS) and on feeding behavior and physiology of the organisms [14]. At steady-state, the biota sediment accumulation factor (BSAF), i.e., the ratio between concentrations in the organism tissues and in sediments, may be considered a measure of mercury bioavailability in a specific environment [6,15].
A relatively consolidated technique for determining chemical labile metal species in aquatic ecosystems is diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) [16,17]. The functioning of the DGTs is based on the diffusion capacity of metals in a hydrogel and on the exchange capacity of a chelating resin. The resin is selective for free or weakly complexed species, so DGTs provide an integrated measure over time of the labile concentration of metals in sediments [18]. By concentrating mercury in the resin, these systems allow to overcome the limitations of instant sampling, providing a time-integrated measure of bioavailability during deployment, comparable to that obtained by direct exposure of organisms to contaminated environments [18]. To our knowledge, only a few publications address mercury lability in sediments by using DGTs in comparison with aquatic organisms [5,19,20]. We previously used DGTs in field deployments in the Toce River (Northern Italy) and we found a good agreement with concentrations in tissues of native benthic invertebrates [21].
To further deepen this comparison, our aim was then to evaluate mercury bioavailability from Toce sediments by co-exposing the Dipteran C. riparius and DGT passive samplers in a time-dependent lab experiment. Moreover, to evaluate the efficiency of aquatic insects of transporting mercury from sediments to aquatic and terrestrial food chains, bioaccumulation in the organism tissues was analyzed in chironomid mature larvae and in adults. The analysis was addressed on total mercury analysis, since official monitoring in Italy is carried out in different environmental compartments (water, sediments, biota) considering the total metal concentrations. Part of this work was carried out with the aim of providing stakeholders with effective tools for monitoring mercury contamination in riverine ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sediment Sampling and Analysis
Sediments were collected in the Toce River (Piedmont Region, Northern Italy), which is characterized by a legacy contamination released by a mercury cell chlor-alkali plant, located along the river course at about 20 km upstream from the river mouth. This river is one of the main tributaries of Lake Maggiore, and it is an active source of Hg and DDx contamination for the lake, as reported in [21,22]. Four sampling points were selected along the study reach: one station (Prata) upstream from the industrial site, and three (Bosco Tenso, Premosello, Ornavasso) downstream (Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Table S1). Further details on the study area and sampling sites are provided in [21,22], which report previous studies on mercury contamination at the same stations. At each site, about 30 L of sediments were collected in November 2014 (used for Test 1, see Section 2.2) and in February 2015 (used for Test 2) and preserved in acid-washed polythene bins at 4 °C. Sediments were collected in depositional areas of the river (pools), characterized by the accumulation of fine sediments. Different sub-samples were collected with a stainless-steel spoon and mixed to obtain sample homogenization. An aliquot of each samples was freeze-dried (72 h at 0.1 atm) and sieved to separate the finest fraction (<63 μm grain size) for chemical analysis.
Mercury analysis was carried out using an Automated Mercury Analyzer (AMA-254, FKV, Bergamo, Italy). The instrument detection limit (LOD) is 0.01 ng Hg, the working range is 0.05 to 600 ng Hg. The limit of quantification (LOQ), calculated as ten times the standard deviation of the blank and considering a sample mass (sediment or organism tissue) of 25 mg, is 0.009 mg kg−1.
For sediments, total mercury concentrations were determined by thermal decomposition, amalgamation and atomic absorption spectrometry according to US-EPA method 7473 [23]. The certified reference material GBW07305 Stream sediment powder from the National Standard Centre of China was analyzed (reference value = 0.1 mg kg−1), obtaining a mean recovery of 101 ± 3% (n = 6) of certified values. Precision was checked by triplicate analysis, and coefficient of variation was ≤5%.
Organic carbon content (OC) was determined in 0.5 g d.w. samples according to Walkley-Black procedure [24]. The LOD of the method is 0.14% OC, the LOQ is 0.46% OC, calculated as 3.3 times the LOD value [25]. Coefficient of variation for triplicate analysis was <5%.
2.2. Mercury Bioaccumulation in Chironomus riparius
Sediments were used to perform two bioaccumulation tests in the lab (Test 1 and Test 2) with C. riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae). This organism was selected because it can be considered representative of riverine aquatic insects and it is easy to culture [26]. The aim was to analyze mercury bioaccumulation in larvae and in adults. Sediments collected in November 2014 were used to perform Test 1 and those collected in February 2015 for Test 2. In Test 1, for Premosello and Ornavasso sediments, i.e., the most contaminated ones, bioaccumulation was analyzed at different exposure times, to obtain uptake kinetics.
Both tests were carried out with the same protocol, following OEDC protocol n. 218 [27], with slight modifications. The midges derived from a continuous culture held at CNR-IRSA laboratory. Per each treatment (i.e., sediment sample), 3–5 replicates per each exposure time were set (Table 1). Each replicate consisted in a 19 × 19 × 18 cm glass vessel containing a 3 cm-thick layer of the Toce River sediments and 1 cm-thick layer of river water (about 1 L, collected in an unimpacted river stretch). Each control vessel contained a 3 cm-thick layer of natural sediment collected in an unimpacted river stretch and 1 cm-thick layer of river water. According to OECD protocol n. 218 [27], 0.5% d.w. finely ground leaves of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) were added to sediments as food necessary to ensure survival and natural growth. In fact, organic carbon (OC) analysis showed low levels in the Toce sediments (1.0 ± 0.4% OC, Supplementary Table S2). In this way, it was not necessary to feed the larvae during the test.

Table 1.
Experimental design of the lab Test 1 and and Test 2 of mercury (bio)accumulation using C. riparius and DGTs (piston- and probe-shaped). Numbers in the table represent the replicates per each experiment/exposure time. In backets: replicates used for adult emergence. - = not analyzed.
Tests were carried out in a climate room at a temperature of 20 ± 1 °C, 60% relative humidity and a light:dark rhythm of 16:8 h (500–1000 lux). The replicates of each treatment and exposure time were grouped under a 150 µm mesh size cage (60 × 45 × 50 cm), to allow adult emergence. Oxygen concentration in the water was maintained >60% saturation by air pumps. Water/sediment systems were allowed to condition for 35 days before addition of the larvae. Water evaporation was compensated by adding demineralized water. After this phase, 150 5-day-old larvae were inoculated in each vessel, deriving from 24 egg ropes of the lab culture hatched in the river water.
During the tests, water temperature, conductivity, dissolved oxygen and pH were measured every 3–5 days using field multiprobes.
During Test 1, exposure times were defined basing on larval development and on beginning of pupation: ideally, we wanted to test 7, 14, and 21 days, but we had to retrieve larvae at 7, 11 and 16 days because larval development was faster than we supposed according to preliminary tests. For Test 2, only a 21-day exposure was carried out, i.e., until the beginning of pupation.
For both tests, at each exposure time, 3–4 replicates per treatment were sieved to recover all larvae (Table 1). The organisms were left in the river water for 6 h for gut-purging. Then, they were sieved, gently dried with absorbent paper, counted, weighted, and freeze-dried for mercury analysis. For the remaining replicates, at the end of emergence time adults were collected in each cage. Ten males and ten females per treatment were dried at 34 °C for 24 h and weighted with a precision balance to determine dry weight [28]. The other adults were counted, weighted, and freeze-dried for mercury analysis.
Mercury analysis was carried out using AMA-254 analyzer (FKV, Bergamo, Italy) [23]. The certified reference material BCR-CRM278 Mussel tissue of the Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements was analyzed (certified value = 0.196 ± 0.007 mg kg−1), obtaining a mean recovery of 102 ± 2% (n = 6) of certified values. Precision was ≤5%. At least 25 mg d.w. of larval tissue was necessary for each analysis, thus in some cases we had to merge different replicates to obtain sufficient larval material for duplicate/triplicate analysis. In any case, for each exposure time and for each site, at least two replicates (or merged replicates) were analyzed separately. For adults, duplicate/triplicate samples analysis was carried out using at least 15 mg d.w., and coefficient of variation was ≤15%.
Mercury bioavailability from sediments at steady-state can be calculated as the biota sediment accumulation factor (BSAF), according to the following formula, derived from [29]:
where Css is Hg concentration (mg kg−1 d.w.) in tissue at steady-state, C0 is the tissue concentration (mg kg−1 d.w.) at time 0, and Csed is Hg concentration (mg kg−1 d.w.) in sediments during the experiment.
Mercury bioaccumulation kinetic may be described using a one-compartment model, using the following equation [13]:
where Ct is Hg concentration (mg kg−1 d.w.) in tissue at time t (d), C0 is the tissue concentration (mg kg−1 d.w.) at time 0, a is the uptake rate (mgHg × kglarva × d−1), kg is the growth rate constant (d−1), and ke is the excretion rate constant (d−1).
2.3. Evaluation of Mercury Bioavailability Using DGT Passive Samplers
The same sediments used for bioaccumulation Test 1 were also used to perform an accumulation test with mercury-specific DGT passive samplers. DGTs were purchased from DGT Research Ltd. (Lancaster, UK). Two different sampler types were tested: piston- and probe-shaped samplers.
Piston DGTs are composed of a plastic base (2.5 cm diameter) loaded with resin gel (Spheron-Thiol), diffusive gel (agarose, 0.76 mm thickness) and filter (0.45 µm pores, 0.40 mm thickness) and covered with a plastic top which leaves a 3.14 cm2 window area. As already proved in previous works (e.g., [30]), Spheron-Thiol resin shows an excellent performance in mercury accumulation. Moreover, agarose diffusive gel proved to accumulate less mercury than other gel types, thus being most suitable for experiments with mercury [5]. For piston DGTs, one or two additional replicates per each sediment sample were set as described above for C. riparius. Aeration was provided with air pumps. As for Chironomid replicates, water/sediment systems were allowed to condition for 35 days before DGT deployment. At time 1, when larvae were inoculated, pistons were deployed horizontally at the water–sediment interface, with the DGT window facing toward the sediments and embedded 1 cm deep in the sediments (Supplementary Figure S2). Deployment times were the same used for C. riparius, and for Premosello and Ornavasso sediments also a longer deployment time (28 days) was tested (Table 1). Two DGTs for each deployment time were used (Table 1). At each retrieval, pistons were gently washed with ultrapure water, the resin was separated with Teflon tweezers and sectioned into two parts using a ceramic blade. Mercury analysis was carried out by directly inserting each resin part into AMA-254 analyzer to obtain mercury absolute nanograms. For quality assurance, a mercury standard solution of 5 µg L−1 was prepared daily by diluting a stock solution of 1000 mg Hg L−1 in 1% HCl solution and analyzed in triplicate, obtaining CVs < 5%. Measured values were on average 4.93 ± 0.045 µg L−1 (n = 18). Two DGT units were analyzed prior to the test to obtain the “blank” value.
Probe DGTs are composed of a plastic base (18 × 4 cm) loaded with resin gel (Spheron-Thiol), diffusive gel (agarose, 0.76 mm thickness) and filter (0.45 µm pores, 0.40 mm thickness) and covered with a plastic top which leaves a 27 cm2 (i.e., 15 × 1.8 cm) window area. This type of sampler is deployed vertically into sediments to obtain vertical profiles of mercury lability [31]. A previous work [5] showed that this DGT type may better mimic mercury accumulation in sediment-dwelling organisms. In order to deploy probes into sediments for their entire length, five 35.6 × 23.4 × 22.8 cm plastic aquaria were set with the same sediments used for C. riparius experiment. In this case, a 18 cm sediment thickness was used, covered by 3 cm thick river water. Aeration was provided with air pumps. After 35 days, probes were inserted vertically into sediments, except for the first 2 cm, which were covered by the water, with their windows facing outwards (Supplementary Figure S2). Deployment times were the same used for C. riparius (Table 1). At each retrieval, two probes were gently washed with ultrapure water, the resin was separated with Teflon tweezers and sectioned into 1 cm sections using a ceramic blade. Mercury analysis was carried out by directly inserting each resin part into AMA-254 analyzer to obtain mercury absolute nanograms. Two DGT units were analyzed prior to the test to obtain the “blank” value.
Mercury flux F (ng s−1 cm−2) into the resins was calculated according to [16] as:
where M is the mercury mass accumulated in the resin (ng), t is the deployment time (s), and A is the diffusive area (cm2).
The labile Hg concentration in sediment porewater Cb (ng cm−3) was calculated according to [16] as:
where Δg is the diffusive layer thickness (0.116 cm), D (cm2 s−1) is the diffusion coefficient of Hg in the agarose gel at the experiment temperature, t is the deployment time and A is the diffusive area. The diffusion coefficient of mercury was derived from [30] and [32] (9.07 10−6 cm2 s−1 at 25 °C for Hg2+, which is close to the value of 9.06 10−6 cm2 s−1 for CH3Hg+) and it can be adapted to the mean water temperature measured during the experiment using [16]’s formula (7.52 10−6 cm2 s−1 at 18.3 °C).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Pearson correlations between mercury in DGTs, in C. riparius tissue and in sediments were calculated, considering as significant p values < 0.05. Normality of data was tested with the Komogorov–Smirnov test. Wilcoxon matched pairs test was used to compare mercury body burdens in mature larvae and in adults. Statistical analyses were performed using Statistica 8.0 (StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA) and Past 4.03 (Palaeontological Association, Durham, UK) [33].
3. Results and Discussion
Water parameters were checked during both Test 1 and Test 2. Oxygen saturation remained always ≥73% in the test water, pH values were comprised between 7.3 and 8.1, water conductivity was between 277 and 427 µS cm−1 and mean water temperature was 18.3 ± 1.7 °C. At the end of the tests, emergence was ≥70% in all treatments. This result was expected, because effects on survival have been reported at mercury concentrations above 3.84 mg kg−1 d.w. [34]. The same authors reported a significant delay in adult emergence at concentrations above 0.93 mg kg−1 d.w. Our sediment samples showed mercury concentrations between 0.038 and 0.285 mg kg−1 d.w. (Supplementary Table S2), thus ecotoxicological effects bound to mercury were not expected, even if other contaminants may be present, such as DDx and arsenic, as reported in [21,22]. These latter studies were conducted in the same period (2014–2015) and sampling sites as this study, reporting Hg concentrations in sediments ranging between 0.029 and 0.242 mg kg−1 d.w., similar to those found here. As well, OC content showed levels (1.14 ± 0.41%) comparable to this study (1.0 ± 0.4%) (Supplementary Table S2). Analysis of MeHg showed values of 0.7–3.8% of total mercury [21], in line with MeHg fractions in other river sediments (e.g., [20]). Here also, MeHg analysis (in GC-MS) showed concentrations below the limit of quantification of 1.4 µg kg−1 d.w. [35], thus representing a minimal fraction of total mercury (<3%). Pisanello et al. [21] deployed DGT pistons in the Toce River at the sediment surface for 7–11 days and their Hg accumulation was compared with bioaccumulation in different taxa of native invertebrates (Diptera Tipulidae, Limoniidae and Tabanidae, Ephemeroptera Heptageniidae and Crustacea Gammaridae). A comparison of those outcomes with this lab experiment can be carried out.
For Test 1, labile Hg concentrations in sediment porewater (Cb) were estimated using DGT samplers, according to Equation (4). Considering any deployment time, Cb values were generally in the order of some ng L−1 (3–36 ng L−1) (Supplementary Table S3). Such values are in line with those reported in [21] (29–56 ng L−1) and in other studies on rivers sediments (e.g., [20,31]) and are below ecotoxicological thresholds for C. riparius [26]. However, the estimation of Cb in sediments using DGTs may be biased by a number of confounding factors. First, results of our time-dependent experiments showed that the flux of mercury in the resins, calculating according to Equation (3), decreased with time in both Premosello and Ornavasso sediments, proving that porewater mercury around the samplers was not adequately resupplied from the labile sediment-bound metal (Figure 1). This resulted in a gradual depletion of mercury in the vicinity of the DGTs and an apparent plateau of the Hg mass accumulated in the resins was approximated (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S3). This behavior is expected in sediment deployments, especially in lab experiments, where static conditions may not favor porewater resupply [5]. For this reason, Cb decreased with time in both sediment samples (Supplementary Table S3). In general, for a reliable Cb calculation, deployment times should be short enough to maintain a proportionality between the mass of Hg accumulated in the resin and the exposure times, in accordance with the principle of DGT [4]. In field deployments, according to our experience [21], Hg resupply at the water–sediment interface can be faster than in the lab due to water current, but one of the main constraints is the variation of temperature, as well as other water parameters, at the water–sediment interface [36], which can be hardly controlled during the exposure. Moreover, sediment heterogeneity may determine high standard deviations for Hg mass accumulated in the DGT units [21], and this drawback can be observed also in lab deployments, notwithstanding sediment homogenization [5] (Supplementary Table S3). Another crucial point is the choice of the diffusion coefficient D, which in sediment porewater could be lower than expected due to the presence of different forms of mercury, in particular Hg-DOM complexes [4,32,36,37]. This means that the effective D value may be site-specific. In a preliminary lab experiment, we estimated for Ornavasso sediments a diffusion coefficient of 4.38 × 10−6 cm2 s−1 at 18.3 °C (Supplementary Figure S3), which is actually lower that the value reported in [30,32], that we used for Cb calculation (Supplementary Table S3). By using our experimental value in Equation (4), Cb would rise of 1.7 times. For Ornavasso sediments, Cb would reach 35 ng L−1, in line with the concentration calculated in the field in February 2015 at the same site [21].
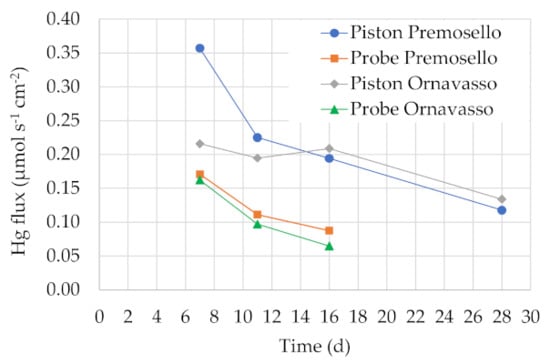
Figure 1.
Mercury flux into the resin of piston and probe DGTs deployed at different times in Premosello and Ornavasso sediments.
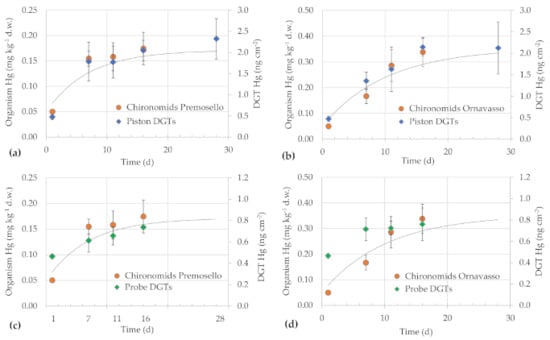
Figure 2.
Concentrations of mercury in C. riparius tissue and in DGTs at different exposure times: in sediments of Premosello using: (a) DGT pistons and (b) DGT probes; in sediments of Ornavasso using (c) DGT pistons and (d) DGT probes. Grey lines represent tentative fits to tissue concentrations according to Equation (2). Bars represent ± standard deviation.
For both bioaccumulation tests, mercury concentrations in the organisms of the control remained stable in time and the mean was considered as the “blank” value for Chironomids (C0 = 0.050 ± 0.003 mg kg−1 d.w.). Mercury concentration in control sediments was 0.010 ± 0.0004 mg kg−1 d.w., thus a small fraction was likely bioavailable to larvae. Sediments collected at Premosello and Ornavasso, i.e., the most contaminated sites, were used in Test 1 for analyzing time-dependent concentrations of mercury in the organisms (Figure 2). Concentrations in chironomid larvae exposed to Premosello sediments rapidly increased in the first seven days and then approximated a maximum value of about 170 mg kg−1 d.w. (Figure 2a). Kinetic studies generally report a rapid increase of metal concentrations in a few days, until an apparent steady-state is reached between uptake and efflux [6,13]. Concentrations in larvae exposed to Ornavasso sediments showed a more gradual increase and a clear plateau could not be observed (Figure 2c). This may mirror higher bioavailability of mercury in this sediment sample in comparison to Premosello one. This was also proved by BSAF calculation (Equation 1), considering the tissue concentrations at day 16 as the steady-state value: an average BSAF value of 1.2 ± 0.3 was obtained for Premosello and of 2.5 ± 0.5 for Ornavasso. These values are in line with those calculated for native benthic invertebrates collected in the Toce River at the same sites [21], confirming higher Hg bioavailability at Ornavasso (BSAF values of 0.9–3) than at Premosello (0.5–1.6). Different sediment characteristics, e.g., organic carbon content, gran size composition (Supplementary Table S2), presence of other toxicants, etc., may also explain the different bioaccumulation performance of C. riparius.
A tentative calculation of bioaccumulation kinetics according to Equation (2) was carried out, even if more exposure times would be necessary for a reliable model calculation [38,39,40]. The ingestion rates of sediments for C. riparius are scarcely known [9,13], as well as the assimilation efficiency from sediments (considered as food) [38]. Notwithstanding these limitations, we calculated empirically the mercury uptake rates as the slope of linear regression of tissue concentrations versus time (in days) for the linear portion of the uptake phase [6,13]: for Premosello, the uptake between days 1 and 7 was calculated and a coefficient a of 0.017 ± 0.002 mgHg × kglarva × d−1 was obtained. For Ornavasso, since the tissue concentrations increased proportionally with time, we considered the steepest portion of the line, i.e., between days 7 and 11, obtaining a coefficient a value of 0.030 ± 0.008 mgHg × kglarva × d−1. Growth rate coefficients of larvae in terms of fresh mass per day were calculated using logistic growth models, obtaining a mean kg value of 0.144 ± 0.030 d−1 for Premosello and of 0.098 ± 0.012 d−1 for Ornavasso. Excretion rates (ke) reported in the literature are generally low in comparison with kg values (e.g., 0.02–0.06 d−1 for Daphnia magna and bivalves [39,40]). Thus, we tried to calculate the model considering ke as negligible (Figure 2). In general, the assumption of uptake and excretion (or larval growth) constants seems respected. However, for Ornavasso sediments a better fit would be obtained with a linear model (r2 = 0.97). The application of kinetic models to metals in sediments may be difficult because bioavailability (both from the dissolved and solid phase) may influence uptake rates, while the production of metal-binding proteins may affect excretion constants [6].
DGTs were deployed in the same sediments and were retrieved at the same times as the organisms, to compare their uptake kinetics. An additional deployment time of 28 days was considered for pistons only, to analyze the behavior for longer exposure times. Probes were sectioned into 1 cm-layers to obtain mercury vertical profiles. For comparison with organism bioaccumulation, we considered the total mercury content in the entire probes (Figure 2b,d). In fact, concentrations remained almost stable over the entire vertical profiles (Supplementary Figure S4). Only at the water–sediment interface, values were slightly higher than below the sediment surface. This may be bound to oxygenation conditions, which may enhance mercury release at the water–sediment interface [20]. This may explain why pistons, which were placed at the top of the sediment surface, showed an overall higher mercury accumulation capacity than probes, considering Hg nanograms per cm2 of resin.
There was a good correspondence between uptake kinetics in the larvae and in the DGTs (Figure 2). For Premosello sediments, the correlation between concentrations in Chironomids and in the DGTs was significant (r = 0.99 for pistons and r = 0.95 for probes, p < 0.05) (Figure 2a,c). For Ornavasso, DGT pistons approximated better the organism bioaccumulation kinetic than probes (Figure 2b,d). In fact, correlation showed a coefficient r = 0.97 for pistons (p < 0.05) and r = 0.89 for probes (p > 0.05). Considering that the organisms were cultured into 3 cm thick sediment layers, pistons potentially mimicked better than probes the exposure conditions experienced by larvae. In contrast, Amirbahman et al. [5] found that paddle-like DGTs better approximated mercury bioaccumulation of the amphipod Leptocheirus plumulosus than pistons, probably as a response of the borrowing behavior of this invertebrate species.
Considering all exposure times and all sediment samples of Test 1 (also those collected at Prata and Bosco Tenso), correlations between mercury in DGTs and mercury in tissue concentrations were calculated (Figure 3). Both piston and probe DGTs showed significant correlations with larval tissue values, with a coefficient r of 0.74 and 0.79, respectively (p < 0.05). These results are in line with the outcomes of Pisanello et al. [21], who reported positive correlations between Cb evaluated with DGT pistons and Hg concentrations in native invertebrates (r between 0.97 and 0.99). In that case, concentrations in the organisms were not correlated with those in sediments (spot samples), as result of spatial and temporal variability of sediment composition. On the contrary, concentrations in C. riparius in our lab tests 1 and 2 were correlated with mercury levels in sediments, as result of higher sediment homogeneity (r = 0.89, p < 0.05). Positive correlations between DGTs and organisms were obtained also by Amirbahman et al. [5] for three estuarine invertebrate species (R2 between 0.57 and 0.90). The authors concluded that DGTs are a good indicator of the uptake kinetics and of concentrations of mercury in benthic invertebrates. Our results seem in line with those conclusions. It should be noted that the mechanisms which regulate mercury accumulation in organisms and in DGTs are substantially different. DGT resins accumulate Hg as soon as it is in free forms (or resupplied from labile forms) until saturation and the uptake is irreversible [5]. Larvae accumulate bioavailable forms from the environment (both from the solid and dissolved phase) as result of equilibrium between uptake and excretion. If the contaminant is removed, then concentrations in the organisms would likely decrease with time [13,26]. However, in riverine sediments the two mechanisms may be comparable because the behavior of both DGTs and larvae is regulated by the lability of sediment-bound Hg species. For instance, DGTs approximated a plateau as result of limited resupply (i.e., desorption) of free forms from sediments. Similarly, the organisms, even if they can move into sediments and ingest them as food, reached a steady-state as response to the availability of bioavailable forms and to the equilibrium between uptake and excretion. Thus, both approaches may be used to assess mercury bioavailability in sediments. This experiment confirmed that the timing to reach the steady-state shows a good agreement between them [5].
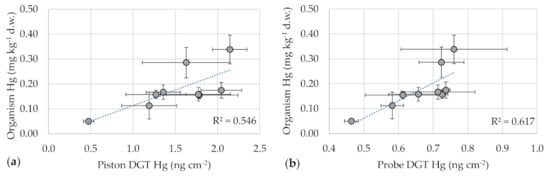
Figure 3.
Correlations between concentrations of mercury in DGTs and in C. riparius tissue using: (a) DGT pistons and (b) DGT probes. Coefficients of determination are reported. Bars represent ± standard deviation.
Bioaccumulation tests 1 and 2 were carried out also with the aim of comparing mercury burdens in mature larvae and in adults, to assess the ability of these organisms to transfer contamination from sediments to the terrestrial environment. Results, expressed as body burdens, are reported in Figure 4. Values in larvae did not differ from those in adults (p > 0.05, Wilcoxon matched pairs test). This result is in contrast with Rossaro et al. [41], who found in adults an average of 29% of total mercury concentration measured in larvae exposed to spiked solutions. However, it is in line with results by Cid et al. [42], which showed similar concentrations between nymphs and adults of the mayfly Ephoron virgo collected in mercury contaminated river sites. Similarly, specimens of the dragonfly Gomphus flavipes collected in a metal contaminated river showed similar body burdens between larvae and adults for Cu and Zn and in some sites also for Cr, Pb, and Sr [12]. These examples show that metamorphosis does not necessarily imply a significant elimination of metals, especially when the main accumulation organ is not the exoskeleton, as proved for Hg and Cd in E. virgo moults [42] and for Hg in C. riparius [13]. This latter research proved that Hg in the entire body homogenate of this dipteran is a good approximation of the cytosolic fraction, which accounts for most of the body burden (90%), while exoskeleton, gut content and cellular debris accounts only for 10%. Moreover, Chételat et al. [10] proved that MeHg:THg ratio may increase from larval to adult stage in chironomids, reaching up to 82% in imagos, corresponding to MeHg concentrations 2.9 times higher than in larvae. These studies, as well as our results, confirm the ability of aquatic insects to actively transfer contamination from sediments to terrestrial environments, where adults become easily available to higher trophic levels.
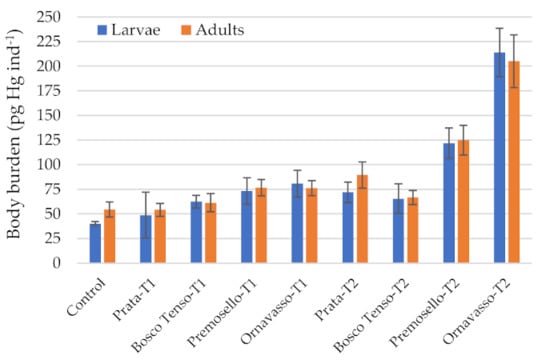
Figure 4.
Body burden of mercury in mature larvae and adults of C. riparius exposed to different sediment samples collected in the Toce River. T1 = Test 1; T2 = Test 2. Bars represent ± standard deviation.
Concentrations in mature larvae, expressed on wet weight, were comprised between 19 and 140 µg kg−1 w.w.. Most values exceeded the European Environmental Quality Standard (EQS) for biota of 20 µg kg−1 w.w., which aims at protecting the top predators from secondary poisoning [43]. The EQS was derived by the lowest available no observed effect concentration (NOEC) for MeHg for birds and mammals exposed though the diet and, in the Italian legislation, is referred to fish. The exceedance of this value at lower trophic position (primary consumers) means that in Toce River, where a mercury legacy contamination is present, an ecological risk is still present. This observation was confirmed also by mercury analysis in native benthic invertebrates collected at the same sites [21], which showed concentrations comprised between 9 and 42 µg kg−1 w.w.. As result, fish collected in the Toce River are expected to exceed the EQS. In fact, some preliminary surveys carried out in the river in 2017–2019 revealed Hg concentrations in fish muscle of 35 ± 7 µg kg−1 w.w. in Salmo trutta, 107 ± 2 µg kg−1 w.w. in Barbus barbus and from 290 ± 4 to 509 ± 10 µg kg−1 w.w. in Squalius cephalus, considering pools of 2–6 specimens of similar age [44,45]. The exceedance in benthic invertebrates was highlighted also in other case studies, e.g., for zebra mussels collected in Rhine and Elbe rivers [43]. Benthic invertebrates represent one of the basal levels of the aquatic food chain, being prey for other invertebrates and for fish in the aquatic environments and for birds and bats in the terrestrial habitat. Thus, body burdens in adults, potentially associated with higher concentrations of MeHg than in preimaginal stages, show that the risk in not limited to the aquatic environment, but it is efficiently transferred to terrestrial biota.
4. Conclusions
Our experiments proved once again the important role of fluvial sediments as source of mercury for biota, even when the primary source of the contamination has been limited and concentrations in the environment are relatively low.
DGTs resulted as a promising tool to describe the first step of mercury bioaccumulation, i.e., the transfer from abiotic compartments to biota. These systems proved to mimic the bioaccumulation kinetics and values of sediment feeders such as C. riparius, which are exposed to contamination mainly through the ingestion of sediments. Thus, DGTs proved to be useful tools to assess the lability of sediment-bound mercury. Compared to using organisms, DGTs are easier to handle and may be more reproducible in different sites and environmental conditions, where the response of biota in terms of bioaccumulation may be biased by ecotoxicological concerns and/or by different sediment characteristics.
In addition, aquatic insects proved to actively transfer mercury from sediments to terrestrial environments through emergence, becoming available to higher trophic levels. These organisms showed high efficiency in mercury uptake from sediments and can be used as sentinels for a potential ecological risk, showing exceedance of the EQS for biota even at the basis of the aquatic food chain.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3298/8/2/7/s1, Figure S1: map of the study area, Figure S2: experimental setting in the lab, Figure S3: preliminary time-series experiment with DGT pistons in sediments collected at Ornavasso site, Figure S4: vertical profiles of mercury in probe DGTs, Table S1: geographical coordinates of sampling points, Table S2: sediments characteristics, Table S3: concentrations of mercury in pore water, estimated with DGTs, and in Chironomids of Test 1; Preliminary test with DGT pistons in Ornavasso sediments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M; investigation, L.M. and L.V.; formal analysis, L.M.; writing, L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the International Commission for the Protection of Italian-Swiss Waters (CIPAIS). Research Programs 2013-2015 and 2019-2021 (www.cipais.org).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are mostly available in Supplementary material and can be requested to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Jessica Monterosso and Federica Rosignoli for help in lab work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lavoie, R.A.; Jardine, T.D.; Chumchal, M.M.; Kidd, K.A.; Campbell, L.M. Biomagnification of mercury in aquatic food webs: A worldwide meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13385–13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amos, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Kocman, D.; Horowitz, H.M.; Zhang, Y.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Horvat, M.; Corbitt, E.S.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Sunderland, E.M. Global biogeochemical implications of mercury discharges from rivers and sediment burial. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9514–9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, S.M.; Tanton, T.W.; Abdrashitova, S.A. Mercury in the aquatic environment: A review of factors affecting methylation. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 31, 241–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gómez, C.; Dimock, B.; Hintelmann, H.; Díez, S. Development of the DGT technique for Hg measurement in water: Comparison of three different types of samplers in laboratory assays. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirbahman, A.; Massey, D.I.; Lotufo, G.; Steenhaut, N.; Brown, L.E.; Biedenbach, J.M.; Magar, V.S. Assessment of mercury bioavailability to benthic macroinvertebrates using diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrahy, E.A.; Clements, W.H. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of a mixture of heavy metals in Chironomus tentans (Diptera: Chironomidae) in synthetic sediment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žižek, S.; Horvat, M.; Gibičar, D.; Fajon, V.; Toman, M.J. Bioaccumulation of mercury in benthic communities of a river ecosystem affected by mercury mining. Sci. Total. Environ. 2007, 377, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva-Murray, K.; Chasar, L.C.; Bradley, P.M.; Burns, D.A.; Brigham, M.E.; Smith, M.J.; Abrahamsen, T.A. Spatial patterns of mercury in macroinvertebrates and fishes from streams of two contrasting forested landscapes in the eastern United States. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1530–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bervoets, L.; De Bruyn, L.; Van Ginneken, L.; Blust, R. Accumulation of137Cs by larvae of the midge Chironomus riparius from sediment: Effect of potassium. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chételat, J.; Amyot, M.; Cloutier, L.; Poulain, A.J. Metamorphosis in chironomids, more than mercury supply, controls methylmercury transfer to fish in high arctic lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9110–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.M.; Walters, D.M.; Wesner, J.S.; Stricker, C.A.; Schmidt, T.S.; Zuellig, R.E. Metamorphosis alters contaminants and chemical tracers in insects: Implications for food webs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10957–10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, E.; Tóthmérész, B.; Kis, O.; Jakab, T.; Szalay, P.E.; Vincze, A.; Baranyai, E.; Harangi, S.; Miskolczi, M.; Dévai, G.; et al. Environmental-friendly Contamination Assessment Of Habitats Based On The Trace Element Content Of Dragonfly Exuviae. Water 2019, 11, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbert, F.; Geffard, A.; Guédron, S.; Dominik, J.; Ferrari, B.J.D. Mercury tissue residue approach in Chironomus riparius: Involvement of toxicokinetics and comparison of subcellular fractionation methods. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 171, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.P.; Laporte, J.-M.; Andres, S. Factors controlling the bioaccumulation of mercury, methylmercury, arsenic, selenium, and cadmium by freshwater invertebrates and fish. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 38, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jędruch, A.; Bełdowska, M.; Ziółkowska, M. The role of benthic macrofauna in the trophic transfer of mercury in a low-diversity temperate coastal ecosystem (Puck Lagoon, southern Baltic Sea). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Davison, W. Performance characteristics of diffusion gradients in thin films for the in situ measurement of trace metals in aqueous solution. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S.; Yang, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L. Development of a new diffusive gradient in the thin film (DGT) method for the simultaneous measurement of CH3Hg+ and Hg2+. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 7976–7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarisse, O.; Lotufo, G.R.; Hintelmann, H.; Best, E.P.H. Biomonitoring and assessment of monomethylmercury exposure in aqueous systems using the DGT technique. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 416, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndu, U.; Christensen, G.A.; Rivera, N.A.; Gionfriddo, C.M.; Deshusses, M.A.; Elias, D.A.; Hsu-Kim, H. Quantification of mercury bioavailability for methylation using diffusive gradient in thin-film samplers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8521–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Bryan, A.L.; Mills, G.L.; Korotasz, A.M. Mercury speciation, bioavailability, and biomagnification in contaminated streams on the Savannah River Site (SC, USA). Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 668, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanello, F.; Marziali, L.; Rosignoli, F.; Poma, G.; Roscioli, C.; Pozzoni, F.; Guzzella, L. In situ bioavailability of DDT and Hg in sediments of the Toce River (Lake Maggiore basin, Northern Italy): Accumulation in benthic invertebrates and passive samplers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 10542–10555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marziali, L.; Rosignoli, F.; Drago, A.; Pascariello, S.; Valsecchi, L.; Rossaro, B.; Guzzella, L. Toxicity risk assessment of mercury, DDT and arsenic legacy pollution in sediments: A triad approach under low concentration conditions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 593–594, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency (US-EPA). Method 7473—Mercury in Solids and Solutions by Thermal Decomposition, Amalgamation, and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry; US-EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, B.A. Methods for the Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) in Soils and Sediments; Ecological Risk Assessment Support Center: Las Vegas, NV, USA, April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- De Vos, B.; Lettens, S.; Muys, B.; Deckers, J.A. Walkley–Black analysis of forest soil organic carbon: Recovery, limitations and uncertainty. Soil Use Manag. 2007, 23, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo-Pereira, H.M.V.S.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Effects of mercury on growth, emergence, and behavior of Chironomus riparius Meigen (Diptera: Chironomidae). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 59, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Test No. 233: Sediment-Water Chironomid Toxicity Using Spiked Sediment. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, C.; Nowak, C.; Diogo, J.B.; Oetken, M.; Schwenk, K.; Oehlmann, J. Multi-generation studies with Chironomus riparius—Effects of low tributyltin concentrations on life history parameters and genetic diversity. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2192–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimbert, F.; de Vaufleury, A.; Douay, F.; Scheifler, R.; Coeurdassier, M.; Badot, P.-M. Modelling chronic exposure to contaminated soil: A toxicokinetic approach with the terrestrial snail Helix aspersa. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docekalová, H.; Diviš, P. Application of diffusive gradient in thin films technique (DGT) to measurement of mercury in aquatic systems. Talanta 2005, 65, 1174–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diviš, P.; Leermakers, M.; Dočekalová, H.; Gao, Y. Mercury depth profiles in river and marine sediments measured by the diffusive gradients in thin films technique with two different specific resins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelcová, P.; Dočekalová, H.; Kleckerová, A. Development of the diffusive gradient in thin films technique for the measurement of labile mercury species in waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 819, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Chibunda, R.T. Chronic toxicity of mercury (HgCl2) to the benthic midge Chironomus riparius. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2009, 3, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, L.; Roscioli, C.; Zanini, C.; Schiavon, A.; Guzzella, L.; Marziali, L. Determinazione del metilmercurio in sedimenti e biota d’acqua dolce mediante analizzatore automatico di mercurio e GC-MS. Not. Metodi Anal. IRSA News 2020, 1, 20–29. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.S.; Rifkin, E.; Bouwer, E.J. Combination of diffusive gradient in a thin film probe and IC-ICP-MS for the simultaneous determination of CH3Hg+and Hg2+in oxic water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6429–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarisse, O.; Foucher, D.; Hintelmann, H. Methylmercury speciation in the dissolved phase of a stratified lake using the diffusive gradient in thin film technique. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, B.J.D.; Vignati, D.A.L.; Roulier, J.-L.; Coquery, M.; Szalińska, E.; Bobrowski, A.; Czaplicka, A.; Dominik, J. Chromium bioavailability in aquatic systems impacted by tannery wastewaters. Part 2: New insights from laboratory and in situ testing with Chironomus riparius Meigen (Diptera, Chironomidae). Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 653, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, M.T.K.; Wang, W.-X. Uptake and elimination routes of inorganic mercury and methylmercury in Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Wang, W.-X. Mercury accumulation in marine bivalves: Influences of biodynamics and feeding niche. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2500–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossaro, B.; Gaggino, G.F.; Marchetti, F. Accumulation of mercury in larvae and adults, Chironomus riparius (Meigen). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1986, 37, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid, N.; Ibáñez, C.; Palanques, A.; Prat, N. Patterns of metal bioaccumulation in two filter-feeding macroinvertebrates: Exposure distribution, inter-species differences and variability across developmental stages. Sci. Total. Environ. 2010, 408, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepom, P.; Irmer, U.; Wellmitz, J. Mercury levels and trends (1993–2009) in bream (Abramis brama L.) and zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) from german surface waters. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission for the Protection of the Italian-SwissWaters. Indagini Sulle Sostanze Pericolose Nell’ecosistema del Lago Maggiore. Programma 2016–2018; CIPAIS: Verbania, Italy, 2018; Available online: http://www.cipais.org/ (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- International Commission for the Protection of the Italian-Swiss Waters. Indagini Sulle Sostanze Pericolose Nell’ecosistema del Lago Maggiore. Programma 2019–2021; CIPAIS: Verbania, Italy, 2020; Available online: http://www.cipais.org/ (accessed on 13 January 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).