Leaching Potential of Phosphite Fertilizer in Sandy Soils of the Southern Coastal Plain, USA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Properties
2.2. Experimental
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phosphite Leached
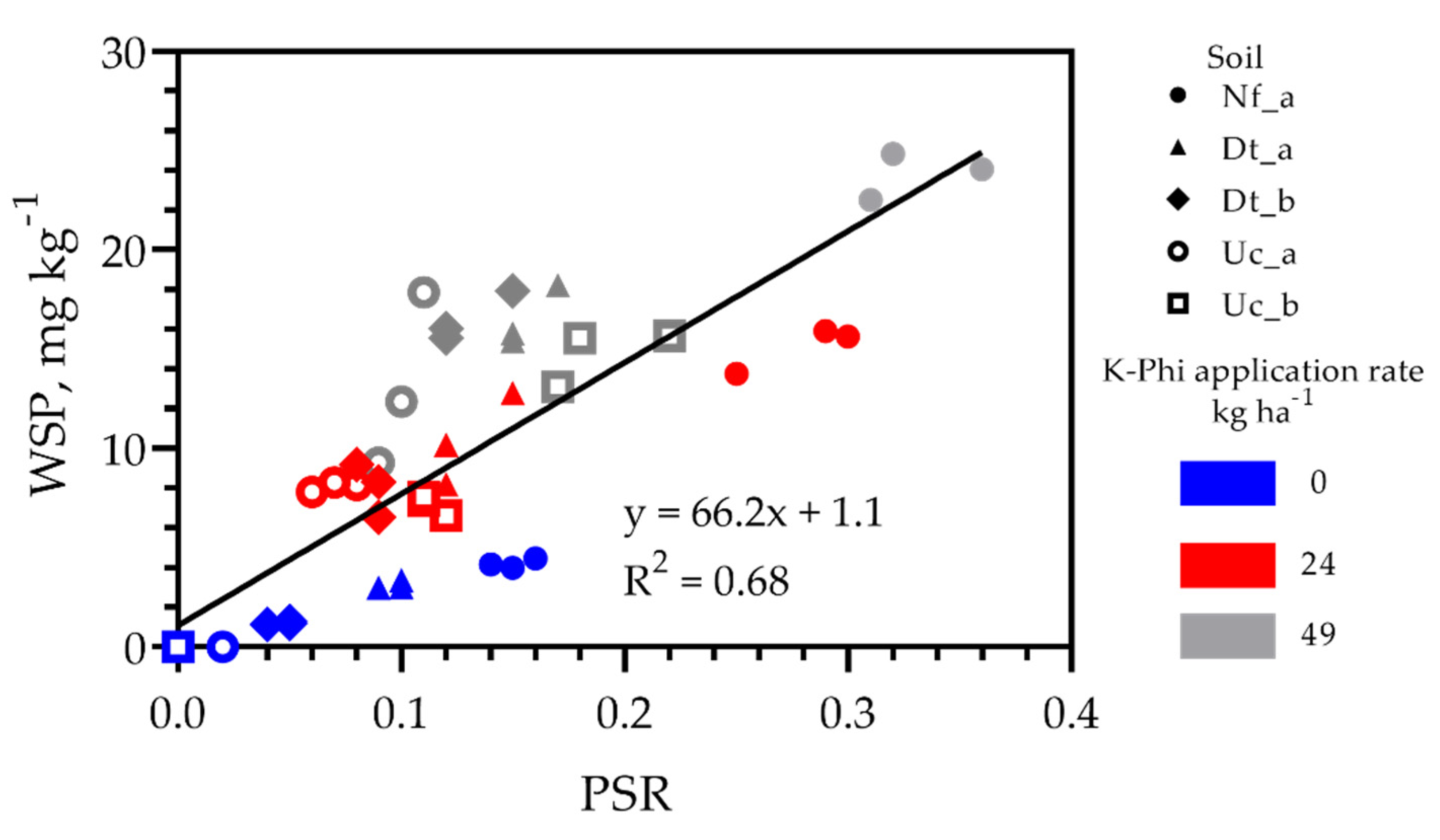
3.2. Phosphite Interaction in the Leached Soils
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Soil | Pi Rate | Volume Leached |
|---|---|---|
| kg ha−1 | mL | |
| Dt_a | 0 | 110 (48) |
| 24 | 110 (48) | |
| 49 | 112 (47) | |
| Dt_b | 0 | 116 (46) |
| 24 | 119 (42 | |
| 49 | 123 (42) | |
| Nf_a | 0 | 116 (53) |
| 24 | 118 (53) | |
| 49 | 114 (51) | |
| Uc_a | 0 | 125 (39) |
| 24 | 124 (39) | |
| 49 | 123 (39) | |
| Uc_b | 0 | 138 (30) |
| 24 | 137 (34) | |
| 49 | 138 (36) |
References
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A critical review on soil chemical processes that control how soil pH affects phosphorus availability to plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerven, V.; Novak, J.M.; Szögi, A.A.; Pantuck, K.; Watts, D.W.; Johnson, M.G. The occurrence of legacy P soils and potential mitigation practices using activated biochar. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szogi, A.A.; Vanotti, M.B.; Ro, K.S. Methods for treatment of animal manures to reduce nutrient pollution prior to soil application. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.-O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuer, S.; Gaxiola, R.; Schilling, R.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; López-Arredondo, D.; Wissuwa, M.; Delhaize, E.; Rouached, H. Improving phosphorus use efficiency: A complex trait with emerging opportunities. Plant J. 2017, 90, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Arredondo, D.L.; Herrera-Estrella, L. Engineering phosphorus metabolism in plants to produce a dual fertilization and weed control system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeks, J.J., Jr.; Hettiarachchi, G.M. A review of the latest in phosphorus fertilizer technology: Possibilities and pragmatism. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guest, D.; Grant, B. The complex action of phosphonates as antifungal agents. Biol. Rev. 1991, 66, 159–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, H.T.B.; Yamakawa, T. Phosphite (phosphorous acid): Fungicide, fertilizer or bio-stimulator? Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2009, 55, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovatt, C.; Mikkelsen, R. Phosphite fertilizers: What are they? Can you use them? What can they do. Better Crop. 2006, 90, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, A.E.; Grant, B.R.; Plaxton, W.C. Phosphite (phosphorous acid): Its relevance in the environment and agriculture and influence on plant phosphate starvation response. J. Plant Nutr. 2001, 24, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratjen, A.M.; Gerendás, J. A critical assessment of the suitability of phosphite as a source of phosphorus. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahampun, H.N.; López-Arredondo, D.; Xu, X.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; Wang, K. Assessment of ptxD gene as an alternative selectable marker for Agrobacterium-mediated maize transformation. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achary, V.M.M.; Ram, B.; Manna, M.; Datta, D.; Bhatt, A.; Reddy, M.K.; Agrawal, P.K. Phosphite: A novel P fertilizer for weed management and pathogen control. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandeya, D.; López-Arredondo, D.L.; Janga, M.R.; Campbell, L.M.; Estrella-Hernández, P.; Bagavathiannan, M.V.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; Rathore, K.S. Selective fertilization with phosphite allows unhindered growth of cotton plants expressing the ptxD gene while suppressing weeds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6946–E6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, F.; Conrad, J.P.J.S.S. Transition of phosphite to phosphate in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1953, 75, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B.L.; White, A.K. Most probable number quantification of hypophosphite and phosphite oxidizing bacteria in natural aquatic and terrestrial environments. Arch. Microbiol. 2012, 194, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, T.F.; Murrell, T.S.; Beegle, D.B.; Camberato, J.J.; Ferguson, R.B.; Grove, J.; Ketterings, Q.; Kyveryga, P.M.; Laboski, C.A.; McGrath, J.M. Strengths and limitations of nitrogen rate recommendations for corn and opportunities for improvement. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szogi, A.A.; Bauer, P.J.; Vanotti, M.B. Vertical distribution of phosphorus in a sandy soil fertilized with recovered manure phosphates. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.; Waerstad, K. Crystallography and equilibrium solubility for ammonium and potassium orthophosphites and hypophosphites. Fertil. Res. 1992, 32, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbaum, H.P.; Baillie, W.J.H. The use of red phosphorus as a fertiliser. 4. Phosphite and phosphate retention in soils. N. Z. J. Sci. 1964, 7, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, S.C.; Glindemann, D.; Wang, X.; Niu, X.; Edwards, M. Analysis of reduced phosphorus in samples of environmental interest. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4369–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, S.S. Soil taxonomy: A basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. In Agriculture Handbook (USDA); Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Crozier, C.; Hardy, D.; Kissel, D.; Mitchell, C.; Oldham, J.; Phillips, S.; Sonon, L. Soil Testing and Recommendations for Cotton on Coastal Plain Soils, Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin no.10; Auburn University: Auburn, AL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, W.; Miller, D. A micro-pipette method for soil mechanical analysis. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1987, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karathanasis, A.D.; Shumaker, P.D. Organic and inorganic phosphate interactions with soil hydroxy-interlayered minerals. J. Soils Sediments 2009, 9, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, W.; Norman White, G. X-ray diffraction techniques for soil mineral identification. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 5 Mineralogical Methods; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2008; pp. 81–115. [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis, A. Thermal analysis of soil minerals. In Methods of Soil Analysis Part 5 Mineralogical Methods; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2008; pp. 117–160. [Google Scholar]
- Self-Davis, M.; Moore, P.; Joern, B.; Kovar, J.; Pierzynski, G. Water-or dilute salt-extractable phosphorus in soil. In Methods for Phosphorus Analysis for Soils, Sediments, Residuals, and Waters; Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin; Virginia Tech University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2009; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, J.T. Soil test phosphorus: Principles and methods. In Methods of Phosphorus Analysis for Soils, Sediments, Residuals and Waters, 2nd ed.; Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin; Virginia Tech University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2009; pp. 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Anions in Water by Suppressed Ion Chromatography ASTM Standard D4327-11; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McDowell, M.M.; Ivey, M.M.; Lee, M.E.; Firpo, V.V.; Salmassi, T.M.; Khachikian, C.S.; Foster, K.L. Detection of hypophosphite, phosphite, and orthophosphate in natural geothermal water by ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1039, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, E.; Crutchfield, J.; Vandiviere, M. Rapid, sensitive, microscale determination of phosphate in water and soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 2206–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maguire, R.O.; Sims, J.T. Soil testing to predict phosphorus leaching. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.D. Soil phosphorus saturation ratio for risk assessment in land use systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dari, B.; Nair, V.D.; Colee, J.; Harris, W.G.; Mylavarapu, R. Estimation of phosphorus isotherm parameters: A simple and cost-effective procedure. Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mylavarapu, R.; Miller, R. Mehlich-1. Soil test methods from the Southeastern United States. In Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin No. 419; Clemson University: Clemson, SC, USA, 2014; pp. 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, D.; Ritchie, G.; Anderson, G.; Deeley, D. Phosphorus leaching in sandy soils. I. Short-term effects of fertilizer applications and environmental conditions. Soil Res. 1988, 26, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, H.; Bergström, L.; Djodjic, F.; Ulén, B.; Kirchmann, H. Topsoil and subsoil properties influence phosphorus leaching from four agricultural soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastisse, E. Sub-surface applications of fertilizer phosphorus in soils. Compte Rendu Hebd. Seances L’academie Sci. 1970, 271, 1820–1822. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.A.; Velayudhan, K.; Vasu, K.; Ramachandran, V.; Bhai, R.S.; Unnikrishnan, G. Interaction of potassium phosphonate fungicide in laterite soil. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2005, 47, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cline, M.G. Origin of the term Latosol. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1975, 39, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlin, J.L.; Schlegel, A.J. Review of Phosphite as a Plant Nutrient and Fungicide. Soil Syst. 2021, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohoulande, C.D.; Stone, K.; Szogi, A.; Bauer, P. An investigation of seasonal precipitation patterns for rainfed agriculture in the Southeastern region of the United States. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacinski, G.; Konetzka, W.A. Bacterial oxidation of orthophosphite. J. Bacteriol. 1966, 91, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, B. Phosphite in Soil and Turfgrass. Master’s Thesis, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schroetter, S.; Angeles-Wedler, D.; Kreuzig, R.; Schnug, E. Effects of phosphite on phosphorus supply and growth of corn (Zea mays). Landbauforsch. Volkenrode 2006, 56, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Pandeya, D.; Campbell, L.M.; Nunes, E.; Lopez-Arredondo, D.L.; Janga, M.R.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; Rathore, K.S. ptxD gene in combination with phosphite serves as a highly effective selection system to generate transgenic cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 95, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
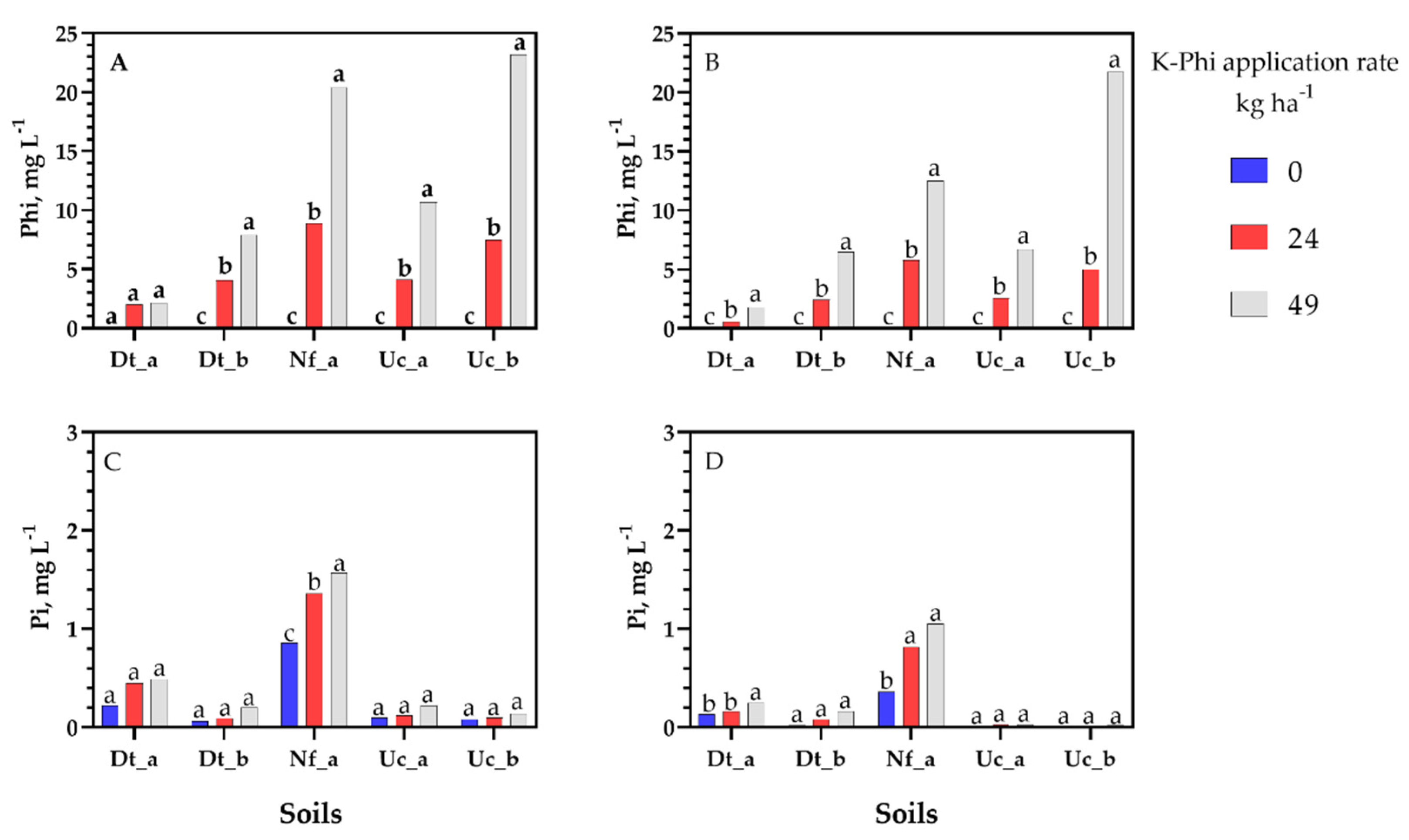


| Soil 1 | Depth | Sand | Silt | Clay | Soil C | pH | CEC 2 | M1-Pi 3 | Ca | Mg | Sorption | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi | Phi | |||||||||||
| cm | % | % | % | g kg−1 | cmolc kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||
| Dt_a | 0–15 | 66 | 18 | 16 | 13.4 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 25 | 466 | 79 | 98.0 | 95.5 |
| Dt_b | 15–30 | 81 | 10 | 9 | 7.4 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 12 | 502 | 107 | 70.6 | 77.8 |
| Nf_a | 0–15 | 79 | 16 | 5 | 7.0 | 5.9 | 4.6 | 21 | 402 | 50 | 42.0 | 43.9 |
| Uc_a | 0–15 | 91 | 6 | 3 | 8.7 | 4.7 | 3.3 | 6 | 67 | 11 | 78.1 | 93.6 |
| Uc_b | 15–30 | 91 | 6 | 3 | 1.5 | 5.0 | 1.6 | 4 | 37 | 7 | 72.2 | 37.1 |
| Soil 1 | DW | Mehlich 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS 2 | S 3 | Recovery | NS | S | Recovery | |
| mg L−1 | mg L−1 | % | mg L−1 | mg L−1 | % | |
| Dt_a | 0.85 | 6.01 | 97 | 1.39 | 6.31 | 101 |
| Dt_b | 1.19 | 6.26 | 98 | 1.44 | 6.56 | 98 |
| Nf_a | 1.63 | 6.64 | 99 | 1.85 | 6.98 | 98 |
| Uc_a | 1.13 | 6.29 | 97 | 1.86 | 7.29 | 93 |
| Uc_b | 1.49 | 6.52 | 99 | 2.16 | 7.42 | 96 |
| WSP | Mehlich 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Regression line | Regression coefficient (R2) | Regression line | Regression coefficient (R2) |
| Dt_a | y = 0.30x − 0.19 | 0.83 | y = 1.34x − 34.8 | 0.88 |
| Dt_b | y = 0.91x − 0.53 | 0.91 | y = 0.17x − 6.5 | 0.85 |
| Nf_a | y = 1.7x − 6.5 | 0.93 | y = 0.67x − 9.6 | 0.96 |
| Uc_a | y = 1.0x + 1.1 | 0.74 | y = 0.66x − 2.5 | 0.83 |
| Uc_b | y = 3.0x − 2.7 | 0.92 | y = 1.77x − 17.2 | 0.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szogi, A.A.; Shumaker, P.D.; Billman, E.D.; Bauer, P.J. Leaching Potential of Phosphite Fertilizer in Sandy Soils of the Southern Coastal Plain, USA. Environments 2021, 8, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110126
Szogi AA, Shumaker PD, Billman ED, Bauer PJ. Leaching Potential of Phosphite Fertilizer in Sandy Soils of the Southern Coastal Plain, USA. Environments. 2021; 8(11):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110126
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzogi, Ariel A., Paul D. Shumaker, Eric D. Billman, and Philip J. Bauer. 2021. "Leaching Potential of Phosphite Fertilizer in Sandy Soils of the Southern Coastal Plain, USA" Environments 8, no. 11: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110126
APA StyleSzogi, A. A., Shumaker, P. D., Billman, E. D., & Bauer, P. J. (2021). Leaching Potential of Phosphite Fertilizer in Sandy Soils of the Southern Coastal Plain, USA. Environments, 8(11), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110126







