Microplastic Contamination in Freshwater Environments: A Review, Focusing on Interactions with Sediments and Benthic Organisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Firstly, the main sources, formation mechanisms, and accumulation routes in freshwater systems will be presented;
- -
- The main impacts of MPs in freshwater systems observed in recent studies will be exposed;
- -
- In the central part of the paper, the ecotoxicology of MPs in freshwater systems will be discussed, focusing on the main issues for sediments and the benthic community, which are poorly understood;
- -
- The most used sampling and analytical techniques will be presented, analysing their advantages and drawbacks;
- -
- Finally, the future perspectives for MP studies to understand impacts, especially on freshwater sediments and benthic biota, will be presented.
2. From Plastic to Microplastic (MP): Sources and Aquatic Environments
3. Microplastics in Surface Freshwater Systems
MPs in Rivers, A Major Route for MP Transport
4. Ecotoxicology of MPs in Freshwater
4.1. MPs in Freshwater Food Webs
4.2. Interaction of MPs with Micropollutants
4.3. Ecotoxicological Effects of MPs on Benthic Organisms
5. Sampling and Analysis of Environmental MPs
5.1. Sampling of Floating MPs and Those Along the Water Column
5.2. Sampling of Beaches and Sediments
5.3. Sampling of Biota
5.4. Sample Processing
5.4.1. Separation of MPs from the Inorganic Matrix
5.4.2. Removal of Organic Matter
5.5. Qualification and Quantification of MPs
6. Future Perspectives in Microplastic Research for Freshwaters
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivleva, N.P.; Wiesheu, A.C.; Niessner, R. Microplastic in Aquatic Ecosystems. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1720–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and societal benefits of plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: Evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, C.M.; Jensen, O.P.; Mason, S.A.; Eriksen, M.; Williamson, N.J. High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
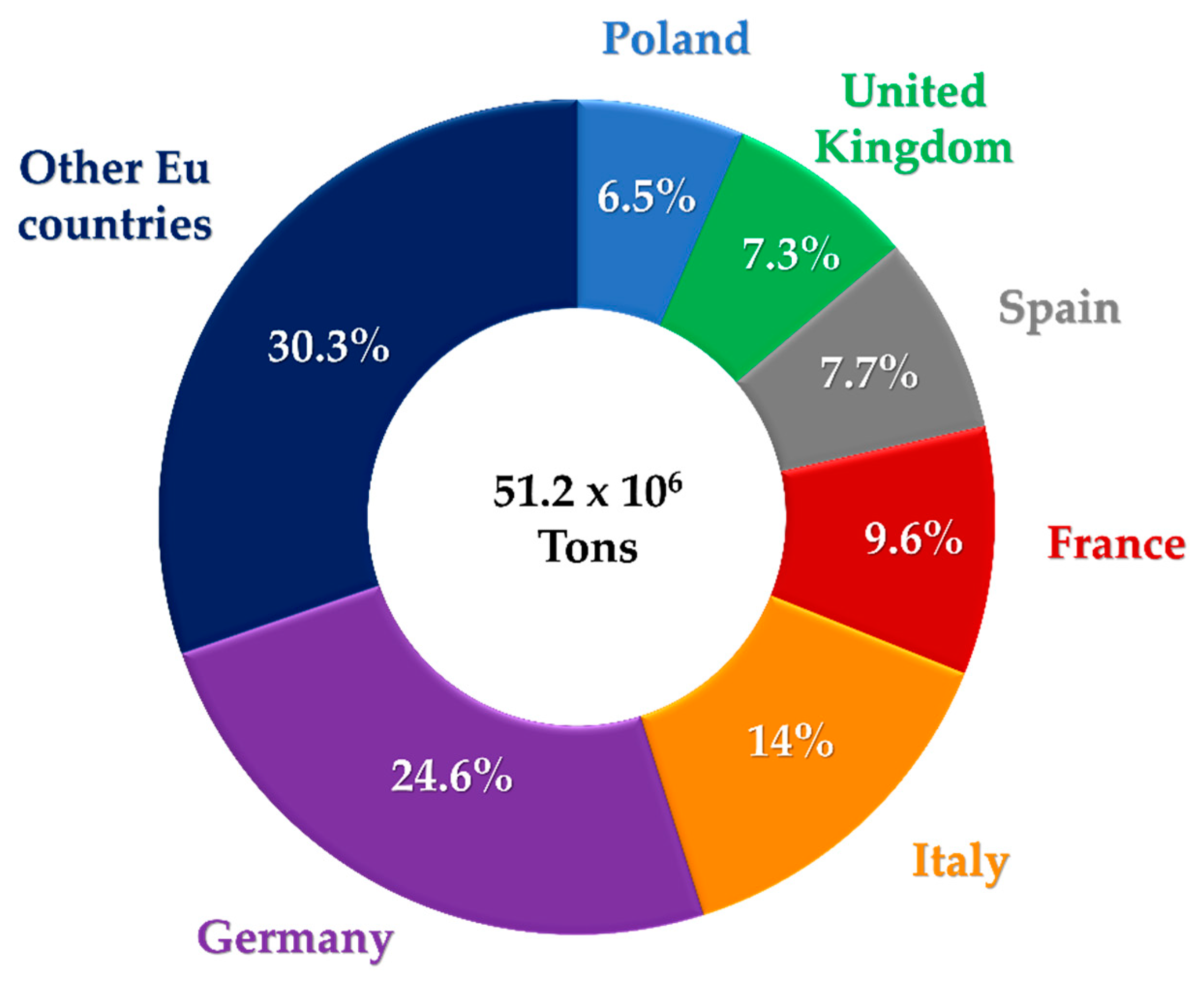
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics—The Facts 2018. Available online: https://www.plasticseurope.org/it/resources/publications/619-plastics-facts-2018 (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Hammer, J.; Kraak, M.H.S.; Parsons, J.R. Plastics in the Marine Environment: The Dark Side of a Modern Gift. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781461434146. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.; Scherer, C.; Alvarez-Muñoz, D.; Brennholt, N.; Bourrain, X.; Buchinger, S.; Fries, E.; Grosbois, C.; Klasmeier, J.; Marti, T.; et al. Microplastics in freshwater ecosystems: What we know and what we need to know. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2014, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S. Microplastics in Freshwater Systems: Analysis, Occurrence, and Sorption of Organic Contaminants. Ph.D. Dissertation, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Paul Chen, J. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaibachi, R.; Callaghan, A. Impact of polystyrene microplastics on Daphnia magna mortality and reproduction in relation to food availability. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, F.; Corbaz, M.; Baecher, H.; De Alencastro, L.F. Pollution due to plastics and microplastics in lake Geneva and in the Mediterranean sea. Arch. des Sci. 2012, 65, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zbyszewski, M.; Corcoran, P.L. Distribution and degradation of fresh water plastic particles along the beaches of Lake Huron, Canada. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2011, 220, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eubeler, J.P.; Zok, S.; Bernhard, M.; Knepper, T.P. Environmental biodegradation of synthetic polymers I. Test methodologies and procedures. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.C.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.J.; Shim, W.J. Estimation of lost tourism revenue in Geoje Island from the 2011 marine debris pollution event in South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lithner, D.; Damberg, J.; Dave, G.; Arsson, Å. Leachates from plastic consumer products—Screening for toxicity with Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, Y.; Takada, H.; Mizukawa, K.; Hirai, H.; Iwasa, S.; Endo, S.; Mato, Y.; Saha, M.; Okuda, K.; Nakashima, A.; et al. International Pellet Watch: Global monitoring of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in coastal waters. 1. Initial phase data on PCBs, DDTs, and HCHs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: Sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blettler, M.C.M.; Abrial, E.; Khan, F.R.; Sivri, N.; Espinola, L.A. Freshwater plastic pollution: Recognizing research biases and identifying knowledge gaps. Water Res. 2018, 143, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Zhou, B.; Lu, Y.H.; Yin, Y.; Zong, Y.Q.; Chen, M.T.; O’Donnell, Z. A review of microplastics in sediments: Spatial and temporal occurrences, biological effects, and analytic methods. Quat. Int. 2019, 519, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Ru, S.; Liu, X. High levels of microplastic pollution in the sediments and benthic organisms of the South Yellow Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Alsina, M.A.; Yuen, J.; Packman, A.I.; Gaillard, J.F. Effects of resuspension on the mobility and chemical speciation of zinc in contaminated sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlekat, C.E.; Decho, A.W.; Chandler, G.T. Bioavailability of particle-associated silver, cadmium, and zinc to the estuarine amphipod Leptocheirus plumulosus through dietary ingestion. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Gutow, L.; Klages, M. Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; ISBN 9783319165103. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, R.M. Micro- and Nanoplastic Pollution of Freshwater and Wastewater Treatment Systems. Springer Sci. Rev. 2017, 5, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syberg, K.; Khan, F.R.; Selck, H.; Palmqvist, A.; Banta, G.T.; Daley, J.; Sano, L.; Duhaime, M.B. Microplastics: Addressing ecological risk through lessons learned. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.; Ewins, C.; Carbonnier, F.; Quinn, B. Wastewater Treatment Works (WwTW) as a Source of Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5800–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Imhof, H.; Sanchez, W.; Gasperi, J.; Galgani, F.; Tassin, B.; Laforsch, C. Beyond the ocean: Contamination of freshwater ecosystems with (micro-)plastic particles. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepp, R.G.; Erickson, D.J.; Paul, N.D.; Sulzberger, B. Effects of solar UV radiation and climate change on biogeochemical cycling: Interactions and feedbacks. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2011, 10, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Rowe, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion decreases energy reserves in marine worms. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R1031–R1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan Kole, P.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Ragas, A.M.J. Wear and tear of tyres: A stealthy source of microplastics in the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment—A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.E.; Fernandes, J.N.; David, L.M. Key issues for sustainable urban stormwater management. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6787–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, T.; Hauk, A.; Walter, U.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics profile along the Rhine River. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, P.K.; Fok, L. Characterisation of plastic microbeads in facial scrubs and their estimated emissions in Mainland China. Water Res. 2017, 122, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.A.; Garneau, D.; Sutton, R.; Chu, Y.; Ehmann, K.; Barnes, J.; Fink, P.; Papazissimos, D.; Rogers, D.L. Microplastic pollution is widely detected in US municipal wastewater treatment plant effluent. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gies, E.A.; LeNoble, J.L.; Noël, M.; Etemadifar, A.; Bishay, F.; Hall, E.R.; Ross, P.S. Retention of microplastics in a major secondary wastewater treatment plant in Vancouver, Canada. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Sui, Q.; Lyu, S.; Wang, D.; Zhao, W. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the urban river across the megacity Shanghai: Occurrence, source apportionment and a snapshot of influence of rainfall. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzetto, L.; Futter, M.; Langaas, S. Are Agricultural Soils Dumps for Microplastics of Urban Origin? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10777–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Saad, M.; Mirande, C.; Tassin, B. Synthetic fibers in atmospheric fallout: A source of microplastics in the environment? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “plastisphere”: Microbial communities on plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forum, W.E. The Fourth Industrial Revolution. In Proceedings of the World Economic Forum Annual Meeting 2016, Davos-Klosters, Switzerland, 20–23 January 2016; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olson, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, R.E. The Complex Interaction between Marine Debris and Toxic Chemicals in the Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12302–12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Úbeda, B.; Hernández-León, S.; Palma, Á.T.; Navarro, S.; García-de-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuelle, M.; Dekiff, J.H.; Remy, D.; Fries, E. A new analytical approach for monitoring microplastics in marine sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Lambert, S. Freshwater Microplastics; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9783319616148. [Google Scholar]
- Imhof, H.K.; Ivleva, N.P.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Laforsch, C. Contamination of beach sediments of a subalpine lake with microplastic particles. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R867–R868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, F.; Demars, C.; Wieser, O.; Kunz, M.; De Alencastro, L.F. Plastic pollution in Swiss surface waters: Nature and concentrations, interaction with pollutants. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.K.; Paglialonga, L.; Czech, E.; Tamminga, M. Microplastic pollution in lakes and lake shoreline sediments—A case study on Lake Bolsena and Lake Chiusi (central Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sighicelli, M.; Pietrelli, L.; Lecce, F.; Iannilli, V.; Falconieri, M.; Coscia, L.; Di, S.; Nuglio, S.; Zampetti, G. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of Italian Subalpine Lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legambiente Microplastiche nelle acque interne italiane: Le indagini della Goletta dei Laghi di Legambiente ed Enea. 2018. Available online: https://www.legambiente.it/sites/default/files/docs/microplastiche_nei_laghi_2016-2017_legambiente-enea.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2020).
- Kataoka, T.; Nihei, Y.; Kudou, K.; Hinata, H. Assessment of the sources and inflow processes of microplastics in the river environments of Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, K.L.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Maximenko, N.A.; Proskurowski, G.; Peacock, E.E.; Hafner, J.; Reddy, C.M. Plastic accumulation in the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Science 2010, 329, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, P.L. Benthic plastic debris in marine and fresh water environments. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegerbaeumer, A.; Mueller, M.-T.T.; Fueser, H.; Traunspurger, W. Impacts of Micro- and Nano-Sized Plastic Particles on Benthic Invertebrates: A Literature Review and Gap Analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, L.C.M.; Van Der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrady, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Krauth, T.; Wagner, S. Export of Plastic Debris by Rivers into the Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12246–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Marine Plastic Debris and Microplastics: Global Lessons and Research to Inspire Action and Guide Policy Change; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016; ISBN 9210601602. [Google Scholar]
- Lechner, A.; Keckeis, H.; Lumesberger-Loisl, F.; Zens, B.; Krusch, R.; Tritthart, M.; Glas, M.; Schludermann, E. The Danube so colourful: A potpourri of plastic litter outnumbers fish larvae in Europe’s second largest river. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 188, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Wal, M.; Van Der Meulen, M.; Tweehuijsen, G.; Peterlin, M.; Palatinus, A.; Kovač Viršek, M.; Coscia, L.; Kržan, A. Identification and Assessment of Riverine Input of (Marine) Litter; European Commission: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Wang, T.; Li, D. Suspended microplastics in the surface water of the Yangtze Estuary System, China: First observations on occurrence, distribution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, S.S.; Thompson, R.C. On the quantity and composition of floating plastic debris entering and leaving the Tamar Estuary, Southwest England. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, J.; Dris, R.; Bonin, T.; Rocher, V.; Tassin, B. Assessment of floating plastic debris in surface water along the Seine River. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 195, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Svendsen, C.; Williams, R.; Spurgeon, D.; Lahive, E. Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames, UK—Abundance, sources and methods for effective quantification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, A.; Rees, A.; Rowe, R.; Stevens, J.; Wright, P. Microplastics in the Solent estuarine complex, UK: An initial assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.A.; Brandsma, S.H.H.; van Velzen, M.J.M.J.M.; Vethaak, A.D.D. Microplastics en route: Field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GESAMP. Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection Sources. In Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Global Assessment; Reports Stud.; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2015; Volume 90, p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Yonkos, L.T.; Friedel, E.A.; Perez-Reyes, A.C.; Ghosal, S.; Arthur, C.D. Microplastics in Four Estuarine Rivers in the Chesapeake Bay, U.S.A. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14195–14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.R.; Lewis, C.; Goodhead, R.M.; Beckett, S.J.; Moger, J.; Tyler, C.R.; Galloway, T.S. Uptake and retention of microplastics by the shore crab carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8823–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, C.D.; Löder, M.G.J.; Fricke, N.F.; Lang, T.; Griebeler, E.M.; Janke, M.; Gerdts, G. Plastic ingestion by pelagic and demersal fish from the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.; Gilbert, B.; Compère, P.; Eppe, G.; Das, K.; Jauniaux, T.; Parmentier, E. Microplastics in livers of European anchovies (Engraulis encrasicolus, L.). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, R.S.; Maiztegui, T.; Colautti, D.C.; Paracampo, A.H.; Gómez, N. Microplastics in gut contents of coastal freshwater fish from Río de la Plata estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, N.C.; Gallardo, C.; Lenz, M.; Thiel, M. Capture, swallowing, and egestion of microplastics by a planktivorous juvenile fish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordós, G.; Urbányi, B.; Micsinai, A.; Kriszt, B.; Palotai, Z.; Szabó, I.; Hantosi, Z.; Szoboszlay, S. Identification of microplastics in fish ponds and natural freshwater environments of the Carpathian basin, Europe. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slootmaekers, B.; Catarci Carteny, C.; Belpaire, C.; Saverwyns, S.; Fremout, W.; Blust, R.; Bervoets, L. Microplastic contamination in gudgeons (Gobio gobio) from Flemish rivers (Belgium). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, J.S. Improving microplastic research. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2019, 6, 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Potential for Plastics to Transport Hydrophobic Contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7759–7764. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.J.; Warrack, S.; Langen, V.; Challis, J.K.; Hanson, M.L.; Rennie, M.D. Microplastic contamination in Lake Winnipeg, Canada. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B. Investigating microplastics bioaccumulation and biomagnification in seafood from the Persian Gulf: A threat to human health? Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolandhasamy, P.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Qu, X.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H. Adherence of microplastics to soft tissue of mussels: A novel way to uptake microplastics beyond ingestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.R.; Urbina, M.A.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Lewis, C.; Galloway, T.S. Effect of Microplastic on the Gills of the Shore Crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5364–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, A.; Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M.; Kamermans, P.; Koelmans, A.A. Effects of nanopolystyrene on the feeding behavior of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2490–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lusher, A.L.; Rotchell, J.M.; Deudero, S.; Turra, A.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Sun, C.; Shahadat Hossain, M.; Li, Q.; Kolandhasamy, P.; et al. Using mussel as a global bioindicator of coastal microplastic pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Ecology, Epidemiology, and Evolution of Parasitism in Daphnia; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2005; ISBN 1932811060. [Google Scholar]
- DeMott, W.R. The role of taste in food selection by freshwater zooplankton. Oecologia 1986, 69, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, S.; Yuyama, M.; Takada, H. Desorption kinetics of hydrophobic organic contaminants from marine plastic pellets. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velzeboer, I.; Kwadijk, C.J.A.F.; Koelmans, A.A. Strong sorption of PCBs to nanoplastics, microplastics, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4869–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, L.M.; Jones, P.R.; Moore, C.; Narayan, U.V. Quantitation of persistent organic pollutants adsorbed on plastic debris from the Northern Pacific Gyre’s “eastern garbage patch”. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, J. Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products to polyethylene debris. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8819–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H. Adsorption of antibiotics on microplastics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Santos-Echeandía, J.; Rocha-Santos, T. Significance of interactions between microplastics and POPs in the marine environment: A critical overview. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J. Different partition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon on environmental particulates in freshwater: Microplastics in comparison to natural sediment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, J.F.M.; Shashoua, Y.; Syberg, K.; Khan, F.R. Considerations on the use of equilibrium models for the characterisation of HOC-microplastic interactions in vector studies. Chemosphere 2018, 210, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascall, M.A.; Zabik, M.E.; Zabik, M.J.; Hernandez, R.J. Uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) from an aqueous medium by polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polystyrene films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Transport of persistent organic pollutants by microplastics in estuarine conditions. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 140, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Wegner, A.; Foekema, E.M. Plastic as a carrier of POPs to aquatic organisms: A model analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7812–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Jürgens, M.D.; Lahive, E.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Vijver, M.G. The influence of exposure and physiology on microplastic ingestion by the freshwater fish Rutilus rutilus (roach) in the River Thames, UK. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, L.; Rogers, E.; Altin, D.; Salaberria, I.; Booth, A.M. Sorption of PAHs to microplastic and their bioavailability and toxicity to marine copepods under co-exposure conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verla, A.W.; Enyoh, C.E.; Verla, E.N.; Nwarnorh, K.O. Microplastic–toxic chemical interaction: A review study on quantified levels, mechanism and implication. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Velis, C.A.; Weber, R.; Iacovidou, E.; Purnell, P. An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munier, B.; Bendell, L.I. Macro and micro plastics sorb and desorb metals and act as a point source of trace metals to coastal ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R.; Syberg, K.; Shashoua, Y.; Bury, N.R. Influence of polyethylene microplastic beads on the uptake and localization of silver in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, K.; Holmes, L.; Turner, A. Association of metals with plastic production pellets in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedolin, M.C.; Teophilo, C.Y.S.; Turra, A.; Figueira, R.C.L. Spatial variability in the concentrations of metals in beached microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradney, L.; Wijesekara, H.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Obadamudalige, N.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Kirkham, M.B. Particulate plastics as a vector for toxic trace-element uptake by aquatic and terrestrial organisms and human health risk. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 104937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Lo, H.S.; Wong, H.M.; Zhou, M.; Wong, C.Y.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Cheung, S.G. Heavy metals contamination of sedimentary microplastics in Hong Kong. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennecke, D.; Duarte, B.; Paiva, F.; Caçador, I.; Canning-Clode, J. Microplastics as vector for heavy metal contamination from the marine environment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 178, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Lang, M.; Yu, X.; Wu, R.; Yang, X.; Guo, X. Aging mechanism of microplastics with UV irradiation and its effects on the adsorption of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, V.; Blázquez, G.; Calero, M.; Quesada, L.; Martín-Lara, M.A. The potential of microplastics as carriers of metals. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Heavy metal fractions and ecological risk assessment in sediments from urban, rural and reclamation-affected rivers of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Livio, F.; Piasini, P.; Zhang, C. Anomalously high concentration of Ni as sulphide phase in sediment and in water of a mountain catchment with serpentinite bedrock. J. Geochemical Explor. 2018, 190, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Livio, F. An integrated interdisciplinary approach to evaluate potentially toxic element sources in a mountainous watershed. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A. Mobilisation kinetics of hazardous elements in marine plastics subject to an avian physiologically-based extraction test. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Holmes, L.A. Adsorption of trace metals by microplastic pellets in fresh water. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, X. Adsorption of three bivalent metals by four chemical distinct microplastics. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, C.; Morin, M.; Bendell, L.I. The influence of cosmetic microbeads on the sorptive behavior of cadmium and lead within intertidal sediments: A laboratory study. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triebskorn, R.; Braunbeck, T.; Grummt, T.; Hanslik, L.; Huppertsberg, S.; Jekel, M.; Knepper, T.P.; Krais, S.; Müller, Y.K.; Pittroff, M.; et al. Relevance of nano- and microplastics for freshwater ecosystems: A critical review. TrAC - Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.A.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic as a Vector for Chemicals in the Aquatic Environment: Critical Review and Model-Supported Reinterpretation of Empirical Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Qiao, R.; An, H.; Zhang, Y. Influence of microplastics on the accumulation and chronic toxic effects of cadmium in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 202, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xia, T.; Qi, Y.; Yao, Y.; Guo, X.; Ji, R.; Chen, W. Polystyrene Nanoplastics-Enhanced Contaminant Transport: Role of Irreversible Adsorption in Glassy Polymeric Domain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2677–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R.; Boyle, D.; Chang, E.; Bury, N.R. Do polyethylene microplastic beads alter the intestinal uptake of Ag in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)? Analysis of the MP vector effect using in vitro gut sacs. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorakis, S.; Drouillard, K.G. Effect of Microplastic Amendment to Food on Diet Assimilation Efficiencies of PCBs by Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10796–10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieg, H.; Huppertsberg, S.; Knepper, T.P.; Krais, S.; Reitter, K.; Rezbach, F.; Ruhl, A.S.; Köhler, H.-R.; Triebskorn, R. Polystyrene microplastics do not affect juvenile brown trout (Salmo trutta f. fario) or modulate effects of the pesticide methiocarb. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, V.A.; Bakir, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Assessment of microplastic-sorbed contaminant bioavailability through analysis of biomarker gene expression in larval zebrafish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Jin, S.-R.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Gao, J.-Z.; Liu, Y.-N.; Liu, J.-H.; Feng, X.-S. Single and combined effects of microplastics and cadmium on the cadmium accumulation, antioxidant defence and innate immunity of the discus fish (Symphysodon aequifasciatus). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.; Traunspurger, W. The effects of predation by juvenile fish on the meiobenthic community structure in a natural pond. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 2392–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettinetti, R.; Quadroni, S.; Boggio, E.; Galassi, S. Recent DDT and PCB contamination in the sediment and biota of the Como Bay (Lake Como, Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzella, L.M.; Novati, S.; Casatta, N.; Roscioli, C.; Valsecchi, L.; Binelli, A.; Parolini, M.; Solcà, N.; Bettinetti, R.; Manca, M.; et al. Spatial and temporal trends of target organic and inorganic micropollutants in Lake Maggiore and Lake Lugano (Italian-Swiss water bodies): Contamination in sediments and biota. Hydrobiologia 2018, 824, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väinölä, R.; Witt, J.D.S.; Grabowski, M.; Bradbury, J.H.; Jazdzewski, K.; Sket, B. Global diversity of amphipods (Amphipoda; Crustacea) in freshwater. In Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 241–255. [Google Scholar]
- Berglund, E.; Fogelberg, V.; Nilsson, P.A.; Hollander, J. Microplastics in a freshwater mussel (Anodonta anatina) in Northern Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: Effects of fabric type and washing conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blarer, P.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics affect assimilation efficiency in the freshwater amphipod Gammarus fossarum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23522–23532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannilli, V.; Pasquali, V.; Setini, A.; Corami, F. First evidence of microplastics ingestion in benthic amphipods from Svalbard. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, S.; Hirsch, P.E.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Biodegradable and petroleum-based microplastics do not differ in their ingestion and excretion but in their biological effects in a freshwater invertebrate Gammarus fossarum. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Falahudin, D.; Peeters, E.T.H.M.; Koelmans, A.A. Microplastic Effect Thresholds for Freshwater Benthic Macroinvertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2278–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec, A.; Horvat, P.; Kunej, U.; Bele, M.; Kržan, A. Uptake and effects of microplastic textile fibers on freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseling, E.; Wegner, A.; Foekema, E.M.; van den Heuvel-Greve, M.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Effects of Microplastic on Fitness and PCB Bioaccumulation by the Lugworm Arenicola marina (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziajahromi, S.; Kumar, A.; Neale, P.A.; Leusch, F.D.L. Environmentally relevant concentrations of polyethylene microplastics negatively impact the survival, growth and emergence of sediment-dwelling invertebrates. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, C.B.; Won, E.J.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, M.C.; Hwang, D.S.; Hwang, U.K.; Zhou, B.; Souissi, S.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.S. Microplastic Size-Dependent Toxicity, Oxidative Stress Induction, and p-JNK and p-p38 Activation in the Monogonont Rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, S.; Gagné, F.; André, C.; Della Torre, C.; Auclair, J.; Hanana, H.; Parenti, C.C.; Bonasoro, F.; Binelli, A. Evaluation of uptake and chronic toxicity of virgin polystyrene microbeads in freshwater zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomer, J.; Müller, M.F.; Barcelona, A.; Serra, T. Mediated food and hydrodynamics on the ingestion of microplastics by Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wu, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, Z.; Shi, H.; Raley-Susman, K.M.; He, D. Microplastic particles cause intestinal damage and other adverse effects in zebrafish Danio rerio and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.Y.; Bruce, T.F.; Bridges, W.C.; Klaine, S.J. Responses of Hyalella azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Laforsch, C. Hazardous or not—Are adult and juvenile individuals of Potamopyrgus antipodarum affected by non-buoyant microplastic particles? Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qu, M.; Wong, G.; Wang, D. Transgenerational toxicity of nanopolystyrene particles in the range of μg L-1 in the nematode: Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Khan, F.R. Ecotoxicology of micronized tire rubber: Past, present and future considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, F.; Kochleus, C.; Bänsch-Baltruschat, B.; Brennholt, N.; Reifferscheid, G. Sampling techniques and preparation methods for microplastic analyses in the aquatic environment—A review. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermsen, E.; Mintenig, S.M.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A. Quality Criteria for the Analysis of Microplastic in Biota Samples: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10230–10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masura, J.; Baker, J.; Foster, G.; Arthur, C. Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015.
- Ng, K.L.; Obbard, J.P. Prevalence of microplastics in Singapore’s coastal marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Bao, L.J.; Shi, L.; Wong, C.S.; Zeng, E.Y. A review of methods for measuring microplastics in aquatic environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11319–11332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianello, A.; Boldrin, A.; Guerriero, P.; Moschino, V.; Rella, R.; Sturaro, A.; Da Ros, L. Microplastic particles in sediments of Lagoon of Venice, Italy: First observations on occurrence, spatial patterns and identification. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 130, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebezeit, G.; Dubaish, F. Microplastics in beaches of the East Frisian Islands Spiekeroog and Kachelotplate. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claessens, M.; Cauwenberghe, L.V.; Vandegehuchte, M.B.; Janssen, C.R. New techniques for the detection of microplastics in sediments and field collected organisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L.; Welden, N.A.; Sobral, P.; Cole, M. Sampling, isolating and identifying microplastics ingested by fish and invertebrates. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, H.K.; Schmid, J.; Niessner, R.; Ivleva, N.P.; Laforsch, C. A novel, highly efficient method for the separation and quantification of plastic particles in sediments of aquatic environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto da Costa, J.; Reis, V.; Paço, A.; Costa, M.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Micro(nano)plastics—Analytical challenges towards risk evaluation. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsing, S.; Kochleus, C.; Buchinger, S.; Brennholt, N.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. A new approach in separating microplastics from environmental samples based on their electrostatic behavior. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, R.R.; Lusher, A.L.; Olsen, M.; Nizzetto, L. Validation of a Method for Extracting Microplastics from Complex, Organic-Rich, Environmental Matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7409–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foekema, E.M.; De Gruijter, C.; Mergia, M.T.; van Franeker, J.A.; Murk, A.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Plastic in North Sea Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8818–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Tahir, A.; Williams, S.L.; Baxa, D.V.; Lam, R.; Miller, J.T.; Teh, F.C.; Werorilangi, S.; Teh, S.J. Anthropogenic debris in seafood: Plastic debris and fibers from textiles in fish and bivalves sold for human consumption. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Experimental development of a new protocol for extraction and characterization of microplastics in fish tissues: First observations in commercial species from Adriatic Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.J.; Hong, S.H.; Eo, S.E. Identification methods in microplastic analysis: A review. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagg, A.S.; Sapp, M.; Harrison, J.P.; Ojeda, J.J. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics in Wastewater Using Focal Plane Array-Based Reflectance Micro-FT-IR Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6032–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Thomas, K.V.; Luo, Z.; Gowen, A.A. FTIR and Raman imaging for microplastics analysis: State of the art, challenges and prospects. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käppler, A.; Fischer, D.; Oberbeckmann, S.; Schernewski, G.; Labrenz, M.; Eichhorn, K.-J.; Voit, B. Analysis of environmental microplastics by vibrational microspectroscopy: FTIR, Raman or both? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8377–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, A.; Gerdts, G.; Völker, C.; Niebühr, V. Using FTIRS as pre-screening method for detection of microplastic in bulk sediment samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, C.F.; Nolasco, M.M.; Ribeiro, A.M.P.; Ribeiro-Claro, P.J.A. Identification of microplastics using Raman spectroscopy: Latest developments and future prospects. Water Res. 2018, 142, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-M.; Wagner, J.; Ghosal, S.; Bedi, G.; Wall, S. SEM/EDS and optical microscopy analyses of microplastics in ocean trawl and fish guts. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, M.E.; Duffus-Hodson, C.A.; Clark, A.; Prendergast-Miller, M.T.; Thorpe, K.L. Plastic Bag Derived-Microplastics as a Vector for Metal Exposure in Terrestrial Invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4714–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C. Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments and organisms of the Western Pacific Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, M.; Guerranti, C.; Blašković, A. Microplastic contents from maricultured and natural mussels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

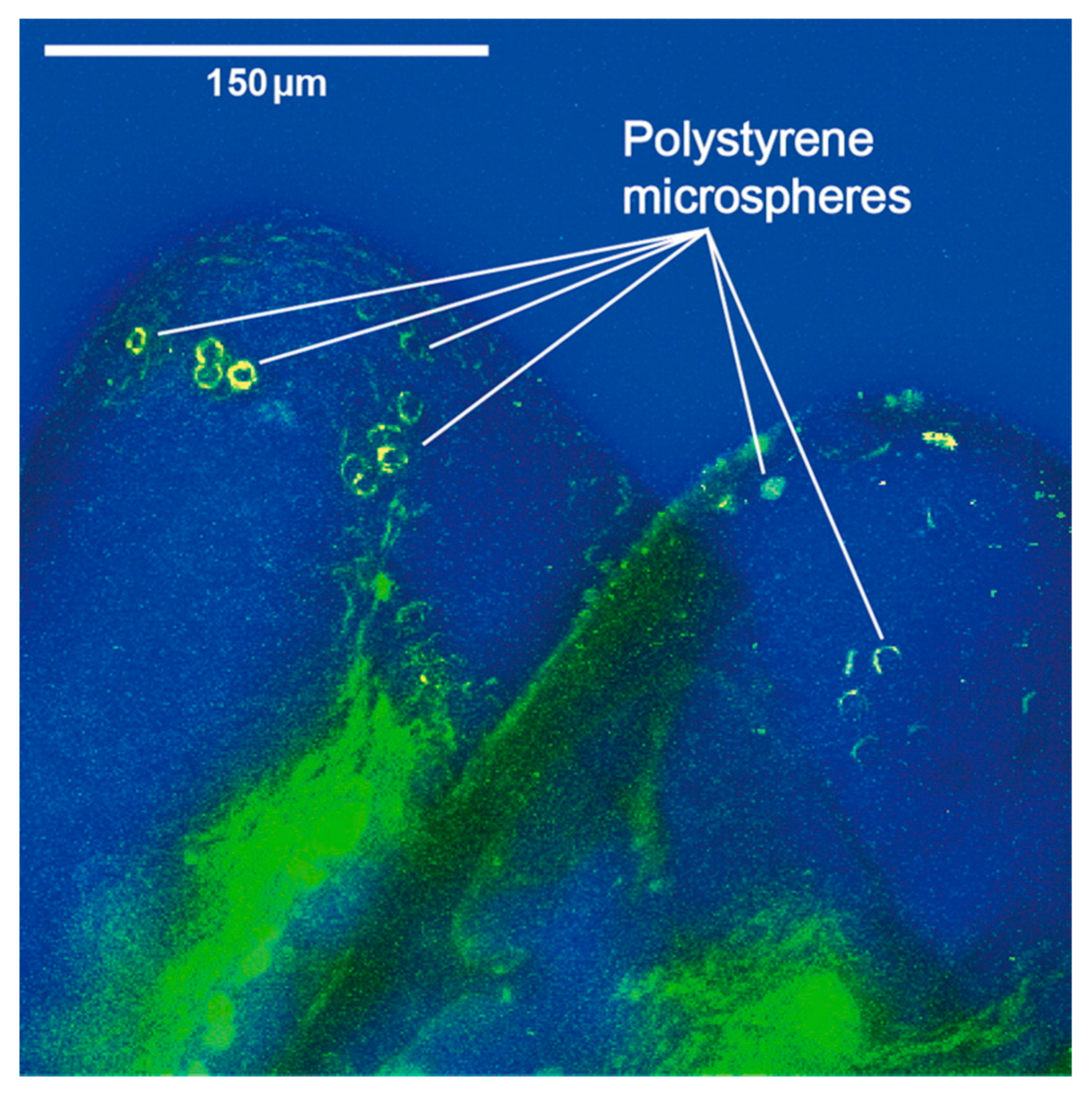
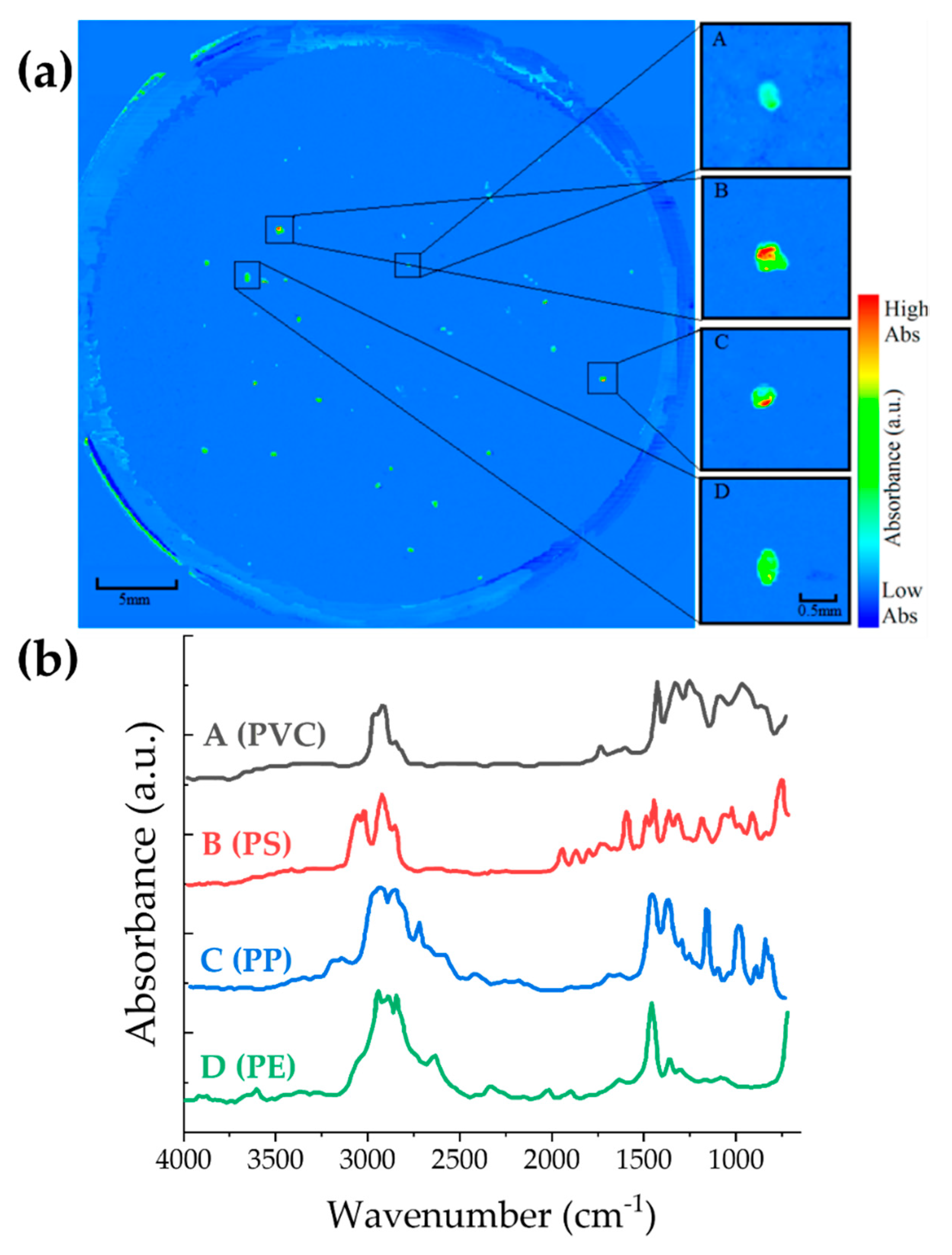
| LAKES | WATER | SEDIMENTS | REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Garda | 2.5 × 10⁴ ± 14,900 p/m² | 1108 ± 983 p/m² (north) 108 ± 55 p/m² (south) | Imhof et al., 2013 [53]; Sighicelli et al., 2018 [56] |
| Maggiore | 3.83 × 10⁴ ± 20,666 p/m² | average: 1100 ± 2300 p/m² min–max: 20–6900 p/m² | Faure et al., 2015 [54]; Sighicelli et al., 2018 [56] |
| Iseo | 4.04 × 10⁴ ± 20,333 p/m² | Sighicelli et al., 2018 [56] | |
| Geneva | 4.81 × 104 p/km2 | average: 2100 ± 2000 p/m² min–max: 78–5000 p/m² | Faure et al., 2012 [14]; Faure et al., 2015 [54] |
| Constance | 61,000 ± 12,000 p/km2 | average: 320 ± 220 p/m² min–max: 140–620 p/m² | Faure et al., 2015 [54] |
| Neuchâtel | 61,000 ± 24,000 p/km2 | average: 700 ± 1100 p/m² min–max: 67–2300 p/m² | Faure et al., 2015 [54] |
| Zurich | 11,000 ± 2600 p/km2 | average: 460 ± 350 p/m² min–max: 89–800 p/m² | Faure et al., 2015 [54] |
| Brienz | 36,000 ± 23,000 p/km2 | average: 2500 ± 3000 p/m² min–max: 89–7200 p/m² | Faure et al., 2015 [54] |
| Bolsena | - | 1922 ± 662 p/m² | Fischer et al., 2016 [55] |
| Chiusi | - | 2117 ± 695 p/m² | Fischer et al., 2016 [55] |
| LOCATION | COMPARTMENT | MPs DENSITIES | REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Danube river, Austria, Europe | Surface water | Average: 0.3168 ± 4.6646 p/m3 | Lechner et al., 2014 [66] |
| Rhine river, Germany, Europe | Surface water | Average: 892,777 ± 1,063,042 p/km2 | Mani et al., 2015 [37] |
| Rhine river, Germany, Europe | Sediment | Min–max: 1784–30,106 p/m2 | Klein et al., 2015 [10] |
| Seine river, France, Europe | Surface Water | Min–max: 0.28–0.47 p/m3 | Dris et al., 2015 [31] |
| Po river, Italy, Europe | Surface water | Average: 2,043,069.8 ± 336,637.4 p/km2 | Van der Walt et al., 2015 [67] |
| Tamar Estuary, United Kingdom, Europe | Surface water | 0.028 p/m3 | Sadri and Thompson, 2014 [69] |
| Thames river, United Kingdom, Europe | Sediment | Min–max: 18.5 ± 4.2–66 ± 7.7 p/100 g | Horton et al., 2017 [71] |
| ORDER | SPECIES | POLYMER | UPTAKE | EGESTION | PARAMETER | EFFECTS | REFERENCES |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphipoda | Gammarus fossarum | PMMA 1 | + | 1-Feeding rate 2-Assimilation efficiency 3-Weight change | 1-No sign. effect 2-Decrease of efficiency 3-Weight loss | Straub et al., 2017 [141] | |
| Diptera | Chironomus tepperi | PE | + | 1-Survival 2-Growth 3-Emergence rate | 1-MP size-dependent 2-MP size-dependent 3-Decrease from 90% to 17.5% | Ziajahromi et al., 2018 [145] | |
| Myida | Dreissena polymorpha | PS | + | 1-Cellular stress 2-Oxidative damage 3-Neurogenotoxicity | 1-No sign. effect 2-Increase of CAT 1and decrease of GPx 2 3-Increase of DOP 3 | Magni et al., 2018 [147] | |
| Cladocera | Daphnia magna | PS | + | 1-Filtration capacity | 1-Decrease of filtration capacity | Colomer et al., 2019 [148] | |
| Amphipoda | Gammarus pulex | PS | + | 1-Mortality 2-Growth 3-Feeding rate | 1-No sign. effect 2-Reduction in size 3-No sign. effect | Redondo-Hasselerharm et al., 2018 [142] | |
| Amphipoda | Hyalella azteca | PS | - | - | 1-Mortality 2-Growth 3-Feeding rate | 1-No sign. effect 2-No sign. effect 3-No sign. effect | Redondo-Hasselerharm et al., 2018 [142] |
| Isopoda | Asellus aquaticus | PS | 1-Mortality 2-Growth 3-Feeding rate | 1-No sign. effect 2-No sign. effect 3-No sign. effect | Redondo-Hasselerharm et al., 2018 [142] | ||
| Sferida | Sphaerium corneum | PS | 1-Mortality 2-Growth 3-Feeding rate | 1-No sign. effect 2-No sign. effect 3-No sign. effect | Redondo-Hasselerharm et al., 2018 [142] | ||
| Lumbriculidae | Lumbriculus variegatus | PS | + | 1-Mortality 2-Growth 3-Feeding rate | 1-No sign. effect 2-No sign. effect 3-No sign. effect | Redondo-Hasselerharm et al., 2018 [142] | |
| Oligochaeta | Tubifex spp. | PS | + | 1-Mortality 2-Growth 3-Feeding rate | 1-No sign. effect 2-No sign. effect 3-No sign. effect | Redondo-Hasselerharm et al., 2018 [142] | |
| Rhabditidae | Caenorhabditis elegans | PA, PE, PP, PVC, PS | + | 1-Mortality 2-Body length 3-Reproduction 4-Intestinal Ca levels | 1-Sign. effect (size-related for PVC and PS) 2-Reduction 3-Inhibition 4-Decrease (concentration-related for PS) | Lei et al., 2018 [149] | |
| Amphipoda | Gammarus fossarum | PA and PS | + | + (PA) | 1-Assimilation efficiency 2-Feeding rate 3-Weight change 4-Mortality | 1-Reduced for PA. No effect for PS 2-No sign. effect 3-No sign. effect 4-Increase | Blarer et al., 2016 [139] |
| Unionida | Anodonta anatina | Microfibers, PA | + | Berglund et al., 2019 [137] | |||
| Amphipoda | Hyalella azteca | PE and PP | + | + | 1-Mortality 2-Growth 3-Reproduction (PE) | 1-Dose-dependent 2-No sign effect (PE). Dose-dependent (PP) 3-decrease | Au et al., 2015 [150] |
| Littorinimorpha | Potamopyrgus antipodarum | 1-Mortality 2-Dimension 3-Reproduction 4-Embryos without shell | 1-No sign. Effect 2-Decrease in juveniles 3-No sign. Effect 4- No sign. effect | Imhof and Laforsch, 2016 [151] | |||
| Rhabditidae | Caenorhabditis elegans | nanoPS | + | + | 1-Intestinal ROS 4 production 2-Locomotion behaviour 3-Brood size 4-Intestinal permeability | 1-Increase 2-Decrease 3-Reduction of size 4-Increase | Zhao et al., 2017 [152] |
| Cladocera | Daphnia magna | PET | + | 1-Mortality 2-Growth | 1-Higher in non-pre-feeders 2-No sign. effect | Jemec et al., 2016 [143] |
| Characteristics | FT-IR | RAMAN SPECTROSCOPY |
|---|---|---|
| Typology | Spectroscopic technique | Spectroscopic technique |
| Operation mode | Absorption of IR radiation | Inelastic scattering of monochromatic light |
| Source of light | Laser | Laser |
| Range of light | Infrared | UV, visible, NIR |
| Detection limit | 10–20 µm | 1 µm |
| Visual response | Spectra | Spectra |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellasi, A.; Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Galafassi, S.; Volta, P.; Bettinetti, R. Microplastic Contamination in Freshwater Environments: A Review, Focusing on Interactions with Sediments and Benthic Organisms. Environments 2020, 7, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7040030
Bellasi A, Binda G, Pozzi A, Galafassi S, Volta P, Bettinetti R. Microplastic Contamination in Freshwater Environments: A Review, Focusing on Interactions with Sediments and Benthic Organisms. Environments. 2020; 7(4):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellasi, Arianna, Gilberto Binda, Andrea Pozzi, Silvia Galafassi, Pietro Volta, and Roberta Bettinetti. 2020. "Microplastic Contamination in Freshwater Environments: A Review, Focusing on Interactions with Sediments and Benthic Organisms" Environments 7, no. 4: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7040030
APA StyleBellasi, A., Binda, G., Pozzi, A., Galafassi, S., Volta, P., & Bettinetti, R. (2020). Microplastic Contamination in Freshwater Environments: A Review, Focusing on Interactions with Sediments and Benthic Organisms. Environments, 7(4), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7040030








