Statistical Analysis of Nutrient Loads from the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin (MARB) to the Gulf of Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
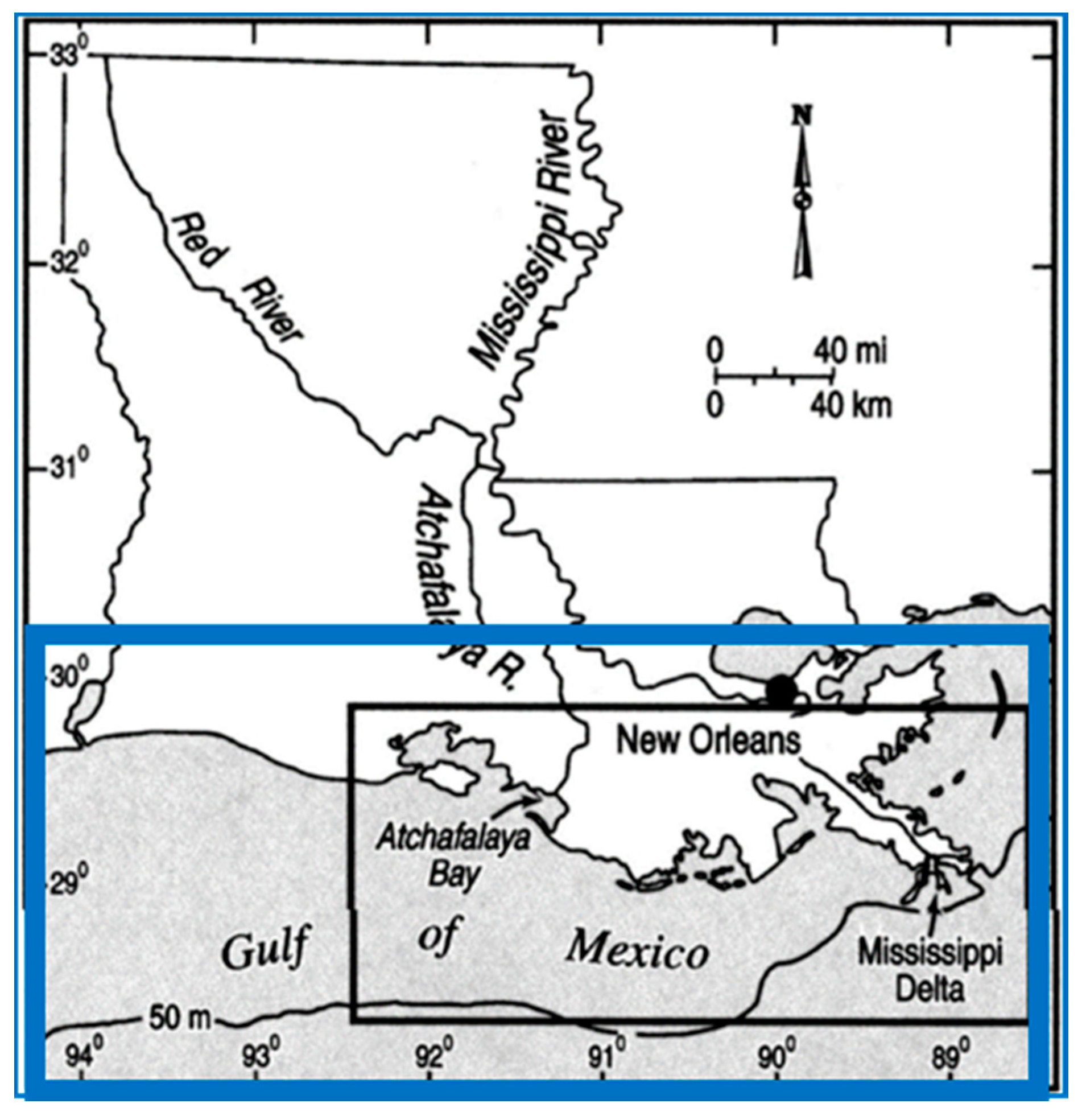
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.3. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
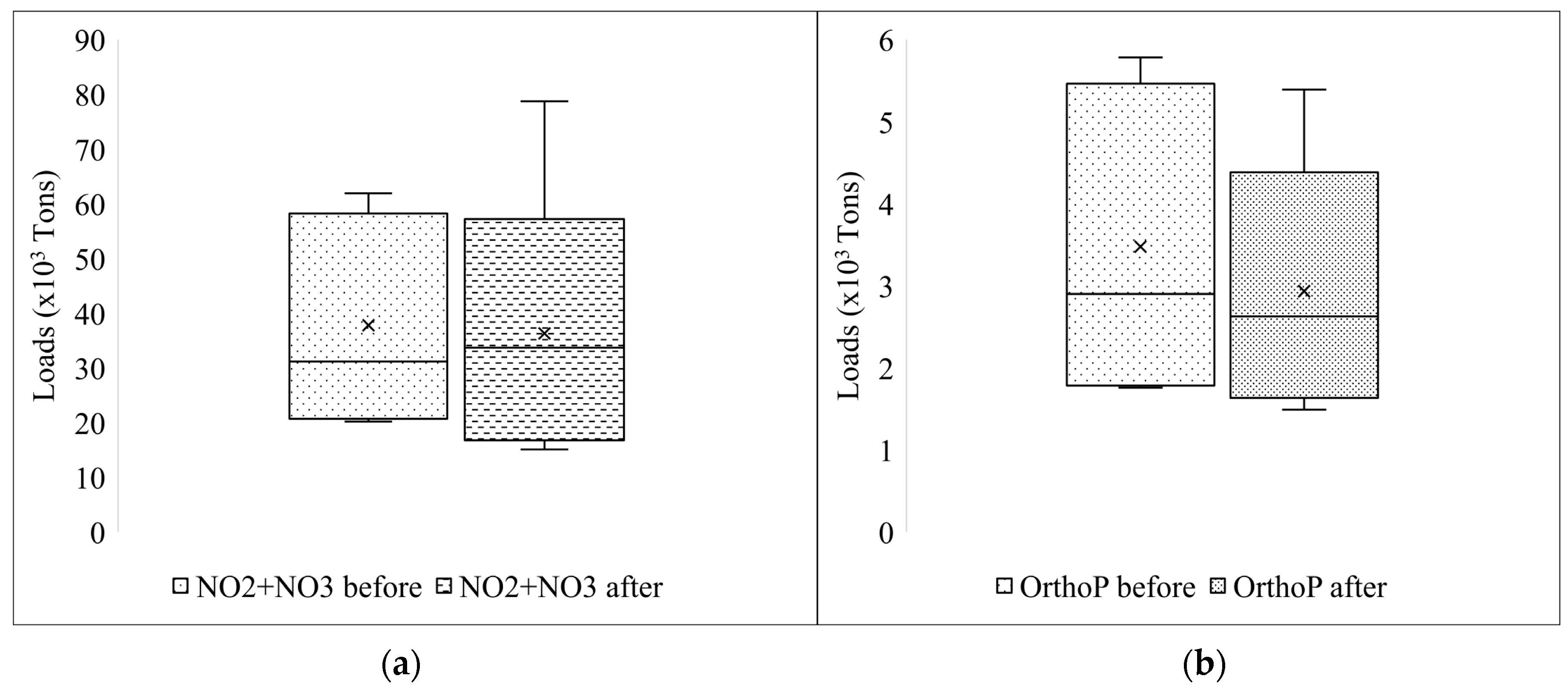
3.1. Annual Variation
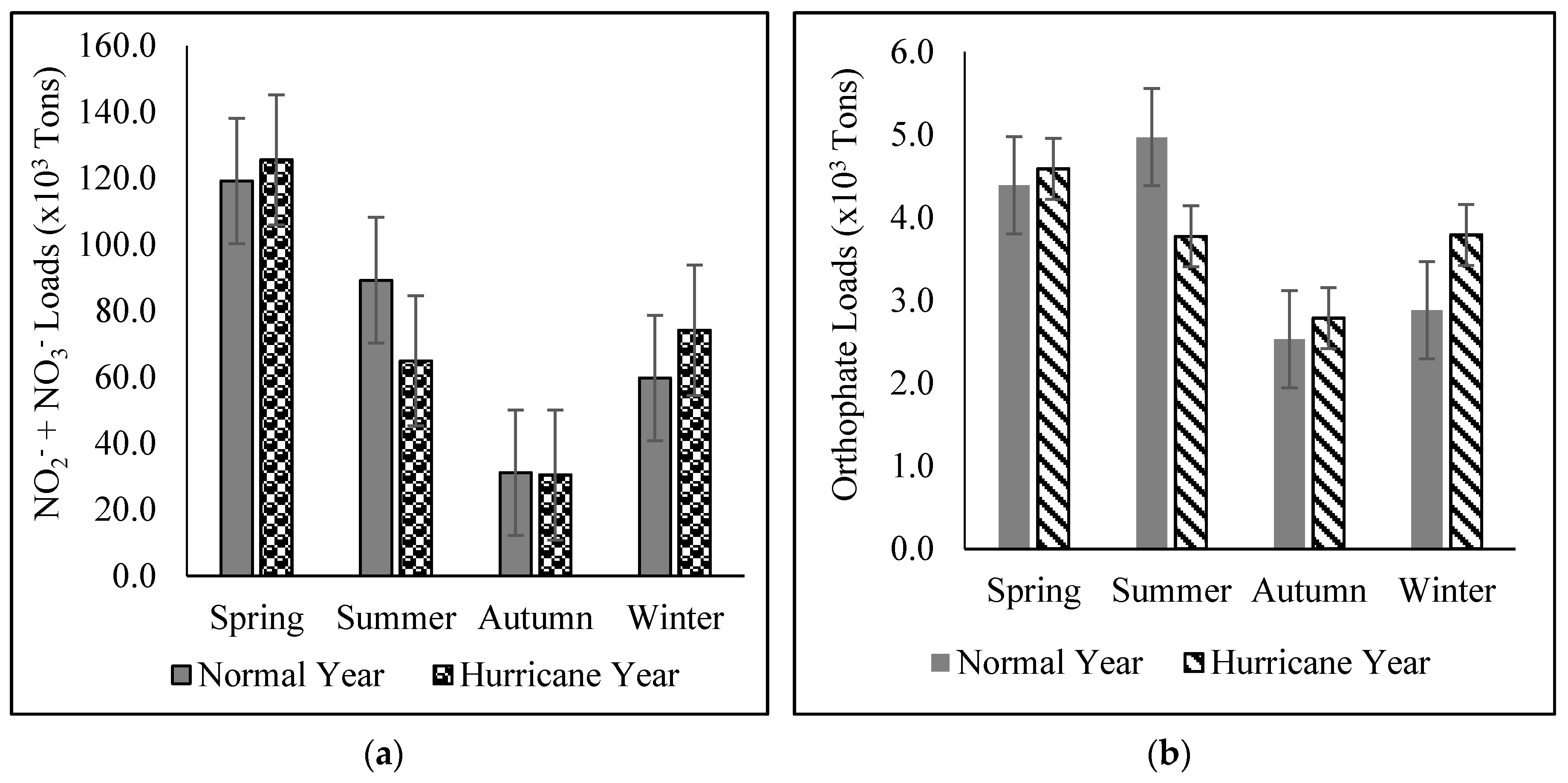
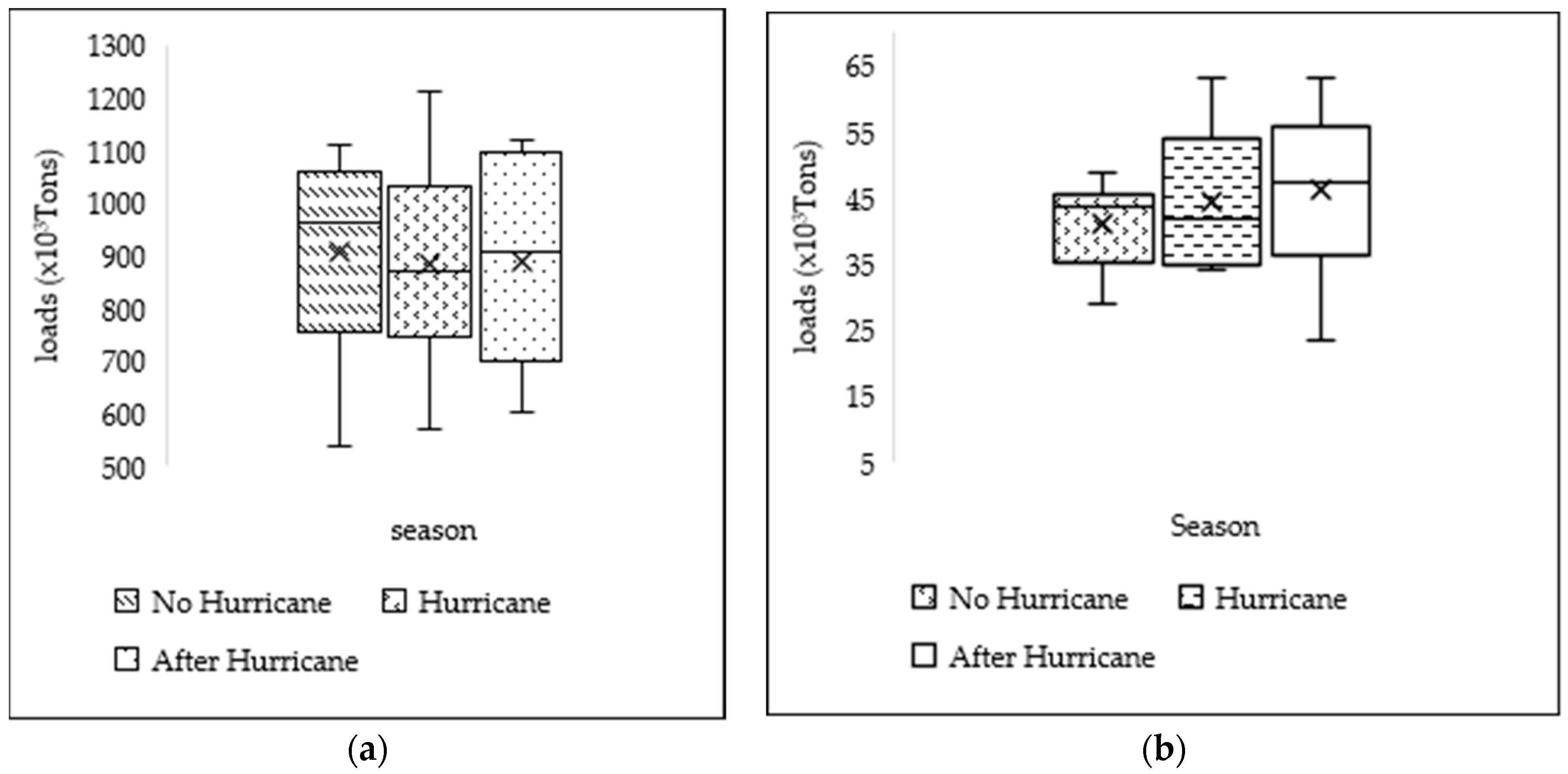
3.2. Seasonal Variation
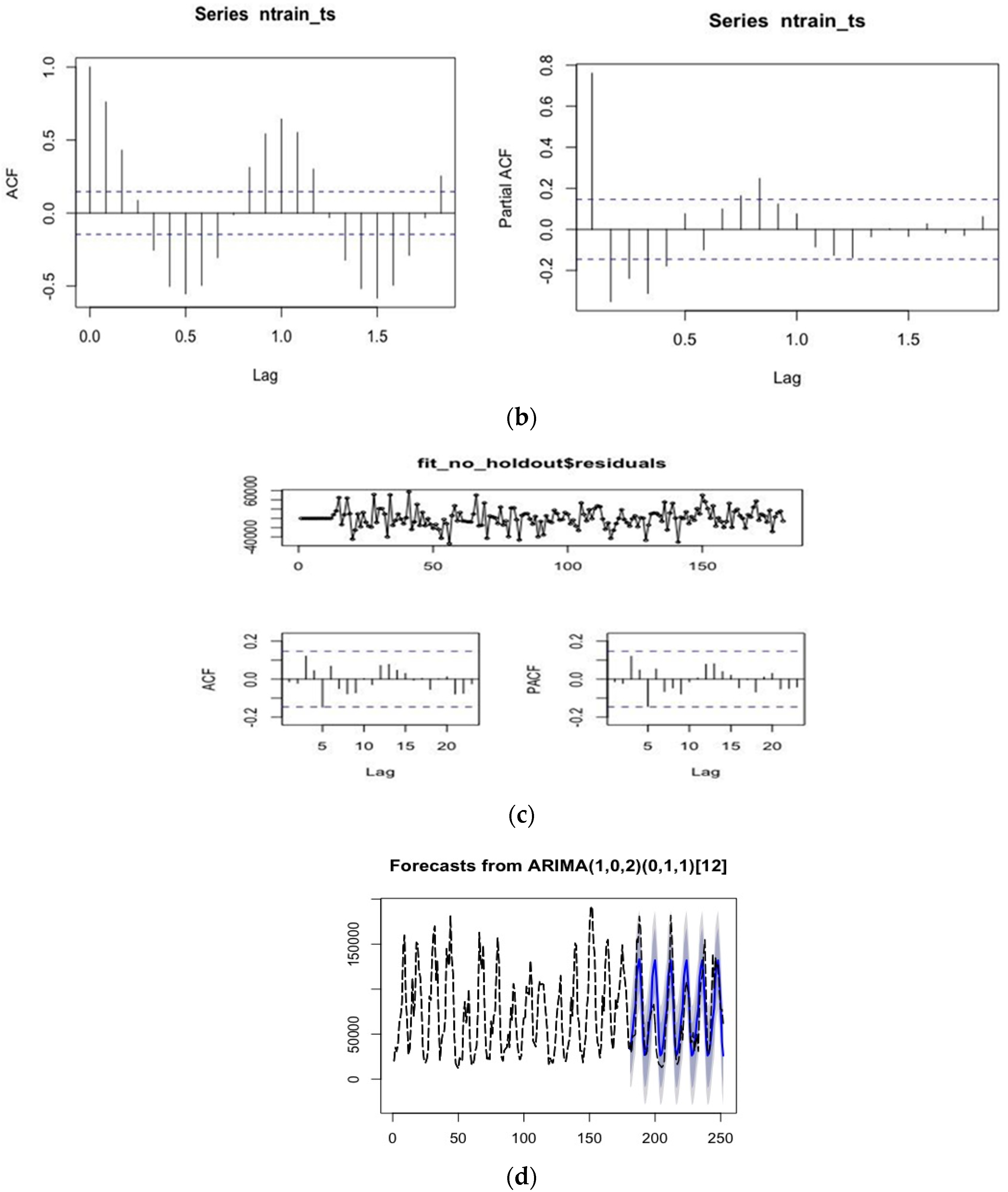
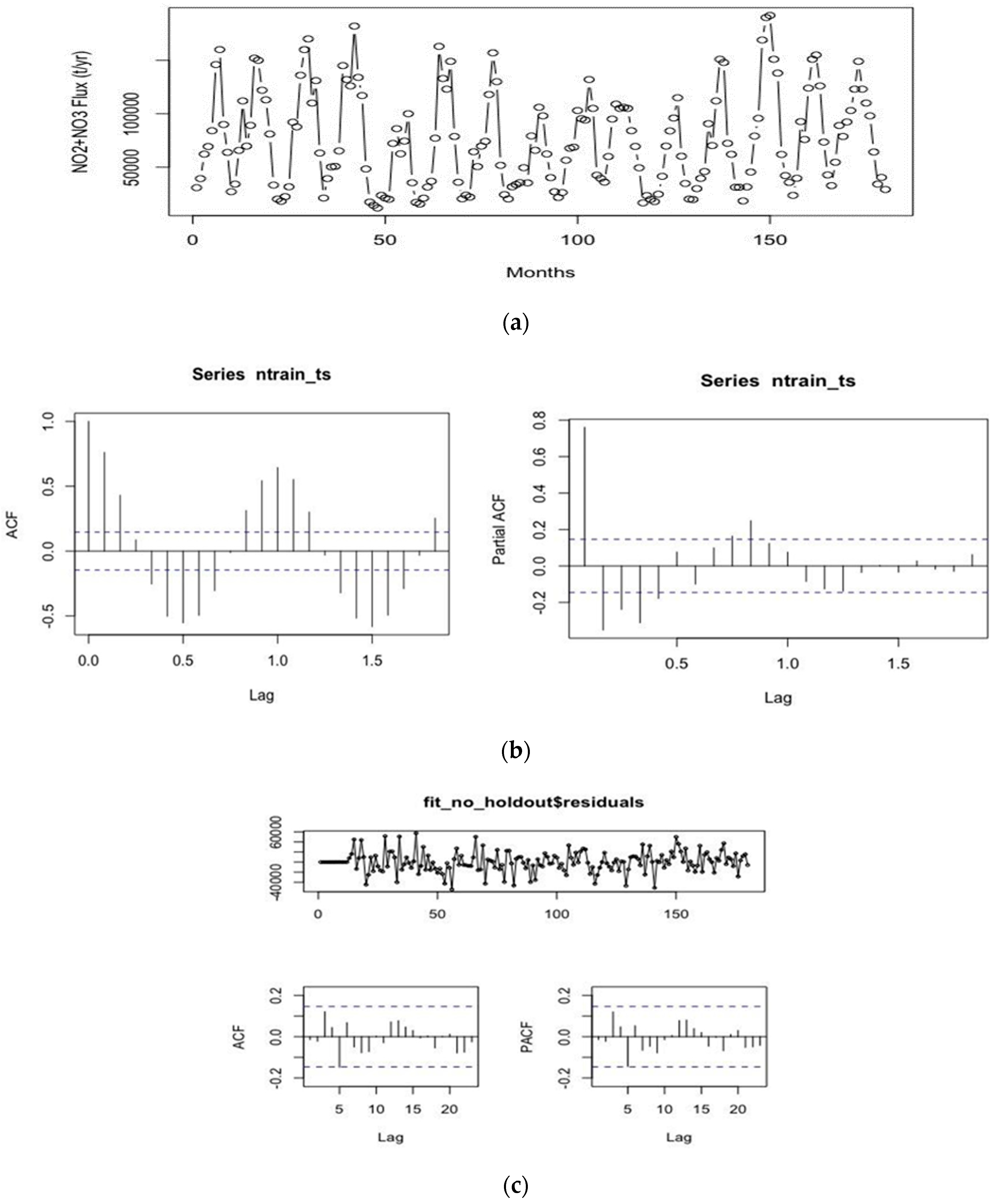
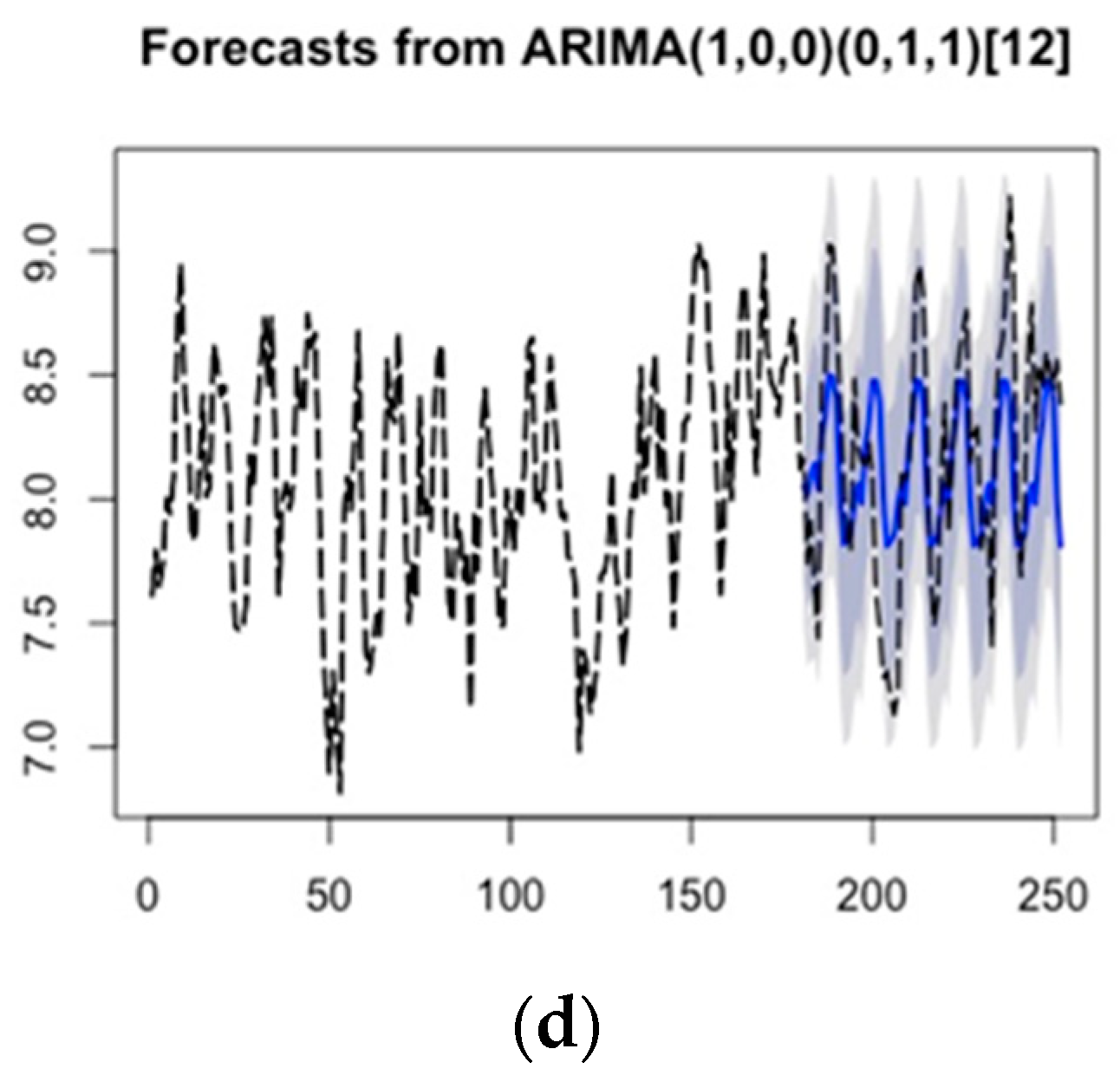
3.3. Nutrient Load Prediction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, J.L.; Feng, H.; Nie, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Witherell, B.B. Characterisation and assessment of spatiotemp oral variations in nutrient concentrations and fluxes in an urban watershed: Passaic River Basin, New Jersey, USA. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 63, 154–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.; Santos, A.; Callejo’n, M.; Jime’nez, J. Speciation as a screening tool for the determination of heavy metal surface water pollution in the Guadiamar River basin. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Takara, K.; Luo, P.; Nover, D.; Sahu, N.; Yamashiki, Y. Spatiotemporal evaluation of water quality incidents in Japan between 1996 and 2007. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagó, A.; Bouraoui, F.; Grizzetti, B.; De Roo, A. Modelling nutrient fluxes into the Mediterranean Sea. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 22, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabotyagov, S.; Campbell, T.; Jha, M.; Gassman, P.W.; Arnold, J.; Kurkalova, L.; Kling, C.L. Least-cost control of agricultural nutrient contributions to the Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 1542–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabotyagov, S.S.; Campbell, T.D.; White, M.; Arnold, J.G.; Atwood, J.; Norfleet, M.L.; Turner, R.E. Cost-effective targeting of conservation investments to reduce the northern Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18530–18535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufford, D.L.; Samarghitan, C.L.; McKellar, H.N., Jr.; Porter, D.E.; Hussey, J.R. Impacts of urbanization on nutrient concentrations in small southeastern coastal streams 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 39, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzier, R.; Tusseau-Vuillemin, M.H.; dit Meriadec, C.M.; Rousselot, O.; Mouchel, J.M. Trace metal speciation and fluxes within a major French wastewater treatment plant: Impact of the successive treatments stages. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvelas, M.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Samara, C. Occurrence and fate of heavy metals in the wastewater treatment process. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Feng, H.; Witherell, B.B.; Alebus, M.; Mahajan, M.D.; Zhang, W.; Yu, L. Causes, Assessment, and Treatment of Nutrient (N and P) Pollution in Rivers, Estuaries, and Coastal Waters. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.B.; Smith, R.A.; Schwarz, G.E.; Boyer, E.W.; Nolan, J.V.; Brakebill, J.W. Differences in phosphorus and nitrogen delivery to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River Basin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, M.B.; Drinkwater, L.E.; McIsaac, G.F. Sources of nitrate yields in the Mississippi River Basin. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goolsby, D.A.; Battaglin, W.A. Long-term changes in concentrations and flux of nitrogen in the Mississippi River Basin, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1209–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goolsby, D.A.; Battaglin, W.A.; Lawrence, G.B.; Artz, R.S.; Aulenbach, B.T.; Hooper, R.P.; Stensland, G.J. Flux and Sources of Nutrients in the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin: Topic 3 Report for the Integrated Assessment on Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico. 1999. Available online: http://www.cop.noaa.gov/pubs/das/das17.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- McCasland, M.; Trautmann, N.M.; Wagenet, R.J. Nitrate: Health Effects in Drinking Water; Cornell Cooperative Extension: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Fennel, K.; Testa, J.M. Biogeochemical controls on coastal hypoxia. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2019, 11, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, D.B.; Chesney, E.J.; Munnelly, R.T.; Baltz, D.M.; Maiti, K. Trophic ecology of sheepshead and stone crabs at oil and gas platforms in the northern Gulf of Mexico’s hypoxic zone. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2019, 148, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Justic, D.; Dortch, Q.; Wiseman, W.J.; Gupta, B.K.S. Nutrient changes in the Mississippi River and system responses on the adjacent continental shelf. Estuaries 1996, 19, 386–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Justic, D.; Turner, R.E. Nutrient changes in the Mississippi River and system responses on the adjacent continental shelf. Oceanogr. Lit. Rev. 1997, 3, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Wiseman, W.J., Jr. Gulf of Mexico hypoxia, aka “The dead zone”. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Rabalais, N.N.; Justic, D. Gulf of Mexico hypoxia: Alternate states and a legacy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2323–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2018 Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Forecast. Available online: scavia.seas.umich.edu/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/2019-Gulf-of-Mexico-Hypoxic-Forecast.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Robertson, D.M.; Schwarz, G.E.; Saad, D.A.; Alexander, R.B. Incorporating uncertainty into the ranking of SPARROW model nutrient yields from Mississippi/Atchafalaya river basin watersheds. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 534–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelstet, A.R.; Gilmore, T.E.; Messer, T.; Rudnick, D.R.; Heatherly, T. Evaluationof selected watershed characteristics to identify best management practices to reduce Nebraskan nitrate loads from Nebraska to the Mississippi/Atchafalaya River basin. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 277, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meter, K.J.; Basu, N.B.; Van Cappellen, P. Two centuries of nitrogen dynamics: Legacy sources and sinks in the Mississippi and Susquehanna River Basins. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.J.; Santhi, C.; Kannan, N.; Arnold, J.G.; Harmel, D.; Norfleet, L.M.; Allen, P.; Diluzio, M.E.; Wang, X.; Atwood, J.D.; et al. Nutrient delivery from the Mississippi River to the Gulf of Mexico and effects of cropland conservation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, Y.; Gassman, P.W.; Jha, M.K.; Kling, C.L.; Campbell, T.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.G. A refined regional modeling approach for the Corn Belt—Experiences and recommendations for large-scale integrated modeling. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, Y.; Gassman, P.W.; Kling, C.L.; Cibin, R.; Chaubey, I. Water quality assessment of large-scale bioenergy cropping scenarios for the upper Mississippi and Ohio-Tennessee river basins. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2017, 53, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.M.; Saad, D.A. SPARROW models used to understand nutrient sources in the Mississippi/Atchafalaya River Basin. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 1422–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.M.; Saad, D.A.; Schwarz, G.E. Spatial Variability in Nutrient Transport by HUC 8, State, and Subbasin Based on Mississippi/Atchafalaya River Basin SPARROW Models. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 988–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.M.; Roberts, H.H.; Stone, G.W. Mississippi River delta: An overview. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 698–716. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, M.A.; Demas, C.R.; Ebersole, B.A.; Kleiss, B.A.; Little, C.D.; Meselhe, E.A.; Vosburg, B.M. A water and sediment budget for the lower Mississippi-Atchafalaya River in flood years 2008–2010: Implications for sediment discharge to the oceans and coastal restoration in Louisiana. J. Hydrol. 2012, 432, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, B.P. The Atchafalaya River Basin: History and ecology of an American wetland; Texas A&M University Press: University City, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A. New Orleans: Including Cajun Country and the River Road Plantations; Moon Travel: Chico, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pionke, H.B.; Gburek, W.J.; Schnabel, R.R.; Sharpley, A.N.; Elwinger, G.F. Seasonal flow, nutrient concentrations and loading patterns in stream flow draining an agricultural hill-land watershed. J. Hydrol. 1999, 220, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cao, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Xu, J. Seasonal variation, flux estimation, and source analysis of dissolved emerging organic contaminants in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, E.E.; Shurman, G.E.; Burwell, R.E. Seasonal runoff losses of nitrogen and phosphorus from Missouri valley loess water sheds. Environ. Qual. 1978, 7, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, L.B.; Edwards, W.M.; van Keuren, R.W. Baseflow and stormflow transport of nutrients from mixed agricultural watersheds. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Große, F.; Fennel, K.; Laurent, A. Quantifying the relative importance of riverine and open-ocean nitrogen sources for hypoxia formation in the northern Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 5451–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, I.C.; Dangremond, E.M.; Devlin, D.J.; Lovelock, C.E.; Proffitt, C.E.; Rodriguez, W. Nutrient enrichment intensifies hurricane impact in scrub mangrove ecosystems in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida, USA. Ecology 2015, 96, 2960–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Coefficients | ar1 | ma1 | ma2 | sma1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARIMA (1,0,2)(0,1,1)12 | 0.8013 | −0.1799 | −0.179 | −0.96 |
| s.e | 0.0913 | 0.1191 | 0.0981 | 0.226 |
| Coefficients | ar1 | sma1 |
|---|---|---|
| ARIMA(1,0,0)(0,1,1)12 | 0.7213 | −0.8996 |
| s.e | 0.0535 | 0.1021 |
| Nutrient Loads | Observation | Prediction |
|---|---|---|
| 1996–2016 | 2017–2022 | |
| NO2− + NO3− | 892 ± 192 | 1100 ± 22 |
| Orthophosphate | 44.3 ± 10.5 | 41.7 ± 5.25 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okwan, P.; Zhen, Y.; Feng, H.; Yoo, S.; Kambhampati, M.S.; Walker, A.; Boykin, S.; Omojola, J.; Blackburn, N. Statistical Analysis of Nutrient Loads from the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin (MARB) to the Gulf of Mexico. Environments 2020, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7010008
Okwan P, Zhen Y, Feng H, Yoo S, Kambhampati MS, Walker A, Boykin S, Omojola J, Blackburn N. Statistical Analysis of Nutrient Loads from the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin (MARB) to the Gulf of Mexico. Environments. 2020; 7(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkwan, Phyllis, Yi Zhen, Huan Feng, Shinjae Yoo, Murty S. Kambhampati, Abreione Walker, Shayne Boykin, Joe Omojola, and Noel Blackburn. 2020. "Statistical Analysis of Nutrient Loads from the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin (MARB) to the Gulf of Mexico" Environments 7, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7010008
APA StyleOkwan, P., Zhen, Y., Feng, H., Yoo, S., Kambhampati, M. S., Walker, A., Boykin, S., Omojola, J., & Blackburn, N. (2020). Statistical Analysis of Nutrient Loads from the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin (MARB) to the Gulf of Mexico. Environments, 7(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7010008






