Abstract
The majority of studies on biofilms have focused on autotrophic and bacterial taxa, without considering the potential effects on biofilm grazers. In this work, we investigated the effects of realistic environmental concentrations of zirconium (Zr) on periphyton algal growth and micromeiofauna biodiversity. Glass slides were submerged in a pond for four weeks to colonize biofilms and exposed for four weeks in aquaria to targeted Zr concentrations of 0, 1, and 10 nM, which were monitored over time (average measured concentrations were 0.2 ± 0.1, 0.5 ± 0.3, and 2.9 ± 0.3 nM Zr). The four-week exposure to the highest concentration (3 nM) affected the micromeiofauna structure of biofilms and modified the autotrophic biofilm structure by increasing the proportion of green algae and decreasing the abundance of cyanobacteria and brown algae. Rotifers and the ciliate Aspidisca cicada appeared to be the most sensitive organisms among the observed micromeiofauna. A toxic effect of Zr on rotifers could explain such results. Indirect effects, such as reduced food availability given the reduced algal growth in the presence of Zr, could also play a role in the changes of micromeiofauna community structure. These results are among the few published data on the effects of Zr.
1. Introduction
Increased global use of metals has led to an increase in metallic elements mobilized in aquatic systems in the last century. Although the effect of metals on freshwater ecosystems is well documented, studies on the impacts of tetravalent metals are very scarce. Zirconium (Zr) is a tetravalent element, predominantly found as zircon (ZrSiO4), and constitutes 0.023% of the earth’s crust. Measurements of surface water concentrations of Zr are scarce. Gobeil et al. (2005) found average dissolved Zr concentrations of 7 ± 5 ng·L−1 (0.08 ± 0.05 nM) to 22 ± 8 ng·L−1 (0.24 ± 0.09 nM) in the Saint Lawrence River (Canada). In the same study, Zr associated with suspended particulate matter showed concentrations one order of magnitude higher. Dissolved forms are generally present at concentrations of less than 1 nM due to the low solubility of the hydroxide Zr(OH)4 [1,2,3]. Australia and South Africa are the largest producers of Zr minerals in the world. The global demand for Zr has been steadily increasing in the last few decades due to its anticorrosive properties and for nuclear fuel cladding [4,5,6,7]. This element is also included in the composition of cosmetics and deodorants. In tetrachloride form (ZrCl4), it is used for phosphorus precipitation in water effluents [8]. All these activities may lead to an increase in Zr concentrations in natural freshwaters. Despite this, very few ecotoxicological studies have been performed on Zr uptake and effects on algal communities. Thus, it is important to understand its potential impact on aquatic ecosystems to contribute to the environmental risk assessment for this metal.
Several biomonitoring tools have been developed to assess metal exposure on aquatic organisms. In particular, periphyton (benthic microorganism communities) have shown promising potential [9,10,11]. These microorganisms are able to internalize and sequester metallic contaminants, which allows for the detection of ultra-trace elements up to several days after contamination events in natural freshwater ecosystems [12,13]. Periphytic diatoms react to contamination, eutrophication, and acidification, and are thus very useful for water quality monitoring, including metal impact assessment [14,15]. Diatom biochemical responses such as anti-oxidant enzymes and gene expressions related to oxidative stress can be also used to determine the effects of metal contamination on biofilm microorganisms [16,17,18]. The majority of studies on biofilms focus on autotrophic and bacterial taxa, without considering the effect of contamination on biofilm grazers. When studied, the only grazers considered are macroinvertebrates [19] or fish [20], while grazing microbes are rarely considered [21]. However, micromeiofauna communities represent important aquatic ecosystem components which play a key role in the biofilm food web [22,23]. Some microorganisms can also have effects on bacterial activity by excreting growth-stimulating compounds [24,25]. Contamination impacts on micromeiofauna can disturb trophic food webs and the taxonomic structure of periphytic biofilm.
In this work, we investigated the effect of realistic environmental concentrations of Zr on periphyton algal growth and micromeiofauna biodiversity to better understand the impacts of this metal on the taxonomic structure of the biofilm. The results obtained will help to improve the use of periphytic biofilms as a contamination assessment tool for zirconium and to better understand its potential impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
Glass slides of 220 cm2 were submerged in Gazinet-Cestas Pond, France (South West France, geographical coordinates: 44°46′30.1′′ N, 0°41′44.3′′ W), for 4 weeks in October 2016 for periphyton to colonize. The slides were then randomly distributed to three aquaria containing a synthetic culture medium (Dauta) [26]. Targeted Zr concentrations were 0 nM (C0), 1 nM (C1), and 10 nM (C10), which do not exceed the Zr solubility limit (Log Ksp = −62.46 ± 0.10) [27]. Before the beginning of the experiment, aquaria were filled with the different exposure media to pre-equilibrate the metal with the adsorption sites of glass walls. The light flux was 9.20 µmol photon·m−2·s−1 and the photoperiod was 14:10 for day and night, respectively. Water temperature and pH were monitored weekly, before and after water renewal, and were maintained at 21.5 ± 0.7 °C and between 7.5 and 8.0, respectively. Each aquarium was divided into three separate sections to obtain three experimental replicates. One slide per aquarium section was sampled after 1, 2, and 4 weeks of exposure. Exposure solutions were renewed weekly. Total concentrations of Zr, orthophosphates, and nitrates were monitored once a week throughout the 4 weeks of exposure, along with pH, oxygen, and temperature before and after media renewal. Zr concentrations were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after an addition of 500 µL of nitric acid to 4.5 mL of sample. The calibration curve was validated with certified control solution 401 (SCP Science—Fournisseur de Solutions Innovantes pour les Chimistes Analytiques). Each exposure medium was sampled in three replicate sections of the aquaria. Zirconium speciation in solution was estimated using the MINEQL thermodynamic model.
The slides sampled were rinsed with fresh Dauta medium without Zr before scraping and re-suspending the biofilm in 50 mL of Dauta medium. A volume of 1 mL was sampled for the subsequent analyses: Dry weight, chlorophyll a fluorescence, photosynthetic activity, and microscopic microorganism identification. Biofilm dry weight was quantified after filtration of a 20 mL aliquot on pre-weighted and dried glass fiber filters, and lyophilization according to the French standard method [28].
2.2. Biofilm Microorganisms Analysis
To determine the proportion of green and brown algae and cyanobacteria, in vivo chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements were conducted on samples with a PhytoPAM (Heinz Walz GmbH, Germany). To determine diatom growth, living and dead cells were counted using a DMLS Leica microscope. They were counted using a Nageotte cell at 200× magnification after fixation (final concentration of 0.01% Lugol).
Micromeiofauna individuals were also enumerated after Lugol fixation (0.01%) using a Nageotte counting cell as described for diatoms. Determination of the protozoan composition within micromeiofauna was established with the help of the user-friendly identification key for ciliates [29], and the Precis of Protistology for other protozoans, such as flagellates, heliozoans, amoebae, and thecamoebians [30]. Rotifers were identified with the help of The Rotifer World Catalog [31].
2.3. Data Treatment
The number of individuals (ind) was normalized for the dry weight (dw) of the samples. To determine significant differences between treatment groups and exposure times, analyses of variance (ANOVA) were computed using Tukey’s post hoc with the R software (car and MASS packages). Significant differences between diatom growth curves were determined by an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) [32]. An NMDS ordination analysis (non-metric multidimensional scaling) was performed using R with the vegan package to represent the structure of the biofilm community in the different treatment over the 4-week exposure. This NMDS was based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarity. This cluster analysis, performed with the same R package, was done to estimate the degree of similarity within and between the different sampling times and exposure conditions [33].
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Conditions
Nutrient concentrations (orthophosphates and nitrates) and water temperature presented in Table 1 were constant over exposure time and not statistically different (ANOVA, p < 0.05) between treatments. Concentrations of Zr in C1 and C10 exposure conditions were lower than the targeted nominal concentrations. Note that the measured Zr concentrations for the C10 condition are statistically higher than those of the C0 and C1 treatments (p < 0.05). Very few thermodynamic data are available for Zr. However, due to its high valence, it is expected that the tetra-hydroxo complex (ZrOH4) is the dominant species in our experimental conditions.

Table 1.
Physicochemical parameters (mean ± standard error; n = 3) in the C0, C1, and C10 exposure conditions during the 4 weeks of exposure. A two-way ANOVA was performed to detect significant differences between exposure times, and these differences are indicated by * (p < 0.05; n = 3).
3.2. Biofilm Biomass and Zr Effects on Autotrophic Organism Composition
Biofilm biomasses were measured at 0, 1, 2, and 4 (t0 to t4) weeks of exposure, as shown in Figure 1. The statistical analyses by two-way ANOVA showed that the biomass increased significantly for all Zr concentrations tested between t2 and t4.
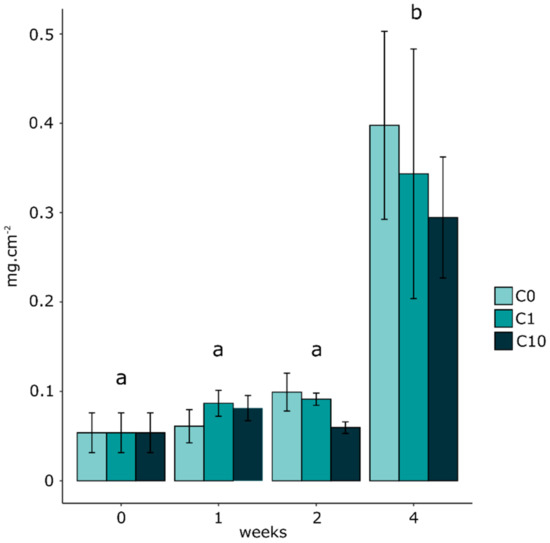
Figure 1.
Biofilm biomasses over time in control (C0 = 0.2 ± 0.1 nM) and Zr exposures (C1 = 0.5 ± 0.3 nM and C10 = 2.9 ± 0.3 nM). Values are averages and standard errors. Two-way ANOVA was performed to detect significant differences between exposure times, and these differences are indicated by letters (p < 0.05; n = 3).
Diatom cell densities followed a linear relation with time on a natural log-scale, as shown in Figure 2A, which indicates that algae were in an exponential growth phase. The growth rate appeared to be similar for the C0 (1.15 ± 0.40 week−1) and C1 exposures (1.08 ± 0.50 week−1), whereas in the C10 condition this rate (0.78 ± 0.35 week−1) and the quantity of cells was significantly lower. Figure 2B shows the chlorophyll a (Chl a) fluorescence of green (Gr), blue (Bl), and brown (Br) algae. The values obtained for control exposures were slightly lower at t0 and did not vary over the two first weeks of exposure. At t4, green algae were no longer detected in any Zr exposure condition. Based on green fluorescence (Gr), the concentration of Chl increased from t0 to t2 with 2.4 ± 0.3 and 6.9 ± 0.8 µg Chl·mg−1 dw in the C1 condition and was significantly higher than the control. The Chl in the C10 condition was also significantly higher than the control except at t2. Cyanobacteria Chl (Bl) values were low at t0 and t1 for all exposure conditions. The control C0 conditions remained low until t2, with a mean value of 0.5 ± 0.2 µg Chl·mg−1 dw, and increased at t4 to 42 ± 18 µg Chl·mg−1 dw. In the C1 condition, the amount of Chl began to slightly increase at t2 and continued until the last exposure time with mean values of 8.5 ± 1.4 and 55 ± 18 µg Chl·mg−1 dw, respectively. The amount of Chl in the C10 condition did not vary during the experiment (1.3 ± 0.6 µg Chl·mg−1 dw) and was lower than the two other conditions at t4, however, this difference was not significant. The variation in the population of the brown algae Chl (Br) followed the same pattern as that of the cyanobacteria Chl fluorescence throughout the exposure. The lower fluorescence at t4 for the C10 condition corresponded to the lower diatom density found in Figure 2A for the same condition and time.
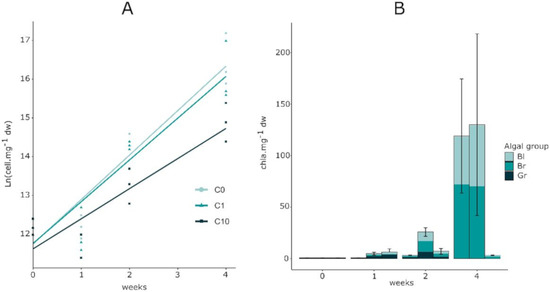
Figure 2.
(A) Diatom growth measured in the biofilm of controls (C0 = 0.2 ± 0.1 nM) and Zr exposures (C1 = 0.5 ± 0.3 nM and C10 = 2.9 ± 0.3 nM). A two-way ANCOVA was performed to detect significant differences between exposure times (p < 0.05; n = 3). (B) Blue (Bl), brown (Br), and green (Gr) chlorophyll fluorescence from biofilm autotrophs measured in control and Zr exposures (C1 and C10). Values are means and standard errors of total Chl fluorescence, no significant differences were found between conditions using a two-way ANOVA (p < 0.05; n = 3).
3.3. Effect on Micromeiofauna Composition
3.3.1. Total Counted Individuals
Figure 3A shows the total micromeiofauna individuals counted in the biofilm over the 4 weeks of exposure. The two-way ANOVA analysis showed a significant combined effect of time and concentration (p < 0.05). The total number of individuals remained constant throughout all experimental conditions, except for C10. In C10, values increased at t2 (21.5 (± 1.5) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw) but decreased at t4 to a level lower than that of the control and the C1 conditions (4.84 (± 0.80) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw).
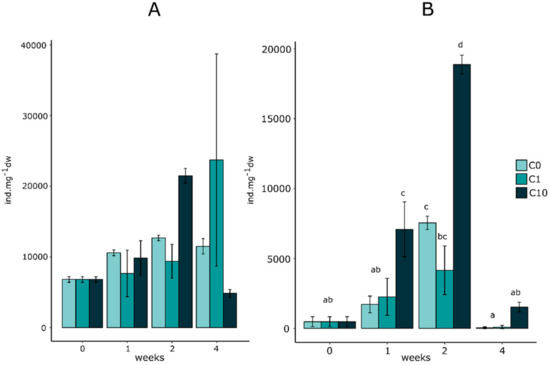
Figure 3.
The number of individuals per mg of biofilm dry weight in control C0 = 0.2 ± 0.1 nM) and Zr exposures (C1 = 0.5 ± 0.3 nM and C10 = 2.9 ± 0.3 nM). Values represent means ± standard errors. (A) Total micromeiofauna individuals. (B) The number of ciliate individuals. A two-way ANOVA was performed to detect significant differences between exposure times (p < 0.05; n = 3).
3.3.2. Micromeiofauna Composition
During the 4 weeks of exposure, rotifers and ciliates were the most prevalent taxa in all conditions. The population of all the other taxa counted, such as amoeba or flagellates, did not vary significantly between the exposure conditions.
Ciliates
Figure 3B presents the variation of individual ciliates counted during the experiment. Total individuals counted increased between t0 and t2 and decreased at t4 in all exposure conditions. The numbers of individuals in the C10 condition were significantly greater at t1 and t2 with 7.1 (± 2.0) × 103 and 18.9 (± 0.7) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw, respectively. During the experiment, the most numerous ciliate family observed was Trachelophyllum sp., as shown in Figure 4. The number of Aspidisca cicada individuals stayed relatively constant between t0 and t1, increased at t2 and decreased at t4 in all exposure conditions. At t2, the C10 values were significantly lower than the controls with 0.911 (± 0.087) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw and 1.51 (± 0.13) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw. The number of Uronema sp. individuals stayed constant over exposure time in all conditions, except at t2, for which the individuals in C10 were significantly higher than for C0 with 8.3 (± 3.1) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw. Trachelophyllum and undefined heterotrich individuals followed the same pattern as Uronema. For the undefined heterotrichs, the number of individuals in the C10 exposure condition was significantly greater than that observed in the control from the first week of exposure with 2.18 (± 0.41) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw. At t1, the number of Trachelophyllum individuals also tended to be higher than the control with 0.420 (± 0.073) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw. Treatments and time did not significantly affect the number of counted Vorticella sp.
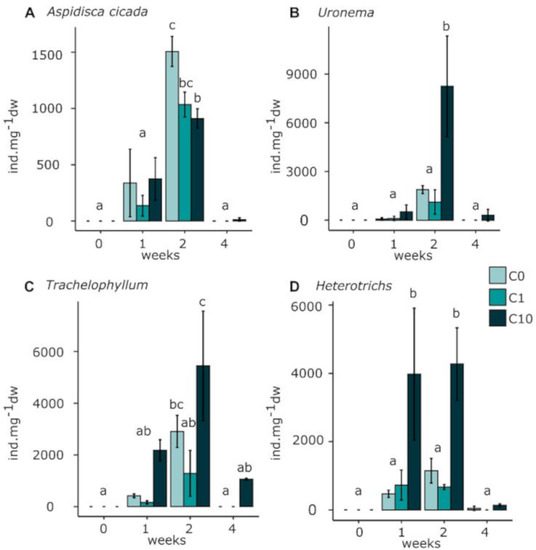
Figure 4.
Ciliates Aspidisca cicada [29], Uronema sp., Trachelophyllum sp., and undefined heterotrich species individuals present per mg of biofilm dry weight in control (C0 = 0.2 ± 0.1 nM) and Zr exposures (C1 = 0.5 ± 0.3 nM and C10 = 2.9 ± 0.3 nM). Values are means and standard errors. A two-way ANOVA was performed to detect significant differences between treatments as indicated by letters (p < 0.05; n = 3).
Rotifers
Figure 5 presents the number of rotifers and associated eggs as a function of time for the different metal exposure concentrations. Across all treatment conditions, the number of rotifers decreased significantly as the exposure time increased. The values for C10 (0.73 (± 0.52) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw) were significantly lower than for C0 (2.13 (± 0.22) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw) at t1 and t2 with 0.25 (± 0.16) and 1.64 (± 0.29) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw, respectively. The number of rotifer eggs counted increased drastically between t0 and t1 for the C0 and C1 exposure conditions and less so for C10. C0 values (5.49 (± 0.38) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw) were significantly higher than those of C1 (3.28 (± 0.66) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw) and C10 (0.48 (± 0.17) × 103 ind·mg−1 dw). Values decreased between t1 and t2 in C0 and C1 and did not change significantly until t4 while values stayed relatively constant in C10 over time.
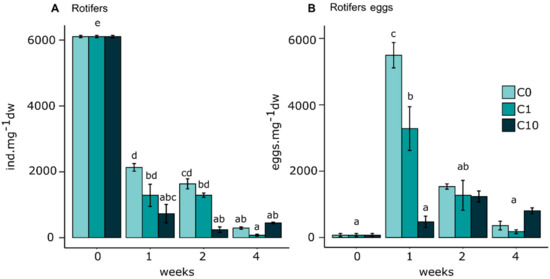
Figure 5.
Number of individuals (A) and rotifer eggs (B) per mg of biofilm dry weight in control (C0 = 0.2 ± 0.1 nM) and Zr exposures (C1 = 0.5 ± 0.3 nM and C10 = 2.9 ± 0.3 nM). Values are means and standard errors. A two-way ANOVA was performed to detect significant differences between treatments as indicated by letters (p < 0.05; n = 3).
The NMDS ordination plot (stress 0.09) of biofilm taxonomic samples, as shown in Figure 6, revealed a similar evolution of the control and the C1 conditions over the 4-week experiment while, for the C10 condition, the global evolution appears to be different from the first week of exposure. A Bray–Curtis cluster analysis was also performed on the data. This analysis distinguished three groups. The first containing the t0, C0 and C1 at t1 associated with rotifers and Vorticella. The second grouping t2 samples from all conditions, the last week of exposure for C10, all associated with ciliates (except Vorticella) and diatoms. The third group contained the C0 and C1 samples for the last week of exposure.
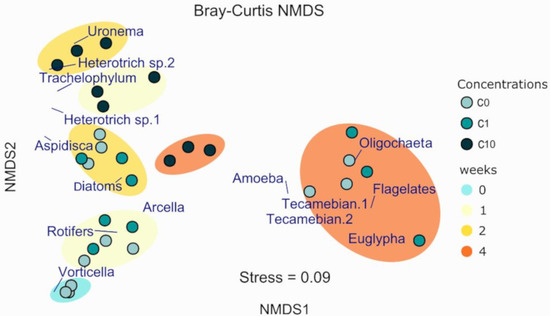
Figure 6.
Ordination (non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS)) of the biofilm community in control (C0 = 0.2 ± 0.1 nM) and Zr exposures (C1 = 0.5 ± 0.3 nM and C10 = 2.9 ± 0.3 nM).
4. Discussion
4.1. Exposure Conditions
Differences observed between nominal and measured Zr concentrations could be due to Zr adsorption to aquaria walls despite the 2 days of pre-equilibration of adsorption sites followed by full medium-renewal before the start of the experiment. However, the concentration observed for the C10 condition was significantly higher than the two other conditions.
4.2. Effects on Autotrophic Community Structure
The increase of biofilm biomasses and diatom growth over the 4-week experiment showed that the biofilm had not reached its maturity stage when the exposure began. The presence of Zr affected diatom growth in the C10 condition and autotroph biofilm structure notably with the increased proportion of green algae in C10 at t1 and C1 at t2. Green algae are known to be more tolerant than other phototrophs to metals [34,35]. The disappearance of green algae Chl a in all conditions during the last 2 weeks of exposure could be explained by environmental changes between the pond and the laboratory aquaria, increasing competition between algal groups. The nutrient-rich Dauta culture medium, which stimulates the growth of diatoms, and the lower incident light in the laboratory could explain such changes. Biofilm biomasses tended to be less as Zr concentration increased at t2 and t4. These differences were not significant at t4 despite diatom growth being less in the C10 exposure and the disappearance of green algae Chl a in all conditions at t4. These results suggest that the biomass contribution of heterotrophs or cyanobacteria could be more important than that of diatoms. The presence of Zr modified the autotrophic biofilm structure by increasing the proportion of green algae and decreasing the abundance of cyanobacteria and brown algae at the end of the fourth week of the C10 exposure.
4.3. Effects on Micromeiofauna Community Structure
4.3.1. Rotifers
From t0 to t1, the number of rotifer eggs increased drastically while individual numbers decreased. The Lugol fixation mainly allows the counting of the rotifer individuals belonging to the class of Monogononta, while all rotifer class eggs can be observed. This former class of rotifers have a solid cuticle (lorica) which preserves the individual shape during fixation [36,37]. This group is the most diverse, with approximately 80% of rotifer species known, and is notable for cyclical parthenogenetic and occasional sexual reproduction [37,38]. Moreover, the majority of rotifers observed within the fresh samples of this study were Monogononta, thus, we can assume that the bulk of eggs originated from this taxon. The rotifers mictic and amictic oviposition and hatching depend on environmental conditions such as light, food, and competition from other rotifers [38,39,40]. Therefore, the increase of oviposition during the first week of exposure in the control and C1 exposures could be due to the environmental changes from the pond to the aquaria. However, the number of eggs in C10 did not increase significantly from t0 to t1, and those in the C1 exposure conditions were significantly lower than in C0. This shows a dose-response effect of the Zr on the oviposition of rotifers. Several studies showed that metals such as copper, cadmium, and chromium can decrease rotifer offspring production [41,42]. During the first 2 weeks of exposure, we also observed a dose-response effect on the number of rotifers counted, with significantly lower numbers in C10 compared to control and C1 conditions.
4.3.2. Ciliates
Aspidisca cicada was the only ciliate species counted that was negatively impacted by Zr in this study. This species is known to crawl and to be dominant in benthic microorganism communities. Two metal toxicity studies on ciliates from activated sludge treatment plants showed that this species was one of the least sensitive to metal contamination [43,44]. However, A. cicada predominantly feeds itself by grazing bacteria and algae [23,45,46], thus the lower diatom growth could have contributed to the decreased number of species in this Zr exposure. Some studies also report that crawling ciliate species seem to be more sensitive to metals than attached ciliates [43,44,47].
Rotifers decreased over exposure time along with ciliates during the last 2 weeks of exposure, even though total micromeiofauna individual numbers remained constant. This can be explained by the increase of other microorganisms counted, such as amoeba or flagellates (data not shown). Moreover, the decrease in the number of individuals at t4 for these two taxa can be explained by the varying environmental conditions between the colonization period in the pond and the exposure in the aquaria, and by the disappearance of green algae. The effects of Zr were not similar among these two taxa. While the number of rotifer individuals and eggs decreased under C1 and C10 conditions during the first 2 weeks of exposure, the majority of ciliate species observed seemed to increase in the presence of Zr. The increase in the number of ciliates during t1 and t2 in Zr exposure conditions could be linked to the lower number of rotifers in the same treatments. The decrease in rotifers likely led to a decrease in predation pressure on algae and bacteria, and probably left more food available for ciliates.
In this study, Zr affected the micromeiofauna structure of biofilm at the highest Zr concentration tested (3 nM). Rotifera and the ciliate Aspidisca cicada appeared to be the most sensitive organisms among the observed micromeiofauna. A toxic effect of Zr on rotifers could explain such results. However, indirect effects such as a decrease in food source with lower algal growth in the presence of Zr could also play a role in the changes of micromeiofauna community structure. The NMDS and Bray–Curtis cluster analysis showed that the C10 exposure condition impacted significantly the evolution of the biofilm taxonomic structure. The presence of the C10 samples of the last week exposure in the same group as the C0 and C1 samples of t2 suggests that the highest Zr concentration slowed or stopped the community development. These results suggest that a Zr contamination in natural freshwater may affect aquatic ecosystem structure and function by destabilizing the first trophic chain level.
5. Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that a study investigated the effect of Zr on several biological compartments of periphytic biofilms, such as autotrophic organisms and benthic micromeiofauna. It was shown that this tetravalent metallic element can affect the periphyton microorganism composition and could disturb key periphyton functions, such as those previously observed for zinc, copper, and lead [48,49,50]. Biofilm microbial life in freshwaters is responsible for major ecosystem processes and plays a large role in biogeochemical fluxes [51]. Effects of metals on micromeiofauna are still scarcely investigated and their understanding could improve the risk assessment of metal repercussions on aquatic ecosystems [52,53].
Author Contributions
Experimental design and methodology, D.C., M.S., and F.C.; data analysis, D.C. and V.J.; writing—original draft preparation, D.C. and V.J.; writing—review and editing, M.S. and F.C.; supervision, F.C.; funding acquisition, F.C.
Funding
This research was funded by Fonds de recherche du Québec sur la nature et les technologies (FRQNT), grant number 2015-MI-190537. F.C. is supported by the Canada Research Chair program (grant number 950-231107).
Acknowledgments
The mobility funding provided by LabEx COTE and IRSTEA is acknowledged. D.C. acknowledges the language assistance received from Nicholas Gibb and Scott Hepditch, as well as statistical help provided by Jean-Paul Maalouf, Marie Wach, and David Carayon.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- A Literature Review of the Concentration Ratios of Selected Radionuclides in Freshwater and Marine Fish; Poston, T.M., Klopfer, D.C., Eds.; Pacific Northwest Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Boswell, S.M.; Elderfield, H. The determination of zirconium and hafnium in natural waters by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Mar. Chem. 1988, 25, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeil, C.; Rondeau, B.; Beaudin, L. Contribution of municipal effluents to metal fluxes in the St. Lawrence river. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedinger, G.M. 2012 Minerals Yearbook. Zirconium and Hafnium; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2016; Volume 85, pp. 1–8. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/nmic/minerals-yearbook-metals-and-minerals (accessed on 27 April 2018).
- Abollino, O.; Aceto, M.; Malandrino, M.; Mentasti, E.; Sarzanini, C.; Barberis, R. Distribution and mobility of metals in contaminated sites. Chemometric investigation of pollutant profiles. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 119, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulin, R.; Curchod, F.; Mondeshka, M.; Daskalova, A.; Keller, A. Heavy metal contamination along a soil transect in the vicinity of the iron smelter of Kremikovtzi (Bulgaria). Geoderma 2007, 140, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.G.; Lee, C.T.A. Sequential extraction of labile elements and chemical characterization of a basaltic soil from Mt. Meru, Tanzania. J. African Earth Sci. 2010, 57, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couture, P.; Cluis, D.; Bastien, C. Phosphorus removal from swine manure supernatant: Precipitant efficiency. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1988, 4, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, M.; Boutry, S.; Tison-Rosebery, J.; Delmas, F. Improvements of the Biological Diatom Index (BDI): Description and efficiency of the new version (BDI-2006). Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, S.; Gómez, N.; Tornés, E.; Licursi, M.; Rosebery, J. Aquatic Biofilms: Ecology, Water Quality and Wastewater Treatment; Romaní, A.M., Guasch, H., Balaguer, M.D., Eds.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2016; ISBN 9781910190173. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, I.; Lavoie, M.; Fortin, C. A mine of information: Benthic algal communities as biomonitors of metal contamination from abandoned tailings. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behra, R.; Landwehrjohann, R.; Vogel, K.; Wagner, B.; Sigg, L. Copper and zinc content of periphyton from two rivers as a function of dissolved metal concentration. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 64, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holding, K.L.; Gill, R.A.; Carter, J. The relationship between epilithic periphyton (biofilm) bound metals and metals bound to sediments in freshwater systems. Environ. Geochem. Health 2003, 25, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prygiel, J.; Coste, M.; Bukowska, J. Review of the major diatom-based techniques for the quality assessment of rivers - State of the art in Europe. In Use of algae for monitoring rivers III; Prygiel, J., Whitton, B.A., Bukowska, J., Eds.; Agence de l’Eau Artois-Picardie: Douai, France, 1999; pp. 224–238. ISBN 2-9502083-5-5. Available online: https://books.google.de/books/about/Use_of_Algae_for_Monitoring_Rivers_III.html?id=eQG8tAEACAAJ&redir_esc=y (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Morin, S.; Cordonier, A.; Lavoie, I.; Arini, A.; Blanco, S.; Duong, T.T.; Tornés, E.; Bonet, B.; Corcoll, N.; Faggiano, L.; et al. Consistency in Diatom Response to Metal-Contaminated Environments. In Handbook of Environmental Chemistry vol 19: Emerging and Priority Pollutants in Rivers; Guasch, H., Ginebreda, A., Geiszinger, A., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 117–146. ISBN 978-3-642-25722-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kim Tiam, S.; Feurtet-Mazel, A.; Delmas, F.; Mazzella, N.; Morin, S.; Daffe, G.; Gonzalez, P. Development of q-PCR approaches to assess water quality: Effects of cadmium on gene expression of the diatom. Eolimna minima. Water Res. 2012, 46, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paule, A.; Lauga, B.; Ten-Hage, L.; Morchain, J.; Duran, R.; Paul, E.; Rols, J.L.; Lambert, A.S.; Pesce, S.; Foulquier, A.; et al. Experimental evaluation of the contribution of acidic pH and Fe concentration to the structure, function and tolerance to metals (Cu and Zn) exposure in fluvial biofilms. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1270–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnineau, C.; Tlili, A.; Faggiano, L.; Montuelle, B.; Guasch, H. The use of antioxidant enzymes in freshwater biofilms: Temporal variability vs. toxicological responses. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 136–137, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasch, H.; Ricart, M.; López-Doval, J.; Bonnineau, C.; Proia, L.; Morin, S.; Muñoz, I.; Romaní, A.M.; Sabater, S. Influence of grazing on triclosan toxicity to stream periphyton. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, F.; Baudrimont, M.; Mornet, S.; Mesmer-Dudons, N.; Lacomme, S.; Etcheverria, B.; Simon, O.; Feurtet-Mazel, A. Gold nanoparticle trophic transfer from natural biofilm to grazer fish. Gold Bull. 2018, 51, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neury-Ormanni, J.; Vedrenne, J.; Morin, S. Who eats who in biofilms? Exploring the drivers of microalgal and micromeiofaunal abundance. Bot. Lett. 2016, 163, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, J.R.; Cairns, J. Functional groups in the Protozoa: Roles in differing ecosystems. J. Protozool. 2007, 32, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madoni, P.; Zangrossi, S. Ciliated protozoa and saprobical evaluation of water quality in the Taro River (Northern Italy). Ital. J. Zool. 2009, 72, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, B. Heterotrophic Feeding. In Nutrition and Feeding Strategies in Protozoa; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Horan, N.J. (Ed.) Biological wastewater treatment systems: Theory and operation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989; ISBN 9780471924258. [Google Scholar]
- Dauta, A. Conditions de développement du phytoplancton. Etude comparative du comportement de huit espèces en culture. I. Détermination des paramètres de croissance en fonction de la lumière et de la température. Ann. Limnol. 1982, 18, 217–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Sasaki, T.; Takagi, I.; Moriyama, H. Solubility of Zirconium (IV) Hydrous Oxides. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2007, 44, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AFNOR Qualité de l’eau - Dosage des matières en suspension - Méthode par filtration sur filtre en fibres de verre. NF EN 872. Available online: https://www.boutique.afnor.org/norme/nf-en-872/qualite-de-l-eau-dosage-des-matieres-en-suspension-methode-par-filtration-sur-filtre-en-fibres-de-verre/article/722523/fa135090 (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Foissner, A.; Berger, H. A user friendly guide to the ciliates. Freshw. Biol. 1996, 35, 375–482. [Google Scholar]
- De Puytorac, P.; Grain, J.; Mignot, J.-P. Précis de protistologie; Editions Boubée: Paris, France, 1987; ISBN 2850040495 9782850040498. [Google Scholar]
- Jersabek, C.D.; Leitner, M.F. The rotifer world catalog. World Wide Web electronic publication. Available online: http://www.rotifera.hausdernatur.at/ (accessed on 6 December 2018).
- Fienberg, S.E.; Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J.; Rohlf, F.J.; Sokal, R.R. Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research statistical tables. Biometrics 2012, 26, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Nonmetric multivariate analysis in community-level ecotoxicology. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldo, D.; Behra, R. Long-term effects of copper on the structure of fresh water periphyton communities and tolerance to copper, zinc, nickel and silver. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 47, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, P.L. Metal resistances of Chlorophyta from rivers polluted by heavy metals. Freshw. Biol. 1982, 12, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, H.H.; Yule, C.M. Rotifera: Monogononta. In Freshwater Invertebrates of the Malaysian Region; Academy of Sciences Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2012; pp. 106–120. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, R.L.; Snell, T.W. Rotifera. In Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates; Covich, J.T.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 173–235. ISBN 9780123748553. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, M.; Aparici, E.; Carmona, M.J. When to be sexual: Sex allocation theory and population density-dependent induction of sex in cyclical parthenogens. J. Plankton Res. 2008, 30, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonson, W.T. Reproductive rate of planktonic rotifers as related to food and temperature in nature. Ecol. Monogr. 1965, 35, 61–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna Rao, T.; Sarma, S.S.S. Mitic and amitic modes of reproduction in the rotifer Brachionus patulus. Curr. Sci. Assoc. 2018, 54, 499–501. [Google Scholar]
- Dahms, H.U.; Hagiwara, A.; Lee, J.S. Ecotoxicology, ecophysiology, and mechanistic studies with rotifers. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Garrido, I.; Lubián, L.M.; Soares, A.M.V.M. In vitro populations of rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Muller demonstrate inhibition when fed with copper-preaccumulating microalgae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 44, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madoni, P.; Esteban, G.; Gorbi, G.; Agua, D.I.; Poveda, L.; Rey, A. Acute toxicity of cadmium, copper, mercury and zinc to ciliates from activated sludge plants. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1992, 49, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madoni, P.; Davoli, D.; Gorbi, G. Acute toxicity of lead, chromium, and other heavy metals to ciliates from activated sludge plants. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 53, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gücker, B.; Fischer, H. Flagellate and ciliate distribution in sediments of a lowland river: Relationships with environmental gradients and bacteria. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 31, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curds, C.R. The ecology and Role of Protozoa in aerobic sewage treatment processes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1982, 46, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madoni, P. Protozoa in wastewater treatment processes: A minireview. Ital. J. Zool. 2011, 78, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancion, P.Y.; Lear, G.; Dopheide, A.; Lewis, G.D. Metal concentrations in stream biofilm and sediments and their potential to explain biofilm microbial community structure. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J.; Neish, B.; Trett, M.W.; Best, J.G.; Weightman, A.J.; Morgan, P.; Fry, J.C. Comparison of microbial and meiofaunal community analyses for determining impact of heavy metal contamination. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 45, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Lauber, C.; Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A. Testing the functional significance of microbial community composition. Ecology 2009, 90, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Besemer, K.; Bengtsson, M.M.; Romani, A.M.; Packmann, A.I. The ecology and biogeochemistry of stream biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; James, A.; Bharose, R. Biological assessment of water pollution using periphyton productivity: A review. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2017, 16, 559–567. [Google Scholar]
- Barranguet, C.; Charantoni, E.; Plans, M.; Admiraal, W. Short-term response of monospecific and natural algal biofilms to copper exposure. Eur. J. Phycol. 2000, 35, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).