Abstract
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics (FQs) are widely applied in veterinary practice and animal husbandry and frequently persist in organic waste liquids (OWLs), creating substantial environmental and health risks when untreated. A high-capacity mesoporous silica aerogel (SA-60) was produced via a cost-effective sol–gel route from water glass, followed by ambient pressure drying at 60 °C for 6 h. SA-60 exhibited pronounced selectivity, providing a maximum adsorption capacity of 630.18 mg·g−1 for enrofloxacin (ENR) in acetonitrile. Adsorption efficiency was weakly dependent on pH. Mechanistic analysis indicated combined physical and chemical interactions, with intra-particle diffusion governing the overall rate. Thermodynamic evaluation showed a spontaneous and endothermic process for ENR adsorption. Organic solvent type and water content were major determinants of adsorption efficiency. Durable performance was observed, with capacity retention above 80% after five adsorption-desorption cycles. The mesoporous architecture (surface area 249.21 m2·g−1; average pore diameter 10.81 nm) supported the high uptake. These results identify SA-60 as a sustainable adsorbent for removing hazardous FQs from OWLs, offering a simple, energy-efficient approach for the source-level control of antibiotic pollution and improved environmental management.
1. Introduction
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) are a class of broad-spectrum antibiotics widely used in clinical veterinary medicine and livestock farming [1]. Due to their unmetabolized form (up to 70%), inefficient wastewater treatment, and improper disposal of expired drugs, FQs are commonly found in natural waters and wastewater systems [2,3]. The improper disposal of FQ-containing animal waste or laboratory solvents can lead to the accumulation of these antibiotics in organic waste liquids (OWLs), posing significant risks to ecosystems and human health. For instance, if OWLs are incinerated directly without pretreatment, toxic byproducts may be released into the atmosphere due to the presence of FQs and their halogenated derivatives [4]. Therefore, it is crucial to purify OWLs to fully remove FQs and other contaminants prior to disposal [5]. However, traditional adsorbents for FQs removal often suffer from low adsorption capacities or complex synthesis processes [6]. Although biochar provides a cost-effective option, its selectivity and anti-interference capacity require further enhancement [7]. Despite the high adsorption capacities of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), their practical application is hindered by low removal efficiency [8]. Polymer composite materials often require complex functionalization, leading to challenges such as high production costs and the potential toxicity of the adsorbents [9]. These limitations highlight the need for more effective and easily prepared adsorbents for FQ remediation. Additionally, the adsorption mechanism of FQs involves electrostatic attraction, hydrophobic interaction, H-bonding, diffusion pore, π–π interaction, and acid-base interactions [10].
Silica aerogels (SAs) possess a highly porous structure with pore sizes ranging from a few nanometers to several micrometers, which results in a high specific surface area. These characteristics contribute to their remarkable adsorption properties, making them ideal for capturing a broad spectrum of molecules, such as water [11], organic solvents [12], and gases [13]. The adsorption capacity of silica aerogels can be tailored by modifying their surface chemistry or by doping them with other materials. For instance, hydrophobic silica aerogels outperform granulated activated carbon in adsorbing toxic organic compounds from water, while aerogels modified with sulfhydryl groups demonstrate high efficiency in removing heavy metals like Cu(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solutions, achieving removal efficiencies exceeding 99% [14].
The unique properties of silica aerogels make them highly versatile for a wide range of applications across various fields. In environmental remediation, they are utilized as adsorbents for the removal of pollutants from water and air, effectively adsorbing heavy metals [15], organic contaminants [16], and oils [17]. For instance, chitosan–silica composite aerogels have shown promise in removing cupric ions from contaminated water [14]. Additionally, super-flexible silica aerogels have been developed for oil–water separation, demonstrating exceptional potential for oil spill cleanup efforts [18]. The low thermal conductivity of aerogels makes them excellent thermal insulators, notably applied in aerospace engineering for providing thermal protection with minimal weight [19]. In catalysis, silica aerogels serve as supports for catalysts, enhancing the efficiency of chemical reactions [20]. Their biocompatibility and high porosity also make them promising candidates for controlled drug release systems in drug delivery [21]. Moreover, SAs are emerging as promising materials in analytical chemistry, particularly for sample preparation and pollutant adsorption [22]. Their tunable porous structure and surface chemistry enable interaction with various chemical species, suggesting potential applications in trapping antibiotic molecules from complex media.
SAs are typically synthesized through a sol–gel process, followed by a drying step that preserves the porous network of the gel [23]. Common drying methods include supercritical drying, freeze-drying, and ambient pressure drying (APD). Among these, APD is particularly appealing due to its lower cost and scalability, especially with recent advancements in surface modification and solvent exchange techniques that minimize pore collapse during drying [24,25]. By using inexpensive precursors, such as sodium silicate, and employing mild drying conditions, APD can produce SAs with excellent structural integrity while avoiding the need for high pressure or supercritical CO2, thereby significantly reducing both production complexity and cost.
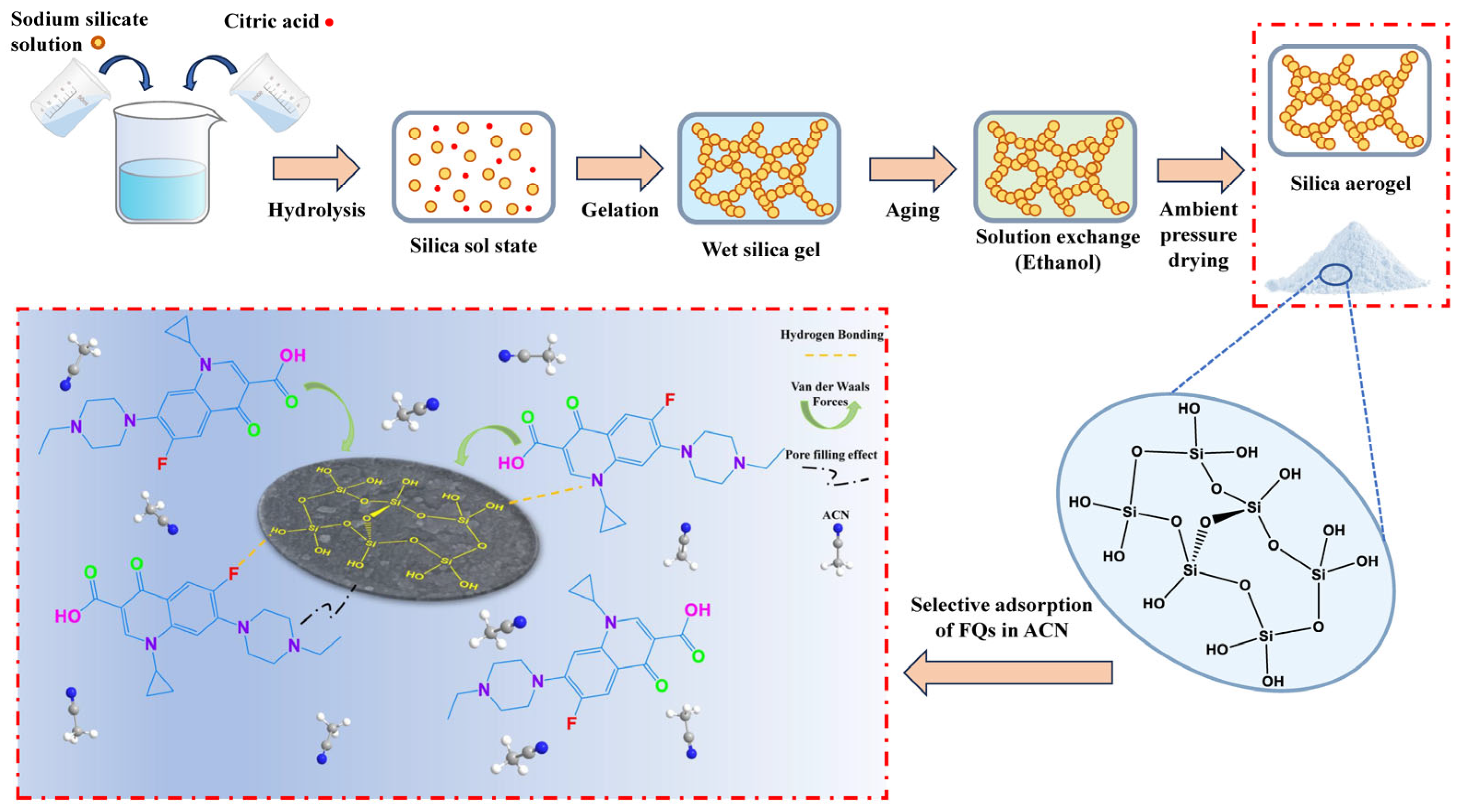
Despite the extensive research on SAs, their application in adsorbing antibiotics, particularly FQs, from OWLs, remains underexplored [26,27]. This study aims to (i) synthesize a mesoporous silica aerogel (SA-60) using a low-energy sol–gel process and APD (Figure 1); (ii) evaluate its adsorption capacity and selectivity for FQs in simulated OWLs; and (iii) investigate the effects of operational parameters, adsorption mechanisms, and reusability. The novelty of this work lies in the use of a simply prepared, ambient-pressure-dried silica aerogel for the selective adsorption of FQs from organic solvent-rich waste streams, achieving a high adsorption capacity (630.18 mg·g−1) and excellent reusability without the need for strict pH control. This study demonstrates an energy-efficient and straightforward strategy for removing FQs from OWLs, offering a new approach for OWL purification and contributing to sustainable antibiotic pollution control.
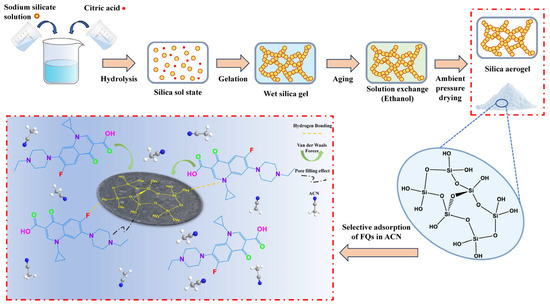
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration on the simple synthesis of mesoporous SA-60 and its adsorption affinity towards FQs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All chemicals used were of analytical grade unless otherwise specified. Sodium silicate (water glass), citric acid monohydrate, ferrous chloride (FeCl2), magnesium sulfate (MgSO4), zinc chloride (ZnCl2), copper (II) chloride (CuCl2), ammonia solution (NH3·H2O), and hydrochloric acid (HCl) were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Formic acid (FA) was obtained from Fluka (Seelze, Germany). Acetic acid (HAc), acetonitrile (ACN), methanol (MeOH), absolute ethanol (EtOH), isopropanol (IPA), ethyl acetate (EA), and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were provided by J.T. Baker (Phillipsburg, NJ, USA). HPLC-grade ACN and MeOH were purchased from ANPEL (Shanghai, China). Enrofloxacin (ENR) was supplied by Shanghai Aladdin Reagent Co. (Shanghai, China). High-purity standards for six drug categories were obtained from First Standard (Tianjin, China), including carbofuran (CBF, pesticide), mometasone furoate (NASONEX, steroid hormone), various fluoroquinolones (FQs), sulfadiazine (SD, sulfonamide), lincomycin (LCM, macrolide), and nitrazepam (NZP, sedative). Additionally, four structural analogues of FQs (analogues-1 to analogues-4) were custom-synthesized by Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co. (Shanghai, China); detailed information on these compounds is provided in Table S1. Deionized water used in all experiments was produced by a Milli-Q® Direct purification system.
2.2. Preparation of SAs and SA Composites
The silica aerogels (SAs) were synthesized via a sol–gel process followed by APD treatment [28]. Initially, a sodium silicate stock solution was prepared by dissolving 50 g of sodium silicate in 200 mL of deionized water. Simultaneously, 30 g of citric acid monohydrate was dissolved in 100 mL of deionized water to prepare an acid catalyst solution. To initiate gelation, 30 mL of the sodium silicate solution was rapidly mixed with 11.4 mL of the citric acid solution at room temperature. Gelation occurred within approximately 5 min, forming a silica hydrogel. The hydrogel was then aged in a water bath at 50 °C for 4 h to strengthen the gel network. After aging, solvent exchange was performed by immersing the hydrogel in EtOH for 15 h, replacing the water in the gel pores with EtOH. Finally, the gel was dried under ambient pressure to yield the SAs. Specifically, the EtOH-exchanged gel was heated at a moderate temperature (40–60 °C) for at least 6 h until a dry SA (denoted SA-60 for drying at 60 °C) was obtained. For comparison, additional SAs were prepared by varying the drying temperature to 40, 90, 120, and 150 °C (yielding samples SA-40, SA-90, SA-120, and SA-150, respectively), while keeping all other steps identical. Metal-doped SA composites were also prepared by adding 1.0 g of a metal salt (FeCl2, MgSO4, ZnCl2, or CuCl2) into the citric acid catalyst solution before mixing with the silicate. These composites yielded Fe-SA-60, Mg-SA-60, Zn-SA-60, and Cu-SA-60 composites after undergoing the same aging, solvent exchange, and drying procedures.
2.3. Characterization
The morphology of the SAs was examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Porosity and surface area were determined via nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms employing the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method, while the pore size distribution was calculated using the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method. The crystalline structure of the samples was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). Surface functional groups were identified through Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The elemental composition and surface chemical states before and after ENR adsorption were investigated using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Thermal stability was assessed by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The quantification of ENR, other drug standards (six categories), and four FQs analogues in ACN solutions, before and after adsorption, was performed using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (HPLC-HRMS). Detailed information on the instrument models and operating conditions is provided in Appendix A.1 Characterization.
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
Batch adsorption experiments were conducted to assess the uptake of ENR by the SAs under varying conditions. In a typical experiment, a known mass of SAs was added to glass bottles containing a fixed concentration of ENR solution (dissolved in ACN) at the desired initial concentration. For pH-dependent studies, the pH of the ENR solution was adjusted with 0.1 M HCl or NH3·H2O prior to the addition of the adsorbent. The mixture was stirred at 100 rpm in a temperature-controlled shaker bath until adsorption equilibrium was reached, indicated by no further change in ENR concentration. The suspension was then filtered (or centrifuged) to separate the SAs, and the remaining ENR concentration in the solution was quantified by HPLC-HRMS. The ENR adsorption capacity (mg·g−1) and adsorption rate (R, %) were calculated using Equations (A1) and (A2) [29,30] from Appendix A.2, based on the difference between the initial and equilibrium ENR concentrations. Each data point represents the mean of three replicates, with error bars indicating measurement variability.
The effects of various parameters on the adsorption of ENR by SA-60 were systematically evaluated, including (1) initial solution pH, which was adjusted over a range while other factors remained constant; (2) adsorbent dosage, varying the mass of SA-60 added while keeping the ENR concentration fixed; (3) initial ENR concentration (200–800 mg·L−1); (4) contact time, to assess adsorption kinetics; (5) temperature, to evaluate thermodynamic parameters; and (6) selectivity. Detailed experimental conditions and the models employed for isotherm and kinetic analysis (Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms, adsorption thermodynamics, pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order, and intraparticle diffusion kinetics) are provided in Appendix A.3, Appendix A.4, Appendix A.5 and Appendix A.6. The isotherm parameters were derived by fitting equilibrium data to the respective models (Equations (A3)–(A5)), thermodynamic parameters were calculated using Equations (A6) and (A7), and kinetic parameters were obtained by fitting time-course data to Equations (A8)–(A10). Selectivity was calculated using Equations (A11) and (A12).
2.5. Application in OWLs Treatment
To demonstrate the practical application of SA-60, its performance in treating simulated ACN-based OWLs was evaluated. Laboratory-simulated ACN waste was prepared by mixing ACN with water and adding a small amount of acid (FA or HAc) to mimic common OWLs. ENR was spiked into these solutions at a concentration of 200 mg·L−1. Subsequently, 20 mg of SA-60 was added to 10 mL of each simulated waste solution (solid-to-liquid ratio = 2 g·L−1). After reaching adsorption equilibrium under stirring, the residual ENR concentration was measured using HPLC-HRMS, and the equilibrium adsorption capacity was calculated according to Equation (A1). The water content in ACN was varied from 0% to 90% to investigate the effect of increasing water proportion in OWLs on ENR adsorption. Additionally, the adsorption efficiency of SA-60 for ENR in various pure solvents and solvent mixtures (water, ACN, MeOH, EtOH, IPA, EA, and acidified ACN) was compared to examine the influence of solvent polarity and protic/aprotic nature on adsorption. To evaluate the reusability of the adsorbent, five consecutive adsorption-desorption cycles were conducted. After each ENR adsorption test (using 2 g·L−1 SA-60 in a 200 mg·L−1 ENR solution, pH = 7, 25 °C), the ENR-loaded SA-60 was regenerated by treating it with 1% FA in MeOH (stirred for 10 min), followed by thorough washing with MeOH and drying. The regenerated SA-60 was then reused in the subsequent cycle, and ENR removal efficiency was measured to assess performance retention.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of SA-60
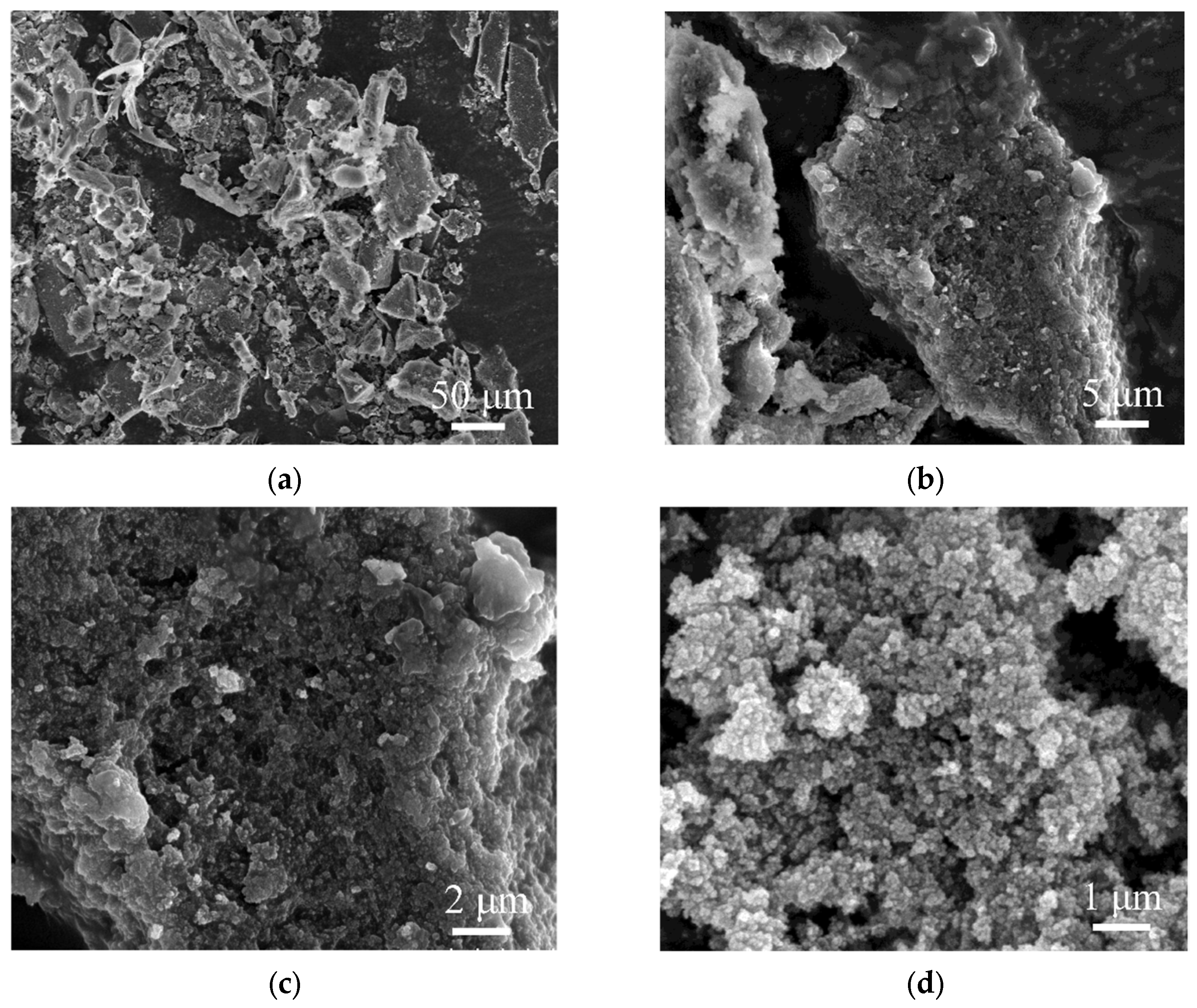
The morphology of the synthesized SA-60 was characterized using SEM. As shown in Figure 2a,b, the SA-60 displays a network of interconnected particles with a rough, gully-like surface texture and significant agglomeration. At higher magnifications (Figure 2c–e), a typical nanoporous structure is observed: presumed silica nanoparticles are linked in a pearl-necklace fashion, forming a web of pores and cracks of various sizes, which is consistent with previous results [31,32]. The presence of larger clusters and particles suggests the partial collapse or shrinkage of the mesopores, likely caused by capillary stress during the ambient drying process [33]. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) elemental mapping (Figure 2f) reveals that Si is the predominant element in SA-60, with trace amounts of residual Na, attributed to incomplete removal of sodium ions during solvent exchange.
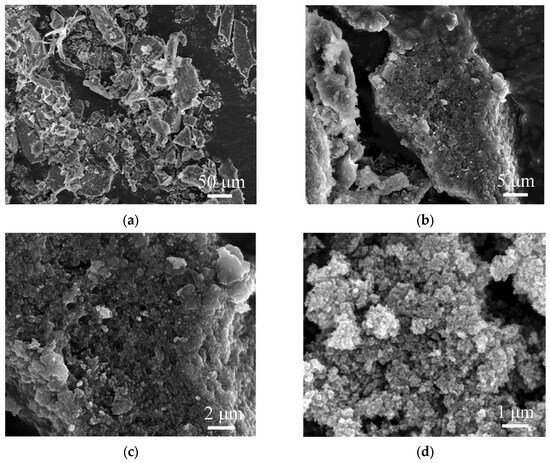
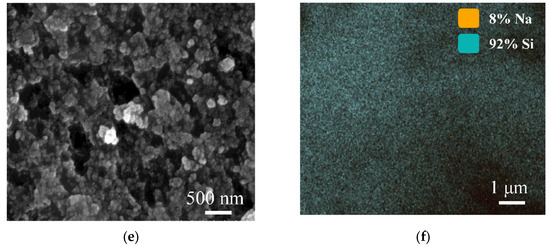
Figure 2.
SEM images of SA-60 (a–e); Si and Na element mapping (f).
The crystalline structure of SA-60 was analyzed using XRD (Figure S1a). The XRD pattern does not show any sharp diffraction peaks within the 2θ range of 10–80°; instead, only a broad diffuse hump appears around 15–30°, indicating that SA-60 is predominantly an amorphous silica material without a long-range ordered crystalline structure [34,35]. Thermal stability and composition were assessed via TGA (Figure S1b). The TGA curve exhibits two major weight loss stages. The first stage, between 25 °C and 200 °C, shows a sharp mass loss of 9.22%, primarily due to the evaporation and decomposition of water molecules. The second stage, from 200 °C to 600 °C, shows a more gradual mass loss, attributed to the decomposition of organic groups such as Si–OH [36]. Beyond 600 °C, the mass stabilizes, indicating the excellent thermal stability of the SA framework after the removal of volatiles.
FT-IR spectroscopy was employed to identify functional groups on SA-60 (Figure S1c). The broad peak observed at 3460 cm−1 corresponds to the stretching vibration of the –OH group in Si–OH, while the peak around 1636 cm−1 can be attributed to Si–OH and adsorbed water on the surface of the sample. The peak near 1393 cm−1 represents the bending vibration band caused by the C–H bond of the ethoxy group attached to silicon [37]. Additionally, the peak around 958 cm−1 is a characteristic peak of surface Si–OH in SAs [32]. The vibration bands at 1090 cm−1 and 800 cm−1 are associated with Si–O–Si anti-symmetric and symmetric stretching modes, respectively, while the peak at 469 cm−1 is attributed to O–Si–O bending vibration [38]. These peaks confirm the successful preparation of the sample, as they are typical of SAs.
The adsorption capability of an adsorbent is closely related to its structure and surface properties. Therefore, a N2 adsorption-desorption experiment was conducted to determine the specific surface area and pore size distribution of the sample. As shown in Figure S1d, the N2 adsorption-desorption curve is characteristic of type IV, with a sharp increase observed at P/P0 > 0.4 and a distinct hysteresis loop, indicating the presence of mesopores. The pore size distribution curves show that the pore size of the sample is predominantly concentrated within the mesopore range and exhibits small pore diameters. Furthermore, as shown in Table S2, the specific surface area of the sample is 249.21 m2·g−1, with an average pore size of 10.81 nm, confirming its highly mesoporous structure.
3.2. Adsorption Performance Under Different Conditions
3.2.1. Effect of Drying Temperature and Metal Doping
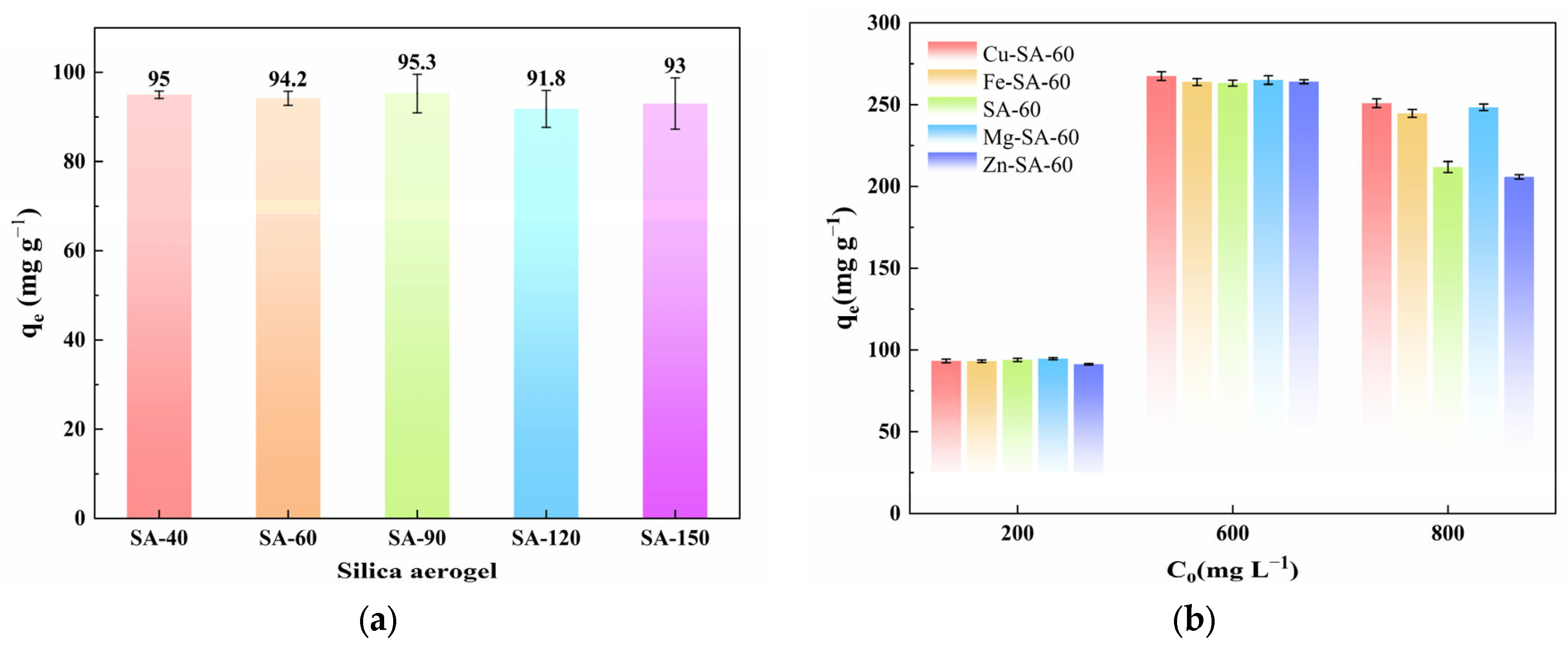
The initial adsorption screening indicated that all SAs samples (SA-40 to SA-150) prepared at varying drying temperatures exhibited similar ENR adsorption capacities (ranging from 91.8 to 95.3 mg·g−1 in 4 h tests with 200 mg·L−1 ENR; Figure 3a). Considering production efficiency and energy costs, SA-60 (dried at 60 °C) was selected for further investigation. Subsequently, SA-60 and four SAs composites doped with different metal ions (Fe-SA-60, Mg-SA-60, Zn-SA-60, Cu-SA-60) were evaluated for ENR adsorption over a 4 h period. At an initial ENR concentration of 200–800 mg·L−1, all samples displayed an increase followed by a slight decrease in adsorption capacity as the ENR concentration increased (Figure 3b). This pattern likely arises from the elevated ENR concentration, which causes equilibrium shifts in the adsorption process, while the number of reactive sites on the sample surfaces remains finite [39]. At 800 mg·L−1 ENR, the adsorption capacity of SA-60 was slightly lower than that of Fe-SA-60, Mg-SA-60, and other samples, potentially due to the additional binding sites provided by the metal ions. However, the use of metal-doped SAs presents a risk of metal leaching, which could undermine sample stability and pose environmental concerns [40]. Therefore, undoped SA-60 was selected as the adsorbent of mechanism studies and practical applications.
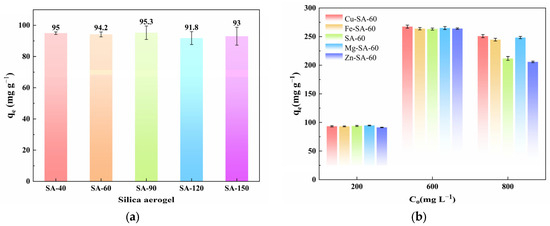
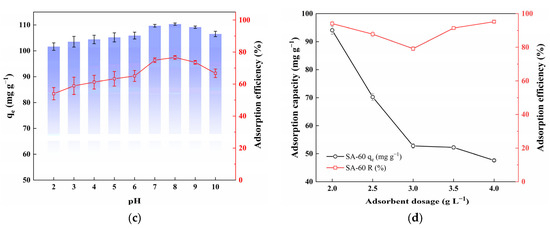
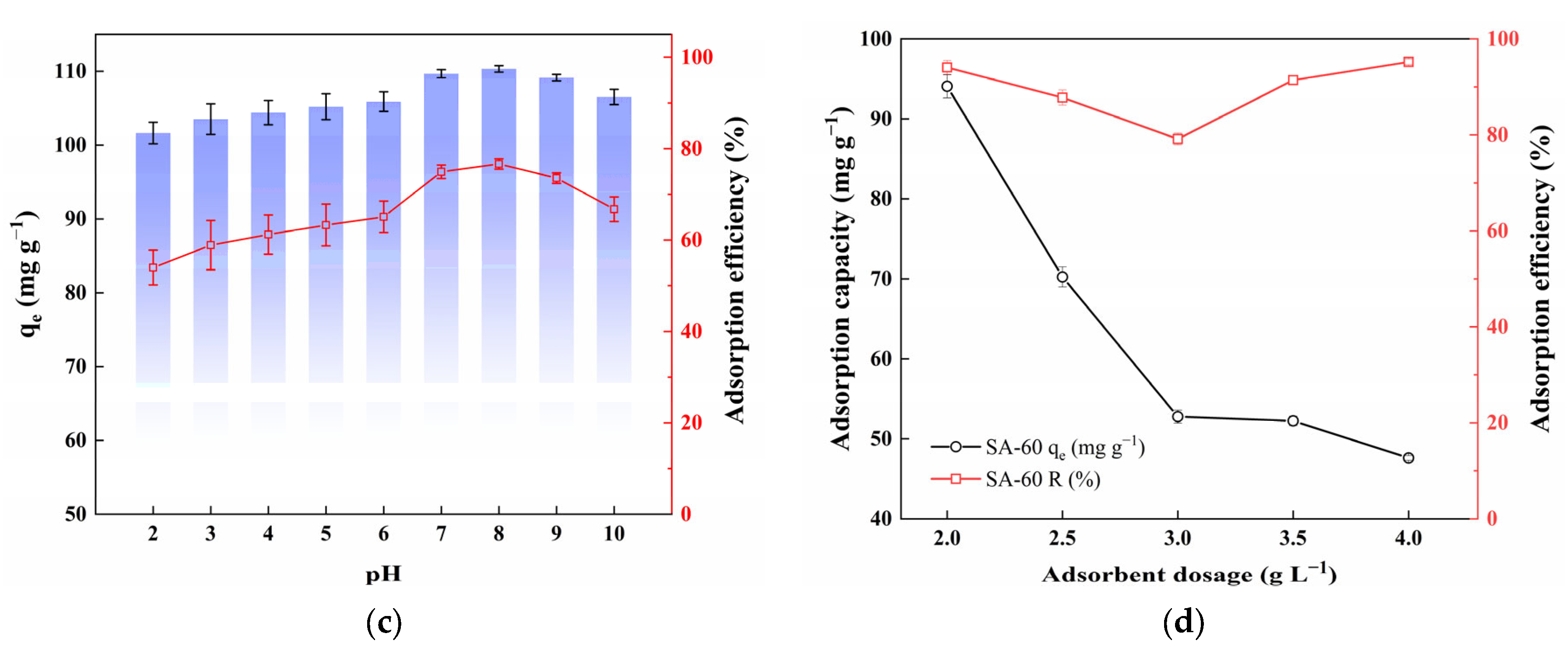
Figure 3.
(a) Adsorption capacity of ENR for SAs prepared with various drying temperatures (C0 = 200 mg·L−1, m/V = 2 g·L−1, pH = 7, and T = 298 K); (b) Adsorption capacity of five SAs at different initial ENR concentrations (T = 298 K); (c) Effect of pH on adsorption capacity and efficiency of SA-60 (C0 = 200 mg·L−1, pH = 7, and T = 298 K); (d) Effect of adsorbent dosage on adsorption capacity and efficiency of SA-60 (C0 = 200 mg·L−1, pH = 7, and T = 298 K).
3.2.2. Effect of pH
Solution pH significantly affects both the surface charge of the adsorbent and the ionization state of ENR, thereby influencing its adsorption capacity [41]. As shown in Figure 3c, the adsorption capacity of ENR on SA-60 remains high over a wide pH range (pH 3–9), with a slight increase followed by a minor decrease as pH increases. ENR exhibits two pKa values (6.17 and 7.72), indicating that it can exist in cationic, zwitterionic, or anionic forms depending on the pH [42]. Below pH 6, ENR predominantly exists in a protonated cationic form. The excess H+ in the solution competes with the cationic ENR for negatively charged silanol sites on SA-60, which accounts for the moderate reduction in adsorption under strongly acidic conditions. As the pH approaches neutral, ENR transitions to a zwitterion or anionic state, and competition from H+, diminishes, leading to an increase in adsorption. Under alkaline conditions (pH > 8), both ENR (as anions) and the SA surface (with deprotonated silanolate groups) carry negative charges, resulting in electrostatic repulsion, which causes a slight decrease in adsorption at pH 9. Nevertheless, SA-60 maintains a relatively high adsorption capacity even under mildly acidic or basic conditions, suggesting that factors beyond electrostatic interactions contribute to ENR uptake. It should be noted that the SA framework may be damaged under extremely acidic conditions; however, the structure remained intact within the tested pH range.
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
The effect of adsorbent dosage was evaluated by varying the SA-60 concentration between 2 to 4 g·L−1, while maintaining a constant ENR concentration. As shown in Figure 3d, the ENR adsorption capacity decreases with increasing adsorbent dosage. With a higher adsorbent amount, the total ENR mass is distributed over a larger sorbent mass, leading to a reduced adsorption per gram of sorbent. It is hypothesized that, at excessive adsorbent dosages, the adsorbents tend to aggregate, causing unbound active sites to overlap, thus reducing the effective surface area available for adsorption [39]. Furthermore, the adsorption capacity significantly decreased beyond 2 g·L−1, with the removal efficiency (% of ENR adsorbed) reaching a minimum at 3 g·L−1, before increasing slightly. The initial drop in removal efficiency could be attributed to unsaturated binding sites at lower ENR-to-adsorbent ratios, while the slight increase may be due to improved contact at high solid concentrations after overcoming aggregation. Based on these findings, an adsorbent dosage of 2 g·L−1 was selected as optimal for subsequent experiments, as it strikes a balance between high adsorption capacity and efficient material use. The maximum capacity achieved in this study is comparable to that of other adsorbents designed for similar applications, as reported in the literature (Table 1).

Table 1.
Comparison of maximum antibiotic adsorption capacities of various adsorbents in literature.
3.2.4. Selective Adsorption in Mixed Systems
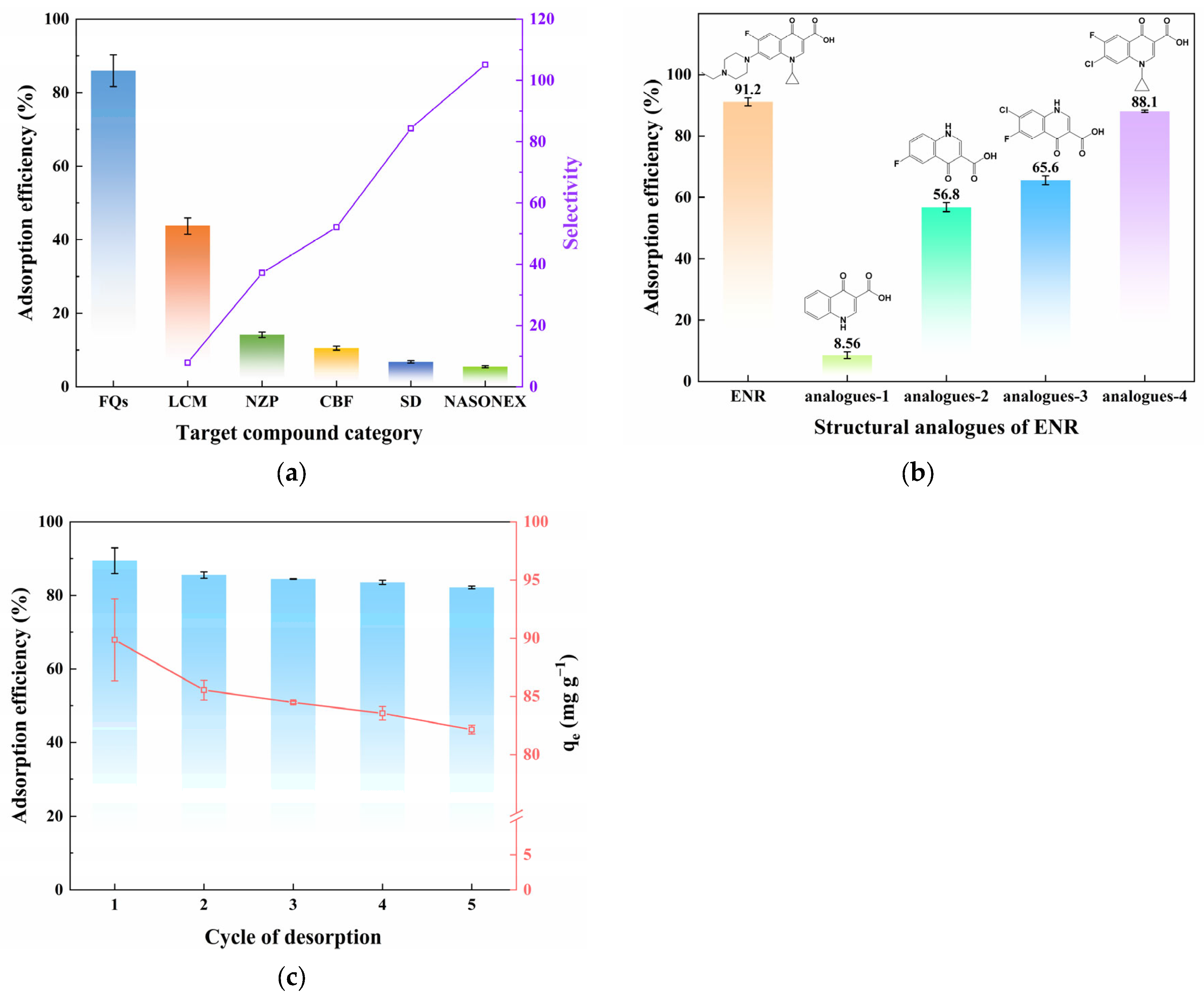
The selectivity of SA-60 was evaluated by testing it in a mixed solution containing multiple compounds (the six categories of drugs described in Section 2.1, each at a concentration of 50 µg·L−1), as shown in Figure 4a and Table 2. SA-60 exhibited the highest adsorption efficiency for FQs (86.0%), whereas significantly lower efficiencies were observed for the other compounds: LCM (43.7%), NZP (14.1%), CBF (10.5%), SD (6.8%), and NASONEX (5.5%). This clear preference suggests that SA-60 has an inherent selectivity for FQ molecules in a competitive environment. One contributing factor could be the molecular size relative to pore size. An interesting observation is that the adsorption capacity of SA-60 may correlate with molecular weight (MW), the relative size of the compound molecules, and the pore diameter of the adsorbent [51]. Specifically, molecules with sizes smaller than or comparable to the pores of the adsorbent could more effectively enter the mesopores and adsorb onto active sites. In contrast, molecules that do not match the pore sizes may only access smaller surface areas. Activation energy is required for adsorbate molecules to enter the nanometer-scale spaces as they approach the mesopores, and even slight variations in size could lead to significant changes in activation energy, resulting in selective adsorption. Moreover, differences in functional groups among the compounds can affect their interactions: FQs contain specific functional groups (such as carboxylic acids, often a fluorine atom, and a piperazine ring), which may strongly interact with the silanol-rich surface, while other drugs lacking these features bind weakly [52].
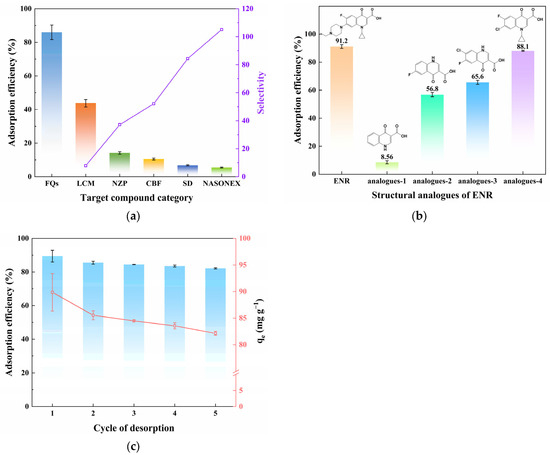
Figure 4.
(a) Multicomponent adsorption performance of SA-60 (C0 = 50 µg·L−1, m/V = 10 g·L−1, pH = 7, and T = 298K); (b) Adsorption efficiency of structurally similar analytes on SA-60 (C0 = 5 mg·L−1, m/V = 2 g·L−1, pH = 7, and T = 298 K); (c) Adsorption efficiency and capacity of ENR on SA-60 after five repeated cycles (C0 = 200 mg·L−1, m/V = 2 g·L−1, pH = 7, and T = 298 K).

Table 2.
Selectivity of FQs from a multicomponent solution.
To identify which structural features of FQs contribute most to adsorption, experiments were performed with four structural analogues (analogues-1 to analogues-4, see Table S1 for structures). Each analogue isolates certain functional groups found in ENR. As shown in Figure 4b, analogue-1 (a basic quinolone core without halogens or piperazine) displayed a very low adsorption efficiency (8.56%), indicating that the quinolone backbone alone is insufficient for strong adsorption on SA-60. Analogue-4, which lacks the 1-ethylpiperazine group but retains other parts of ENR, was adsorbed at approximately 88.1% efficiency, nearly as high as ENR itself. This suggests that the piperazine ring is not the most critical factor for adsorption. In contrast, analogue-2, which contains a fluoroquinolone structure with fluorine but no cyclopropyl group, showed moderate adsorption (56.8%), while analogue-3, which includes a cyclopropyl group but no fluorine, had about 65.6% adsorption. These results suggest that the presence of the fluorine (halogen) substituent on the quinolone ring plays a major role in enhancing adsorption, likely through hydrogen bonding or polar interactions between the electronegative F and the surface –OH groups of SA-60. The cyclopropyl groups may also contribute by generating interactions with active sites on the surface of the adsorbent. While increasing the water solubility of ENR, the piperazine moiety seems less important for binding to silica. Thus, halogen atoms (particularly fluorine) appear to significantly contribute to the observed selective adsorption, likely forming hydrogen bonds with Si–OH groups in the analytes.
3.2.5. Reusability
The stability and reusability of SA-60 were evaluated through five adsorption-desorption cycles, using ENR (100 mg·L−1 in ACN) as the target. As shown in Figure 4c, the ENR removal efficiency of SA-60 remained above 80% after five cycles, with a minor decline from 89.9% in the first cycle to 82.1% in the fifth. Correspondingly, the adsorption capacity decreased slightly from 89.4 mg·g−1 to approximately 82.1 mg·g−1. This favorable cycling performance suggests that the structure and active sites of SA-60 are largely maintained during regeneration. The mild regeneration procedure, involving a 1% FA-acidified MeOH wash, likely removes the bound ENR without causing significant damage to the silica framework. These consistent results further confirm that SA-60 is a durable adsorbent that can be regenerated and reused, a critical characteristic for practical applications.
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms and Thermodynamics
3.3.1. Adsorption Isotherms
The adsorption isotherm of ENR on SA-60 was analyzed at five temperatures (288, 298, 308, 318, 328 K) over a concentration range of 50–600 mg·L−1 (Figure S2). Initially, the adsorption capacity of SA-60 increased rapidly due to the abundance of available adsorption sites on the surface, which facilitated the interaction between ENR and the adsorbent. However, as the active sites became occupied and the number of available adsorption sites decreased, the adsorption capacity gradually decreased until equilibrium was reached [53]. To comprehensively investigate the adsorption behavior of SA-60, the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin–Radushkevich (D-R) models were applied for analysis. The fitting parameters for these isotherm models are provided in Table S3. The Langmuir model exhibited a high correlation (R2 > 0.998 at most temperatures), indicating a homogeneous distribution of adsorption sites on the surface and suggesting that the adsorption process may occur at specific sites, leading to the formation of monolayer coverage [51].
However, at 328 K, the Freundlich isotherm model provided a better fit with an R2 value of 0.9964, surpassing the Langmuir model. This indicates that, under these conditions, a multilayer adsorption process may also be involved [54]. These results suggest a multistep adsorption process, where the initial phase involves monolayer adsorption, followed by a second phase of multilayer adsorption.
T The theoretical maximum adsorption capacities for SA-60 were found to be 585.2 mg·g−1, 503.4 mg·g−1, 355.2 mg·g−1, 555.5 mg·g−1, and 630.2 mg·g−1 at the five different temperatures, respectively. Additionally, the parameter (kJ·mol−1) can be used to distinguish between physical adsorption ( < 8 kJ·mol−1) and chemisorption ( > 16 kJ·mol−1) [55]. The calculated values for SA-60 at different temperatures exceeded 16 kJ·mol−1, indicating that chemisorption was the dominant mechanism.
The thermodynamic parameters of ENR adsorption were evaluated using the Van’t Hoff equation, based on the isotherm data from 308 K to 328 K. The standard Gibbs free energy change (), enthalpy change (), and entropy change () for the adsorption process were determined [56]. In Table S4 and Figure S3, the values at all temperatures were negative (ranging from −0.270 to −3.027 kJ·mol−1), confirming that ENR adsorption on SA-60 is spontaneous [51]. The positive value of denoted that the adsorption process of the ENR was endothermic. In addition, the positive value of entropy, , suggested that the randomness of the system increased.
An intriguing observation in the isotherm data was the non-monotonic temperature effect: the adsorption capacity decreased slightly at 308 K compared to 298 K, but increased again at 318 and 328 K (Figure S2f and Table S3). This ‘sag’ in the adsorption vs. temperature curve reflects complex adsorption behavior. While the general increase in adsorption capacity with temperature suggests an endothermic process, the transient decrease at 308 K indicates the presence of competing factors. The subsequent recovery of adsorption capacity at higher temperatures (318–328 K) strongly supports chemisorption as the dominant mechanism, consistent with the thermodynamic analysis.
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
The kinetics of ENR adsorption on SA-60 were investigated by measuring the uptake over time at three different temperatures (288, 298, and 308 K), as shown in Figure S4a–c. In all cases, ENR adsorption was rapid during the initial stage: within the first 30 min, a significant fraction of ENR was removed from the solution. Approximately 120 min were sufficient to reach near equilibrium, with little further increase in ENR uptake beyond this time. This rapid initial adsorption can be attributed to the abundant active sites on the SA-60 surface and the high concentration gradient that drives ENR from the solution to the adsorbent. As these sites become occupied, the adsorption rate slows and eventually reaches a plateau at equilibrium.
Pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models, along with the intraparticle diffusion model, were applied to the time-course data to elucidate the rate-controlling steps (Table S5). The pseudo-second-order model provided a much better fit (R2 > 0.99) to all kinetic data than the pseudo-first-order model, and the equilibrium capacities calculated from the pseudo-second-order model (271.57, 270.41, and 262.00 mg·g−1 at 288, and 298, and 308 K, respectively) were in excellent agreement with the experimental values (around 262.71–272.89 mg·g−1). This suggests that the overall adsorption rate is controlled by chemisorption, involving valence forces through the sharing or exchange of electrons between ENR and surface sites [57].
The intraparticle diffusion plots (Figure S4d) exhibited multi-linearity, indicating that the adsorption process occurs in stages: an initial external mass transfer (film diffusion) phase, a subsequent intraparticle diffusion phase, and a final equilibrium phase. None of the regression lines in the intraparticle diffusion model passed through the origin (Table S6), and the calculated intercepts (C) for these lines were non-zero, increasing for later stages (C1 < C2 < C3). This implies that intraparticle diffusion, while significant, is not the sole rate-controlling step; a boundary layer effect and external diffusion also contribute to the overall rate [58]. Among these, intraparticle diffusion (the migration of ENR into the interior pores of SA-60) appears to be the slowest step (rate-limiting) once the external surface sites are filled [59]. Furthermore, a higher kinetic rate constant was observed at 288 K compared to 308 K during the initial phase, which could be due to a stronger driving force (a higher initial concentration gradient as slightly more ENR remains in the solution at lower temperatures) or differences in viscosity affecting diffusion. Overall, the kinetic analysis suggests that chemisorption coupled with diffusion governs the uptake of ENR on SA-60.
3.3.3. Mechanistic Insights from Spectroscopy
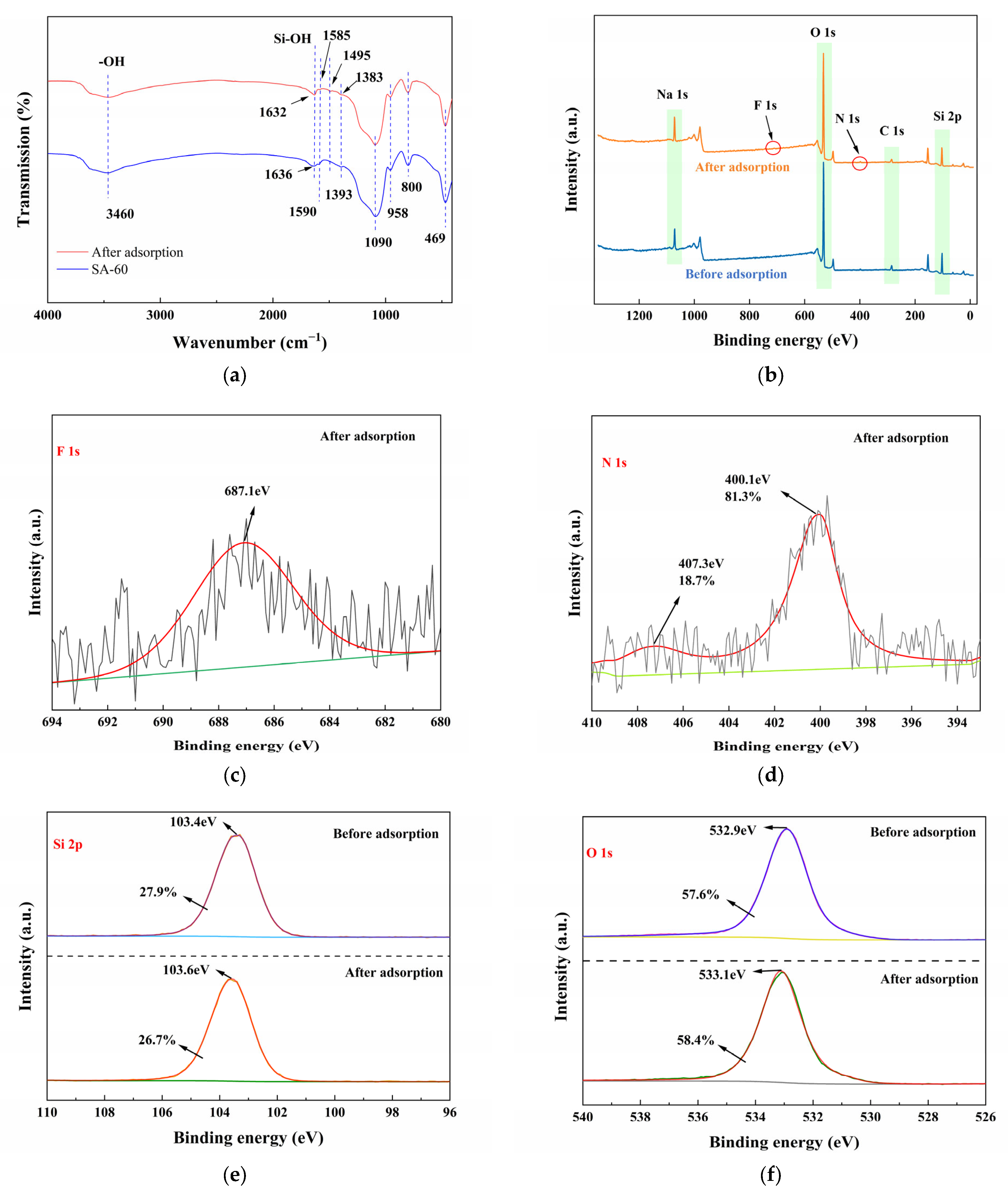
To further investigate the mechanisms underlying the adsorption of ENR onto SA-60, FT-IR and XPS analyses were performed to observe the changes before and after the adsorption, as shown in Figure 5. The FT-IR analysis (Figure 5a) reveals a broad absorption band around 3460 cm−1 prior to adsorption, corresponding to the O–H stretching vibrations of surface silanol (Si–OH) groups and adsorbed water. After ENR adsorption, the intensity of this O–H band decreases, and its position shifts slightly, indicating the involvement of these –OH groups in hydrogen bonding with ENR molecules. A subtle shift of the peak from 1636 cm−1 to 1632 cm−1 (associated with the bending vibrations of –OH and adsorbed water) further suggests an interaction between ENR and the surface –OH groups. Additionally, new bands at 1585 cm−1 and 1495 cm−1 observed on the ENR-loaded SA-60 are attributed to the aromatic ring vibrations of ENR [60], confirming the presence of ENR molecules on the adsorbent surface. Compared to the pre-adsorption state, the peak corresponding to the C–H bond of the ethoxy group bonded to silicon at 1393 cm−1 undergoes a blue shift, likely due to the adsorption of ENR molecules.
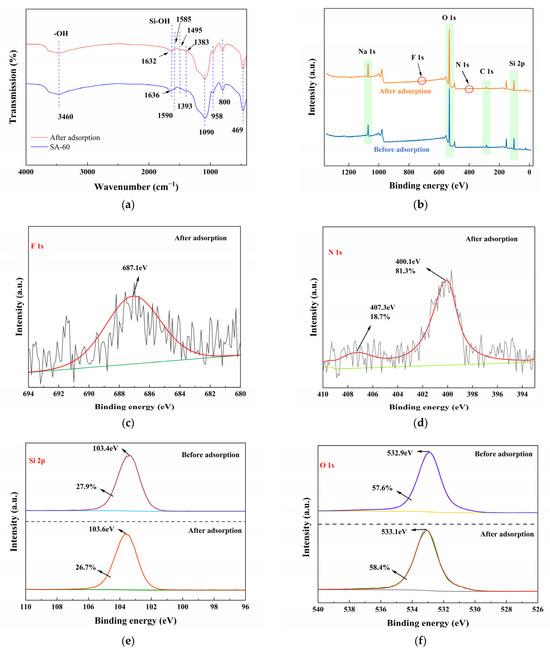
Figure 5.
(a) FT-IR of SA-60 before and after adsorption of ENR; XPS spectra of SA-60 before and after adsorption of ENR: (b) survey; (c) F 1s; (d) N 1s; (e) Si 2p; (f) O 1s.
XPS analysis was conducted to further investigate changes in the content and chemical states of surface elements before and after the adsorption of ENR onto SA-60. The XPS survey spectrum (Figure 5b) of ENR-loaded SA-60 displayed new signals corresponding to F 1s and N 1s, which were absent in the original SA-60, confirming the presence of F and N from ENR on the surface. Although the N 1s and F 1s peaks exhibited low intensities, owing to the minor content of ENR relative to the silica matrix, their binding energies provided valuable information regarding the nature of bonding. The F 1s spectrum (Figure 5c) showed a peak at 687.1 eV, characteristic of fluorine bound to carbon (F–C) in an organic molecule [30], indicating that intact ENR molecules are adsorbed rather than decomposed. The N 1s spectrum (Figure 5d) could be deconvoluted into two components at 400.1 eV and 407.3 eV. The peak near 400 eV corresponds to tertiary amine nitrogen, which is present in the piperazine ring of ENR, while the higher binding energy peak suggests the presence of protonated or positively charged nitrogen species. This could indicate that some ENR molecules or fragments became protonated or interacted strongly, forming quaternary ammonium-like environments on the surface. These N 1s features support the involvement of the amine functional group in the adsorption process, likely via electrostatic attraction to deprotonated silanol groups or hydrogen bonding.
The Si 2p and O 1s peaks of SA-60 exhibited minor shifts after ENR adsorption (Figure 5e,f). The Si 2p peak of pure SA-60 is centered around 103.4 eV, and, after adsorption, a slight shift or change in peak shape was observed. Similarly, the O 1s peak, located at approximately 532.9 eV, also showed subtle alterations. These changes suggest that the attachment of ENR modifies the local environment of Si and O atoms on the surface, likely through hydrogen bonding between ENR (containing –COOH and –C=O groups) and surface –OH groups, as well as possible coordination or dipole interactions involving Si–O– groups. Specifically, the decrease in the relative atomic percentage of Si 2p (from 27.9% to 26.7%) and the slight increase in O 1s (from 57.6% to 58.4%) after adsorption may indicate that some surface silanols are now interacting with ENR [39,57]. These FT-IR results, in conjunction with the XPS data, support a mechanism involving multiple interactions: hydrogen bonding (between the –COOH or –NH groups of ENR and the –OH groups of SA-60), electrostatic interactions (between protonated ENR amino groups and the deprotonated silanol sites), and possibly π–π stacking interactions.
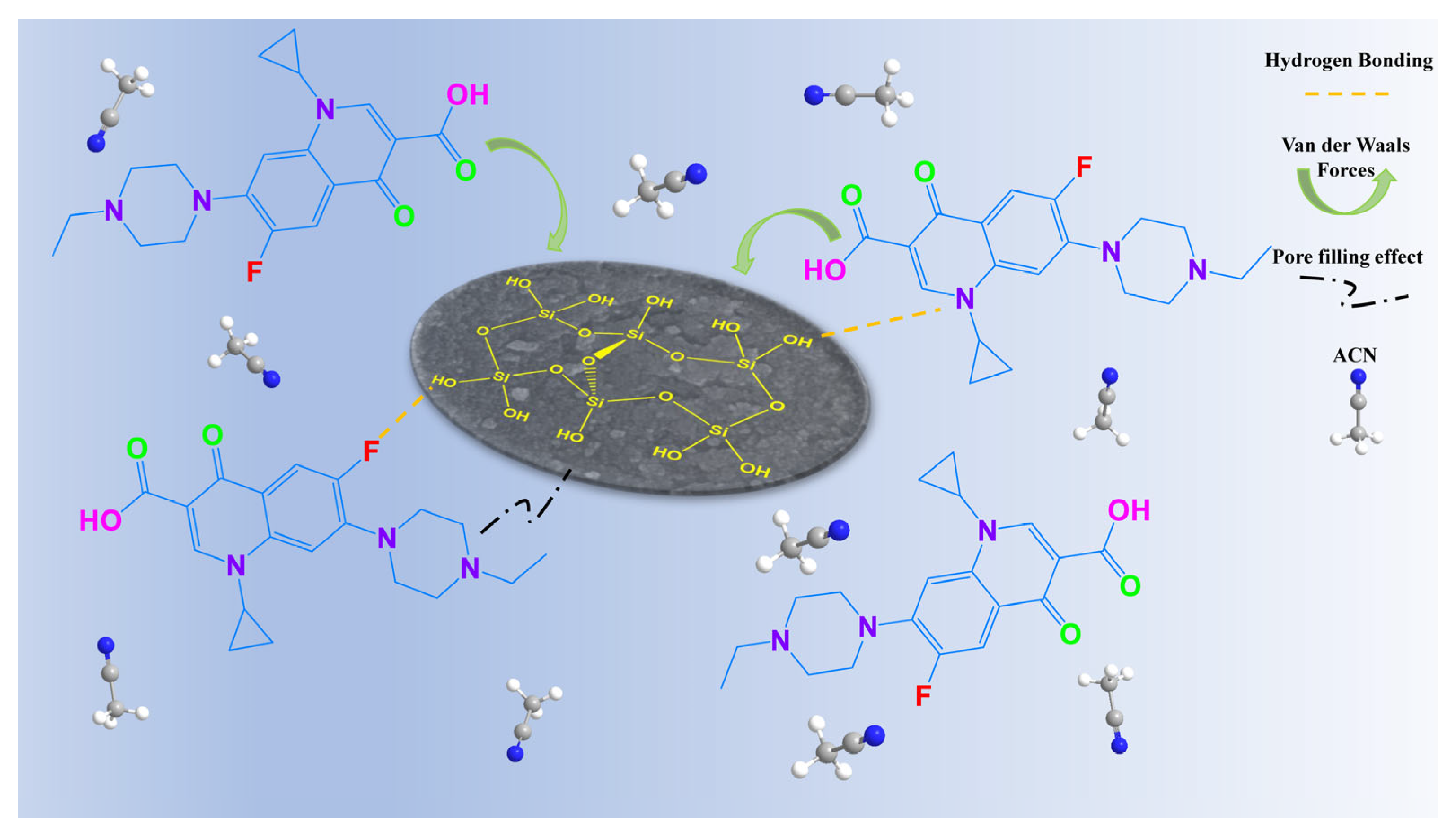
Based on experimental data (isotherms, kinetics, FT-IR, XPS, and selective adsorption tests with analogues; Figure 3c, Figure 4a,b, Figures S2 and S3, respectively, along with the characterization results (Figure 5), a schematic mechanism for ENR adsorption onto SA-60 is proposed in Figure 6. In summary, the mesoporous SA-60 acts as a high-surface-area scaffold rich in silanol group. Upon the introduction of ENR, it can enter the pores and adhere to the surface through hydrogen bonding (e.g., the fluorine atom of ENR interacting with the –OH group on silica) and electrostatic interactions. The presence of specific functional groups in ENR promotes a better fit and stronger interaction, explaining the selectivity for FQs. During the adsorption process, ENR first diffuses to the external surface, then gradually penetrates into the pores, forming the aforementioned bonds until the surface sites become saturated.
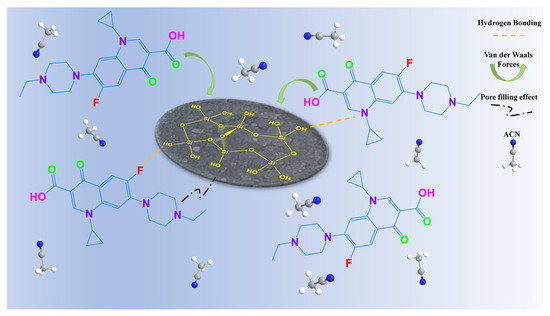
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of ENR adsorption mechanism over SA-60 in ACN.
3.3.4. Application in Treating ACN-Water Waste
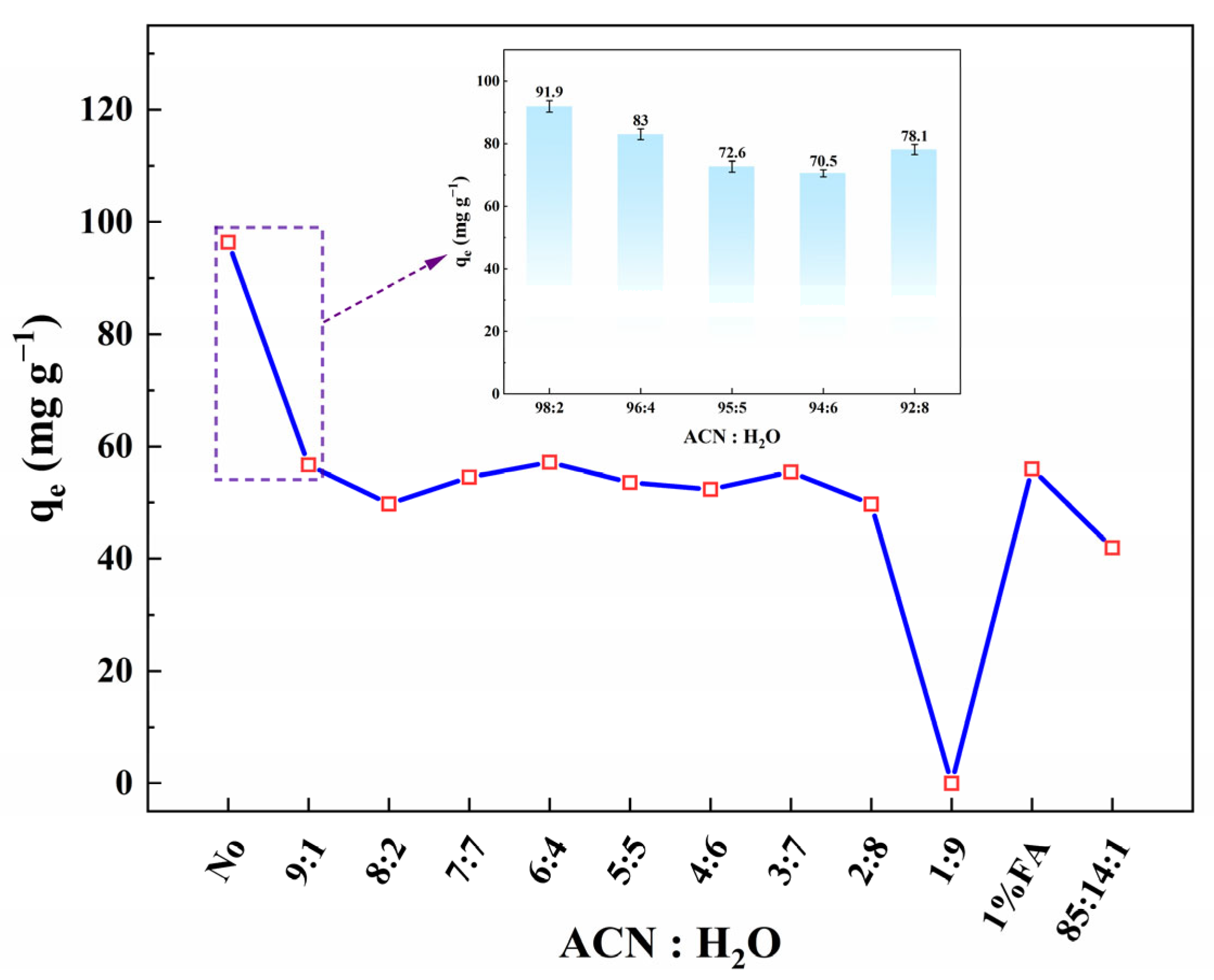
As shown in Figure 7, the performance of SA-60 in adsorbing ENR from simulated ACN-water OWLs, acidified with FA or HAc, was investigated. It was observed that the presence of water significantly affected adsorption capacity. When using pure ACN (without water, containing only a small amount of acid), SA-60 demonstrated a high ENR uptake, which is consistent with previous findings. However, as the water content in the ACN waste increased up to 10%, the adsorption capacity of SA-60 for ENR markedly decreased. This reduction is likely due to water, a highly polar protic solvent, competing with ENR for the active sites on SA-60. Water molecules can easily form hydrogen bonds with the surface –OH groups on SA-60, effectively occupying these sites [61].
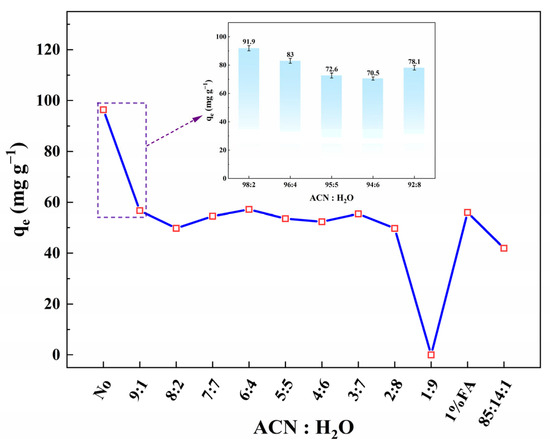
Figure 7.
Effect of water ratio on ENR adsorption by SA-60 (C0 = 200 mg·L−1, m/V = 2 g·L−1, pH = 7, and T = 298 K).
Water can induce slight swelling or structural changes in the pore structure of SA-60, and its high dielectric constant may reduce electrostatic interactions [62]. Notably, as the water content increased beyond 10% (to 20%, 40%, and 80%), the ENR adsorption capacity on SA-60 did not continue to decrease but stabilized between 49.7 and 57.2 mg·g−1. This stabilization indicates that, once water saturates most of the surface –OH sites and occupies some of the pores, further increases in water content do not significantly displace ENR. Instead, ENR likely occupies available sites or adsorbs in multilayers or on the outer surface. However, at a water content of 90%, ENR adsorption was nearly completely suppressed, as the aqueous solvent system promotes stronger interactions with the predominantly ionic ENR than the hydrophobized silica surface.
The solvent dependency of ENR adsorption was further confirmed by comparing the adsorption behavior in different pure solvents (Table 3). SA-60 exhibited significantly higher adsorption efficiency in aprotic solvents (e.g., ACN and EA) compared to protic solvents (e.g., H2O, MeOH, EtOH, IPA). For instance, in pure ACN, ENR removal reached 93.7%, while in pure water it was essentially 0%, indicating negligible adsorption. Protic solvents such as MeOH and other alcohols achieved only about 69% removal. Despite having a low dielectric constant, aprotic solvents like EA still yielded higher ENR adsorption (88.9%). This trend suggests that protic solvents hinder ENR adsorption on SA-60 by donating protons and forming hydrogen bonds with the adsorbent surface, thus occupying active sites. In contrast, dipolar aprotic solvents like ACN, which possess strong polarity (high dielectric constant) but are unable to effectively donate hydrogen bonds (due to their non-polar hydrogens), do not compete strongly with ENR for surface sites. Notably, ACN, with a relatively high dielectric constant (37.5) and being aprotic, provided the most favorable medium for ENR adsorption. This is likely due to its ability to solvate ENR sufficiently to maintain its mobility, while not interfering with the interaction of ENR with SA-60. Furthermore, the observation that a neutral pH (or less protic environment) enhances adsorption aligns with the solvent effect: the presence of acids in ACN reduces performance (Figure 3c).

Table 3.
Adsorption rate of dry and wet SA-60 for ENR in various solvents.
The effect of pre-wetting SA-60 with water was also investigated. Dry SA-60 significantly outperformed wet SA-60: when the SA-60 was saturated with water prior to use, its ENR adsorption rate in ACN decreased from 93.66% (dry) to 68.57% (wet). This reduction is attributable to the pre-adsorbed water blocking many adsorption sites. However, when the wet SA-60 was re-dried, its performance in ACN was almost completely restored (86.21% adsorption), indicating that the decrease in adsorption was due to reversible surface occupation by water, rather than permanent damage. In a 90% ACN-water mixture, wet SA-60 exhibited only 26.84% ENR removal, compared to 56.72% for dry SA-60, emphasizing the importance of keeping the SA dry for optimal performance in partially aqueous systems. These results demonstrate that SA-60 is highly effective for ENR removal from OWLs (such as those from analytical labs or pharmaceutical manufacturing), even in the presence of some water. However, its capacity diminishes as the system becomes more aqueous. Practically, this suggests that SA-60 is best suited for OWLs with low to moderate water content. Nonetheless, even in an 80% water-ACN solution, SA-60 still captured a significant amount of ENR (49.73 mg·g−1), which is promising for real-world scenarios where OWLs typically contain some water.
3.4. Comparison with Other Adsorbents
To contextualize the performance of SA-60, a comparison was made with other reported adsorbents for antibiotic removal (Table S7). SA-60 stands out for its simple, green synthesis and high efficiency. Many conventional adsorbents, such as activated carbons, clays, and molecularly imprinted polymers, either exhibit lower adsorption capacities for FQs or require more complex and energy-intensive preparation methods. In contrast, SA-60 achieves an adsorption capacity exceeding 600 mg·g−1 for ENR in ACN, particularly when considering its selectivity and reusability. Furthermore, SA-60 does not require stringent pH control for optimal performance, whereas some adsorbents only function within narrow pH ranges. The APD of SA-60, coupled with its avoidance of toxic solvents (using only ethanol and water) and room-temperature aging, significantly reduces energy consumption and waste treatment demands compared to other high-performance adsorbents. While direct cost comparisons would require industrial-scale trials, these characteristics align with established green chemistry principles, supporting scalable production. These features position SA-60 as one of the more environmentally friendly options, with potential for cost-effective production. Another notable advantage is its selectivity for FQs: in a mixture of 14 different FQs (listed in Table S1) and other drugs, SA-60 preferentially adsorbs FQs, which is advantageous when targeting this class of contaminants. Many other adsorbents lack such selectivity and adsorb a broad range of organic compounds, which can be disadvantageous when specifically removing antibiotics from complex matrices. Compared to existing materials, SA-60 offers a compelling combination of easy synthesis, high capacity, selectivity, and reusability, indicating strong potential for real-world applications in wastewater or OWLs treatment involving antibiotics.
4. Conclusions
In this study, mesoporous silica aerogel (SA-60) was successfully synthesized via a straightforward sol–gel process combined with ambient pressure drying, and its efficacy as a selective adsorbent for the removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics (FQs) from organic waste liquids (OWLs) was demonstrated. The experimental results revealed that adsorption efficiency was influenced by parameters such as pH, adsorbent dosage, initial ENR concentration, contact time, and temperature. Batch experiments indicated that the adsorption of ENR followed the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic models, suggesting that chemisorption was the dominant adsorption mechanism at the molecular level. Furthermore, FT-IR and XPS analyses provided insights into the adsorption mechanism, identifying hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions, and pore matching as key factors. SA-60 exhibited a high adsorption capacity (630.18 mg·g−1), excellent selectivity for FQs, and robust reusability (80% retention after 5 cycles) under the tested conditions, while showing low sensitivity to changes in pH and moisture content in organic solutions. These characteristics collectively highlight its potential as a high-performance adsorbent. Additionally, SA-60 demonstrates scalability potential due to its simple synthesis, selectivity, and reusability, although future studies should further explore the underlying mechanisms (e.g., non-monotonic temperature dependence and functional group interactions) and validate its performance in rich-water-content environments and complex OWLs. The practical deployment of SA-60 requires overcoming challenges such as scalable production, cost-effective reusability, long-term stability under real conditions, and compliance with regional effluent standards. In conclusion, the facilely prepared SA-60 shows promise for potential applications in antibiotic remediation, pending further evaluation under real OWLs conditions. Its environmentally friendly synthesis and superior performance under controlled laboratory conditions demonstrate the material’s potential for antibiotic removal applications. While its selective adsorption mechanism and reusability are promising, further validation in complex real-world OWL matrices is needed to assess its practical applicability. These findings provide a foundational approach for developing selective adsorbents to address emerging pollutants, with potential for adaptation to real-world conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information is available for downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/environments12090300/s1. Figure S1: (a) XRD pattern of SA-60; (b) TGA weight loss curve of SA-60; (c) FT-IR spectra of SA-60; (d) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm of SA-60. Figure S2: Adsorption isotherm data for ENR on SA-60 at different temperatures, fitted with the Langmuir, Freundlich, and D–R models: (a) 288 K; (b) 298 K; (c) 308 K; (d) 318 K; (e) 328 K (adsorbent dose m/V = 2 g·L−1, pH = 7); (f) The effect of temperature on ENR adsorption by SA-60 (C0 = 600 mg·L−1). Figure S3: Relationship between 1/T and lnK0 for ENR adsorption on SA-60 (initial concentration C0 = 600 mg·L−1, adsorbent dose m/V = 2 g·L−1, pH = 7). Figure S4: Adsorption kinetics of ENR on SA-60 at various temperatures: pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic model fits at (a) 288 K; (b) 298 K; (c) 308 K; and (d) intra-particle diffusion model plots (initial concentration C0 = 600 mg·L−1, adsorbent dose m/V = 2 g·L−1, pH = 7). Table S1: Detailed information on compounds used for selectivity testing in this study; Table S2: Surface area and porosity of SA-60 determined from N2 adsorption; Table S3: Langmuir, Freundlich, and D–R isotherm parameters for ENR adsorption on SA-60 at different temperatures; Table S4: Thermodynamic parameters for ENR adsorption on SA-60 at different temperatures (Van’t Hoff analysis); Table S5: Kinetic model parameters for ENR adsorption on SA-60 at various temperatures; Table S6: Intra-particle diffusion model fitting parameters for ENR adsorption on SA-60 at different temperatures; Table S7: Comparison of SA-60 with reported adsorbent materials for antibiotic removal. References [63,64,65,66,67] are cited in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.K., X.S. and W.X.; methodology, G.Y. and Z.L.; validation, Y.Z., L.G., W.X. and W.Z.; formal analysis, Y.Z. and P.W.; investigation, Z.L.; data curation, Y.Z., Z.L., J.Z. and P.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z., L.G. and Z.L.; writing—review and editing, C.K., G.Y. and C.F.; supervision, C.K. and C.F.; funding acquisition, C.K. and G.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant number: 2023YFD2401200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 31701698), Shanghai Municipal Commission of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (Grant number: 2024-02-08-00-12-F00033), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant number: 22142201400), Shanghai Key Lab of Forensic Medicine, Key Lab of Forensic Science, Ministry of Justice, China (Academy of Forensic Science) (Grant number: KF202306), and the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, ECSFR, CAFS (Grant number: NO. 2024YC03).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the partners who granted access to their facilities, which was essential for the successful completion of this study. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| FQs | Fluoroquinolone antibiotics |
| OWLs | Organic waste liquids |
| SAs | Silica aerogels |
| APD | Ambient pressure drying |
| FeCl2 | Ferrous chloride |
| MgSO4 | Magnesium sulfate |
| ZnCl2 | Zinc chloride |
| CuCl2 | Copper (II) chloride |
| NH3·H2O | Ammonia solution |
| HCl | Hydrochloric acid |
| FA | Formic acid |
| HAc | Acetic acid |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| EtOH | Absolute ethanol |
| IPA | Isopropanol |
| EA | Ethyl acetate |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ENR | Enrofloxacin |
| CBF | Carbofuran |
| NASONEX | Mometasone furoate |
| SD | Sulfadiazine |
| LCM | Lincomycin |
| NZP | Nitrazepam |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| HPLC-HRMS | High-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Characterization
In this work, scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Regulus8100, HITACHI, Tokyo, Japan) was utilized to observe the morphology and microstructure of the samples. Functional groups present on the samples were analyzed using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy (Bruker Optik GmbH T27 1181, Karlsruhe, Germany) within a scanning range of 400–4000 cm−1. The specific surface area and pore size distribution of the samples were calculated using the multi-point Barrett–Emmett–Teller (BET) method and the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method, based on N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms determined by an accelerated surface area and porosity analyzer (Micromeritics ASAP-2460, Norcross, GA, USA). The crystalline structure of the product was examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD) on a Rigaku D/max-B X-ray diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation. The chemical composition and elemental valence states of the samples, both before and after adsorption, were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, Nexsa, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). A thermo-gravimetric analyzer (TGA, New STA & STA7000, Tokyo, Japan) was employed to investigate the thermal stability of the samples.
Chromatographic analysis was performed using an HPLC system (Dionex UltiMate 3000, Waltham, MA, USA) coupled to a Q-Exactive™ hybrid quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with a heated electrospray ionization source. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 RRHD column (2.1 × 50 mm, 1.8 μm) at 40 °C. The mobile phase consisted of ultrapure water with 5 mM ammonium acetate (solvent A) and methanol (solvent B), both containing 0.2% formic acid, at a flow rate of 0.4 mL·min−1. A gradient elution was used as follows: 0–1 min, 1% B; 1–6 min, linear increase to 20% B; 6–8 min, ramp to 100% B; 8–10 min, hold at 100% B; 10.1–12 min, return to 1% B for re-equilibration. The injection volume was 4 μL. The mass spectrometer was operated in positive electrospray ionization mode with a spray voltage of 4.0 kV. The sheath gas flow was 50 psi, auxiliary gas 15 psi (sweep gas 0 psi), capillary temperature 320 °C, and auxiliary gas heater 50 °C. The S-lens RF level was set to 50. Full-scan mass spectra were acquired over m/z 80–600 at a resolution of 70,000.
Appendix A.2. Adsorption Experiments
The enrofloxacin (ENR) adsorption properties of the silica aerogel were investigated through batch adsorption experiments. In a typical test, a known mass of SA-60 was added to a series of glass vials containing ENR solution in acetonitrile (ACN) at a desired initial concentration. The solution pH was adjusted to the target value using 0.1 M HCl or NH4OH. Each vial was agitated at 100 rpm in a temperature-controlled shaker bath until adsorption equilibrium was reached (as indicated by no further change in ENR concentration). After equilibration, the mixtures were appropriately diluted and filtered, and the remaining ENR concentration was measured by HPLC-HRMS. The ENR adsorption capacity (mg·g−1) and the removal percentage R (%) were calculated as follows [29,30]:
where is the equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg·g−1), is the initial ENR concentration (mg·L−1), is the ENR concentration at equilibrium (mg·L−1), is the volume of the solution (L), m is the mass of the silica aerogel (g), and R is the adsorption percentage (%).
Furthermore, we systematically examined the effects of pH, contact time, initial ENR concentration, adsorbent dosage, and temperature on ENR uptake.
Appendix A.3. Adsorption Isotherms
Equilibrium adsorption isotherm data were fitted to the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) models [55,68,69] to elucidate the adsorption mechanism between ENR and SA-60. The nonlinear forms of these isotherm models are given in Equations (A3)–(A5):
where is the amount of ENR adsorbed at equilibrium (mg g−1), and is the equilibrium ENR concentration in the solution (mg L−1). In the Langmuir model (Equation (A3)), represents the maximum adsorption capacity (mg g−1), and (L mg−1) is the adsorption equilibrium constant. In the Freundlich model (Equation (A4)), is the adsorption equilibrium constant (mg(1−(1/n)) L(1/n) g−1), and n is the heterogeneity factor, representing the bond distribution; values of n in the range of 1 < n < 10 indicate favorable adsorption. According to the D–R model (Equation (A5)), is the adsorption equilibrium constant (mol2 kJ−2), is the Polanyi potential, and E (kJ mol−1) represents the free energy of adsorption.
Appendix A.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
To determine the adsorption thermodynamics of ENR removal, Gibbs free energy (), changes in the enthalpy of the system (), and changes in the entropy () were studied from the temperature-dependent adsorption batch study. Three temperatures were considered: 308 K, 318 K, and 328 K. , , and were calculated according to the following Equations (A6) and (A7) [70,71]:
where is the equilibrium constant, the ratio of the amount adsorbed on adsorbents to the residual concentration in solution at equilibrium; T (K) and R (8.314 J mol−1K−1) represent the operation temperature and the universal gas constant, respectively.
Appendix A.5. Adsorption Kinetics
Adsorption kinetics were studied to evaluate how various factors influence the adsorption rate and to identify the rate-controlling steps of the process. The pseudo-first-order (PFO), pseudo-second-order (PSO), and intra-particle diffusion models were applied to analyze the time-dependent adsorption data as described by Equations (A8)–(A10) [72,73,74]:
where and are as defined above, is time (min), and (min−1), (g mg·min−1), and (mg g−1 min0.5) are the rate constants for the pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order sorption, and intra-particle diffusion models, respectively; (mg·g−1) is a constant related to the boundary layer thickness.
Appendix A.6. Selectivity and Repeatability Experiment
The selective adsorption capability of SA-60 for ENR was first evaluated using a mixed standard solution of fluoroquinolone antibiotics (containing ENR and other FQs). Subsequently, a mixed solution containing representatives of six different categories of compounds (as listed in Table S1: a pesticide, steroid hormone, fluoroquinolone antibiotic, sulfonamide, macrolide antibiotic, and a sedative) was used to further assess selectivity. In each selectivity test, 20 mg of SA-60 was added to 2 mL of the mixed solution with an initial concentration of 50 μg·L−1 for each analyte. After adsorption for 4 h at 25 °C, the solution was diluted, filtered, and the concentrations of the analytes were determined by HPLC-HRMS. The distribution coefficient (L mg−1) and selectivity coefficient are defined as follows [75]:
The adsorption capacity is denoted by ; represents the equilibrium concentration of the competing compounds; refers to the distribution coefficient of the selected compounds between the adsorbent and the solution; and FQs and X represent fluoroquinolone antibiotics and other competing compounds, respectively.
The reusability of SA-60 was investigated through consecutive adsorption-desorption cycles. After each ENR adsorption (200 mg·L−1 ENR in ACN, adsorbent dosage 2 g·L−1, pH 7), the adsorbent was recovered and regenerated by stirring in 1% formic acid in methanol for 10 min, followed by thorough washing with methanol. The regenerated aerogel was separated by centrifugation, dried at ambient conditions, then reused in the next cycle of ENR adsorption under the same conditions. ENR uptake after each cycle was measured as described above.
References
- Suyamud, B.; Chen, Y.; Quyen, D.T.T.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, C.; Hu, J. Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: Occurrence and strategies in Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuprys, A.; Pulicharla, R.; Brar, S.K.; Drogui, P.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Fluoroquinolones metal complexation and its environmental impacts. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 376, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Wang, Z.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Sharma, V.K. Metal-mediated oxidation of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in water: A review on kinetics, transformation products, and toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1136–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Fu, P.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Fang, X.; Yang, T.; Huang, Z.; Huang, C. Separation-and-Recovery Technology for Organic Waste Liquid with a High Concentration of Inorganic Particles. Engineering 2018, 4, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimolade, B.O.; Oladipo, A.O.; Idris, A.O.; Usisipho, F.; Azizi, S.; Maaza, M.; Lebelo, S.L.; Mamba, B.B. Advancements in electrochemical technologies for the removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in wastewater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.-J.; Chung, K.-H.; Lai, Y.-F.; Lai, Y.-K.; Chang, S.-H. Keratin particles generated from rapid hydrolysis of waste feathers with green DES/KOH: Efficient adsorption of fluoroquinolone antibiotic and its reuse. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 173, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Tian, M.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Tao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wen, Z.; et al. Covalent assembly synthesis of covalent organic framework and MXene based composite for the adsorption of fluoroquinolones. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C. Fluorinated/sulfonated dual-functional three-component covalent organic polymer for adsorption of fluoroquinolones: Preparation, adsorption performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, H.; Kanjariya, P.; Ballal, S.; Panigrahi, R.; Ariffin, I.A.; Tantawi, D.; Abosaoda, M.K.; Nathiya, D.; Jayabalan, K.; Chauhan, A.S. Recent advances in the synthesis of magnetic nanocomposites for the adsorption of heavy metal ions from wastewater. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1345, 143019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, V.-A.; Dang, V.D.; Thuy, N.T.; Pandit, B.; Vo, T.-K.-Q.; Khedulkar, A.P. Fluoroquinolones: Fate, effects on the environment and selected removal methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 137762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.N.; Mo, K.H.; Yap, S.P.; Radwan, M.K.H. Towards an energy efficient cement composite incorporating silica aerogel: A state of the art review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çok, S.S.; Koç, F.; Gïzlï, N. Lightweight and highly hydrophobic silica aerogels dried in ambient pressure for an efficient oil/organic solvent adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.-D.; Cheng, X.; Zheng, Y.-M. Facile co-precursor sol-gel synthesis of a novel amine-modified silica aerogel for high efficiency carbon dioxide capture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vareda, J.P.; Matias, P.M.C.; Paixão, J.A.; Murtinho, D.; Valente, A.J.M.; Durães, L. Chitosan–Silica Composite Aerogel for the Adsorption of Cupric Ions. Gels 2024, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Han, H.H.; Parale, V.G.; Kim, T.; Park, W.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Bae, Y.-S.; Park, H.-H. Rigid amine-incorporated silica aerogel for highly efficient CO2 capture and heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhavale, R.P.; Parale, V.G.; Choi, H.; Kim, T.; Lee, K.-Y.; Phadtare, V.D.; Park, H.-H. Epoxy-thiol crosslinking for enhanced mechanical strength in silica aerogels and highly efficient dye adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 642, 158619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert Çok, S.; Koç, F.; Len, A.; Gizli, N.; Dudás, Z. The role of surface and structural properties on the adsorptive behavior of vinyl-methyl decorated silica aerogel-like hybrids for oil/organic solvent clean-up practices. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 334, 125958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, F.; Du, C.; He, S. Preparation of Super-Flexible Silica Aerogel and Its Application in Oil–Water Separation. Gels 2023, 9, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, M.; Chen, Z.; Lu, L.; Ma, Z.; Ding, Y.; Yin, L.; Liu, T.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; et al. A layered aerogel composite with silica fibers, SiC nanowires, and silica aerogels ternary networks for thermal insulation at high-temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 204, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Hendrix, Y.; Schollbach, K.; Brouwers, H.J.H. A silica aerogel synthesized from olivine and its application as a photocatalytic support. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari-Gargari, A.; Moghaddas, J.; Hamishehkar, H.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Carboxylic acid decorated silica aerogel nanostructure as drug delivery carrier. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 323, 111220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Prajapati, A.; Kumar, A.; Acharya, S. Synthesis of silica aerogel and its application for removal of crystal violet dye by adsorption. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2023, 5, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani Dorcheh, A.; Abbasi, M.H. Silica aerogel; synthesis, properties and characterization. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 199, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Orita, Y.; Shimoyama, Y. Photo-thermal CO2 desorption from amine-modified silica/carbon aerogel for direct air capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Ren, J.; Liu, W.; Yan, W.; Zhu, K.; Kong, Y.; Jiang, X.; Shen, X. Facile Synthesis of Polymer-Reinforced Silica Aerogel Microspheres as Robust, Hydrophobic and Recyclable Sorbents for Oil Removal from Water. Polymers 2023, 15, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, F.; Bao, Y.; Zhan, S. A Mini Review on the Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica and its Application in Antibiotic Removal. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2025, 9, 2400634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Tudorache, D.-I.; Bocioagă, M.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Hadibarata, T.; Grumezescu, A.M. An Updated Overview of Silica Aerogel-Based Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, J.; Ahankari, S.S. Nanocellulose-based aerogels for water purification: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 309, 120677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Ma, X. Multi-templates surface molecularly imprinted polymer for rapid separation and analysis of quinolones in water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 7177–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, P.; Zhang, X.; Lan, D.L.; Liu, Y.; Lai, W.; Shehzad, H.; Zhou, L.; Ouyang, J. Synthesis of Zr-based metal-organic framework/MWCNTs composite for adsorption of enrofloxacin from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 334, 126004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çok, S.S.; Koç, F.; Len, A.; Kriechbaum, M.; Dudás, Z. Antibiotic adsorption from aqueous media by using silica aerogels derived from amine-bridged silsesquioxane networks. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 68, 106538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Hong, W.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Duan, X. A novel mesoporous Fe-silica aerogel composite with phenomenal adsorption capacity for malachite green. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 281, 119950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Chen, K.; Ma, D.; Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Qin, S.; Luo, Y. Synthesis of high specific surface area silica aerogel from rice husk ash via ambient pressure drying. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 539, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Qu, M.; Wang, X.; Ai, X.; Tang, P.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Bin, Y. Preparation of Epoxy-Enhanced Silica Aerogels with Thermal Insulation and Hydrophobicity by Ambient Pressure Drying. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 2997–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, X.; Wang, P.; Fang, K.; Li, J.; Hao, D.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; et al. Synergistic mechanisms for efficient and safe antibiotic removal: Effective adsorption and photocatalytic degradation using aerogels. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel Kaya, G.; Yilmaz, E.; Deveci, H. Synthesis of sustainable silica xerogels/aerogels using inexpensive steel slag and bean pod ash: A comparison study. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Sun, W.; Yan, Z.; Ji, X.; Hu, H.; Wei, W. Selective adsorption of organic dyes by porous hydrophilic silica aerogels from aqueous system. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanec, A.M.; Anderson, A.M.; Avanessian, C.; Carroll, M.K. Analysis and characterization of etched silica aerogels. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 94, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Li, Q.; Liao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W. Highly enhanced adsorption performance to uranium(VI) by facile synthesized hydroxyapatite aerogel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, S. Dissolution and leaching mechanisms of calcium ions in cement based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Pan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Xu, Z. Rapid adsorption of directional cellulose nanofibers/3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane/polyethyleneimine aerogels on microplastics in water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Esmorís, C.; Rodríguez-López, L.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Arias-Estévez, M. Influence of pH on the adsorption-desorption of doxycycline, enrofloxacin, and sulfamethoxypyridazine in soils with variable surface charge. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zuo, S.; Liu, Z.; Xiong, K.; Ren, L.; Zhang, X. Adsorption of tetracycline on copper alginate-graphene oxide aerogels prepared by secondary lyophilization under CuSO4 crosslinking. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1338, 142289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, M.; He, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wen, X. Waste cotton-based activated carbon with excellent adsorption performance towards dyes and antibiotics. Chemosphere 2025, 376, 144292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Yang, M.; Zhai, J.; Bai, W.; Dai, L.; Liu, L.; Jiang, S.; Wang, W.; Ren, E.; Cheng, C.; et al. Bamboo cellulose–derived activated carbon aerogel with controllable mesoporous structure as an effective adsorbent for tetracycline hydrochloride. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 12558–12570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Phuong, V.N.; Van, T.N.; Thi, P.N.; Dinh Thi Lan, P.; Pham, H.T.; Cao, H.T. Low-cost hydrogel derived from agro-waste for veterinary antibiotic removal: Optimization, kinetics, and toxicity evaluation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liu, X.; Lv, S.; Wei, D.; Liu, L. Three-dimensional graded porous structure and compressible KGM-GO/CS/SA composite aerogel spheres for efficient adsorption of antibiotics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 346, 127547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-K.-T.; Nguyen, T.-B.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Kumar Patel, A.; Bui, X.-T.; Chen, L.; Singhania, R.R.; Dong, C.-D. Phosphoric acid-activated biochar derived from sunflower seed husk: Selective antibiotic adsorption behavior and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 371, 128593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cui, Z.; Wu, T.; Tian, D. Superelastic and ultralight covalent organic framework composite aerogels modified with different functional groups for ultrafast adsorbing organic pollutants in water. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 36, 110761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordi, Z.; Ghorbani, M.; Ahmadian Khakhiyani, M. Adsorptive removal of enrofloxacin with magnetic functionalized graphene oxide@ metal–organic frameworks employing D-optimal mixture design. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Wen, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.; Qi, L. Characterization and sulfonamide antibiotics adsorption capacity of spent coffee grounds based biochar and hydrochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Liang, J.; Fang, Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Tang, C. Selective adsorption behavior/mechanism of antibiotic contaminants on novel boron nitride bundles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajudheen, P.; Karthikeyan, P.; Ramkumar, K.; Meenakshi, S. Effective removal of organic pollutants by adsorption onto chitosan supported graphene oxide-hydroxyapatite composite: A novel reusable adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babas, H.; Khachani, M.; Warad, I.; Ajebli, S.; Guessous, A.; Guenbour, A.; Safi, Z.; Berisha, A.; Bellaouchou, A.; Abdelkader, Z.; et al. Sofosbuvir adsorption onto activated carbon derived from argan shell residue: Optimization, kinetic, thermodynamic and theoretical approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 356, 119019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, L.; Tang, J.; Liu, Z.; Dai, Y. Adsorption interactions between typical microplastics and enrofloxacin: Relevant contributions to the mechanism. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransing, A.A.; Wang, Q.; Dhavale, R.P.; Choi, H.; Bangi, U.K.H.; Parale, V.G.; Lee, W.; Kanamori, K.; Park, H.-H. Ionotropically-engineered synthesis of mechanically robust hybrid sodium alginate–silica aerogels with enhanced specific surface area for high-capacity and selective dye adsorption from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tao, K.; Xia, W.; Yu, C.; Yang, H. A novel cellulose/lignin/montmorillonite ternary hybrid aerogel for efficiently adsorptive removal of antibiotics from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ning, S.; Yin, X.; Fujita, T.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, X. Synthesis and fabrication of segregative and durable MnO2@chitosan composite aerogel beads for uranium(VI) removal from wastewater. Water Res. 2023, 247, 120819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lu, T.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Li, P.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, F.; Cui, S.; Qi, X.; et al. Efficient adsorptive removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics from water by alkali and bimetallic salts co-hydrothermally modified sludge biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 298, 118833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Shao, Y.-W.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y.-F.; Liang, Z.-X.; Guo, F.-Z.; Li, P.-C.; Wang, Y. Chitosan-Cross-Linked Graphene Oxide/Carboxymethyl Cellulose Aerogel Globules with High Structure Stability in Liquid and Extremely High Adsorption Ability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8775–8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.-C.; Doka Dari, M.; Tang, X.-Q.; Yuan, P.-Q. Diffusion of benzene through water film confined in silica mesopores: Effect of competitive adsorption of solvent. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 224, 115793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchur, Y.; Pavlyuk, O.; Andrushchak, A.S.; Vitusevich, S.; Kityk, A.V. Porous Si Partially Filled with Water Molecules—Crystal Structure, Energy Bands and Optical Properties from First Principles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraban Khaledi, S.; Taherimehr, M.; Hassaninejad-Darzi, S.K. Porous Fe-Porphyrin as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Ciprofloxacin from Water. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 15950–15958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tian, W.; Chu, M.; Zou, M.; Zhao, J. Molecular imprinting functionalization of magnetic biochar to adsorb sulfamethoxazole: Mechanism, regeneration and targeted adsorption. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, K.; Tang, Y. Elastic BN aerogel for efficient adsorption of tetracycline. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2024, 149, 111620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Gong, J.; Ren, Q.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liang, Z. Preparation of Zn/Zr-MOFs by microwave-assisted ball milling and adsorption of lomefloxacin hydrochloride and levofloxacin hydrochloride in wastewater. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yu, B.; Wang, Q.; Owens, G.; Chen, Z. Enhanced removal of pefloxacin from aqueous solution by adsorption and Fenton-like oxidation using NH2-MIL-88B. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 583, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xiong, W.; Yang, Z.; Cao, J.; Jia, M.; Xiang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Xu, Z. Facile fabrication of three-dimensional hierarchical porous ZIF-L/gelatin aerogel: Highly efficient adsorbent with excellent recyclability towards antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Yao, S.; Wang, Z.; Qi, F.; Liu, X. Preparation of nitrogen-doped hierarchical porous carbon aerogels from agricultural wastes for efficient pollution adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Peng, C.; Deng, Q.; Yu, Y.; He, X.; Hu, T.; Jiang, L.; Shan, S.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of l-aspartic acid-based metal organic aerogel (MOA) for efficient removal of oxytetracycline from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 610, 155608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Ghosh, S.; Das, P. Extraction of silica and biochar from biomass waste for the synthesis of aerogel and its application for the removal of dye. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Tang, X.; Qin, Y.; Maimaiti, A.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L. Enhanced removal of methylene blue from wastewater by alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose-melamine sponge composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, P.; Ma, J. Lanthanum modification κ-carrageenan/sodium alginate dual-network aerogels for efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Q.; Wu, F.; Chen, S.; Su, T.; Qi, X. Adsorption of antibiotics by polydopamine-modified salecan hydrogel: Performance, kinetics and mechanism studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brião, G.d.V.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Efficient and Selective Adsorption of Neodymium on Expanded Vermiculite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 4962–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).