Effects of Dietary Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics on the Thyroid Gland in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Husbandry
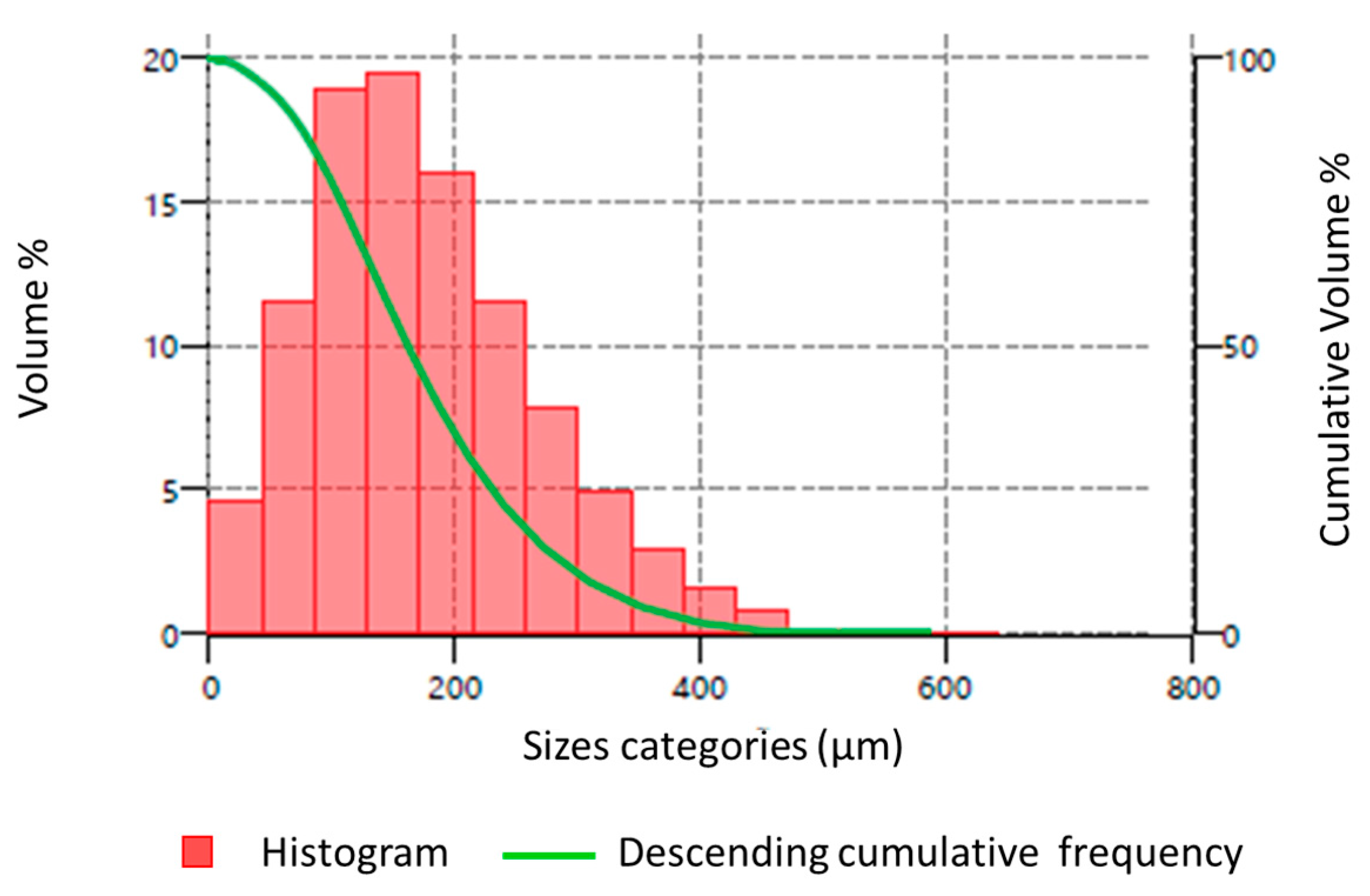
2.2. PS MP Preparation
2.3. Food Contamination
2.4. Exposure Design
2.4.1. Apical Endpoints
2.4.2. Histological Analysis
2.4.3. Electron Microscopy
2.5. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PS MP Characterization, Experimental Conditions, Mortality, Developmental Assessment, and Morphometric Endpoints
3.2. Histological and Electron Microscopy Results
3.2.1. Histopathology of Thyroid Gland
3.2.2. Histopathology of Gonads and Remaining Organs
3.2.3. Electron Microscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duis, K.; Coors, A. Microplastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment: Sources (with a specific focus on personal care products), fate and effects. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Res. 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardi, M.; Pironti, C.; Motta, O.; Miele, Y.; Proto, A.; Montano, L. Microplastics in the Aquatic Environment: Occurrence, Persistence, Analysis, and Human Exposure. Water 2021, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögel, T.; Bjorøy, Ø.; Toto, B.; Bienfait, A.M.; Sanden, M. Micro- and nanoplastic toxicity on aquatic life: Determining factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.P.C.; Lopes Rocha, T.; de Melo e Silva, D.; Malafaia, G. Micro(nano)plastics as an emerging risk factor to the health of amphibian: A scientometric and systematic review. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triebskorn, R.; Braunbeck, T.; Grummt, T.; Hanslik, L.; Huppertsberg, S.; Jekel, M.; Knepper, T.P.; Krais, S.K.; Müller, Y.K.; Pittroff, M.; et al. Relevance of nano- and microplastics for freshwater ecosystems: A critical review. TrAC 2019, 110, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaiser, Z.; Aqeel, M.; Sarfraz, W.; Rizvi, Z.F.; Noman, A.; Naeem, S.; Khalid, N. Microplastics in wastewaters and their potential effects on aquatic and terrestrial biota. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.C.; Ao, S.; Ling, C.; He, F.; Luo, Q.; Wen, Z.; Cai, Q.; Resh, V.H. Meta-ecosystem Frameworks Can Enhance Control of the Biotic Transport of Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 12846–12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyero, L.; López-Rojo, N.; Bosch, J.; Alonso, A.; Correa-Araneda, F.; Pérez, J. Microplastics impair amphibian survival, body condition and function. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, O.W.; Kang, J.H. Size-dependent effects of micro-polystyrene particles in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11278–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Vieira, L.R.; Branco, V.; Figueiredo, N.; Carvalho, F.; Carvalho, C.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics cause neurotoxicity, oxidative damage and energy-related changes and interact with the bioaccumulation of mercury in the European seabass, Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 195, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prüst, M.; Meijer, J.; Westerink, R.H.S. The plastic brain: Neurotoxicity of micro- and nanoplastics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandts, I.; Teles, M.; Gonçalves, A.P.; Barreto, A.; Franco-Martínez, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Martins, M.A.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Tort, L.; Oliveira, M. Effects of nanoplastics on Mytilus galloprovincialis after individual and combined exposure with carbamazepine. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Pu, S.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mandal, S.; Xing, B. Microplastics in aquatic environments: Toxicity to trigger ecological consequences. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.P.C.; Ferreira Silva de Melo, N.; Gonçalves de Oliveira Junior, A.; Postalli Rodriguesa, F.; Fernandes, T.; de Andrade Vieira, J.E.; Lopes Rochad, T.; Malafaia, G. How much are microplastics harmful to the health of amphibians? A study with pristine polyethylene microplastics and Physalaemus cuvieri. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.P.C.; Rodrigues Gomes, A.; Malafaia, G. Hepatotoxicity of pristine polyethylene microplastics in neotropical Physalaemus cuvieri tadpoles (Fitzinger, 1826). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, J.; Thumsová, B.; López-Rojo, N.; Pérez, J.; Alonso, A.; Fisher, M.C.; Boyero, L. Microplastics increase susceptibility of amphibian larvae to the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Browne, M.A.; Halpern, B.S.; Hentschel, B.T.; Hoh, E.; Karapanagioti, H.K.; Rios-Mendoza, L.M.; Takada, H.; Teh, S.; Thompson, R.C. Classify plastic waste as hazardous. Nature 2013, 494, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Kim, E.-S.; Sung, H.-C. Microplastics as an emerging threat to amphibians: Current status and future perspectives. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Ahmad, S.; Guo, X.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, S.; Nabi, G.; Wanghe, K. A review of the endocrine disrupting effects of micro and nano plastic and their associated chemicals in mammals. Front. Endocrinol. Lausanne 2023, 13, 1084236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Test No. 231: Amphibian Metamorphosis Assay, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthsatz, K.; Dausmann, K.H.; Paesler, K.; Babos, P.; Sabatino, N.M.; Peck, M.A.; Glos, J. Shifts in sensitivity of amphibian metamorphosis to endocrine disruption: The common frog (Rana temporaria) as a case study. Conserv. Physiol. 2020, 8, coaa100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloas, W.; Stöck, M.; Lutz, I.; Ziková-Kloas, A. Endocrine disruption in teleosts and amphibians is mediated by anthropogenic and natural environmental factors: Implications for risk assessment. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2024, 379, 20220505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetu, M.H.; Parvin, F.; Tareq, S.M. Identifying the presence of microplastics in frogs from the largest delta of the world. Environ. Adv. 2023, 11, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrieri, A.; Winkler, A.; Scribano, G.; Gazzola, A.; Lastrico, G.; Grioni, A.; Pellitteri-Rosa, D.; Tremolada, P. Differential effects of microplastic exposure on anuran tadpoles: A still underrated threat to amphibian conservation? Environ. Pollut. 2022, 303, 119137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkudlarek, M.; Najbar, B.; Jankowiak, L. Variation in microplastic characteristics among amphibian larvae: A comparative study across different species and the influence of human activity. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tussellino, M.; Ronca, R.; Formiggini, F.; De Marco, N.; Fusco, S.; Netti, P.A.; Carotenuto, R. Polystyrene nanoparticles affect Xenopus laevis development. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, I.; Huy, D.T.N.; Alsaikhan, F.; Opulencia, M.J.C.; Tuan, P.V.; Nurmatova, K.C.; Majdi, A.; Shoukat, S.; Yasin, G.; Margiana, R.; et al. Toxic effects on enzymatic activity, gene expression and histopathological biomarkers in organisms exposed to microplastics and nanoplastics: A review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, M.V.; Beltrán, E.M.; Jiménez, M.A.; García-Hortigüela, P.; Fernández, A.; González-Doncel, M.; Fernández, C. Effect assessment of reclaimed water and carbamazepine exposure on the thyroid axis of X. laevis: Apical and histological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwkoop, P.D.; Faber, J. Normal Tables of Xenopus Laevis (Daudin); Garland Publishing, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- González-Doncel, M.; García-Mauriño, J.E.; Beltrán, E.M.; Fernández-Torija, C.; Andreu-Sánchez, O.; Pablos, M.V. Effects of life cycle exposure to polystyrene microplastics on medaka fish (Oryzias latipes). Environ. Pollut. 2022, 311, 120001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Guidance Document on Amphibian Histology, OECD Series on Testing and Assessment, No. 82; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De FeLice, B.; Bacchetta, R.; Santo, N.; Tremolada, P.; Parolini, M. Polystyrene microplastics did not affect body growth and swimming activity in Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34644–34651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venâncio, C.; Melnic, I.; Tamayo-Belda, M.; Oliveira, M.; Martins, M.A.; Lopes, I. Polymethylmethacrylate nanoplastics can cause developmental malformations in early life stages of Xenopus laevis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, A.; Keckeis, H.; Lumesberger-Loisl, F.; Zens, B.; Krusch, R.; Tritthart, M.; Glas, M.; Schludermann, E. The Danube so colourful: A potpourri of plastic litter outnumbers fish larvae in Europe’s second largest river. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 188, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Xia, J.; Pan, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Fu, Z. Polystyrene microplastics induce microbiota dysbiosis and inflammation in the gut of adult zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Lu, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ru, S. Adaptation of life-history traits and trade-offs in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) after whole life-cycle exposure to polystyrene microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, L.; Lo, L.S.H.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, J. Parental exposure to polystyrene microplastics at environmentally relevant concentrations has negligible transgenerational effects on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisada, S.; Yoshida, M.; Karita, K. Polyethylene microbeads are more critically toxic to the eyes and reproduction than the kidneys or growth in medaka, Oryzias latipes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, M.C.; Rosenberg, M.; Cheng, L. Increased oceanic microplastic debris enhances oviposition in an endemic pelagic insect. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, B.; Sabatini, V.; Antenucci, S.; Gattoni, G.; Santo, N.; Bacchetta, R.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Parolini, M. Polystyrene microplastics ingestion induced behavioral effects to the cladoceran Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edo, C.; González-Pleiter, M.; Leganés, F.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Fate of microplastics in wastewater treatment plants and their environmental dispersion with effluent and sludge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossatto, A.; Zimmer Ferreira Arlindo, M.; Saraiva de Morais, M.; Denardi de Souza, T.; Saraiva Ogrodowski, C. Microplastics in aquatic systems: A review of occurrence, monitoring and potential environmental risks. Environ. Adv. 2023, 13, 100396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAPEA. Science Advice for Policy by European Academies. A Scientific Perspective on Microplastics in Nature and Society; SAPEA: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leusch, F.D.L.; Ziajahromi, S. Converting mg/L to particles/L: Reconciling the occurrence and toxicity literature on microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 11470–11472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ory, N.C.; Gallardo, C.; Lenz, M.; Thiel, M. Capture, swallowing, and egestion of microplastics by a planktivorous juvenile fish. Environ. Poll. 2018, 240, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarghouei, S.; Hedayati, A.; Raeisi, M.; Hadavand, B.S.; Rezaei, H.; Abed-Elmdoust, A. Size-dependent effects of microplastic on uptake, immune system, related gene expression and histopathology of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Chemosphere 2021, 276, 129977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Ling, L.; Ling, L.; Luo, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, P. Combined effects of co-exposure to microcystin-LR and polystyrene microplastics on growth, brain pathology and thyroid hormone homeostasis in adult zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 291, 117855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coady, K.K.; Lehman, C.M.; Currie, R.J.; Marino, T.A. Challenges and approaches to conducting and interpreting the amphibian metamorphosis assay and the fish short-term reproduction assay. Birth Defects Res. 2014, 101, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Chernick, M.; Hinton, D.E.; Shi, H. Microplastics in Small Waterbodies and Tadpoles from Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8885–8893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Su, L.; Xue, Y.; Mu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Shi, H. Uptake, accumulation and elimination of polystyrene microspheres in tadpoles of Xenopus tropicalis. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Qingfang, D.; Zhanga, Q.; Zhoua, X.; Chena, R.; Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Chen, H. Hazards of microplastics exposure to liver function in fishes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 196, 106423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, D.; Xiao, F. Keap1-Nrf2 pathway up- regulation via hydrogen sulfide mitigates polystyrene microplastics induced–hepatotoxic effects. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 402, 123933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sales-Ribeiro, C.; Brito-Casillas, Y.; Fernandez, A.; Caballero, M.J. An end to the controversy over the microscopic detection and effects of pristine microplastics in fish organs. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Replicates | Mortality to Day 7 a | % Mortality to Day 7 | Mortality from Day 7 to Day 21 b | % Mortality from Day 7 to Day 21 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control A | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| Control B | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| Control C | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| Control D | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| PS1XA | 4 * | 20% | 5 * | 33.3% |
| PS1XB | 0 | 0% | 1 | 6.7% |
| PS1XC | 2 | 10% | 2 | 13.3% |
| PS1XD | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| PS10XA | 1 | 5% | 1 | 6.7% |
| PS10XB | 1 | 5% | 1 | 6.7% |
| PS10XC | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| PS10XD | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
| N&F Stage Development on Day 7 a (n = 60) | N&F Stage Development on Day 21 a (n = 170) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | N&F 53 | N&F 54 | Groups | N&F 56 | N&F 57 | N&F 58 | N&F 59 | N&F 60 |
| Control (n = 20) | 7 | 13 | Control (n = 60) | 0 | 2 | 18 | 39 | 1 |
| PS 1X MPs (n = 20) | 9 | 11 | PS 1X MPs (n = 52) | 1 | 1 | 13 | 33 | 4 |
| PS 10X MPs (n = 20) | 7 | 13 | PS 10X MPs (n = 58) | 0 | 3 | 12 | 37 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pablos, M.V.; Jiménez, M.d.l.Á.; Beltrán, E.M.; García-Hortigüela, P.; de Saint-Germain, M.L.; González-Doncel, M. Effects of Dietary Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics on the Thyroid Gland in Xenopus laevis. Environments 2025, 12, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12080252
Pablos MV, Jiménez MdlÁ, Beltrán EM, García-Hortigüela P, de Saint-Germain ML, González-Doncel M. Effects of Dietary Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics on the Thyroid Gland in Xenopus laevis. Environments. 2025; 12(8):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12080252
Chicago/Turabian StylePablos, María Victoria, María de los Ángeles Jiménez, Eulalia María Beltrán, Pilar García-Hortigüela, María Luisa de Saint-Germain, and Miguel González-Doncel. 2025. "Effects of Dietary Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics on the Thyroid Gland in Xenopus laevis" Environments 12, no. 8: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12080252
APA StylePablos, M. V., Jiménez, M. d. l. Á., Beltrán, E. M., García-Hortigüela, P., de Saint-Germain, M. L., & González-Doncel, M. (2025). Effects of Dietary Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics on the Thyroid Gland in Xenopus laevis. Environments, 12(8), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12080252






