Coupling Coagulation–Flocculation–Sedimentation with Adsorption on Biosorbent (Corncob) for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
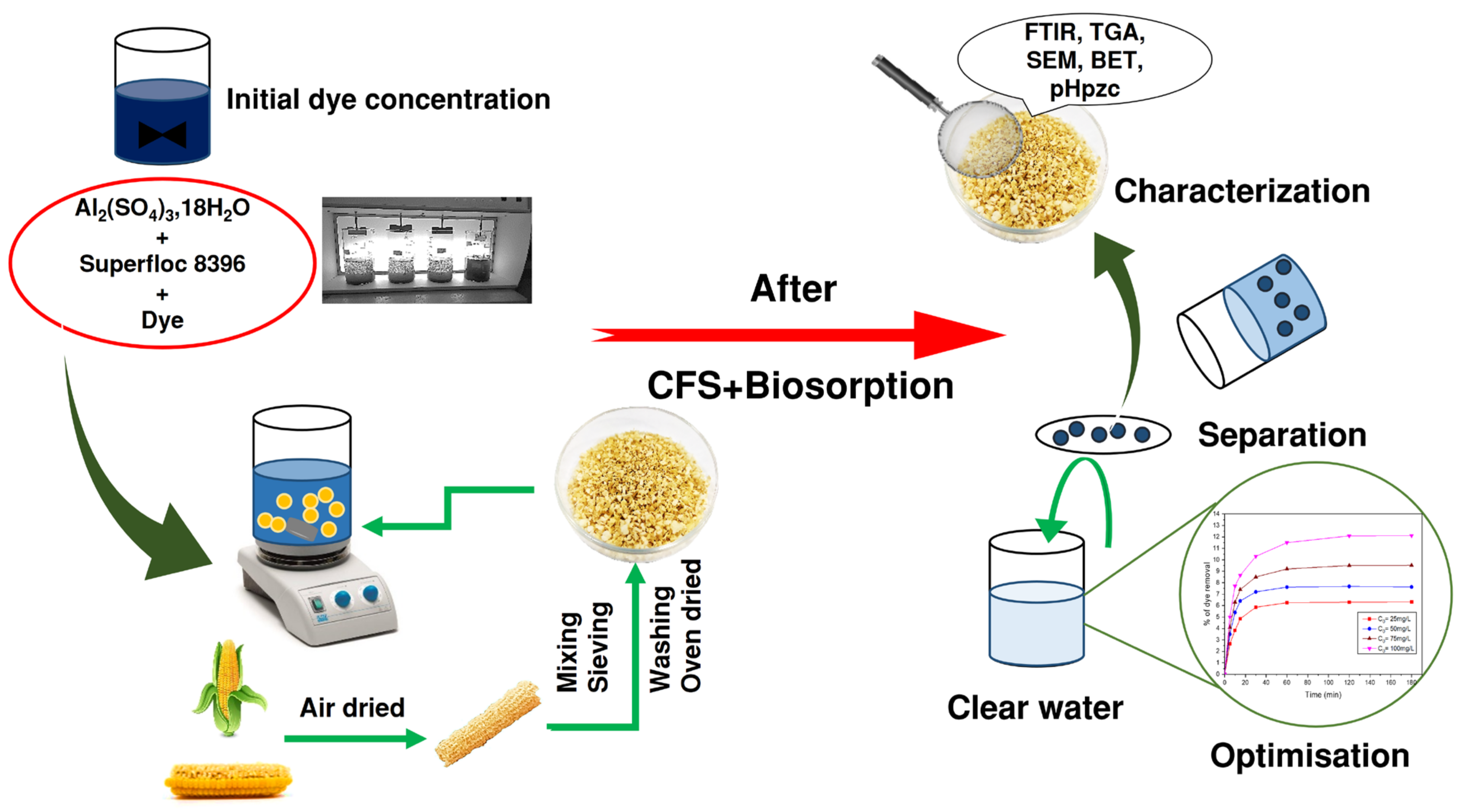
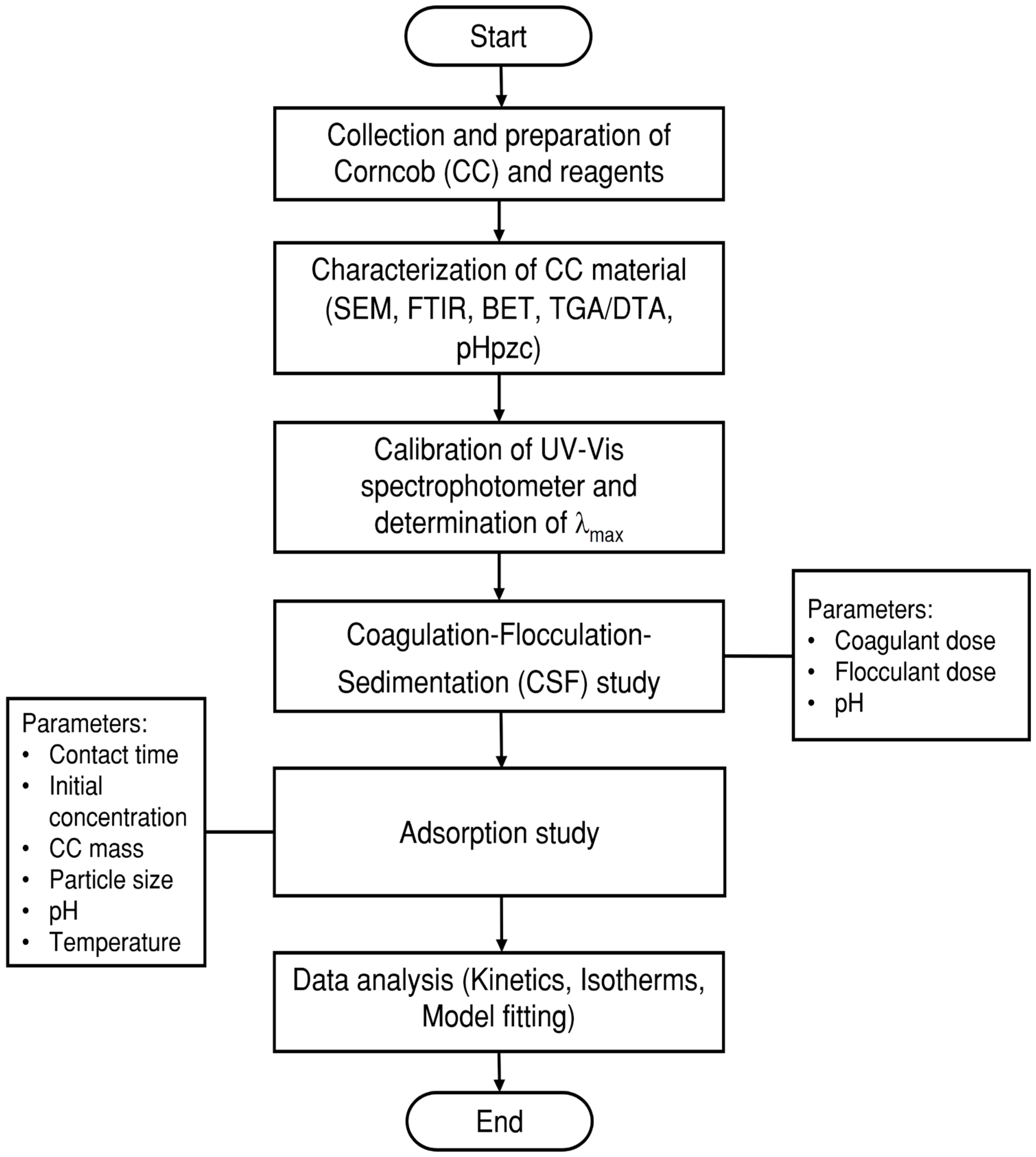
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dyes, Coagulants, and Flocculants
2.2. Adsorbent Material
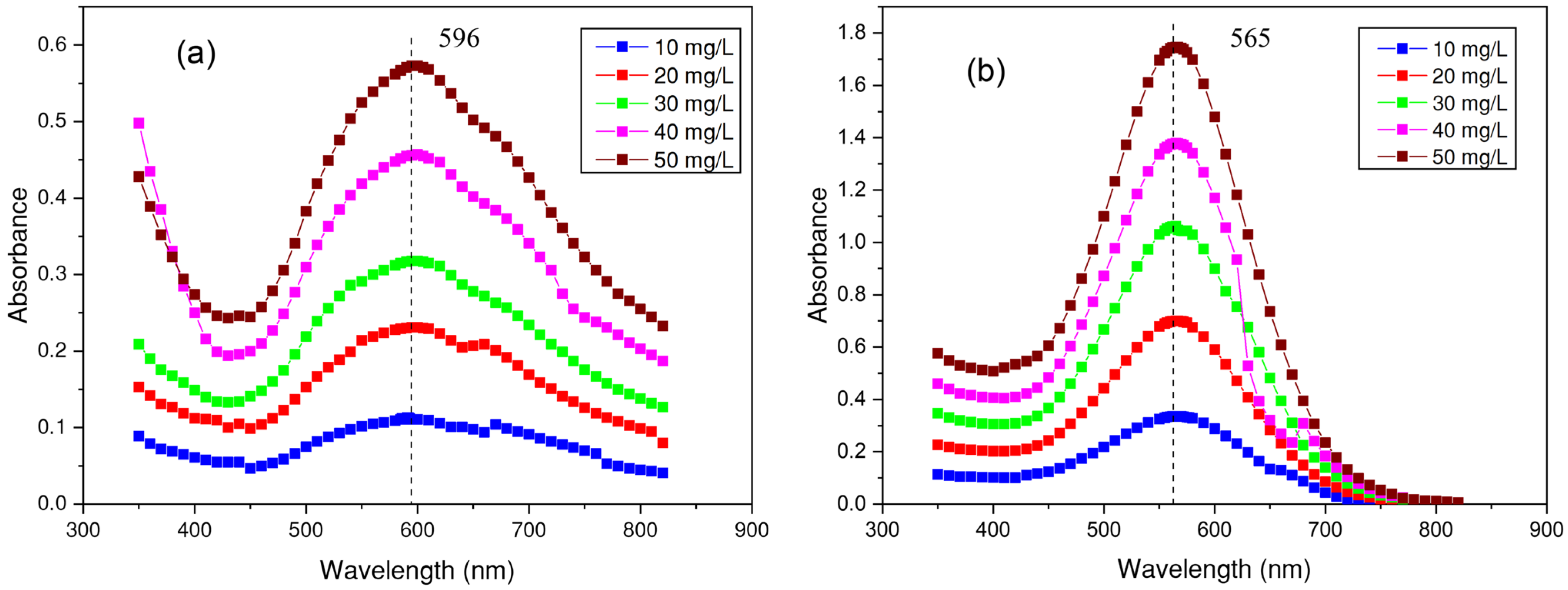
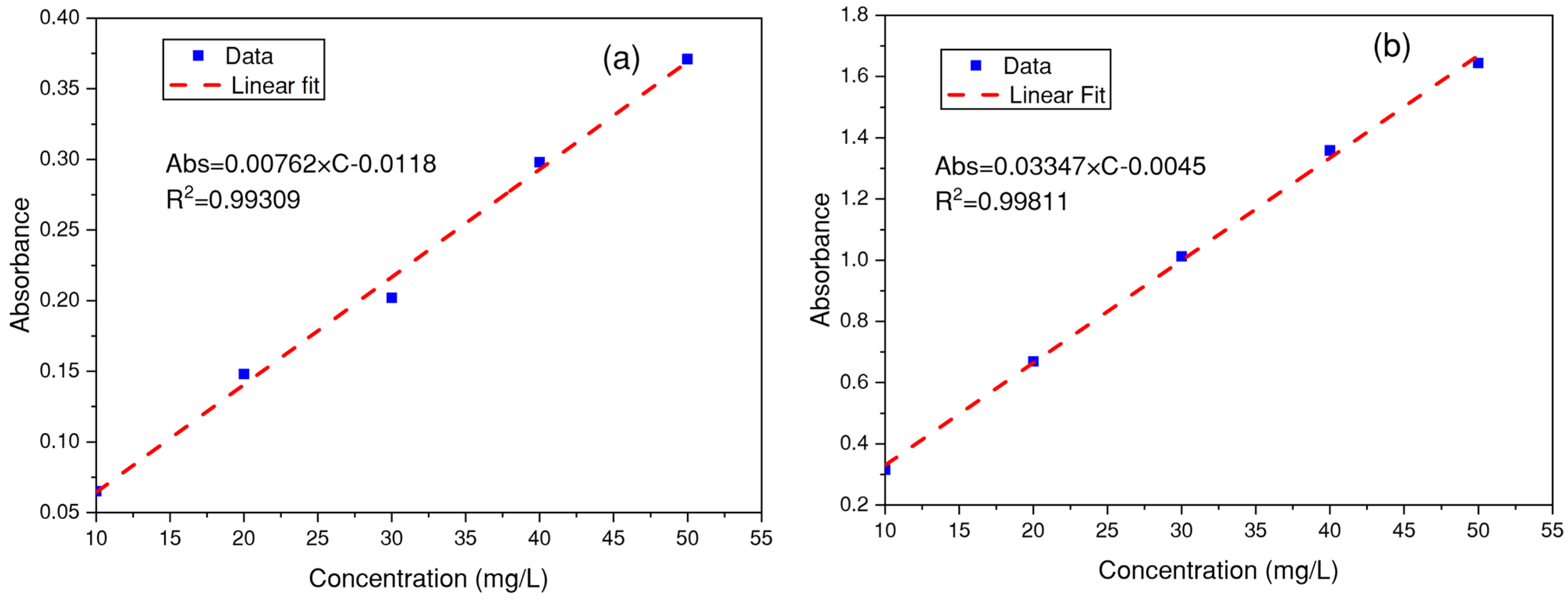
2.3. Determination of the Wavelength and Absorbance of Dyes
2.4. Coagulation–Flocculation–Sedimentation Process
2.5. Adsorption Processes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Corncob Characterization
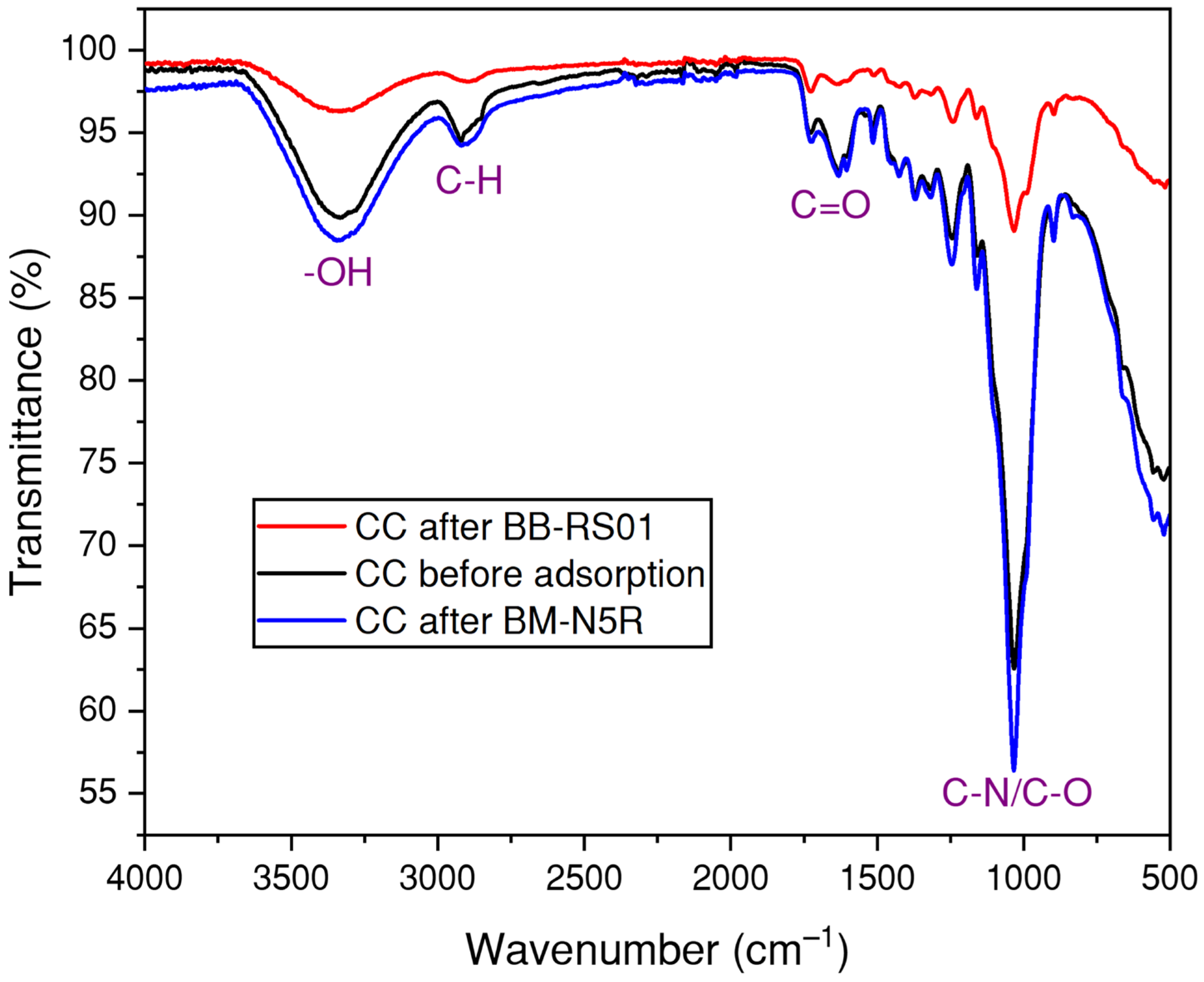
3.1.1. Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.1.2. TGA Thermogravimetric/Differential Thermal Analysis (TGA/DTA)
3.1.3. BET Analysis
3.1.4. pHpzc Corncob Determination
3.2. Determination of the Wavelength for Each Dye
3.3. Coagulation–Flocculation Sedimentation Study
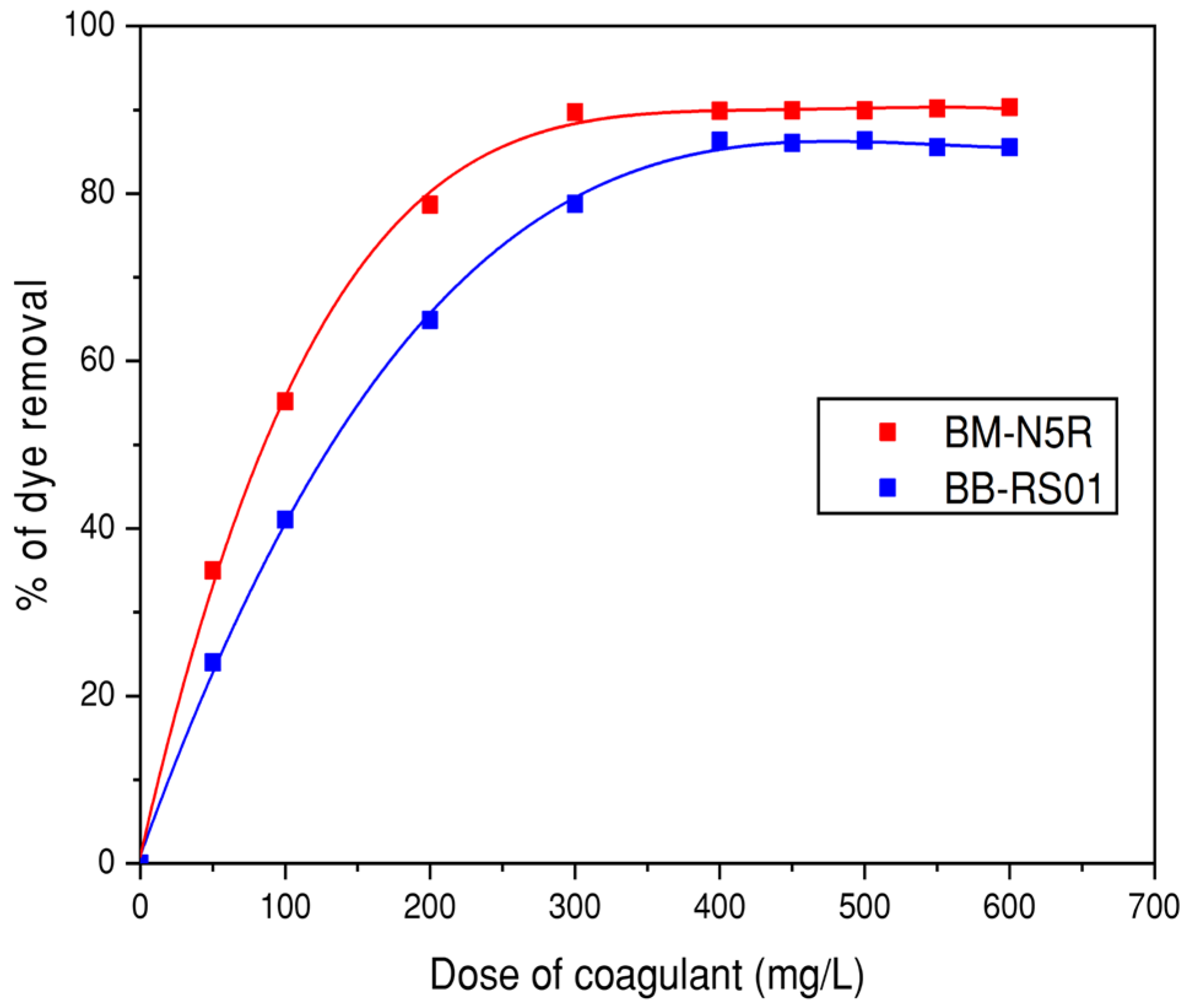
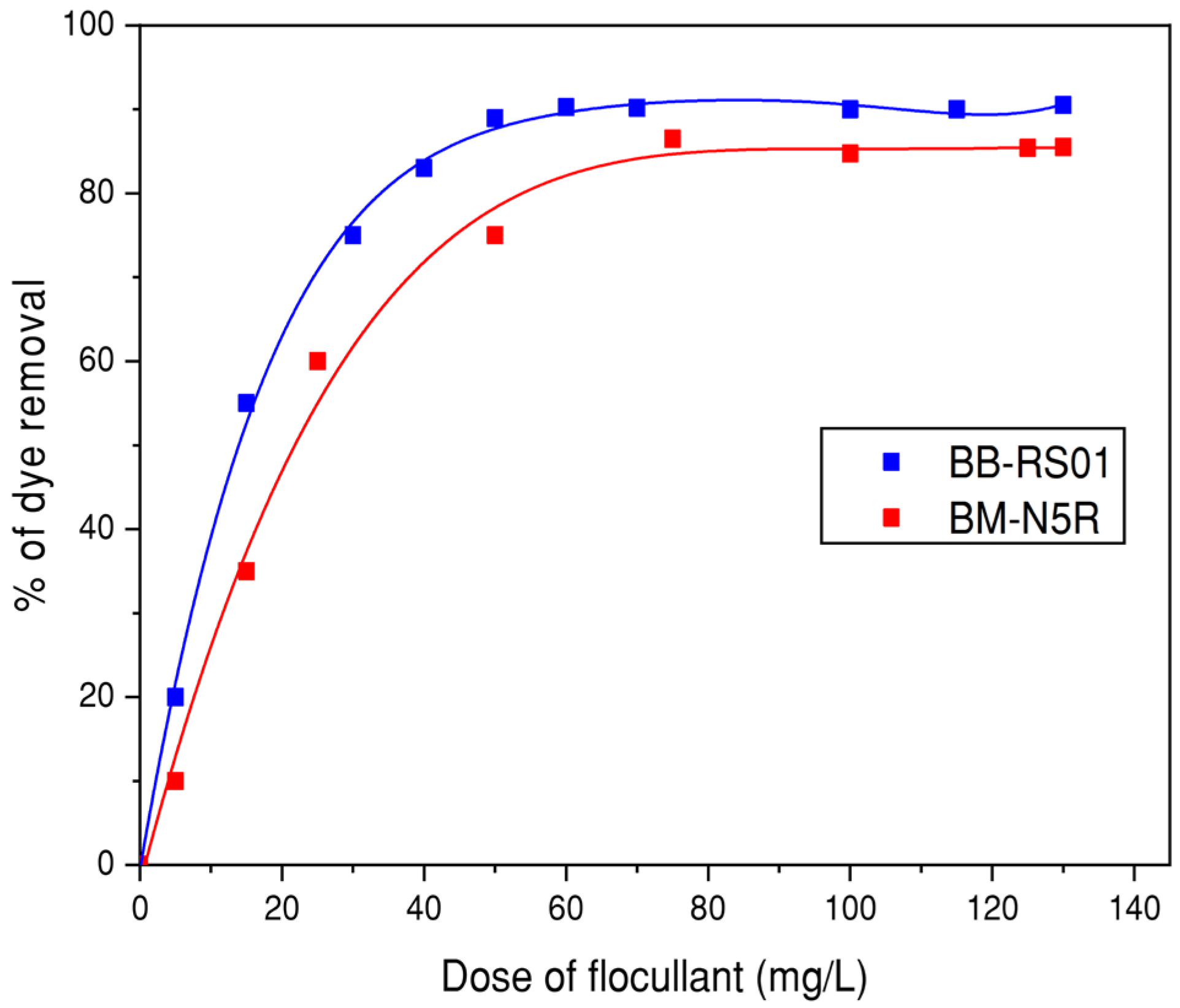
3.3.1. Effect of Coagulant and Flocculent Doses
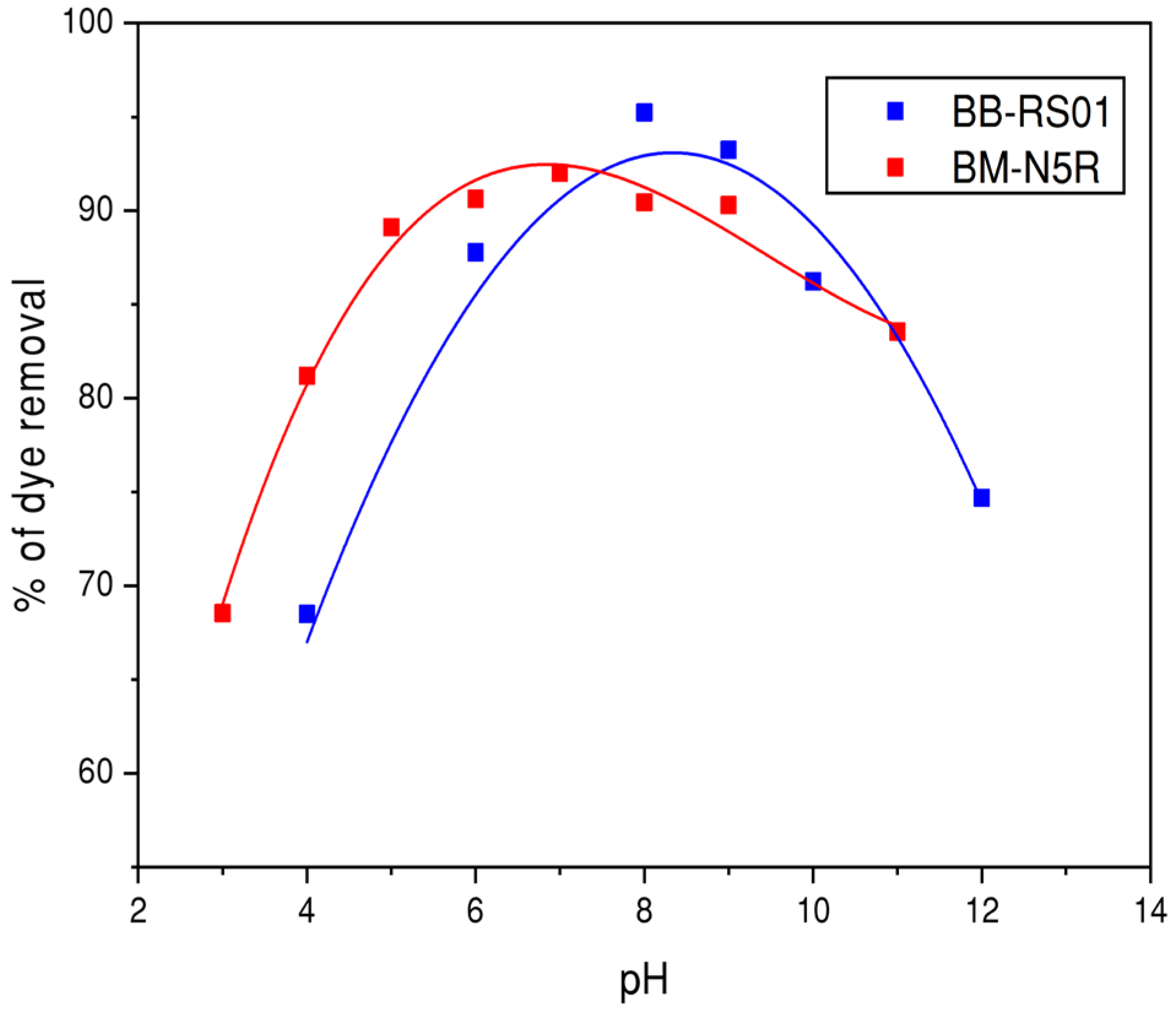
3.3.2. Effect of Solution pH on CFS Efficiency
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
- The initial pH of the solutions for BM-N5R dye was set at around 6.5 and the initial dye concentration (C0) was 50 mg/L;
- For the BB-RS01 dye, the initial pH (pHi) of solutions was adjusted to near 8, and the initial dye concentration (C0) was 25 mg/L;
- In both cases, the m/V ratio was maintained at 1 g/L (CC had a mass of 1 g and the volume of the solution was 1 L). CC with a uniform particle diameter (dp) of 1.25/2 mm was used to ensure consistency. The solution was kept at a constant temperature of 25 ± 2 °C and the agitation speed (N) was held at 400 rpm to facilitate contact between the adsorbate and the adsorbent.
3.4.1. Influence of Initial Dye Concentration and Contact Time
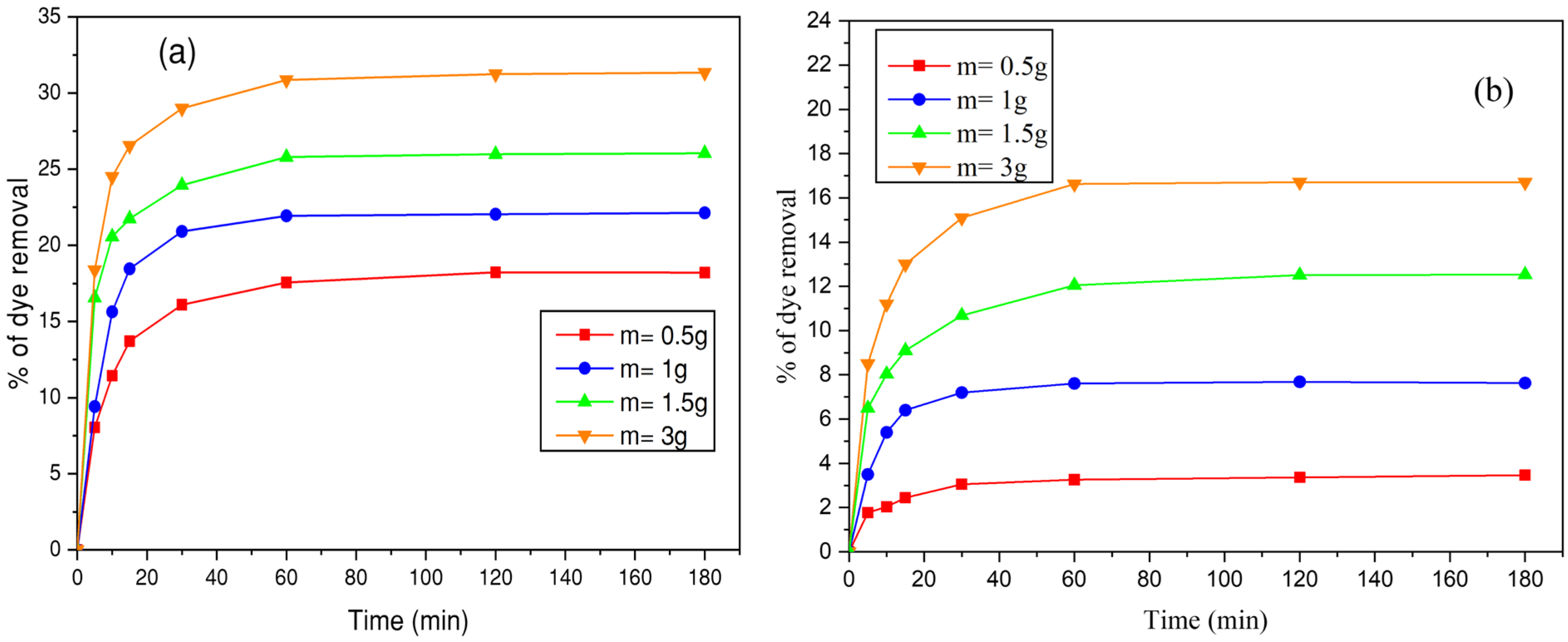
3.4.2. Effect of Biosorbent Mass
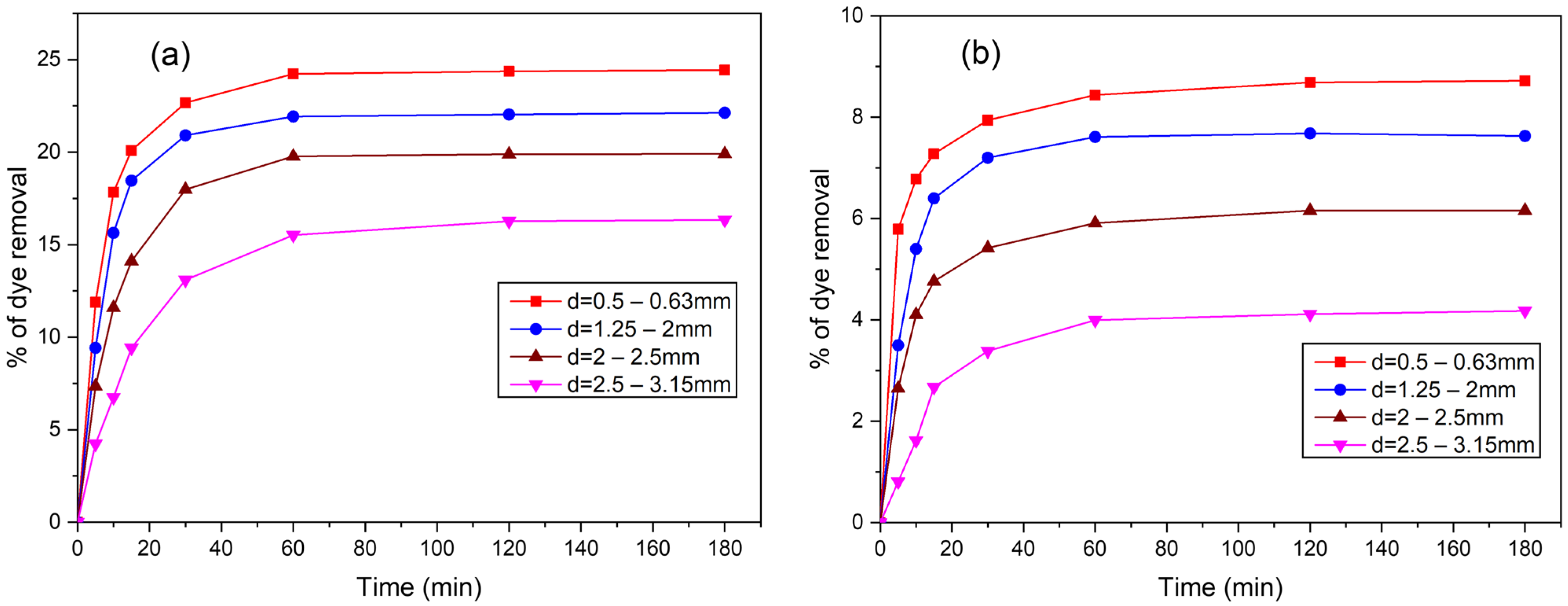
3.4.3. Influence of Adsorbent Particle Size
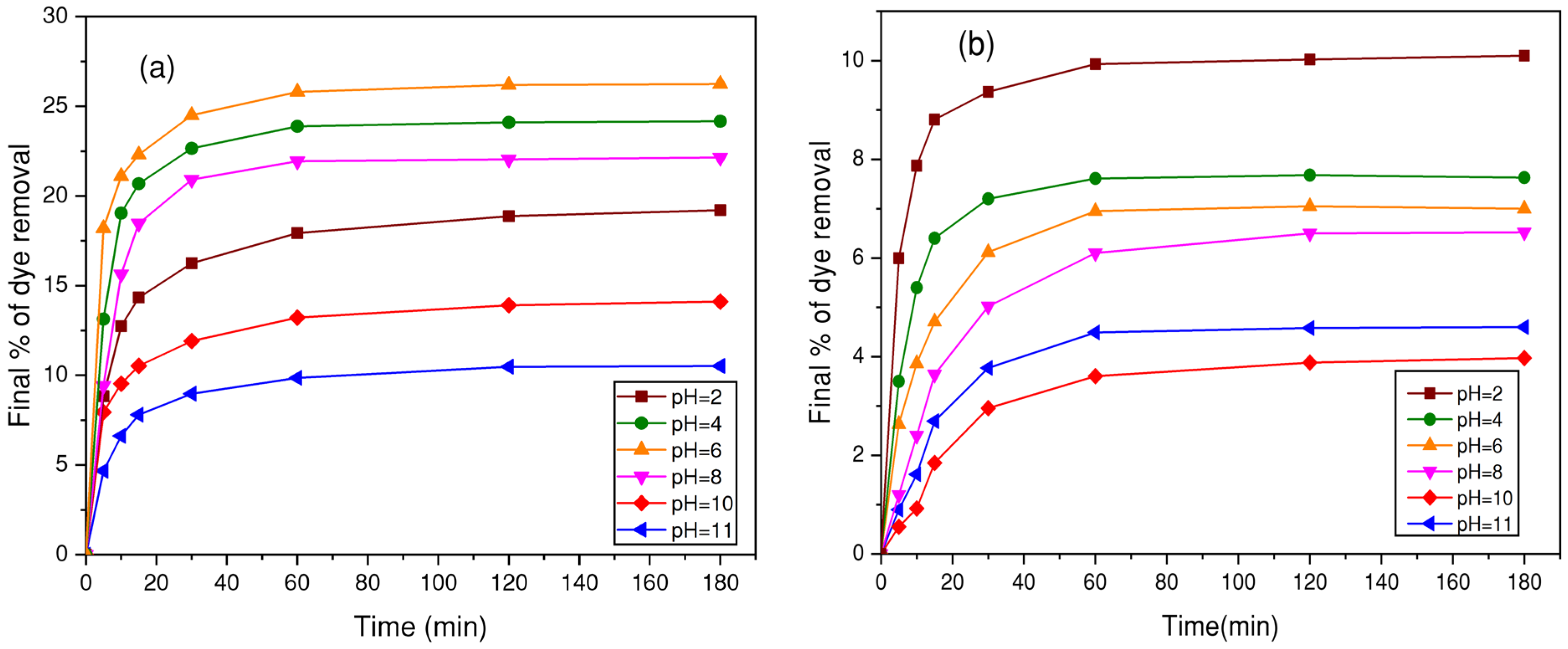
3.4.4. Effect of pH
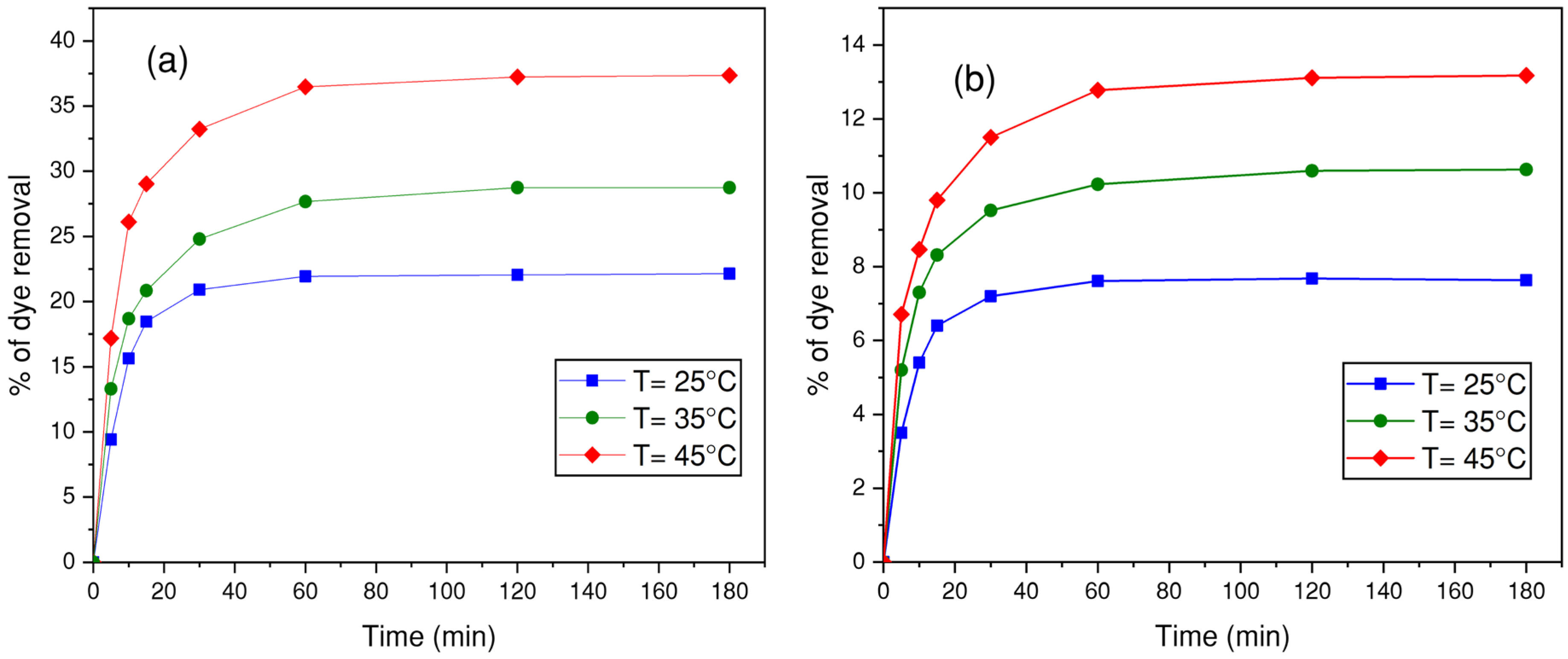
3.4.5. Effect of Temperature
3.5. Equilibrium Adsorption
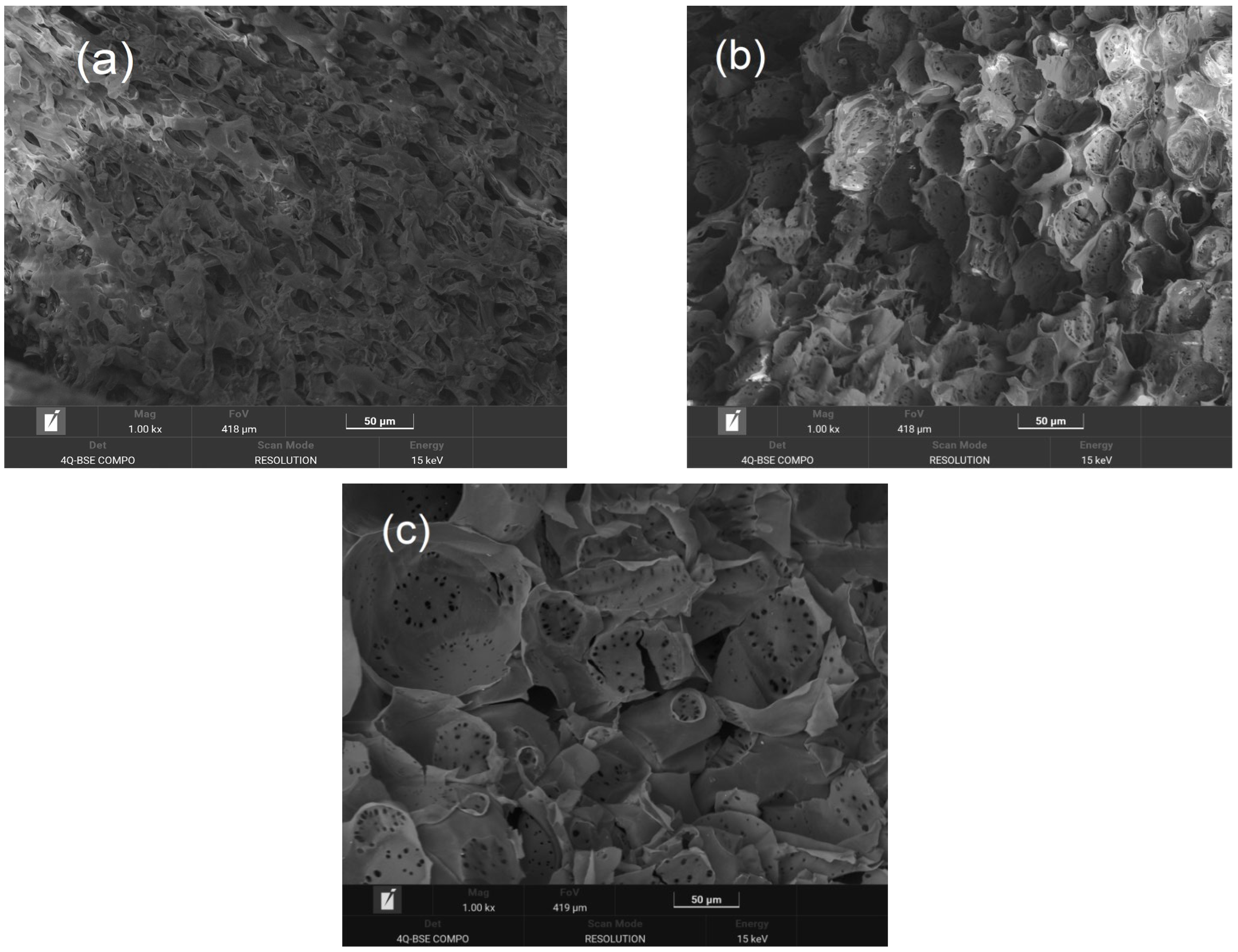
3.6. Scanning Electronic Microscopy (SEM)
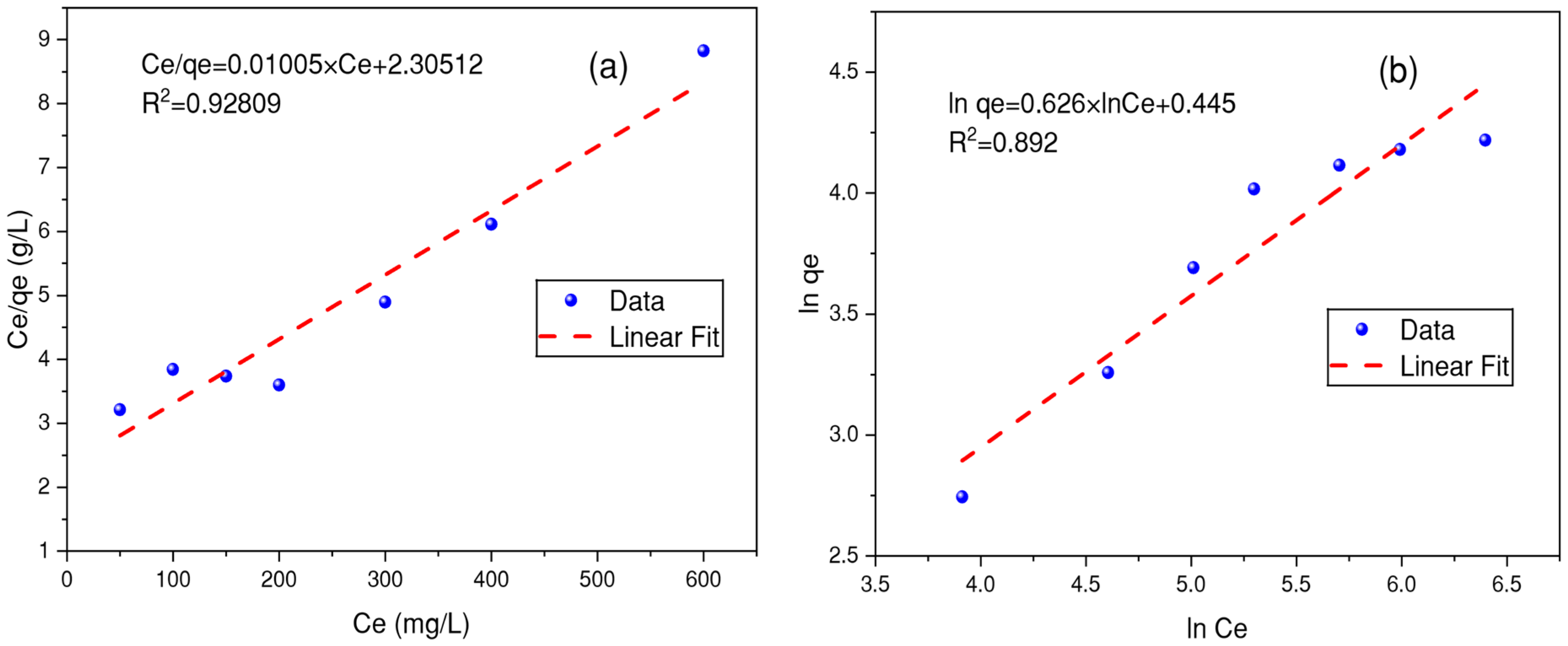
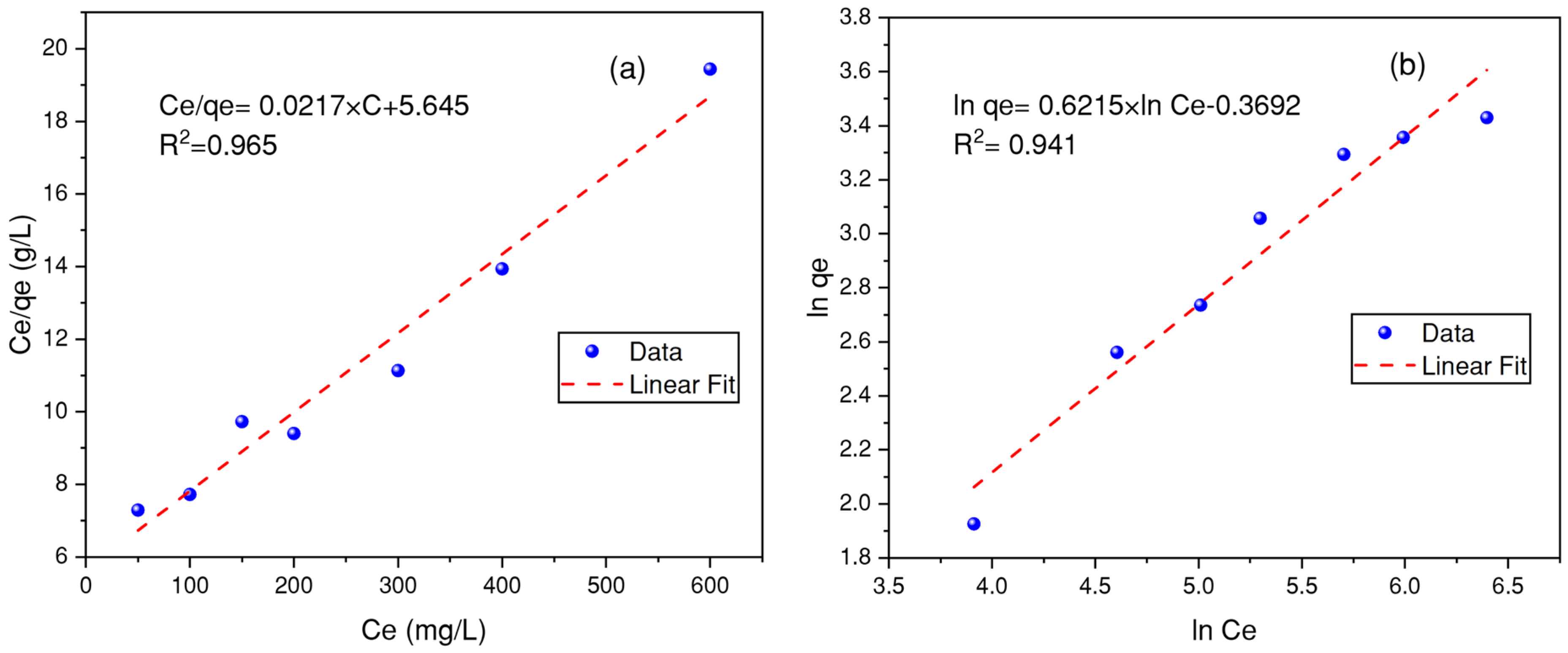
3.7. Modeling of the Adsorption Isotherms
- -
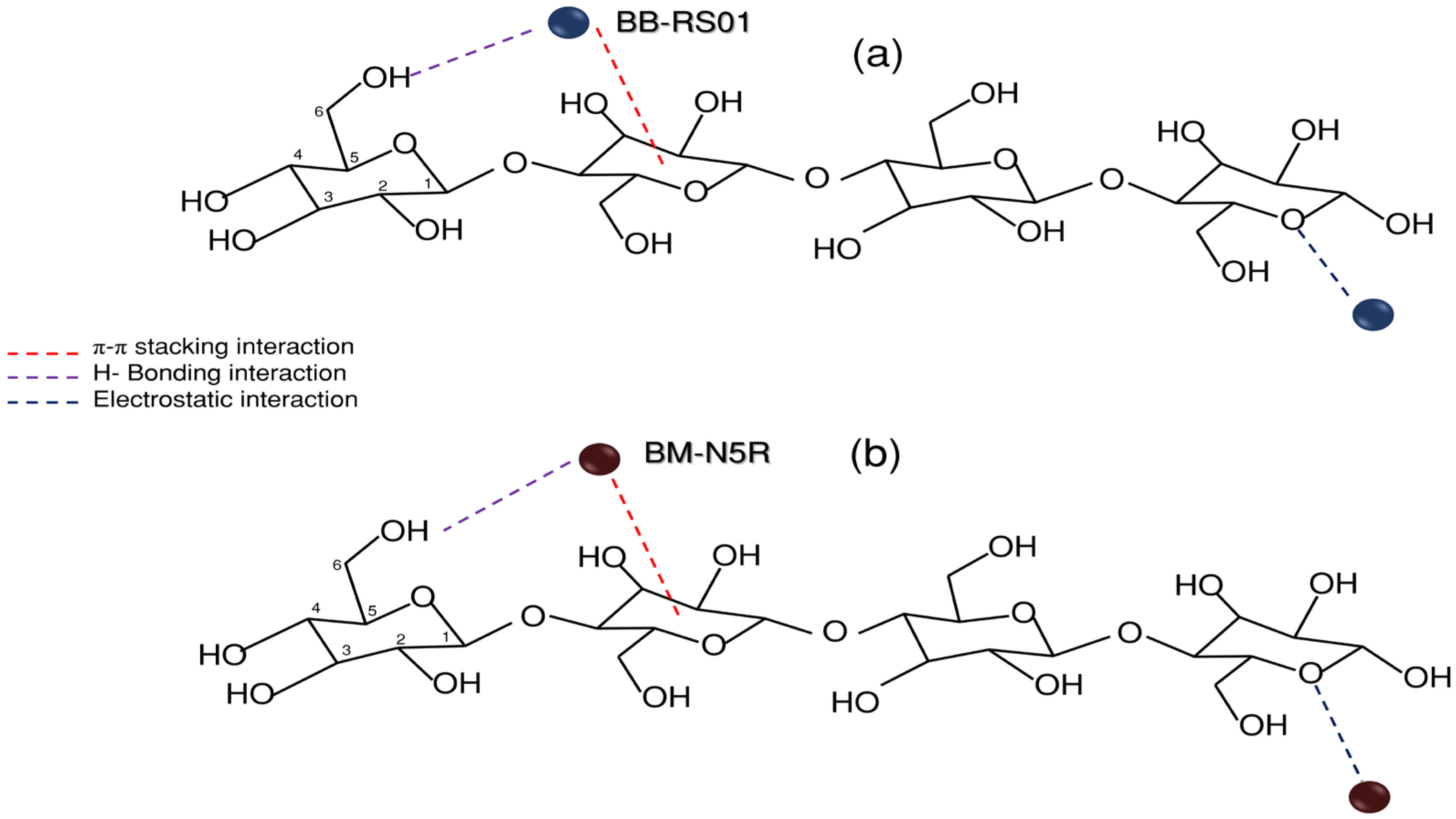
- The BB-RS01 molecule shows a more favorable π–π stacking alignment and stronger hydrogen bonding with the biosorbent surface compared to BM-N5R.
- -
- Differences in molecular size, structure, and functional group distribution between BB-RS01 and BM-N5R influence the accessibility and interaction energy at the active sites of the biosorbent.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Xie, M.; Seo, D.H.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Environmental impacts and remediation of dye-containing wastewater. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 785–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.U.; Ahmed, S.; Dhoble, Y.; Madhav, S. A critical review of hazardous waste generation from textile industries and associated ecological impacts. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihinezhad, M.; Baghdadi, M.; Shahin, M.S.; Torabian, A. Catalytic ozonation of real textile wastewater by magnetic oxidized g-C3N4 modified with Al2O3 nanoparticles as a novel catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 283, 120208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittal, V.; Gracias, M.; Anu, A.; Saha, P.; Rao, K.B. Biodecolorization and biodegradation of azo dye reactive orange-16 by marine Nocardiopsis sp. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, e1551. [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger, H. Color Chemistry: Syntheses, Properties, and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, I. Treatability of a simulated disperse dye-bath by ferrous iron coagulation, ozonation, and ferrous iron-catalyzed ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 85, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P. Recent Advances in the Remediation of Textile-Dye-Containing Wastewater: Prioritizing Human Health and Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, A.; Bakhoum, E.S.; Zaher, K. Coagulation/flocculation process for textile mill effluent treatment: Experimental and numerical perspectives. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2021, 14, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, C.; Musteret, C.-P.; Afrasinei, M.-A. The Use of Coagulation–Flocculation for Industrial Colored Wastewater Treatment—(I) The Application of Hybrid Materials. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaha, Y.G.; Zewge, F.; Yohannes, T.; Kebede, S. Application of hybrid electrocoagulation and electrooxidation process for treatment of wastewater from the cotton textile industry. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louhichi, B.; Gaied, F.; Mansouri, K.; Jeday, M.R. Treatment of textile industry effluents by Electro-Coagulation and Electro-Fenton processes using solar energy: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbatea, A.A.; Nosier, S.A.; Zatout, A.A.; Hassan, I.; Sedahmed, G.H.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; El-Naggar, M.A. Removal of reactive red 195 from dyeing wastewater using electro-Fenton process in a cell with oxygen sparged fixed bed electrodes. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, F.; Nori Kohbanan, N. Removal of Reactive Blue 19 Dye Using Fenton From Aqueous Solution. Avicenna J. Environ. Health Eng. 2018, 5, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süzen, Y.; Ozmetin, C. Removal of Reactive Black 5 dye using Fenton oxidation from aqueous solutions and optimization of response surface methodology. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 172, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-B.; Xiao, F.; Xu, W.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Li, K.; Gao, X.-W. Efficient self-photo-degradation of cationic textile dyes involved triethylamine and degradation pathway. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, V.; Lal, B. Exploration of Performance Kinetics and Mechanism of Action of a Potential Novel Bioflocculant BF-VB2 on Clay and Dye Wastewater Flocculation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Zahoor, M.; El-Saber Batiha, G. Biodegradation and decolorization of textile dyes by bacterial strains: A biological approach for wastewater treatment. Z. Phys. Chem. 2021, 235, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumediene, M.; Benaïssa, H.; George, B.; Molina, S.; Merlin, A. Effects of pH and ionic strength on methylene blue removal from synthetic aqueous solutions by sorption onto orange peel and desorption study. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 1700–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Hammood, Z.A.; Chyad, T.F.; Al-Saedi, R. Adsorption Performance of Dyes Over Zeolite for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2021, 28, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Asthana, A.; Chakraborty, R.; Jain, B.; Singh, A.K.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Susan, M.A.B.H. Cationic Dye Removal Using Novel Magnetic/Activated Charcoal/β-Cyclodextrin/Alginate Polymer Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszałek, J.; Żyłła, R. Recovery of water from textile dyeing using membrane filtration processes. Processes 2021, 9, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, R.M.; da Silva, L.H.B.R.; Vieira, M.F.; de Amorim, M.T.P.; Bergamasco, R.; Vieira, A.M.S. Enhanced filtration membranes with graphene oxide and tannic acid for textile industry wastewater dye removal. Environ. Technol. 2025, 46, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, N.R.; Huang, R.; Du, E.; Peng, M.; Pan, Z.; Ding, H.; Shan, G.; Ling, L.; Xie, Z. A review of the textile wastewater treatment technologies with special focus on advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), membrane separation and integrated AOP-membrane processes. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 206, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Mavukkandy, M.O.; Giwa, A.; Elektorowicz, M.; Katsou, E.; Khelifi, O.; Naddeo, V.; Hasan, S.W. Recent developments in hazardous pollutants removal from wastewater and water reuse within a circular economy. NPJ Clean. Water 2022, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.A. Wastewater Treatment and Reuse for Sustainable Water Resources Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; De, S.; Basu, J.K.; DasGupta, S. Treatment of a textile effluent: Application of a combination method involving adsorption and nanofiltration. Desalination 2005, 174, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Torres, M.; Gutiérrez-Bouzán, C.; Crespi, M. Combination of coagulation–flocculation and nanofiltration techniques for dye removal and water reuse in textile effluents. Desalination 2010, 252, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartal, O.; Madinzi, A.; Rifi, S.K.; Haddaji, C.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Anouzla, A.; Souabi, S. Optimization of coagulation-flocculation process for wastewater treatment from vegetable oil refineries using chitosan as a natural flocculant. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, K.Q.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Hamad, S.M. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Preparation methods, functions, adsorption and coagulation/flocculation in wastewater treatment. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchana-Rosero, M.J.; Lima, E.C.; Mella, B.; Costa, D.d.; Poll, E.; Gutterres, M. A coagulation-flocculation process combined with adsorption using activated carbon obtained from sludge for dye removal from tannery wastewater. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2018, 63, 3867–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihaddaden, S.; Aberkane, D.; Boukerroui, A.; Robert, D. Removal of methylene blue (basic dye) by coagulation-flocculation with biomaterials (bentonite and Opuntia ficus indica). J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudjil, S.; Guergazi, S.; Ghernaout, D.; Temim, D.; Masmoudi, T. Brilliant green and methyl violet 2B dyes removal using aluminium sulfate (AS) in single and binary systems. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui Tan, Q.; Chung Chong, K.; Chan Chong, W.; Onn Lai, S.; Ling Pang, Y.; Hoong Shuit, S.; Yoong Lee, T. The effect of concentration and pH of poly-aluminum chloride on the treatment of industrial textile wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2025, 1467, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzin, E. Synthesis and Use of Complex Titanium-Containing Coagulant in Water Purification Processes. Inorganics 2025, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhiyar, H.; Thanki, A.; Kumar Singh, N.; Pandey, S.; Yadav, M.; Chand Yadav, T. Parametric and kinetic investigations on segregated and mixed textile effluent streams using Moringa oleifera seed powders of different sizes. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiha, O.; Hadoudi, N.; Zaki, N.; Salhi, A.; Amhamdi, H.; Akichouh, E.H.; Mourabit, F.; Ahari, M. Comprehensive review on the adsorption of pharmaceutical products from wastewater by clay materials. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somashekara, D.; Mulky, L. Sequestration of Contaminants from Wastewater: A Review of Adsorption Processes. ChemBioEng Rev. 2023, 10, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.E.; Olin, T.J.; Bricka, R.M.; Adrian, D.D. A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmamouchi, S.; Abbad, Y.; El Yacoubi, A.; Boulouiz, A.; Sallek, B.; El Idrissi, B.C. Optimization study of methylene blue dye adsorption on Chamaerops humilis fibers biosorption using a central composite design. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahmatkesh, S.; Karimian, M.; Chen, Z.; Ni, B.-J. Combination of coagulation and adsorption technologies for advanced wastewater treatment for potable water reuse: By ANN, NSGA-II, and RSM. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Singh, H.; Bhattacharya, J. Treatment of textile industry wastewater based on coagulation-flocculation aided sedimentation followed by adsorption: Process studies in an industrial ecology concept. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourmoradi, H.; Zabihollahi, S.; Pourzamani, H.R. Removal of a common textile dye, navy blue (NB), from aqueous solutions by combined process of coagulation–flocculation followed by adsorption. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 5200–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Koumanova, B. Decolourisation of water/wastewater using adsorption. J. Univ. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2005, 40, 175–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Sorption of copper (II) from aqueous solution by peat. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 158, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, I.; Graba, Z.; Bezzi, N.; Merzeg, F.A.; Bait, N.; Ferhati, A.; Kaci, M.M. Biosorption of Basic Red 46 using raw cactus fruit peels: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 14, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumediene, M.; Benaïssa, H.; George, B.; Molina, S.; Merlin, A. Characterization of two cellulosic waste materials (orange and almond peels) and their use for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2015, 17, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajialigol, S.; Masoum, S. Optimization of biosorption potential of nano biomass derived from walnut shell for the removal of Malachite Green from liquids solution: Experimental design approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 286, 110904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Wen, H.-Y.; Wen, J.-C.; Gutha, Y.; Tian, Z.; Reddy, G.M.; Garcia, J.R. Anionic congo red dye removal from aqueous medium using Turkey tail (Trametes versicolor) fungal biomass: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics, reusability, and characterization. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 1785–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berber-Villamar, N.K.; Netzahuatl-Muñoz, A.R.; Morales-Barrera, L.; Chávez-Camarillo, G.M.; Flores-Ortiz, C.M.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Corncob as an effective, eco-friendly, and economic biosorbent for removing the azo dye Direct Yellow 27 from aqueous solutions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain Gardazi, S.M.; Ashfaq Butt, T.; Rashid, N.; Pervez, A.; Mahmood, Q.; Maroof Shah, M.; Bilal, M. Effective adsorption of cationic dye from aqueous solution using low-cost corncob in batch and column studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 28981–28998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.J.; Kareem, A.S.A.; Anwer, S.S. Adsorption of anionic dyes from textile wastewater utilizing raw corncob. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, E. Coagulation des Substances Humiques Aquatiques par le fer Ferrique en Milieu Aqueux: Effet de la Préoxydation. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Poitiers, Poitiers, France, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Semmens, M.J.; Field, T.K. Coagulation: Experiences in organics removal. J.-Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1980, 72, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Water Works Association. AWWA Manual M32-Distribution Network Analysis for Water Utilities; AWWA: Denver, CO, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchelkia, N.; Benazouz, K.; Mameri, A.; Belkhiri, L.; Hamri, N.; Belkacemi, H.; Zoukel, A.; Amrane, A.; Aoulmi, F.; Mouni, L. Study and Characterization of H3PO4 Activated Carbons Prepared from Jujube Stones for the Treatment of Industrial Textile Effluents. Processes 2023, 11, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, I.; Graba, Z.; Bezzi, N.; Kaci, M.M.; Merzeg, F.A.; Bait, N.; Ferhati, A.; Dotto, G.L.; Benguerba, Y. Effective removal of cationic dye on activated carbon made from cactus fruit peels: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 3027–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, M.; Benturki, O.; Girods, P.; Donnot, A.; Fontana, S. Adsorption ability of activated carbons from Phoenix dactylifera rachis and Ziziphus jujube stones for the removal of commercial dye and the treatment of dyestuff wastewater. Microchem. J. 2019, 148, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Cao, X.; Lu, D.; Luo, F.; Shao, W. Preparation and evaluation of orange peel cellulose adsorbents for effective removal of cadmium, zinc, cobalt and nickel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, H.; Nimina, P.V.M.; Krishnan, K.A. An environmental green approach for the effective removal of malachite green from estuarine waters using Pistacia vera L. shell-based active carbon. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Yuan, M.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Sun, D. Plant-mediated synthesis of highly active iron nanoparticles for Cr (VI) removal: Investigation of the leading biomolecules. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Luo, Y.-M. The adsorption mechanism of anionic and cationic dyes by Jerusalem artichoke stalk-based mesoporous activated carbon. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydın Varol, E.; Mutlu, Ü. TGA-FTIR Analysis of Biomass Samples Based on the Thermal Decomposition Behavior of Hemicellulose, Cellulose, and Lignin. Energies 2023, 16, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.A.; Khass, T.M.; Mostafa, M.E. Thermal degradation behaviour and chemical kinetic characteristics of biomass pyrolysis using TG/DTG/DTA techniques. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 17779–17803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Z. Thermal Decomposition of Kraft Lignin under Gas Atmospheres of Argon, Hydrogen, and Carbon Dioxide. Polymers 2018, 10, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arica, T.A.; Balci, F.M.; Balci, S.; Arica, M.Y. Highly Porous Poly(o-Phenylenediamine) Loaded Magnetic Carboxymethyl Cellulose Hybrid Beads for Removal of Two Model Textile Dyes. Fibers Polym. 2022, 23, 2838–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hung, Y.-T. Electrochemical wastewater treatment processes. In Advanced Physicochemical Treatment Technologies; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 57–106. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, K.M.V.; Phan, A.V.N.; Dang, N.T.; Tran, T.Q.; Duong, H.K.; Nguyen, H.N.; Nguyen, M.V. Efficiently improving the adsorption capacity of the Rhodamine B dye in a SO3 H-functionalized chromium-based metal–organic framework. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 2636–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.; Camino, G.; Levchik, S. Comparative study of the thermal decomposition of pure cellulose and pulp paper. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1995, 49, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-García, F.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Tascón, J.M.D. A comparative study of the thermal decomposition of apple pulp in the absence and presence of phosphoric acid. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 75, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Chen, X.; Xu, W.; Lu, Y. A facile strategy for one-step hydrothermal preparation of porous hydroxyapatite microspheres with core–shell structure. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonwane, C.G.; Bhatia, S.K. Characterization of Pore Size Distributions of Mesoporous Materials from Adsorption Isotherms. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 9099–9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suteu, D.; Malutan, T.; Bilba, D. Agricultural waste corn cob as a sorbent for removing reactive dye orange 16: Equilibrium and kinetic study. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2011, 45, 413. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaili, Z.; Barikbin, B.; Shams, M.; Alidadi, H.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Bonyadi, Z. Biosorption of metronidazole using Spirulina platensis microalgae: Process modeling, kinetic, thermodynamic, and isotherm studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.; Abewaa, M.; Adino, E.; Gizachew, E.; Abdu, J. The application of Rumex abyssinicus based activated carbon for Brilliant Blue Reactive dye adsorption from aqueous solution. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Haddad, M.; Mamouni, R.; Slimani, R.; Saffaj, N.; Ridaoui, M.; ElAntri, S.; Lazar, S. Adsorptive removal of Reactive Yellow 84 dye from aqueous solutions onto animal bone meal. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Villacañas, F.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Figueiredo, J.L. Adsorption of simple aromatic compounds on activated carbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 293, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrémont, S.A. Mémento Technique de L’eau; Le tome 1, 2; Degrémont Suez: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán-Heredia, J.; Sánchez-Martín, J.; Delgado-Regalado, A.; Jurado-Bustos, C. Removal of Alizarin Violet 3R (anthraquinonic dye) from aqueous solutions by natural coagulants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, R. Le Traitement des Eaux, 2nd ed.; Ecole Polytechnique: Palaiseau, France, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Q. Gradient Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Crystal Violet onto Compound Microporous Silica from Aqueous Medium. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 28382–28392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Habacha, M.; Dabagh, A.; Lagdali, S.; Miyah, Y.; Mahmoudy, G.; Sinan, F.; Chiban, M.; Iaich, S.; Zerbet, M. An efficient and adsorption of methylene blue dye on a natural clay surface: Modeling and equilibrium studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 62065–62079. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11356-023-27413-3 (accessed on 15 July 2024). [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Naushad, M.; Kumar, A.; Rana, S.; Sharma, S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Stadler, F.J.; Ghfar, A.A.; Khan, M.R. Efficient removal of coomassie brilliant blue R-250 dye using starch/poly(alginic acid-cl-acrylamide) nanohydrogel. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man Mohan, K.; Kiran Kumar, V.; Gajalakshmi, S. Biosorption of AB-193 Dye Using Rice Straw Biomass and Post-Biosorption Application of Treated Wastewater in Olla-Pot Coupled Microbial Fuel Cells (OPMFCs). Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2023, 14, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofomaja, A.; Ho, Y. Equilibrium sorption of anionic dye from aqueous solution by palm kernel fibre as sorbent. Dyes Pigments 2007, 74, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S.; Chiang, C.-C.; Hsu, Y.-C. Sorption kinetics for dye removal from aqueous solution using activated clay. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2001, 36, 2473–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, A.; Abdul Raman, A.A.; Wan Daud, W.M.A. Advanced oxidation processes for in-situ production of hydrogen peroxide/hydroxyl radical for textile wastewater treatment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yi, L.; Deng, H.; Sun, P. Dyes adsorption using a synthetic carboxymethyl cellulose-acrylic acid adsorbent. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyah, Y.; Lahrichi, A.; Idrissi, M.; Khalil, A.; Zerrouq, F. Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions onto walnut shells powder: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 11, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güzel, F.; Sayğılı, H.; Akkaya Sayğılı, G.; Koyuncu, F. New low-cost nanoporous carbonaceous adsorbent developed from carob (Ceratonia siliqua) processing industry waste for the adsorption of anionic textile dye: Characterization, equilibrium and kinetic modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 206, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salh, D.M.; Aziz, B.K.; Kaufhold, S. High Adsorption Efficiency of Topkhana Natural Clay for Methylene Blue from Medical Laboratory Wastewater: A Linear and Nonlinear Regression. Silicon 2020, 12, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; MacEwan, T.H.; Nakhwa, S.N.; Smith, D. 786. Studies in adsorption. Part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J. Chem. Soc. (Resumed) 1960, 3973–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadurai, G.; Juang, R.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Use of cellulose-based wastes for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arami, M.; Limaee, N.Y.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Tabrizi, N.S. Removal of dyes from colored textile wastewater by orange peel adsorbent: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 288, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Adsorption in solids. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bendary, N.; El-Etriby, H.K.; Mahanna, H. High-performance removal of iron from aqueous solution using modified activated carbon prepared from corn cobs and luffa sponge. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 213, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrick, M.R.; Stulik, D.; Landry, J.M. Infrared Spectroscopy in Conservation Science; Getty Publications: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, C.W.M.; Ku, S.K.A.; Choi, P.S.R.; Kan, C.W.; Tsang, S.Y. Determining Functional Groups of Commercially Available Ink-Jet Printing Reactive Dyes Using Infrared Spectroscopy. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2005, 9, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Ahsaine, H.; Zbair, M.; Anfar, Z.; Naciri, Y.; El Haouti, R.; El Alem, N.; Ezahri, M. Cationic dyes adsorption onto high surface area ‘almond shell’ activated carbon: Kinetics, equilibrium isotherms and surface statistical modeling. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 8, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyinbor, A.A.; Adekola, F.A.; Olatunji, G.A. Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic modeling of liquid phase adsorption of Rhodamine B dye onto Raphia hookerie fruit epicarp. Water Resour. Ind. 2016, 15, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taifi, A.; Alkadir, O.K.A.; Oda, A.A.; Aljeboree, A.M.; Al Bayaa, A.L.; Alkaim, A.F.; Abed, S.A. Biosorption by Environmental, Natural and Acid-Activated Orange Peels as Low-Cost Aadsorbent: Optimization of Disperse Blue 183 as a Model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1029, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiza, S.; Ghiloufi, K.; Bagane, F.M. Utilization of waste Tunisian palm tree date as low-cost adsorbent for the removal of dyes from textile wastewater. Mediterr. J. Chem. 2014, 3, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Belaid, K.D.; Kacha, S. Study of the kinetics and thermodynamics of the adsorption of a basic dye on sawdust. J. Water Sci. 2011, 24, 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Akperov, E.O.; Akperov, O.H. The wastage of the cotton stalks (Gossypium hirsutum L.) as low-cost adsorbent for removal of the Basic Green 5 dye from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumchita, S.; Lahrichi, A.; Benjelloun, Y.; Lairini, S.; Nenov, V.; Zerrouq, F. Removal of cationic dye from aqueous solution by a food waste: Potato peel. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Abhinaya, R.V.; Gayathri Lashmi, K.; Arthi, V.; Pavithra, R.; Sathyaselvabala, V.; Dinesh Kirupha, S.; Sivanesan, S. Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by agricultural waste: Equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Colloid J. 2011, 73, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Parveen, N.; Gupta, H. Adsorptive decontamination of rhodamine-B from water using banana peel powder: A biosorbent. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 12, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocine, H.; Debab, A.; Benettayeb, A.; Al-Farraj, S.; Alkahtane, A.A.; Olivier, J.; Sillanpaa, M. Effectiveness of Opuntia ficus indica (cactus) fruit juice for sludge conditioning. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameters | Optimal Conditions | |
|---|---|---|
| BB-RS01 | BM-N5R | |
| Agitation (rpm) | 400 | 400 |
| pH of solution | 6 | 4 |
| Temperature (°C) | 45 | 45 |
| Adsorbant size (mm) | 0.5/0.63 | 0.5/0.63 |
| Adsorbant mass (g) | 3 | 3 |
| Agitation time (h) | 8 | 8 |
| Isotherms | Parameters | BB-RS01 | BM-N5R |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 99.5 | 46.08 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.0044 | 0.0038 | |
| R2 | 0.9280 | 0.9650 | |
| Freundlich | KF | 1.5603 | 0.6913 |
| n | 0.626 | 0.6215 | |
| R2 | 0.8920 | 0.9410 |
| Adsorbent | Dye | qmax (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Almond shell | Methylene Blue (MB) | 833.33 | [100] |
| Raphia Hookerie | Rhodamine-B | 666.67 | [101] |
| Almond shell | Crystal Violet (CV) | 625 | [100] |
| Orange peel | Methylene blue | 218 | [47] |
| Banana peel | Congo Red | 164.6 | [49] |
| Acid-activated carbon orange peel | Disperse Blue 183 | 149.344 | [102] |
| Corncob | Bemacron Blue-RS01(BB-RS01) | 99.5 | In this study |
| Cactus fruit peel | Basic Red 46 | 82.58 | [46] |
| Palm tree date | Congo red | 73.53 | [103] |
| Wood sawdust | Neutral Red C.I.50040 | 64.06 | [104] |
| Banana peel | Reactive Black 5 | 49.2 | [49] |
| Corncob | Bemacid Marine-N5R(BM-N5R) | 46.08 | In this study |
| Cotton stalks | Basic Green 5 | 42.37 | [105] |
| Potato peel | Methylene blue | 32.70 | [106] |
| Corncob | Reactive dye orange 16 | 26.11 | [73] |
| Walnut shell | Malachite Green | 11.76 | [48] |
| Corncob | Methyl Orange | 7.50 | [52] |
| Cashew nutshell | Methylene blue | 5.311 | [107] |
| Banana peel powder | Rhodamine-B | 3.88 | [108] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahmoun, H.B.; Boumediene, M.; Ghenim, A.N.; Da Silva, E.F.; Labrincha, J. Coupling Coagulation–Flocculation–Sedimentation with Adsorption on Biosorbent (Corncob) for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Environments 2025, 12, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060201
Rahmoun HB, Boumediene M, Ghenim AN, Da Silva EF, Labrincha J. Coupling Coagulation–Flocculation–Sedimentation with Adsorption on Biosorbent (Corncob) for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Environments. 2025; 12(6):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060201
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahmoun, Hadj Boumedien, Maamar Boumediene, Abderahmane Nekkache Ghenim, Eduardo Ferreira Da Silva, and João Labrincha. 2025. "Coupling Coagulation–Flocculation–Sedimentation with Adsorption on Biosorbent (Corncob) for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Aqueous Solutions" Environments 12, no. 6: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060201
APA StyleRahmoun, H. B., Boumediene, M., Ghenim, A. N., Da Silva, E. F., & Labrincha, J. (2025). Coupling Coagulation–Flocculation–Sedimentation with Adsorption on Biosorbent (Corncob) for the Removal of Textile Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Environments, 12(6), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12060201







