Abstract
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are a family of synthetic chemicals that were used to improve the quality of several commercial products by making them resistant to heat, oil, stains, and grease. By containing a fluorinated carbon tail and a hydrophilic head (-COOH, -SO3H), PFASs act as surfactants that are attracted to bubble–water interfaces. Foam fractionation is the process of facilitating PFAS–air bubble interactions for the purpose of removing contaminants from tainted water. In this paper, we report on the use of foam fractionation and electrochemical oxidation (EO) under stirred batch conditions (200 mL) to remediate PFAS-contaminated water. We used radiolabeled PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid; 14C-PFOA) as a representative surrogate to quickly screen treatment variables of flow rate, pH, temperature, and soap mass. Using radiolabeled PFASs eliminated the possibility of cross-contamination and greatly reduced analytical costs and processing time. The results showed that foam fractionation can remove 80 to 90 percent of PFOA from water within 30 min and that 90 to 100 percent of the PFOA in the concentrated foamate can be oxidized via electrochemical oxidation (-14COOH → 14CO2). We also tested the efficacy of the combined foam fractionation–EO treatment in natural waters by spiking 14C-PFOA and a cosolvent (CTAB) into PFAS-contaminated water obtained from two field sites with divergent PFAS concentrations and differing sources of PFAS contamination (natural drainage ditch vs. WWTP). Using a larger-scale tank (3500 mL), we observed that foam fractionation was 90% effective in removing 14C-PFOA from the WWTP effluent but only 50% effective for the drainage ditch water. Regardless, EO was highly effective in oxidizing 14C-PFOA in the foamate from both sources with half-lives (T1/2) ranging from 8.7 to 15 min. While water chemistry differences between source waters may have influenced foam fractionation and require additional investigations, tank experiments provide the first proof-of-concept experiment using 14C-PFASs that foam fractionation and electrochemical oxidation can be used in tandem to treat PFAS-contaminated water.
1. Introduction
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are a family of manmade chemicals that have been heavily used in manufacturing, often without adequate disposal. Commonly used to improve the quality of commercial products by making them resistant to heat, oil, stains, and grease, PFASs are found in many household goods and industrial products like surfactants, emulsifiers, and fire-fighting foams.
Unfortunately, the chemical properties that make PFASs useful from a commercial perspective also make them mobile and recalcitrant once released into the environment [1]. As true xenobiotics, PFASs have no known natural decomposition processes, and the stability of the C-F bond makes them almost undegradable by natural attenuation [2,3].
Now that toxicological studies have linked PFASs with a host of health problems, including kidney, testicular, bladder, and prostate cancer, as well as immune, reproductive, and hormonal dysfunction [4,5,6,7], federal, state, and land owners have an environmental liability to delineate the extent of PFAS contamination, determine migration patterns, and offer realistic solutions to safeguard the public.
One treatment for removing PFASs from contaminated water is through the creation of foams, which can concentrate and remove PFASs from aqueous solutions. The idea that natural organic foams could absorb and partition organic contaminants is not new and was first reported almost 30 years ago. In 1996, USGS scientists [8] published one of the first reports on the geochemistry of natural aquatic foams and detailed the increased hydrophobicity, aliphatic character, and composition of the foams. They also proposed that aquatic foams may be able to concentrate and transport organic contaminants. Natural foams are created when air is introduced into water containing mixtures of naturally derived surfactants, such as organic acids, lipids, and proteins from decaying plants and organic matter. When these dissolved organic materials are present, the formation of eddies (circular currents), cascading water in culverts, or water running atop rock formations can lead to pockets of foam. Previous research has shown natural foams can preferentially concentrate PFASs from natural waters by 10- to >4000-fold [9]. Further, Schwichtenberg et al. [9] found that, of the 50 targeted PFASs investigated, 16 PFASs, encompassing eight different classes, were found above detection limits in foam, while only 5 PFASs were quantified in the underlying bulk water.
The practice of purposefully inducing foam with cosolvents for PFAS removal is more recent. Lee et al. [10] is one of the first to report the removal of PFOA from a dilute solution through foam flotation [11]. Foam fractionation is the process of adding a surfactant to cause PFASs to combine with air bubbles and be carried toward the surface for removal. Air is typically bubbled through an aqueous solution of amphiphiles—compounds with hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions, so that they adsorb to the surface of rising bubbles and form a froth/foam layer above the liquid, which can then be removed and condensed to form a “foam liquid” (i.e., foamate) [12]. The surfactant nature of PFASs makes them well suited to this foaming process and offers a unique approach for separating PFASs from contaminated water. Since Lee et al. [10], several publications have been reported on PFAS removal via foam fractionation and excellent literature reviews and books are currently available [11,13] as well as historical reports and literature on the hydrodynamics of foam fractionation [14,15].
While foam fractionation of PFASs has been well researched and has become commercialized (EPOC Enviro, http://epocenviro.com, accessed 27 May 2025), the product of foam fractionation is a liquid foamate enriched in PFASs. The best way to treat PFAS-foamate is still being investigated. We report herein on a series of experiments that used foam fractionation to generate PFAS-enriched foamate and then provide results on the efficacy of using electrochemical oxidation via boron-doped diamond electrodes to remove the PFASs from the foamate. In this paper, we used a radiolabeled PFAS compound (14C-PFOA; C8F15O2H) as a means to quickly screen the treatment variables of flow rate, pH, temperature, and soap mass. Using a radiolabeled PFAS eliminated the possibility of cross-contamination, facilitated mass balance calculations, and greatly reduced analytical processing time and costs. While conventional PFAS analysis, via a commercial laboratory, can range from USD 250 to USD 400 per sample, depending on the methodology (i.e., EPA Method 1633; ASTM D8421; USEPA Method 537 modified), the detection of 14C-PFOA at environmentally relevant concentrations (~µg/L) is simple, straightforward, and only requires the cost of a scintillation cocktail (6 mL per sample, <USD 1.00) and access to a liquid scintillation counter (LCS). Moreover, by using 14C-labeled perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and tracking the temporal changes in 14C-activity during electrochemical oxidation, we report reaction kinetics and show that oxidation of the carboxylic head is possible (-14COOH → 14CO2).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Chemicals were purchased from a variety of vendors and used as received. These chemicals included the following: perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA; C8F15O2H; >95% purity). (Fisher, Fair Lawn, NJ, USA). We also used 14C-labeled perfluorooctanoic acid (14C-PFOA; 55 mCi mmol−1; American Radiolabeled Chemicals, St. Louis, MO, U.S.A.), sodium sulfate, and H2SO4 (Fisher, Fair Lawn, NJ, USA). All solutions were prepared with Millipore water (18.2 MΩ cm−1 resistivity, 25 °C) from a Nanopure Barnstead E-pure system (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.2. Foam Fractionation Experiments—Batch Conditions
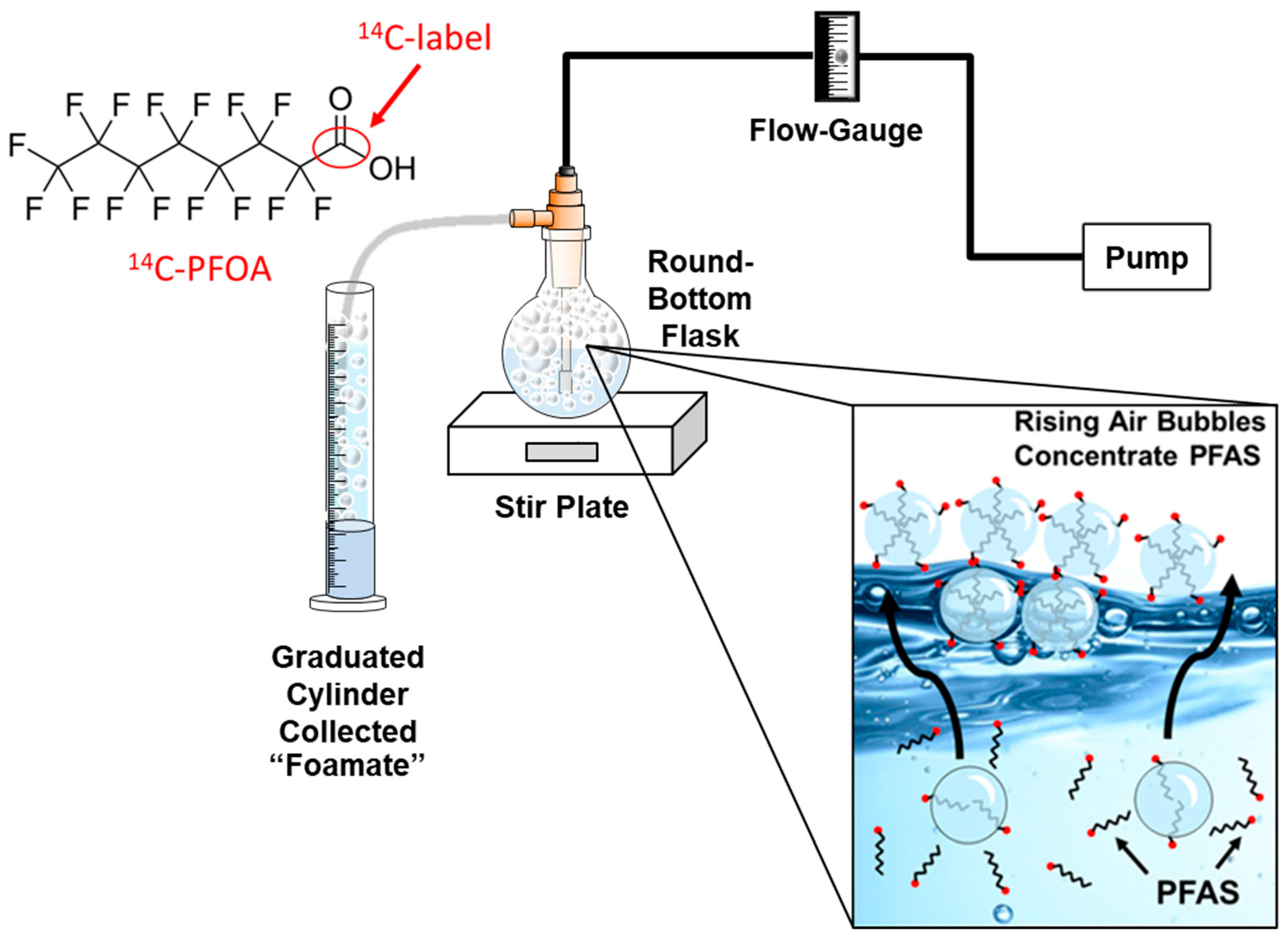
Aerated foam fractionation experiments were conducted in 250 mL round-bottom flasks containing either 200 mL of distilled or field-collected water, a surfactant, 14C-PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid), and a magnetic stir bar (Figure 1). The experimental unit was placed atop a stir plate and constantly mixed during aeration. An electrical pump and flow-gauge provided a constant flow rate of air (6 L/min) into a fritted glass diffuser. The bubbles (foam) produced inside the round-bottom flask were diverted to a 250 mL graduated cylinder that contained 1.5 mL of the commercial anti-foaming chemical, No Foam (Liquid Harvest, Sanco Ind, Inc, Fort Wayne, IN, USA). No Foam contains the active ingredient dimethylpolysiloxane, which quickly condensed the incoming foam into liquid.
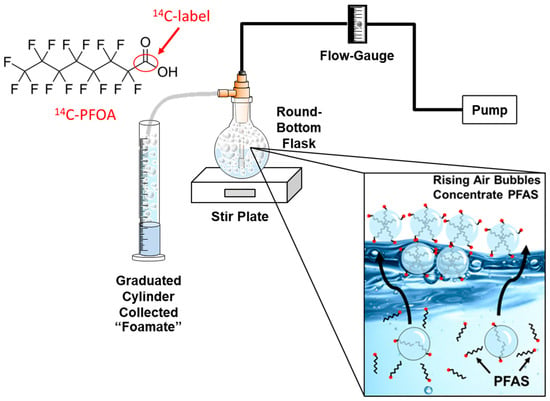
Figure 1.
Foam-fractionation of 14C-PFOA-tainted water.
Typical screening experiments involved taking three 1 mL subsamples at T = 0 min from the round-bottom flask and then aerating the flask for 30 mins. The round-bottom flask was then resampled (T = 30 min) along with the liquified foam collected in the graduated cylinder (Figure 1). The volume of foam produced was recorded for mass balance calculations. Experimental treatments were typically pretested (without the use of 14C-PFOA) to determine that adequate foam volumes were produced. After which, the treatment was repeated, and the experimental unit was spiked with 0.250 mL of 14C-PFOA.
Carbon-14 activity (14C-activity) was determined by removing 1 mL subsamples from the round-bottom flasks and graduated cylinder and mixing with 6 mL of Ultima Gold liquid scintillation cocktail (Packard, Meriden, CT, USA). The samples were then mixed and analyzed on a Packard 1900TR liquid scintillation counter (LSC; Packard Instrument, Downers Grove, IL, USA). A blank consisting of 6 mL Ultima Gold liquid scintillation cocktail was analyzed prior to running the samples and used to correct sample activity values (dpms).
Following analysis, 14C enrichment in foam (Equation (1)) and 14C recovered in foamate (Equation (2)) were calculated as follows:
In addition to the radioisotope concentrations provided by the LCS, the specific activity of the 14C-PFOA (55 mCi mmol−1) allows for the conversion of radioisotope readings (dpms/mL) to a mole or mass of PFOA per volume (e.g., mmole/L; µg/L). A sample conversion calculation is provided in the Supplementary Material (SM). Most foam fractionation experiments were run with starting solutions between 1000 to 3000 dpms/mL. For comparison, a 14C-PFOA concentration of 1185 dpms/mL converts to 4.06 µg/L (4060 ng/L) (see SM), which is environmentally relevant to concentrations observed at sites with known PFAS contamination in stormwater runoff.
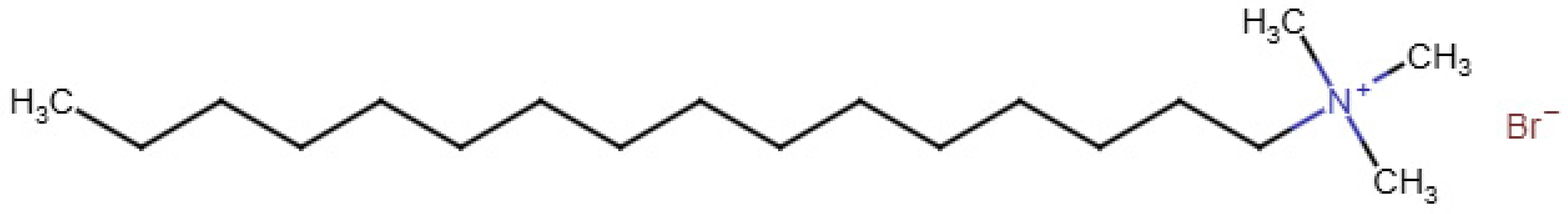
The treatment variables quantified under batch conditions included soap mass, flow rate, pH, and temperature. While a few commercial soaps were tested and reported (Table S1), most experiments used cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB, Figure 2), a cation surfactant. We tested foam formation using 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, and 0.08 g of CTAB, under one flow rate (6 L/min). Using a flow-gauge, three different flow rates were also compared (4, 6, and 8 L/min). The solution pH was set at 3.6, 6.4, and 9.4 by adjusting the pH downward with dilute H2SO4. Finally, with the aid of a water bath and water-jacketed glassware, the efficacy of bubble formation under hot and cold temperatures was evaluated. The four different temperatures tested included the following: 16, 20, 23, and 26 °C at a flow rate of 6 L/min.
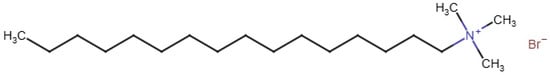
Figure 2.
Chemical structure of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB).
2.3. Foam Fractionation Experiments—Tank Experiments
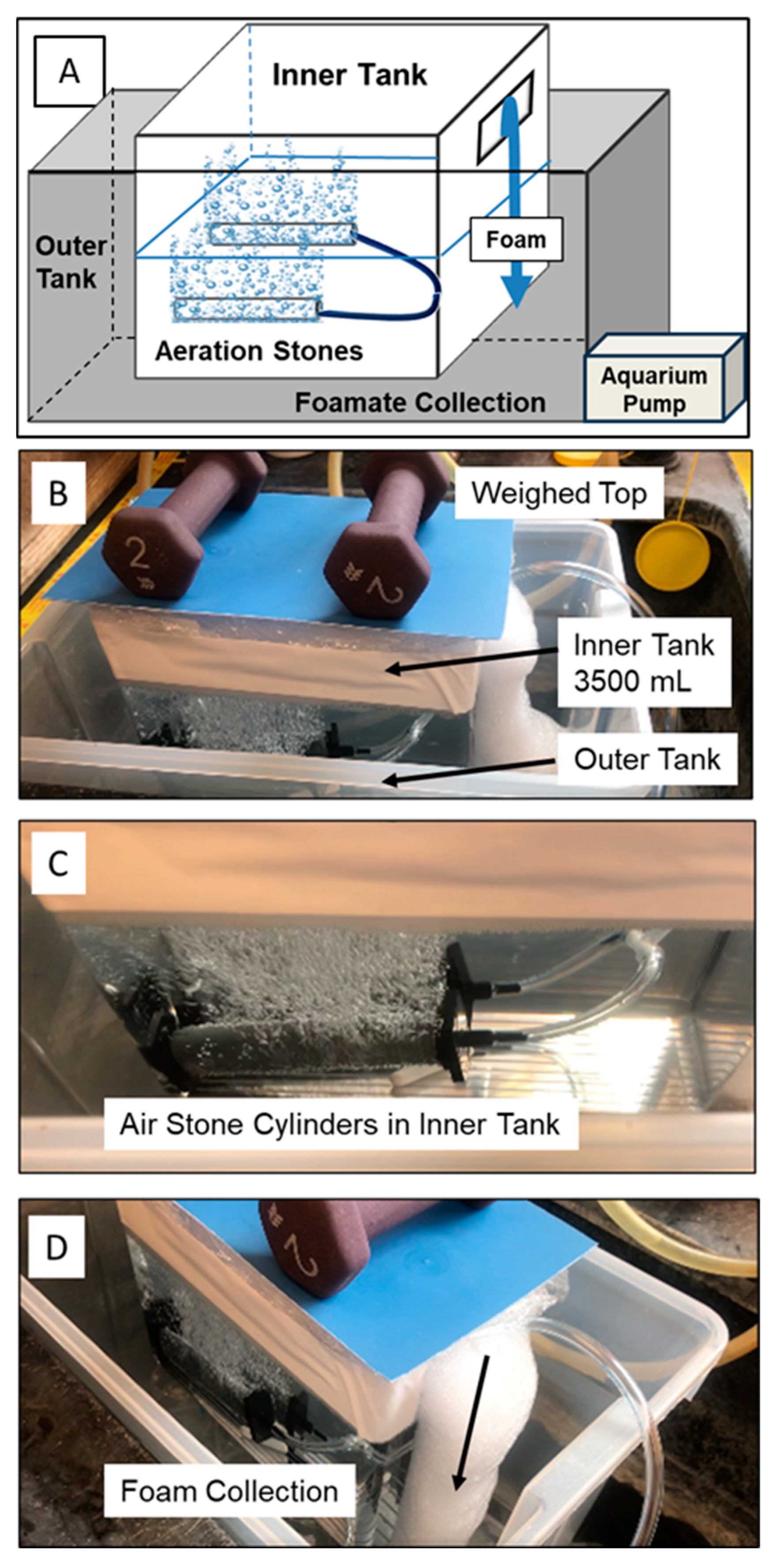
The foam fractionation experiments were also carried out at a larger scale using a tank containing 3500 mL of solution. Here, the experimental unit (inside tank) was encased in a larger tank that collected the foam as it emanated from the inside tank (Figure 3). 14C-PFOA was spiked into 3500 mL of distilled water or field-collected water and enough cosolvent (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, CTAB) to bring the starting concentration to 150 mg/L. In the tank experiments, two bubbling stone cylinders were aerated at 1.2 L/min. The inner tank had a weighted (sealed) top that forced the foam to exit from the side of the tank and cascade into the larger tank that contained 2.0 mL of “No-Foam” to facilitate the foamate formation.
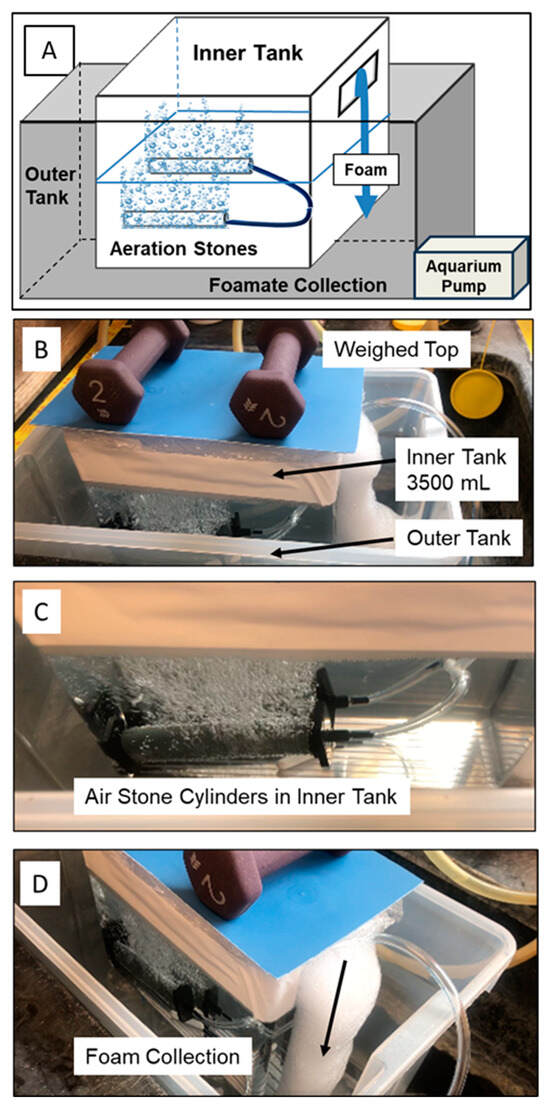
Figure 3.
(A) Schematic of double tank setup; (B) experimental unit tank (3500 mL) inside larger tank with weighed top to force foam out the side; (C) close-up of aerated stone cylinders; (D) side view of foam cascading out of small tank into larger tank.
2.4. Water Sampling PFAS-Tainted Water
Surface water samples were collected at two field locations in July 2023, both with histories of PFAS contamination related to the use of aqueous film-forming foams (AFFFs). Both field locations are in the Great Lakes region of the Unites States. Due to confidentiality and conflicting interests, the names of the sites cannot be disclosed. Water from the first site (hereinafter referred to as Site A) was collected from a stormwater outfall pipe that flows into a vegetated drainage ditch. Past sampling of the stormwater outfall found that the total PFAS concentrations varied between 8 and 44 µg/L.
The second field site (hereinafter referred to as Site B) was a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). This WWTP consists of three treatment cells that apply aeration and phosphate removal. The water samples used in our experiment were collected from the last treatment cell, prior to chlorination. PFAS sampling of this site is ongoing, but earlier reports show total PFAS concentrations below 1 µg/L. Thus, the two field samples used as background matrices in our foam fractionation and electrochemical oxidation experiments represented high (>1 µg/L, Site A) and low (<1 µg/L, Site B) background PFAS concentrations.
2.5. Electrochemical Oxidation
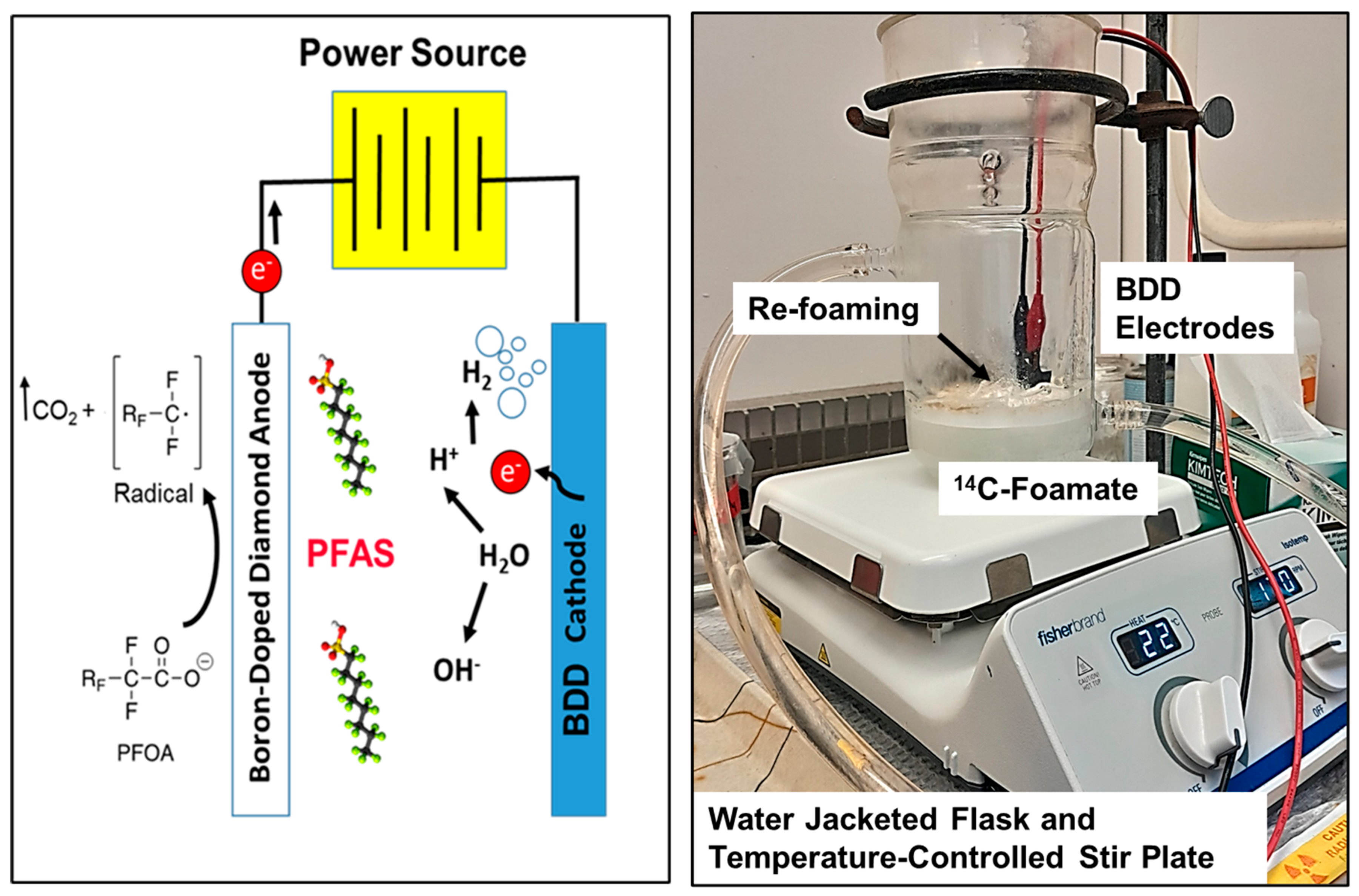
A series of laboratory batch experiments were undertaken using boron-doped diamond (BDD) anode/cathodes to electrochemically oxidize (EO) PFOA. The advantage electrochemical oxidation has over other technologies is that BDD anodes can initiate an electron removal from the ionic head of PFOA (Figure 4, [16,17,18,19,20]). The key factor for enhanced oxidation via EO treatment is the interaction the EO-generated hydroxyl radicals have with the electrode surface. In general, high-oxidation-power anodes are characterized by weak electrode–hydroxyl radical interactions resulting in a high current efficiency for organic oxidation and a low electrochemical activity for oxygen evolution [21]. Based on this, boron-doped diamond can be considered as one of the ideal anode materials for the electrochemical mineralization of organic contaminants [22].
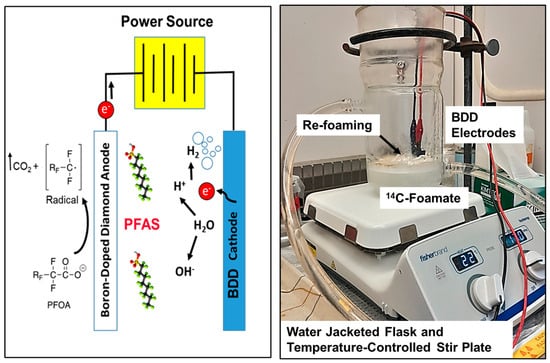
Figure 4.
Schematic and photo of electrochemical oxidation using boron-doped diamond electrodes.
Most electrochemical experiments were run under similar stirred, single-batch conditions as previously described by Yanagida et al. [21]. The typical experimental setup consisted of a 600 mL water-jacketed Erlenmeyer flask filled with 200 mL of a PFAS foamate. Enough electrolyte salt (Na2SO4) was added to bring the concentration to 1 mM Na2SO4. The solution was then spiked with 1 to 3 mL of stock 14C-PFOA (55 mCi mmol−1), which brought the solution’s 14C-activity to approximately 1500 to 3000 dpms mL−1, and diluted H2SO4 acid (10% v/v with H2O) to decrease the solution to pH 3.0. The experimental unit received a magnetic stir bar, was placed on a stir plate, and then mixed at a stir speed of 170 rpm. Samples were taken in triplicate at 0, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, and 120 min.
We used two boron-doped diamond electrodes (NeoCoat®, La Chaux-de Fonds, Switzerland). The NeoCoat® electrodes consisted of a polycrystalline boron-doped diamond coating (5 µm coating, 2500 ppm B) deposited on both sides of a mesh niobium substrate. The dimensions of the mesh BDD electrodes were 25 × 100 × 1.4 mm. A plastic holder was fabricated [21] that maintained an electrode spacing of 5 mm. These electrodes were connected to a DC power supply (30 V/20 A, Extech instruments, Nashua, NH, USA) and suspended in the solution so that they were submerged as fully as possible without the electrical alligator clips touching the solution. The electrical current was set between 0.2 and 1.0 A, and is specified in the presented graphs (Figure 5). The supplied voltage varied with the current density and the electrolyte concentration and is reported on the presented graphs.
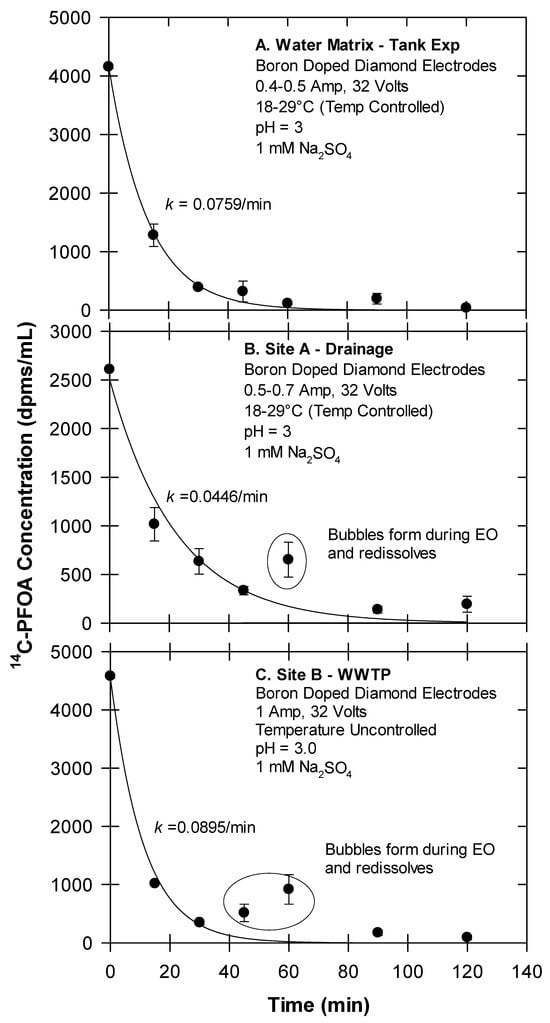
Figure 5.
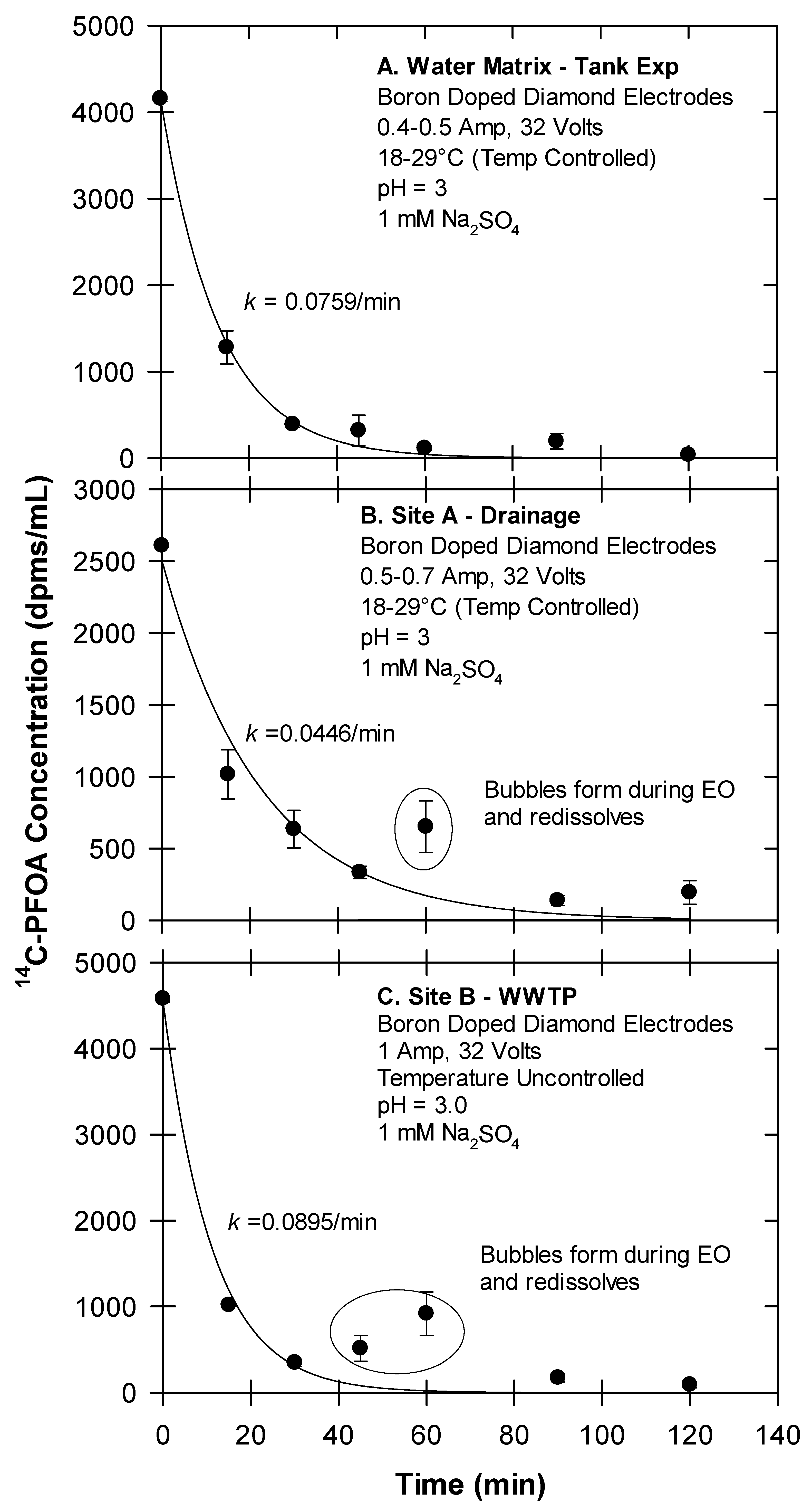
Temporal changes in 14C-PFOA following electrochemical oxidation of foamates. Foamates were generated from (A) water; (B) Site A drainage water; (C) Site B WWTP.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using Minitab® 22 was used to determine differences in the percentage of 14C-PFOA recovered in the foamate and 14C enrichment between tested variables using Tukey’s multiple comparison procedures. Tukey’s multiple comparison procedure was used in conjunction with the ANOVA to determine whether the means of two sets of data, among multiple data, were significantly different from each other. In the data tables presented (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5), the data values followed with similar letters within columns (i.e., levels within a treatment, e.g., flow rates) are not statistically different, but values followed by different letters (i.e., a vs. b) are significantly different using Tukey’s multiple comparison procedure ([23] Steel and Torrie, 1980) with a 5% probability of a Type I error (α = 0.05).
3. Results and Discussion
The amphiphilic structures of PFASs allow removal via adsorption at the air–water interface of bubbles. While the formation of naturally forming foams has been readily observed in coastal waters and streams [9], a more focused generation of foams for remedial purposes requires the addition of cosolvents. Adding cosurfactants reduces the surface tension of the water, which stabilizes the air bubbles and increases foam formation [24,25]. Types of surfactants used in the past include cationic, anionic, non-ionic, and zwitterionic [11]. Given that most PFASs contain either a sulfonic or carboxyl anionic head, using a countering cationic surfactant to facilitate electrostatic interactions along the bubble interfaces has resulted in greater removal. Generally, a higher surfactant dosage increases foaming and more removal, but tradeoffs between volume of foam produced versus PFAS enrichment in the foam needs to be considered.
3.1. Effects of Cosolvent Mass on PFAS Recovery and Enrichment
Initial experiments showed that, as the mass of CTAB increased from 0.02 g to 0.08 g (per 200 mL liquid), the foamate volume increased, but the 14C enrichment decreased (Table 1). In these experiments, statistical analysis showed both enrichment and recovery were significantly different for each CTAB mass, but the highest removal occurred at 0.06 g (Table 1), which is equivalent to a starting CTAB concentration of 300 mg/L. Li et al. [26] and Buckley et al. [27] similarly reported that CTAB could remove ≥ 95% PFOA after 20 to 30 min of foaming. Buckley et al. [27] also reported that short-chain PFAS species, such as PFBS and perfluorobutanoic acid (PFBA) could also be removed at ≥95% efficiency with CTAB after 30 min of foaming. Meng et al. [25] similarly indicated that an increasing foam volume can reduce PFAS enrichment in foam.

Table 1.
Effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) surfactant mass on PFOA foam fractionation.
Table 1.
Effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) surfactant mass on PFOA foam fractionation.
| Surfactant Mass | Foamate Volume | 14C Enrichment in Foam † | 14C Recovered in Foamate |
|---|---|---|---|
| g | mL | % | |
| 0.02 | 32 | 3.51 a ‡ | 56.99 a |
| 0.04 | 64 | 2.33 b | 75.75 b |
| 0.06 | 104 | 1.75 c | 92.35 c |
| 0.08 | 122 | 1.32 d | 81.80 d |
† (PFOA concentration in foamate)/(Initial PFOA concentration in water). ‡ Values within columns with same letter are not significantly different (α = 0.05).
Li et al. [26] further evaluated concentration mass effects on PFOA removal using two other cationic surfactants, octyltrimethylammonium bromide (OTAB) and dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB). They reported 98% PFOA removal and few concentration effects between 1.25 mM and 5.0 mM. The 1.25 mM concentration for these two surfactants would be equivalent to 315 mg/L (OTAB) and 385 mg/L (DTAB), which is similar to the concentrations used in our experiments.
3.2. Effect of Flow Rate
While some sophisticated methods of bubble generation have been used to remove PFASs, such as nucleation, mechanical agitation, and liquid jet entrapment, most foam fractionation studies have used air sparging due to its simplicity and low energy consumption ([11]). When air is sparged (i.e., injected) into an experimental unit and allowed to flow upwards, bubbly flow will occur. In bubbly flow, the liquid flow rate is high enough to break up the gas into bubbles and provide air–water interfaces for PFAS adsorption but not high enough to cause the bubbles to redissolve within the liquid phase. The bubbles vary widely in shape and size, but most are nearly spherical [28]. While an increasing flow rate can increase bubble size, larger bubbles provide less total surface area and can reduce PFAS removal. Also, higher flow rates can possibly cause bubbles that initially form to break, thereby decreasing removal efficiency [29]
The results using our experimental setup (Figure 1) showed that, as the flow rate increased (4→8 L/min), the foamate volume increased and the 14C enrichment decreased (Table 2). The highest 14C recovered (91%) was at a flow rate of 8 L/min (Table 2). This flow rate is lower than that used by Dai et al. [30], where increases in PFAS removal increased from 75% to 88% when the gas flow rate increased from 15 L/min to 30 L/min.

Table 2.
Effect of flow rate on PFOA foam fractionation.
Table 2.
Effect of flow rate on PFOA foam fractionation.
| Flow Rate | Foamate Volume | 14C Enrichment in Foam † | 14C Recovered in Foamate |
|---|---|---|---|
| L/min | mL | % | |
| 4 | 94 | 1.78 a ‡ | 85.02 a |
| 6 | 118 | 1.49 b | 88.89 ab |
| 8 | 126 | 1.43 c | 91.13 bc |
† (PFOA concentration in foamate)/(Initial PFOA concentration in water). ‡ Values within columns with same letter are not significantly different (α = 0.05).
3.3. Effect of pH
Foam fractionation experiments that altered the pH showed that the highest 14C enrichment occurred at pH 6.4 (Table 3). There were slight declines in the volume of foamate generated as the pH increased from 3.6 to 9.4, but this change was relatively minor (124 → 110 mL). Overall, the highest 14C recovered was at pH 6.4. This is an encouraging observation because it indicates that circumneutral pHs are likely optimal and no pH adjustments would be needed to treat natural waters under pi.
Du et al. ([31]) investigated bubble size at pHs of 3.5, 4.5, 6.5, and 9.7. They reported that the bubble size was largest at pH 3.5 and 4.5 and that the foam was less stable. At pH 6.5 and 9.7, the bubble size was smaller, and the foam was more stable, resulting in higher enrichment and mass recovery of the protein, ovalbumin.

Table 3.
Effect of pH on PFOA foam fractionation.
Table 3.
Effect of pH on PFOA foam fractionation.
| pH | Foamate Volume | 14C Enrichment in Foam † | 14C Recovered in Foamate |
|---|---|---|---|
| mL | % | ||
| 3.6 | 124 | 1.40 a ‡ | 88.32 a |
| 6.4 | 112 | 1.64 b | 93.19 ab |
| 9.4 | 110 | 1.55 c | 86.42 bc |
† (PFOA concentration in foamate)/(Initial PFOA concentration in water). ‡ Values within columns with same letter are not significantly different (α = 0.05).
3.4. Effect of Temperature
Foam fractionation conducted at 16, 20, 23, and 26 °C showed some improvement in 14C recovery in the foamate at 20 and 23 °C (Table 4). This means room temperatures were better than the colder or hotter temperatures. Morrison et al. ([32]) recently reported that temperatures of 4, 22, and 37 °C had negligible effects on long-chain PFAS recovery. This was not the case for short-chain PFASs (i.e., perfluorobutanesulfonic acid, PFBS), where recovery decreased from 40% (4 °C) to 10% (22 °C) to 0% (37 °C) as the temperature increased (4 °C → 37 °C).

Table 4.
Effect of temperature on PFOA foam fractionation.
Table 4.
Effect of temperature on PFOA foam fractionation.
| Temperature | Foamate Volume | 14C Enrichment in Foam † | 14C Recovered in Foamate |
|---|---|---|---|
| °C | mL | % | |
| 16 | 124 | 1.38 c ‡ | 86.99 a |
| 20 | 122 | 1.52 a | 93.75 c |
| 23 | 140 | 1.30 d | 92.48 c |
| 26 | 122 | 1.45 b | 89.49 b |
† (PFOA concentration in foamate)/(Initial PFOA concentration in water). ‡ Values within columns with same letter are not significantly different (α = 0.05).
3.5. Tank Experiments
Tank experiments were run using 3500 mL of solution in a double tank setup (Figure 3). By scaling up experiments from 200 mL to 3500 mL, the 14C-enrichment factors increased. In batch experiments (200 mL), enrichment factors from deionized water were generally under 2.0. By going to a larger volume, and thus greater potential mass of 14C-PFOA available, the enrichment factors increased to 4.0 (Table 5) (other experiments, also exhibited this). By spiking 14C-PFOA into the source water from two field sites, the enrichment factors were 2.3 to 2.6 in field-collected water. These values, however, are underestimating enrichment because, at the end of 30 min, foam was still on top of the inner box’s water. Because this foam could not be collected and quantified, we waited until the foam had redissolved. The presence of other PFAS compounds (not 14C labeled) may have competed for bubble–water interface sites or, as previously mentioned, as the foamate volume increases, the 14C enrichment decreases. This was evident when comparing the foamate volume generated from DI water versus Site B (drainage) field water. The volume of foamate nearly doubled from the Site B water versus the DI water (Table 5). Again, Site B had background PFASs, and these surfactants could have aided bubble formation. The results from the tank experiment showed little benefit of increasing foam fractionation times from 30 to 60 min (Table 5).

Table 5.
Effect of water source on PFOA foam fractionation. All tank experiments used CTAB (~150 mg/L).
Table 5.
Effect of water source on PFOA foam fractionation. All tank experiments used CTAB (~150 mg/L).
| Water Source | Foamate Volume (mL) | 14C-Enrichment Factor † | 14C Recovered in Foamate (%) | Mass Balance | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DI Water | 659 | 4.00 a ‡ | 75.50 b ‡ | 94 | 30 |
| Site B WWTP | 1206 | 2.60 b | 89.47 a | 91 | 30 |
| Site B WWTP | 1306 | 2.31 b | 86.19 a | 91 | 60 |
| Site A Drainage | 663 | 2.67 b | 50.78 c | 111 | 30 |
† (PFOA concentration in foamate)/(Initial PFOA concentration in water). ‡ Values within columns with same letter are not significantly different (α = 0.05).
Water from Site A reacted differently from the DI and Site B. The volume of foamate generated from Site A water was similar (663 mL) to that produced from DI water (659 mL), but the enrichment was like the Site B water (2.60, Table 5) not the DI water (4.0). This resulted in a recovery of 14C in the foamate of only 50%. This lower recovery may be due to artifacts or matrix-specific effects. Future investigations into the differences in water chemistries between Sites A and B are needed to elucidate the differences in the foam fractionation results. Moreover, quantifying physiochemical changes in water properties before and after treatment is recommended for future experiments.
3.6. Electrochemical Oxidation of Foamate
Using the experimental variables determined by Yanagida et al. ([21]), our electrochemical oxidation (EO) treatments were conducted at pH 3, a current of 0.4–1.0 Amp, 32 V, and with a 1 mM Na2SO4 matrix. Under these conditions, the 14C-PFOA in the foamate generated from the tank experiment (water matrix) decreased at a first-order rate of k = 0.0759 min−1. The foamates generated from the field site waters (Site A and B) also decreased at a rate of k = 0.0446 min−1 for Site A and k = 0.0895 min−1 for Site B (Figure 5). Conversion of these first-order rates corresponds to PFOA half-lives of approximately 8.6 to 15 min. Smith et al. ([33]) similarly reported first-order removal rates of various PFASs by EO. One notable observation from our experiment is that EO treatment can cause an increase in temperature, which was controlled by a water bath connected to a water-jacketed glassware (Figure 4). This, along with bubble generation around the BDD electrodes leads to some foaming. As this foam redissolves, PFOA concentrations (as dpms/mL) can temporally increase (Figure 5). It is also noteworthy that the loss of radioactivity (dpms/mL) from the foamate can be equated with the mineralization of the carboxyl head (-14COOH → 14CO2). While not used during these reported experiments, a gas trapping system (Figure S1) previously showed the capture of 14CO2 during EO experiments.
While the exact mechanisms for the electrochemical oxidation of PFASs are complex, there is general agreement that the rate-limiting step is the direct electron transfer at the anode, which results in the cleavage of the head group (-COOH) to produce the corresponding perfluoroalkyl radical (Figure 4); the perfluoroalkyl radical can then quickly react with •OH, O2, or H2O and degrade to the one-carbon-shorter perfluoroheptanecarboxylate. The newly produced, one-carbon-shorter carboxylate then undergoes the same degradation cycle as the original PFOA, sequentially converting the carboxylic acid head to carbon dioxide, the fluorine atoms to hydrogen fluoride, and the -CF2 end group to another carboxylic acid group [21]. Additional details on the treatment of PFASs with boron-doped diamond electrodes can be found in an excellent review recently published by Tasca et al. [34].
Radjenovic et al. [35] indicated that the use of high PFAS concentrations (i.e., 10–100 mg/L) in laboratory experiments likely overestimates electrochemical oxidation performance and makes extrapolating results to environmentally relevant matrices difficult. As previously stated, the use of 14C-PFOA provided the advantage of making the analysis simple, quick, and negated any PFAS cross-contamination interferences. Moreover, by measuring the 14C activity of the foamate (dpms mL−1), converting to µCi, and then using the specific activity of the PFOA label (55 mCi mmol−1), the PFOA concentration could be calculated. In most tank experiments, the foamate had 14C-PFOA concentrations between 3000 and 5000 dpms mL−1, which would be equivalent to starting concentrations (Co) between 10 and 17 µg PFOA L−1, which would be environmentally relevant.
The coupling of foam fractionation and electrochemical oxidation has only recently been reported [33,36]. Smith et al. [33] reported a 94% reduction in PFOA in foamate generated from groundwater and an 80% reduction in foamate generated from landfill leachate. Uwayezu et al. [37] also recently used electrochemical oxidation to treat foamate from soil washing experiments and achieved 90% removal of serval PFAS compounds within 2 h.
4. Summary and Conclusions
In summary, the practical treatment of PFAS compounds from various environmental matrices will undoubtedly require a treatment train technology [38]. For PFAS-tainted liquids, an ideal treatment would be one that concentrates the PFASs and reduces the volume, while the secondary treatment would remove or destroy the PFASs, preferentially through mineralization. While water chemistry differences between source waters may influence foam fractionation and require additional investigations, tank experiments provided proof-of-concept that foam fractionation and electrochemical oxidation can be used in tandem to treat PFAS-contaminated water. By starting with a spiked 14C-PFAS surrogate (14C-PFOA), we were able to track removal and destruction without any ambiguity or uncertainty caused by cross-contamination. Based on the data presented, the proposed two-step process of foam fractionation and electrochemical oxidation using boron-doped diamond electrodes is a plausible approach and one ready for pilot or field-scale evaluation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/environments12060185/s1: Table S1: Effect of Surfactant type on PFOA foam fractionation. Figure S1: Photograph of gas trapping system used to confirm mineralization of 14C-PFOA in previous experiments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C., A.A.d.S. and J.P.; Investigation, A.A.d.S., J.P., R.C., A.M. and R.F.D.; Resources, S.C.; Data curation, A.A.d.S., J.P., R.C. and A.M.; Writing—original draft, S.C.; Writing—review & editing, A.A.d.S., J.P., R.C. and A.M.; Funding acquisition, R.F.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are very grateful for the scholarship granted by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development—Brazil (CNPq), Process No. 200168/2023-1, to Amanda Araújo Silva. Renato Falcão Dantas is grateful for the financial support for the project granted by CNPq—Process No. 401012/2022-0.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Suthersan, S.S.; Horst, J.; Ross, I.; Kalve, E.; Quinnan, J.; Houtz, E.; Burdick, J. Responding to emerging contaminant impacts: Situational management. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2016, 36, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, B.L.; Howell, R.D.; Criddle, C.S. Fluorinated organics in the biosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hagan, D. Understanding organofluorine chemistry. An introduction to the C-F bond. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conder, J.M.; Hoke, R.A.; Wolf, W.D.; Russell, M.H.; Buck, R.C. Are PFCAs Bioaccumulative? A critical review and comparison with regulatory criteria and persistent lipophilic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Anitole, K.; Hodes, C.; Lai, D.; Pfahles-Hutchens, A.; Seed, J. Perfluoroalkyl acids: A review of monitoring and toxicological findings. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 366–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, N.; Eriksson, P.; Viberg, H. Neonatal exposure to PFOS and PFOA in mice results in changes in proteins which are important for neuronal growth and synaptogenesis in the developing brain. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.H.; Sasaki, K.; Saito, N.; Sato, I.; Tsuda, S. Human nails analysis as biomarker of exposure to perfluoroalkyl compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8144–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.S.; Thurman, E.M.; Ertel, J.; Thorn, K.A. Chapter 11: Organic Geochemistry and sources of natural aquatic foams. In Humic and Fulvic Acids; Gaffney, J.S., Marley, N.A., Clark, S.B., Eds.; PFAS and Microplastic Enrichment in Surface Water Foams; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 151–192. [Google Scholar]
- Schwichtenberg, T.; Bogdan, D.; Carignan, C.C.; Reardon, P.; Rewerts, J.; Wanzek, T.; Field, J. PFAS and Dissolved Organic Carbon Enrichment in Surface Water Foams on a Northern U.S. Freshwater Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14455–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Wang, P.Y.; Lo, S.L.; Huang, C.P. Recovery of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) from dilute water solution by foam flotation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- We, A.C.E.; Zamyadi, A.; Stickland, A.D.; Clarke, B.O.; Freguia, S. A review of foam fractionation for the removal of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from aqueous matrices. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.J.; Stevenson, P.; Murphy, P.J.C. PFAS removal from groundwaters using Surface—Active Foam Fractionation. Remediat. J. 2021, 31, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, T.; Karanam, K.; Xu, X.; Shukla, P.; Firouzi, M.; Rudolph, V. Effect of mono- and di-valent cations on PFAS removal from water using foam fractionation—A modelling and experimental study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghoff, B. Foam fractionation applications. J Biotechnol. 2012, 161, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, P.; Li, X. Foam Fractionation: Principles and Process Design, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, K.E.; Farrel, J. Oxidative destruction of perfluorooctane sulfate using boron-doped diamond film electrodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 6111–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Farrell, J. Electrochemical oxidation of perfluorobutane sulfonate using boron-doped diamond film electrodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 1993–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Tipton, M.J.; Farmer, A.T.; Steen, A.D.; Carter, K.E. Understanding electrochemically activated persulfate and its application to Ciprofloxacin abatement. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5875–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Andaya, C.; Urtiaga, A.; McKenzie, E.R.; Higgins, C.P. Electrochemical treatment of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) in groundwater impacted by aqueous film forming foams (AFFFs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, C.E.; Andaya, C.; Burant, A.; Condee, C.W.; Urtiagad, A.; Strathmann, T.J.; Higgins, C.P. Electrochemical treatment of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate: Insights into mechanisms and application to groundwater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, A.; Webb, E.; Harris, C.E.; Christenson, M.; Comfort, S. Using Electrochemical Oxidation to Remove PFAS in Simulated Investigation-Derived Waste (IDW): Laboratory and Pilot-Scale Experiments. Water 2022, 14, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapałka, A.; Fóti, G.; Comninellis, C. Kinetic modelling of electrochemical mineralization of organic pollutants for wastewater treatment. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2008, 38, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H. Principles and procedures of statistics. In A Biometrical Approach, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 172–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, H.; Ouyang, M.; Kong, M.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhuang, L. Experimental and DFT studies on foam performances of lauryl ether sulfate-based anionic surface active ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 117519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.; Deng, S.; Maimaiti, A.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cousins, I.T.; Yu, G. Efficient removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate from aqueous film-forming foam solution by aeration-foam collection. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-F.; Chien, W.-Y.; Liu, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lo, S.-L.; Hu, C.-Y. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) removal by flotation with cationic surfactants. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, T.; Karanam, K.; Han, H.; Vo, H.N.P.; Shukla, P.; Firouzi, M.; Rudolph, V. Effect of different co-foaming agents on PFAS removal from the environment by foam fractionation. Water Res. 2023, 230, 119532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisman, J. Chapter 15: Two-phase flow patterns. In Handbook of Fluids in Motion; Cheremisinoff, N.P., Gupta, R., Eds.; Ann Arbor Science Publ.: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1983; pp. 409–425. [Google Scholar]
- Boonyasuwat, S.; Chavadej, S.; Malakul, P.; Scamehorn, J.F. Anionic and cationic surfactant recovery from water using a multistage foam fractionator. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 93, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Xie, Z.; Dorian, B.; Gray, S.; Zhang, J. Comparative study of PFAS treatment by UV, UV/ozone, and fractionations with air and ozonated air. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Prokop, A.; Tanner, R.D. Effect of pH on the Startup of a Continuous Foam Fractionation Process Containing Ovalbumin. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 1093–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.L.; Strezov, V.; Niven, R.K.; Taylor, M.P.; Wilson, S.P.; Wang, J.; Burns, D.J.; Murphy, P.J.C. Impact of salinity and temperature on removal of PFAS species from water by aeration in the absence of additional surfactants: A novel application of green chemistry using adsorptive bubble fractionation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 5635–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Lauria, M.; Ahrens, L.; McCleaf, P.; Hollman, P.; Bj¨alkefur Seroka, S.; Hamers, T.; Arp, H.P.H.; Wiberg, K. Electrochemical oxidation for treatment of pfas in contaminated water and fractionated foam—A pilot-scale study. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasca, A.L.; Uwayezu, J.N.; Carabante, I.; Kumpiene, J. Electrochemical remediation of PFAS by Boron-Doped Diamond electrodes: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenovic, J.; Duinslaeger, N.; Avvl, S.S.; Chaplin, B.P. Facing the challenge of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in water: Is electrochemical oxidation the answer? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14815–14829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.; Schaefer, C.E.; Bamer, J.T.; Lanza, H.A.; Wintle, D.; Maynard, K.G.; Murphy, P.; Anderson, R.H. Bench-scale testing of a novel soil PFAS treatment train for informed remedial planning and decision-making. Remediat. J. 2023, 33, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwayezu, J.N.; Ren, Z.; Sonnenschein, S.; Leiviskä, T.; Lejon, T.; van Hees, P.; Karlsson, P.; Kumpiene, J.; Carabante, I. Combination of separation and degradation methods after PFAS soil washing. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Sha, S.; Luo, J.; Huang, Z.; Jackie, X.Z. Treatment train approaches for the remediation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).