Modeling the Atmospheric CO2 Concentration in the Beijing Region and Assessing the Impacts of Fossil Fuel Emissions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. WRF-Chem Model
2.2. CO2 Observations
2.3. Statistical Parameters
| Option | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Simulation period | January 2019 to January 2021 |
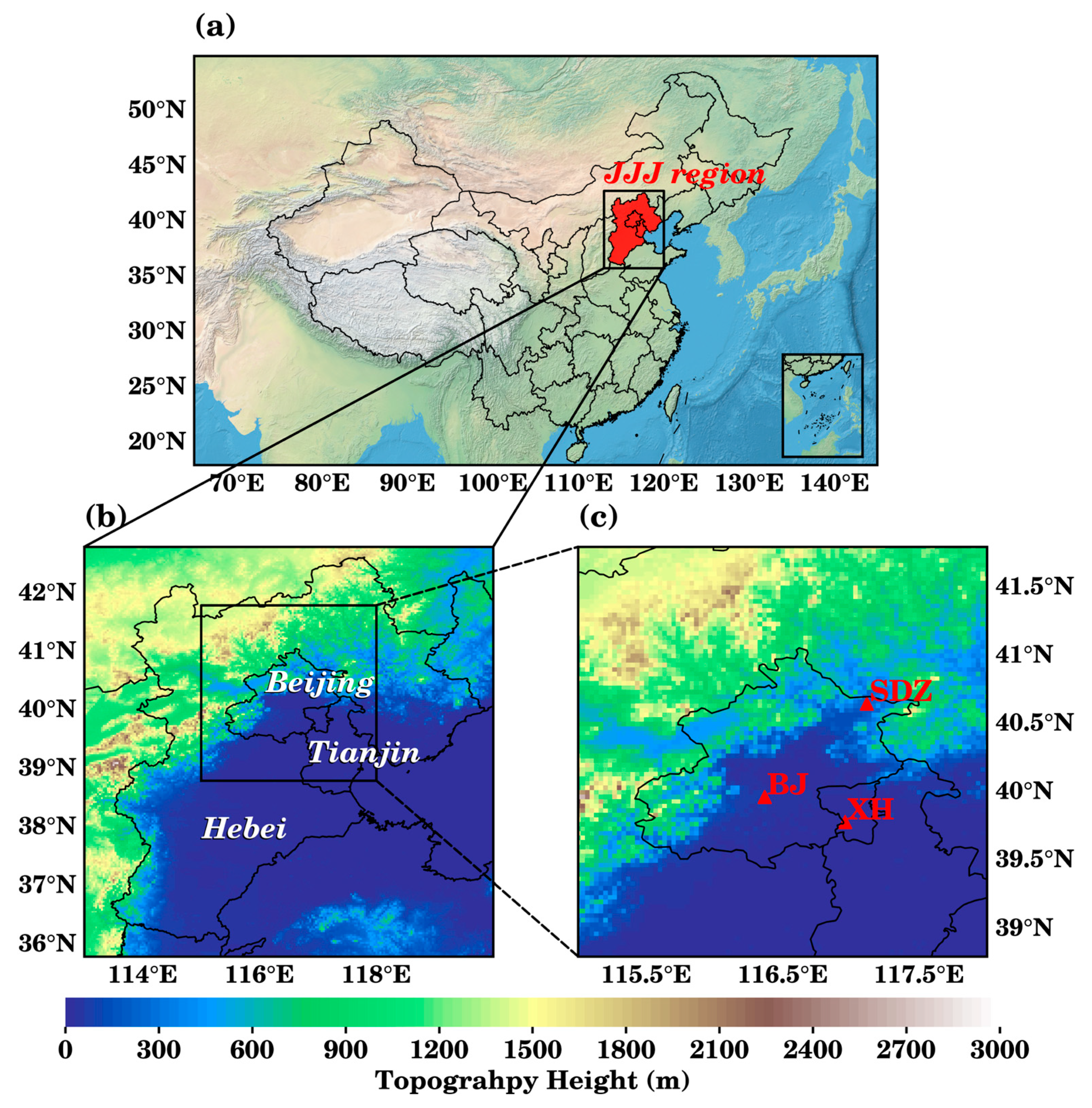
| Simulation region | Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China (Figure 1) |
| Domain center | 116.5° E and 39.3° N |
| Horizontal resolution | 9 km × 9 km |
| Vertical levels | 39 vertical levels (from the surface to 50 hPa) |
| Microphysics scheme | WRF single-moment 5-class scheme [42] |
| Boundary layer scheme | Yonsei University scheme [43] |
| Surface layer scheme | MM5 similarity scheme [44] |
| Land surface scheme | Unified Noah land surface model [45] |
| Longwave radiation scheme | Rapid radiative transfer model (RRTM) longwave scheme [46] |
| Shortwave radiation scheme | Goddard shortwave scheme [47] |
| Meteorological field | NCEP 0.25° × 0.25° reanalysis data |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Modeled CO2 Concentration
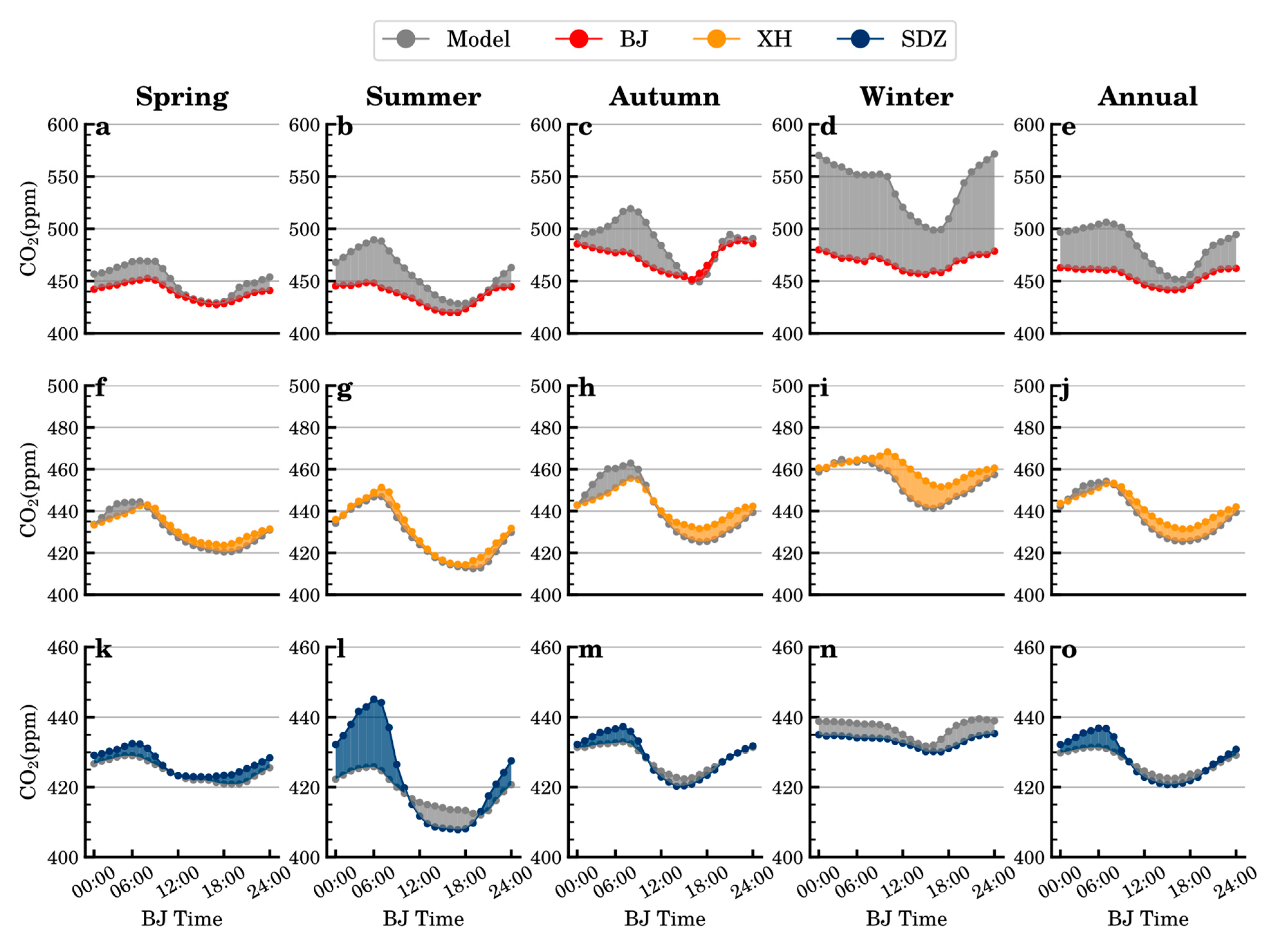
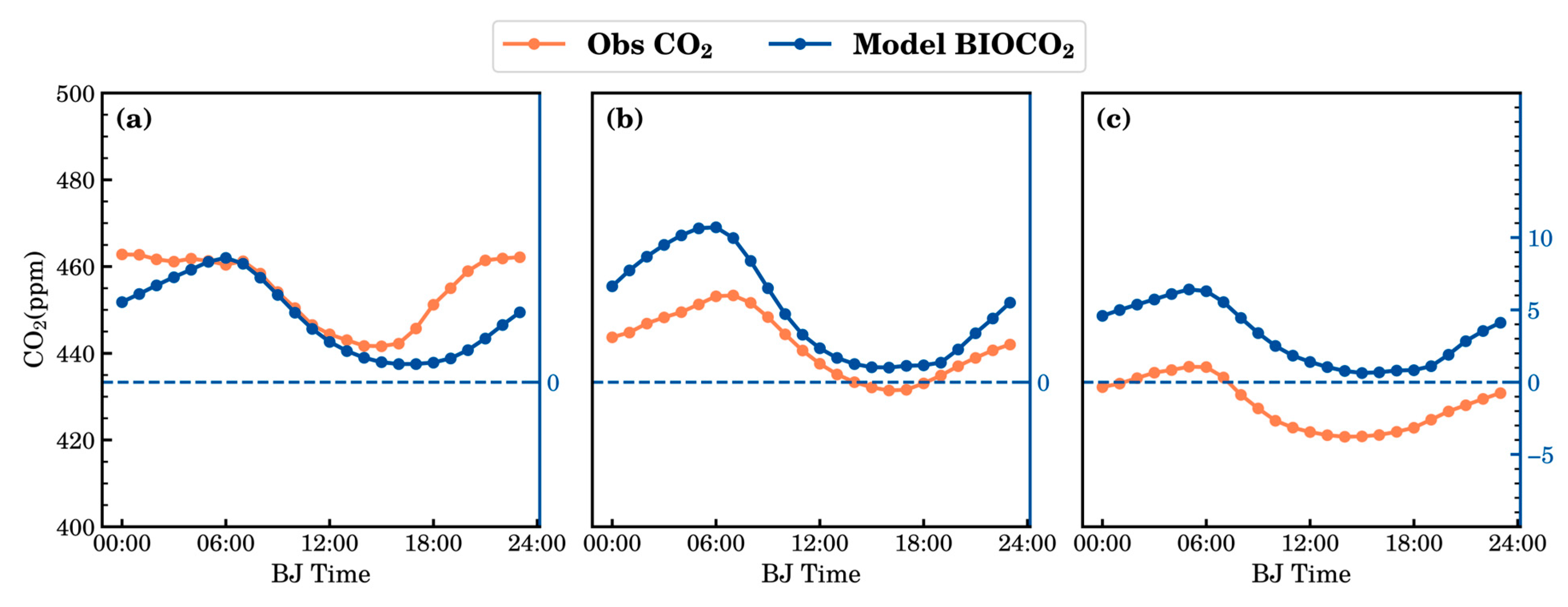
3.2. Diurnal Variation in the CO2 Concentration
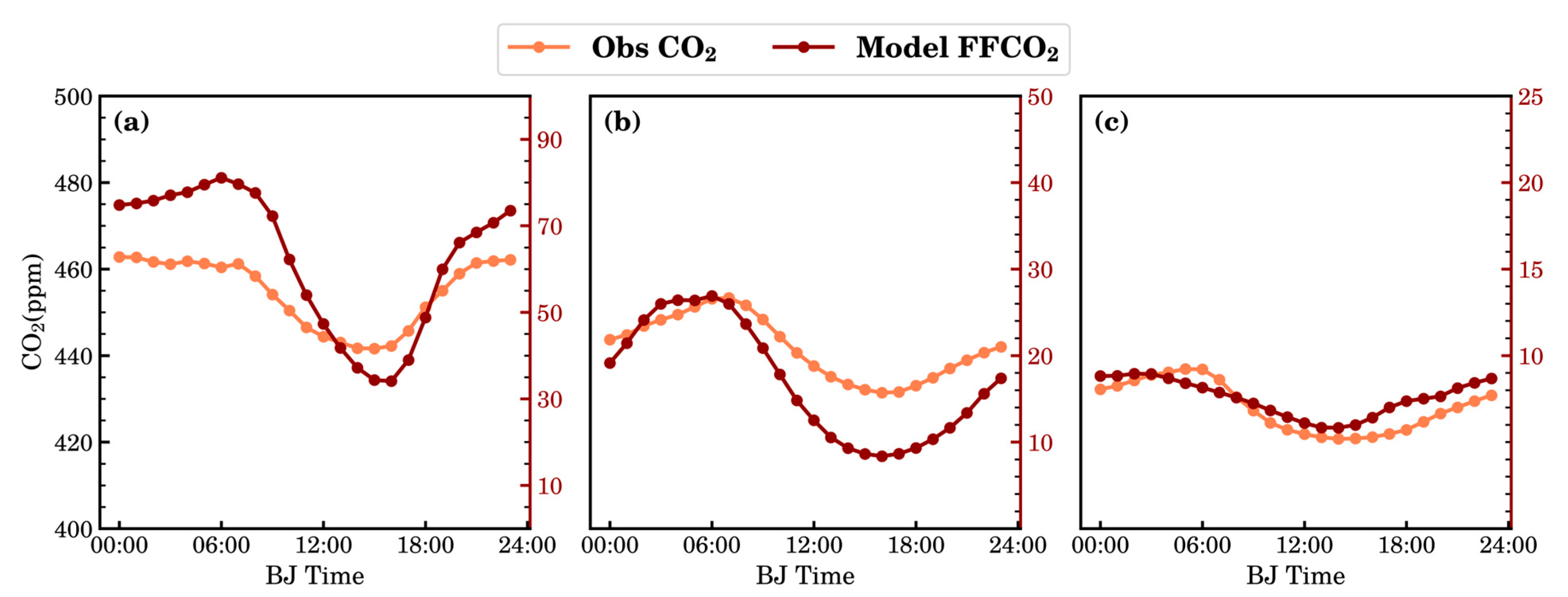
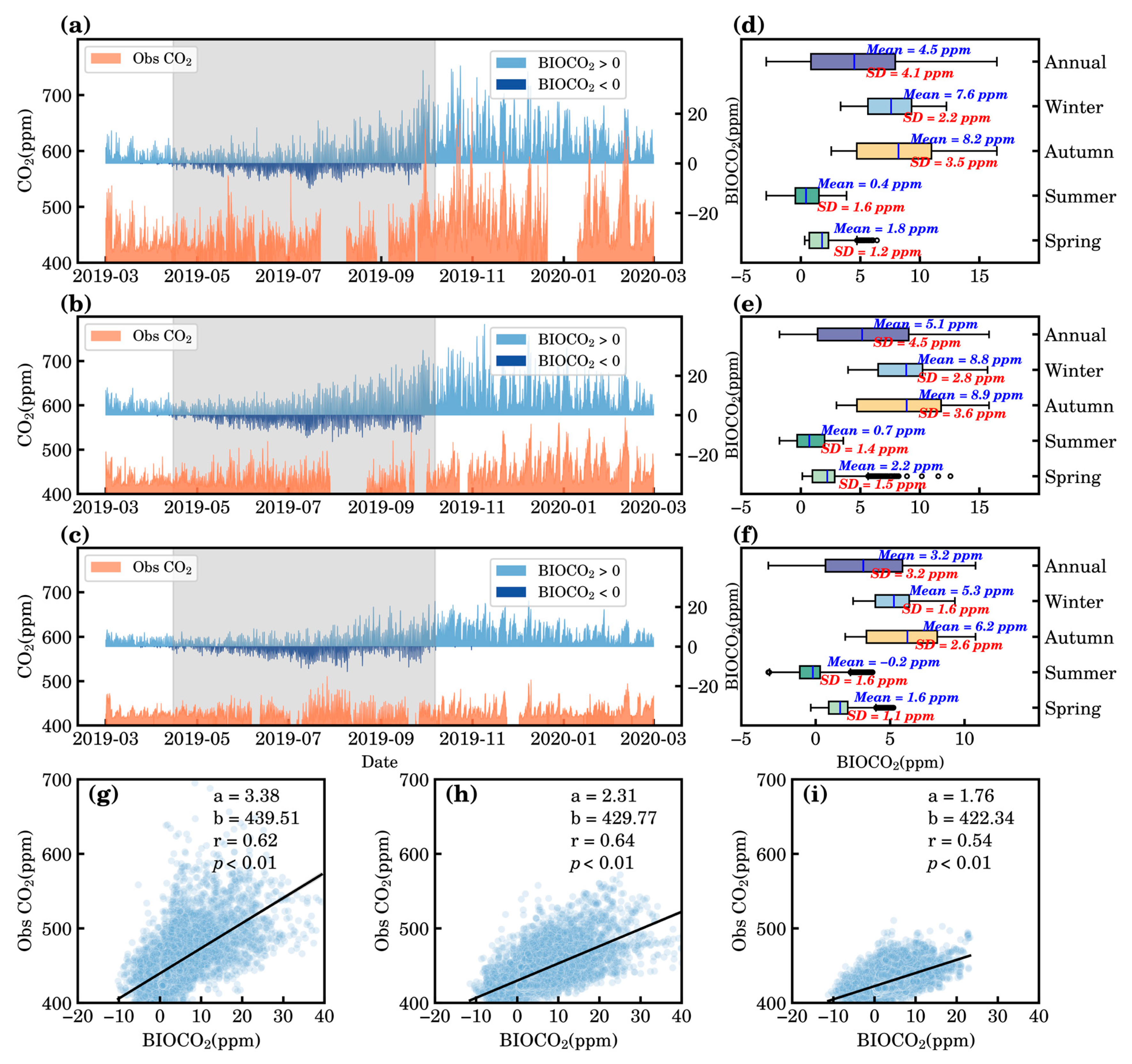
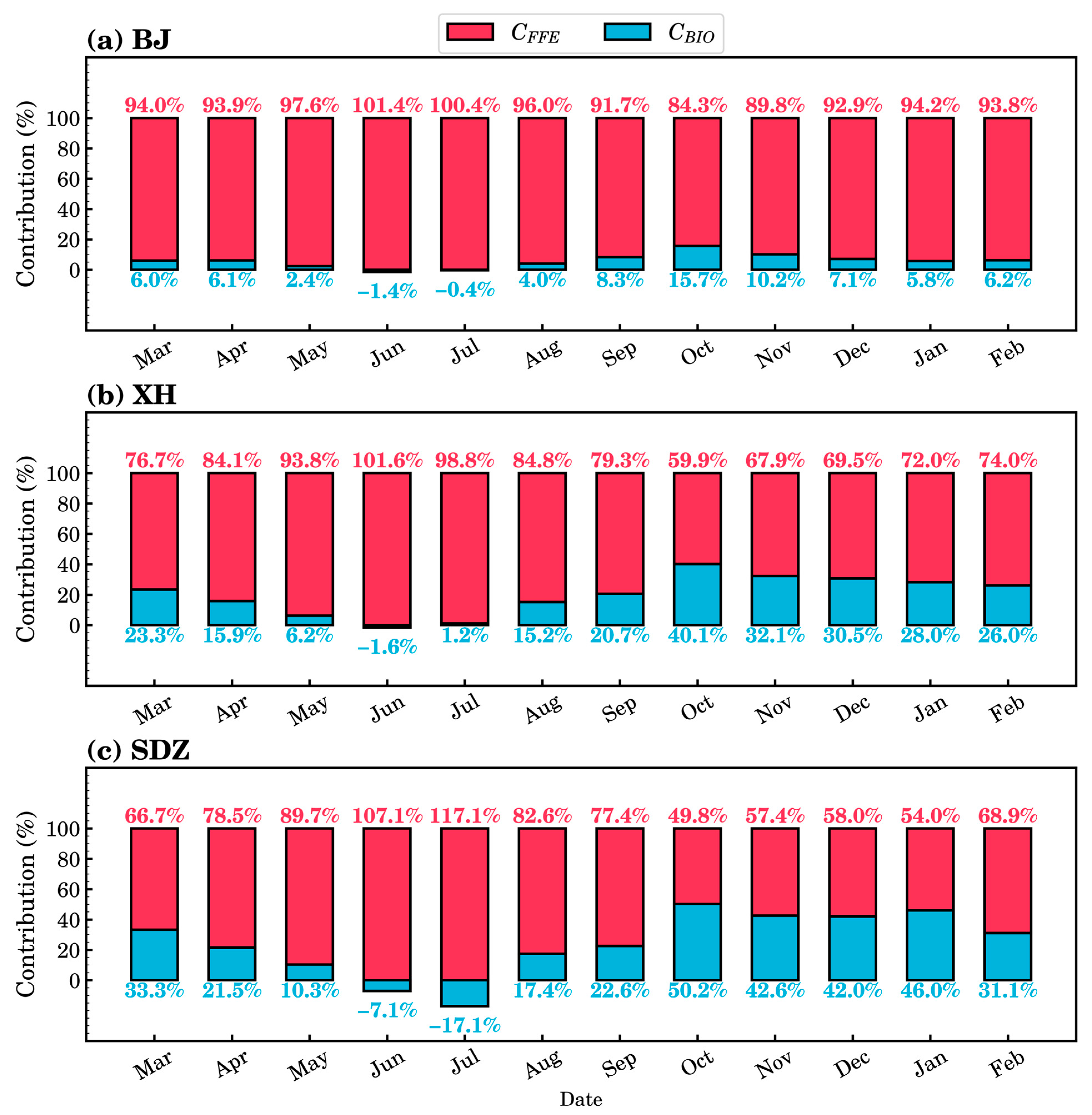
3.3. Characteristics of the Modeled FFCO2 and BIOCO2
3.4. Characteristics of the Modeled PBLH
4. Conclusions
- We quantified the FFCO2 effects on atmospheric CO2 concentrations from urban to regional background sites. There was a positive correlation between the modeled FFCO2 and the observed CO2 concentration at each site, particularly during spring and winter. The BJ and XH sites exhibited the greatest contributions of FFCO2 to the total modeled CO2 concentration.
- We separated the biosphere contribution to CO2 variations. There was a negative correlation of modeled BIOCO2 and observed CO2 concentration in summer.
- We studied the impacts of meteorological factors on CO2 variations. The negative correlation between modeled PBLH and observed CO2 had been confirmed.
- Resolution: At present, the resolution of our simulation research is not fine enough for local scale. If we need to study some details in urban areas, such as street level, we should combine higher-resolution local inventory and model grids;
- The impact of high value point sources: through the elimination of the sources, we could quantitatively analyze its contribution to different sites;
- The impact of COVID: The mismatch between the model and observation are partly due to variations in carbon emissions during COVID. By adding factors affecting carbon emissions during COVID, the accuracy of simulation is expected to be improved.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| JJJ | Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei |
| BJ | Beijing |
| XH | Xianghe (A County in Langfang, Hebei) |
| SDZ | Shangdianzi (In Miyun District, Beijing) |
| FFCO2 | Fossil fuel CO2 |
| BIOCO2 | Biospheric CO2 |
| BGCO2 | Background CO2 |
| NDRC | National Development and Reform Commission |
| MEIC | Multiresolution Emission Inventory for China |
| NOAA | National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration |
| NECP | National Centers for Environmental Prediction |
| VEGAS | Vegetation Global Atmosphere Soil |
| DGVM | Dynamic Global Vegetation Model |
| CRDS | Cavity ring-down spectroscopy |
| CMA | China Meteorological Administration |
| The contribution of FFCO2 | |
| The contribution of BIOCO2 |
References
- Schneider, S.H. The greenhouse effect: Science and policy. Science 1989, 243, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021. In The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V.P., Zhai, A., Pirani, S.L., Connors, C., Péan, S., Berger, N., Caud, Y., Chen, L., Goldfarb, M.I., Gomis, M., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Friedlingstein, P.; Osullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Hauck, J.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; Sitch, S.; et al. Global carbon budget 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.; Eby, M.; Brovkin, V.; Ridgwell, A.; Cao, L.; Mikolajewicz, U.; Caldeira, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Munhoven, G.; Montenegro, A.; et al. Atmospheric lifetime of fossil-fuel carbon dioxide. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2009, 37, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marland, G.; Hamal, K.; Jonas, M. How uncertain are estimates of CO2 emissions? J. Ind. Ecol. 2009, 13, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, R.J.; Boden, T.A.; Bréon, F.M.; Ciais, P.; Davis, S.; Erickson, D.; Gregg, J.S.; Jacobson, A.; Marland, G.; Miller, J.; et al. A synthesis of carbon dioxide emissions from fossil-fuel combustion. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1845–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T.; Morikawa, T.; Hanayama, S.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Fukui, T.; Kawashima, K.; Akimoto, H. Emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases over Asian regions during 2000–2008: Regional Emission inventory in ASia (REAS) version 2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 11019–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Lauvaux, T.; Newman, S.; Rao, P.; Ahmadov, R.; Deng, A.; Díaz-Isaac, L.I.; Duren, R.M.; Fischer, M.L.; Gerbig, C.; et al. Los Angeles megacity: A high-resolution land–atmosphere modelling system for urban CO2 emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9019–9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, K.R.; Mendoza, D.L.; Zhou, Y.; Fischer, M.L.; Miller, C.C.; Geethakumar, S.; de la Rue du Can, S. High resolution fossil fuel combustion CO2 emission fluxes for the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5535–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, K.R.; Razlivanov, I.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Benes, B.; Abdul-Massih, M. Quantification of fossil fuel CO2 emissions on the building/street scale for a large US city. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12194–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gruber, N.; Brunner, D. Spatiotemporal patterns of the fossil-fuel CO2 signal in central Europe: Results from a high-resolution atmospheric transport model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 14145–14169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, J.; Rayner, P.; Miller, J.; Naegler, T.; Ciais, P.; Cozic, A. On the use of 14CO2 as a tracer for fossil fuel CO2: Quantifying uncertainties using an atmospheric transport model. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D22302–D22313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gurney, K.R.; Rayner, P.; Baker, D.; Liu, Y.P. Sensitivity of simulated CO2 concentration to sub-annual variations in fossil fuel CO2 emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys 2016, 16, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shusterman, A.A.; Teige, V.E.; Turner, A.J.; Newman, C.; Kim, J.; Cohen, R.C. The BErkeley Atmospheric CO2 Observation Network: Initial evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys 2016, 16, 13449–13463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Graf, P.; Meyer, J.; Pentina, A.; Dominik, B.; Perez-Cruz, F. Integration and calibration of NDIR CO2 low-cost sensors, and their operation in a sensor network covering Switzerland. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss 2019, 2019, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadov, R.; Gerbig, C.; Kretschmer, R.; Körner, S.; Rödenbeck, C.; Bousquet, P.; Ramonet, M. Comparing high resolution WRF-VPRM simulations and two global CO2 transport models with coastal tower measurements of CO2. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Bocquet, M.; Lauvaux, T.; Chevallier, F.; Rayner, P.; Davis, K. Optimal representation of source-sink fluxes for mesoscale carbon dioxide inversion with synthetic data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauvaux, T.; Miles, N.L.; Deng, A.; Richardson, S.J.; Cambaliza, M.O.; Davis, K.J.; Gaudet, B.; Gurney, K.R.; Huang, J.; OKeefe, D.; et al. High-resolution atmospheric inversion of urban CO2 emissions during the dormant season of the Indianapolis Flux Experiment (INFLUX). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5213–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, C.; Stwertka, C.; Bowling, D.R.; Stephens, B.B.; Ehleringer, J.R. Urban carbon dioxide cycles within the Salt Lake Valley: A multiple-box model validated by observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lac, C.; Donnelly, R.P.; Masson, V.; Pal, S.; Riette, S.; Donier, S.; Queguiner, S.; Tanguy, G.; Ammoura, L.; Xueref-Remy, I. CO2 dispersion modelling over Paris region within the CO2-MEGAPARIS project. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4941–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Zeng, N.; Karion, A.; Mueller, K.; Ghosh, S.; Lopez-Coto, I.; Gurney, K.R.; Oda, T.; Prasad, K.; Liu, Y.; et al. Investigating sources of variability and error in simulations of carbon dioxide in an urban region. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Zeng, N.; Oda, T.; Lin, X.; Crippa, M.; Guan, D.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; Shan, Y.; et al. Evaluating China’s fossil-fuel CO2 emissions from a comprehensive dataset of nine inventories. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11371–11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wu, S.; Cheng, P.; Lu, X.; Xiong, X.; Du, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, G. Atmospheric fossil fuel CO2 traced by Δ14C in Beijing and Xiamen, China: Temporal variations, inland/coastal differences and influencing factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5474–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, P.; Wu, S.; Xiong, X.; Lu, X.; Du, H. Emission characteristics of atmospheric carbon dioxide in Xi’an, China based on the measurements of CO2 concentration, △14C and δ13C. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Zeng, N.; Oda, T.; Zhang, W.; Lin, X.; Liu, D.; Cai, Q.; Ma, X.; Meng, W.; Wang, G.; et al. A city-level comparison of fossil-fuel and industry processes-induced CO2 emissions over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region from eight emission inventories. Carbon Balance Manag. 2020, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wen, X.; Sun, X. Mixing ratio and carbon isotopic composition investigation of atmospheric CO2 in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Cui, Y.; Lian, A.; Tian, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Xue, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, B. Vehicle emissions of primary air pollutants from 2009 to 2019 and projection for the 14th Five-Year Plan period in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, C.; Su, M.; Chen, B.; Cai, Y.; Xing, T. Urban energy consumption and related carbon emission estimation: A study at the sector scale. Front. Earth Sci. 2013, 7, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.F.; Pan, S.Y.; Yu, H.; Wei, Y.M. Potential impacts of industrial structure on energy consumption and CO2 emission: A case study of Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pan, S.Y.; Tang, B.J.; Mi, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.M. Urban energy consumption and CO2 emissions in Beijing: Current and future. Energy Effic. 2014, 8, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Ding, Y.; Pan, J.; Wang, H.; Gregg, J. Climate change-the Chinese challenge. Science 2008, 319, 730–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhou, W.; Wu, S.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, P.; Xiong, X.; Li, G. High-resolution simulation of wintertime fossil fuel CO2 in Beijing, China: Characteristics, sources, and regional transport. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong-Yun, L.; Meng, Z.; Yan-Xia, L. A high spatial resolution CO2 emission inventory in Beijing. Clim. Change Res. 2022, 18, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Tong, D.; Xiao, Q.; Qin, X.; Chen, C.; Yan, L.; Cheng, J.; Cui, C.; Hu, H.; Liu, W.; et al. MEIC-global-CO2: A new global CO2 emission inventory with highly-resolved source category and sub-country information. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Mariotti, A.; Wetzel, P. Terrestrial mechanisms of interannual CO2 variability. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.; Napier-Linton, L.; Gurney, K.R.; Andres, R.J.; Oda, T.; Vogel, F.R.; Deng, F. Improving the temporal and spatial distribution of CO2 emissions from global fossil fuel emission data sets. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zeng, N.; Liu, Y.; Kalnay, E.; Asrar, G.; Wu, B.; Cai, Q.; Liu, D.; Han, P. Improving the joint estimation of CO2 and surface carbon fluxes using a constrained ensemble Kalman filter in COLA (v1.0). Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 5511–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Z.; Feng, J.W.; Järvi, L.; Vesala, T. Four-year (2006–2009) eddy covariance measurements of CO2 flux over an urban area in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7881–7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.L.; Liu, X.M.; Liu, Y.J.; Hu, F. Characteristics of CO2 concentration and flux in the Beijing urban area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1785–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, T.; Yao, B.; Han, P.; Ji, D.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, P. Spatial and temporal variations of CO2 mole fractions observed at Beijing, Xianghe, and Xinglong in North China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 11741–11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, J.G.; Liu, Y.F.; Liang, X.; Yang, S.Q.; Xian, Y. Concentration Variation Characteristics of Atmospheric Greenhouse Gases at Waliguan and Shangdianzi in China. Earth Sci. 2021, 46, 2984–2998. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S. A Revised Approach to Ice Microphysical Processes for the Bulk Parameterization of Clouds and Precipitation. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beljaars, A.C. The parametrization of surface fluxes in large-scale models under free convection. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 121, 255–270. [Google Scholar]
- Tewari, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Dudhia, J.; LeMone, M.A.; Mitchell, K.E.; Ek, M.B.; Gayno, G.; Wegiel, J.W.; Cuenca, R. Implementation and verification of the unified NOAH land surface model in the WRF model. In Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting/16th Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Seattle, WA, USA, 14 January 2004; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Zhang, S.Q.; Lang, S.E.; Tao, W.K.; Ichoku, C.; Peters-Lidard, C.D. Impact of radiation frequency, precipitation radiative forcing, and radiation column aggregation on convection-permitting West African monsoon simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BJ | 12.0 | 18.1 | 26.4 | 43.5 |
| XH | 15.1 | 23.6 | 29.5 | 31.7 |
| SDZ | 16.4 | 26.3 | 31.6 | 25.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zeng, N.; Tang, W.; Han, P.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, W.; Yao, B.; Wang, P.; Liu, Z. Modeling the Atmospheric CO2 Concentration in the Beijing Region and Assessing the Impacts of Fossil Fuel Emissions. Environments 2025, 12, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050156
Liang Z, Cai Q, Zeng N, Tang W, Han P, Zhang Y, Quan W, Yao B, Wang P, Liu Z. Modeling the Atmospheric CO2 Concentration in the Beijing Region and Assessing the Impacts of Fossil Fuel Emissions. Environments. 2025; 12(5):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050156
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Zhoutong, Qixiang Cai, Ning Zeng, Wenhan Tang, Pengfei Han, Yu Zhang, Weijun Quan, Bo Yao, Pucai Wang, and Zhiqiang Liu. 2025. "Modeling the Atmospheric CO2 Concentration in the Beijing Region and Assessing the Impacts of Fossil Fuel Emissions" Environments 12, no. 5: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050156
APA StyleLiang, Z., Cai, Q., Zeng, N., Tang, W., Han, P., Zhang, Y., Quan, W., Yao, B., Wang, P., & Liu, Z. (2025). Modeling the Atmospheric CO2 Concentration in the Beijing Region and Assessing the Impacts of Fossil Fuel Emissions. Environments, 12(5), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050156






