Evaluation of Cadmium Removal in an Aqueous Solution by Biosorption in a Batch System with Banana, Peanut, and Orange Husks
Abstract
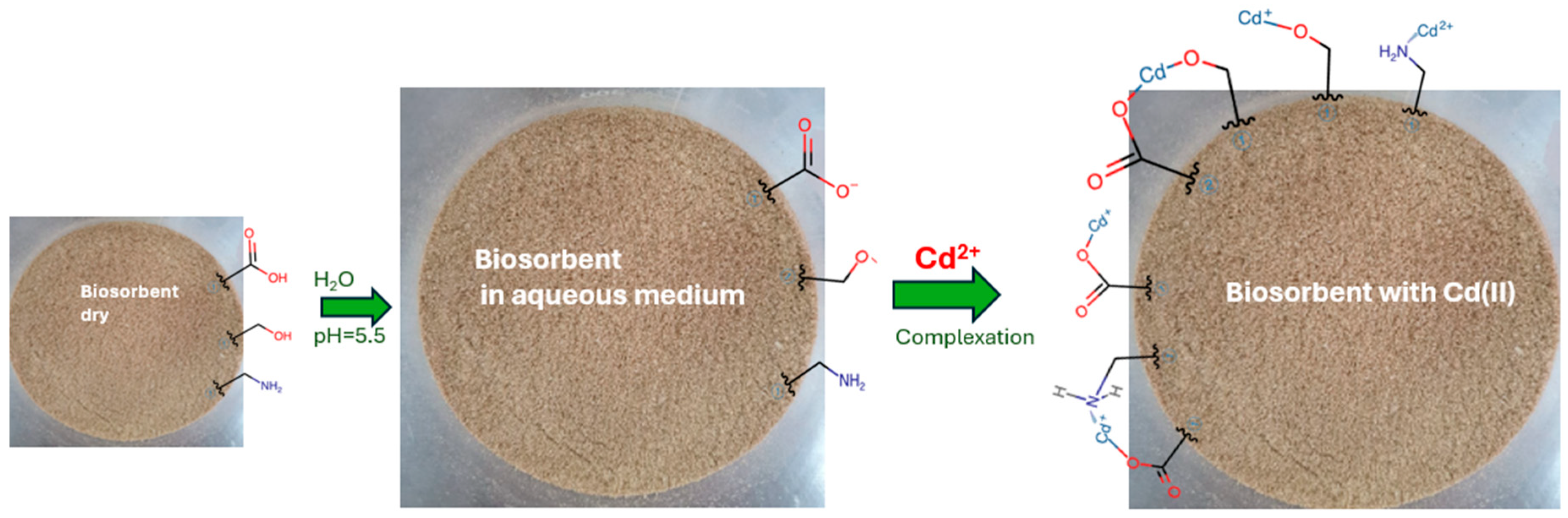
1. Introduction
| Biosorbent | Heavy Metal | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | Treated | ||
| Plantain skewer [26] | Cadmium | 476.19 | 80 |
| Chrome | 625 | 277.7 | |
| Lead | 370.7 | 196.1 | |
| Zinc | 116.3 | 147.05 | |
| Corn rachis [27] | Lead | 4.97 | 12.44 |
| Orange peel [28] | Cadmium | 0.476 | 0.071 |
| Rice husk [28] | 0.596 | 7.007 | |
| Orange peel [29] | Lead | 496.33 | 49.98 |
| Banana peel [29] | Lead | 193 | 359 |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biomass Extraction
2.2. Chemically Modified Biomasses
2.3. Characterization
- Characterization of biosorbents before and after biosorption.
- Batch study for biosorption of cadmium.
- Characterization, identification, and quantification of cadmium by cyclic voltammetry.
3. Results
3.1. Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3. Square-Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry (SWV)
3.4. Zeta Potential
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez, M.; Vargas, D.; Cabañas, M.; Gamboa, X. Evaluación del proceso de biosorción con cáscaras de naranja para la eliminación del colorante comercial Lanasol Navy CE en aguas residuales de la industria textil. Ingeniería 2009, 13, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Vardhan, K.; Harsha, K.; Ponnusamy, S.; Panda, C. A review on heavy metal pollution, toxicity and remedial measures: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111197. [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Heavy metals and metalloids: Sources, risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 431–444. [Google Scholar]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean Water. 2021, 4, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Alba, A.R.; García, P.L.; García, R.R.; Valiño, M.D.; Fernández, S.V.; García, J.M.S. Tratamientos Avanzados de Aguas Residuales Industriales. 2006. Available online: www.madrimasd.org (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Miretzky, P.; Cirelli, A.F. Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.; Cai, L.; Coulter, A.; Cheema, A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Ma, W.; Farooq, M. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, M.; Gómez, S.; Tlamani, J.; Juárez, J. Concentraciones de metales pesados totales en aguas residuales vertidas a ecosistemas acuáticos por dos parques industriales en Puebla, México. Rev. Iberoam. Prod. Académica Y Gestión Educ. 2014, 1, 20–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, A.; Cabañas, D.; Zepeda, A. Evaluación del poder biosorbente de cáscara de naranja para la eliminación de metales pesados, Pb (II) y Zn (II). Ing. Rev. Académica 2013, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Suazo, E.; Morales, L.; Cristiani, M.; Cristiani, E. Efecto del pH sobre la biosorción de níquel (II) por Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. ellipsoideus. Rev. CENIC Cienc. Químicas 2010, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, A.; Pagnanelli, F.; Lodi, A.; Solisio, C.; Vegliò, F. Biosorption of heavy metals by Sphaerotilus natans: An equilibrium study at different pH and biomass concentrations. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 60, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Payán, S. Estudio y Diseño de Biofiltro a Partir de Materia orgánica para el Tratamiento de Agua [Internet]. Centro de Investigación en Materiales Avanzados. 2016. Available online: https://cimav.repositorioinstitucional.mx/jspui/bitstream/1004/583/1/Tesis%20Sergio%20Arturo%20Pay%C3%A1n%20G%C3%B3mez.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Chaidir, Z.; Zein, R.; Hasanah, Q.; Nurdin, H.; Aziz, H. Adsorption of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) metals in aqueous solution using Mangosteen Rind (Pithecellobium jiringa(jack) prain.). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 948–956. [Google Scholar]
- Jacques, A.; Lima, C.; Dias, P.; Mazzocato, C.; Pavan, A. Yellow passion-fruit shell as biosorbent to remove Cr(III) and Pb(II) from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 57, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ibáñez, J.; Umetsu, Y. Uptake of trivalent chromium from aqueous solutions using protonated dry alginate beads. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 72, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Chen, J.P. Biosorption of hexavalent chromium onto raw and chemically modified Sargassum sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Fahim, N.F.; Barsoum, B.N.; Eid, A.E.; Khalil, M.S. Removal of chromium(III) from tannery wastewater using activated carbon from sugar industrial waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Sattar, M.S.; Shakoor, M.B.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Jilani, A. Comparative efficiency of peanut shell and peanut shell biochar for removal of arsenic from water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18624–18635. [Google Scholar]
- Hebbani, A.V.; Anantha, R.; Kasaba Manjunath, G.; Kulkarni, A.; Sam, R.; Mishra, A. Evaluation of cadmium biosorption property of de-oiled palm kernel cake. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2021, 23, 522–529. [Google Scholar]
- Macías, J.M.F.; Agudelo, V.R.N.; Isiordia, G.E.D.; Ortiz Medina, O.L. Evaluation of bean pod red cargamanto (BPRC) as biosorbent material in the removal of cadmium (C2+) in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Hydrol. 2018, 2, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Li, X.M.; Wang, F.; Yang, Q.; Deng, P.; Zeng, G.M. Adsorption removal of cadmium and copper from aqueous solution by areca—A food waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 490–495. [Google Scholar]
- Payán, S.; Flores, N.; Pérez, A.; Piñón, M.; Glossman, D. Computational molecular characterization of the flavonoid Morin and its Pt(II), Pd(II) and Zn(II) complexes. J. Mol. Model. 2011, 17, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Farooqi, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Ali, F.; Ali, S.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Arshad, M. Arsenic(V) biosorption by charred orange peel in aqueous environments. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2016, 18, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, P.; Manchola, I. Estudio Isotérmico de Biosorción de Cadmio, Cromo, Plomo y zinc en Solución Acuosa Empleando el Pinzote (Ranqui) de Plátano (Musa paradisiaca L.). 2012. Available online: https://dspace.ups.edu.ec/bitstream/123456789/4065/1/UPS-QT02922.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Lavado, C.; Oré, F. Estudio de la biosorción de plomo divalente de soluciones acuosas usando biomasa modificada de marlo de maíz (Zea mays). Rev. Soc. Química Perú 2016, 82, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, S.; Corne, V.; Azario, R.; García, C. Aprovechamiento de residuos lignocelulósicos regionales para la remoción de cadmio en solución. Av. En Cienc. E Ing. 2020, 11, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Paccha, C.; Paccha, P. Capacidad de adsorción de desechos agroindustriales para remover contaminantes de aguas residuales. Rev. Inst. Investig. Fac. Minas Metal. Y Cienc. Geográficas 2023, 26, e25258. [Google Scholar]
- Mollinedo, L. Propuesta de un Sistema Natural Utilizando la Cáscara de Banano para la Remoción de Plomo II [Internet] [Tesis]. [Guatemala]: Universidad del Valle de Guatemala. 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.uvg.edu.gt/handle/123456789/3981 (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Meza, M.; César, J.; Behling, E.; Colina, G.; Rincón, N.; Arturo, C. Bioabsorción de Pb (II) y Cr (III) usando la planta acuática Pistia Stratioides. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Cent. Venez. 2013, 28, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Afolabi, O.; Musonge, P.; Bakare, F. Bio-sorption of a bi-solute system of copper and lead ions onto banana peels: Characterization and optimization. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobet, O.; Nassio, S.; Seynou, M.; Remy, B.; Zerbo, L.; Sanou, I.; Sawadogo, M.; Millogo, Y.; Gilles, E. Characterization of Peanut Shells for Their Valorization in Earth Brick. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2020, 8, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşar, Ş.; Kaya, F.; Özer, A. Biosorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous solution by peanut shells: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I.; Martínez, M.; Miralles, N.; Poch, J.; Serarols, J. Sorption of Pb(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solution by olive stone waste. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanakornsiri, A.; Rattanawan, P.; Sanmueng, T.; Satchawan, S.; Jamnongkan, T.; Phuengphai, P. Local fruit peel biosorbents for lead (II) and cadmium (II) ion removal from waste aqueous solution: A kinetic and equilibrium study. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 42, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadurai, G.; Juang, R.S.; Lee, D.J. Adsorption of heavy metals from water using banana and orange peels. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenwari, K.A.; Dhevagi, P.; Chitdeshwari, T.; Avudainayagam, S.J. Biosorption of Cadmium from Aqueous Solutions by Banana Peel Powder. Madras Agric. J. 2018, 105, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenwari, K.A.; Priyatharshini, S.; Dhevagi, P.; Chitdeshwari, T.; Avudainayagam, S. Removal of Lead and Cadmium from Aqueous Solutions by Banana Peel Biochar. Madras Agric. J. 2019, 106, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ángel, J.; Li, Q.; Thompson, P. Biorefinery of waste orange peel. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2010, 30, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zarazúa, G.; Ávila, P.; Tejeda, S.; Valdivia, M.; Zepeda, C.; Macedo, G. Evaluación de los metales pesados Cr, Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn y pb en sombrerillo de agua (Hydrocotyle Ranunculoides) del curso alto del río Lerma, México. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2013, 29, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Valencia, J. Implementación de un Método Para la Obtención de Carbón Activado a Partir de Cascara de Cacahuate (Arachis Hypogaea l) [Internet]. [Tuxtla Gutierrez Chiapas]: Instituto Tecnológico de Tuxtla Gutiérrez. 2019. Available online: http://repositoriodigital.tuxtla.tecnm.mx/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/1578/1953.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Soto, E.; Dávila, N.; Cervantes, C. Producción de carbón activado a partir de la cáscara de frijol de soya para su aplicación como adsorbente en el tratamiento de aguas residuales contaminadas con metales pesados. Quimica Hoy 2022, 10, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, C.N. Biosorción de Cromo (VI) en aguas usando material lignocelulósico modificado. Rev. Educ. En Ing. 2014, 9, 86–97. [Google Scholar]
- Sanga, W. Remoción de Metales Pesados Utilizando la Pectina Como Material Biodegradable [Internet]. Universidad Nacional del Altiplano. 2016. Available online: https://repositorioslatinoamericanos.uchile.cl/handle/2250/3273957 (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Sánchez, G. Ecotoxicología del Cadmio. Riesgo para la Salud de la utlización de los Suelos Ricos en Cadmio. [Internet]. Universidad Complutense de Madrid. 2016. Available online: http://147.96.70.122/web/tfg/tfg/memoria/gara%20sanchez%20barron.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Sociedad Argentina de Ciencia y Tecnología Ambiental. Enfoques Interdisciplinarios para la Sustentabilidad del Ambiente [Internet]. 2015. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287205151_Enfoques_Interdisciplinares_para_la_Sustentabilidad_Ambiental (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Quiñones, É.; Tejada, C.; Ruiz, V. Remediación de aguas contaminadas con cromo utilizando diferentes biomateriales residuales. Rev. Cienc. E Ing. Al Día 2014, 9, 2357–5409. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, J. Biosorción de Plomo (II) por Cáscara de Naranja ‘citrus Cinensis’ Pretratada. [Internet] [Tesis]. [Lima Perú]: Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos. 2007. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/323353409.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- de Castro, F.H.B.; García, G.B.; de Hoces, M.C.; Martín-Lara, M.Á. Influencia de algunas variables en la biosorción de plomo con residuos agrícolas. Afinidad J. Chem. Eng. Theor. Appl. Chem. 2008, 65. Available online: https://raco.cat/index.php/afinidad/article/view/282175 (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Guerrero, J.; Trejo, M.; Moreno, J.; Pascual, S.; Lira, A. Extracción de fibra de los desechos agroindustriales de cacahuate, para su aplicación en el desarrollo de alimentos. Fac. Cienc. Biol. UANL 2016, 1, 806–812. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, M.; Florez, D.; Yactayo, M.; Lovera, D.; Quispe, J.; Landauro, C.; Pardave, W. Remoción de metales pesados desde efluentes mineros, mediante cáscaras de frutas. Aibi Rev. Investig. Adm. E Ing. 2020, 8, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B. Uso de la Cáscara de Banano (Musa Paradisiaca) Maduro Deshidratada (seca) Como Proceso de Bioadsorción Para la Retención de Metales Pesados, Plomo y Cromo en Aguas Contaminada. [Internet] [Maestria]. [Guayas Ecuador]: Universidad de Guayaquil. 2015. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Uso-de-la-c%C3%A1scara-de-banano-(musa-paradisiaca)-como-Pastor/78277d4239b94d90f8d448a1c7359f2d78f1b0ad (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Bibi, A.; Naz, S.; Uroos, M. Evaluating the Effect of Ionic Liquid on Biosorption Potential of Peanut Waste: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 22259–22271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pabón, S.E.; Benítez, R.; Sarria, R.A.; Gallo, J.A.; Pabón, S.E.; Benítez, R. Contaminación del agua por metales pesados, métodos de análisis y tecnologías de remoción. Una revisión. Entre Cienc. E Ing. 2020, 14, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Abid, H.; Amanat, A.; Ahmed, D.; Qamar, T. Adsorption efficacy of Carissa opaca roots residual biomass for the removal of copper from contaminated water. Chem. Int. 2023, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Alaa El-Din, G.; Amer, A.A.; Malsh, G.; Hussein, M. Study on the use of banana peels for oil spill removal. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia, P.; Pavez, O.; Garrido, N.; Sepúlveda, B. Remoción de iones de cobre y niquel con cascara de maní. HOLOS 2018, 3, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Karnwal, A. Unveiling the promise of biosorption for heavy metal removal from water sources. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100523. [Google Scholar]
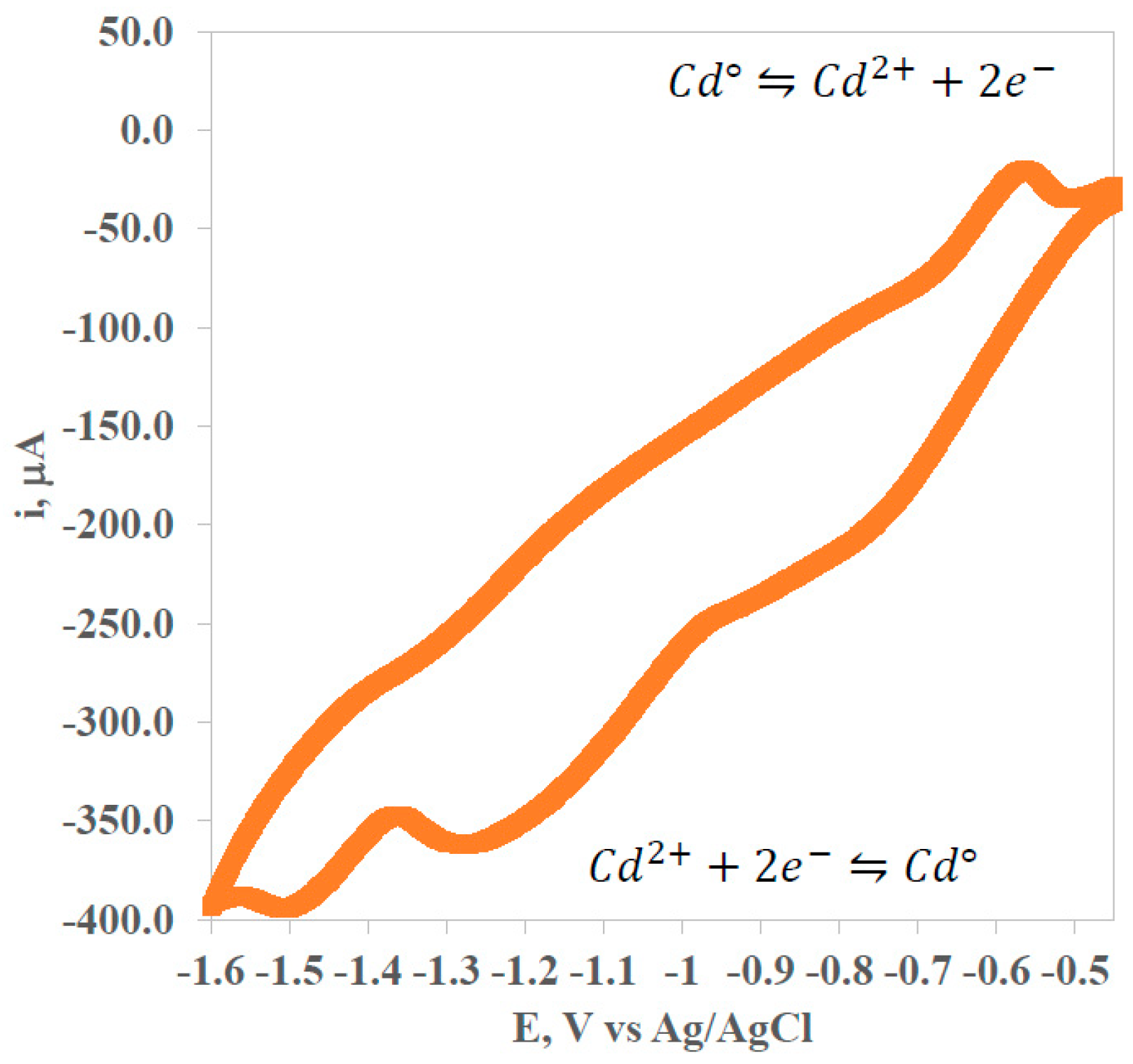
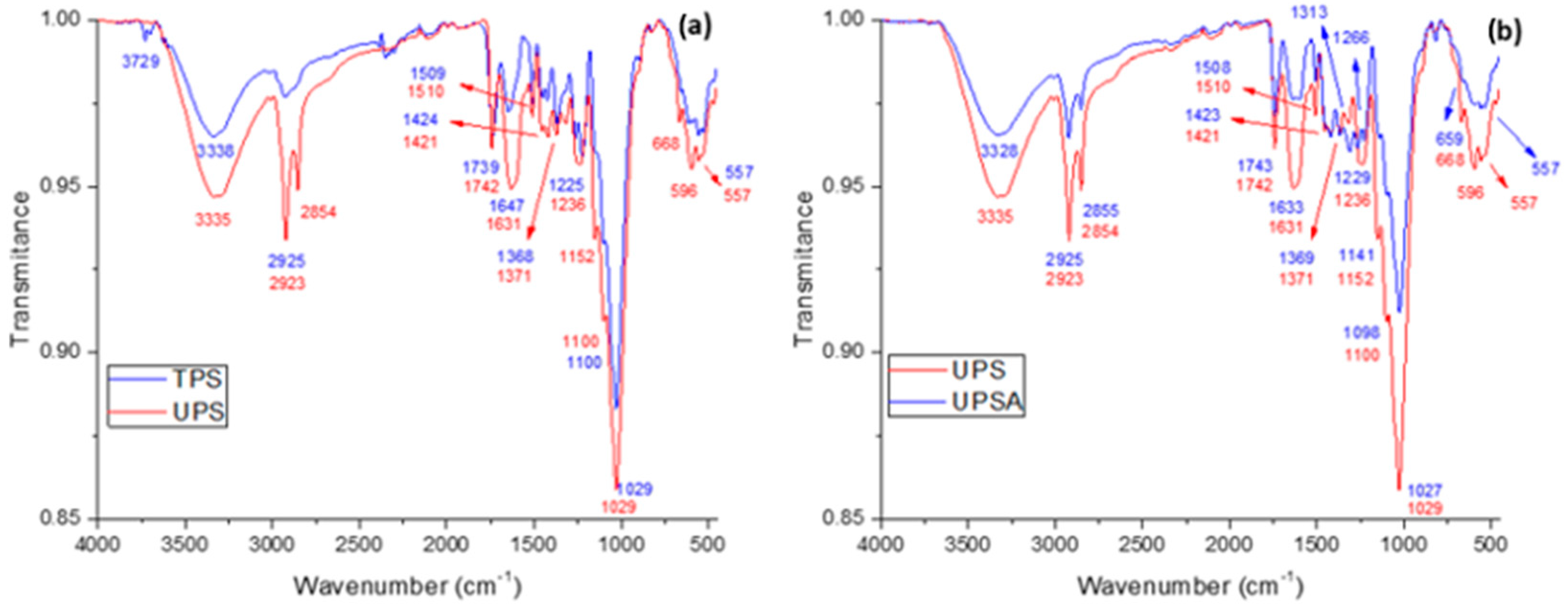



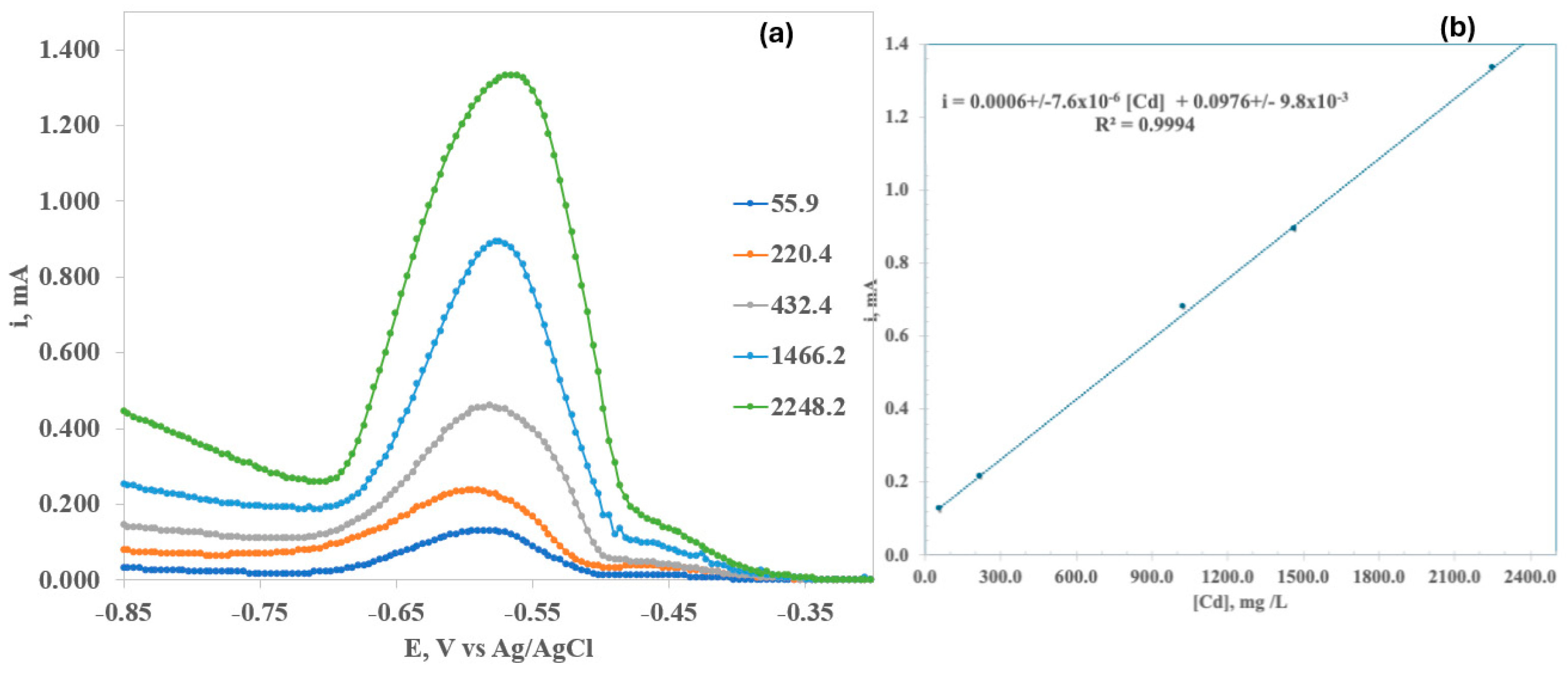
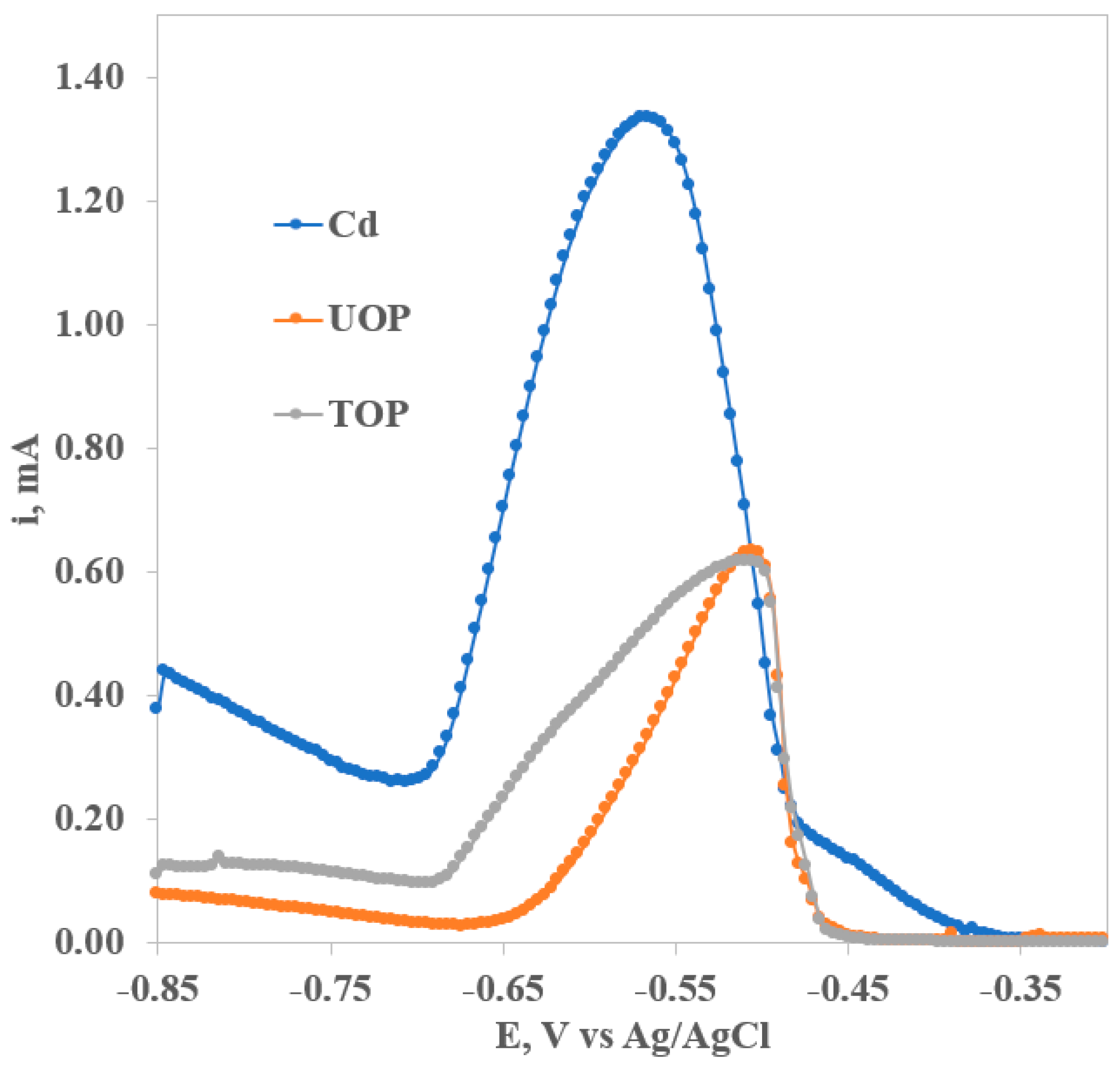


| Carbon | Oxygen | Cadmium | Others | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBPA | 48.92 | 35.63 | 13.60 | 1.85 |
| UBPA | 56.53 | 37.51 | 5.42 | 0.54 |
| TOPA | 54.32 | 36.87 | 8.29 | 0.52 |
| UOPA | 42.83 | 40.07 | 15.57 | 1.53 |
| TPSA | 62.21 | 34.13 | 2.71 | 0.94 |
| UPSA | 52.41 | 34.71 | 12.04 | 0.83 |
| Biosorbent | Adsorption Capacity (qc) mg/g | Adsorption Efficiency (%RE) |
|---|---|---|
| UPSA | 284.20 | 59.60 |
| TPSA | 147.33 | 30.89 |
| UOPA | 275.76 | 57.83 |
| TOPA | 153.08 | 32.10 |
| UBPA | 208.26 | 43.67 |
| TBPA | 229.22 | 48.07 |
| Biosorbent | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|
| UPS | −28.13 ± 0.2 |
| TPS | −6.09 ± 0.5 |
| UOP | −22.40 ± 0.8 |
| TOP | −11.73 ± 0.1 |
| UBP | −28.83 ± 0.9 |
| TBP | −35.53 ± 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arizpe-Díaz, D.O.; Gama-Lara, S.A.; Roa-Morales, G.; Vilchis-Néstor, A.R.; Parada-Flores, A.; Balderas-Hernández, P. Evaluation of Cadmium Removal in an Aqueous Solution by Biosorption in a Batch System with Banana, Peanut, and Orange Husks. Environments 2025, 12, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040097
Arizpe-Díaz DO, Gama-Lara SA, Roa-Morales G, Vilchis-Néstor AR, Parada-Flores A, Balderas-Hernández P. Evaluation of Cadmium Removal in an Aqueous Solution by Biosorption in a Batch System with Banana, Peanut, and Orange Husks. Environments. 2025; 12(4):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040097
Chicago/Turabian StyleArizpe-Díaz, Dayana Odette, Sergio Arturo Gama-Lara, Gabriela Roa-Morales, Alfredo Rafael Vilchis-Néstor, Alejandro Parada-Flores, and Patricia Balderas-Hernández. 2025. "Evaluation of Cadmium Removal in an Aqueous Solution by Biosorption in a Batch System with Banana, Peanut, and Orange Husks" Environments 12, no. 4: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040097
APA StyleArizpe-Díaz, D. O., Gama-Lara, S. A., Roa-Morales, G., Vilchis-Néstor, A. R., Parada-Flores, A., & Balderas-Hernández, P. (2025). Evaluation of Cadmium Removal in an Aqueous Solution by Biosorption in a Batch System with Banana, Peanut, and Orange Husks. Environments, 12(4), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12040097








