Recreational Water Risk from Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli of Broiler Origin: A Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Model Scope
2.2. Farm Module
2.3. Soil Module
2.4. River Transport and Decay
| Module | Parameter | Unit | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farm | Excretion rate of ESBL E. coli () | fraction | 0.3 | [24] |
| Farm | Initial load per ESBL positive broiler | CFU/broiler | 100 | [24] |
| Farm | Growth rate for ESBL E. coli in the broiler’s intestine () | log10 CFU | Uniform (0–5) | [24] |
| Farm | Fraction of ingested contaminated feces along with feed () | fraction | 0.014 | [24] |
| Farm | Transmission rate ( | /day | 0.31 | [25] |
| Farm | Initial prevalence of colonized broilers () | fraction | 0.01 | Expert opinion |
| Farm | Litter quantity per square meter (L) | g/m2 | 1000 | [24] |
| Soil | First-order decay rate () | /day | 0.0362 | [26] |
| Soil | Broiler litter applied to field surface () | kg/m2 | 2 | User defined |
| Soil | Field area (A) | m2 | 4046.86 | User defined |
| River | Bacteria partition coefficient ( | fraction | 0.95 | [27] |
| River | Mobile-phase cells () | fraction | 0.50 | [27] |
| River | River-water temperature (T) | °C | 21–28 | [18] |
| River | Salinity ( | fraction | Uniform (0.035–0.075) | [18] |
| River | Global solar irradiance (IA) | Ly/h | Triangle (17.3–25.4) | [18] |
| River | Light-extinction coefficient (et) | /m | Uniform (0.26–0.31) | [18] |
| River | Mean water-column depth (H) | m | Uniform (0.5–6) | [18] |
| River | Effective pool volume at water site ( | L | Uniform (6.75 × 107–8.25 × 107) | [18] |
2.5. Swimming Exposure Assessment
2.6. Downstream Mixing
2.7. Ingestion Dose
2.8. Dose–Health Endpoints and DALY
2.9. Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis
2.10. Software
3. Results and Discussion
Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wellington, E.M.H.; Boxall, A.; Cross, P.; Feil, E.; Gaze, W.; Hawkey, P.; Johnson-Rollings, A.; Jones, D.; Lee, N.; Otten, W.; et al. The Role of the Natural Environment in the Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendonk, T.U.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Cytryn, E.; Walsh, F.; Bürgmann, H.; Sørum, H.; Norström, M.; Pons, M.-N.; et al. Tackling Antibiotic Resistance: The Environmental Framework. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantziaras, I.; Boyen, F.; Callens, B.; Dewulf, J. Correlation between Veterinary Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance in Food-Producing Animals: A Report on Seven Countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierikx, C.M.; van der Goot, J.A.; Smith, H.E.; Kant, A.; Mevius, D.J. Presence of ESBL/AmpC -Producing Escherichia coli in the Broiler Production Pyramid: A Descriptive Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikarainen, P.E.; Pohjola, L.K.; Pietola, E.S.; Heikinheimo, A. Direct Vertical Transmission of ESBL/pAmpC-Producing Escherichia coli Limited in Poultry Production Pyramid. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 231, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallioris, P.; Teunis, G.; Lagerweij, G.; Joosten, P.; Dewulf, J.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Stegeman, A.; Mughini-Gras, L. Biosecurity and Antimicrobial Use in Broiler Farms across Nine European Countries: Toward Identifying Farm-Specific Options for Reducing Antimicrobial Usage. Epidemiol. Infect. 2023, 151, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robé, C.; Blasse, A.; Merle, R.; Friese, A.; Roesler, U.; Guenther, S. Low Dose Colonization of Broiler Chickens with ESBL-/AmpC- Producing Escherichia coli in a Seeder-Bird Model Independent of Antimicrobial Selection Pressure. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Overbeek, L.; Duhamel, M.; Aanstoot, S.; van der Plas, C.L.; Nijhuis, E.; Poleij, L.; Russ, L.; van der Zouwen, P.; Andreo-Jimenez, B. Transmission of Escherichia coli from Manure to Root Zones of Field-Grown Lettuce and Leek Plants. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnino, N.; Basak, S.; Collineau, L.; Merle, R. Pathways of Escherichia coli Transfer from Animal Manure: Risks and Mitigation in Agriculture. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1568621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manini, E.; Baldrighi, E.; Ricci, F.; Grilli, F.; Giovannelli, D.; Intoccia, M.; Casabianca, S.; Capellacci, S.; Marinchel, N.; Penna, P.; et al. Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Variability of Faecal Pollution along Coastal Waters during and after Rainfall Events. Water 2022, 14, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, F.; Hubbart, J.A. Spatial and Temporal Characterization of Escherichia Coli, Suspended Particulate Matter and Land Use Practice Relationships in a Mixed-Land Use Contemporary Watershed. Water 2020, 12, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siller, P.; Daehre, K.; Thiel, N.; Nübel, U.; Roesler, U. Impact of Short-Term Storage on the Quantity of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase–Producing Escherichia coli in Broiler Litter under Practical Conditions. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, E.; Young, B.J.; Pérez, D.J.; Pellegrini, M.C.; Carciochi, W.D.; Lavallén, C.M.; Ponce, A.G.; Dopchiz, M.C.; Hernández Guijarro, K.; del Franco, M.R.; et al. Effect of On-Farm Poultry Litter Composting Processes on Physicochemical, Biological, and Toxicological Parameters and Reduction of Antibiotics and Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli. Waste Manag. 2024, 174, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasova, A.; Amon, T.; Friese, A.; Rösler, U.; Merle, R.; Herrmann, C.; Kraus, A.; Kabelitz, T. Effects of Carbon–to–Nitrogen Ratio and Temperature on the Survival of Antibiotic-Resistant and Non-Resistant Escherichia coli During Chicken Manure Anaerobic Digestion. Poultry 2025, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schijven, J.; Blaak, H.; Schets, F.; Roda Husman, A.M. Fate of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli from Faecal Sources in Surface Water and Probability of Human Exposure through Swimming. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11825–11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.B.; Søraas, A.V.; Arnesen, L.S.; Leegaard, T.M.; Sundsfjord, A.; Jenum, P.A. A Comparison of Extended Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Escherichia coli from Clinical, Recreational Water and Wastewater Samples Associated in Time and Location. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, E.; Solimini, A.; Pantanella, F.; Cummins, E. The Potential Human Exposure to Antibiotic Resistant-Escherichia coli through Recreational Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappier, S.P.; Liguori, K.; Ichida, A.M.; Stewart, J.R.; Jones, K.R. Antibiotic Resistance in Recreational Waters: State of the Science. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crettels, L.; Champon, L.; Burlion, N.; Delrée, E.; Saegerman, C.; Thiry, D. Antimicrobial Resistant Escherichia coli Prevalence in Freshwaters in Belgium and Human Exposure Risk Assessment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnino, N.; Basak, S.; Collineau, L.; Merle, R. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Transfer from Broiler Litter to Fresh Lettuce Consumption. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Sarnino, N.; Merle, R.; Collineau, L. Quantification of the Risk of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Producing Escherichia coli Colonization in Humans through Occupational Exposure in Broiler Production. Microb. Risk Anal. 2025, 30, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, J.L. Numerical Estimates of Coliform Mortality Rates under Various Conditions. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1978, 50, 2477–2484. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, E.; Correia-Carreira, G.; Projahn, M.; Käsbohrer, A. Modeling the Impact of Management Changes on the Infection Dynamics of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in the Broiler Production. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame-Korevaar, A.; Kers, J.G.; Goot, J.; Velkers, F.; Ceccarelli, D.; Mevius, D.; Stegeman, A.; Fischer, E. Competitive Exclusion Prevents Colonization and Compartmentalization Reduces Transmission of ESBL-Producing Escherichia coli in Broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 566619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Millner, P.D.; Hashem, F.; Vinyard, B.T.; East, C.L.; Handy, E.T.; White, K.; Stonebraker, R.; Cotton, C.P. Survival of Escherichia coli in Manure-Amended Soils Is Affected by Spatiotemporal, Agricultural, and Weather Factors in the Mid-Atlantic United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02392-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowah, R.; Bradshaw, K.; Snyder, B.; Spidle, D.; Molina, M. Evaluation of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) for Simulating, E. Coli Concentrations at the Watershed-Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 140669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heida, A.; Hamilton, M.T.; Gambino, J.; Sanderson, K.; Schoen, M.E.; Jahne, M.A.; Garland, J.; Ramirez, L.; Quon, H.; Lopatkin, A.J.; et al. Population Ecology-Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment (QMRA) Model for Antibiotic-Resistant and Susceptible E. coli in Recreational Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 4266–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouillot, R.; Delignette-Muller, M.L.; Kelly, D.L.; Denis, J.B. The Mc2d Package. 2016. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/mc2d/mc2d.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Grothendieck, M.G. Package ‘Nls2.’ Non-linear regression with brute force. 2013. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/nls2/nls2.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Bengtsson, H. A Unifying Framework for Parallel and Distributed Processing in R Using Futures. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnell, R. Package ‘Lhs.’ 2016. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lhs/lhs.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Iooss, B.; Da Veiga, S.; Janon, A.; Pujol, G.; Iooss, M.B.; Rcpp, L. Package ‘Sensitivity’. 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=sensitivity (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- van Heijnsbergen, E.; Niebaum, G.; Lämmchen, V.; Borneman, A.; Hernández Leal, L.; Klasmeier, J.; Schmitt, H. (Antibiotic-Resistant) E. Coli in the Dutch–German Vecht Catchment─Monitoring and Modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 15064–15073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraccini, P.A.; Mattioli, M.C.M.; Sassoubre, L.M.; Cao, Y.; Griffith, J.F.; Ervin, J.S.; Van De Werfhorst, L.C.; Boehm, A.B. Solar Inactivation of Enterococci and Escherichia coli in Natural Waters: Effects of Water Absorbance and Depth. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5068–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.L.; Boehm, A.B.; Davies-Colley, R.J.; Dodd, M.C.; Kohn, T.; Linden, K.G.; Liu, Y.; Maraccini, P.A.; McNeill, K.; Mitch, W.A.; et al. Sunlight-Mediated Inactivation of Health-Relevant Microorganisms in Water: A Review of Mechanisms and Modeling Approaches. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 1089–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochelle-Newall, E.J.; Ribolzi, O.; Viguier, M.; Thammahacksa, C.; Silvera, N.; Latsachack, K.; Dinh, R.P.; Naporn, P.; Sy, H.T.; Soulileuth, B.; et al. Effect of Land Use and Hydrological Processes on Escherichia coli Concentrations in Streams of Tropical, Humid Headwater Catchments. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckerfield, S.J.; Quilliam, R.S.; Waldron, S.; Naylor, L.A.; Li, S.; Oliver, D.M. Rainfall-Driven, E. coli Transfer to the Stream-Conduit Network Observed through Increasing Spatial Scales in Mixed Land-Use Paddy Farming Karst Terrain. Water Res. X 2019, 5, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslovaite, V.; Pickett, H.; Speight, V.; Shucksmith, J.D. Forecasting Acute Rainfall Driven E. coli Impacts in Inland Rivers Based on Sewer Monitoring and Field Runoff. Water Res. 2024, 248, 120838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyness, A.J.; Paterson, D.M.; Rimmer, J.E.V.; Defew, E.C.; Stutter, M.I.; Avery, L.M. Assessing Risk of E. Coli Resuspension from Intertidal Estuarine Sediments: Implications for Water Quality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnet, J.-B.; Habash, M.; Hachad, M.; Khanafer, Z.; Prévost, M.; Servais, P.; Sylvestre, E.; Dorner, S. Automated Targeted Sampling of Waterborne Pathogens and Microbial Source Tracking Markers Using Near-Real Time Monitoring of Microbiological Water Quality. Water 2021, 13, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwka, P.; Moreno, D.S.; Korzeniowski, P.; Milcarz, A.; Kuczkowski, M.; Kolenda, R.; Kozioł, S.; Narajczyk, M.; Roesler, U.; Tomaszewska-Hetman, L.; et al. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli-Targeting Phages for Biofilm Biocontrol in the Poultry Industry. Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 301, 110363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Idler, C.; Ammon, C.; Amon, T. Applied Research Note: Survival of Escherichia coli and Temperature Development during Composting of Chicken Manure with a Typically Low Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio and Moisture Content. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2024, 33, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, H.; Lynch, G.; Italiaander, R.; Hamidjaja, R.A.; Schets, F.M.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Multidrug-Resistant and Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Dutch Surface Water and Wastewater. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.L.; Bolster, C.H.; Ayers, K.A.; Reynolds, D.N. Escherichia coli Diversity in Livestock Manures and Agriculturally Impacted Stream Waters. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Weir, M.H.; Hull, N.M. Fluence-Based QMRA Model for Bacterial Photorepair and Regrowth in Drinking Water after Decentralized UV Disinfection. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poopipattana, C.; Suzuki, M.; Kumar, M.; Furumai, H. Prediction of Sunlight- and Salinity-Driven Inactivation Kinetics of Microbial Indicators with Validation in a 3D Water Quality Model. Water 2024, 16, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary Tract Infections: Epidemiology, Mechanisms of Infection and Treatment Options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Idler, C.; Ammon, C.; Herrmann, C.; Amon, T. Inactivation of ESBL-/AmpC-Producing Escherichia coli during Mesophilic and Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

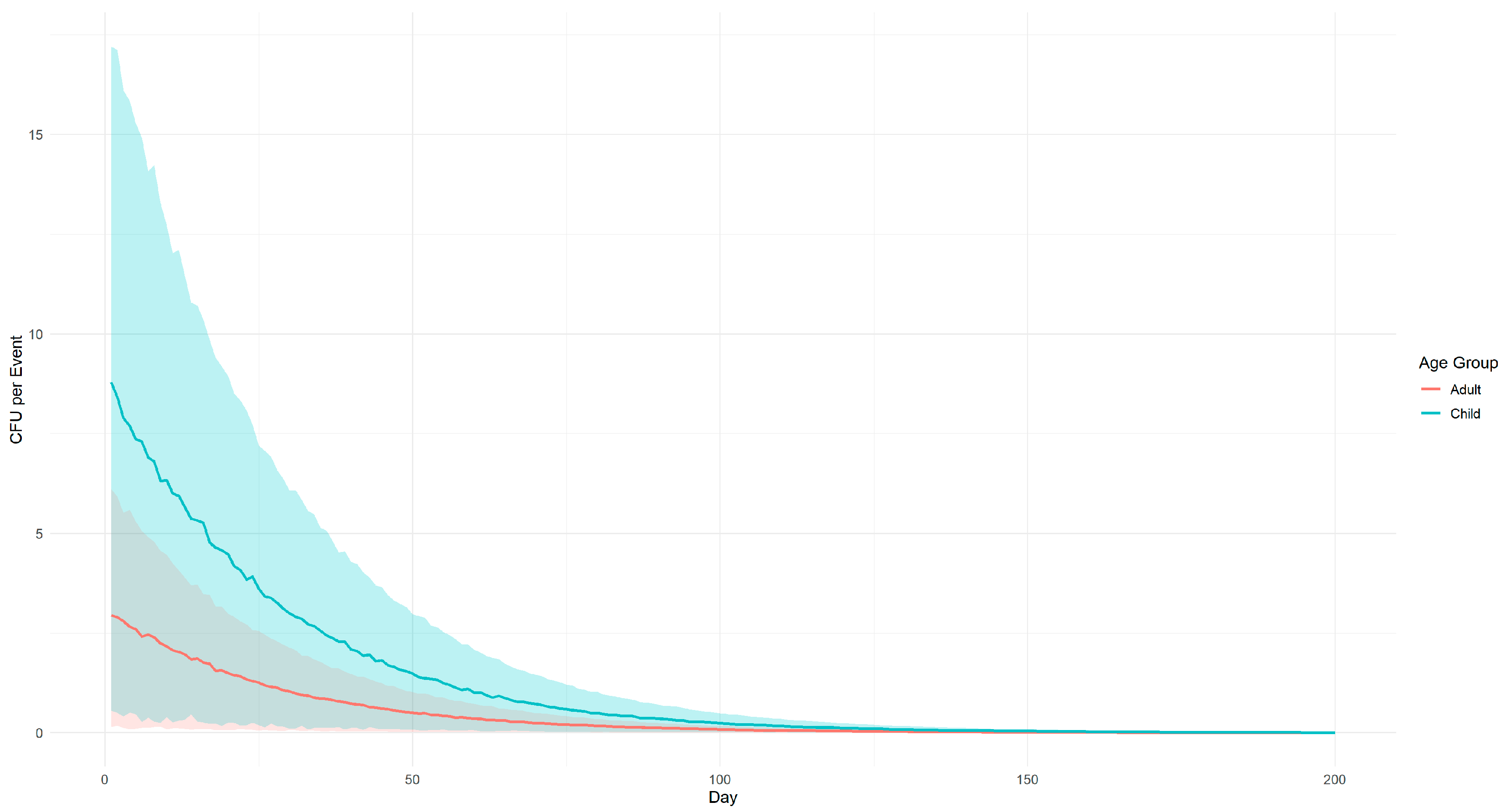
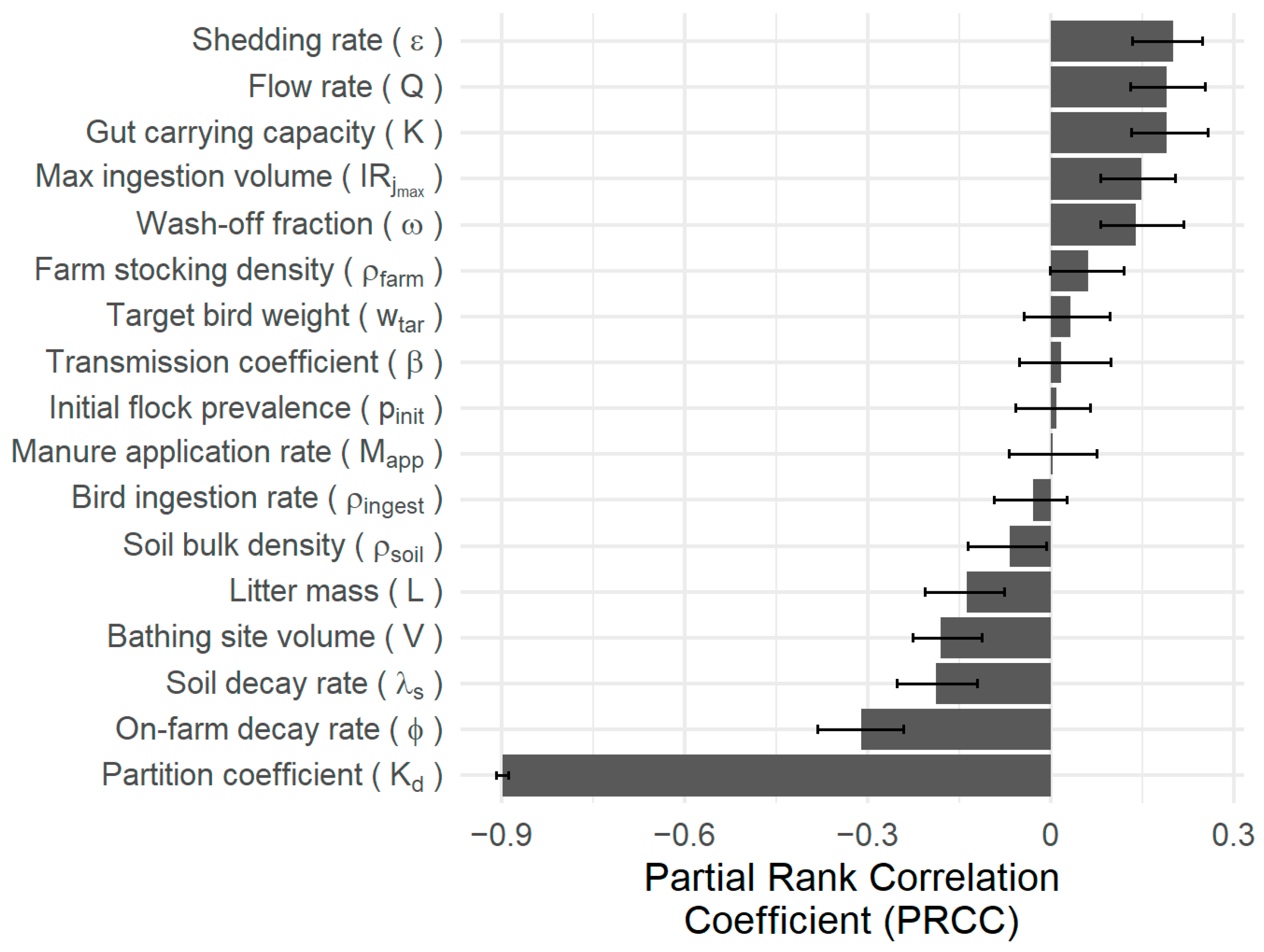
| Variable | Description | Source | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESBL E. coli concentration in the watershed | [21] | CFU/mL | Stochastic | |
| Daily inflow to bathing reach (dilution) | [18] | m3/day | Triangular (67,500, 75,000, 82,500) | |
| Instantaneous water volume for dilution | [18] | m3 | Uniform (67,500, 82,500) | |
| Ingestion volume per adult swim | [18] | mL/event | Uniform (0–70.67) | |
| Ingestion volume per child swim | [18] | mL/event | Uniform (0–205.33) | |
| Exponential dose–response parameter | [28] | /CFU | 2.18 × 10−6 | |
| Fraction of E. coli that are uropathogenic | [28] | fraction | 0.1 | |
| P (urinary colonization |gut colonization) | [28] | probability | Uniform (0.35, 0.46) | |
| P (symptomatic UTI| urinary colonization) | [28] | probability | 0.067 | |
| DALY burden per UTI case | [28] | DALY/case | Uniform (3.7, 12.84) |
| Day | Mean Risk (GI) | Mean Risk (UTI) | Mean DALY | Age Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.75 × 10−7 | 1.56 × 10−8 | 1.29 × 10−7 | Adult |
| 10 | 4.21 × 10−7 | 1.14 × 10−8 | 9.76 × 10−8 | |
| 50 | 9.84 × 10−8 | 2.66 × 10−9 | 2.20 × 10−8 | |
| 100 | 1.59 × 10−8 | 4.33 × 10−10 | 3.70 × 10−9 | |
| 150 | 2.67 × 10−9 | 7.26 × 10−11 | 6.13 × 10−10 | |
| 200 | 4.39 × 10−10 | 1.19 × 10−11 | 9.71 × 10−11 | |
| 1 | 1.71 × 10−6 | 4.65 × 10−8 | 3.83 × 10−7 | |
| 10 | 1.23 × 10−6 | 3.35 × 10−8 | 2.80 × 10−7 | |
| 50 | 2.89 × 10−7 | 7.84 × 10−9 | 6.54 × 10−8 | Child |
| 100 | 4.66 × 10−8 | 1.27 × 10−9 | 1.07 × 10−8 | |
| 150 | 7.78 × 10−9 | 2.12 × 10−10 | 1.78 × 10−9 | |
| 200 | 1.27 × 10−9 | 3.43 × 10−11 | 2.80 × 10−10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarnino, N.; Basak, S.; Collineau, L.; Merle, R. Recreational Water Risk from Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli of Broiler Origin: A Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment. Environments 2025, 12, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12110403
Sarnino N, Basak S, Collineau L, Merle R. Recreational Water Risk from Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli of Broiler Origin: A Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment. Environments. 2025; 12(11):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12110403
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarnino, Nunzio, Subhasish Basak, Lucie Collineau, and Roswitha Merle. 2025. "Recreational Water Risk from Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli of Broiler Origin: A Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment" Environments 12, no. 11: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12110403
APA StyleSarnino, N., Basak, S., Collineau, L., & Merle, R. (2025). Recreational Water Risk from Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli of Broiler Origin: A Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment. Environments, 12(11), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12110403






