Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Application on N2O Emissions from Rice Cultivation: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. N2O Production in Rice Cultivation
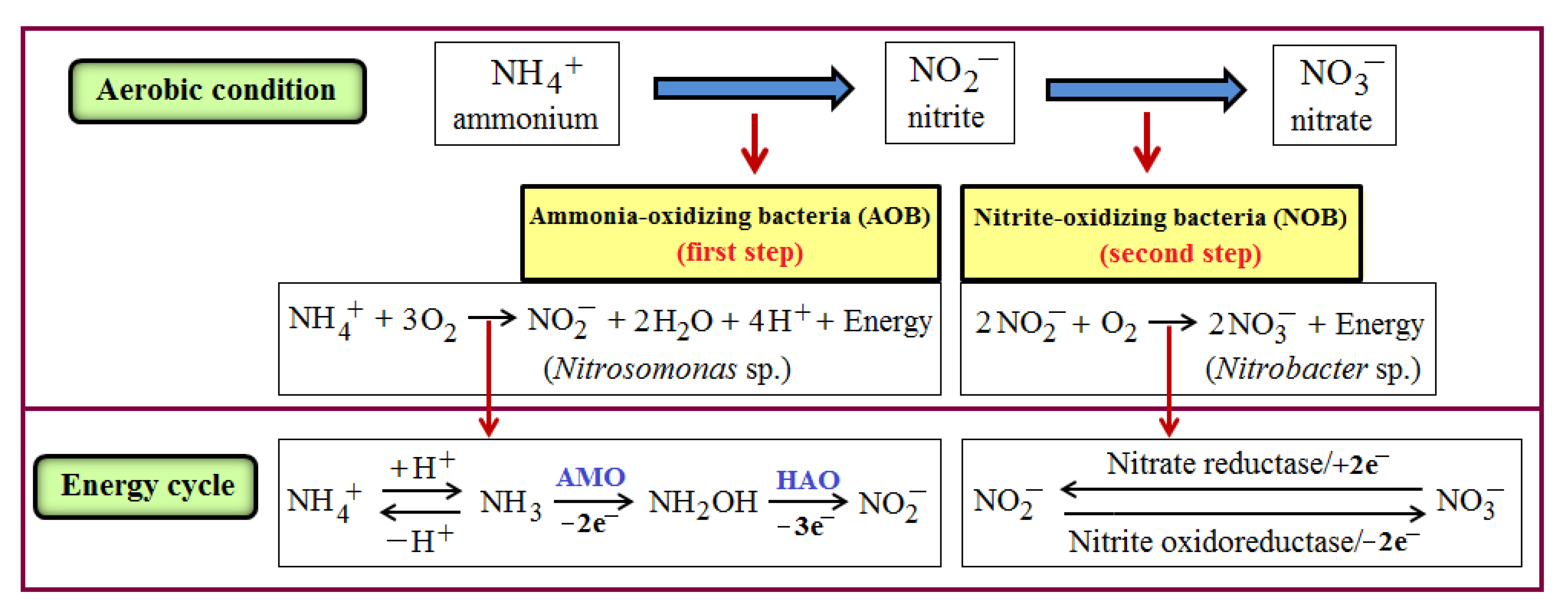
2.1. Nitrification
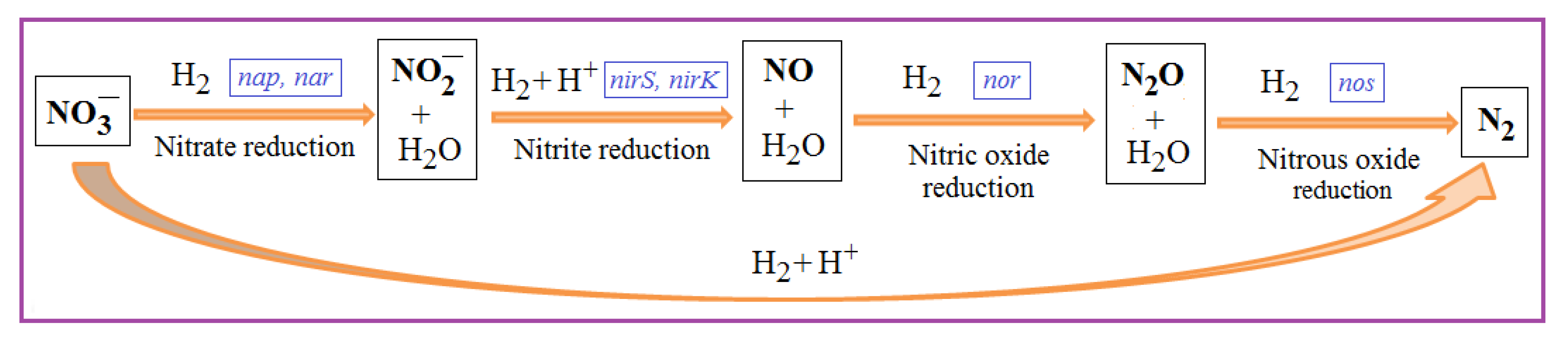
2.2. Denitrification
3. Mitigation Strategies
3.1. Optimized Fertilizer Use
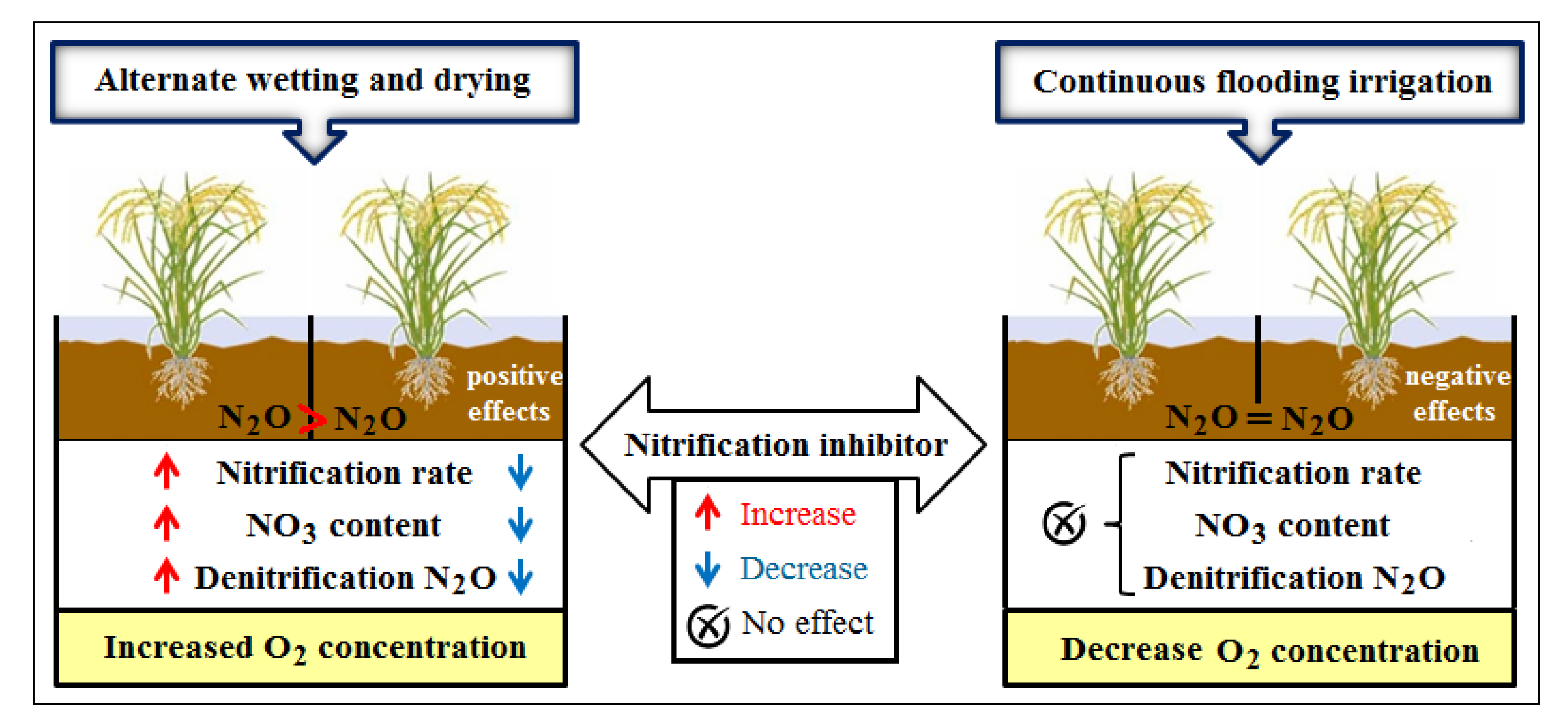
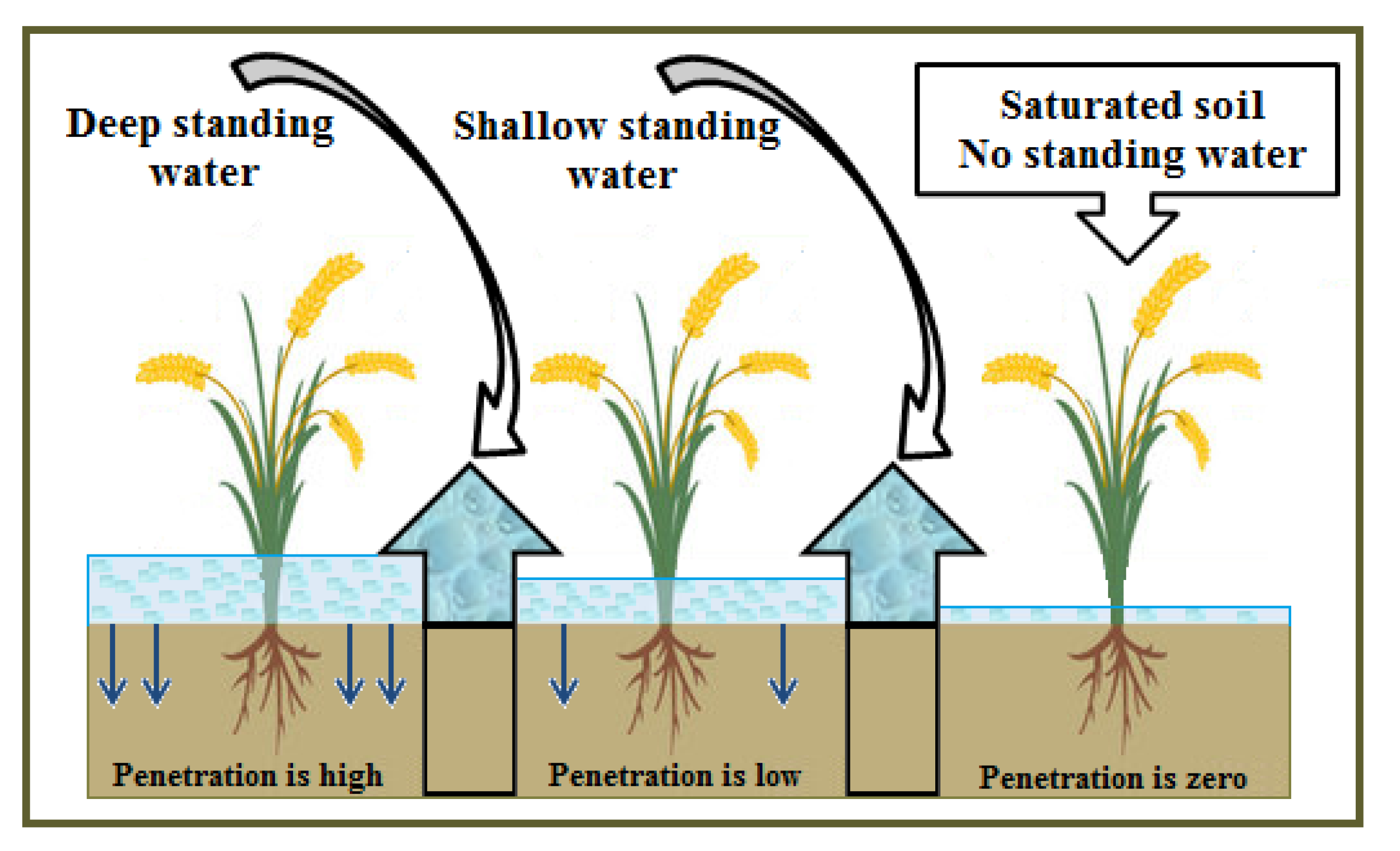
3.2. Improved Drainage and Water Management
3.3. Organic Amendments
4. Current Challenges and Future Research Directions
4.1. Current Challenges
4.2. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raza, T.; Qadir, M.F.; Khan, K.S.; Eash, N.S.; Yousuf, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Manzoor, R.; ur Rehman, S.; Oetting, J.N. Unraveling the potential of microbes in decomposition of organic matter and release of carbon in the ecosystem. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasar, H.G.W.; Lamichhane, S.; Dou, F.; Gentry, T. The environmental trade-offs of applying soil amendments: Microbial biomass and greenhouse gas emission dynamics in organic rice paddy soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 208, 105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buragienė, S.; Šarauskis, E.; Romaneckas, K.; Adamavičienė, A.; Kriaučiūnienė, Z.; Avižienytė, D.; Marozas, V.; Naujokienė, V. Relationship between CO2 emissions and soil properties of differently tilled soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, W.; Chi, M.; Sun, Y.; An, J.; Yu, N.; Zou, H. Simulating the effects of soil temperature and soil moisture on CO2 and CH4 emissions in rice straw-enriched paddy soil. CATENA 2020, 194, 104677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubiello, F.N. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Due to Agriculture. In Elsevier Encyclopedia of Food Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC 2019. Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashermes, G.; Recous, S.; Alavoine, G.; Janz, B.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Ernfors, M.; Laville, P. N2O emissions from decomposing crop residues are strongly linked to their initial soluble fraction and early C mineralization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz-Almeida, R.; Lopes, S.N.; Wendling, B. How does N mineral fertilizer influence the crop residue N credit? Nitrogen 2020, 1, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Khanam, M.; Rahman, M.M. Environment-friendly nitrogen management practices in wetland paddy cultivation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1020570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Wang, X.; Uzair, M.; Fatima, H.; Fiaz, S.; Maqbool, Z.; Rehman, O.U.; Yousuf, M.; Khan, M.R. Recent trends in nitrogen cycle and eco-efficient nitrogen management strategies in aerobic rice system. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 960641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Yang, J. Nitrogen (N) transformation in paddy rice field: Its effect on N uptake and relation to improved N management. Crop Environ. 2022, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zheng, G.; Tao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Effect of Soil Texture on Soil Nutrient Status and Rice Nutrient Absorption in Paddy Soils. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, F.; Soriano, J.; Tabien, R.E.; Chen, K. Soil Texture and Cultivar Effects on Rice (Oryza sativa, L.) Grain Yield, Yield Components and Water Productivity in Three Water Regimes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Y.; Ran, X.; Liu, K.; Shi, W.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Ding, Y.; et al. Effects of warming on rice production and metabolism process associated with greenhouse gas emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajbonshi, M.P.; Mitra, S.; Bhattacharyya, P. Agro-technologies for greenhouse gases mitigation in flooded rice fields for promoting climate smart agriculture. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 350, 123973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.U.; Aamer, M.; Mahmood, A.; Awan, M.I.; Barbanti, L.; Seleiman, M.F.; Bakhsh, G.; Alkharabsheh, H.M.; Babur, E.; Shao, J.; et al. Management Strategies to Mitigate N2O Emissions in Agriculture. Life 2022, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, Z.; Song, Z.; Chen, W.; Tian, D.; Tang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Variations and controlling factors of soil denitrification rate. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 2133–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, H.; Sveen, T.R.; Zhang, Y. Soil moisture determines nitrous oxide emission and uptake. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Jiang, M.; Khan, I.; Zhao, J.; Hu, R. Rice planting reduced N2O emissions from rice-growing seasons due to increased nosZ gene abundance under a rice-wheat rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 152, 127025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Tang, S.; Hu, R.; Wang, J.; Duan, P.; Xu, C.; Wenju, Z.W.; Xu, M. Increased N2O emission due to paddy soil drainage is regulated by carbon and nitrogen availability. Geoderma 2023, 432, 116422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Norton, J.M.; Stark, J.M. Ammonium availability and temperature control contributions of ammonia oxidizing bacteria and archaea to nitrification in an agricultural soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, R.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H. The different responses of AOA and AOB communities to irrigation systems in the semi-arid region of Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1374618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Myrold, D.D.; Wang, D.; Guo, X.; Chu, H. AOA and AOB communities respond differently to changes of soil pH under long-term fertilization. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2019, 1, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Ren, G.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Peng, X.; Jia, Z. Ecosystem-specific selection of microbial ammonia oxidizers in an acid soil. Biogeosci. Discuss. 2013, 10, 1717–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Sediment ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in two plateau freshwater lakes at different trophic states. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, H.; Lin, Y.-P.; Anthony, J. Ammonia Oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in East Asian Paddy Soils—A Mini Review. Environments 2017, 4, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, G.; Liao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Contributions of ammonia-oxidising bacteria and archaea to nitrification under long-term application of green manure in alkaline paddy soil. Geoderma 2020, 374, 114419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rütting, T.; Schleusner, P.; Hink, L.; Prosser, J.I. The contribution of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria to gross nitrification under different substrate availability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Uzair, M.; Maqbool, Z.; Fiaz, S.; Yousuf, M.; Yang, S.H.; Khan, M.R. Improving Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Aerobic Rice Based on Insights Into the Ecophysiology of Archaeal and Bacterial Ammonia Oxidizers. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 913204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yin, N.; Hu, Z.; Shen, L.; Islam, A.T.; Wei, Z.; Chen, S. Characteristics of soil N2O emission and N2O-producing microbial communities in paddy fields under elevated CO2 concentrations. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, L.; Hu, R.; Ma, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L. Patterns and determinants of nitrification and denitrification potentials across 24 rice paddy soils in subtropical China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 361, 108799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, B.; Chandra, R.; Ram, S.; Pareek, N. Long-term effects of fertilization and manuring on productivity and soil biological properties under rice (Oryza sativa)—Wheat (Triticum aestivum) sequence in mollisols. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 1109–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzyb, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Niewiadomska, A. The Significance of Microbial Transformation of Nitrogen Compounds in the Light of Integrated Crop Management. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, O.O.; Kant, S.; Adedire, O.M.; Li, C.; Yuan, G.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q. Unlocking the potentials of nitrate transporters at improving plant nitrogen use efficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1074839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Wei, L.; Wei, S. Effect of Streptomyces JD211 application on soil physicochemical properties and N2O emission characteristics of rice rhizosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micucci, G.; Sgouridis, F.; McNamara, N.P.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I.; Roos, F.; Well, R.; Ullah, S. The 15N-Gas flux method for quantifying denitrification in soil: Current progress and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 184, 109108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbalán, M.; Da Silva, C.; Barahona, A.; Huiliñir, C.; Guerrero, L. Nitrification–Autotrophic Denitrification Using Elemental Sulfur as an Electron Donor in a Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR): Performance and Kinetic Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Long, C.; Cheng, X. Stronger effects of environmental factors than denitrifying genes on soil denitrification under a subtropical land use change. CATENA 2023, 222, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankara, A.R.; Daniel, J.S.; Portmann, R.W. Nitrous oxide (N2O): The dominant ozone-depleting substance emitted in the 21st century. Science 2009, 326, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Wang, E.; Zhang, Y.; Mosier, A.; Chen, D. A global synthesis of soil denitrification: Driving factors and mitigation strategies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 327, 107850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleken, M.A.; Rittl, T.R. Soil pH-increase strongly mitigated N2O emissions following ploughing of grass and clover swards in autumn: A winter field study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žurovec, O.; Wall, D.P.; Brennan, F.P.; Krol, D.J.; Forrestal, P.J.; Richards, K.G. Increasing soil pH reduces fertiliser derived N2O emissions in intensively managed temperate grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 311, 107319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Lu, Q.; Lin, T.; Dong, L.; Wu, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, L. Straw Returning with Decomposition Agent Enhanced Rice Yield and Decreased Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions in Tropical Paddy Fields. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Sheng, X.; Bloszies, S.; et al. Intermediate soil acidification induces highest nitrous oxide emissions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Hong, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F.; Ye, J.; Lu, J.; Long, A. Denitrification contributes to N2O emission in paddy soils. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1218207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, K.; Xiao, F.; Gong, P.; Xue, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L. Effect of Biological Denitrification Inhibitor on N2O Emissions from Paddy Soil and Microbial Mechanisms. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Shao, D.; Gu, W. Effects of temperature and soil moisture on gross nitrification and denitrification rates of a Chinese lowland paddy field soil. Paddy Water Environ. 2018, 16, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Di, H. Heterotrophic nitrification and denitrification are the main sources of nitrous oxide in two paddy soils. Plant Soil 2019, 445, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Guo, L.P.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.G.; Yang, R.Q.; Li, M.; Ma, F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y.C. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and water management practices on nitrogen leaching from a typical open field used for vegetable planting in northern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Larsen, K.S.; Hansen, L.V.; Jensen, L.S.; Bruun, S. Effect of nitrification inhibitor (DMPP) on nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural fields: Automated and manual measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, H.; Wang, J.; Dai, F.; Wu, Y.; Chapman, S. Nitrification and urease inhibitors improve rice nitrogen uptake and prevent denitrification in alkaline paddy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 154, 103665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zeng, K.; Song, Y. Biological nitrification inhibitor for reducing N2O and NH3 emissions simultaneously under root zone fertilization in a Chinese rice field. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.; Suter, H.; Mosier, A.R.; Chen, D. Using nitrification inhibitors to mitigate agricultural N2O emission: A double-edged sword? Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyan, S.K.; Maithani, D.; Kumar, V. Nitrous Oxide Production and Mitigation Through Nitrification Inhibitors in Agricultural Soils: A Mechanistic Understanding and Comprehensive Evaluation of Influencing Factors. Nitrogen 2025, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelliher, F.M.; van Kotena, C.; Kear, M.J.; Sprosenc, M.S.; Ledgardc, S.F.; de Kleind, C.A.M.; Letica, S.A.; Luo, J.; Rys, G. Effect of temperature on dicyandiamide (DCD) longevity in pastoral soils under field conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 186, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, S.T.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C. Effects of commonly used nitrification inhibitors-dicyandiamide (DCD), 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP), and nitrapyrin on soil nitrogen dynamics and nitrifiers in three typical paddy soils. Geoderma 2020, 380, 114637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triozzi, M.; Ilacqua, A.; Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; Losacco, D. Assessment of the Nitrification Inhibitor Nitrapyrin on Nitrogen Losses and Brassica oleracea Growth: A Preliminary Sustainable Research. Nitrogen 2025, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Lokesh Goud, D.; Hareesh Reddy, C.H.; Mahender Kumar, R.; Sundaram, R.M. Efficient Nitrogen Management Technologies for Sustainable Rice Production. J. Rice Res. 2022, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Zheng, S.; Yang, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Comparison of yield and nitrogen use efficiency of different types of nitrogen fertilizers for different rice cropping systems under subtropical monsoon climate in China. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 90, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuchi, K.; Kobayashi, A. The effect of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on nitrification inhibition and its use for basal nitrogen application to paddy rice. Jpn. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 90, 147–152. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hatano, S.; Fujita, Y.; Nagumo, Y.; Ohtake, N.; Sueyoshi, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Sato, T.; Tanabata, S.; Higuchi, K.; Saito, A.; et al. Effect of the Nitrification Inhibitor 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate on the Deep Placement of Nitrogen Fertilizers for Soybean Cultivation. Int. J. Agron. 2019, 2019, 9724214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, W.; Xie, N.; Che, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Wu, G.; Yang, S.; Dong, Z.; Song, H. Oxygen Availability Governs the Mitigating Effect of 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Paddy Soils under Various Water Managements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 5781–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Fan, Q.; Yu, J.; Ma, Y.; Yin, J.; Liu, R. A meta-analysis to examine whether nitrification inhibitors work through selectively inhibiting ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadell, J.G.; Monteiro, P.M.S.; Costa, M.H.; Cotrim da Cunha, L.; Cox, P.M.; Eliseev, A.V.; Henson, S.; Ishii, M.; Jaccard, S.; Koven, C.; et al. Global Carbon and other Biogeochemical Cycles and Feedbacks. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 673–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Bashir, A.; Husnain, M.I. Impact of agricultural land use and economic growth on nitrous oxide emissions: Evidence from developed and developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdous, J.; Mahjabin, F.; Abdullah al Asif, M.; Jahan Riza, I.; Mofizur Rahman Jahangir, M. Gaseous Losses of Nitrogen from Rice Field: Insights into Balancing Climate Change and Sustainable Rice Production. In Sustainable Rice Production—Challenges, Strategies and Opportunities; Huang, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; He, R.; Hou, P.; Ding, C.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Ding, C.; Chen, L.; et al. Combined controlled-released nitrogen fertilizers and deep placement effects of N leaching, rice yield and N recovery in machine-transplanted rice. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Bordoloi, N. Agriculture’s Contribution to the Emission of Greenhouse Gas Nitrous Oxide (N2O) and Its Feasible Mitigation Strategies. In Climate Smart Greenhouses—Innovations and Impacts; Abdelhafez, A.A., Abbas, M.H.H., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Clough, T.J.; Elberling, B. Flooding-induced N2O emission bursts controlled by pH and nitrate in agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, X. Effects of N management optimization practices on rice productivity and N loss: A meta-analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1485144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pélissier, P.-M.; Parizot, B.; Jia, L.; De Knijf, A.; Goossens, V.; Gantet, P.; Champion, A.; Audenaert, D.; Xuan, W.; Beeckman, T.; et al. Nitrate and ammonium, the yin and yang of nitrogen uptake: A time-course transcriptomic study in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1343073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lu, C.; Khan, Z.; Li, Z.; Duan, S.; Shen, H.; Fu, Y. Mixed Ammonium-Nitrate Nutrition Regulates Enzymes, Gene Expression, and Metabolic Pathways to Improve Nitrogen Uptake, Partitioning, and Utilization Efficiency in Rice. Plants 2025, 14, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Kan, C.-C.; Hung, T.-H.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-Y.; Hsieh, M.-H. Identification of early ammonium nitrate-responsive genes in rice roots. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Park, G.; Reeves, S.; Zahmel, M.; Heenan, M.; Salter, B. Nitrous oxide emission and fertiliser nitrogen efficiency in a tropical sugarcane cropping system applied with different formulations of urea. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Lin, S.; Zuo, Q.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Urea deep placement reduces yield-scaled greenhouse gas (CH4 and N2O) and NO emissions from a ground cover rice production system. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 11415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, D.; Liu, S.; Liao, Y.; Han, J. Can Controlled-Release Urea Replace the Split Application of Normal Urea in China? A Meta-Analysis Based on Crop Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2022, 275, 108343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, W.; Luo, J. Urea Fertilization Significantly Promotes Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils and Is Attributed to the Short-Term Suppression of Nitrite-Oxidizing Bacteria during Urea Hydrolysis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaihre, Y.K.; Singh, U.; Bible, W.D.; Fugice, J.; Sanabria, J. Mitigating N2O and NO Emissions from Direct-Seeded Rice with Nitrification Inhibitor and Urea Deep Placement. Rice Sci. 2020, 27, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, O.; Kang, N.; Soh, H.; Park, J.-S.; Choi, E.; Jeong, H. Nitrous Oxide Emissions during Cultivation and Fallow Periods from Rice Paddy Soil under Urea Fertilization. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.W.; Kim, P.J.; Khan, M.I.; Lee, S.-J. Effect of Rice Planting on Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Emission under Different Levels of Nitrogen Fertilization. Agronomy 2021, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.M.M.; Gaihre, Y.K.; Biswas, J.C.; Singh, U.; Ahmed, N.; Sanabria, J.; Saleque, M.A. Nitrous oxide and nitric oxide emissions from lowland rice cultivation with urea deep placement and alternate wetting and drying irrigation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, J.R.; Champness, M.; Hornbuckle, J.; Quayle, W.C. Soil greenhouse gas emissions under enhanced efficiency and urea nitrogen fertilizer from Australian irrigated aerobic rice production. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2024, 7, e70004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustina, R.; Fajar, R.; Redjeki, E.; Ardiansyah, H. Initial Growth and Physiological Response of Rice with Ammonium Sulfate and Chromolaena odorata Under Water Stress. Yuz. Yıl Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 34, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndille, C.N.; Ballah, M.A.; Safi, S.; Mupeta, I. Effect of Ammonium Sulfate Application Levels on the Growth and Yield of IR-28 Rice. Asian J. Agric. Food Sci. 2021, 9, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndille, C.N.; Lena, E.M.; Mupeta, I.; Nkengafac, N.J. Effect of the Amount and Timing of Ammonium sulfate single top-dressing application on growth and yield of Akitakomachi rice (Oryza sativa L.). Asian J. Agric. Food Sci. 2021, 9, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanova, N.I.; Vizirskaya, M.M.; Zhdanov, V.Y. Prospects for the use of calcium ammonium nitrate on acidic soils of the Non-Black Earth Area. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 285, 06010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, R.; Zheng, X.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. A global meta-analysis of yield-scaled N2O emissions and its mitigation efforts for maize, wheat, and rice. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; He, Y.; Qi, Z.; Jiang, Q. Drainage in paddy systems maintains rice yield and reduces total greenhouse gas emissions on the global scale. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamira, A.; Aminda, F.R. Rice Production Risk in Main Producing Countries 1961–2021. Bul. Penelit. Sos. Ekon. Pertan. Fak. Pertan. Univ. Haluoleo 2023, 25, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampayan, R.M.; Samoy-Pascual, K.C.; Sibayan, E.B.; Ella, V.B.; Jayag, O.P.; Cabangon, R.J.; Bouman, B.A.M. Effects of alternate wetting and drying (AWD) threshold level and plant seedling age on crop performance, water input, and water productivity of transplanted rice in Central Luzon, Philippines. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritee, K.; Nair, D.; Zavala-Araiza, D.; Proville, J.; Rudek, J.; Adhya, T.K.; Loecke, T.; Esteves, T.; Balireddygari, S.; Dava, O.; et al. High nitrous oxide fluxes from rice indicate the need to manage water for both long- and short-term climate impacts. Sustain. Sci. 2018, 115, 9720–9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, C.; Brye, K.R.; Humphreys, J.; Norman, R.J.; Gbur, E.E.; Hardke, J.T.; Willett, C.; Evans-White, M.A. N2O emissions and global warming potential as affected by water management and rice cultivar on an Alfisol in Arkansas, USA. Geoderma Reg. 2018, 4, e00170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Li, W.; Wei, Z.; Dong, Z.; Meng, Y.; Na Lv, N.; Zhang, L. Effects of mild alternate wetting and drying irrigation and rice straw application on N2O emissions in rice cultivation. Soil 2022, 8, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Fu, Z.; Chen, G.; Zou, G.; Song, X. A two-year field measurement of methane and nitrous oxide fluxes from rice paddies under contrasting climate conditions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Vu, Q.D.; Jensen, L.S.; de Tourdonnet, S.; Sander, B.O.; Wassmann, R.; Mai, T.V.; de Neergaard, A. Mitigating CH4 and N2O emissions from intensive rice production systems in northern Vietnam: Efficiency of drainage patterns in combination with rice residue incorporation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 249, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoud, Y.A.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Shaghaleh, H.; Chen, S.; Hassan, A.; Bakour, A. Effects of irrigation regime and soil clay content and their interaction on the biological yield, nitrogen uptake and nitrogen-use efficiency of rice grown in southern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q. Quantitative assessment and mitigation strategies of greenhouse gas emissions from rice fields in China: A data-driven approach based on machine learning and statistical modeling. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 210, 107929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YuYu, H.; Wang, T.; Huang, Q.; Song, K.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Xu, H. Effects of elevated CO2 concentration on CH4 and N2O emissions from paddy fields: A meta-analysis. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Pan, G. Effect of mid-season drainage on CH4 and N2O emission and grain yield in rice ecosystem: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Jabeen, N.; Chachar, Z.; Chachar, S.; Ahmed, S.; Ahmed, N.; Laghari, A.A.; Sahito, Z.A.; Farruhbek, R.; Yang, Z. The role of biochar in enhancing soil health & interactions with rhizosphere properties and enzyme activities in organic fertilizer substitution. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1595208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Ohoro, C.R.; Ojukwu, V.E.; Oniye, M.; Shaikh, W.A.; Biswas, J.K.; Seth, C.S.; Mohan, G.B.M.; Chandran, S.A.; Rangabhashiyam, S. Biochar for ameliorating soil fertility and microbial diversity: From production to action of the black gold. iScience 2025, 28, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, M.N.; Muniza, N.T.; Ahmed, A. Low-Cost Biochar: A Sustainable Approach to Improve Soil Fertility and Crop Yield for Small-Scale Farmers. Am. J. Environ. Econ. 2025, 4, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.M.; Saha, B.K.; Scopa, A.; Drosos, M. Biochar in Agriculture: A Review on Sources, Production, and Composites Related to Soil Fertility, Crop Productivity, and Environmental Sustainability. C 2025, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Ande, O.T.; Dahunsi, S.O.; Ogunwole, J. Sole and Combined Application of Biodigestate, N, P, and K Fertilizers: Impacts on Soil Chemical Properties and Maize Performance. Sci. World J. 2024, 2024, 6685906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Bass, A.M.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.I. Benefits of biochar, compost and biochar–compost for soil quality, maize yield and greenhouse gas emissions in a tropical agricultural soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshori, A.; Sunarminto, B.H.; Haryono, E.; Pramono, A.; Mujiyo. Effect of organic fertilizers on CH4 and N2O production from organic paddy field. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 724, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.Y.; Bong, C.; Lee, C.T.; Lim, J.S.; Sarmidi, M.; Klemeš, J. A Review on the Impacts of Compost on Soil Nitrogen Dynamics. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2018, 63, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüst-Galley, C.; Heller, S.; Ammann, C.; Paul, S.; Doetterl, S.; Leifeld, J. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice grown on organic soils in the temperate zone. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 356, 108641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Amirahmadi, E. Effect of rice husk Biochar (RHB) on some of chemical properties of an acidic soil and the absorption of some nutrients. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2018, 22, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.P.S.; Ghimire, N.P.; Paudel, P.; Mehata, D.K.; Bhujel, S. Advancing effective methods for mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from rice (Oryza sativa L.) fields. J. Sustain. Agric. Environ. 2024, 3, e70012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, P.; Gu, Z.; Song, Y.; Cai, X.; Yu, G.; Xu, X.; Kuzyakov, Y. Biochar reduces N2O emission from fertilized cropland soils: A meta-analysis. Carbon Res. 2025, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajh, G.; Ch’ng, H.Y. Enhancing Soil Nitrogen Availability and Rice Growth by Using Urea Fertilizer Amended with Rice Straw Biochar. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramono, A.; Adriany, T.A.; Yulianingsih, E.; Sopiawati, T.; Hervani, A. Combined compost with biochar application to mitigate greenhouse gas emission in paddy field. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 653, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamer, M.; Bilal Chattha, M.; Mahmood, A.; Naqve, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Shaaban, M.; Rasul, F.; Batool, M.; Rasheed, A.; Tang, H.; et al. Rice Residue-Based Biochar Mitigates N2O Emission from Acid Red Soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, C.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L. Rice straw biochar mitigated more N2O emissions from fertilized paddy soil with higher water content than that derived from ex situ biowaste. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Peng, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, C. The Effect of Biochar and Straw Return on N2O Emissions and Crop Yield: A Three-Year Field Experiment. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Hu, R.; Xu, X.; Xian, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, Z. Effect of rice straw and swine manure biochar on N2O emission from paddy soil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vat, V.; Chidthaisong, A.; Towprayoon, S. Effect of biochar and its combined application with manure and fertilizer on nitrogen leaching, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and grain yield under alternate wetting and drying (AWD) system. J. Agric. Crop Res. 2020, 8, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Wang, H.; Lazcano, C.; Voroney, P.; Elrys, A.; Gou, G.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. Biochar amendments to tropical paddy soil increase rice yields and decrease N2O emissions by modifying the genes involved in nitrogen cycling. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwaltney, L.; Brye, K.R.; Lunga, D.D.; Roberts, T.L.; Fernandes, S.B.; Daniels, M.B. Biochar type and rate effects on greenhouse gas emissions from furrow-irrigated rice. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2025, 8, e70186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Ma, S.; Han, Z.; Yan, X.; Shan, J. Biochar mitigates N2O emissions by promoting complete denitrification in acidic and alkaline paddy soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 74, e13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, T.; Arouna, A.; Labarta, R.; Huelgas, Z.; Mohanty, S. Adoption and impacts of international rice research technologies. Glob. Food Secur. 2016, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Benefits | Environmental Considerations |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen is vital for vegetative growth and directly impacts the quantity and quality of agricultural produce. | Runoff from fields can carry nitrates into water bodies, causing eutrophication and harming aquatic ecosystems. |
| Adequate nitrogen supply accelerates plant growth, helping crops reach maturity more quickly. | In flooded conditions, nitrate can be lost as nitrogen gas through microbial processes, reducing fertilizer efficiency. |
| Some nitrogen fertilizers can improve the microbial activity and nutrient balance in the soil. | Overuse of nitrogen can lead to soil acidification and loss of beneficial microorganisms. |
| Applying nitrogen in smaller doses reduces the risk of excessive nitrification and nitrate leaching. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dăncilă, A.M.; Modrogan, C.; Orbuleț, O.D. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Application on N2O Emissions from Rice Cultivation: A Review. Environments 2025, 12, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100383
Dăncilă AM, Modrogan C, Orbuleț OD. Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Application on N2O Emissions from Rice Cultivation: A Review. Environments. 2025; 12(10):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100383
Chicago/Turabian StyleDăncilă, Annette Madelene, Cristina Modrogan, and Oanamari Daniela Orbuleț. 2025. "Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Application on N2O Emissions from Rice Cultivation: A Review" Environments 12, no. 10: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100383
APA StyleDăncilă, A. M., Modrogan, C., & Orbuleț, O. D. (2025). Effects of Nitrogen Fertilizer Application on N2O Emissions from Rice Cultivation: A Review. Environments, 12(10), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12100383










