Seasonal and Spatial Discrimination of Sandy Beaches Using Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis: A Comparative Study of Maltese Bays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. Physical Parameters
2.3. Potentially Toxic Elemental Concentrations
2.4. Chemometrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Parameters Study
3.2. Descriptive Statistics
3.3. Non-Parametric Analysis
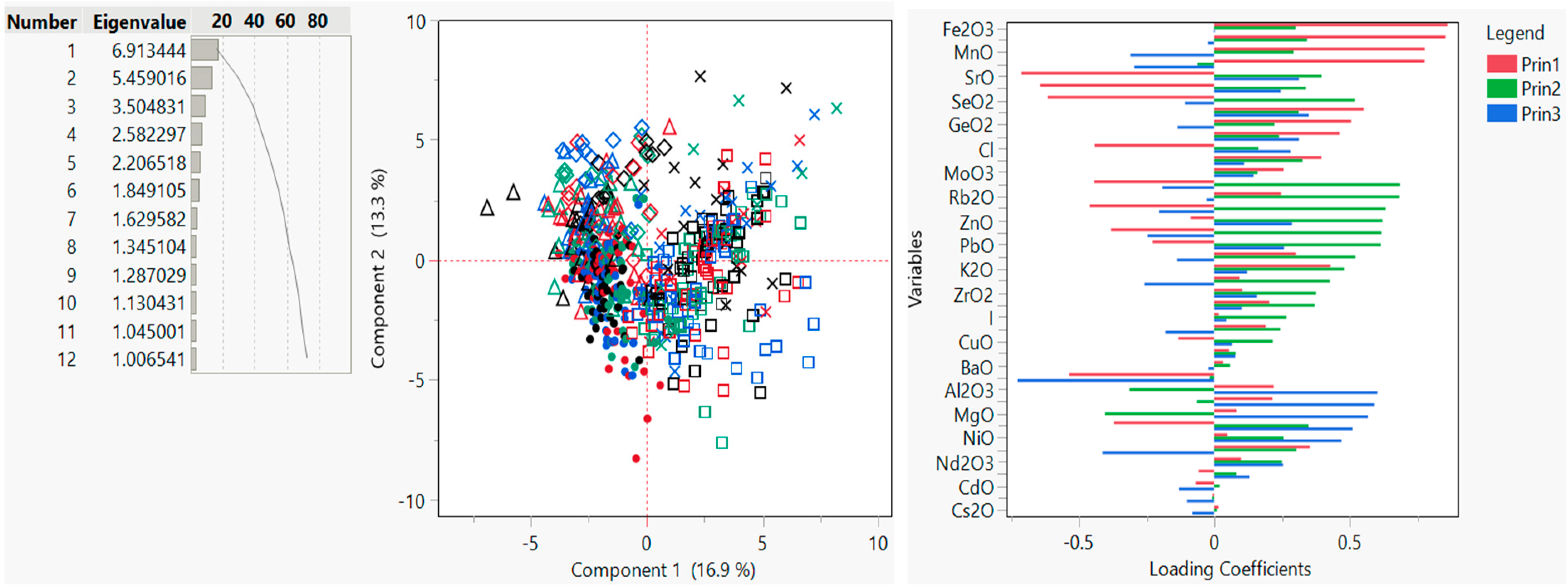
3.4. Unsupervised Chemometric Techniques—PCA and FA
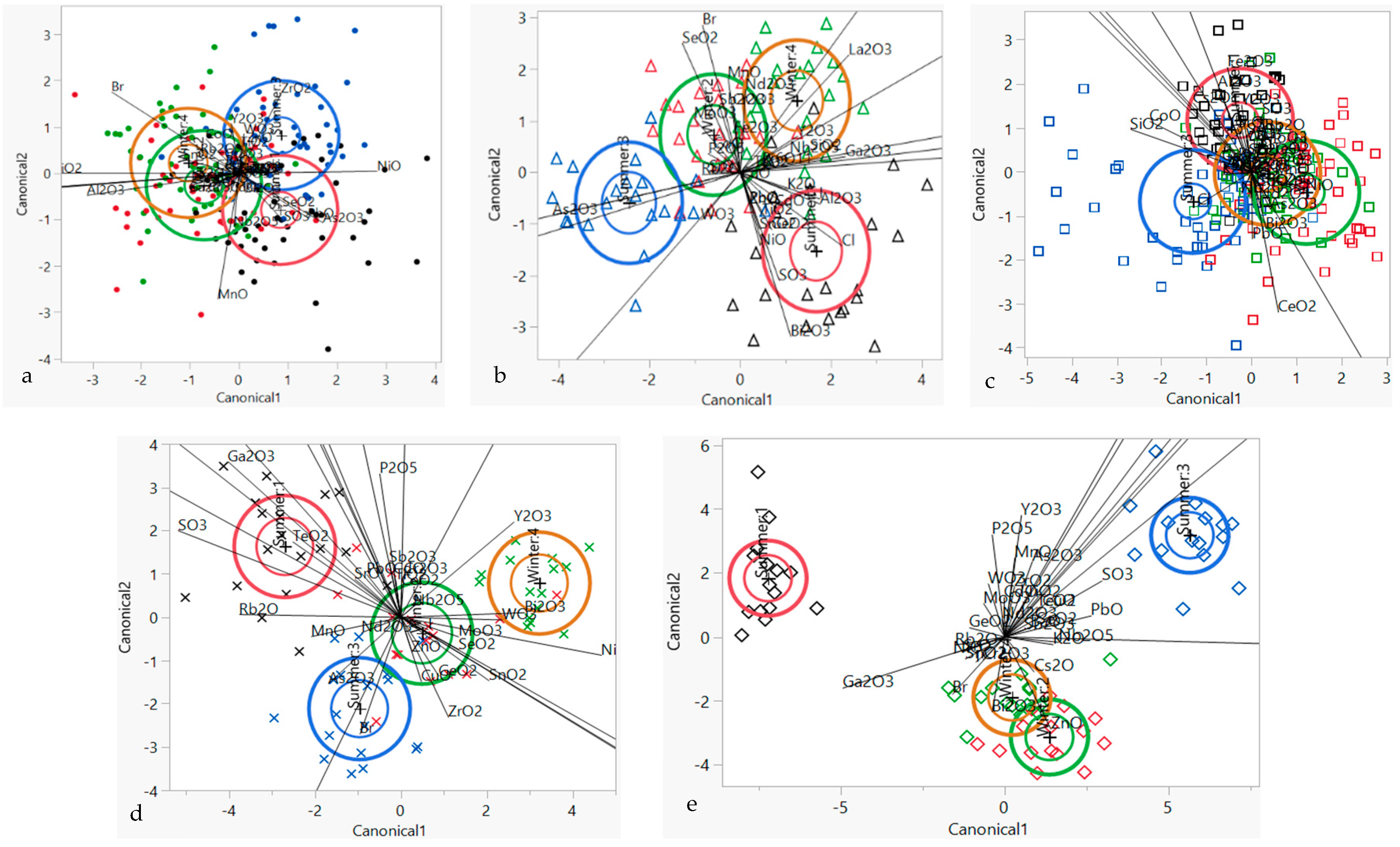
3.5. Supervised Chemometric Techniques—LDA
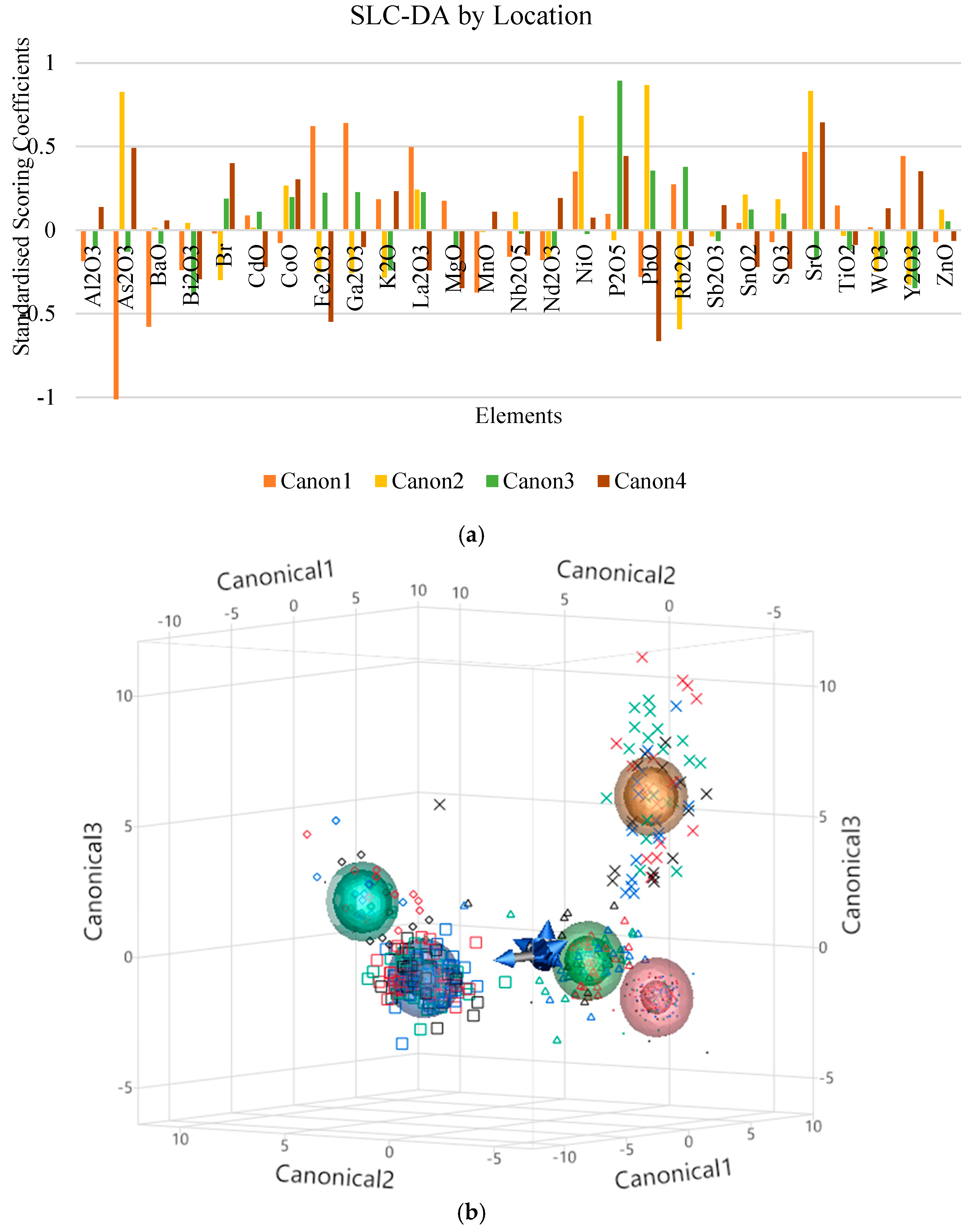
3.6. Supervised Chemometric Techniques—Stepwise Linear Canonical Discriminant Analysis (SLC-DA)
3.7. Supervised Chemometric Techniques—Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gauci, M.; Deidun, A.; Schembri, P. Faunistic diversity of Maltese pocket sandy and shingle beaches: Are these of conservation value? Oceanologia 2005, 47, 219–241. [Google Scholar]
- Schembri, P.J. Physical geography and ecology of the Maltese Islands: A brief overview. In Malta: Food, Agriculture, Fisheries and the Environment; Busuttil, S., Lerin, F., Mizzi, L., Eds.; Options Méditerranéennes ser.B: Etudes et Recherches No7; CIHEAM: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Cassar, L.F.; Stevens, D.T. Coastal sand Dunes Under Siege: A Guide to Conservation for Environmental Managers. University of Malta. International Environment Institute. Available online: https://www.um.edu.mt/library/oar/handle/123456789/45793 (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Robledo Ardila, P.A.; Álvarez-Alonso, R.; Árcega-Cabrera, F.; Durán Valsero, J.J.; Morales García, R.; Lamas-Cosío, E.; Oceguera-Vargas, I.; DelValls, A. Assessment and Review of Heavy Metals Pollution in Sediments of the Mediterranean Sea. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Amier, Y.A.; Bonanomi, G.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M. Assessment of heavy metals contamination and ecological risks in coastal sediments of the Mediterranean seashore. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 63, 103017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.F.; Nasr, S.M.; Okbah, M.A. Potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments from the Mediterranean coast. Egypt. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahdy, H.; Khaled, A. Heavy Metals Contamination in Sediments of the Western Part of Egyptian Mediterranean Sea. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2009, 3, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar]
- Saddik, M.; Fadili, A.; Makan, A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments along the Mediterranean coast of Morocco. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantzi, I.; Shimmield, T.M.; Pergantis, S.A.; Papageorgiou, N.; Black, K.D.; Karakassis, I. Heavy metals, trace elements and sediment geochemistry at four Mediterranean fish farms. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duodu, G.O.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Potential bioavailability assessment, source apportionment and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediment of Brisbane River estuary, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bilali, L.; Rasmussen, P.E.; Hall, G.E.M.; Fortin, D. Role of sediment composition in trace metal distribution in lake sediments. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Ide, Y.; Sato, D.; Kench, P.S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yokoki, H.; Kayanne, H. Heavy metal contamination of coastal lagoon sediments: Fongafale Islet, Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kang, X.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Song, J.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y. Heavy metals in surface sediments along the Weihai coast, China: Distribution, sources and contamination assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesar, A. Análisis Ecotoxicológico Integrado de la Contaminación Marina en los Sedimentos de la Costa De Murcia: El Caso de Portmán, Sudeste–España. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Murcia, Murcia, Spain, January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Palanques, A.; Diaz, J.I. Anthropogenic heavy metal pollution in the sediments of the Barcelona continental shelf (Northwestern Mediterranean). Mar. Environ. Res. 1994, 38, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzopardi, I.; Lia, F.; Costa, C. Assessment of Heavy Metal Distributions in Sand Beaches in the Maltese Islands. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sikaily, A. Health risk assessment in relation to heavy metals pollution of western Mediterranean Sea. Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Biol Fish 2003, 7, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontas, A.; Uluturhan, E.; Akcali, I.; Darilmaz, E.; Altay, O. Spatial Distribution Patterns, Sources of Heavy Metals, and Relation to Ecological Risk of Surface Sediments of the Cyprus Northern Shelf (Eastern Mediterranean). Environ. Forensics 2015, 16, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, M.; Kucuksezgin, F.; Atalar, M.; Akcali, B. Geochemistry of the northern Cyprus (NE Mediterranean) shelf sediments: Implications for anthropogenic and lithogenic impact. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asare, E.A.; Iya, N.I.D.; Kwabena, D.E. Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry. Eurasian J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 14, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, S.R.G.; Nozaki, J.; De Oliveira, E.; Do Nascimento Filho, V.F.; Aragão, P.H.A.; Scarminio, I.S.; Barreto, W.J. Comparison of metal analysis in sediments using EDXRF and ICP-OES with the HCl and Tessie extraction methods. Talanta 2004, 64, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, W.; El-Saeed, M.; Khalil, A.; Fikry, M. Detection of heavy metal elements by using advanced optical techniques. J. Egypt. Soc. Basic Sci.-Phys. 2024, 1, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaeteanu, G.; Maria, R.; Mot, A. An overview of methods used for quantification of heavy metal contents in vegetal samples. Romanian J. Ecol. Environ. Chem. 2021, 3, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, N.K.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Rathi, M.S.; Khanna, P.P.; Purohit, K.K. Trace Element Estimation in Soils: An Appraisal of Ed-Xrf Technique Using Group Analysis Scheme. J. Trace Microprobe Tech. 2002, 20, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreščanin, V.; Mikelić, I.L.; Mikelić, L.; Lulić, S. Applicability of MiniPal 4 compact EDXRF spectrometer for soil and sediment analysis. X-ray Spectrom. 2008, 37, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arado, O.D.; Rizo, O.D.; López-Pino, N.; D’Alessandro, K.; Olivares, S.; Gelen, A.; Casanova, O.A.; Padilla, F.; Corrales, Y.; Maidana, N.L. Evaluation of the InSTEC’s EDXRF assembly for Marine Sediment Pollution Studies. AIP Conf. Proc. 2009, 1139, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Barroso, M.; García-Morales, J.L.; Coello, M.D.; Quiroga, J. An assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediment using statistical analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 163, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, P.A.R.; Alonso, R.Á.; Valsero, J.J.D.; García, R.M.; Cabrera, F.Á.; Cosío, E.L.; Laforet, S.D. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in marine sediments from southwest of Mallorca island, Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 16852–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briffa, J.; Blundell, R.; Sinagra, E.; Grech, J. Validation of X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer Technique to Determine Heavy Metal Concentrations in Soil Samples. Glob. J. Sci. Front. Res. 2022, 22, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.R.B.; Makara, C.N.; Munaro, A.P.; Schnitzler, D.C.; Wastowski, A.D.; Poleto, C. Comparison of the analytical performance of EDXRF and FAAS techniques in the determination of metal species concentrations using protocol 3050B (USEPA). Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2016, 14, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.J.; Slemmons, A.K.; Canavan, H.E. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Methods for Environmental Characterization of Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2318–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzweiler, J.; Vendemiatto, M.A. Analysis of Sediments and Soils by X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Using Matrix Corrections Based on Fundamental Parameters. Geostand. Geoanalytical Res. 2004, 28, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tykot, R.H. A Decade of Portable (Hand-Held) X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer Analysis of Obsidian in the Mediterranean: Many Advantages and Few Limitations. MRS Adv. 2017, 2, 1769–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzoni, L.; Kulchytska, O.; Ruschioni, G. XRF Semi-Quantitative Analysis and Multivariate Statistics for the Classification of Obsidian Flows in the Mediterranean Area. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.; Song, W.; Long, W.; Zhu, R.; Chang, R.; Zhang, L. Evaluation of 20 Elements in Soils and Sediments by ED-XRF of Monochromatic Excitation. Metals. 2022, 12, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olawoyin, R.; Heidrich, B.; Oyewole, S.; Okareh, O.T.; McGlothlin, C.W. Chemometric analysis of ecological toxicants in petrochemical and industrial environments. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škrbić, B.; Đurišić-Mladenović, N. Chemometric interpretation of heavy metal patterns in soils worldwide. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Toriman, M.E.; Juahir, H.; Zain, S.M.; Habir, N.L.A.; Retnam, A.; Kamaruddin, M.K.A.; Umar, R.; Azid, A. Spatial assessment and source identification of heavy metals pollution in surface water using several chemometric techniques. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauler, R.; Peré-Trepat, E.; Lacorte, S.; Barceló, D. Chemometrics Modelling of Environmental Data. June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hanć, A.; Komorowicz, I.; Sek, K.; Baralkiewicz, D. Test of the relationships between the content of heavy metals in sewage sludge and source of their pollution by chemometric methods. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2009, 44, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; O’Connor, D.; Nathanail, P.; Tian, L.; Ma, Y. Integrated GIS and multivariate statistical analysis for regional scale assessment of heavy metal soil contamination: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, M.G.; Ilhan, S. Multivariate Analyses to Determine the Origin of Potentially Harmful Heavy Metals in Beach and Dune Sediments from Kizkalesi Coast (Mersin). Turkey. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeonov, V.; Einax, J.; Tsakovski, S.; Kraft, J. Multivariate statistical assessment of polluted soils. Open Chem. 2005, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qishlaqi, A.; Moore, F. Statistical Analysis of Accumulation and Sources of Heavy Metals Occurrence in Agricultural Soils of Khoshk River Banks, Shiraz, Iran. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2007, 2, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Shan, Y.; Shao, W. A Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of an oasis agricultural region in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857 Pt 3, 159543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. Monte Carlo Simulation-Based Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Soil Pollution —A Case Study in the Qixia Mining Area, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2012, 18, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Martín, J.D. Bioavailability and health risk of toxic heavy metals (As, Hg, Pb and Cd) in urban soils: A Monte Carlo simulation approach. Environ. Res. 2022, 214 Pt 1, 113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, P.; Hu, Z.; Shu, Q.; Chen, Y. Identification of the sources and influencing factors of the spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments along the northern Jiangsu coast. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesiada, M. Simulations in health risk assessment. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2001, 14, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cova, T.F.; Pereira, J.L.; Pais, A.A. Is standard multivariate analysis sufficient in clinical and epidemiological studies? J. Biomed. Inform. 2013, 46, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zielinski, A.A.F.; Haminiuk, C.W.I.; Nunes, C.A.; Schnitzler, E.; van Ruth, S.M.; Granato, D. Chemical Composition, Sensory Properties, Provenance, and Bioactivity of Fruit Juices as Assessed by Chemometrics: A Critical Review and Guideline. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootveld, M. Introduction to the Applications of Chemometric Techniques in “Omics” Research: Common Pitfalls, Misconceptions and “Rights and Wrongs”; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sde Vallejuelo, F.-O.; Arana, G.; de Diego, A.; Madariaga, J.M. Pattern recognition and classification of sediments according to their metal content using chemometric tools. A case study: The estuary of Nerbioi-Ibaizabal River (Bilbao, Basque Country). Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, E.; Friedman, J.H. A Statistical View of Some Chemometrics Regression Tools. Technometrics 1993, 35, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szefer, P. Chapter 18 Application of Chemometric Techniques in Analytical Evaluation of Biological and Environmental Samples. 2003. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/CHAPTER-18-APPLICATION-OF-CHEMOMETRIC-TECHNIQUES-IN-Szefer/fc4bb2391b95d30f5f6e66154a9842f9e2909c69 (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Bianco, L. Geochemistry, mineralogy and textural properties of the lower globigerina limestone used in the built heritage. Minerals 2021, 11, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchuk, V.; Yaroshenko, I.; Legin, A.; Semenov, V.; Kirsanov, D. Application of chemometric methods to XRF-data—A tutorial review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1040, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lia, F.; Mangion, M.Z.; Farrugia, C. Application of Fourier Transform Mid-Infra-Red Attenuated Total Reflectance (FT-MIR-ATR) for the authentication of Maltese extra virgin olive oil. Riv. Ital. Delle Sostanze Grasse May 2021, 98, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.C.; Liong, C.-Y.; Jemain, A.A. Partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) for classification of high-dimensional (HD) data: A review of contemporary practice strategies and knowledge gaps. Analyst 2018, 143, 3526–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.G.N. Accuracy, Sensitivity and Specificity Measurement of Various Classification Techniques on Healthcare Data. IOSR J. Comput. Eng. 2013, 11, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, N.; Singh, K.K.; Singh, A. Chapter 5—Diagnosing of disease using machine learning. In Machine Learning and the Internet of Medical Things in Healthcare; Singh, K.K., Elhoseny, M., Singh, A., Elngar, A.A., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearn, T. Sensitivity and Specificity. NIR News 2009, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
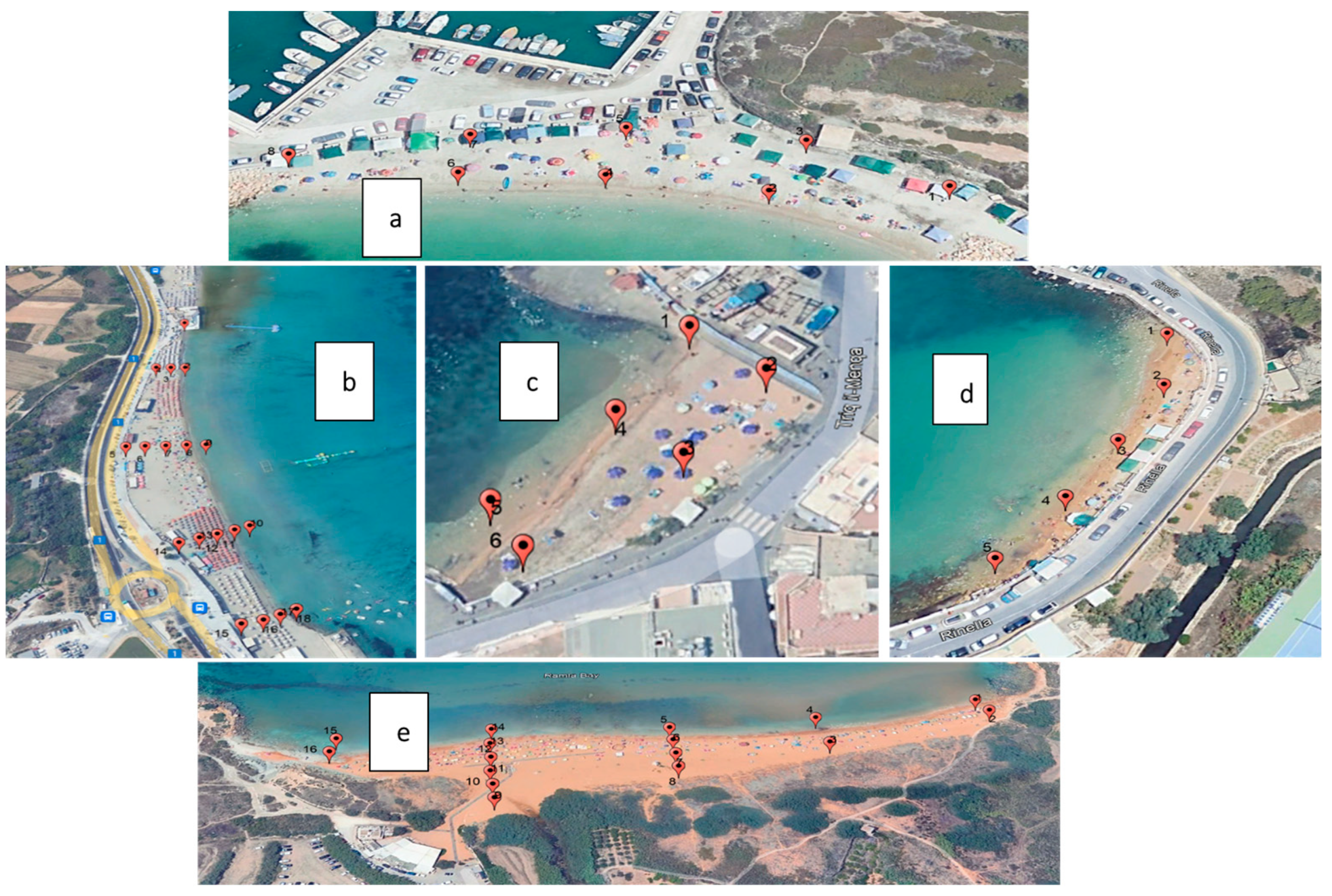

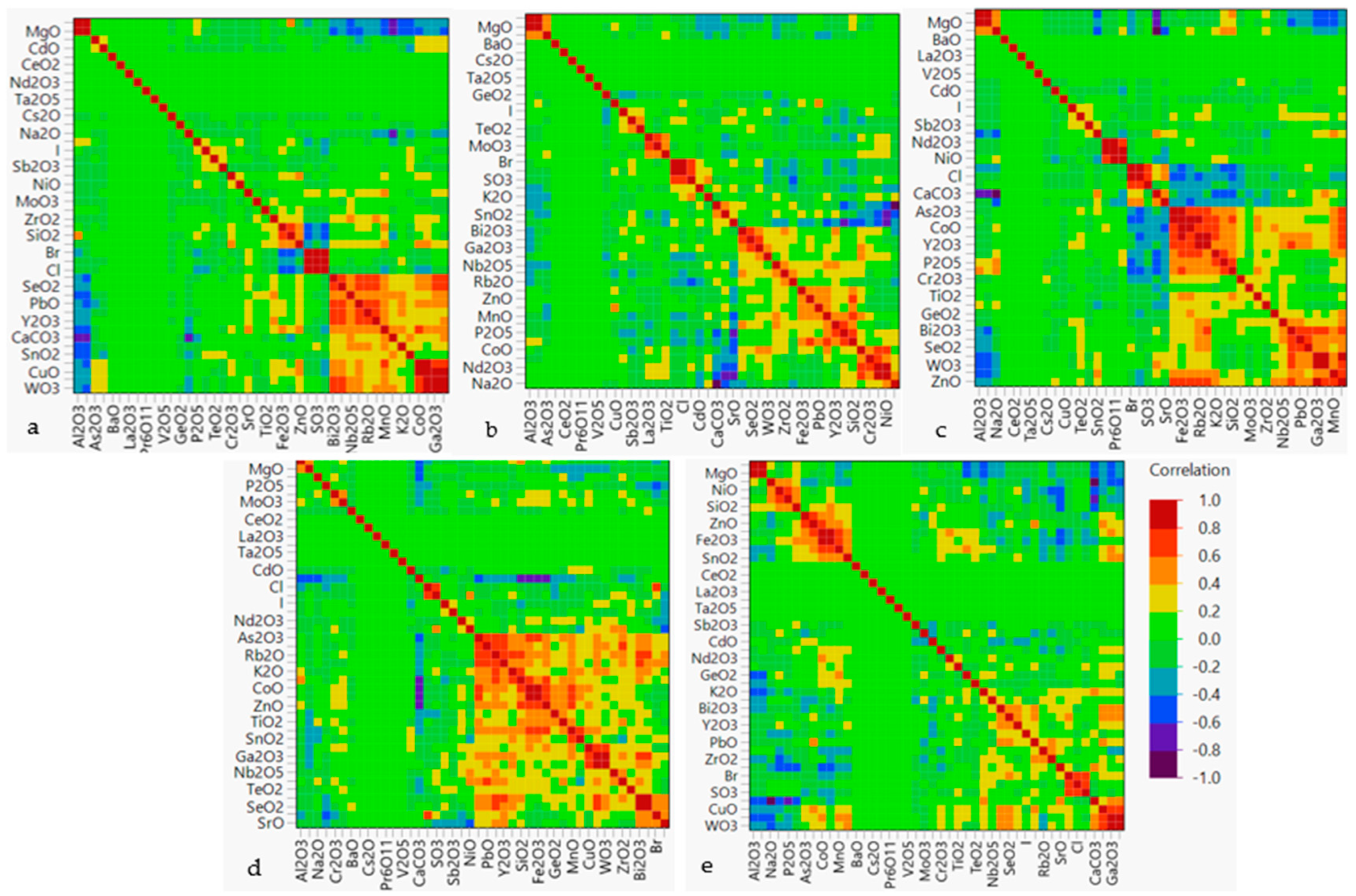


| Bay | % Water Content | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Għadira Bay | Average | 17.804 | 8.013 |
| Standard Deviation | 8.662 | 0.350 | |
| Ballut Reserve Bay | Average | 16.506 | 7.495 |
| Standard Deviation | 2.952 | 0.280 | |
| Marsalforn Bay | Average | 7.866 | 6.885 |
| Standard Deviation | 3.996 | 0.255 | |
| Ramla Bay | Average | 11.152 | 7.604 |
| Standard Deviation | 6.082 | 0.556 | |
| Rinella Bay | Average | 15.877 | 7.344 |
| Standard Deviation | 8.255 | 0.208 |
| Element | Ghadira Bay | Ballut Reserve Bay | Ramla Bay | Marsalforn Bay | Rinella Bay | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Conc. | Std. Error | % Conc. | Std. Error | % Conc. | Std. Error | % Conc. | Std. Error | % Conc. | Std. Error | |
| Al2O3 | 0.18344 | 0.02081 | 0.16022 | 0.02832 | 0.16109 | 0.02161 | 0.38461 | 0.05902 | 0.14927 | 0.02758 |
| As2O3 | 0.00029 | 0.00003 | 0.00023 | 0.00007 | 0.00555 | 0.00006 | 0.00180 | 0.00008 | 0.00099 | 0.00005 |
| Bi2O3 | 0.00233 | 0.00004 | 0.00252 | 0.00007 | 0.00200 | 0.00004 | 0.00178 | 0.00008 | 0.00236 | 0.00008 |
| CdO | 0.00126 | 0.00003 | 0.00132 | 0.00008 | 0.00122 | 0.00003 | 0.00125 | 0.00007 | 0.00124 | 0.00005 |
| CeO2 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00036 | 0.00018 | 0.00004 | 0.00004 | 0.00008 | 0.00008 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| CoO | 0.00174 | 0.00004 | 0.00223 | 0.00008 | 0.00976 | 0.00022 | 0.01259 | 0.00080 | 0.00737 | 0.00051 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.00040 | 0.00010 | 0.00211 | 0.00037 | 0.00152 | 0.00023 | 0.00212 | 0.00050 | 0.00194 | 0.00047 |
| Cs2O | 0.00003 | 0.00003 | 0.00040 | 0.00029 | 0.00008 | 0.00006 | 0.00041 | 0.00030 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 |
| CuO | 0.00266 | 0.00004 | 0.00423 | 0.00031 | 0.00264 | 0.00035 | 0.00299 | 0.00019 | 0.00458 | 0.00021 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.28217 | 0.00425 | 0.29454 | 0.00783 | 2.14177 | 0.04414 | 3.14241 | 0.21297 | 1.85277 | 0.12152 |
| Ga2O3 | 0.00133 | 0.00002 | 0.00153 | 0.00005 | 0.00117 | 0.00002 | 0.00121 | 0.00006 | 0.00132 | 0.00006 |
| GeO2 | 0.00013 | 0.00002 | 0.00029 | 0.00006 | 0.00050 | 0.00003 | 0.00047 | 0.00005 | 0.00027 | 0.00005 |
| La2O3 | 0.00030 | 0.00030 | 0.00663 | 0.00304 | 0.00046 | 0.00046 | 0.00505 | 0.00245 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| MgO | 0.64304 | 0.06887 | 0.43748 | 0.09222 | 0.52885 | 0.07213 | 0.61854 | 0.14603 | 0.72577 | 0.13309 |
| MnO | 0.00790 | 0.00020 | 0.00738 | 0.00036 | 0.01853 | 0.00031 | 0.01697 | 0.00092 | 0.01358 | 0.00097 |
| MoO3 | 0.00002 | 0.00000 | 0.00003 | 0.00001 | 0.00004 | 0.00001 | 0.00011 | 0.00003 | 0.00004 | 0.00001 |
| Nb2O5 | 0.00028 | 0.00002 | 0.00019 | 0.00002 | 0.00026 | 0.00001 | 0.00030 | 0.00004 | 0.00023 | 0.00002 |
| Nd2O3 | 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.00218 | 0.00073 | 0.00082 | 0.00030 | 0.00312 | 0.00095 | 0.00023 | 0.00016 |
| NiO | 0.00011 | 0.00006 | 0.00110 | 0.00025 | 0.00032 | 0.00009 | 0.00081 | 0.00026 | 0.00028 | 0.00006 |
| P2O5 | 0.26229 | 0.00461 | 0.49111 | 0.01565 | 0.37449 | 0.00813 | 1.20701 | 0.03905 | 0.28645 | 0.00531 |
| PbO | 0.00245 | 0.00004 | 0.00374 | 0.00014 | 0.00247 | 0.00005 | 0.00313 | 0.00017 | 0.00953 | 0.00014 |
| Pr6O11 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00013 | 0.00013 | 0.00015 | 0.00011 | 0.00027 | 0.00027 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| Rb2O | 0.00109 | 0.00002 | 0.00126 | 0.00003 | 0.00113 | 0.00002 | 0.00144 | 0.00006 | 0.00112 | 0.00004 |
| Sb2O3 | 0.00249 | 0.00011 | 0.00290 | 0.00026 | 0.00267 | 0.00014 | 0.00267 | 0.00030 | 0.00217 | 0.00025 |
| SeO2 | 0.00131 | 0.00002 | 0.00144 | 0.00005 | 0.00102 | 0.00002 | 0.00100 | 0.00005 | 0.00124 | 0.00004 |
| SnO2 | 0.01582 | 0.00004 | 0.01550 | 0.00010 | 0.01648 | 0.00006 | 0.01662 | 0.00009 | 0.01702 | 0.00018 |
| SrO | 0.08731 | 0.00060 | 0.15000 | 0.00131 | 0.04753 | 0.00064 | 0.05671 | 0.00124 | 0.16048 | 0.00192 |
| TeO2 | 0.00200 | 0.00009 | 0.00244 | 0.00022 | 0.00235 | 0.00009 | 0.00272 | 0.00019 | 0.00213 | 0.00011 |
| TiO2 | 0.00720 | 0.00084 | 0.00731 | 0.00160 | 0.01274 | 0.00087 | 0.02479 | 0.00307 | 0.01680 | 0.00279 |
| V2O5 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00062 | 0.00031 | 0.00006 | 0.00004 | 0.00068 | 0.00035 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| WO3 | 0.00233 | 0.00004 | 0.00256 | 0.00008 | 0.00206 | 0.00005 | 0.00196 | 0.00010 | 0.00243 | 0.00013 |
| Y2O3 | 0.00172 | 0.00002 | 0.00193 | 0.00006 | 0.00181 | 0.00003 | 0.00218 | 0.00009 | 0.00141 | 0.00004 |
| ZnO | 0.00227 | 0.00006 | 0.00372 | 0.00007 | 0.00260 | 0.00005 | 0.00452 | 0.00074 | 0.00889 | 0.00022 |
| ZrO2 | 0.00139 | 0.00018 | 0.00217 | 0.00039 | 0.00118 | 0.00012 | 0.00295 | 0.00071 | 0.00131 | 0.00016 |
| Element | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | H10 | H11 | H12 | H13 | H14 | H15 | H16 | H17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | Not computed | ||||||||||||||||
| As2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| BaO | |||||||||||||||||
| Bi2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Br | |||||||||||||||||
| CaCO3 | |||||||||||||||||
| CdO | |||||||||||||||||
| CeO2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cl | |||||||||||||||||
| CoO | |||||||||||||||||
| Cr2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Cs2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| CuO | |||||||||||||||||
| Fe2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Ga2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| GeO2 | |||||||||||||||||
| I | |||||||||||||||||
| K2O | |||||||||||||||||
| La2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| MgO | |||||||||||||||||
| MnO | |||||||||||||||||
| MoO3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Na2O | |||||||||||||||||
| Nb2O5 | |||||||||||||||||
| Nd2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| NiO | |||||||||||||||||
| P2O5 | |||||||||||||||||
| PbO | |||||||||||||||||
| Pr6O11 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rb2O | |||||||||||||||||
| Sb2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| SeO2 | |||||||||||||||||
| SiO2 | |||||||||||||||||
| SnO2 | |||||||||||||||||
| SO3 | |||||||||||||||||
| SrO | |||||||||||||||||
| TeO2 | |||||||||||||||||
| TiO2 | |||||||||||||||||
| V2O5 | |||||||||||||||||
| WO3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Y2O3 | |||||||||||||||||
| ZnO | |||||||||||||||||
| ZrO2 |
 Retained
Retained  Rejected.
Rejected.| Group | Eigenvalues | Percentage | Canonical Correlation | Wilks’ Lambda | Approx. F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEASON | 0.768 | 5.068 | |||
| CANONICAL 1 | 0.189 | 66.967 | 0.399 | ||
| CANONICAL 2 | 0.067 | 23.706 | 0.251 | ||
| CANONICAL 3 | 0.026 | 9.327 | 0.160 | ||
| LOCATION | 0.0000586 | 230.269 | |||
| CANONICAL 1 | 37.453 | 59.129 | 0.987 | ||
| CANONICAL 2 | 17.712 | 27.963 | 0.973 | ||
| CANONICAL 3 | 5.569 | 8.792 | 0.921 | ||
| CANONICAL 4 | 2.607 | 4.116 | 0.850 | ||
| DEPTH | 0.970 | 4.653 | |||
| CANONICAL 1 | 0.030 | 97.206 | 0.170 | ||
| CANONICAL 2 | 0.001 | 2.794 | 0.029 | ||
| DISTANCE FROM SHORELINE | 0.614 | 5.639 | |||
| CANONICAL 1 | 0.258 | 48.614 | 0.453 | ||
| CANONICAL 2 | 0.172 | 32.362 | 0.383 | ||
| CANONICAL 3 | 0.063 | 11.826 | 0.243 | ||
| CANONICAL 4 | 0.023 | 4.346 | 0.150 | ||
| CANONICAL 5 | 0.015 | 2.851 | 0.122 | ||
| a | ||||
| Groups | Season | Location | Depth | Distance from Shoreline |
| Factors | 3 | 14 | 1 | 12 |
| VIP > 0.8 | 18 | 15 | 17 | 16 |
| % Cumulative X | 55.619 | 96.773 | 32.465 | 92.012 |
| % Cumulative Y | 9.245 | 86.487 | 1.544 | 11.204 |
| PRESS | * | 0.391 | * | * |
| T2 | * | 1.428 | * | * |
| p > T2 | * | 0.870 | * | * |
| % Accuracy (R2) | * | 86.067% | * | * |
| No. of Included Misclassified Observations. | 183 | 13 | 333 | 425 |
| b | ||||
| No. of Excluded. Misclassified Observations | 46 | 7 | 83 | 107 |
| % Included Misclassified Observations | 36.895% | 2.621% | 67.137% | 85.685% |
| % Excluded Misclassified Observations | 37.398% | 5.691% | 67.480% | 86.992% |
| % Misclassified Accuracy | 36.995% | 3.231% | 67.205% | 85.945% |
| % Sensitivity | 60.968% | 99.739% | 99.390% | 97.507% |
| % Specificity | 61.564% | 98.208% | 1.675% | 22.848% |
| % Prediction | 61.564% | 99.479% | 66.476% | 83.881% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, C.; Lia, F.; Sinagra, E. Seasonal and Spatial Discrimination of Sandy Beaches Using Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis: A Comparative Study of Maltese Bays. Environments 2024, 11, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11120299
Costa C, Lia F, Sinagra E. Seasonal and Spatial Discrimination of Sandy Beaches Using Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis: A Comparative Study of Maltese Bays. Environments. 2024; 11(12):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11120299
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Christine, Frederick Lia, and Emmanuel Sinagra. 2024. "Seasonal and Spatial Discrimination of Sandy Beaches Using Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis: A Comparative Study of Maltese Bays" Environments 11, no. 12: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11120299
APA StyleCosta, C., Lia, F., & Sinagra, E. (2024). Seasonal and Spatial Discrimination of Sandy Beaches Using Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis: A Comparative Study of Maltese Bays. Environments, 11(12), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments11120299






