The Contribution of the Hulene-B Waste Dump (Maputo, Mozambique) to the Contamination of Rhizosphere Soils, Edible Plants, Stream Waters, and Groundwaters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
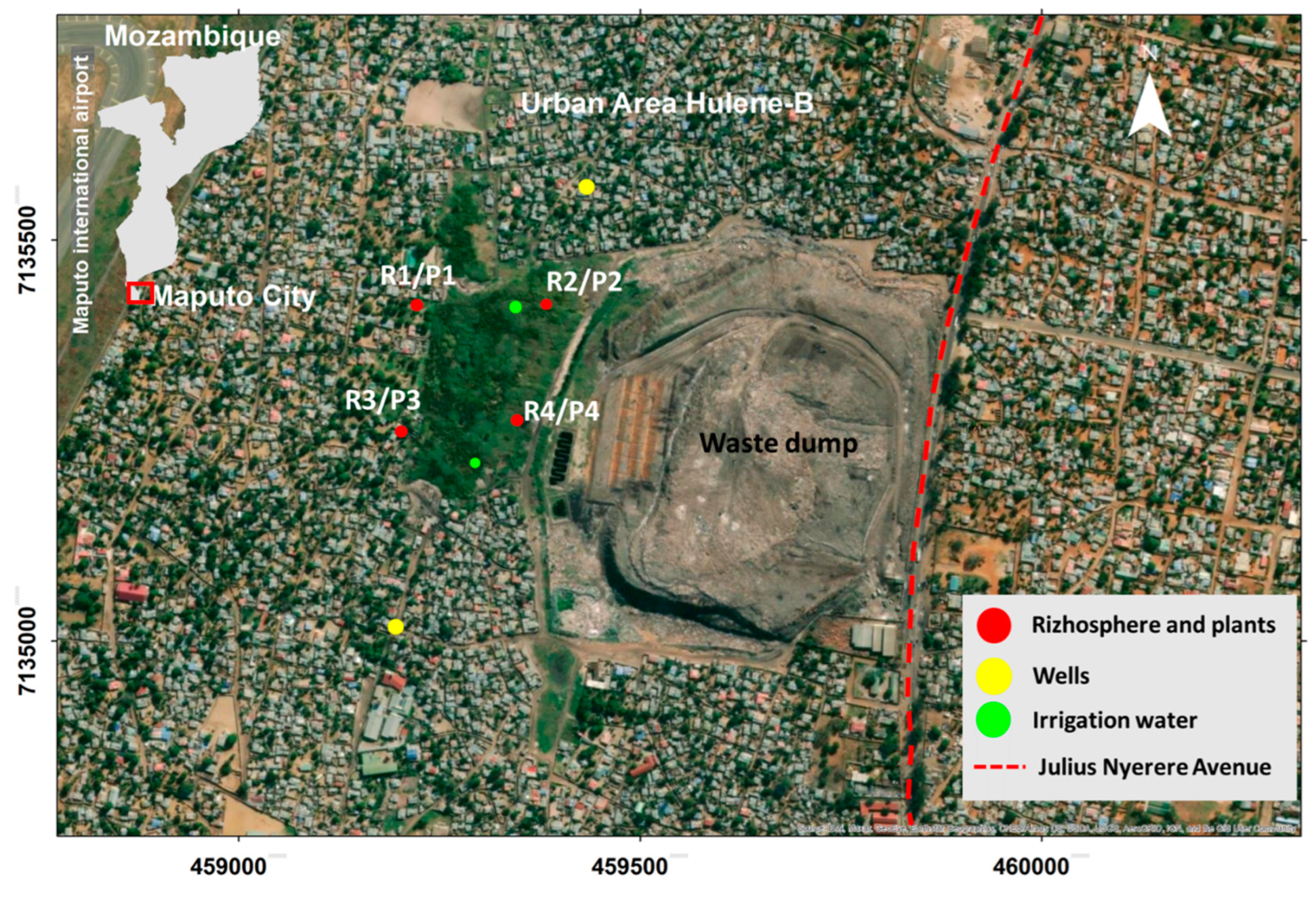
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Rhizosphere Sampling and Analysis
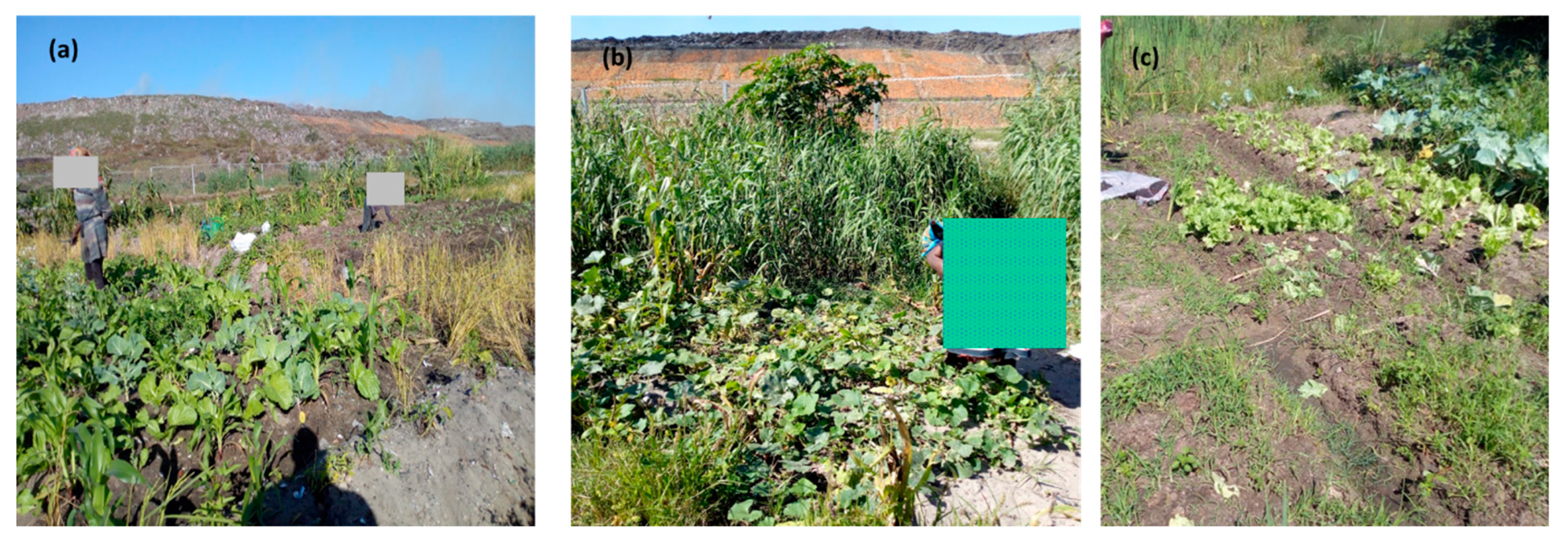
2.3. Edible Plants Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Soil Indexes and Health Risk Assessment (SHRA)
2.6. Soil/Plant Transfer Factor (TF)
2.7. Plant Health Risk Assessment (PHRA)
2.8. Water Pollution Index (WPI)
2.9. Water Health Risk Assessment (WHRA)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Analysis
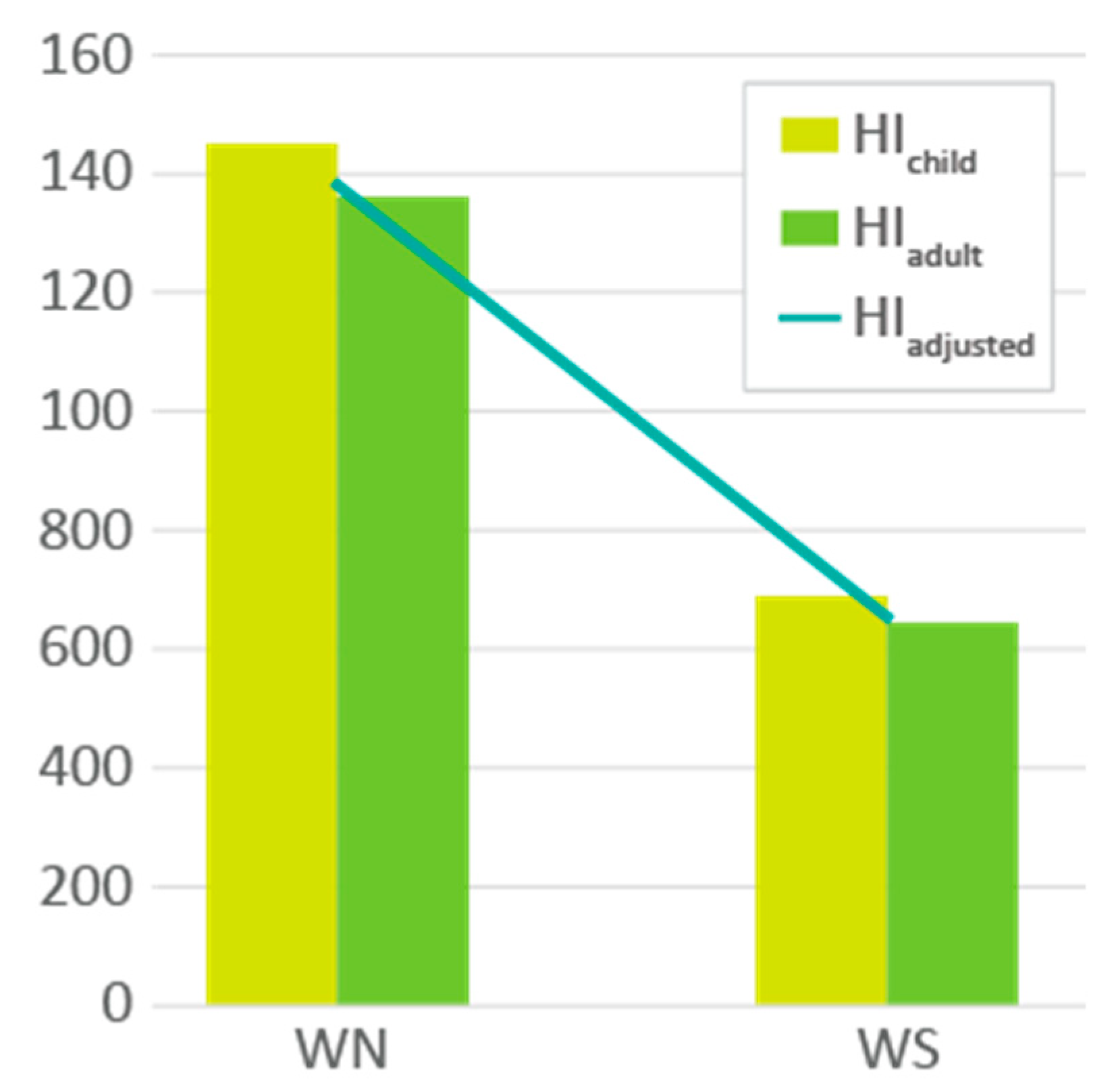
3.2. Water Analysis
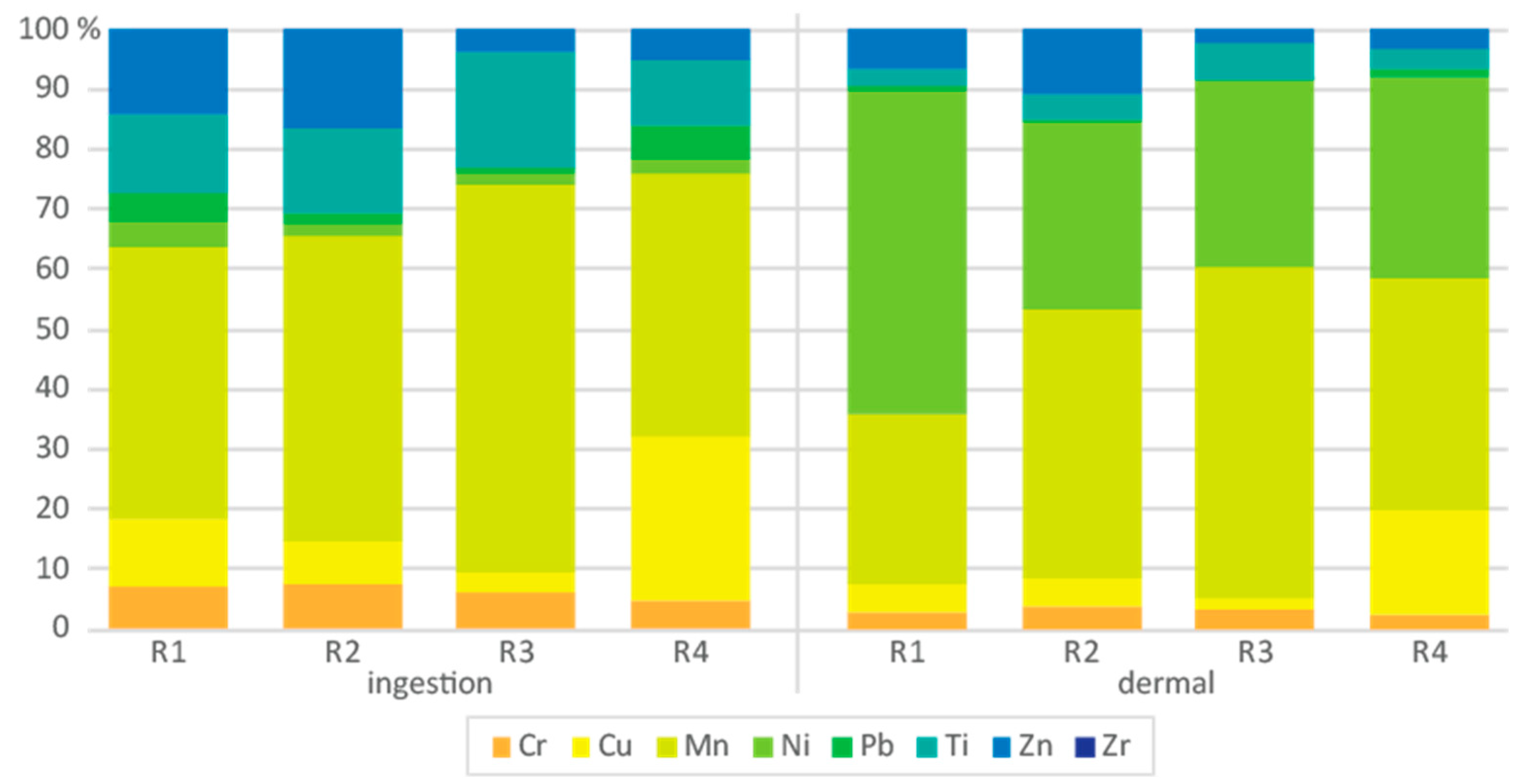
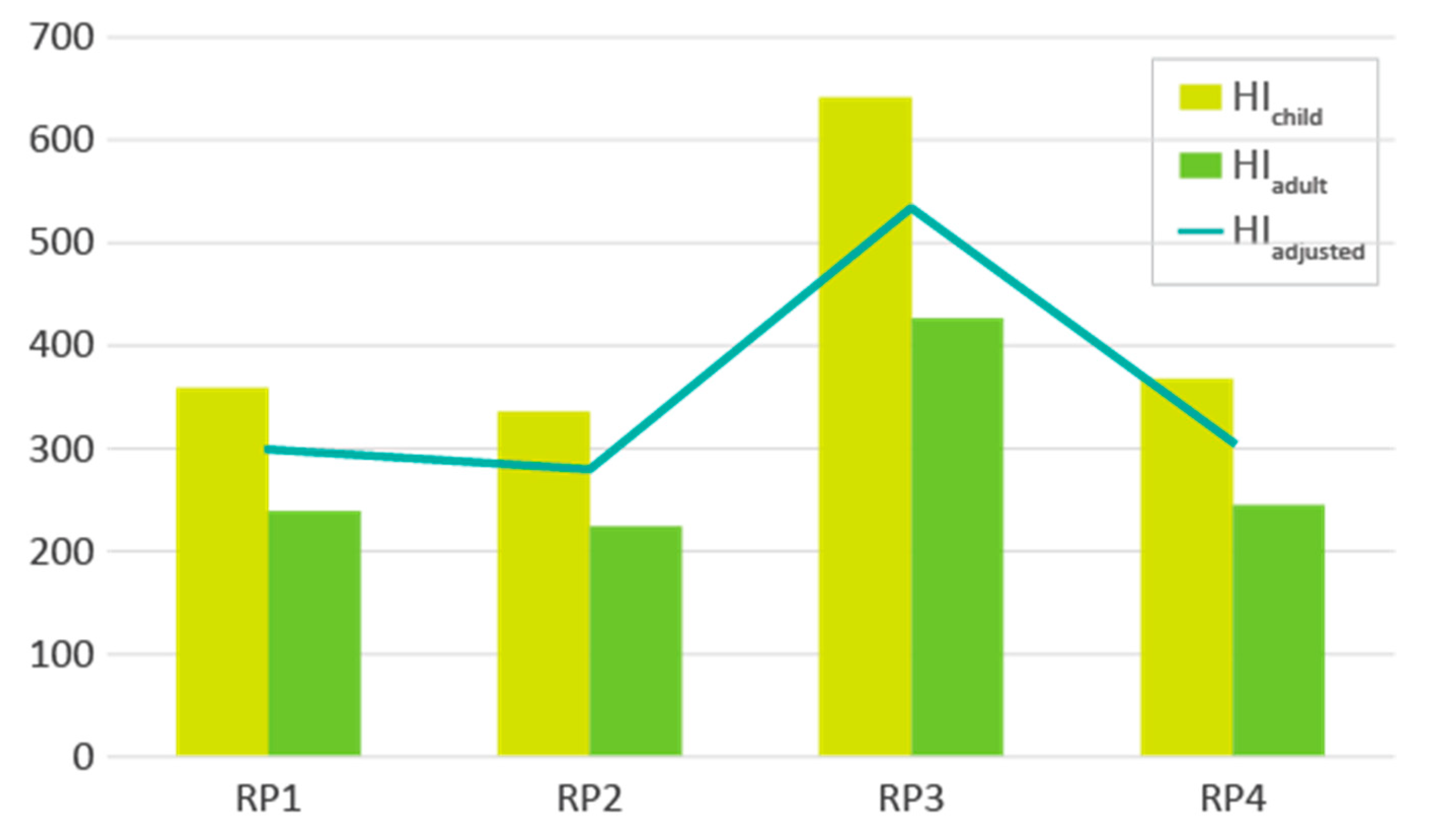
3.3. Edible Plants
3.4. Data Integration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dharwal, M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Sarin, V.; Gola, K. The state of solid waste management for sustainable development in India: Current state and future potential. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 60, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, A.K.; Ibelli-Bianco, C.; Anache, J.A.; Coutinho, J.V.; Pelinson, N.S.; Nobrega, J.; Rosalem, L.M.; Leite, C.M.; Niviadonski, L.M.; Manastella, C.; et al. Pollution threat to water and soil quality by dumpsites and non-sanitary landfills in Brazil: A review. Waste Manag. 2021, 131, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, D.; Banerji, S. Urban hydrodynamics in the planned township of New Town, West Bengal, India. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 123, 102277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Song, K.; He, X.; Peng, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, J. Identification of Groundwater Pollution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of a Landfill in a Low Permeability Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M.; Yoneda, K.; Mohd-Zaki, Z.; Amir, A.; Othman, N. Heavy metals in leachate, impacted soils and natural soils of different landfills in Malaysia: An alarming threat. Chemosphere 2020, 267, 128874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, F.; Tareq, S.M. Impact of landfill leachate contamination on surface and groundwater of Bangladesh: A systematic review and possible public health risks assessment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattak, S.A.; Rashid, A.; Tariq, M.; Ali, L.; Gao, X.; Ayub, M.; Javed, A. Potential risk and source distribution of groundwater contamination by mercury in district Swabi, Pakistan: Application of multivariate study. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 2279–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongyuan, S.; Khantamoon, T.; Aendo, P.; Binot, A.; Tulayakul, P. Ecological and health risk assessment, carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects of heavy metals contamination in the soil from municipal solid waste landfill in Central, Thailand. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 27, 876–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.; González, I.; Martín, J.M.; Vázquez, M.A.; Ortiz, P. Risk assessment of particle dispersion and trace element contamination from mine-waste dumps. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 37, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, A. Role of temperature, wind, and precipitation in heavy metal contamination at copper mines: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 4056–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongdala, N.; Tran, H.-D.; Xuan, T.D.; Teschke, R.; Khanh, T.D. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Water, Soil, and Plants of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Vientiane, Laos. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; An, J.; Yin, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, B.; Wei, S. Heavy metals uptake and translocation of typical wetland plants and their ecological effects on the coastal soil of a contaminated bay in Northeast China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 803, 149871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kaur, I.; Nagpal, A.K. Contamination of rice crop with potentially toxic elements and associated human health risks—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 12282–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, V.; Krishnan, S.; Kumar, S.; Nejad, Z.D.; Khan, M.M.; Alam, J. Evaluating heavy metals contamination in soil and vegetables in the region of North India: Levels, transfer and potential human health risk analysis. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 82, 103563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, W.-T.; Zhou, X.; Liu, L.; Gu, J.-F.; Wang, W.-L.; Zou, J.-L.; Tian, T.; Peng, P.-Q.; Liao, B.-H. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Vegetable Species Planted in Contaminated Soils and the Health Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, S.; Agüero, J.; Dolle, P.; Fernández, E.; Schmidt, C.; Yang, M. Perspectives of Urban Agriculture in Maputo and Cape Town. 2018. Available online: https://www.sle-berlin.de/files/sle/publikationen/S%20275-Maputo-Internet-Klein.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Application of Geophysics in geo-environmental diagnosis on the surroundings of the Hulene-B waste dump, Maputo, Mozambique. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 185, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C. Da Problemática Ambiental à Mudança: Rumo à um Mundo Melhor; Editora Escolar: Maputo, Mozambique, 2012; ISBN 0A9789896700300. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Tvedten, I.; Candiracci, S. “Flooding our eyes with rubbish”: Urban waste management in Maputo, Mozambique. Environ. Urban. 2018, 30, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendón, D.I.; Haldorsen, S.; Chen, J.; Hankin, S.; Nogueira, G.; Momade, F.; Achimo, M.; Muiuane, E.; Mugabe, J.; Stigter, T.Y. Hydrogeochemical aquifer characterization and its implication for groundwater development in the Maputo district, Mozambique. Quat. Int. 2019, 547, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, G.; Stigter, T.; Zhou, Y.; Mussa, F.; Juizo, D. Understanding groundwater salinization mechanisms to secure freshwater resources in the water-scarce city of Maputo, Mozambique. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 661, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Characterization of the Dynamics of Leachate Contamination Plumes in the Surroundings of the Hulene-B Waste Dump in Maputo, Mozambique. Environments 2022, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, E.M.; Jermy, C.A.; Schreiner, H.D. Urban Geology of Maputo, Mozambique; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2006; Volume 338, pp. 1–13. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.606.7220&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Soil Risk Assessment in the Surrounding Area of Hulene-B Waste Dump, Maputo (Mozambique). Geosciences 2022, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INE. Boletim de Estatísticas Demográficas e Sociais, Maputo Cidade 2019; Instituto Nacional de Estatistica: Maputo, Mozambique, 2020. Available online: https://www.ine.gov.mz/estatisticas/estatisticas-demograficas-e-indicadores-sociais/boletim-de-indicadores-demograficos-22-de-julho-de-2020.pdf/at_download/fileinportuguese (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Matsinhe, F.O.; Paulo, M. Estudo Etnográfico sobre os catadores de Lixo da Lixeira de Hulene (Maputo). Cad. De África Contemp. 2020, 3, 11–28. [Google Scholar]
- dos Muchangos, L.S.; Tokai, A.; Hanashima, A. Analyzing the structure of barriers to municipal solid waste management policy planning in Maputo city, Mozambique. Environ. Dev. 2015, 16, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrão, D.A.G. Evaluation of Removal and Disposal of Solid Waste in Maputo City, Mozambique. Master’s Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2006. Available online: https://open.uct.ac.za/bitstream/handle/11427/4851/thesis_sci_2006_ferrao_d_a_g.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Palalane, J.; Segala, I.O. Urbanização e Desenvolvimento Municipal em Moçambique: Gestão de Resíduos Sólidos. 2008. Available online: https://limpezapublica.com.br/urbanizacao-e-desenvolvimento-municipal-em-mocambique-capitulo-gestao-de-residuos-solidos/ (accessed on 20 October 2021). (In Portuguese).
- VOA (Voice of America News). Desabamento de Lixeira Deixa 17 Mortos em Maputo. 2018. Available online: https://www.voaportugues.com/a/desabamento-lixeira-17-mortos-maputo/4260624.html (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Muchimbane, A.B.D.A. Estudo dos Indicadores de Contaminação das Águas Subterrâneas por Sistemas de Saneamento “In Situ” Distrito Urbano 4, Cidade de Maputo-Moçambique. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momade, F.J.; Ferrara, M.; Oliveira, J.T. Notícia Explicativa da Carta Geológica 2532 Maputo (Escala 1:50000); Instituto Nacional de Estatistica: Maputo, Mozambique, 1996. (In Portuguese)
- CIAT. Climate-Smart Agriculture in Mozambique. Center for Tropical Agriculture. 2017. Available online: https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/sites/default/files/2019-06/CSA-inMozambique.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2022).
- USDA. Rangeland Soil Quality-Organic Matter; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. Available online: https://www.ftw.nrcs.usda.gov/glti (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Munsell Color. Munsell Soil Color Book; Color Charts; Munsell Color Company Inc.: Newburgh, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. Soil Quality Indicators: pH. Managing Soils and Terrestrial Systems; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. Available online: http://soils.usda.gov (accessed on 24 July 2022).
- USDA. Soil Health—Electrical Conductivity; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 1–9. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_052803.pdf (accessed on 22 July 2022).
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-154995-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Soni, R.; Gupta, S.K.; Shukla, D.P. Mercury, arsenic, lead and cadmium in waters of the Singrauli coal mining and power plants industrial zone, Central East India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candeias, C.; Ávila, P.F.; Sequeira, C.; Manuel, A.; Rocha, F. Potentially toxic elements dynamics in the soil rhizospheric-plant system in the active volcano of Fogo (Cape Verde) and interactions with human health. Catena 2021, 209, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, J.; Tan, M.L.; Kung, H.-T.; Johnson, V.C. Pollutant source, ecological and human health risks assessment of heavy metals in soils from coal mining areas in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAIS. The Risk Assessment Information System (RAIS); U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Operations Office (ORO): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2021. Available online: https://rais.ornl.gov/ (accessed on 24 July 2022).
- Candeias, C.; Da Silva, E.F.; Ávila, P.F.; Teixeira, J.P. Identifying Sources and Assessing Potential Risk of Exposure to Heavy Metals and Hazardous Materials in Mining Areas: The Case Study of Panasqueira Mine (Central Portugal) as an Example. Geosciences 2014, 4, 240–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehoiu, G.; Murarescu, O.; Radulescu, C.; Dulama, I.D.; Teodorescu, S.; Stirbescu, R.M.; Bucurica, I.A.; Stanescu, S.G. Heavy metals accumulation and translocation in native plants grown on tailing dumps and human health risk. Plant Soil 2020, 456, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunwale, T.O.; Ogar, P.A.; Kayode, G.F.; Salami, K.D.; Oyekunle, J.A.O.; Ogunfowokan, A.O.; Akindolani, O.A. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Toxicity Utilizing Eatable Vegetables from Poultry Farm Region of Osun State. J. Environ. Pollut. Hum. Health 2021, 9, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. In Volume I Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Rout, P.R.; Bae, J. The applicability of anaerobically treated domestic wastewater as a nutrient medium in hydroponic lettuce cultivation: Nitrogen toxicity and health risk assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 780, 146482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.-A.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Deng, C.; Nie, N. Assessment of Water Quality and Identification of Polluted Risky Regions Based on Field Observations & GIS in the Honghe River Watershed, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibare, A.O.; Ogungbile, P.O.; Ayeku, P.O. Evaluation of water pollution monitoring for heavy metal contamination: A case study of Agodi Reservoir, Oyo State, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Venkatayogi, S. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes and Integrated Interpretation with Water Quality Index Studies. Environ. Process 2018, 5, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Duan, R.; Li, P.; Li, W. Water quality characteristics and health risk assessment of main water supply reservoirs in Taizhou City, East China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assessment Int. J. 2021, 27, 2142–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Mercury in Drinking-Water, Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; WHO/SDE/WS, WHO/SDE/WSH/05.08/10; Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/mercuryfinal.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Ahmad, W.; Alharthy, R.D.; Zubair, M.; Ahmed, M.; Hameed, A.; Rafique, S. Toxic and heavy metals contamination assessment in soil and water to evaluate human health risk. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, B.; Mahapatra, D.M.; Sitharam, T.; Sivapullaiah, P.; Ramachandra, T. Physico-chemical and biological characterization of urban municipal landfill leachate. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajaje, K.; Ultra, V.U.; David, P.W.; Rantong, G. Rhizosphere properties and heavy metal accumulation of plants growing in the fly ash dumpsite, Morupule power plant, Botswana. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20637–20649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrbić, B.; Novaković, J.; Miljević, N. Mobility of heavy metals originating from bombing of industrial sites. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2002, 37, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sun, J.; Gui, H.; Xia, D.; Wang, Y. Physiochemical properties, heavy metal leaching characteristics and reutilization evaluations of solid ashes from municipal solid waste incinerator plants. Waste Manag. 2021, 138, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaaou, A.; Chikhaoui, M.; Naimi, M.; El Miad, A.K.; Achemrk, A.; Seif-Ennasr, M.; El Harche, S. Mapping soil salinity risk using the approach of soil salinity index and land cover: A case study from Tadla plain, Morocco. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wang, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, F. Crop yield and water productivity under salty water irrigation: A global meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Soil Health Quality Indicators: Chemical Properties, Soil Electrical Conductivity, 3rd ed.; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/health/assessment/?cid=stelprdb1237387 (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Huang, B.; Yuan, Z.; Li, D.; Zheng, M.; Nie, X.; Liao, Y. Effects of soil particle size on the adsorption, distribution, and migration behaviors of heavy metal(loid)s in soil: A review. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2020, 22, 1596–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisari, A.; Sujatha, C. Assessment of trace metal contamination in the Kol wetland, a Ramsar site, Southwest coast of India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, M.; Le Roux, J.; Mazerolles, R.; Bousserrhine, N. Assessment of leaching risk of trace metals, PAHs and PCBs from a brownfield located in a flooding zone. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 3600–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Soil properties and environmental risk assessment of soils in the surrounding area of Hulene-B waste dump, Maputo (Mozambique). Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D. Multielement Contamination of Land in the Margin of Highways. Land 2021, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Suburban areas in flames: Dispersion of potentially toxic elements from burned vegetation and buildings. Estimation of the associated ecological and human health risk. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asowata, I.T. Geophagic clay around Uteh-Uzalla near Benin: Mineral and trace elements compositions and possible health implications. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Nie, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, W. Cotransport of heavy metals and SiO2 particles at different temperatures by seepage. J. Hydrol. 2020, 597, 125771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Satyam, N.; Reddy, K.R.; Chrysochoou, M. Multiple heavy metal immobilization and strength improvement of contaminated soil using bio-mediated calcite precipitation technique. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 51827–51846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Integration of Electrical Resistivity and Modified DRASTIC Model to Assess Groundwater Vulnerability in the Surrounding Area of Hulene-B Waste Dump, Maputo, Mozambique. Water 2022, 14, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, Z.; Arani, M.H.; Panahande, M.; Kermani, M.; Kazemi, Z. Chemical quality assessment and health risk of heavy metals in groundwater sources around Saravan landfill, the northernmost province of Iran. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheela, V.R.S.; Goel, S.; John, M.; Dubey, B. Characterization of municipal solid waste based on seasonal variations, source and socio-economic aspects. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2021, 3, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennou, B.; El Meray, M.; Romane, A.; Arjouni, Y. Assessment of heavy metal availability (Pb, Cu, Cr, Cd, Zn) and speciation in contaminated soils and sediment of discharge by sequential extraction. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 5849–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githaiga, K.B.; Njuguna, S.M.; Gituru, R.W.; Yan, X. Water quality assessment, multivariate analysis and human health risks of heavy metals in eight major lakes in Kenya. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesil, H.; Molaey, R.; Calli, B.; Tugtas, A.E. Extent of bioleaching and bioavailability reduction of potentially toxic heavy metals from sewage sludge through pH-controlled fermentation. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CCME. Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environmental and Human Health-Nickel; Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment: Canberra, ACT, Canada, 2015. Available online: https://ccme.ca/en/res/nickel-canadian-soil-quality-guidelines-for-the-protection-of-environmental-and-human-health-en.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Ruengruehan, K.; Junggoth, R.; Suttibak, S.; Sirikoon, C.; Sanphoti, N. Contamination of Cadmium, Lead, Mercury and Manganese in Leachate from Open Dump, Controlled Dump and Sanitary Landfill Sites in Rural Thailand: A Case Study in Sakon Nakhon Province. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2021, 20, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.G.; Aly, A.A.; Ibrahim, H.M. Assessing the environmental impacts of municipal solid waste landfill leachate on groundwater and soil contamination in western Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamd, S.; Idris, A.M.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Phoungthong, K.; Ali, M.M.; Kabir, H. Geochemical variation and contamination level of potentially toxic elements in land-uses urban soils. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.R.; Ugarte, O.M.; Lima, L.H.V.; Silva, J.R.; da Silva, F.B.V.; Lins, S.A.D.S.; Nascimento, C.W.A.D. Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and edible parts of vegetables grown on sites contaminated by an abandoned steel plant in Havana. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, T.D.; Dougill, A.J.; Whitfield, S.; Peacock, C.L.; Eze, S.; Thierfelder, C. Combining local knowledge and soil science for integrated soil health assessments in conservation agriculture systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrell, R.; Egli, I. Iron bioavailability and dietary reference values. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, S1461–S1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Silver and zirconium phosphate. In Federal Register; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; Volume 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, G.; Eggenberger, U.; Schlumberger, S.; Mäder, U.K. Chemical associations and mobilization of heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration. Waste Manag. 2017, 62, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasooriya, S.; Diyabalanage, S.; Yatigammana, S.K.; Ileperuma, O.A.; Chandrajith, R. Major and trace elements in rice paddy soils in Sri Lanka with special emphasis on regions with endemic chronic kidney disease of undetermined origin. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 1841–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, I.; Ahmad, F.; Sharif, A.; Altaf, A.R.; Teng, H. Heavy metals assessment in water, soil, vegetables and their associated health risks via consumption of vegetables, District Kasur, Pakistan. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.U.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Abbas, Q.; Ullah, H.; Munir, M.A.M.; Fu, B. Pollution characteristics and human health risks of potentially (eco)toxic elements (PTEs) in road dust from metropolitan area of Hefei, China. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Manganese Compounds Hazard Summary. In Health Effects Notebook for Hazardous Air Pollutants; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-10/documents/manganese.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Wani, A.L.; Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (Ans), E.P.O.F.A.A.N.S.A.T.F.; Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Dusemund, B.; Filipič, M.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; et al. Evaluation of four new studies on the potential toxicity of titanium dioxide used as a food additive (E 171). EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, G.A.V.; Stauber, J.L.; Holland, A.; Koppel, D.J.; Van Genderen, E.J.; Ryan, A.C.; Jolley, D.F. The Influence of pH on Zinc Lability and Toxicity to a Tropical Freshwater Microalga. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 2836–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.V.; Piatak, N.M.; Bedinger, G.M. Zirconium and Hafnium. In U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1802; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. V1–V26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Air Pollution. In Compendium of WHO and Other UN Guidance on Health and Environment Chapter 2; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–25. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/who-compendium-on-health-and-environment/who_compendium_chapter2_01092021.pdf?sfvrsn=14f84896_5 (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- WHO. WHO Guideline for Clinical Management of Exposure to Lead Executive Summary; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240036888 (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Ekawanti, A.; Priyambodo, S.; Kadriyan, H.; Syamsun, A.; A Lestarini, I.; Wirasaka, G.; Ardianti, A.R. Mercury pollution in water and its effect on renal function of school age children in gold mining area Sekotong West Lombok. IOP Conf. Series Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 637, 012055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonge, B.A.; Larissa, M.T.; Egbe, A.M.; Afanga, Y.A.; Fru, N.G.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M. An assessment of heavy metal exposure risk associated with consumption of cabbage and carrot grown in a tropical Savannah region. Sustain. Environ. 2021, 7, 1909860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, M.; Hwang, H.-M. Influence of Highway Pavement on Metals in Road Dust: A Case Study in Houston, Texas. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obasi, P.N.; Akudinobi, B.B. Potential health risk and levels of heavy metals in water resources of lead–zinc mining communities of Abakaliki, southeast Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ID | pH | EC | OM | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 8.1 | 510 | 3.6 | blackish |
| R2 | 8.4 | 571 | 1.7 | greyish |
| R3 | 8.2 | 310 | 0.98 | greyish |
| R4 | 8.4 | 810 | 2.3 | greyish |
| Var | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | Bkg * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 18.5 | 13.0 | 6.8 | 8.9 | 33.5 |
| Cu | 184 | 88 | 24 | 351 | 9.2 |
| Fe | 15,966 | 5954 | 3195 | 5480 | 6801 |
| Mn | 153 | 120 | 93 | 113 | 140 |
| Ni | 14.6 | 4.2 | 2.6 | 4.9 | 3.9 |
| Pb | 156 | 39.0 | 9.7 | 156 | 7.8 |
| Ti | 2782 | 2116 | 1775 | 1703 | 1754 |
| Zn | 35.7 | 38.7 | 3.7 | 9.8 | 3.0 |
| Zr | 289 | 207 | 170 | 148 | 123 |
| Var | PI | PLI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | ||
| Cr | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| Cu | 20.0 | 9.6 | 2.6 | 38.2 | 4748 |
| Fe | 2.4 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| Mn | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.1 |
| Ni | 3.7 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.8 |
| Pb | 20.0 | 5.0 | 1.2 | 20.0 | 618 |
| Ti | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Zn | 11.9 | 7.2 | 0.4 | 3.3 | 26.4 |
| Zr | 2.4 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| Var | Samples | Guidelines | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS | WN | IWN | IWS | Drinking Water | Stream Water | Reference | |
| pH | 6.1 | 8.4 | 9.1 | 10.3 | 6.5−8.50 | 5.5–7.5 | WHO [53] |
| Pb | 6 | nd | 79 | nd | 10 | 20 | WHO [53] |
| Hg | 36 | 76 | nd | 25 | 6 | 5 | WHO [53] |
| Zn | 63 | 13 | 7 | 9 | 3 | ≤5.000 | WHO [53]; CCME [77] |
| ID | Pb | Hg | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|
| WS | 0.6 | 6.0 | 2.1 |
| WN | - | 12.7 | 4.3 |
| IWS | 4.0 | - | 1.8 |
| IWN | - | 5.0 | 0.6 |
| Var | RP1 | RP2 | RP3 | RP4 | AL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 974 | 852 | 2968 | 1161 | 2.3 a |
| Cu | 1142 | 1245 | 778 | 1099 | 10–40 a |
| Fe | 56,324 | 30,031 | 32,643 | 18,687 | 18 a |
| Mn | 1030 | 1183 | 1436 | 1544 | 500 a |
| Ni | 108 | 238 | 1128 | 538 | 10 a |
| Pb | 394 | 56 | 190 | nd | 0.3 a |
| Ti | 4990 | 5910 | 8392 | 3519 | 0.7 a |
| Zn | 5730 | 2596 | 1511 | 3519 | 50 a |
| Zr | nd | 761 | 708 | 198 | 4.2 b |
| Var | RP1 | RP2 | RP3 | RP4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIM | HRI | DIM | HRI | DIM | HRI | DIM | HRI | |
| Cr | 0.41 | 135.29 | 0.36 | 118.37 | 1.24 | 412.17 | 0.48 | 161.26 |
| Cu | 0.48 | 128.58 | 0.52 | 140.23 | 0.32 | 87.61 | 0.46 | 123.68 |
| Fe | 23.47 | 1.30 | 12.51 | 0.70 | 13.60 | 0.76 | 7.79 | 0.43 |
| Mn | 0.43 | 3.07 | 0.49 | 3.52 | 0.60 | 4.27 | 0.64 | 4.60 |
| Ni | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 2.35 | 0.22 | 1.12 |
| Pb | 0.16 | 11.73 | 0.02 | 1.67 | 0.08 | 5.65 | nd | nd |
| Ti | 2.08 | 2.97 | 2.46 | 3.52 | 3.50 | 5.00 | 1.47 | 2.09 |
| Zn | 2.39 | 7.96 | 1.08 | 3.61 | 0.63 | 2.10 | 1.47 | 4.89 |
| Zr | nd | nd | 0.32 | 0.08 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. The Contribution of the Hulene-B Waste Dump (Maputo, Mozambique) to the Contamination of Rhizosphere Soils, Edible Plants, Stream Waters, and Groundwaters. Environments 2023, 10, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030045
Bernardo B, Candeias C, Rocha F. The Contribution of the Hulene-B Waste Dump (Maputo, Mozambique) to the Contamination of Rhizosphere Soils, Edible Plants, Stream Waters, and Groundwaters. Environments. 2023; 10(3):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030045
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernardo, Bernardino, Carla Candeias, and Fernando Rocha. 2023. "The Contribution of the Hulene-B Waste Dump (Maputo, Mozambique) to the Contamination of Rhizosphere Soils, Edible Plants, Stream Waters, and Groundwaters" Environments 10, no. 3: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030045
APA StyleBernardo, B., Candeias, C., & Rocha, F. (2023). The Contribution of the Hulene-B Waste Dump (Maputo, Mozambique) to the Contamination of Rhizosphere Soils, Edible Plants, Stream Waters, and Groundwaters. Environments, 10(3), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10030045








