Ecotoxicological Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Waterworks Sludge Amended Soils Using Bermudagrass Bioassay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sludge and Plant Species
2.2. Pot Experiment
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Assessment Benchmark
2.5. Statistical Test
3. Results and Discussion
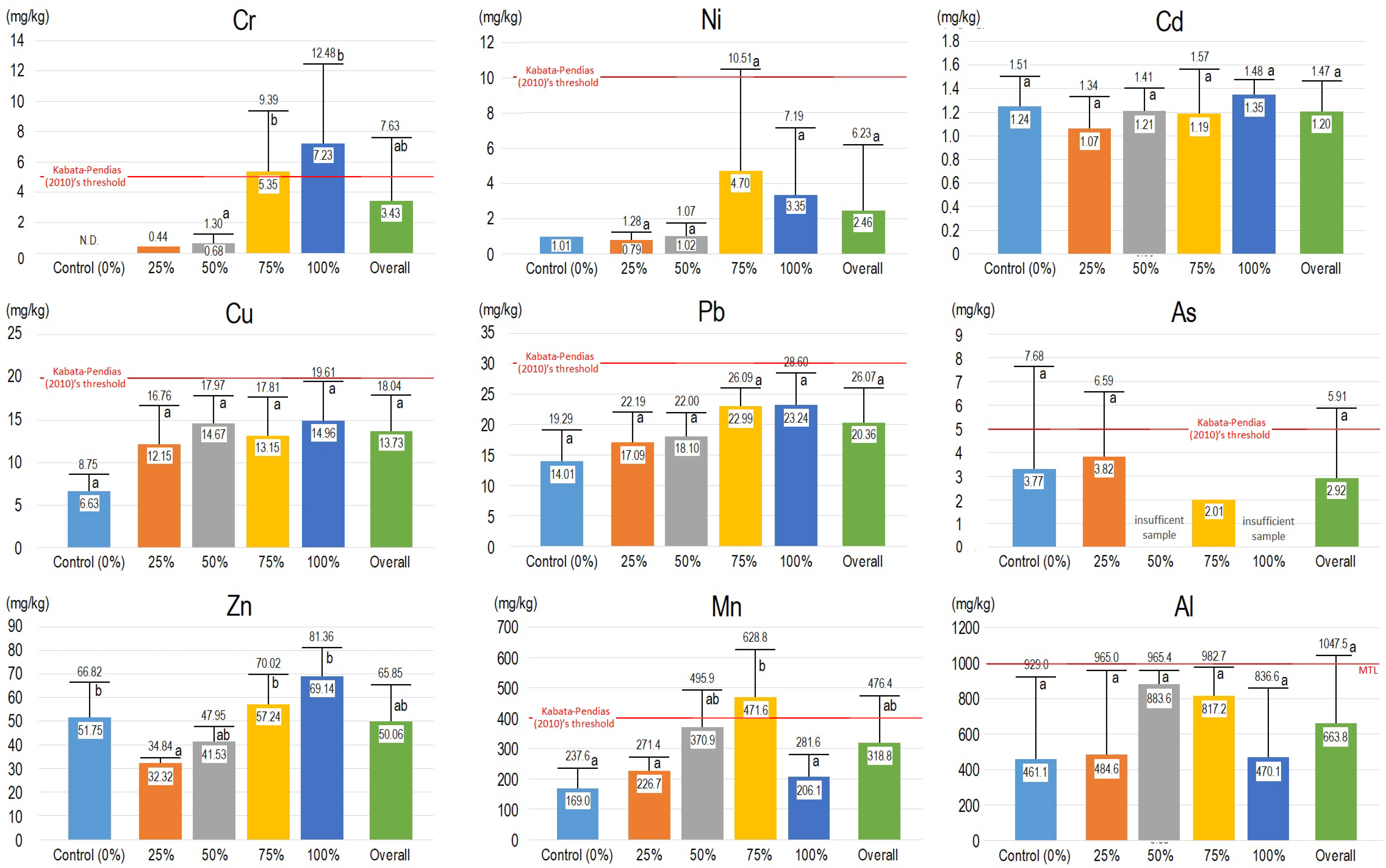
3.1. Experiment 1
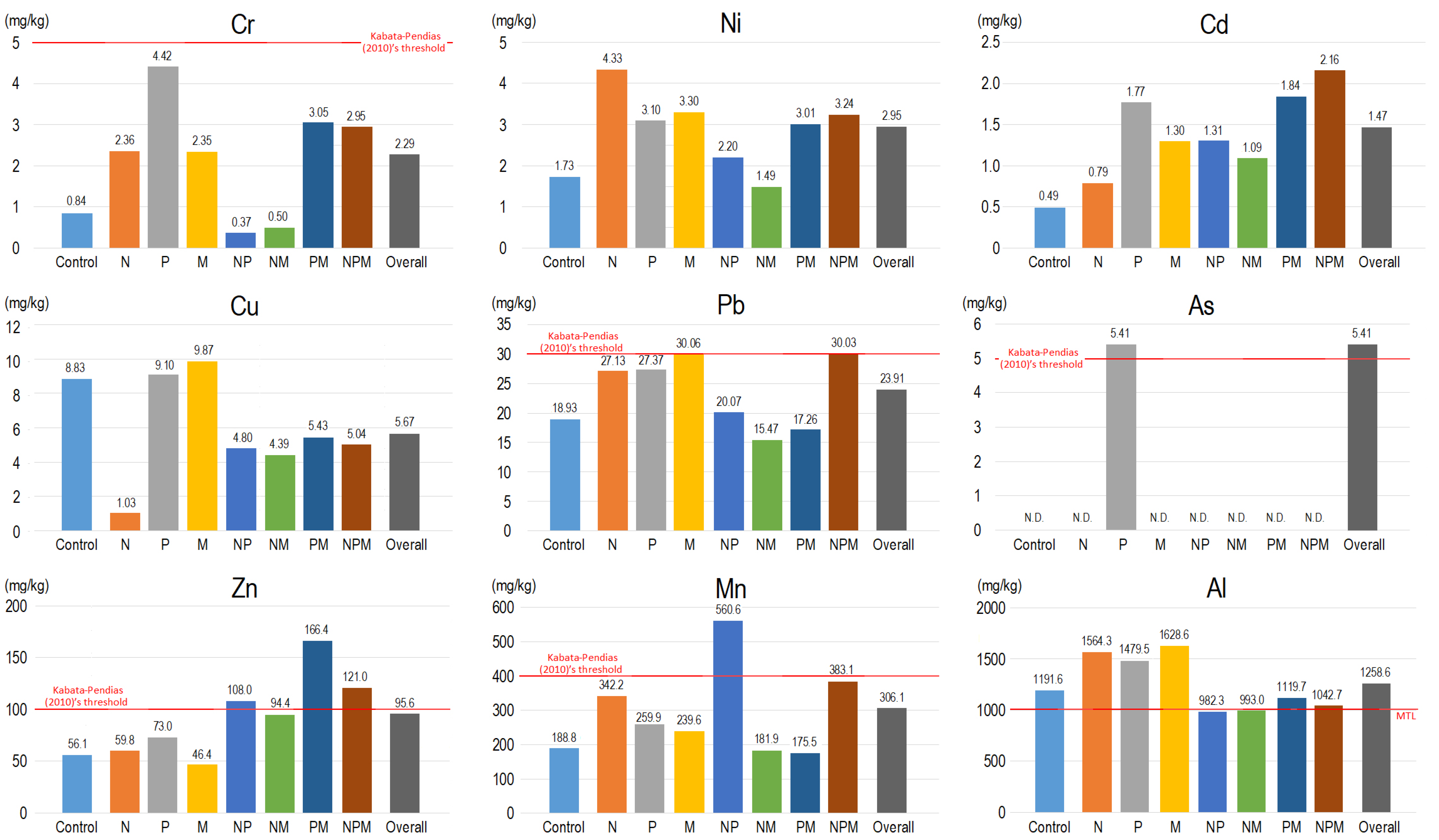
3.2. Experiment 2
4. Conclusions and Limitations
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meier, B.M.; Kayser, G.L.; Amjad, U.Q.; Bartram, J. Implementing an evolving human right through water and sanitation policy. Water Policy 2012, 15, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Drinking Water. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/drinking-water (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Bache, D.H.; Gregory, R. Flocs and separation processes in drinking water treatment: A review. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2010, 59, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, R.; Le, N.P. The role of organic matter and ionic composition in determining the surface charge of suspended particles in natural waters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1990, 44, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, A.; Zhao, Y. Constructive approaches toward water treatment works sludge management: An international review of beneficial reuses. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 37, 129–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nzihou, A.; Ren, B.; Lyczko, N.; Shen, C.; Kang, C.; Ji, B. Waterworks sludge: An underrated material for beneficial reuse in water and environmental engineering. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 4239–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, J.A.; Barbarick, K.A.; Elliott, H.A. Drinking water treatment residuals: A review of recent uses. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebosura, M.; Salehin, S.; Pikaar, I.; Kulandaivelu, J.; Jiang, G.; Keller, J.; Sharma, K.; Yuan, Z. Effects of in-sewer dosing of iron-rich drinking water sludge on wastewater collection and treatment systems. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, C.Y.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Aun, N.C.; Aldahdooh, M.A.A. Sustainable production of concrete with treated alum sludge. Construct. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.; Wheeler, R.; Stone, A.; Oliver, I. Potential alternative reuse pathways for water treatment residuals: Remaining barriers and questions—A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Department. Monitoring of Solid Waste in Hong Kong—Waste Statistics for 2017; Environmental Protection Department: Hong Kong, China, 2018.
- Environmental Bureau. Hong Kong Blueprint for Sustainable Use of Resources, 2013–2022; Government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, China, 2013. Available online: https://www.enb.gov.hk/en/files/WastePlan-E.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Environmental Protection Department. A Policy Framework for the Management of Municipal Solid Waste (2005–2014); Environmental Protection Department: Hong Kong, China, 2005. Available online: https://www.epd.gov.hk/epd/msw/htm_en/content.htm (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Tony, M.A. Valorization of undervalued aluminum-based waterworks sludge waste for the science of “The 5 Rs’ criteria”. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.E.; Lake, C.B.; Gagnon, G.A. Strategic pathways for the sustainable management of water treatment plant residuals. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2008, 7, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muisa, N.; Nhapi, I.; Ruziwa, W.; Manyuchi, M.M. Utilization of alum sludge as adsorbent for phosphorus removal in municipal wastewater: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Liu, R.B.; Morgan, D.; Wei, T. Enhancing wastewater remediation by drinking water treatment residual-augmented floating treatment wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanifar, H.; Deng, Y.; Wu, L.; Sarkar, D. Water treatment residual (WTR)-coated wood mulch for alleviation of toxic metals and phosphorus from polluted urban stormwater runoff. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhuge, Y.; Chow, C.W.K.; Keegan, A.; Li, D.; Pham, P.N.; Huang, J.; Siddique, R. Utilization of drinking water treatment sludge in concrete paving blocks: Microstructural analysis, durability and leaching properties. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Qi, W.; Zhai, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. Magnetic biochar synthesized with waterworks sludge and sewage sludge and its potential for methylene blue removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, E.A.; Basta, N.T. Characterization of drinking water treatment residuals for use as a soil substitute. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwandu, T.; Blake, L.I.; Nezomba, H.; Rurinda, J.; Chivasa, S.; Mtambanengwe, F.; Johnson, K.L. Waste to resource: Use of water treatment residual for increased maize productivity and micronutrient content. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 3359–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.L.; Chu, L.M.; Chan, S.H.; Ma, T.H. The potential use of waterworks sludge in greening: A bioassay with bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.]. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 55, 126856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, K.; Jayasinghe, G.; Surapaneni, A.; Hetherington, C. A review on alum sludge reuse with special reference to agricultural applications and future challenges. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, A.A.H.; Al-Wakel, S.F.A.; Assi, H.A.; Naji, L.A.; Naushad, M. Waterworks sludge-filter sand permeable reactive barrier for removal of toxic lead ions from contaminated groundwater. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Ahmad, K.; Alam, M. Sustainable management of water treatment sludge through 3“R” concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Lee, S.S.; Moon, H.-S.; Kang, I.M. Land application of alum sludge from water purification plant to acid mineral soil treated with acidic water. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2002, 48, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. D 3974; Standard Practices for Extraction of Trace Elements from Sediments. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1981.
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bezerra, M.A.; Santos, A.S.; dos Santos, W.N.L.; Novaes, C.G.; de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Oliveira, M.L.; Garcia, R.L. Atomic absorption spectrometry—A multi-element technique. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 100, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geotechnical Engineering Office. Guide to Rock and Soil Descriptions; Geotechnical Engineering Office: Hong Kong, China, 2017.
- Jim, C.Y. Trees and greening of Hong Kong’s urban landscape: Subaerial and soil constraints. In Remediation and Management of Degraded Lands; Wong, M.H., Wong, J.W.C., Baker, A.J.M., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, T.Y. Characterization of weathered volcanic rocks in Hong Kong. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 1999, 32, 318–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C. (Ed.) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Properties; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A.; Miller, R.; Keeney, D. (Eds.) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.; Page, A.; Helmke, P.; Loeppert, R. (Eds.) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3. Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.J.; Wang, X.-S.; Nandy, S. Confined groundwater zone and slope instability in weathered igneous rocks in Hong Kong. Eng. Geol. 2005, 80, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihtisham, M.; Liu, S.; Shahid, M.O.; Khan, N.; Lv, B.; Sarraf, M.; Ali, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Q. The optimized N, P, and K fertilization for bermudagrass integrated turf performance during the establishment and its importance for the sustainable management of urban green spaces. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, L.B.; Miller, G. Managing Bermudagrass Turf: Selection, Construction, Cultural Practices, and Pest Management Strategies; Sleeping Bear: Chelsea, UK, 2002.
- Basta, N.; Zupancic, R.; Dayton, E. Evaluating soil tests to predict bermudagrass growth in drinking water treatment residuals with phosphorus fertilizer. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Scheffran, J.; Qin, H.; You, Q. Climate-related flood risks and urban responses in the Pearl River Delta, China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maiti, S.K. Effect of organic manures on the growth of Cymbopogon citratus and Chrysopogon zizanioides for the phytoremediation of chromite-asbestos mine waste: A pot scale experiment. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2014, 17, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmaz, A.; Obek, E. The accumulation of arsenic, uranium, and boron in Lemna gibba L. exposed to secondary effluents. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabanli, M.; Yozukmaz, A.; Sel, F. Heavy metal accumulation in the leaves, stem and root of the invasive submerged Macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum L. (Haloragaceae): An example of Kadın Creek (Mugla, Turkey). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2014, 57, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Mineral Tolerance of Domestic Animals, 2nd ed.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.F.; Yamaji, N.; Shen, R.F.; Ma, J.F. The key to Mn homeostasis in plants: Regulation of Mn transporters. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, M.J.; Du Preez, H.H.; Van Vuren, H.J. The freshwater river crab, Potamonautes warreni, as a bioaccumulative indicator of iron and manganese pollution in two aquatic systems. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 41, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.R.; Day, S.D.; Kane, B. Nitrogen fertilization during planting and establishment of the urban forest: A collection of five studies. Urban For. Green. 2008, 7, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivertsen, T.; Garmo, T.H.; Lierhagen, S.; Bernhoft, A.; Steinnes, E. Geographical and botanical variation in concentrations of selenium, cobalt, iodine, zinc and other essential elements in sheep pasture plants in Norway. Acta Agric. Scand. A Anim. Sci. 2014, 64, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | (mg/kg) |
|---|---|
| Cr | 0.6 |
| Ni | 160 |
| Cd | 0.6 |
| Cu | 159 |
| Pb | 51 |
| As | 202 |
| Zn | 199 |
| Al | 112,000 |
| Mg | 1720 |
| Ca | 3,410 |
| Total nitrogen | 10,200 |
| Total phosphorus | 8750 |
| Chemical oxygen demand | 209,000 |
| Parameter | DG | VS |
|---|---|---|
| Soil pH | 5.34 | 4.88 |
| Exchangeable acidity (cmol/kg) | 1.44 | 1.15 |
| Electrical conductivity (mS/cm) | 5.66 | 1.08 |
| Total organic carbon (%) | 0.16 | 1.09 |
| Total nitrogen (%) | 0.11 | 0.09 |
| Total phosphorus (mg/kg) | 0.16 | 0.01 |
| Soil texture (sand%:silt%:clay%) | 72.3:16.6:11.1 | 33.1:25.8:41.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, S.L. Ecotoxicological Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Waterworks Sludge Amended Soils Using Bermudagrass Bioassay. Environments 2023, 10, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10020028
Ng SL. Ecotoxicological Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Waterworks Sludge Amended Soils Using Bermudagrass Bioassay. Environments. 2023; 10(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Sai Leung. 2023. "Ecotoxicological Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Waterworks Sludge Amended Soils Using Bermudagrass Bioassay" Environments 10, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10020028
APA StyleNg, S. L. (2023). Ecotoxicological Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Waterworks Sludge Amended Soils Using Bermudagrass Bioassay. Environments, 10(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10020028






