Abstract
Tire and road wear particles (TRWP), which contribute significantly to microplastic emission, are receiving more attention, but details about particle composition, translocation from source to sink, and particularly the possible effects on ecosystems are largely unknown. We examined the influence of native TRWP-containing sediments from two settling ponds on the mortality and behavior of the aquatic larvae of Chironomus riparius. Both sediments, whether pure or mixed with different proportions of quartz sand and suspended in water, led to increased mortalities with increasing concentrations and were shown to be oxygen consuming. Artificial aeration significantly reduced larval mortality in both sediments. Chironomid larvae show high tolerance to anoxic and polluted environments due to physiological and behavioral adaptations, such as the construction of vertical sediment tubes (chimneys), in which they create oxic compartments. A significant correlation was found between the proportion of contaminated sediment and the number of chimneys: the more contaminated sediment, the fewer chimneys were constructed. The number of chimneys per surviving larva decreased with an increased proportion of contaminated sediment in parallel to increased larval mortality. We hypothesize that contents of these sediments negatively impact the larvae’s ability to survive at low oxygen concentrations due to impairments of essential behavioral and physiological processes.
1. Introduction
Ecotoxicological research is inseparably linked with the ongoing and ever-changing challenges of environmental pollution [1]. When considering the human impact on aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, the topic of plastic pollution is inevitable. But its environmental impact is not limited to macroplastics (>20 mm) alone since it degrades into smaller pieces [2] of macro- or meso-plastics (5–20 mm), microplastics (MP; 0.001–5 mm; [2,3]), and even nanoplastics (NP; 1–1000 nm; [4]). These smaller particles have a higher mobility, can spread much further than their source material, and have a larger total surface area [2,3,5,6].
1.1. Microplastics (MP)
Since the presence of small synthetic fibers and plastic particles in the environment was first noticed [7,8], and since the term ‘microplastics’ was coined [9], countless studies have been published in this fast-growing field, and the extent of MP pollution and its ubiquity quickly became clear. There is evidence of the environmental accumulation of MP all around the world, from densely populated urban areas to even some of the most remote regions (e.g., [2,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]), and for the uptake and excretion of MP/NP via the intestinal tract of vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as its transfer along food chains [18,19]. During this process, the MP/NP particles can mechanically injure those epithelia that come into contact with them and lead to inflammation [20] or can induce immunotoxicity and disturb the gut microbiome [21].
1.2. Tire and Road Wear Particles (TRWP)
It has become clear that inappropriate waste disposal and littering were not the only sources of the large quantities of MP found across many different ecosystems. The abrasion from tires alone (e.g., cars, trucks, bikes) accounts for one-third of the yearly MP emission in societies with high mobility such as, e.g., Germany (330.000 t/a; [22]). Tires are composed of natural and synthetic rubber (elastomer), reinforcing agents (carbon black, silica, silanes), mineral oils, metal and textile reinforcements, vulcanization agents (ZnO, S, Se, Te), and additives such as preservatives (halogenated cyanoalkanes), antioxidants (amines, phenols), desiccants (calcium oxides), plasticizers (aromatic and aliphatic esters), processing aids (mineral oils, peptizers), and other organic compounds [23,24,25,26]. The formulations differ between different tire brands and vehicle types [26,27].
Several terms for tire-associated MP can be found in the current literature. Tire wear particles (TWP; e.g., [26]), road-associated microplastic particles (RAMP; e.g., [28]), and tire and road wear particles (TRWP; e.g., [24]) are most commonly used. Here, TRWP will be used (unless other literature is referenced) to refer to particles created by motorized traffic on paved roads containing a variety of known and indeterminate substances. This term names the two most important components and clarifies that they are created by the process of abrasion or wear.
As the size and shape of TRWP vary, so does their mode of transportation (air, rain, wind; [25,26,27,29]), and not much is known about their translocation from source to sink [25,26]. Settling ponds are artificial basins often very close to busy roads that catch road runoff and attempt to separate water and particles from each other by sedimentation before redirecting the water into connected running waters while retaining the sediment [30].
By now, existing data on TRWP strongly suggest that the particles and their leachates (heavy metals, PAHs, benzothiazoles, or resin acids; [26]) can pose a risk to exposed organisms. TRWP effects have been summarized by Wagner et al. [26]. Furthermore, a recent study by Tian et al. [31] demonstrated unanticipated risks to wildlife despite the testing, approval, and registration of chemicals in tires. The authors showed that N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N’-phenyl-1,4-benzenediamine (6PPD), a chemical that is used as an antiozonant in rubber tires all over the world, transforms into 6PPD-quinone by ozonation, which is highly toxic and causes acute mortality in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) when it reaches their habitat, usually by stormwater runoff. This study illustrates both the importance of the appropriate management of road runoff as well as the need for even more research to gather further information about the emission, composition, fate, and toxicity of TRWP. In this context, Wagner et al. [26] highlighted a need for studies that use ‘real’ TRWP from environmental samples in environmentally relevant concentrations. This requirement is taken into account in the present study.
1.3. Test Organism
The non-biting midge Chironomus riparius meigen, 1804, is a well-established and widely used test organism in ecotoxicology. This species belongs to the large, globally distributed family of Chironomidae with an estimated 15,000 species [32], and their aquatic larvae are among the most abundant biota across a large variety of freshwater ecosystems (up to 50,000 individuals/m2; [32,33]). They construct U-shaped tunnels or J-shaped tubes out of fine-grained sediments, stuck together by silk proteins [32,34]. The larvae of C. riparius are collector-gatherers or deposit feeders, which means that they feed on fine particulate organic matter (FPOM) and bacteria that accumulate on and in sediments. Only their head and anterior body extend outside the burrow, where they forage around its entrance, which reduces the risk of predation [32]. Disturbed larvae stop feeding until they find or construct a new tube [35].
1.3.1. Adaptations to Pollution and Anoxia
The movements of the unburied larvae were described by Brackenbury [36]. While swimming, the larvae form a ‘figure-of-eight’ shape that is typical for chironomids. During respiratory undulation, the whole body moves like a sinusoidal wave, usually inside or close to the animals’ dwellings in order to irrigate them with fresh, oxygen-rich water and to flush metabolites and CO2 out [32,36,37]. Both also facilitate and enable better oxygen uptake by creating a flow of oxygen-rich(er) water over their body surface [32,36]. Studies have shown a negative influence of selected pollutants on the locomotion and ventilation behavior of larvae [38,39]. Another very common stressor in freshwater ecosystems besides chemical pollution is the shortage of oxygen, especially in the fine sediments with high contents of organic matter, the typical habitat of C. riparius [32]. In response to low oxygen content, the larvae construct vertical ‘chimneys’ built up from sediment as an elongation of their burrows [37]. By doing so, the larvae can create ‘oxic sediment compartments’ in hypoxic or anoxic environments, which they irrigate with fresh, oxygen-rich surface water [37]. An increase in body undulation in and around the chimneys can also be observed and serves both oxygen uptake and chimney irrigation [37].
1.3.2. Hemoglobin
The larvae are also physiologically optimized for life at very low oxygen concentrations, which is mostly achieved through large quantities of hemoglobin (Hb), freely dissolved in the hemolymph of the animals, with a very high affinity to oxygen [40,41]. It is also suspected to play a role in removing toxic compounds from cells (pseudoperoxidase activity; monooxygenase-like activity; [32,40]), contributing to the resilience of the larvae against a wide array of pollutants.
1.4. Research Questions
With the present work, we meet the demand [26] to test native TRWP-containing sediment samples from the environment under environmentally relevant conditions for their toxicity to organisms that are behaviorally and physiologically adapted to sediment life. Larvae of C. riparius were exposed to these sediments under different conditions, and their effects on the mortality and behavior of the larvae were documented. In particular, we focused on the interplay of TRWP-contaminated sediment exposure and oxygen deficiency. The aim of this study was thus to get an exemplary impression of the extent to which real sediments from the runoff of busy roads have ecotoxicological significance for a freshwater species highly adapted to extreme conditions and to generally improve the data situation in this scarcely studied subject area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sediment Collection and Preparation
Two fine-grained TRWP-containing sediments from and around two settling ponds in Germany were collected and processed (dried, pulverized, and sieved). The settling ponds are located (i) close to Lake Halensee (HS) in Berlin, next to some of the most heavily traveled roads in Germany (52°29′42.1″ N 13°16′45.7″ E), and (ii) next to Highway B27 (B27), also a heavily traveled road connecting Stuttgart and Tübingen (48°32′02.2″ N 9°06′54.9″ E). The sediment from the settling pond at HS was obtained and processed by the Environmental Research Center (UFZ) Leipzig on 6 December 2018 [42]. Even though a sieve with a mesh size of 0.5 mm was used in the processing of the sediment, the majority of the sediment was finer than this. The average grain size was determined to be 0.026 ± 0.016 mm using the Set Scale function of ImageJ/Fiji [43] and corresponded to fine to medium silt on the Wentworth grain size chart ([44]; Figure 1A).
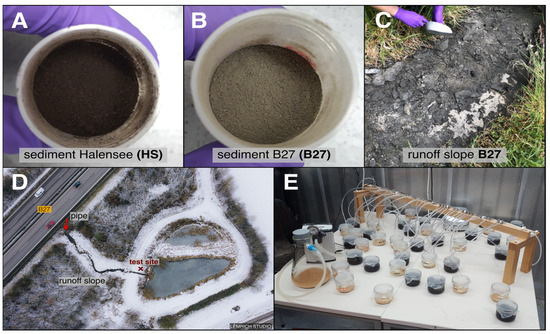
Figure 1.
The dried and pulverized test sediments, the test site B27, and the experimental setup for the ventilation experiments. (A) The black sediment from HS, as provided by the UFZ Leipzig (sample taken directly from the settling pond on 6 December 2018). (B) The dark grey sediment from B27, collected from the runoff slope to the settling pond (28 April 2020, 7 August 2020, and 15 November 2020). (C) Sample collection from the runoff slope (B27). The accumulated TRWP-containing sediment could be scraped off in layers. (D) Drone footage of the settling pond at the B27, taken from above (19 January 2022) by LÊMRICH STUDIO. The road, the runoff slope, and the test site are indicated. (E) Setup of the experiments (in a climate-controlled chamber; 20 °C, light–dark cycle of 12:12 h), where 50% of the treatments and the control were artificially ventilated with an air pump connected to rubber hoses and glass pipettes. In the left corner, the vacuum flask with low oxygen control (negative pressure, NP) can be seen (100 mbar).
The sediment from the settling pond at B27 was collected directly from the runoff slope from the highway to the settling pond (28 April 2020, 7 August 2020, and 15 November 2020; test site; Figure 1C,D). It was dried in a drying cabinet (Memmert GmbH + Co. KG, Schwabach, Germany) at 40 °C for 24 h. Thereafter, it was pulverized using a Quad Blade Chopper CH580 (Kenwood Limited, Havant, UK) and sieved (in accordance with the methods used by the UFZ Leipzig on the HS sediment) using a 0.6 mm sieve. Even though the grain size of the B27 sediment was not explicitly determined, it can be assumed by its dry and wet appearance and the direct visual comparison to the HS sediment that it can also be classified as silt according to the Wentworth grain size chart (Figure 1B).
Both sediments were dark, fine-grained, and powdery. The dry HS sediment was black, while the B27 sediment was dark grey in color (Figure 1A,B).
2.2. Estimation of TRWP Content by Particulate Zn Method
The analysis of both sediments was performed by the UFZ Leipzig; the protocol can be found in [24]. It consists of a gravity separation using sodium polytungstate (SPT), following the determination of Zn content in the fraction from 1.2–1.9 g/cm3 by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), from which the amounts of TRWP were estimated. The detected Zn content of the density fraction (1.2–1.9 g/cm3) was converted by using the weight ratio of this density fraction to represent the non-mineral Zn content of the whole sediment. Klöckner et al. determined pure TP to have a Zn content of 8.7 mg Zn/g TP [24]. Thus, the concentration of TRWP in the whole sediment was calculated. Furthermore, the share of TP in TRWP was estimated at 50%, which was also taken into account.
2.3. Maintenance of C. riparius
The larvae of C. riparius used in this study were obtained from five long-standing cultures kept in a climate-controlled chamber (20 °C, light–dark cycle of 12:12 h) at the University of Tübingen (Germany). The larvae were between 24 and 25 days old (third to fourth instar) at the beginning of each experiment.
They were reared in basins (30 × 55 × 12 cm) filled with washed and annealed quartz sand (3 cm thick layer; particle size 0.2–0.6 mm, corresponding to fine-coarse sand on the Wentworth grain size chart [44]) and a 50%/50% mix of aerated, filtered tap water (activated charcoal filter 0.3 µm; Reiser Blockfilter®, Reiser Filtertechnik GmbH, Hainburg, Germany) and deionized water, which were covered by mesh cages (55 × 65 × 120 cm; mesh size: 0.5 mm) to enable the adult animals to swarm and mate while also restraining them. Half the volume of the water mix in each basin was changed once per week. The larvae were fed dry flaked fish food (TetraMin®, Tetra GmbH, Melle, Germany) three times a week.
2.4. Experimental Design
In advance, the glass vessels (diameter: 7.0 cm, height: 6.5 cm) used in the mortality and behavior experiments were filled with nitric acid (5% HNO3; left for 24 h), rinsed with deionized water, then autoclaved and dried at 80 °C. For the experiments, they were filled with 10 g (dry wt.) of either quartz sand (control; grain size 0.2–0.6 mm, corresponding to fine–coarse sand on the Wentworth grain size chart; [44]), raw test sediment (HSraw, B27raw), or different proportions of test sediment and quartz sand, to achieve a gradient of different TRWP concentrations (Table 1). As the fine-grained test sediments did not disperse easily in water, the sediment and/or sediment and sand were mixed with filtered tap water in Falcon tubes using a vortex mixer to aid with dispersion before transferring it into the glass vessels. To all vessels, a total volume of 100 mL of water was added before they were covered with perforated Parafilm® (Carl Roth GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany).

Table 1.
Overview of all treatments used in experiments. Experiment_1: HSraw: raw, unfractionated sediment from the Halensee (HS) settling pond, dispersed in water. Experiment_2: B27raw: raw sediment from the B27 settling pond (collected 28 April 2020), dispersed in water. Experiments_3 and 4: 10 g HSO2/10 g B27O2: the aerated, dispersed sediment from the HS/B27 settling pond (B27: collected 28 April 2020, 7 August 2020 and 15 November 2020). Refers to the individual aeration of each glass for the whole duration of the experiment. The vacuum flask setup (NP) is not included here because it was only possible to run a single replicate with each experiment (n = 1). All: n refers to the number of glasses (replicates) for each treatment. Each glass contained five larvae. The total number of larvae per treatment is noted under the respective figures. (H2O/water: filtered water; sand: annealed quartz sand; aer.: continuously aerating the water in the glasses; control: pure quartz sand).
In the experiments addressing the influence of oxygen depletion, half of the test and control vessels were individually ventilated with glass pipettes connected to rubber hoses and a HAILEA® air pump (ACO-9620, China) for the purpose of artificial aeration (Figure 1E). During two experiments (n = 2), 20 additional larvae were kept in an airtight vacuum flask at around 100 mbar (maintained by a Standard Duty Diaphragm Pump MPC 090 E; Welch by Gardner Denver; Ilmenau, Germany; controlled by a time switch; runtime: 15 min every other hour) with a 1 cm thick layer of quartz sand and 400 mL of filtered tap water as a low oxygen control with ~1% O2 (NP: negative pressure; Figure S1 and Figure 1E). After adding five larvae to each test vessel, they were kept in a climate-controlled chamber (20 °C, light–dark cycle of 12:12 h) in a randomized setup for 96 h without any additional feeding.
2.5. Determination of Mortality and Assessment of Behavior
Due to the opacity of the water originating from the dispersed, dark test sediments, data on larval behavior (i.e., the number of constructed vertical chimneys per glass vessel) and mortality (i.e., the number of deceased or untraceable individuals) could only be recorded at the end of the experiments after 96 h. As a behavioral endpoint, the number of chimneys constructed per glass vessel was recorded by counting the chimneys with the aid of a flashlight. By illuminating the glass vessels from the side, the chimneys could be counted from above. A larva was considered dead when it remained immobile for 30 s after it was lightly touched with a blunt glass pipette. Data were collected with minimal disturbance to the larvae or the sediments. Whenever the mortality in the control remained ≤ 10% after 96 h, the experiment was considered valid.
2.6. Water Analysis
By using an HQ40D digital two-channel multimeter (HQ40D.99.000000; HACH, Loveland, CO, USA), the following parameters were determined in water samples taken 96 h after the onset of the experiments: water temperature, O2 saturation (with an Intellical LDO101 Field Luminescent/Optical Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Sensor (LDO10105)), pH-value (with an Intellical PHC201 Laboratory General Purposes Gel-Filled pH Electrode (PHC20103)) and the conductivity (with an Intellical CDC401 Laboratory 4-Poles Graphite Conductivity Cell (CDC40101). Further analysis of the water samples was conducted to determine the levels of nitrate, nitrite, ammonia, phosphate, and chloride using NANOCOLOR tube tests for photometric analysis (Ref. 985064 (Nitrate 50), Ref. 985068 (Nitrite 2), Ref. 985003 (Ammonium 3), Ref. 985076 (ortho- and total-Phosphate 1), Ref. 985019 (Chloride 200) used according to instructions; measurements conducted with compact photometer PF-12Plus (Ref. 919250); MACHEREY-NAGEL GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Germany). Water samples were also analyzed for metals (aluminum (ICP-OES), lead, chrome, zinc (all: ICP-MS)) by a commercial provider (DVGW–TZG Wasser, Karlsruhe, Germany). The limits of quantitation for the four elements were as follows: aluminum: 0.020 mg/L, zinc: 0.02 mg/L, lead: 0.001 mg/L, and chromium: 0.0005 mg/L.
2.7. Data Analysis
The statistical analyses of the data for mortality and behavior (chimney construction) were carried out with JMP 15.2.0 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA, 1989–2019). The mortality rates and the frequencies of living and dead larvae at 96 h were compared using a two-sided Fisher’s exact test with subsequent Bonferroni–Holm correction (α-level = 0.05). The relationship between the amount of B27raw sediment and the number of chimneys per glass at 96 h was analyzed by nonlinear regression and subsequent ANOVA.
3. Results
3.1. Description of Test Sediments
The differences in smell and appearance between the two test sediments (HSraw, B27raw) were conspicuous. The sediment from HS was black in color, while the sediment from B27 was dark grey (Figure 1A,B). Once the sediments were dispersed in water, the differences in coloration and smell became even more prominent. The sediment from HS initially created a black and opaque eluate, which, after the suspended matter settled, was colored yellow and smelled strongly of tar. This smell faded over the course of the experiment, but the samples never smelled of decaying organic matter, which was the case for the sediment from the B27. This sediment also produced an opaque eluate with a blueish hue after it settled. After only 24 h, the smell of decomposed matter of the B27 sediment was much stronger than the smell from the HS sediment, and it steadily increased over the course of the experiments (96 h).
3.2. Estimation of TRWP Content by Particulate Zn Method
The analysis of the HS sediment from 2017 showed a TRWP content of 130 ± 15 mg TRWP per gram sediment [24]. The analysis of our samples of the sediment from the B27 (2022) revealed a content of 35 ± 3 mg TRWP per gram sediment. Following the common assumption that tire particles (TP) contribute 50% of TRWP [24,27,45,46,47] suggests a content of 65 mg TP/g (HS) and 17.5 mg TP/g (B27), respectively. The TRWP content of the HS sediment was about four times higher than the TRWP content of the B27 sediment.
3.3. Water Analysis (Experiment 3 and 4)
The analysis of the physical and chemical properties of the composite samples revealed several differences between the sediments, which are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Results of the water analysis of the eluates, recorded at 96 h in a climate-controlled chamber (20 °C). Temperature [°C], O2 [%] (Intellical LDO101 Field Luminescent/Optical Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Sensor (LDO10105)), pH (Intellical PHC201 Laboratory General Purposes Gel-Filled pH Electrode (PHC20103)) and conductivity [µS] (Intellical CDC401 Laboratory 4-Poles Graphite Conductivity Cell (CDC40101)) recorded with HQ40D digital two-channel multimeter (HQ40D.99.000000; multimeter and all sensors by HACH, Loveland, CO, USA). NANOCOLOR tube tests for photometric analysis (Ref. 985064 (Nitrate 50), Ref. 985068 (Nitrite 2), Ref. 985003 (Ammonium 3), Ref. 985076 (ortho- and total-Phosphate 1), Ref. 985019 (Chloride 200) used according to instructions; measurements conducted with compact photometer PF-12Plus (Ref. 919250); MACHEREY-NAGEL GmbH & Co. KG, Dueren, Germany). Metal analysis (aluminum, lead, chrome, zinc) by DVGW–Technologiezentrum Wasser (Karlsruher Straße 84, 76139 Karlsruhe).
The oxygen-consuming properties of the sediments were more pronounced in the B27 sediment than in the HS sediment (O2 content in the eluate at 96 h: HS: 17,5%; B27: 2%). The conductivity of the eluate was also higher in the B27 samples than in the samples from HS (HS: 1085 µS/cm; B27: 2873 µS/cm). The levels of nitrate, nitrite, ammonia, phosphate, and chloride were higher in both test sediments than in the control groups, and they exceeded the concentrations regularly found in unpolluted surface waters (nitrate: 0.4–8 mg/L; nitrite: under 0.001 mg/L; ammonium: under 0.1 mg/L; phosphate: under 0.1 mg/L, chloride: 10–30 mg/L; [48]).
With respect to metal contents, the control samples were below the limits of detection for zinc and lead. However, very low concentrations of aluminum (0.02 mg/L) and chromium (0.0009 mg/L) were detectable. In both sediment samples, the metal thresholds for drinking water in Germany were exceeded or met (aluminum: 0.2 mg/L; lead: 0.01 mg/L, both [49]; zinc: 0.02 mg/L, [48]), or their concentration was elevated compared to the control group (chromium: 0.05 mg/L, [48]). There was a higher aluminum concentration in the sample from the B27 (1.0 mg/L) and a higher zinc concentration in the sample from the HS (1.56 mg/L). The HS sample contained more than twice as much lead and chromium (0.024 mg/L and 0.025 mg/L) as the B27 sample (both 0.01 mg/L).
3.4. Mortality after Exposure to Raw Sediments (Experiments 1 and 2)
While the mortality of the larvae in the control group and the larvae exposed to lower amounts of the HSraw sediment remained <5%, it was significantly increased (36%) in the treatment with 10 g pure HSraw sediment (p < 0.0001 *, Fisher’s exact test: df = 4, n = 250, Table S1, Figure 2). The mortality (18%) of larvae exposed to 2 g B27raw sediment was significantly raised compared to the control (p = 0.0157 *) and the lowest amount tested (1 g B27raw p = 0.0026 *), as was the mortality of the larvae in the experiments with even higher amounts (5 g B27raw: 54%; 10 g B27raw: 45%; all p < 0.0001 *, Table S1). Mortality also significantly differed between 2 g B27raw and both 5 g B27raw (p = 0.0003 *) and 10 g B27raw sediment (p = 0.0049 *) but the mortality caused by the two highest concentrations did not differ significantly from each other (Figure 2; Fisher’s exact test: df = 4, n = 248, p < 0.0001 *).
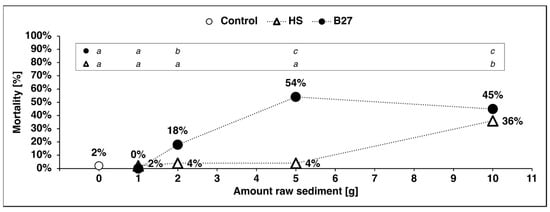
Figure 2.
Mortality of the larvae exposed to sediment from the Halensee (HS) and B27 settling ponds in different concentrations after 96 h. Fisher’s exact test: (HS: df = 4, n = 250, p < 0.0001 *; B27: df = 4, n = 248, p < 0.0001 *) corrected for multiple comparisons using subsequent Bonferroni–Holm correction. Significant differences indicated by letters. Significant differences between the sediments not shown but described in text. Sample size: n = 10; number of larvae: control and all treatments n = 50. (Control: 10 g sand; 1 g: 1 g HS/B27 sediment, 9 g sand; 2 g: 2 g HS/B27 sediment, 8 g sand; 5 g: 5 g HS/B27 sediment, 5 g sand; 10 g: 10 g HS/B27 sediment (pure, no sand); all: 100 mL filtered water).
With both TRWP-containing sediments, larval mortality increased with an increasing proportion of contaminated sediment. However, the reaction of the larvae to the two sediments differed. The mortality of the larvae exposed to the sediment from HS only increased significantly in the larvae exposed to 10 g HSraw sediment while the mortality increase was steeper and reached a plateau at 5 g with the larvae exposed to the sediment from B27. The largest difference between the two sediments was observed at a quantity of 5 g (p < 0.0001 *; HS: 4% mortality, B27: 54% mortality).
3.5. Mortality after Exposure to Aerated and Not Aerated Sediments (Experiments 3 and 4)
During these experiments, 50% of the glasses of the treatments (HS/B27) and controls were individually aerated for the duration of the whole experiment to keep the oxygen content in these glasses artificially high (Figure 1E).
The mortality of the larvae exposed to 10 g of the non-aerated HSraw sediment (46%) was significantly higher compared to the non-aerated control group (p < 0.0001 *). In contrast, the mortality of the larvae exposed to 10 g of this sediment in the aerated HSO2 setup (10%) was significantly lower than in the non-aerated setup (10 g HSraw; p = 0.0001 *). There was no significant difference between the two control groups and none between the treatment (10 g HSO2) and either control (Figure 3; Fisher’s exact test: df = 4, n = 220, p < 0.0001 *). Forty percent of larvae exposed to the non-aerated sediment from B27 (10 g B27raw) died after 96 h (Figure 3), and this mortality was significantly higher than in the non-aerated control (2%; p < 0.0001 *) and in the aerated B27 sediment (B27O2, 10%; p = 0.001 *). No significant differences between the two controls or among the aerated treatments could be detected (Fisher’s exact test: df = 4, n = 220, p < 0.0001 *).
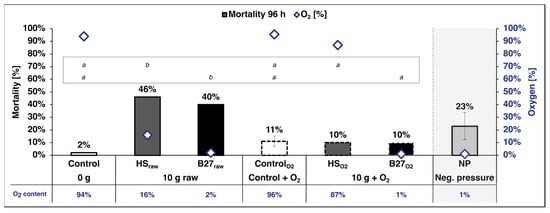
Figure 3.
Mortality of the larvae exposed to sediment from the Halensee (HS) and B27 settling ponds in non-aerated (10 g HSraw/B27raw) and individually aerated glasses (10 g HSO2/B27O2), their measured oxygen content at 96 h, and the mortality in the vacuum flask (low oxygen control; O2 content calculated; Figure S1). The error bars represent the standard deviation. Fisher’s exact test: df = 4, n = 220, p < 0.0001 *; corrected for multiple comparisons using subsequent Bonferroni–Holm correction. Significant differences indicated by letters; upper row: experiment 3 (HS), bottom row: experiment 4 (B27). Sample size: n = 10; number of larvae: all treatments and control n = 50; NP n = 20. (Control: 10 g sand; 10 g HSraw/B27raw: 10 g HS/B27 sediment; ControlO2: 10 g sand, continuous aeration; 10 g HSO2/B27O2: 10 g HS/B27 sediment, continuous aeration; all: 100 mL filtered water. NP: larvae in vacuum flask under negative pressure (NP; calculated mean of two experiments; n = 2); 1 cm sand, ~400 mL filtered water).
In the vacuum flask under negative pressure (NP), a larval mortality of 30% and 15%, respectively, was recorded during the two runs (mean = 23% ± 10.6; n = 2).
The oxygen content was consistently very high in the control groups of all experiments (between 90% and 99%; Figure 3). The water samples of the non-aerated 10 g HSraw had an O2 content of 16%, while the aerated 10 g HSO2 was at 87%. Both experiments applying the sediment from B27 showed a very low O2 content, 2% in 10 g B27raw and 1% in 10 g B27O2.
The O2 content of the water in the vacuum flask could not be measured without breaking the seal, which would have distorted the results, but since a pressure of around 100 mbar and thus a partial pressure of ~2 kPa O2 was maintained for the duration of the experiments, it can be calculated that the O2 content in the water inside the flask was ~1% O2 (Figure 3 and Figure S1).
3.6. Chimney Construction
The number of chimneys the larvae constructed in the fine-grained test sediments (experiments 2, 3, and 4) was recorded at the end of the experiments at 96 h. The mean number of chimneys decreased from 6.2 chimneys/glass to 1.1 chimneys/glass as the amount of B27raw sediment in experiment 2 increased from 1 g to 10 g. This relation was shown to be significant by non-linear regression analysis (Figure 4A) and a subsequent ANOVA (F(2, 36) = 41.6079, p < 0.0001 *). When calculating the quotient of the number of chimneys at 96 h and the number of surviving larvae at 96 h (Figure 4B), a decreasing trend with an increasing amount of B27 sediment could be observed. While a larva exposed to 1 g of B27raw sediment built 1.24 chimneys on average, a larva exposed to 10 g of B27raw sediment built only 0.41. The larval mortality at 96 h (as shown in Figure 4B) followed an opposing trend: the more contaminated sediment, the higher the mortality, and the fewer chimneys were constructed.
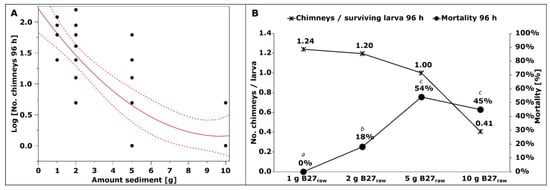
Figure 4.
Chimneys build out of the fine-grained test sediments from the settling ponds at the B27 by the larvae exposed to them and larval mortality at 96 h (experiment 2, sample sizes: Table 1). Significant differences indicated by letters. (A) Nonlinear regression of the number of chimneys depending on the amount of sediment from the B27 (ANOVA: F (2, 36) = 41.6079, p < 0.0001 *). (B) The number of chimneys at 96 h per surviving larva at 96 h and the larval mortality at 96 h in the four different concentrations of B27 sediment. (1 g B27raw: 1 g B27 sediment, 9 g sand; 2 g B27raw: 2 g B27 sediment, 8 g sand; 5 g B27raw: 5 g B27 sediment, 5 g sand; 10 g B27raw: 10 g B27 sediment (pure, no sand); all: 100 mL filtered water).
4. Discussion
4.1. TRWP Content
As expected, the two samples of TRWP-containing sediments from HS and B27 differed in their physical and chemical properties, as well as in their effects on the survival and behavior of the larvae of C. riparius. One reason for this could be the difference in the concentration of TRWP between the two samples. The analyses showed that the TRWP content in the HS sediment (130 ± 15 mg/g) was about four times higher than in the B27 sediment (35 ± 3 mg/g). This is not surprising since the intensity of traffic on the A100 around Berlin’s Halensee is also about four to five times higher (~140.000 motorized vehicles/24 h; [50]) than on the B27 around Tübingen (~30.000 motorized vehicles/24 h; [51]). These results are underlined by the differences in color and odor of the sediments and their eluates. The sampling method (HS: scooped from the bottom of the settling pond; B27: collected from the vegetated runoff slope) might also account for the difference in the amount of organic material and thus TRWP concentration in the samples, as it can be assumed that the TRWP concentration was ‘diluted’ by the elevated amount of detritus in the samples from B27. The fact that the oxygen consumption in the B27 sediment is much higher than in the HS sediment (Figure 3) supports this hypothesis as well since the bacterial decomposition and degradation of organic matter consumes oxygen, which can result in low to very low oxygen levels in sediments [52,53].
4.2. Water Chemistry and Effects on Larvae
The levels of all five water parameters (nitrate, nitrite, ammonia, phosphate, and chloride; Table 2) were higher in both of the undiluted contaminated sediments than they were in the control groups and exceeded the amounts found in unpolluted surface waters. It became clear that both sediments contained (organic) materials besides TRWP, which strongly influenced the basic chemistry of the added water. Indications for a low water quality are for instance a low oxygen content or a high conductivity (Table 2). While increased conductivity caused by elevated amounts of chloride in the sample (e.g., from road salts; [48]) is a sign of poor water quality, hypoxia is an indicator for foreign, oxygen-consuming substances [52,53] and a stressor by itself.
The metal analysis showed relatively high amounts of aluminum, zinc, lead, and chromium in the supernatant of both samples, with the thresholds for drinking water exceeded or reached. All four metals are common highway runoff pollutants [54], indicating the presence of TRWP in both sediments. Zinc and lead are known components of tire wear, brake dust, and motor oil [54], which accumulate in the environment, especially close to roads in soils and road runoff [55]. They have also been shown to contribute to the toxicity of TWP leachates [26]. Chromium, amongst other compounds, can detach from TWP that are dispersed in water [26] and is also found in metal plating and car engine parts [54]. Aluminum is also associated with tire wear and is a known leachate from asphalt surfaces [54]. Aluminum was the only metal found to be more abundant in the B27 sediment than in the sample from HS. As the HS sediment contains a higher concentration of TRWP than B27 sediment, it is likely that TRWP are not the only source of aluminum in this sediment.
Previous studies have shown the negative effects of heavy metals or metal-containing sediments on the larvae of C. riparius. Arambourou et al. [56] demonstrated the negative effects of sediments containing lead and zinc (among others) on gene expression and respiration rate and even found morphological changes (increases in the length of the mentum and the mandible) in the larvae exposed to these sediments. An increase in the expression of heat shock proteins (Hsp40, 70, 90) was found in larvae exposed to aluminum, chromium, and zinc (among others; [57]).
Thus, the high metal content of the investigated sediments compared to the control (quartz sand and filtered tap water) most probably contributes to their toxicity for the exposed larvae. In addition, the other aforementioned water parameters and the low to very low oxygen content most likely interact and amplify each other and cause the mortality and the sublethal effects observed in the experiments. In the next paragraph, we will focus more intensely on the aspect of oxygen depletion in the sediments.
4.3. The Role of Oxygen Content
The previously documented behavior of chimney construction by larvae of C. riparius as a response to low oxygen concentrations [37] was observed within our study as well, and a significant nonlinear relationship could be shown between the amount of oxygen-consuming B27 sediment (Figure 3) and the number of chimneys per glass (Figure 4). The observed relation revealed that the number of chimneys actually decreased with an increased amount of B27 sediment, as did the number of chimneys per surviving larvae (Figure 4), illustrating that the overall decrease is not solely due to the increase in larval mortality. A prerequisite for chimney construction is the ability of the larvae to burrow in the sediment.
Own experiments with the separation agent sodium polytungstate (SPT) and C. riparius larvae (T. Tull and S. Krais, unpublished) demonstrated that this chemical, even in sublethal concentrations, was able to decrease the larvae’s ability to burrow or reburrow in the sand, a behavior that is essential for their feeding and overall survival in their natural habitat [32,35]. It can be hypothesized that the B27 sediment also contains substances that exert negative, sublethal effects on the larvae of C. riparius. These effects likely interfere with the larvae’s natural reactions to hypoxic or anoxic conditions, such as increased respiratory undulation [36], increased hemoglobin production and levels in the hemolymph [41,58], and the construction of chimneys, all of which require and consume energy. It stands to reason that necessary behavioral and metabolic adaptations might not be possible anymore if the larvae were affected by both low oxygen levels and, in parallel, sublethal toxic effects caused by components of the sediment. Consequently, the overall number of chimneys per glass as well as the number per surviving larvae have decreased with an increasing concentration of the contaminated sediment while the mortality significantly increased in the experiments with higher content of contaminated sediment (Figure 4).
Based on our data, it is not possible to decide whether the lack of oxygen plus the larvae’s inability to react to it or, alternatively, the direct toxicity of TRWP, their leachates, or any other components of the B27 sediment ultimately caused the mortality of the larvae. It is likely that all these factors acted together, exerting combined toxicity on the larvae.
In experiment 4, the mortality of the larvae was significantly lowered from 40% to 10% by ventilation in the aerated treatment of B27 (Figure 3); however, the equally low oxygen content in aerated and non-aerated sediments (2% in 10 g B27raw and 1% in 10 g B27O2) does not provide an explanation for this decrease. However, it could be possible that the larvae, due to the high oxygen affinity of their hemoglobin [41], were able to intercept some portion of the introduced oxygen (which was constantly added to the individual glasses by means of an air pump) rather quickly before it was otherwise consumed. The fact that the overall conditions in these aerated glasses and the sediment were still hypoxic would explain the similar chimney construction activity in both the aerated and the non-aerated treatments (10 g B27raw: 1.4 chimneys at 96 h per surviving larva at 96 h, 10 g B27O2: 1.7 chimneys at 96 h per surviving larva at 96 h). Under aerated conditions, the sublethal effects of the B27 sediment may have still impaired the larvae, but the additional oxygen provided by aeration likely has compensated for their inability to perform additional undulations or increase their Hb synthesis, lowering their overall mortality.
While the overall oxygen depletion caused by the HS sediment in experiment 3 was not as pronounced as it was in all treatments of the sediment from B27 (Figure 3), it seemed to be still strong enough to trigger chimney construction in the larvae.
Experiments 3 and 4, using artificial ventilation, illustrate the connection between oxygen content, the mortality of the larvae, and their chimney construction ability very well (Figure 3). In the ventilated HS treatment (10 g HSO2), the oxygen content could be kept at 87%—closer to control conditions than any other treatment—while the oxygen content in the non-aerated HS sediment (10 g HSraw) decreased down to 16%. The low oxygen content coincided with a significantly increased mortality compared to the aerated treatment and the non-aerated control (Figure 3) and also with the frequency of chimney construction (HSraw: 1.40 chimneys/glass; 10 g HSO2: 0.0 chimneys/glass). These results show that the highly resilient and adaptable larvae can survive in TRWP-contaminated sediment despite the present sublethal effects of the TRWP and/or their leachates for 96 h, as long as no additional stressors (such as a lack of oxygen) are introduced. As soon as the oxygen supply decreases, the mortality rises, showing the animals’ inability to survive conditions for which they had evolved mechanisms of tolerance [32], because of the sublethal effects of the sediment.
The reason why no chimneys were recorded in the vacuum flask (NP) is obvious. The larvae, which usually inhabit very fine, silty sediments [32], are not able to construct chimneys out of the rather coarse quartz sand. It cannot be determined whether and to what extent this inability to build chimneys might have contributed to the mortality of the larvae. On the other hand, the comparably low mortality of the larvae in the vacuum flask (NP; Figure 3) attests to the remarkable tolerance of the larvae to very hypoxic conditions for an extended period of time (96 h). Larvae were kept at approximately 1% oxygen during two of the experiments, with mortality rates of 30% and 15%, respectively (Figure 3), when they were exposed just to the single stressor ‘low oxygen content’ and not to multiple stressors. High mortality rates at around 1% of oxygen saturation, ranging between 40% (10 g B27raw; Figure 3) and 83% (B27washed), only occurred when the additional stressor TRWP was applied.
5. Conclusions
Our study does not allow us to decide whether the interaction between O2 depletion and TRWP presence is additive or synergistic, but it clearly shows that even organisms adapted to extreme conditions can be negatively affected by TRWP if they additionally have to cope with the physiological challenges of their natural habitat. We are aware of the uncertainty on the chemical character of the compounds present in the sediments that have effectively elicited behavioral changes and mortality but consider TRWP relevant in this context as existing data on TRWP strongly suggest that they can pose a risk to exposed organisms (e.g., [26,31]).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/environments10020023/s1, Figure S1: Determination of the oxygen content in the vacuum flask at around 100 mbar; Table S1: Overview of all significant P-values across the experiments; Table S2: Raw data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: R.T., H.-R.K., T.T. and S.K.; methodology, T.T and S.K.; formal analysis, T.T., K.P. and S.K.; investigation, T.T., S.K. and S.W.; resources, R.T. and H.-R.K.; data curation, T.T., S.K. and S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, T.T.; writing—review and editing, T.T.; S.K., K.P., S.W., H.-R.K. and R.T.; visualization, T.T.; supervision, R.T. and H.-R.K.; project administration, T.T., S.K., R.T. and H.-R.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the Supplementary Materials (Table S2).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank P. Klöckner, S. Wagner and T. Reemtsma, UFZ Leipzig, for HS sediment sampling and characterization and the technicians D. Kolb and M. Zieseniß (UFZ Leipzig) for the analysis of the B27 sediment. We acknowledge support by Open Access Publishing Fund of University of Tübingen.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Belden, J. Chapter 28—Introduction to Ecotoxicology; Pope, C.N., Liu, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 381–393. ISBN 978-0-12-813602-7. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, A.A.; Walton, A.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E.; Svendsen, C. Microplastics in Freshwater and Terrestrial Environments: Evaluating the Current Understanding to Identify the Knowledge Gaps and Future Research Priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and Fragmentation of Plastic Debris in Global Environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigault, J.; Ter Halle, A.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.-Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.-L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current Opinion: What Is a Nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath, A. Mikroplastik Als Chance. In Mikroplastik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 243–289. [Google Scholar]
- Prata, J.C. Airborne Microplastics: Consequences to Human Health? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, J.B. Pollution by Synthetic Fibres. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1971, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, E.J.; Smith, K.L. Plastics on the Sargasso Sea Surface. Science 1972, 175, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at Sea: Where Is All the Plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.R.; Le Roux, G.; Jiménez, P.D.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric Transport and Deposition of Microplastics in a Remote Mountain Catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; McMahan, C.D.; McNeish, R.E.; Munno, K.; Rochman, C.M.; Hoellein, T.J. A Fish Tale: A Century of Museum Specimens Reveal Increasing Microplastic Concentrations in Freshwater Fish. Ecol. Appl. 2021, 31, e02320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, X. Microplastics are everywhere—but are they harmful. Nature 2021, 593, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materić, D.; Ludewig, E.; Brunner, D.; Röckmann, T.; Holzinger, R. Nanoplastics Transport to the Remote, High-Altitude Alps. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obbard, R.W.; Sadri, S.; Wong, Y.Q.; Khitun, A.A.; Baker, I.; Thompson, R.C. Global Warming Releases Microplastic Legacy Frozen in Arctic Sea Ice. Earth’s Futur. 2014, 2, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.K.; Ramirez-Llodra, E.; Alt, C.H.S.; Amaro, T.; Bergmann, M.; Canals, M.; Davies, J.; Duineveld, G.; Galgani, F.; Howell, K.L. Marine Litter Distribution and Density in European Seas, from the Shelves to Deep Basins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Vanreusel, A.; Mees, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic Pollution in Deep-Sea Sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C. Microplastic Pollution in Deep-Sea Sediments and Organisms of the Western Pacific Ocean. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batel, A.; Linti, F.; Scherer, M.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. Transfer of Benzo[a]Pyrene from Microplastics to Artemia Nauplii and Further to Zebrafish via a Trophic Food Web Experiment: CYP1A Induction and Visual Tracking of Persistent Organic Pollutants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triebskorn, R.; Braunbeck, T.; Grummt, T.; Hanslik, L.; Huppertsberg, S.; Jekel, M.; Knepper, T.P.; Krais, S.; Müller, Y.K.; Pittroff, M.; et al. Relevance of Nano- and Microplastics for Freshwater Ecosystems: A Critical Review. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Moos, N.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Köhler, A. Uptake and Effects of Microplastics on Cells and Tissue of the Blue Mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an Experimental Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11327–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, N.; Body-Malapel, M. Immunotoxicity and Intestinal Effects of Nano-and Microplastics: A Review of the Literature. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertling, J.; Bertling, R.; Hamann, L. Kunststoffe in Der Umwelt: Mikro- Und Makroplastik. Ursachen, Mengen, Umweltschicksale, Wirkungen, Lösungsansätze, Empfehlungen. Kurzfassung Der Konsortialstudie. Fraunhofer Inst. Für Umw. Sicherh. Energ. UMSICHT 2018, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, M.; Sørensen, L.; Jayasena, K.D.R.; Booth, A.M.; Fabbri, E. Chemical Composition and Ecotoxicity of Plastic and Car Tire Rubber Leachates to Aquatic Organisms. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöckner, P.; Reemtsma, T.; Eisentraut, P.; Braun, U.; Ruhl, A.S.; Wagner, S. Tire and Road Wear Particles in Road Environment—Quantification and Assessment of Particle Dynamics by Zn Determination after Density Separation. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Sources of Fine Organic Aerosol. 3. Road Dust, Tire Debris, and Organometallic Brake Lining Dust: Roads as Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire Wear Particles in the Aquatic Environment—A Review on Generation, Analysis, Occurrence, Fate and Effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and Chemical Characterization of Tire-Related Particles: Comparison of Particles Generated Using Different Methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødland, E.S. Ecotoxic potential of road-associated microplastic particles (RAMP). Vann 2019, 3, 166–183. [Google Scholar]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Kochleus, C.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and Road Wear Particles—A Calculation of Generation, Transport and Release to Water and Soil with Special Regard to German Roads. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grung, M.; Petersen, K.; Fjeld, E.; Allan, I.; Christensen, J.H.; Malmqvist, L.M.V.; Meland, S.; Ranneklev, S. PAH Related Effects on Fish in Sedimentation Ponds for Road Runoff and Potential Transfer of PAHs from Sediment to Biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; Gonzalez, M.; Wetzel, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Prat, J.; Mudrock, E.; Hettinger, R.; et al. A Ubiquitous Tire Rubber–Derived Chemical Induces Acute Mortality in Coho Salmon. Science 2020, 371, eabd6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, P.D.; Pinder, L.C.; Cranston, P.S. The Chironomidae: Biology and Ecology of Non-Biting Midges; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1995; ISBN 978-0412452604. [Google Scholar]
- Pinder, L.C.V. Biology of Freshwater Chironomidae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1986, 31, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, L.J.; Nath, B.B. Aquatic Silk Proteins in Chironomus: A Review. J. Limnol. 2018, 77, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, C.; Rodrigues, C. Development of a Test Method for Chironomus riparius Using a Formulated Sediment. Chemosphere 1995, 31, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackenbury, J. Locomotory Modes in the Larva and Pupa of Chironomus plumosus (Diptera, Chironomidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2000, 46, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stief, P.; Nazarova, L.; De Beer, D. Chimney Construction by Chironomus riparius Larvae in Response to Hypoxia: Microbial Implications for Freshwater Sediments. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo-Pereira, H.M.V.S.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Effects of Mercury on Growth, Emergence, and Behavior of Chironomus riparius Meigen (Diptera: Chironomidae). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 59, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo-Pereira, H.M.V.S.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Effects of Imidacloprid Exposure on Chironomus riparius Meigen Larvae: Linking Acetylcholinesterase Activity to Behaviour. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmulski, P.A.; Leyko, W. Paper: Structure, Function and Physiological Role of Chironomus Haemoglobin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. 1986, 85, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.E.; Vinogradov, S.N. Nonvertebrate Hemoglobins: Functions and Molecular Adaptations. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 569–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekel, M.; Anger, P.; Bannick, C.G.; Barthel, A.-K.; Braun, U.; Braunbeck, T.; Dittmar, S.; Eisentraut, P.; Elsner, M.; Gnirß, R. Mikroplastik Im Wasserkreislauf; Universitätsverlag der TU Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2020; ISBN 3798331634. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, C.K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.M.; Chu, J.; Kreider, M.L.; Unice, K.M. Measurement of Airborne Concentrations of Tire and Road Wear Particles in Urban and Rural Areas of France, Japan, and the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 72, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unice, K.M.; Weeber, M.P.; Abramson, M.M.; Reid, R.C.D.; van Gils, J.A.G.; Markus, A.A.; Vethaak, A.D.; Panko, J.M. Characterizing Export of Land-Based Microplastics to the Estuary-Part I: Application of Integrated Geospatial Microplastic Transport Models to Assess Tire and Road Wear Particles in the Seine Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unice, K.M.; Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M. Comparison of Tire and Road Wear Particle Concentrations in Sediment for Watersheds in France, Japan, and the United States by Quantitative Pyrolysis GC/MS Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8138–8147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwedt, G.; Schnepel, F.M. Practical Course in Analytical Chemistry with a View to Environmental Applications. Analytisch-Chemisches Umweltpraktikum. Anleitungen zur Untersuchung von Luft, Wasser und Boden, 1st ed.; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 1981; p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- TrinkwV Verordnung Über Die Qualität von Wasser Für Den Menschlichen Gebrauch (Trinkwasserverordnung—TrinkwV). Available online: http://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/trinkwv_2001/BJNR095910001.html#BJNR095910001BJNG000201310 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- BAST Manuelle Straßenverkehrszählung. Ergebnisse Auf Bundesautobahnen. 2015. Available online: https://www.bast.de/DE/Statistik/Verkehrsdaten/2015/Autobahnen-2015.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=4 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- BAST Manuelle Straßenverkehrszählung. Ergebnisse Auf Bundesstraßen. 2015. Available online: https://www.bast.de/BASt_2017/DE/Statistik/Verkehrsdaten/2015/Bundestrassen-2015.pdf;jsessionid=58777818A695749F2DFC9262BB9C7235.live11294?__blob=publicationFile&v=8 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Charlton, M.N. Hypolimnion Oxygen Consumption in Lakes: Discussion of Productivity and Morphometry Effects. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Human Acceleration of the Nitrogen Cycle: Managing Risks and Uncertainty; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018; ISBN 9789264307421. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, C.R.; Fitzgerald, S.A.; Sherrell, R.D.; Harned, D.A.; Staub, E.L.; Pointer, B.H.; Wehmeyer, L.L. Characterization of Stormwater Runoff from Bridges in North Carolina and the Effects of Bridge Runoff on Selected Receiving Streams. Sci. Investig. Rep. 2011, 110, 2011–5180. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, K.; Tainosho, Y. Characterization of Heavy Metal Particles Embedded in Tire Dust. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arambourou, H.; Llorente, L.; Moreno-Ocio, I.; Herrero, Ó.; Barata, C.; Fuertes, I.; Delorme, N.; Méndez-Fernández, L.; Planelló, R. Exposure to Heavy Metal-Contaminated Sediments Disrupts Gene Expression, Lipid Profile, and Life History Traits in the Midge Chironomus riparius. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-S.; Park, K.; Kwak, I.-S. Stress Evaluation to Heavy Metal Exposure Using Molecular Marker in Chironomus riparius. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 53, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.E. Functions of Invertebrate Hemoglobins with Special Reference to Adaptations to Environmental Hypoxia. Integr. Comp. Biol. 1980, 20, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).