A Deep Survey of Fish Health for the Recognition of Useful Biomarkers to Monitor Water Pollution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.2. Animals and Biological Indices
2.3. Histopathological Analysis
2.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.5. Blood Smear and Staining
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Pollution in the Tusciano and Picentino Rivers
3.2. Biological Indices
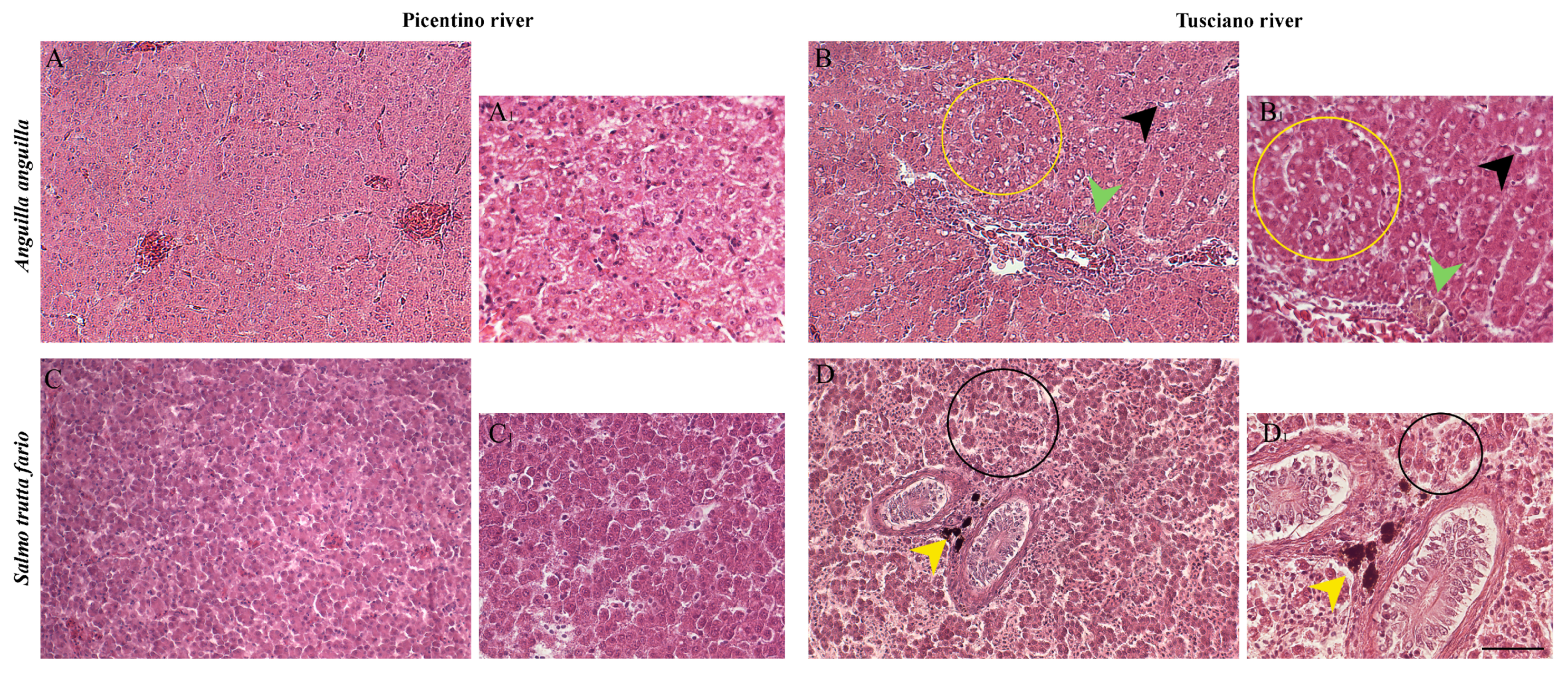
3.3. Liver Histopathology
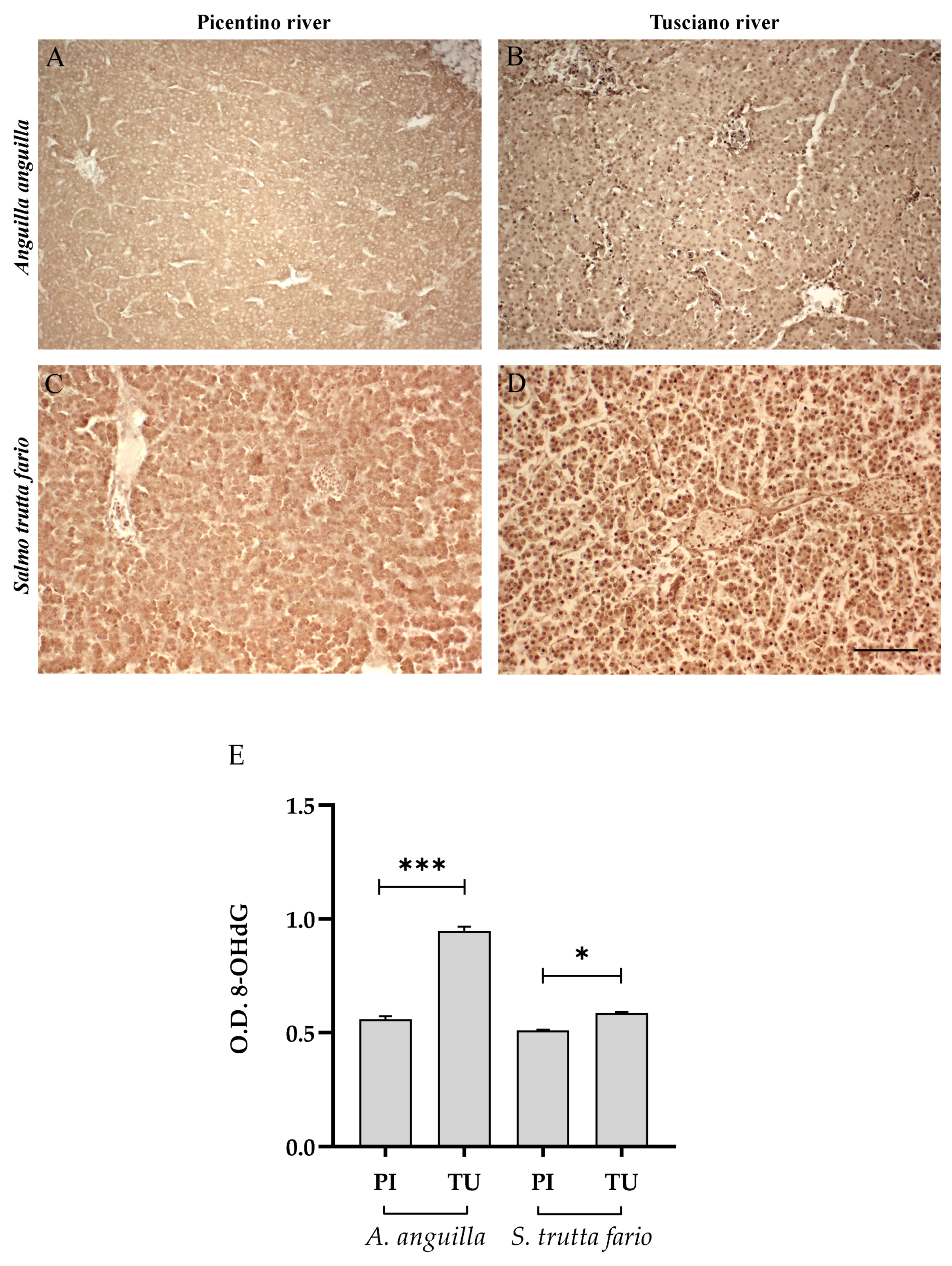
3.4. Liver Immunohistochemistry
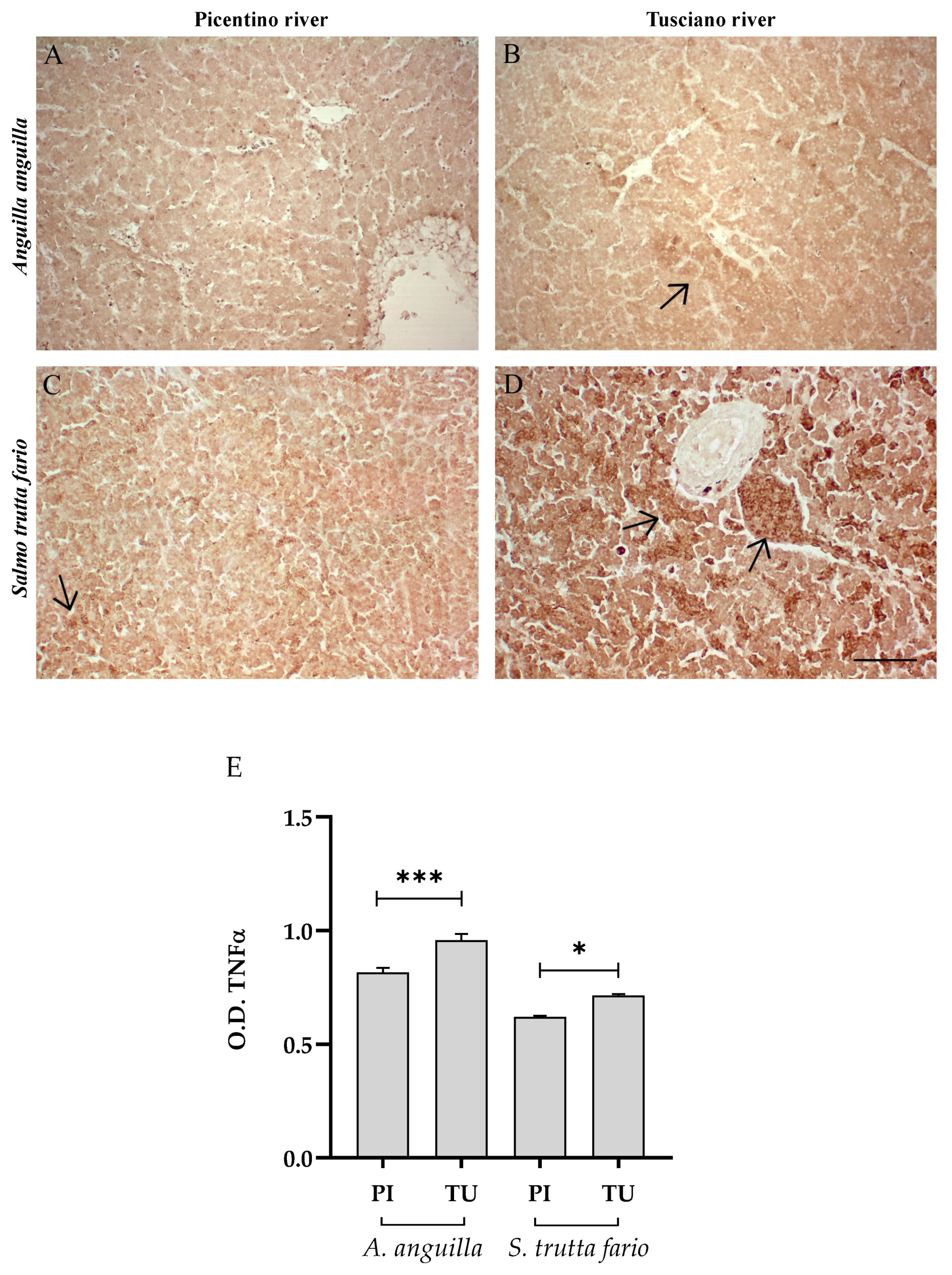
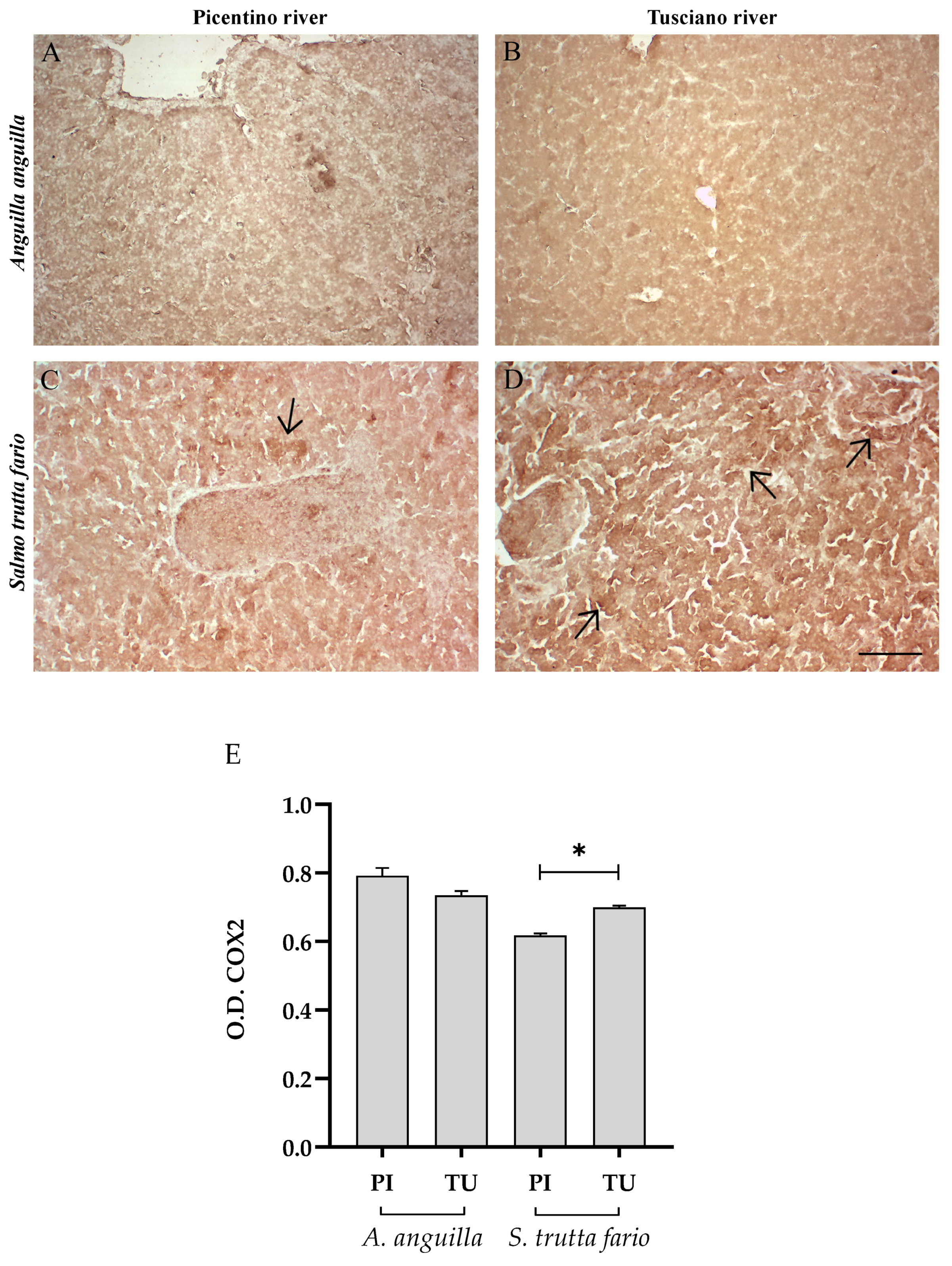
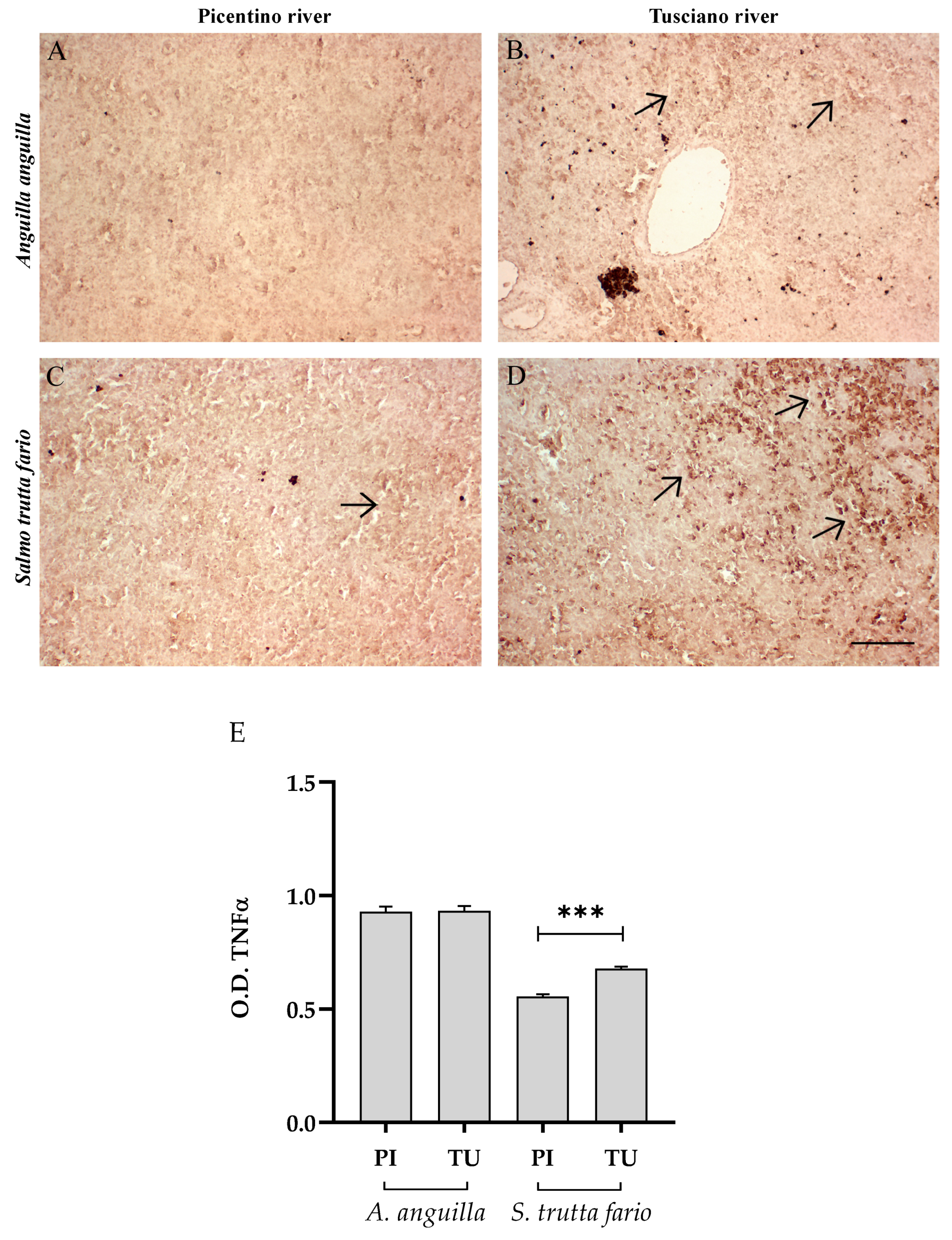
3.4.1. Inflammatory Biomarkers
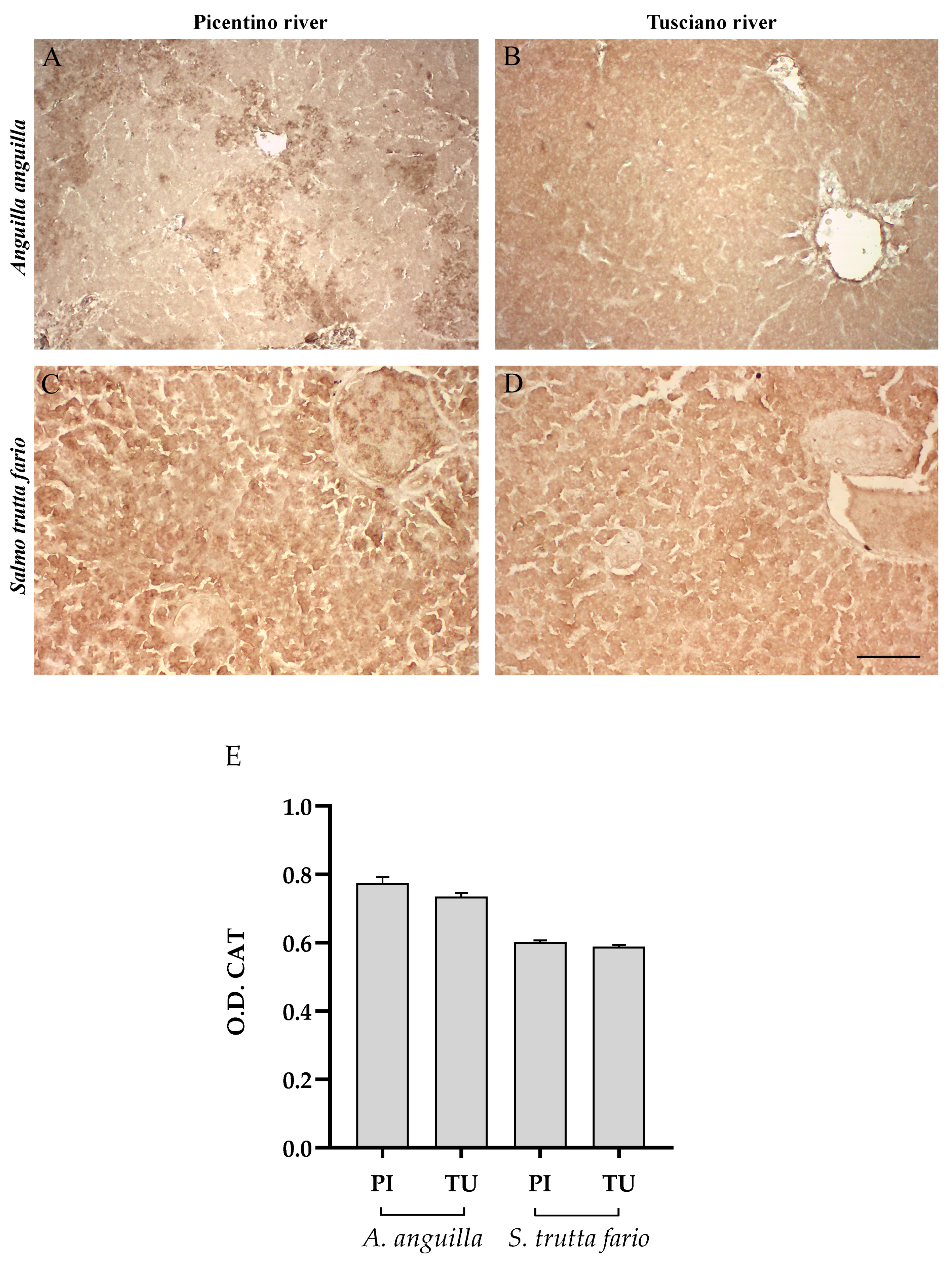
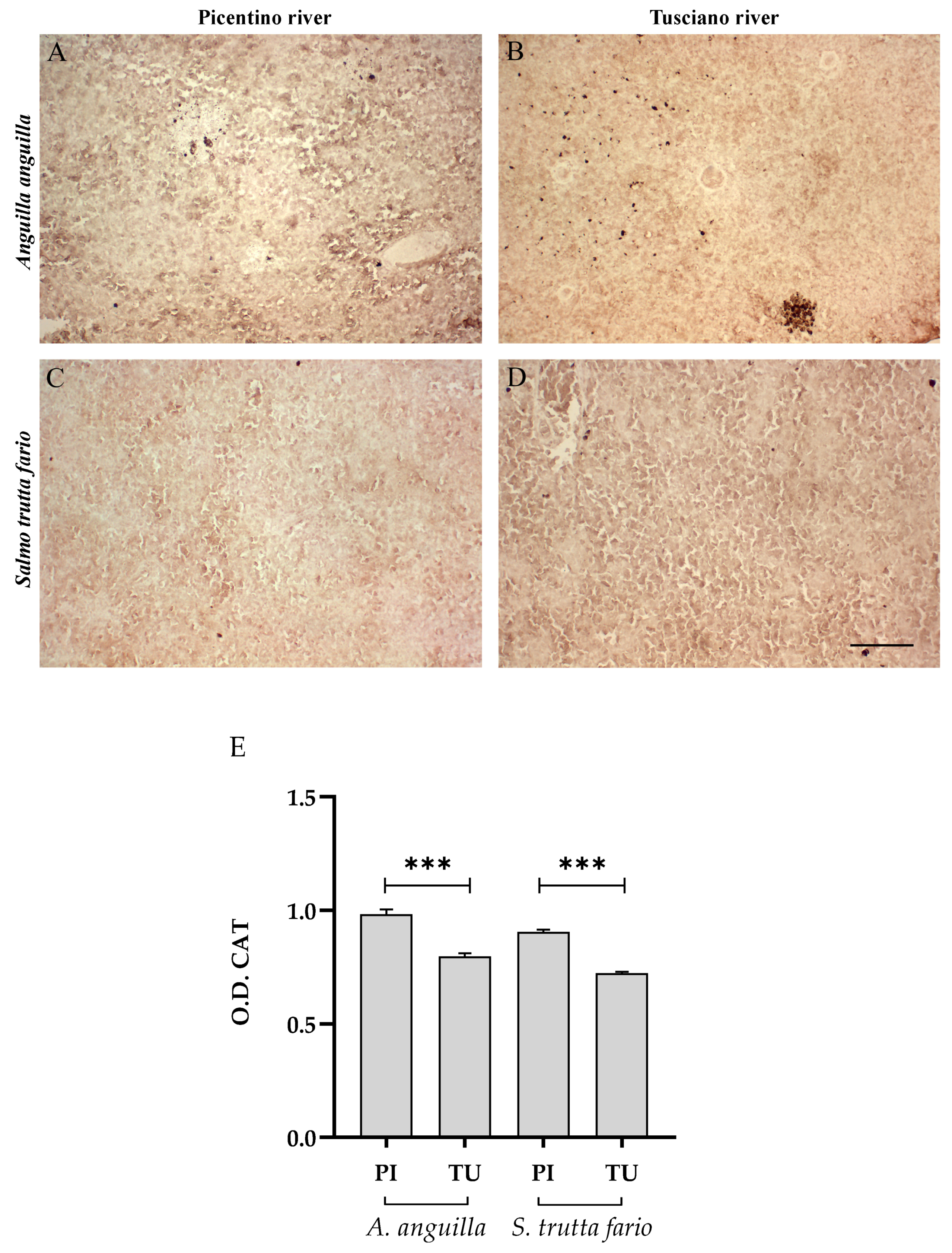
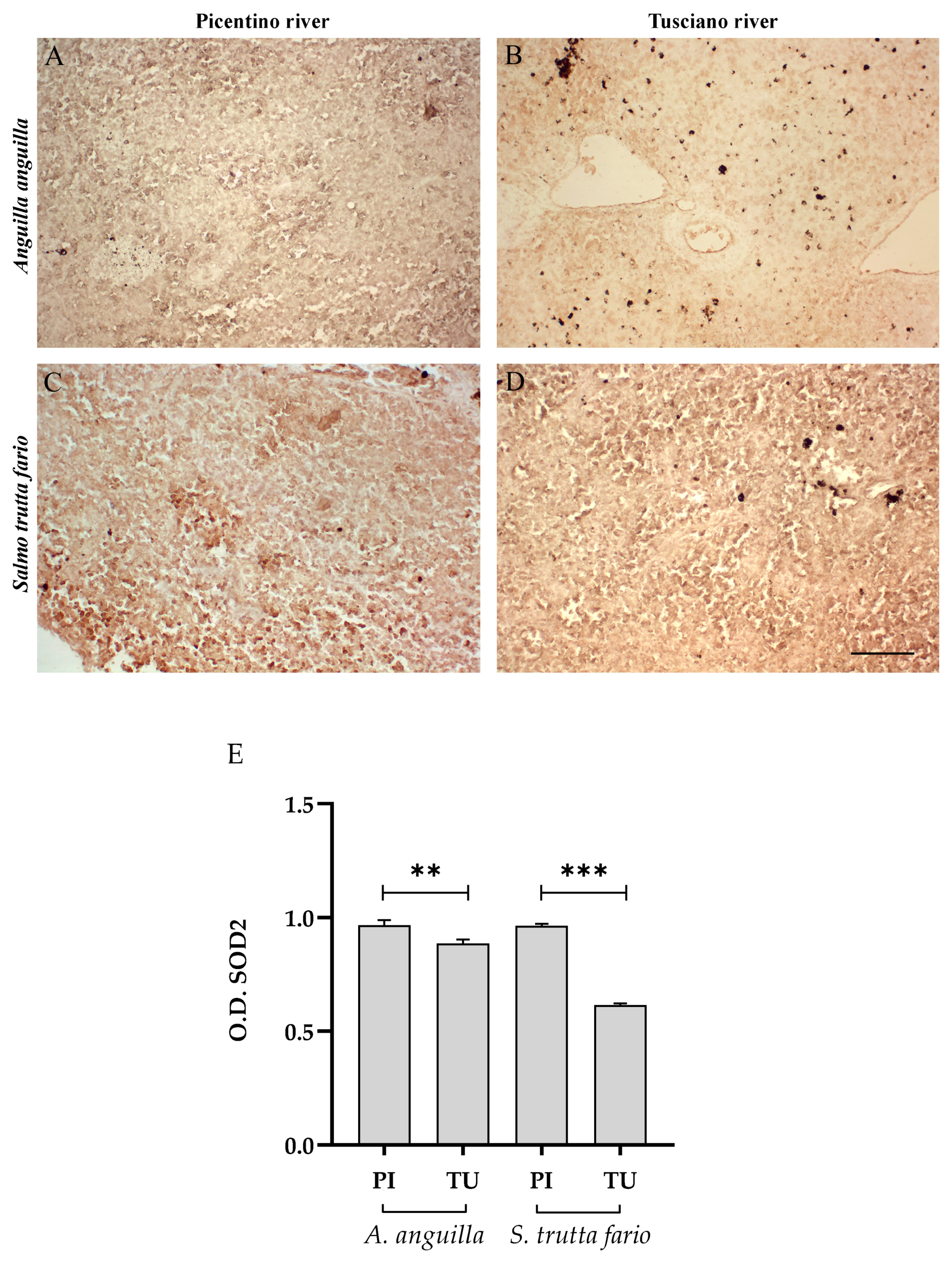
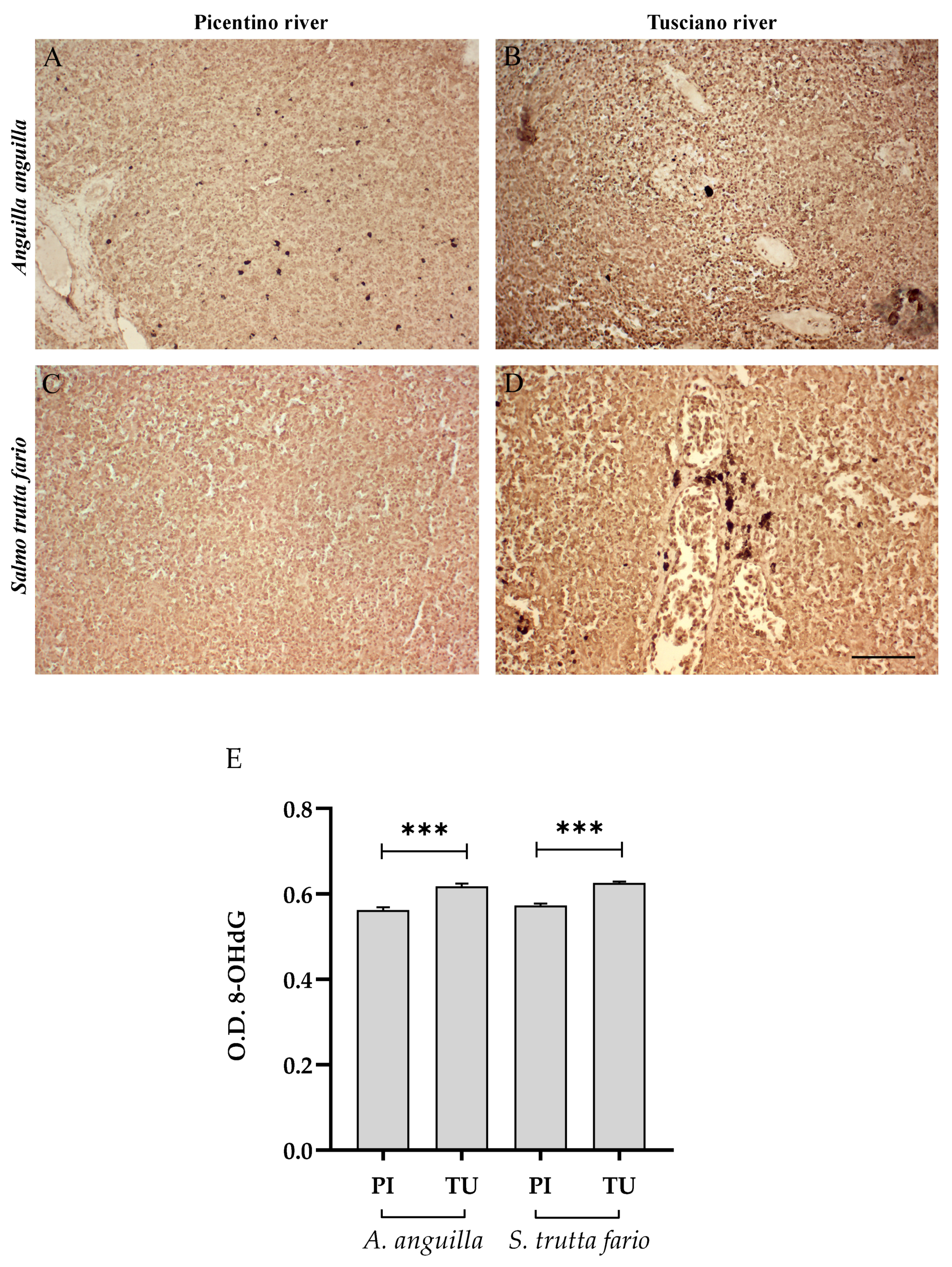
3.4.2. Antioxidant Biomarkers
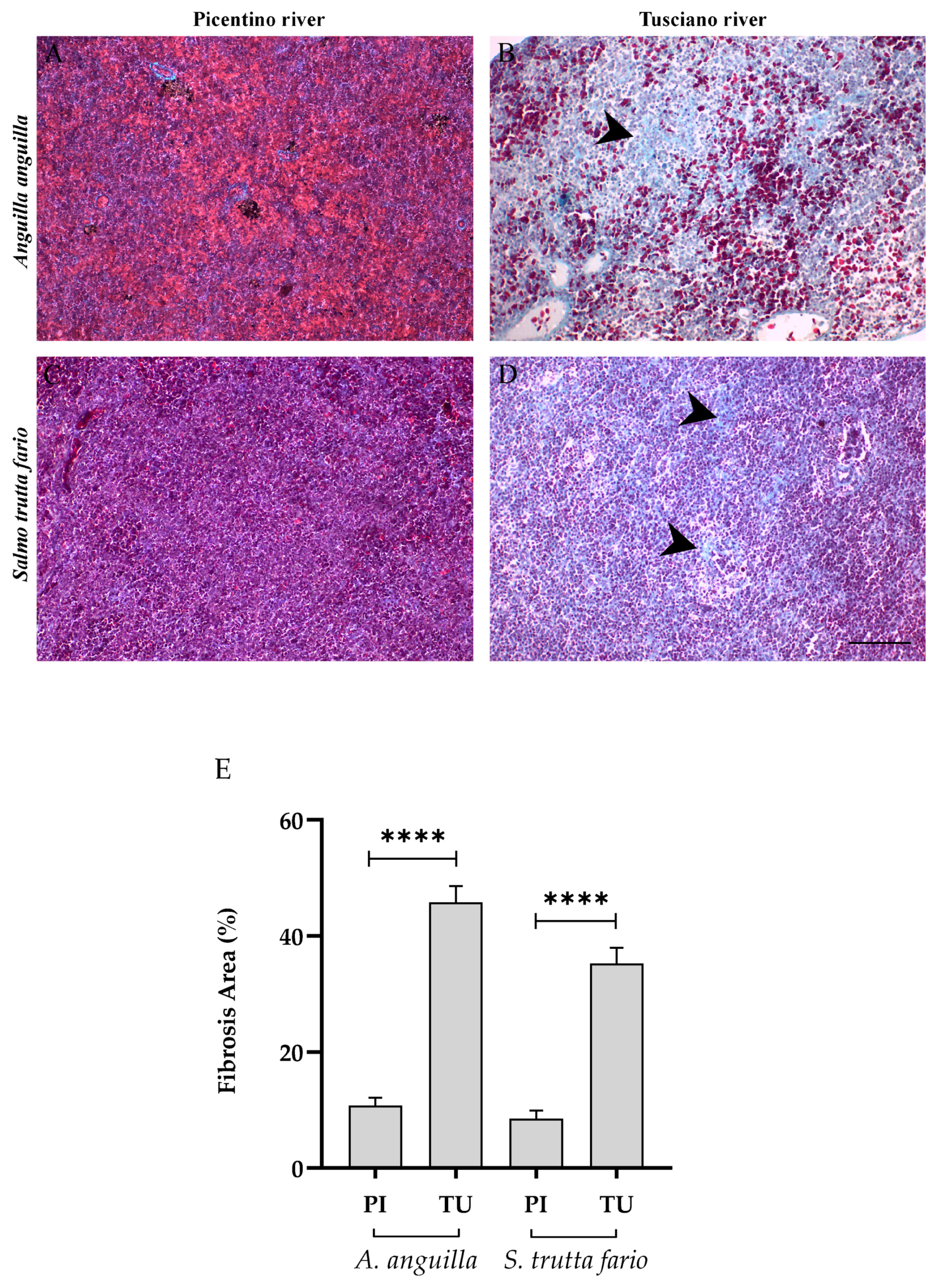
3.5. Spleen Histopathology
3.6. Spleen Immunohistochemistry
3.6.1. Inflammatory Biomarkers
3.6.2. Antioxidant Biomarkers
3.7. Correlation Analysis
3.8. Erythrocyte Abnormalities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onita, M.B.; Albu, P.; Herman, H.; Balta, C.; Lazar, V.; Fulop, A.; Baranyai, E.; Harangi, S.; Keki, S.; Nagy, L.; et al. Correlation between heavy metal-induced histopathological changes and trophic interactions between different fish species. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshkarchy, S.S.; Raesen, A.K.; Najim, S.M. Effect of heavy metals on physiological and histological status in liver of common carp Cyprinus carpio, reared in cages and wild in the Euphrates River, Babil/Iraq. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 779, 012066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.A. Histopathology and heavy metal bioaccumulation in some tissues of Luciobarbus xanthopterus collected from Tigris River of Baghdad, Iraq. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.S.; Yamamoto, F.Y.; Sandrini-Neto, L.; Filipak Neto, F.; Ortolani-Machado, C.F.; Oliveira Ribeiro, C.A.; Prodocimo, M.M. Diffuse sources of contamination in freshwater fish: Detecting effects through active biomonitoring and multi-biomarker approaches. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 149, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Duan, H.Y.; Li, X. Effects of exposure to multiple heavy metals on biochemical and histopathological alterations in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 70, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, T.; Siddique, A.; Sultana, S.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.; Ahmed, Z. Fish scales as a non-lethal tool of the toxicity of wastewater from the River Chenab. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2464–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Sultana, T.; Sultana, S.; Hussain, B.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Nadeem Riaz, M. Seasonal monitoring of River through heavy metal bioaccumulation and histopathological alterations in selected fish organs. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjit, S.A.; Atika, A.S.; Sangeeta, S. Histopathology biomarker responses in fresh water fish, Labeo rohita exposed to Bleaching Powder. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Inventig. 2020, 9, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Merola, C.; Bisegna, A.; Angelozzi, G.; Conte, A.; Abete, M.C.; Stella, C.; Pederiva, S.; Faggio, C.; Riganelli, N.; Perugini, M. Study of heavy metals pollution and vitellogenin levels in brown trout (Salmo trutta trutta) wild fish populations. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linde, A.R.; Arribas, P.; Sanchez-Galan, S.; Garcıa-Vazquez, E. Eel (Anguilla anguilla) and brown trout (Salmo trutta) target species to assess the biological impact of trace metal pollution in freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 31, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belpaire, C.; Goemans, G. The European eel Anguilla anguilla, a rapporteur of the chemical status for the water framework directive? Vie Et Milieu/Life Environ. 2007, 57, 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- Bernet, D.; Schmidt, H.; Meier, W.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Wahli, T. Histopathology in fish: Proposal for a protocol to assess aquatic pollution. J. Fish Dis. 1999, 22, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamat, N.; Zarie, M. Fish histopathology as a tool for use in marine environment monitoring: A review. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 25, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.R.; Chandra, K.J. Seasonal variation of gill, skin, muscle, liver and kidney pathology of mrigal (Cirrhinus cirrhosus) in cultural pond fisheries, my men singh, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Vet. Med. 2018, 16, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alm-Eldeen, A.A.; Donia, T.; Alzahaby, S. Comparative study on the toxic effects of some heavy metals on the Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, in the Middle Delta, Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14636–14646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, J.C.; Cochrane, M.J.; Wagenaar, G.M. Liver histopathology of the sharptooth catfish Clarias gariepinus as a biomarker of aquatic pollution. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dane, H.; Şişman, T. A histopathological study on the freshwater fish species chub (Squalius cephalus) in the Karasu River, Turkey. Turk. J. Zool. 2017, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savassi, L.A.; Paschoalini, A.L.; Arantes, F.P.; Rizzo, E.; Bazzoli, N. Heavy metal contamination in a highly consumed Brazilian fish: Immunohistochemical and histopathological assessments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leknes, I.L. The uptake of foreign ferritin by macrophages in the spleen, trunk kidney and liver of platy. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 1412–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinel, N.C.; Bolnick, D.I. Melanomacrophage centers as a histological indicator of immune function in fish and other poikilotherms. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hong, M.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Insights into the role and interdependence of oxidative stress and inflammation in liver diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4234061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; An, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q. Antioxidative and inflammatory responses in spleen and head kidney of Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) induced by waterborne cadmium exposure. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 20, 8796. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, N.A.; Laban, S.E.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; Attia, M.M. Immunological status and histopathological appraisal of farmed Oreochromis niloticus exposed to parasitic infections and heavy metal toxicity. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 2247–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttelod, A.; García, N.; Malak, D.A.; Temple, H.J.; Katariya, V. The Mediterranean: A biodiversity hotspot under threat. In Wildlife in A Changing World—An Analysis of the 2008 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Vié, J.C., Hilton-Taylor, C., Stuart, S.N., Eds.; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2009; p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- Maurya, K.P.; Malik, D.S.; Krishna, K.Y.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, S. Haematological and histological changes in fish Heteropneustes fossilis exposed to pesticides from industrial waste water. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 1251–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, P.; Solé, M.; Bañón, R.; García-Galea, E.; Durfort, M.; Matamoros, V.; Bayona, J.M.; Vinyoles, D. Effects of industrial pollution on the reproductive biology of Squalius laietanus (Actinopterygii, Cyprinidae) in a Mediterranean stream (NE Iberian Peninsula). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 46, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccia, E.; Imperatore, R.; Orso, G.; Melck, D.; Varricchio, E.; Volpe, M.G.; Paolucci, M. Explants of Oncorhynchus mykiss intestine to detect bioactive molecules uptake and metabolic effects: Applications in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumford, S.; Heidel, J.; Smith, C.; Morrison, J.; MacConnell, B.; Blazer, V. Fish Histology and Histopathology, 4th ed.; U.S. Fish and Wildfife Service; National Conservation Training Center: Shepherdstown, WV, USA, 2007; p. 357. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, M.L.; Cardoso, L.; Furtado, W.; Tancredo, K.R.; Lehmann, N.B.; Figueiredo, A.B.; Steckert, L.D.; Silva, K.A.G.; Padua, S.B.; Ferreira, T.H. Histopathology Guide for Freshwater Fish; Editora UFSC: Florianopolis, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nataraj, B.; Hemalatha, D.; Malafaia, G.; Maharajan, K.; Ramesh, M. “Fishcide” Effect of the fungicide difenoconazole in freshwater fish (Labeo rohita): A multi-endpoint approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerli, S.; Bernet, D.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Vonlanthen, P.; Wahli, T.; Segner, H. Assessment of fish health status in four Swiss rivers showing a decline of brown trout catches. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 69, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoalini, A.L.; Savassi, L.A.; Arantes, F.P.; Rizzo, E.; Bazzoli, N. Heavy metals accumulation and endocrine disruption in Prochilodus argenteus from a polluted neotropical river. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjahan, M.; Khatun, M.S.; Mun, M.M.; Islam, S.M.M.; Uddin, M.H.; Badruzzaman, M.; Khan, S. Nuclear and cellular abnormalities of erythrocytes in response to thermal stress in common carp Cyprinus carpio. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, C.F.; Silva, R.F.; Amaral, M.G.; Domingos, F.F.; Ribeiro, R.I.; Thomé, R.G.; Santos, H.B. Comparative histology in the liver and spleen of three species of freshwater teleost. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2017, 15, e160041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D. Pattern and process in the ecological biogeography of European freshwater fish. J. Anim. Ecol. 2006, 75, 734–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champeau, O.; Ataria, J.M.; Northcott, G.L.; Kume, G.; Barrick, A.; Tremblay, L.A. Assessment of the impacts of anthropogenic activities on a large river using longfin eel as a bioindicator. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, M.; Mirvaghefi, A.; Farahmand, H.; Taghavi, L.; Shahabinia, A.-R. In situ assessment of Karaj River genotoxic impact with the alkaline comet assay and micronucleus test, on feral brown trout (Salmo trutta fario). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 58, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Fan, W. Weight-length relationships and Fulton’s condition factors of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) in the western and central Pacific Ocean. PeerJ 2015, 3, e758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettinetti, R.; Galassi, S.; Quadroni, S.; Volta, P.; Capoccioni, F.; Ciccotti, E.; De Leo, G.A. Use of Anguilla anguilla for biomonitoring persistent organic pollutants (pops) in brackish and riverine waters in central and southern Italy. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 217, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnham, C.; Baxter, C. Condition factor, K, for salmonid fish. Fish. Notes 1998, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaszadeh, M.; Şişman, T. An application of histological technique for monitoring health status of fish species, Leuciscus caspius (Linnaeus, 1758) inhabiting Aras River, Iran. CJES 2021, 19, 187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Morado, C.N.; Araújo, F.G.; Gomes, I.D. The use of biomarkers for assessing effects of pollutant stress on fish species from a tropical river in Southeastern Brazil. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2017, 39, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Authman, M.M.N. Environmental and experimental studies of aluminium toxicity on the liver of Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) fish. Life Sci. 2011, 8, 764–776. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, B.; Antunes, S.C.; Gomes, R.; Campos, J.C.; Braga, M.R.; Ramos, A.S.; Correia, A.T. Acute effects of tetracycline exposure in the freshwater fish Gambusia holbrooki: Antioxidant effects, neurotoxicity and histological alterations. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 68, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukin, A.; Sharova, J.; Belicheva, L.; Camus, L. Assessment of fish health status in the Pechora River: Effects of contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, M.M.P.; Martinez, C.B.R. Histopathology of gills, kidney and liver of a Neotropical fish caged in an urban stream. Neotrop. Ichthyol. 2007, 5, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agamy, E. Histopathological changes in the livers of rabbit fish (Siganus canaliculatus) following exposure to crude oil and dispersed oil. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostić, J.; Kolarević, S.; Kračun-Kolarević, M.; Aborgiba, M.; Gačić, Z.; Paunović, M.; Višnjić-Jeftić, Ž.; Rašković, B.; Poleksić, V.; Lenhardt, M.; et al. The impact of multiple stressors on the biomarkers response in gills and liver of freshwater breams during different seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagné, F.; Blaise, C.; Salazar, M. Histopathological biomarkers in liver and gills of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to crude oil. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, M.; Ahmad, I.; Usmani, N.; Ahmad, M. Studies on biomarkers of oxidative stress and associated genotoxicity and histopathology in Channa punctatus from heavy metal polluted canal. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Dua, A. Induction of histopathological lesions in renal tissue of the fish Labeo rohita upon exposure to municipal wastewater of Tung Dhab Drain, Amritsar, India. Turk. J. Zool. 2016, 40, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.M.M.; Ribeiro, H.J.; Procópio, M.S.; Alvarenga, B.M.; Castro, A.C.S.; Dutra, W.O.; Silva, J.B.B.; Corrêa, J.J.D. What the erythrocytic nuclear alteration frequencies could tell us about genotoxicity and macrophage iron storage? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, F.G.; Gomes, I.D.; Nascimento, A.A.; Santos, M.A.J.; Sales, A. Histopathological analysis of liver of the catfish Pimelodus maculatus in a tropical eutrophic reservoir from Southeastern Brazil. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2019, 41, 41039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passantino, L.; Santamaria, N.; Zupa, R.; Pousis, C.; Garofalo, R.; Cianciotta, A.; Jirillo, E.; Acone, F.; Corriero, A. Liver melanomacrophage centres as indicators of Atlantic bluefin tuna, Thunnus thynnus L. well-being. J. Fish Dis. 2014, 37, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabra, F.S.; Mehana, E.-S.E.-D. Pesticides toxicity in fish with particular reference to insecticides. Asian J. Agric. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 40–60. [Google Scholar]
- Peillex, C.; Pelletier, M. The impact and toxicity of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on health and immunity. J. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 17, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, F. Histopathological effect of heavy metal on different organs of fresh water fish tissues from Garmat Ali River adjacent to Al- Najebyia Power Station. Kufa J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 6, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoulias, D.M.; Velez, V.; Nicks, D.K.; Tillitt, D. Health Assessment and Histopathologic Analyses of Fish Collected from the Kalamazoo River, Michigan, Following Discharges of Diluted Bitumen Crude Oil from the Enbridge Line 6B; Administrative Reports; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014.
- Vieira, C.; Morais, S.; Ramos, S.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Oliveira, M.B. Mercury, cadmium, lead and arsenic levels in three pelagic fish species from the Atlantic Ocean: Intra- and inter-specific variability and human health risks for consumption. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nai, G.A.; Golghetto, G.M.S.; Estrella, M.P.S.; Teixeira, L.D.S.; Moura, F.D.C.; Neto, H.B.; Parizi, J.L.S. The influence of water pH on the genesis of cadmium-induced câncer in a rat model. Histol. Histopathol. 2015, 30, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, M.M.; El-Gameel, S.M.; Ismael, E. Evaluation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α); gamma interferon (IFN-γ) genes and oxidative stress in sheep: Immunological responses induced by Oestrus ovis (Diptera: Oestridae) infestation. J. Parasit. Dis. 2020, 44, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. A Review of Cyclooxygenase-2 Role in Fish. Austin J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 3, 1037. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, S.J.; Prickril, B.; Rasooly, A. Mechanisms of phytonutrient modulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and Inflammation related to cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 70, 350–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, M.S.; Sandrini-Neto, L.; Filipak Neto, F.; Oliveira Ribeiro, C.A.; Di Domenico, M.; Prodocimo, M.M. Biomarker responses in fish exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242 Pt A, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, D.; Atli, G.; Dogan, Z.; Baysoy, E.; Gurler, C.; Eroglu, A.; Canli, M. Response of the antioxidant system of freshwater fish (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to metals (Cd, Cu) in differing hardness. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 14, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Alak, G.; Yeltekin, A.Ç.; Taş, I.H.; Ucar, A.; Parlak, V.; Topal, A.; Kocaman, E.M.; Atamanalp, M. Investigation of 8-OHdG, CYP1A, HSP70 and transcriptional analyses of antioxidant defence system in liver tissues of rainbow trout exposed to eprinomectin. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 65, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, B.P.; Lerner, D.T.; Grau, E.G.; Seale, A.P. The effects of acute salinity challenges on osmoregulation in Mozambique tilapia reared in a tidally changing salinity. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninh, N.H.; Thoa, N.P.; Knibb, W.; Nguyen, N.H. Selection for enhanced growth performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in brackish water (15–20ppt) in Vietnam. Aquaculture 2014, 428–429, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Uddin, M.H.; Uddin, M.J.; Shahjahan, M. Temperature changes influenced the growth performance and physiological functions of Thai pangas Pangasianodon hypophthalmus. Aquacult. Rep. 2019, 13, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiqul, I.M.; Ferdous, Z.; Nannu, M.T.A.; Mostakim, G.M.; Rahman, M.K. Acute exposure to a quinalphos containing insecticide (convoy) causes genetic damage and nuclear changes in peripheral erythrocytes of silver barb, Barbonymus gonionotus. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| General Description | Alterations | Importance Factor (ω) |
|---|---|---|
| Alterations result from a pathological condition of blood and tissue fluid flow | Blood sinusoid dilation | 1 |
| Hemorrhage | 1 | |
| Alterations result in functional redution or loss of the organ. | Cytoplasmic vacuolization | 1 |
| Hemosideriosis | 1 | |
| Irregular arrangement of hepatocytes | 1 | |
| Lipid accumulation | 2 | |
| Necrosis | 3 | |
| Cellular hyperplasia | 2 | |
| Alterations result from increased presence of cells used in tissue repair; response to damaged tissue | Leukocytes infiltration | 2 |
| Melanomacrophage aggregates | 1 | |
| Free melanomacroph ages | 1 |
| Picentino River | Tusciano River | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical parameters | Conductivity (µS/cm) | 387 | 1680 |
| Oxygen (mg/L) | 9.4 | 7.8 | |
| pH | 7.2 | 8.2 | |
| Temperature (°C) | 14.8 | 15.3 | |
| Total Inorganic Carbon mg/L | 45 | 86 | |
| Chlorides mg/L | 7.4 | 22 | |
| Bromine mg/L | <0.1 | 0.2 | |
| Nitrates mg/L | 2.8 | 39 | |
| PTEs | As (µg/L) | <1 | 3.13 |
| Cd (µg/L) | <0.1 | 0.17 | |
| Co (µg/L) | <0.5 | 0.8 | |
| Hg (µg/L) | <0.1 | 0.23 | |
| Ni (µg/L) | <0.5 | 0.77 | |
| Pb (µg/L) | <1 | 1.22 | |
| Pesticides | Boscalid (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.44 |
| Glifosate (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.32 | |
| AMPA (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.85 | |
| Propizamide (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.02 | |
| Terbutryn (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.05 | |
| Fungicide | Metalaxil (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.04 |
| Other contaminants | Tetrachlorethylene (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.17 |
| Toluene (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.15 | |
| Trichloroethylene (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.11 | |
| Trichloromethane (µg/L) | <0.01 | 0.14 |
| PTEs (mg/kg) | PI | TU | PAHs (mg/kg) | PI | TU | PCBs (µg /kg) | PI | TU | OCPs (µg /kg) | PI | TU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 8.7 | 12.5 | Total PAHs | 0.0155 | 0.0182 | PCB 77 | 0.003 | <0.003 | Hexachlorobenzene | 0.005 | 0.113 |
| Be | 3.3 | 5.8 | Dibenzo(a,i)pyrene | <0.005 | 0.0051 | PCB 118 | <0.003 | 0.032 | α-Chlordane | <0.005 | 0.078 |
| Cd | 0.32 | 0.21 | PCB 105 | <0.003 | 0.02 | Chlordane | 0.005 | 0.081 | |||
| Co | 5.7 | 11.2 | PCB 167 | <0.003 | 0.004 | o,p′-DDE | <0.005 | 0.059 | |||
| Cu | 38.8 | 35.8 | PCB 156 | 0.004 | 0.007 | p,p′-DDE | 0.02 | 7.591 | |||
| Cr | 10.4 | 18.3 | PCB 157 | 0.006 | <0.003 | o,p′-DDD | <0.005 | 0.019 | |||
| Hg (µg /kg) | 23 | 23 | PCB 189 | 0.004 | <0.003 | p,p′-DDD | <0.005 | 0.109 | |||
| Ni | 10.5 | 12.6 | PCB-28 | <0.003 | 0.005 | o,p′-DDT | <0.005 | 0.292 | |||
| Pb | 36.1 | 39.9 | PCB-52 | <0.003 | 0.006 | p,p′-DDT | <0.005 | 1.771 | |||
| Sn | 2.5 | 2.7 | PCB-101 | <0.003 | 0.012 | Dieldrin | <0.005 | 0.191 | |||
| Tl | 0.8 | 1.36 | PCB-153 | 0.135 | 0.042 | Endosulphan sulphat | 0.128 | <0.005 | |||
| V | 45 | 80 | PCB-138 | 0.065 | 0.043 | DDD, DDT, DDE | 0.0325 | 9.84 | |||
| Zn | 77.1 | 75.6 | PCB-180 | 0.063 | 0.055 | ||||||
| Trichlorobiphenyls | <0.01 | 0.012 | |||||||||
| Tetrachlorobiphenyls | <0.01 | 0.036 | |||||||||
| Pentachlorobiphenyls | <0.01 | 0.121 | |||||||||
| Hexachlorobiphenyls | <0.01 | 0.16 | |||||||||
| Heptachlorobiphenyls | 0.227 | 0.098 | |||||||||
| Octachlorobiphenyls | 0.081 | 0.013 | |||||||||
| Nonachlorobiphenyls | 0.059 | 0.032 | |||||||||
| Decachlorobiphenyls | 0.051 | 0.064 | |||||||||
| Total PCB | 0.418 | 0.536 |
| Species | River | BW (g) | TL (cm) | K | HSI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European eel (A. anguilla) | Picentino | ||||
| Tusciano | |||||
| Brown trout (S. trutta fario) | Picentino | ||||
| Tusciano |
| Alterations | European Eel (A. anguilla) | Brown Trout (S. trutta fario) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picentino River | Tusciano River | Picentino River | Tusciano River | |
| Blood sinusoid dilation | ||||
| Hemorrhage | ||||
| Cytoplasmic vacuolization | ||||
| Hemosideriosis | ||||
| Irregular arrangement of hepatocytes | ||||
| Lipid accumulation | ||||
| Necrosis | ||||
| Cellular hyperplasia | ||||
| Leukocytes infiltration | ||||
| melanomacrophages centers (MMCs) | ||||
| Alteration | European Eel (A. anguilla) | Brown Trout (S. trutta fario) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Picentino River | Tusciano River | Picentino River | Tusciano River | |
| Free melanomacrophages | ||||
| Hemosideriosis | ||||
| Melanomacrophage aggregates | ||||
| Necrosis | ||||
| Water Pollutants | Soil Pollutants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alterations | Pearson r | p Value (Two-Tailed) | Statistical Significance | Pearson r | p Value (Two-Tailed) | Statistical Significance |
| Blood sinusoid dilation | 0.9417 | 0.0583 | ns | 0.9417 | 0.0583 | ns |
| Hemorrhage | 0.9886 | 0.0114 | * | 0.9886 | 0.0114 | * |
| Cytoplasmic vacuolization | 0.9939 | 0.0061 | ** | 0.9939 | 0.0061 | ** |
| Hemosiderosis | 0.9874 | 0.0126 | * | 0.9874 | 0.0126 | * |
| Irregular arrangement of hepatocytes | 0.9962 | 0.0038 | ** | 0.9962 | 0.0038 | ** |
| Lipid accumulation | 0.9611 | 0.0389 | * | 0.9611 | 0.0389 | * |
| Necrosis | 0.9921 | 0.0079 | ** | 0.9921 | 0.0079 | ** |
| Cellular hyperplasia | 0.9831 | 0.0169 | * | 0.9831 | 0.0169 | * |
| Leukocytes infiltration | 0.9923 | 0.0077 | ** | 0.9923 | 0.0077 | ** |
| MMC | 0.9925 | 0.0075 | ** | 0.9925 | 0.0075 | ** |
| Water Pollutants | Soil Pollutants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alterations | Pearson r | p Value (Two-Tailed) | Statistical Significance | Pearson r | p Value (Two-Tailed) | Statistical Significance |
| Free melanomacrophages | 0.9258 | 0.0742 | ns | 0.9258 | 0.0742 | ns |
| Hemosiderosis | 0.9874 | 0.0126 | * | 0.9874 | 0.0126 | * |
| Melanomacrophage aggregates | 0.7432 | 0.2568 | ns | 0.7432 | 0.2568 | ns |
| Necrosis | 0.7675 | 0.2325 | ns | 0.7675 | 0.2325 | ns |
| ECA | EF | ENA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| European eel (A. anguilla) | Picentino River | 12.7 ± 2 | 1.18 ± 0.3 | 7.7 ± 2.1 |
| Tusciano River | 27.15 ± 2 *** | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 20.3 ± 0.9 ** | |
| Brown trout (S. trutta fario) | Picentino River | 16.3 ± 0.9 | 16.3 ± 0.9 | 9.1 ± 1.6 |
| Tusciano River | 28.6 ± 1.9 ** | 28.6 ± 1.9 *** | 21.1 ± 2.8 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orso, G.; Imperatore, R.; Coccia, E.; Rinaldi, G.; Cicchella, D.; Paolucci, M. A Deep Survey of Fish Health for the Recognition of Useful Biomarkers to Monitor Water Pollution. Environments 2023, 10, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120219
Orso G, Imperatore R, Coccia E, Rinaldi G, Cicchella D, Paolucci M. A Deep Survey of Fish Health for the Recognition of Useful Biomarkers to Monitor Water Pollution. Environments. 2023; 10(12):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120219
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrso, Graziella, Roberta Imperatore, Elena Coccia, Gianluca Rinaldi, Domenico Cicchella, and Marina Paolucci. 2023. "A Deep Survey of Fish Health for the Recognition of Useful Biomarkers to Monitor Water Pollution" Environments 10, no. 12: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120219
APA StyleOrso, G., Imperatore, R., Coccia, E., Rinaldi, G., Cicchella, D., & Paolucci, M. (2023). A Deep Survey of Fish Health for the Recognition of Useful Biomarkers to Monitor Water Pollution. Environments, 10(12), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments10120219








