An EEG Study on Emotional Intelligence and Advertising Message Effectiveness
Abstract
1. Introduction
Hypotheses
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Psychometrics
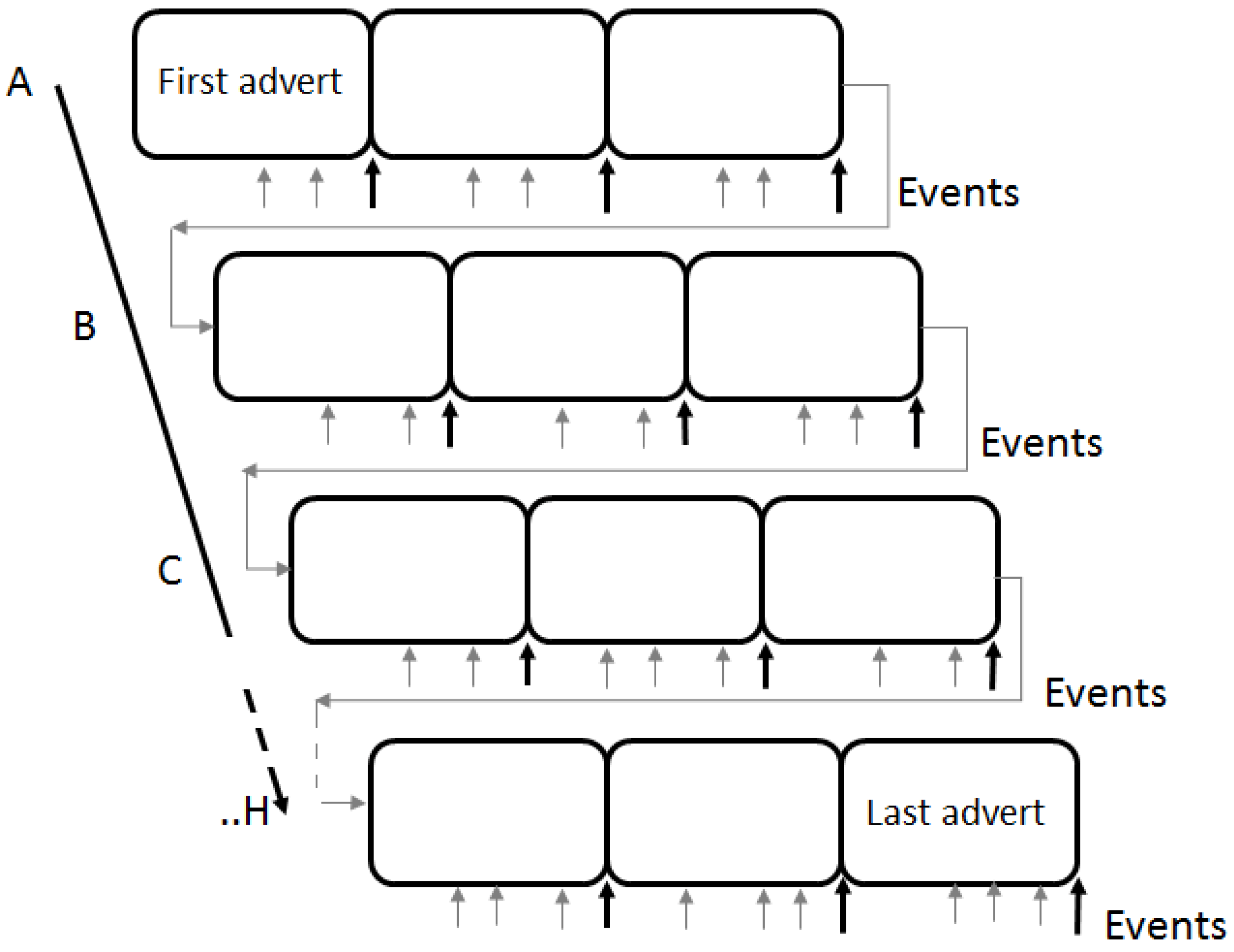
2.3. Electroencephalography (EEG) Stimuli
2.4. EEG Recording
2.5. EEG Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
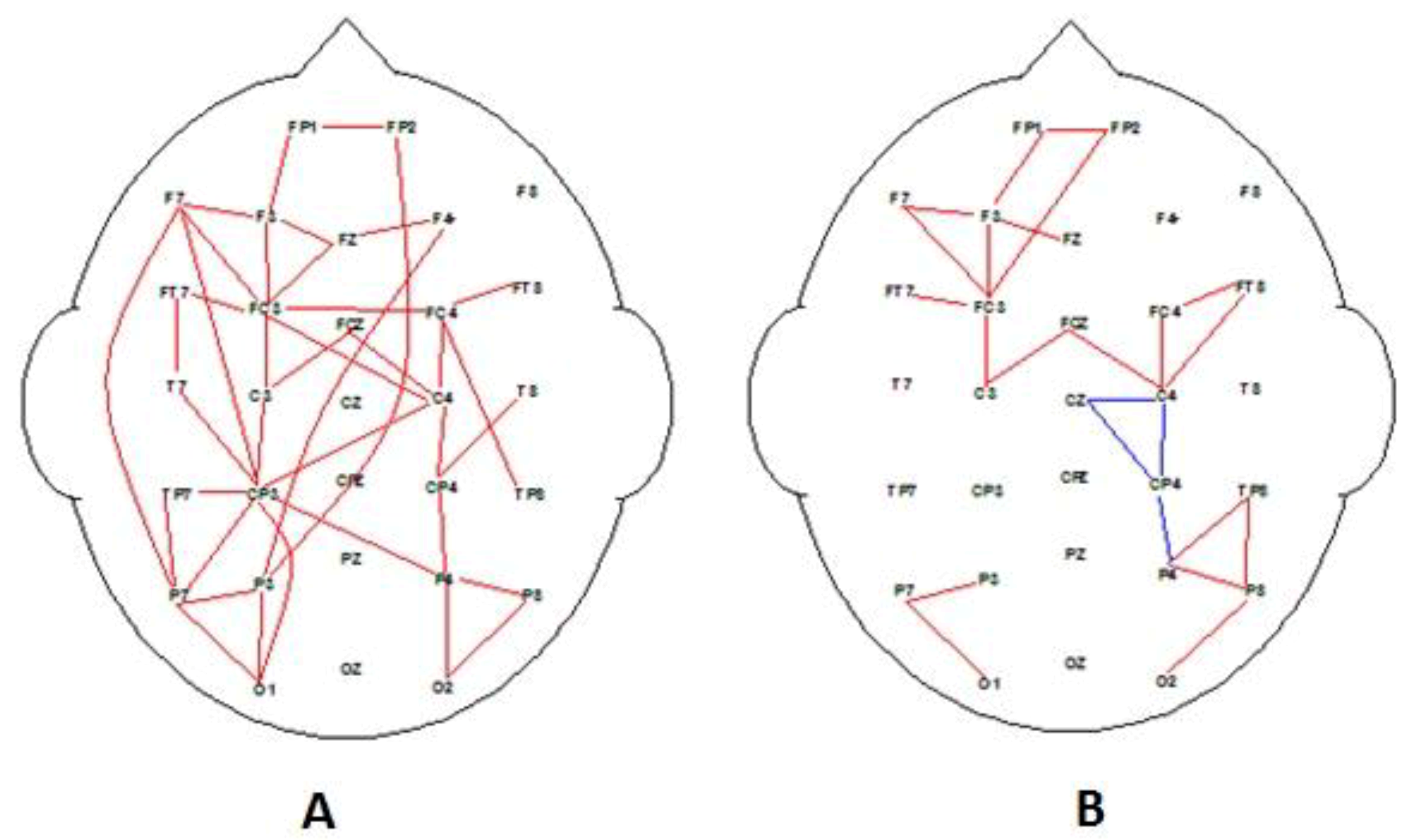
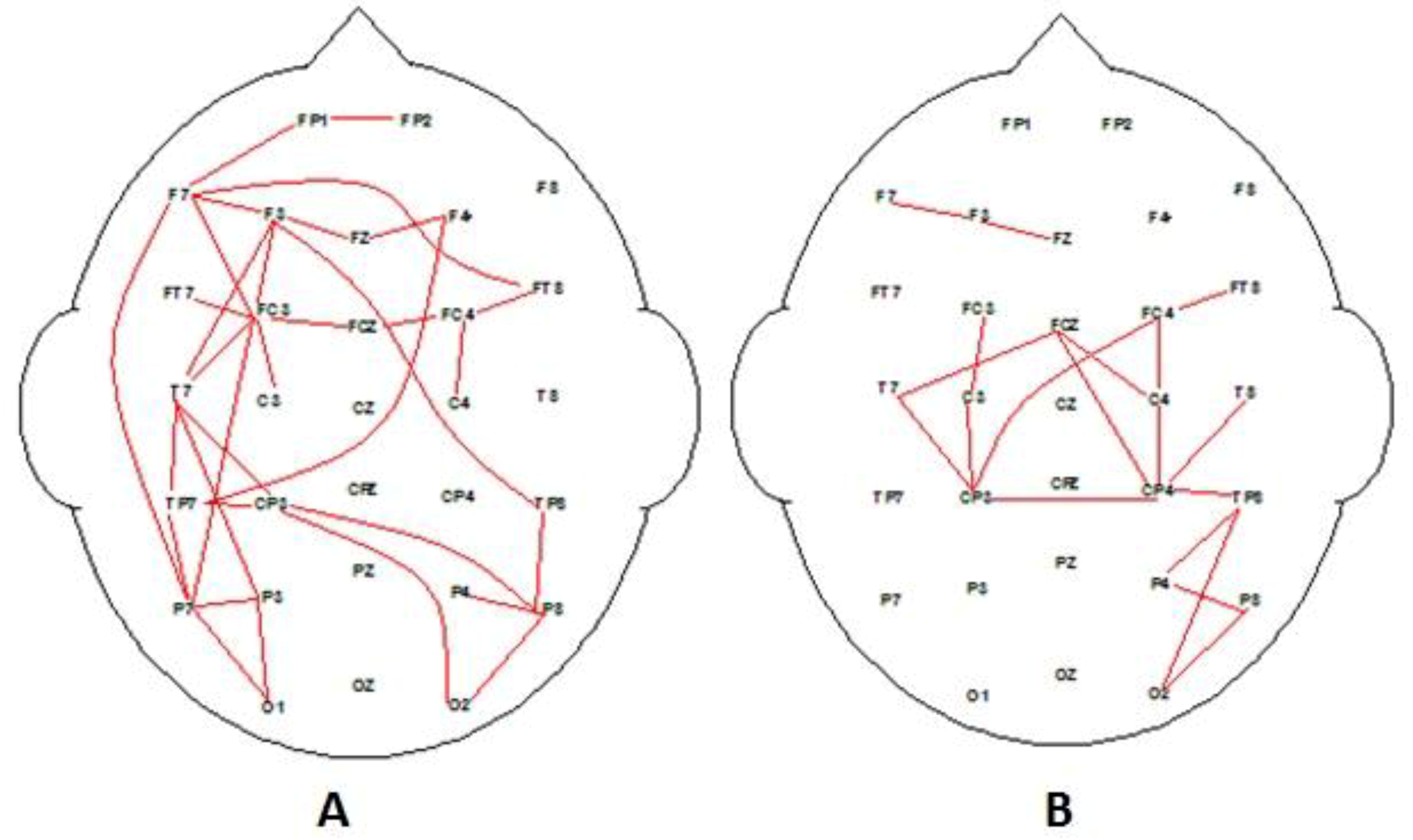
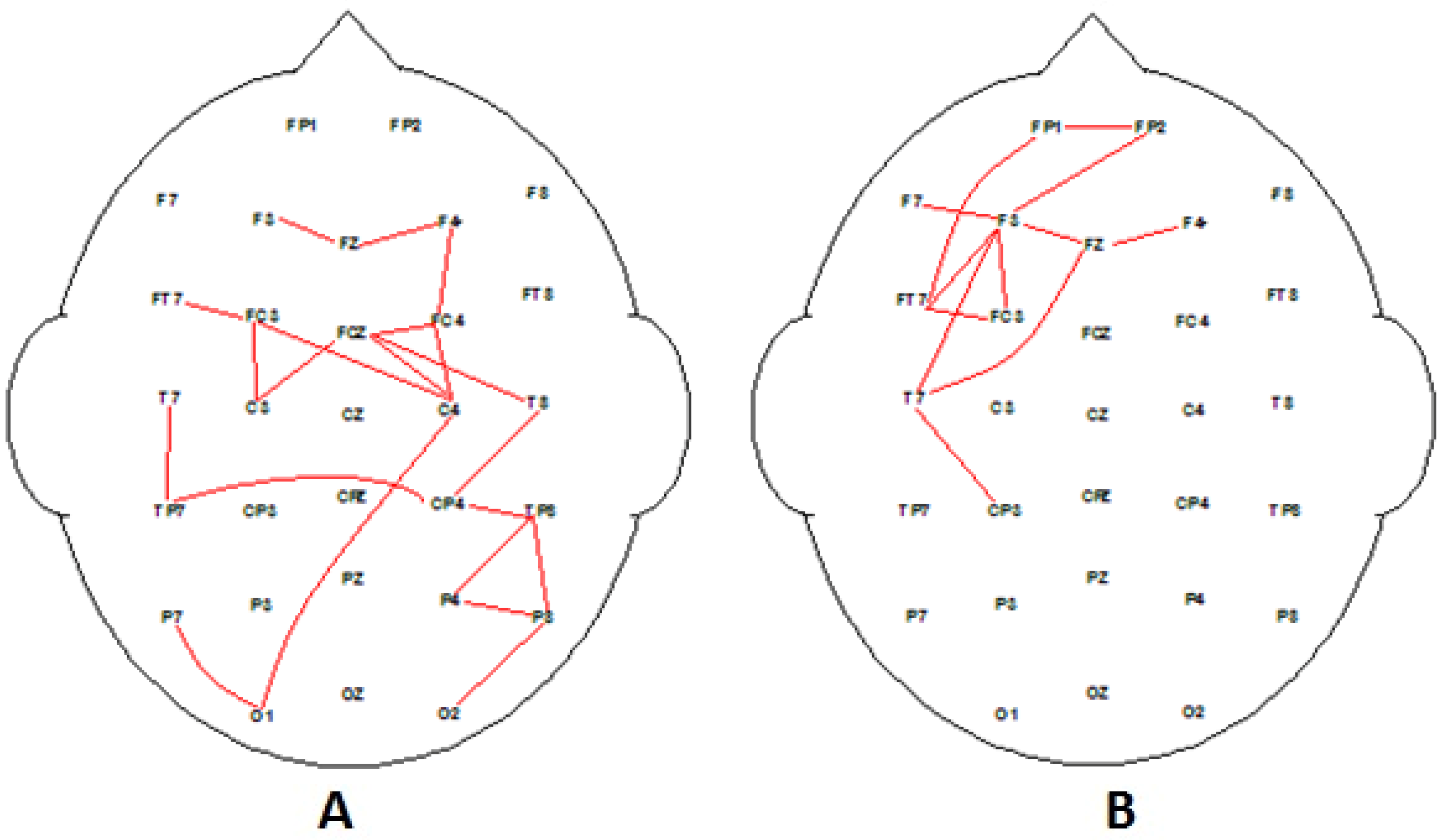
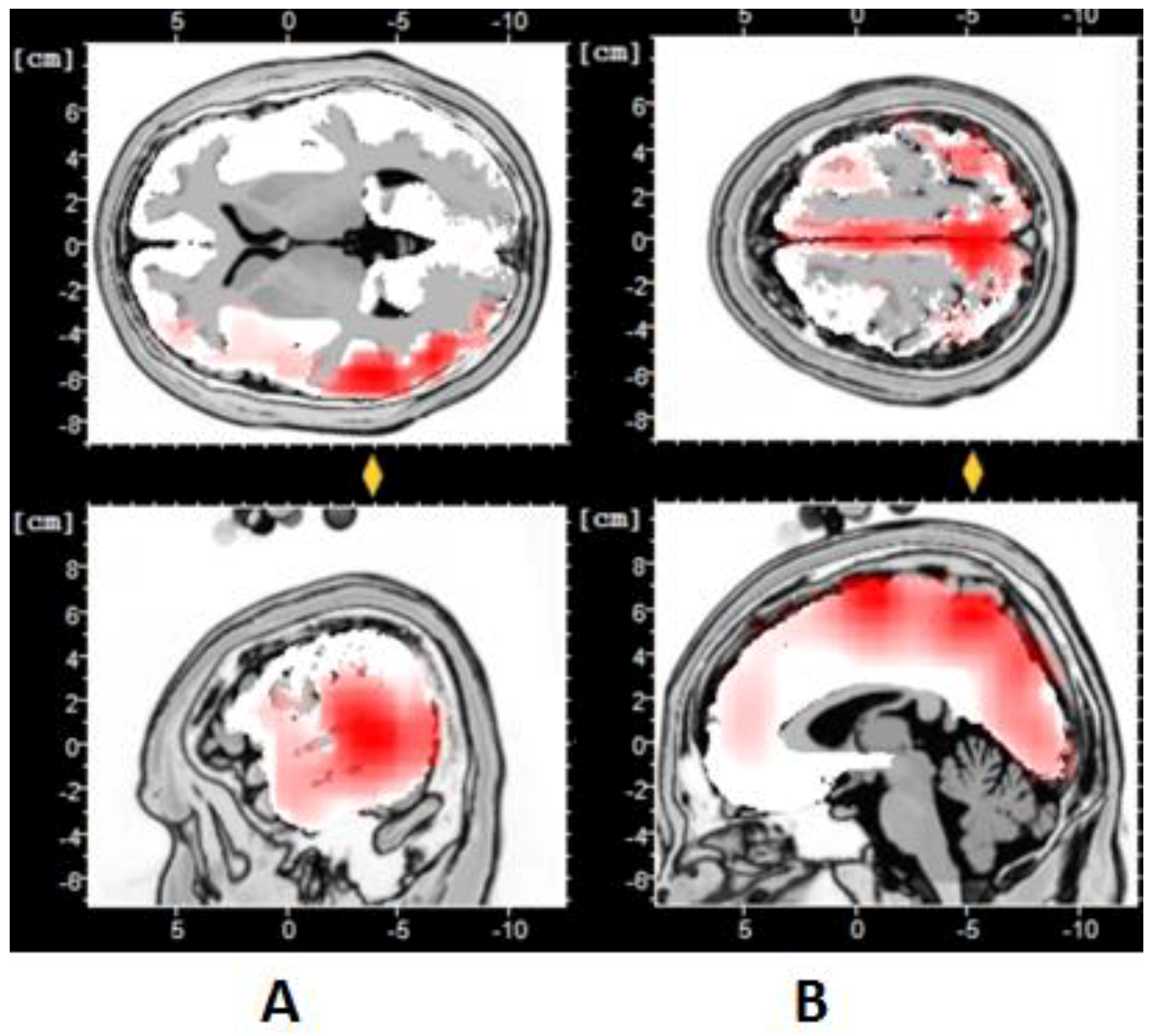
3.1. EEG Findings
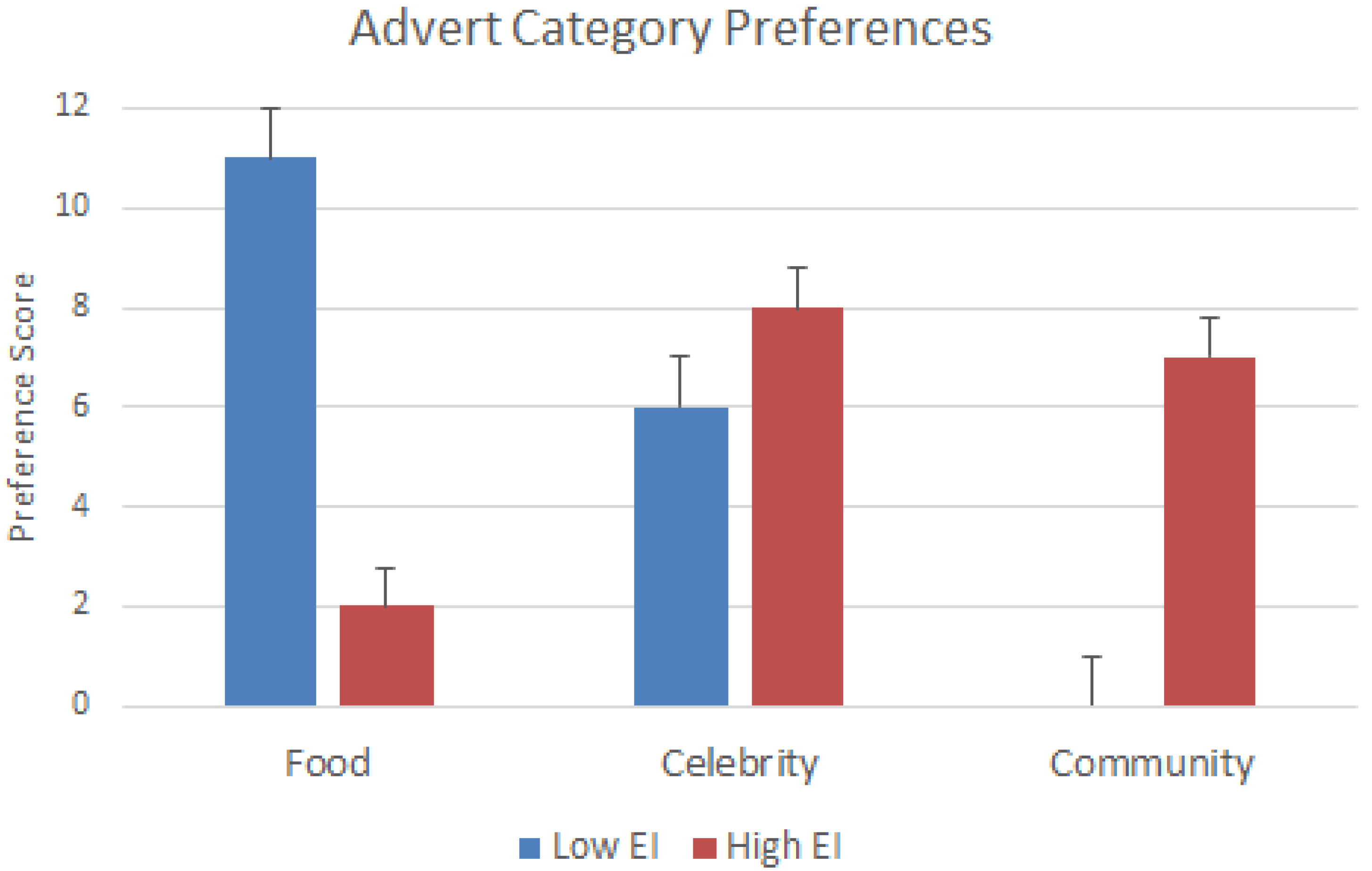
3.2. Behavioral Findings
3.3. Combination EEG and Behavioral Investigation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennis, M.; Rademaker, A.R.; Geuze, E. Neural correlates of personality: An integrative review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gountas, J.; Gountas, S. Personality orientations, emotional states, customer satisfaction, and intention to repurchase. J. Bus. Res. 2007, 60, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaleone, V.; Gountas, J. Personality characteristics of market mavens. Adv. Consum. Res. 2007, 34, 522–527. [Google Scholar]
- Barrash, J.; Tranel, D.; Anderson, S.W. Acquired personality disturbances associated with bilateral damage to the ventromedial prefrontal region. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2000, 18, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furnham, A.; Forde, L.; Cotter, T. Personality and intelligence. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1998, 24, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutafi, J.; Furnham, A.; Crump, J. Demographic and personality predictors of intelligence: A study using the Neo Personality Inventory and the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator. Eur. J. Personal. 2003, 17, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutte, N.S.; Malouff, J.M.; Thorsteinsson, E.B.; Bhullar, N.; Rooke, S.E. A meta-analytic investigation of the relationship between emotional intelligence and health. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2007, 42, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canli, T.; Zhao, Z.; Desmond, J.E.; Kang, E.; Gross, J.; Gabrieli, J.D. An fMRI study of personality influences on brain reactivity to emotional stimuli. Behav. Neurosci. 2001, 115, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashia, T.; Murataa, T.; Hamadab, T.; Omoria, M.; Kosakaa, H.; Kikuchic, M.; Yoshidab, H.; Wadaa, Y. Changes in EEG and autonomic nervous activity during meditation and their association with personality traits. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2005, 55, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, L.A.; Lee, B.; Stough, C. Recruitment Consultant Revenue: Relationships with IQ, personality, and emotional intelligence. Int. J. Sel. Assess. 2011, 19, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasuik, J.C.; Ciorciari, J.; Stough, C. Understanding the Neurobiology of Emotional Intelligence: A review. In Assessing Emotional Intelligence; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 307–320. [Google Scholar]
- Orth, U.; Malkewitz, K.; Bee, C. Gender and Personality Drivers of Consumer Mixed Emotional Response to Advertising. J. Curr. Issues Res. Advert. 2010, 32, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micu, A.C.; Plummer, J.T. Measurable Emotions: How Television Ads Really Work. J. Advert. Res. 2010, 50, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxall, G.R.; Yani-de-Soriamo, M.; Yousefzai, S.Y.; Javed, U. The role of neurophysiology, emotion and contingency in the explanation of consumer choice. In Handbook of Developments in Consumer Behavior; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northampton, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 461–523. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, J.D.; Caruso, D.R.; Salovey, P. Emotional intelligence meets traditional standards for an intelligence. Intelligence 1999, 27, 267–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salovey, P.; Grewal, D. The Science of Emotional Intelligence. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 14, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, D.R.; Mayer, J.D.; Salovey, P. Relation of an ability measure of emotional intelligence to personality. J. Personal. Assess. 2002, 79, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamachek, D. Dynamics of self-understanding and self-knowledge: Acquisition, advantages, and relation to emotional intelligence. J. Humanist. Couns. Educ. Dev. 2000, 38, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.L.; Brackett, M.A.; Shamosh, N.A.; Kiehl, K.A.; Salovey, P.; Gray, J.R. Emotional Intelligence predicts individual differences in social exchange reasoning. NeuroImage 2007, 35, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.M. Emotional intelligence and consumer ethics: The mdiating role of personal moral philosophies. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 142, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, G.; Lee, I.; Guimond, S.; Lutz, O.; Tandon, N.; Nawaz, U.; Brady, R. Individual variation in brain network topology is linked to emotional intelligence. NeuroImage 2019, 189, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, S.; Dan, O.; Zysberg, L. Neural correlates of emotional intelligence in a visual emotional oddball task: An ERP study. Brain Cogn. 2014, 91, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Taki, Y.; Sassa, Y.; Hashizume, H.; Sekiguchi, A.; Fukushima, A.; Kawashima, R. Regional gray matter density associated with emotional intelligence: Evidence from voxel-based morphometry. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, R.; Tranel, D.; Denburg, N.L.; Bechara, A. Exploring the neurological substrate of emotional and social intelligence. Brain 2003, 126, 1790–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, F.; Barbey, A.K.; McCabe, K.; Strenziok, M.; Zamboni, G.; Solomon, J.; Grafman, J. The neural bases of key competencies of emotional intelligence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22486–22491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.; Seitz, R.J.; Kolodny, J.; Bor, D.; Herzog, H.; Ahmed, A.; Emslie, H. A neural basis for general intelligence. Science 2000, 289, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, A.; Arefnasab, Z.; Babamahmoodi, A. Emotional Intelligence and Prefrontal Cortex: A Comparative Study Based on Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST). Iran. J. Psychiatry Behav. Sci. 2011, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaušovec, N.; Jaušovec, K. Differences in induced gamma and upper alpha oscillations in the human brain related to verbal/performance and emotional intelligence. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2005, 56, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaušovec, N.; Jaušovec, K.; Gerlič, I. Differences in event-related and induced EEG patterns in the theta and alpha frequency bands related to human emotional intelligence. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 311, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treleaven-Hassard, S.; Gold, J.; Bellman, S.; Schweda, A.; Ciorciari, J.; Critchley, C. Using the P3a to gauge automatic attention to interactive television advertising. J. Econ. Psychol. 2010, 31, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Edgar, K.; Fox, N.A. Individual differences in children’s performance during an emotional Stroop task: A behavioral and electrophysiological study. Brain Cogn. 2003, 52, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenthaler, H.H.; Fink, A.; Neubauer, A.C. Emotional abilities and cortical activation during emotional information processing. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2006, 41, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M.; Ciorciari, J.; Gountas, J. Consumer Neuroscience and Digital/Social Media Health/Social Cause Advertisement Effectiveness. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, L.M.; Ciorciari, J.; Kyrios, M. Cognitive processes associated with compulsive buying behaviours and related EEG coherence. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2014, 221, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraaykamp, G.; Van Eijck, K. Personality, media preferences, and cultural participation. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2005, 38, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M.; Ciorciari, J.; Gountas, J. Consumer neuroscience for marketing researchers. J. Consum. Behav. 2018, 17, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frith, U.; Frith, C. The Biological Basis of Social Interaction. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2001, 10, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.P.; Macrae, N.C.; Banaji, M.R. Forming impressions of people versus inanimate objects: Social-cognitive processing in the medial prefrontal cortex. NeuroImage 2005, 26, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, H.L.; Frith, C.D. Functional imaging of ‘theory of mind’. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2003, 7, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.; Gutchess, A.H.; Feinberg, F.; Polk, T.A. A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of Neural Dissociations between Brand and Person Judgments. J. Consum. Res. 2006, 33, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacInnis, D.J.; Jaworski, B.J. Information Processing from Advertisements: Toward an Integrative Framework. J. Mark. 1989, 53, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.; Stough, C. Workplace SUEIT: Swinburne University Emotional Intelligence Test–Descriptive Report; Organisational Psychology Research Unit, Swinburne University: Melbourne, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cheshire, M.H.; Strickland, H.P.; Carter, M.R. Comparing traditional measures of academic success with emotional intelligence scores in nursing students. Asia-Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2015, 2, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Standardised low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): Technical details. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Psychol. 2002, 24, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sauseng, P.; Klimesch, W.; Schabus, M.; Doppelmayr, M. Fronto-parietal EEG coherence in theta and upper alpha reflect central executive functions of working memory. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2005, 57, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petsche, H. EEG coherence and mental activity. In Analysis of the Electrical Activity of the Brain; Angeleri, F., Butler, S., Giaquinto, S., Majkowshi, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher, R.W. Neural coherence and the content of consciousness. Conscious. Cogn. 1997, 6, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anokhin, A.P.; Lutzenberger, W.; Birbaumer, N. Spatiotemporal organization of brain dynamics and intelligence: An EEG study in adolescents. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1999, 33, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.C. Correlation and coherence analysis of the EEG: A selective tutorial review. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1984, 1, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Staffan, J.; Maresch, H. ERD mapping and functional topography: Temporal and spatial aspects. In Functional Brain Imaging; Pfurtscheller, G., da Silva, L.F.H., Eds.; Hans Huber Publishers: Bern, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Vecchiato, G.; Astolfi, L.; De Vico Fallani, F.; Cincotti, F.; Mattia, D.; Salinari, S.; Soranzo, R.; Babiloni, F. Changes in brain activity during the observation of TV commercials by using EEG, GSR and HR measurements. Brain Topogr. 2010, 23, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mölle, M.; Marshall, L.; Fehm, H.L.; Born, J. EEG theta synchronization conjoined with alpha desynchronization indicate intentional encoding. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viemose, I.; Møller, P.; Laugesen, J.L.; Schachtman, T.R.; Manoharan, T.; Christoffersen, G.R.J. Appetitive long-term taste conditioning enhances human visually evoked EEG responses. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 253 (Suppl. C), 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudewyn, M.A.; Luck, S.J.; Farrens, J.L.; Kappenman, E.S. How many trials does it take to get a significant ERP effect? It depends. Psychophysiology 2017, 55, e13049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, F.; Ciorciari, J.; Varker, T.; Devilly, G.J. Changes in long term neural connectivity following psychological trauma. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, R.W.; Krause, P.J.; Hrybyk, M. Cortico-cortical associations and EEG coherence: A two-compartmental model. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1986, 64, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappelsberger, P.; Petsche, H. Probability mapping: Power and coherence analyses of cognitive processes. Brain Topogr. 1988, 1, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Review of Methods for Solving the EEG Inverse Problem. Int. J. Bioelectromagn. 1999, 1, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, I.; Warren, C.; Pajot, S.K.; Schairer, D.; Leuchter, A.F. Regional brain activation with advertising images. J. Neurosci. Psychol. Econ. 2011, 4, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; L.Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Baddeley, A. The episodic buffer: A new component of working memory? Trends Cogn. Sci. 2000, 4, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.C.; Downey, L.A.; Ford, T.C.; Lomas, J.E.; Stough, C. Green teens: Investigating the role of emotional intelligence in adolescent environmentalism. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2019, 138, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gountas, J.; Gountas, S.; Reeves, R.; Moran, L. The Desire for Fame: Scale Development and Association with Personal Goals and Aspirations. Psychol. Mark. 2012, 29, 680–689. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, M.; Gountas, J.; Gountas, S.; Sharma, P. Celebrity influences on consumer descion making: New insights and resaerch directions. J. Mark. Manag. 2019, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Esposito, M.; Detre, J.A.; Aguirre, G.K.; Stallcup, M.; Alsop, D.C.; Tippet, L.J.; Farah, M.J. A functional MRI study of mental image generation. Neuropsychologia 1997, 35, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanakawa, T.; Honda, M.; Sawamoto, N.; Okada, T.; Yonekura, Y.; Fukuyama, H.; Shibasaki, H. The Role of Rostral Brodmann Area 6 in Mental-operation Tasks: An Integrative Neuroimaging Approach. Cereb. Cortex 2002, 12, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccino, G.; Binkofski, F.; Fink, G.R.; Fadiga, L.; Fogassi, L.; Gallese, V.; Freund, H.J. Action observation activates premotor and parietal areas in a somatotopic manner: An fMRI study. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, S.; Dan, O.; Arad, H.; Zysberg, L. Behavioral and neural correlates of emotional intelligence: An Event-Related Potentials (ERP) study. Brain Res. 2013, 1526, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebart, M.N.; Hesselmann, G. What Visual Information Is Processed in the Human Dorsal Stream? J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, S.; Van Dyne, L.; Koh, C.; Ng, K.Y.; Templer, K.J.; Tay, C.; Chandrasekar, N.A. Cultural Intelligence: Its Measurement and Effects on Cultural Judgment and Decision Making, Cultural Adaptation and Task Performance. Manag. Organ. Rev. 2007, 3, 335–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, E.; Güntekin, B. A short review of alpha activity in cognitive processes and in cognitive impairment. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2012, 86, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stysko-Kunkowska, M.; Borecka, M. Extraversion and evaluation of humorous advertisements. Psychol. Rep. 2010, 106, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeYoung, C.G.; Gray, J.R. Personality neuroscience: explaining individual differences in affect, behaviour and cognition. In The Cambridge Handbook of Personality Psychology Cambridge; Corr, P.J., Matthews, G., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 323–346. [Google Scholar]
- Knutson, B.; Cooper, J.C. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of reward prediction. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2005, 18, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascalis, V.; Speranza, O. Personality Effects on Attentional Shifts to Emotional Charged Cues: ERP, Behavioural and HR Data. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2000, 29, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.T.; McCrae, R.R. Revised NEO Personality Inventory and NEO Five-factor Inventory Professional Manual. Odessa; Psychological Assessment Resources: Lutz, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bjørnebekk, A.; Fjell, A.M.; Walhovd, K.B.; Grydeland, H.; Torgersen, S. Neuronal correlates of the five factor model (FFM) of human personality: Multimodal imaging in a large healthy sample. Neuroimage 2013, 65, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, A. Brand excellence: Measuring the impact of advertising and brand personality on buying decisions. Meas. Bus. Excell. 2006, 10, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couwenberg, L.E.; Boksem, M.A.S.; Dietvorst, R.C.; Worm, L.; Verbeke, W.J.M.I.; Smidts, A. Neural responses to functional and experiential ad appeals: Explaining ad effectiveness. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2016, 34, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Sicilia, M. The impact of cognitive and/or affective processing styles on consumer response to advertising. J. Bus. Res. 2004, 57, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.D.; Szmerekovsky, J.G. Attraction to Employment Advertisements: Advertisement Wording and Personality Characteristics. J. Manag. Issues 2010, 22, 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Haugtvedt, C.P.; Petty, R.E.; Cacioppo, J.T. Need for Cognition and Advertising: Understanding the Role of Personality Variables in Consumer Behavior. J. Consum. Psychol. 1992, 1, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBarbera, P.A.; Weingard, P.; Yorkston, E.A. Matching The Message to the Mind: Advertising imagery and Consumer Processing Styles. J. Advert. Res. 1998, 38, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Schilo, L.; Kee, D.W. Gender differences in the relationship between emotional intelligence and right hemisphere lateralization for facial processing. Brain Cogn. 2010, 73, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.; Tran, Y.; Hermens, G.; Williams, L.M.; Kemp, A.; Morris, C.; Gordon, E. Psychological and neural correlates of emotional intelligence in a large sample of adult males and females. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2009, 46, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari, R.; Puce, A. MEG-EEG Primer; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciorciari, J.; Pfeifer, J.; Gountas, J. An EEG Study on Emotional Intelligence and Advertising Message Effectiveness. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9080088
Ciorciari J, Pfeifer J, Gountas J. An EEG Study on Emotional Intelligence and Advertising Message Effectiveness. Behavioral Sciences. 2019; 9(8):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9080088
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiorciari, Joseph, Jeffrey Pfeifer, and John Gountas. 2019. "An EEG Study on Emotional Intelligence and Advertising Message Effectiveness" Behavioral Sciences 9, no. 8: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9080088
APA StyleCiorciari, J., Pfeifer, J., & Gountas, J. (2019). An EEG Study on Emotional Intelligence and Advertising Message Effectiveness. Behavioral Sciences, 9(8), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs9080088





