Is Black Always the Opposite of White? An Investigation on the Comprehension of Antonyms in People with Schizophrenia and in Healthy Participants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Antonym Word Pairs
1.2. The Present Study
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
| Demographic/clinical criteria | Patients | Controls | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Min. | Max. | SD | Mean | Min. | Max. | SD | ||
| Sex | M=25; F=14 | M = 25; F = 14 | |||||||
| Age (years) | 31.41 | 20 | 45 | 6.22 | 31.28 | 19 | 45 | 6.31 | 0.93 |
| Education (years) | 12.56 | 10 | 17 | 1.33 | 12.51 | 10 | 17 | 1.48 | 0.88 |
| Drug | SG = 33; FG = 2; FSG = 4 | ||||||||
| Years of illness | 8.97 | 1 | 29 | 5.94 | |||||
| WAIS-R (Verbal Scale) | 91.05 | 62 | 118 | 15.41 | |||||
| WAIS-R (Performance Scale) | 86.31 | 58 | 121 | 19.42 | |||||
| WAIS-R (total score) | 87.82 | 58 | 126 | 18.31 | |||||
| Vocabulary (WAIS-R) | 8.23 | 3 | 15 | 3.24 | 10.77 | 7 | 17 | 2.38 | 0.0001 |
| Phonemic fluency | 28.51 | 15 | 54 | 8.25 | 37.28 | 23 | 58 | 7.68 | 0.0001 |
| Semantic fluency | 38.44 | 25 | 62 | 8.44 | 44.10 | 23 | 56 | 7.74 | 0.003 |
| BADA (errors) | 1.15 | 0 | 5 | 1.18 | 0.03 | 0 | 1 | 0.16 | 0.0001 |
| Digit span (forward) | 5.44 | 3.5 | 7.5 | 0.74 | 5.85 | 4.5 | 7.75 | 0.83 | 0.04 |
| Digit span (backward) | 3.75 | 1.69 | 6.42 | 1.07 | 4.28 | 1.47 | 6.47 | 0.97 | 0.05 |
| Digit span (total score) | 9.18 | 6.44 | 13.29 | 1,51 | 10.13 | 6.97 | 13.92 | 1.57 | 0.02 |
| BPRS | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | |||||
| PANSS (Positive Scale) | 11.64 | 7 | 19 | 3.12 | |||||
| PANSS (Negative Scale) | 11.21 | 7 | 26 | 4.02 | |||||
| PANSS (General Psychopathology Scale) | 23.84 | 18 | 34 | 3.43 | |||||
| PANSS (Total Score) | 46.69 | 34 | 68 | 8.13 | |||||
2.2. Materials
| Number of Letters | Age of Acquisition | Frequency (Ln) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opposite | Non-opposite | p | Opposite | Non-opposite | p | Opposite | Non-opposite | p |
| 6.25 (1.69) | 6.08 (1.49) | 0.32 | 2.72 (0.97) | 2.82 (1.07) | 0.14 | 5.37 (1.37) | 5.02 (1.60) | 0.31 |
2.3. Design and Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
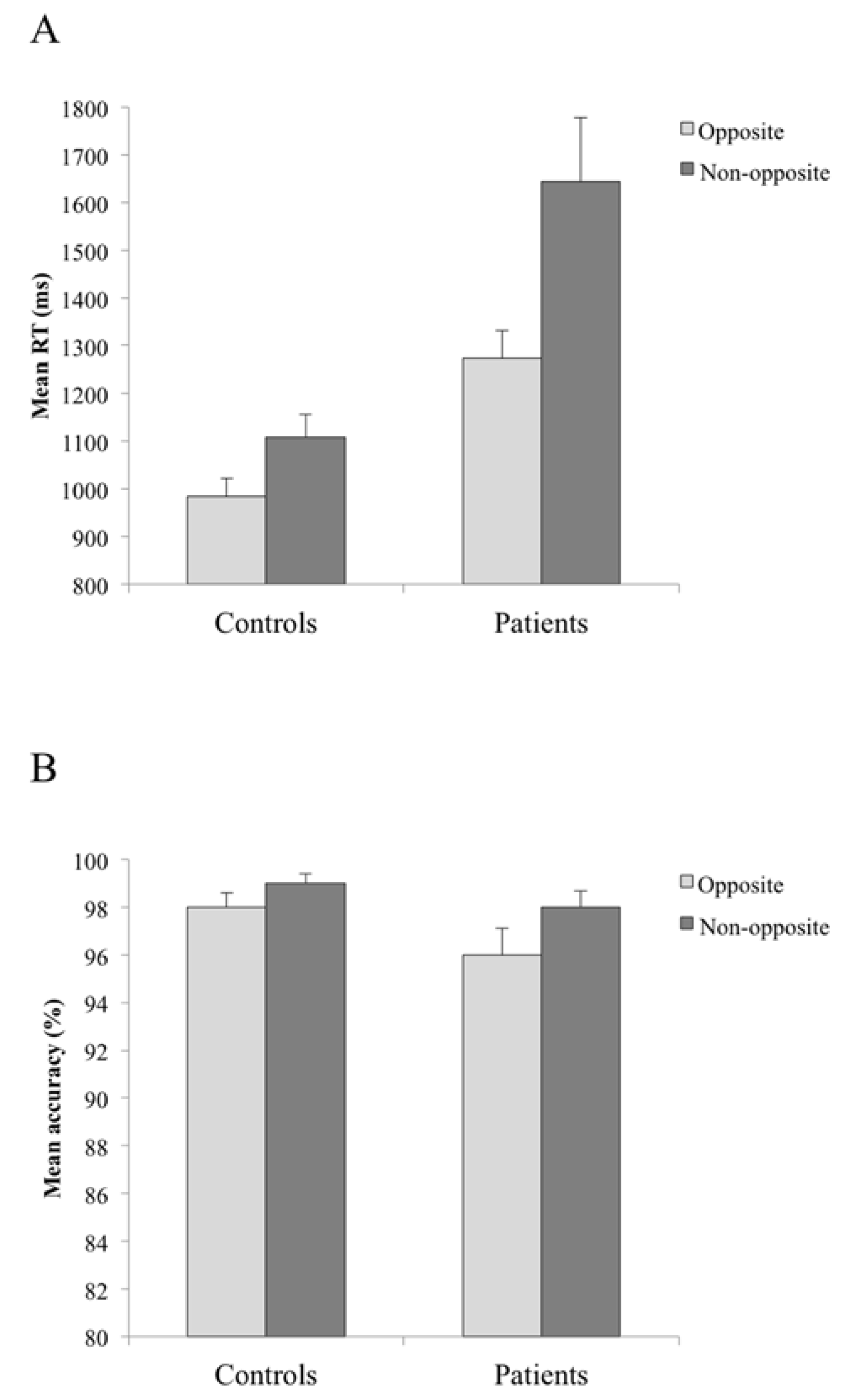
4. General Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Appendix
| W1 | W2 | W3 |
|---|---|---|
| ottimista | pessimista | dilettante |
| inizio | fine | pelle |
| vivo | morto | forte |
| padre | madre | dolce |
| veloce | lento | sordo |
| giorno | notte | fuoco |
| falso | vero | solo |
| chiuso | aperto | presto |
| differente | uguale | lontano |
| maschio | femmina | contento |
| scuro | chiaro | perso |
| destra | sinistra | inverno |
| sotto | sopra | stanza |
| grande | piccolo | verde |
| brutto | bello | giusto |
| pesante | leggero | vicino |
| perdente | vincente | civile |
| vuoto | pieno | ricco |
| colpevole | innocente | commerciante |
| buono | cattivo | spento |
| privato | pubblico | critico |
| alto | basso | bravo |
| rumoroso | silenzioso | divertente |
| maggiore | minore | inutile |
| facile | difficile | fresco |
| lungo | corto | sporco |
| nuovo | vecchio | povero |
| luce | buio | mano |
| largo | stretto | viola |
| bianco | nero | caro |
| caldo | freddo | tenero |
| ottimo | pessimo | intatto |
| uomo | donna | carta |
| asciutto | bagnato | bugiardo |
| attivo | passivo | vorace |
| guerra | pace | gara |
| amore | odio | storto |
| fratello | sorella | favola |
| prima | dopo | come |
| giusto | sbagliato | colorato |
Conflict of Interest
References
- Kuperberg, G.R. Language in Schizophrenia. Part 1. An Introduction. Lang. Linguist. Compass 2010, 4, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperberg, G.R. Language in Schizophrenia. Part 2. What psycholinguistics bring to the study of schizophrenia… and vice versa? Lang. Linguist. Compass 2010, 4, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiang, M. Schizotypy and language: A review. J. Neurolinguist. 2010, 23, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barch, D.M.; Ceaser, A. Cognition in schizophrenia: Core psychological and neural mechanisms. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 1, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, P.D. Cognitive functioning and disability in schizophrenia. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 19, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.L.; Coleman, M.J.; Sung, H.; Ji, F.; Matthysse, S.; Mendell, N.R.; Titone, D. The genetic basis of thought disorder and language and communication disturbances in schizophrenia. J. Neurolinguist. 2010, 23, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.L.; Crow, T.J. Right hemisphere language functions and schizophrenia: The forgotten hemisphere? Brain 2005, 128, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperberg, G.R.; Heckers, S. Schizophrenia and cognitive function. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2000, 10, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraguljac, N.V.; Srivastava, A.; Lahti, A.C. Memory Deficits in Schizophrenia: A Selective Review of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Studies. Behav. Sci. 2013, 30, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minzenberg, M.J.; Ober, B.A.; Vinogradov, S. Semantic priming in schizophrenia: A review and synthesis. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2002, 8, 699–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pomarol-Clotet, E.; Oh, T.M.; Laws, K.R.; McKenna, P.J. Semantic priming in schizophrenia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2008, 192, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Conder, J.A.; Blitzer, D.N.; Shinkareva, S.V. Neural representation of abstract and concrete concepts: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathalon, D.H.; Roach, B.J.; Ford, M. Automatic semantic priming abnormalities in schizophrenia. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2010, 75, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiang, M.; Christensen, B.K.; Kutas, M.; Zipursky, R.B. Electrophysiological evidence for primary semantic memory functional organization deficits in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 196, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brébion, G.; Stephan-Otto, C.; Huerta-Ramos, E.; Usall, J.; Ochoa, S.; Roca, M.; Abellan-Vega, H.; Haro, J.M. Abnormal functioning of the semantic network in schizophrenia patients with thought disorganization. An exemplar production task. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 205, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditman, T.; Goff, D.; Kuperberg, G. Slow and steady: Sustained effects of lexico-semantic associations can mediate referential impairments in schizophrenia. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 11, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.D.; Barch, D.M.; Carter, C.; Servan-Schreiber, D. Context-processing deficits in schizophrenia: Converging evidence from three theoretically motivated cognitive tasks. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1999, 108, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperberg, G.R.; McGuire, P.K.; David, A.S. Reduced sensitivity to linguistic context in schizophrenic thought disorder: Evidence from on-line monitoring for words in linguistically anomalous sentences. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1998, 107, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarley, R.W.; Niznikiewicz, M.A.; Salisbury, D.F.; Nestor, P.G.; O’Donnell, B.F.; Hirayasu, Y.; Grunze, H.; Greene, R.W.; Shenton, M.E. Cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia: Unifying basic research and clinical aspects. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1999, 249, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niznikiewicz, M.A.; Friedman, M.; Shenton, M.E.; Voglmaier, M.; Nestor, P.G.; Frumin, M.; Seidman, L.; Sutton, J.; McCarley, R.W. Processing sentence context in women with schizotypal personality disorder: An ERP study. Psychophysiology 2004, 41, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titone, D.; Levy, D.L.; Holzman, P.S. Contextual insensitivity in schizophrenic language processing: Evidence from lexical ambiguity. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2000, 109, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titone, D.; Holzman, P.S.; Levy, D.L. Idiom processing in schizophrenia: Literal implausibility saves the day for idiom priming. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2002, 111, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.D.; Servan-Schreiber, D. Context, cortex, and dopamine: A connectionist approach to behavior and biology in schizophrenia. Psychol. Rev. 1992, 99, 45–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barch, D.M.; Cohen, J.D.; Servan-Schreiber, D.; Steingard, S.; Steinhauer, S.S.; van Kammen, D.P. Semantic priming in schizophrenia: An examination of spreading activation using word pronunciation and multiple SOAs. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1996, 105, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salisbury, D.F. Semantic memory and verbal working memory correlates of N400 to subordinate homographs. Brain Cogn. 2004, 55, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditman, T.; Kuperberg, G.R. The time course of building discourse coherence in schizophrenia: An ERP investigation. Psychophysiology 2007, 44, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condray, R.; Steinhauer, S.R.; van Kammen, D.P.; Kasparek, A. The language system in schizophrenia: Effects of capacity and linguistic structure. Schizophr. Bull. 2002, 28, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brébion, G.; Bressan, R.A.; Ohlsen, R.I.; Pilowsky, L.S.; David, A.S. Production of atypical category exemplars in patients with schizophrenia. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2010, 16, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditman, T.; Kuperberg, G. Building coherence: A framework for exploring the breakdown of links across clause boundaries in schizophrenia. J. Neurolinguist. 2010, 23, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutch, S.J.; Williams, P.; Ridgway, G.R.; Borgenicht, L. The role of polarity in antonym and synonym conceptual knowledge: Evidence from stroke aphasia and multidimensional ratings of abstract words. Neuropsychologia 2012, 50, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S. Antonymy: A Corpus-Based Perspective; Routledge: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, C.; Willners, C. Antonymy: From convention to meaning-making. Rev. Cogn. Linguist. 2011, 9, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, I.; Savardi, U.; Kubovy, M. Dimensions and their poles: A metric and topological theory of opposites. Lang. Cogn. Process. 2011, 26, 1232–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellbaum, C. WordNet: An Electronic Lexical Database; Fellbaum, C., Ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Willners, C. Antonyms in Context. A Corpus-Based Semantic Analysis of Swedish Descriptive Adjective. Travaux de l’Institut de Linguistique de Lund 40; Department of Linguistics, Lund University: Lund, Sweden, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, M.L. Semantic Relations and the Lexicon: Antonymy, Synonymy and Other Paradigms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Weijr, J.; Paradis, C.; Willners, C.; Lindgren, M. Antonym canonicity: Temporal and contextual manipulations. Brain Lang. 2014, 128, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, C.; Willners, C.; Jones, S. Good and bad opposites: Using textual and psycholinguistic techniques to measure antonym canonicity. Mental Lex. 2009, 4, 380–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, D.; Fischer, U.; Miller, G.A. The organization of adjectival meanings. J. Memory Lang. 1989, 28, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, S.; Giller, D.W. Some verbal aspects of primary-process thought: A partial replication. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1965, 95, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, A.G. Some verbal aspects of primary process thought in schizophrenia. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 1961, 62, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentin, S. Event-related potentials, semantic processes, and expectancy factors in word recognition. Brain Lang. 1987, 31, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, F.; Bornkessel-Schlesewsky, I.; Schlesewsky, M. Parafoveal and foveal N400s dissociate spreading activation from contextual fit. NeuroReport 2009, 20, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehm, D.; Bornkessel-Schlesewsky, I.; Rösler, F.; Schlesewsky, M. To predict or not to predict: Influences of task and strategy on the processing of semantic relations. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1259–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, K.A. Is semantic priming due to association strength or feature overlap? A microanalytic review. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2003, 10, 785–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, P.J.L. Target-error resemblance in French word substitution speech errors and the mental lexicon. Appl. Psycholinguist. 1999, 20, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.A.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Cho, Z.H. Neural substrates of semantic relationships: Common and distinct left-frontal activities for generation of synonyms vs. antonyms. NeuroImage 2009, 48, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutas, M.; Iragui, V. The N400 in a semantic categorization task across six decades. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 108, 456–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Just, M.A.; Carpenter, P.A. A theory of reading: From eye fixations to comprehension. Psychol. Rev. 1980, 87, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperberg, G.R.; Kreher, D.A.; Goff, D.; McGuire, P.K.; David, A.S. Building up linguistic context in schizophrenia: Evidence from self-paced reading. Neuropsychology 2006, 20, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, P.D.; DeSanti, L.A.; Maddox, J.; Harkavy-Friedman, J.M.; Amador, X.F.; Goetz, R.R.; Javitt, D.C.; Gorman, J.M. Visual backward-masking deficits in schizophrenia: Relationship to visual pathway function and symptomatology. Schizophr. Res. 2002, 59, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quelen, F.; Grainger, J.; Raymondet, P. An investigation of semantic priming in schizophrenia using a new priming paradigm. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 80, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, S.; Poole, J.H.; Willis-Shore, J.; Ober, B.A.; Shenaut, G.K. Slower and more variable reaction times in schizophrenia: What do they signify? Schizophr. Res. 1998, 32, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, M.; Braun, U.; Hermle, L.; Maier, S. Associative semantic network dysfunction in thought-disordered schizophrenic patients: Direct evidence from indirect semantic priming. Biol. Psychiatry 1993, 34, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, M.; Weisker, I.; Winter, M.; Maier, S.; Hermle, L.; Maher, B.A. Semantic and phonological priming in schizophrenia. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1994, 103, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, M.; Martens, U.; Weisbrod, M.; Hermle, L.; Spitzer, M. Increased unconscious semantic activation in schizophrenia patients with formal thought disorder. Schizophr. Res. 2009, 114, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safadi, Z.; Lichtenstein-Vidne, L.; Dobrusin, M.; Henik, A. Investigating thought disorder in schizophrenia: Evidence for pathological activation. PLoS One 2013, 8, e82882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salisbury, D.F. Semantic activation and verbal working memory maintenance in schizophrenic thought disorder: Insights from electrophysiology and lexical ambiguity. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2008, 39, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitnikova, T.; Perrone, C.; Goff, D.; Kuperberg, G.R. Neurocognitive mechanisms of conceptual processing in healthy adults and patients with schizophrenia. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2010, 75, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, B.A.; Manschreck, T.C.; Redmond, D.; Beaudette, S. Length of illness and the gradient from positive to negative semantic priming in schizophrenic patients. Schizophr. Res. 1996, 22, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.D.; Crawford, J.R. A meta-analytic review of verbal fluency deficits in schizophrenia relative to other neurocognitive deficits. Cogn. Neuropsychiatry 2005, 10, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.Y.L.; Chen, E.Y.H.; Chan, C.K.Y.; Lam, L.C.W.; Lieh-Mak, F. Verbal fluency in schizophrenia: Reduction in semantic store. Aust. New Zealand J. Psychiatry 2000, 34, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, D.A. Three classes of antonym in English. Lingua 1976, 38, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezek, E. Lessico. Classi di Parole, Strutture e Combinazioni; Il Mulino: Bologna, Italy, 2005. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Duñabeita, J.A.; Avilés, A.; Afonso, O.; Scheepers, C.; Carreiras, M. Qualitative differences in the representation of abstract versus concrete words: Evidence from the visual-world paradigm. Cognition 2009, 110, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kousta, S.T.; Vigliocco, G.; Vinson, D.P.; Andrews, M.; del Campo, E. The representation of abstract words: Why emotion matters. J. Exp. Psychol. 2011, 140, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, D.R. Verbal abstraction in psychiatric illness: Assay of impairment utilizing proverbs. Br. J. Psychiatry 1961, 107, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettino, A.; Lauro, L.R.; Crippa, F.; Anselmetti, S.; Cavallaro, R.; Papagno, C. The comprehension of idiomatic expressions in schizophrenic patients. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesciarelli, F.; Gamberoni, T.; Ferlazzo, F.; lo Russo, L.; Pedrazzi, F.; Melati, E.; Cacciari, C. Is the comprehension of idiomatic sentences indeed impaired in paranoid schizophrenia? A window into semantic processing deficits. Front. Hum. Neurosc. 2014, 8, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; APA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ventura, J.; Lukoff, D.; Nuechterlein, K.H.; Liberman, R.P.; Green, M.E.; Shaner, A. Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS), Expanded Version (4.0): Scales, anchor points, and administration manual. Int. J. Methods Psychiatric Res. 1993, 3, 227–243. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S.R.; Fisz-Bein, A.; Opler, L.A. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohr, J.B.; Braff, D.L. The value of referring to recently introduced antipsychotics as “second generation”. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1371–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, G.; Laudanna, A.; Burani, C.; Capasso, R. Batteria per l’Analisi dei Deficit Afasici (B.A.D.A.); CEPSAG, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore: Roma, Italy, 1994. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Novelli, G.; Papagno, C.; Capitani, E.; Laiacona, N.; Vallar, G.; Cappa, S.F. Tre test clinici di ricerca e produzione lessicale. Taratura su soggetti normali. Arch. Psicol. Neurol. Psichiatr. 1986, 47, 477–506. [Google Scholar]
- Lezak, M.D.; Howieson, D.B.; Loring, D.W. Neuropsychological Assessment, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Della Rosa, P.; Catricalà, E.; Vigliocco, G.; Cappa, S. Beyond the abstract–concrete dichotomy: Mode of acquisition, concreteness, imageability, familiarity, age of acquisition, context availability, and abstractness norms for a set of 417 Italian words. Behav. Res. Methods 2010, 42, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecardeur, L.; Giard, B.; Mickael Laisney, M.; Brazo, P.; Delamillieure, P.; Eustache, F.; Dollfus, S. Semantic hyperpriming in schizophrenic patients: Increased facilitation or impaired inhibition in semantic association processing? Schizophr. Res. 2007, 89, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, E. We know who knows, but why? In Schooling and the Acquisition of Knowledge; Anderson, R.C., Spiro, R.J., Montague, W.E., Eds.; Laurence Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1977; pp. 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Titone, D.; Libben, M.; Niman, M.; Ranbom, L.; Levy, D.L. Conceptual combination in schizophrenia: Contrasting property and relational interpretations. J. Neurolinguist. 2007, 20, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloia, M.S.; Gourovitch, M.L.; Missar, D.; Pickar, D.; Weinberger, D.R.; Goldberg, T.E. Cognitive substrates of thought disorder: Specifying a candidate cognitive mechanism. Am. J. Psychiatry 1998, 155, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Wilkins, A.J.; McKenna, P.J. Semantic memory is both impaired and anomalous in schizophrenia. Psychol. Med. 1994, 24, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvevag, B.; Weickert, T.; Wechsler, M.; Coppola, R.; Weinberger, D.R.; Goldberg, T.E. An investigation of the integrity of semantic boundaries in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2002, 53, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitnikova, T.; Salisbury, D.F.; Kuperberg, G.; Holcomb, P.I. Electrophysiological insights into language processing in schizophrenia. Psychophysiology 2002, 39, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poldrack, R.A.; Wagner, A.D.; Prull, M.W.; Desmond, J.E.; Glover, G.H.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Functional specialization for semantic and phonological processing in the left inferior frontal cortex. NeuroImage 1999, 10, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.J.; Moore, C.J.; Humphreys, G.W.; Wise, R.S.J. Segregating semantic from phonological processes during reading. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cacciari, C.; Pesciarelli, F.; Gamberoni, T.; Ferlazzo, F.; Russo, L.L.; Pedrazzi, F.; Melati, E. Is Black Always the Opposite of White? An Investigation on the Comprehension of Antonyms in People with Schizophrenia and in Healthy Participants. Behav. Sci. 2015, 5, 93-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5010093
Cacciari C, Pesciarelli F, Gamberoni T, Ferlazzo F, Russo LL, Pedrazzi F, Melati E. Is Black Always the Opposite of White? An Investigation on the Comprehension of Antonyms in People with Schizophrenia and in Healthy Participants. Behavioral Sciences. 2015; 5(1):93-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5010093
Chicago/Turabian StyleCacciari, Cristina, Francesca Pesciarelli, Tania Gamberoni, Fabio Ferlazzo, Leo Lo Russo, Francesca Pedrazzi, and Ermanno Melati. 2015. "Is Black Always the Opposite of White? An Investigation on the Comprehension of Antonyms in People with Schizophrenia and in Healthy Participants" Behavioral Sciences 5, no. 1: 93-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5010093
APA StyleCacciari, C., Pesciarelli, F., Gamberoni, T., Ferlazzo, F., Russo, L. L., Pedrazzi, F., & Melati, E. (2015). Is Black Always the Opposite of White? An Investigation on the Comprehension of Antonyms in People with Schizophrenia and in Healthy Participants. Behavioral Sciences, 5(1), 93-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs5010093





