Long-Term Exercise Interventions for Reducing Drug Craving in People with Drug Use Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
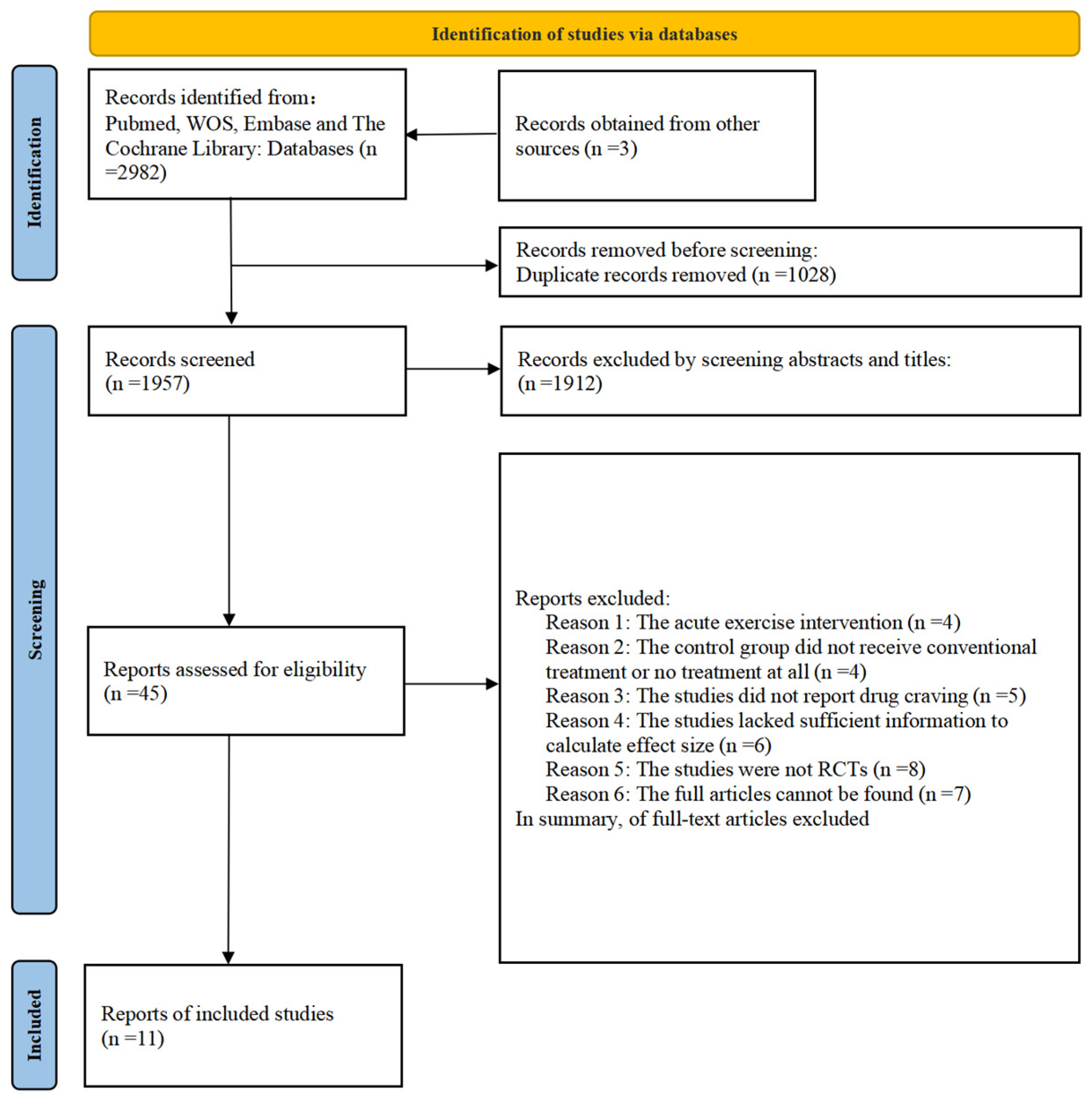
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Participants (P): Adults aged 18–65 diagnosed with drug use disorder;
- (2)
- Intervention (I): Experimental groups received structured and long-term (≥4 weeks) exercise interventions;
- (3)
- Comparison (C): Control groups received routine care (e.g., health education) or no intervention;
- (4)
- Outcome (O): Drug craving was quantified using validated scales (e.g., Visual Analogue Scale (Sayette et al., 2000), Amphetamine Craving Questionnaire (James et al., 2004));
- (5)
- Study design (S): Randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Non-human studies, reviews, conference abstracts, or case reports;
- (2)
- Acute exercise interventions (<4 weeks);
- (3)
- Combined interventions (exercise co-administered with other therapies);
- (4)
- Insufficient data for effect size calculation;
- (5)
- Non-English studies or unavailable full texts.
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.2. Included Literature Quality
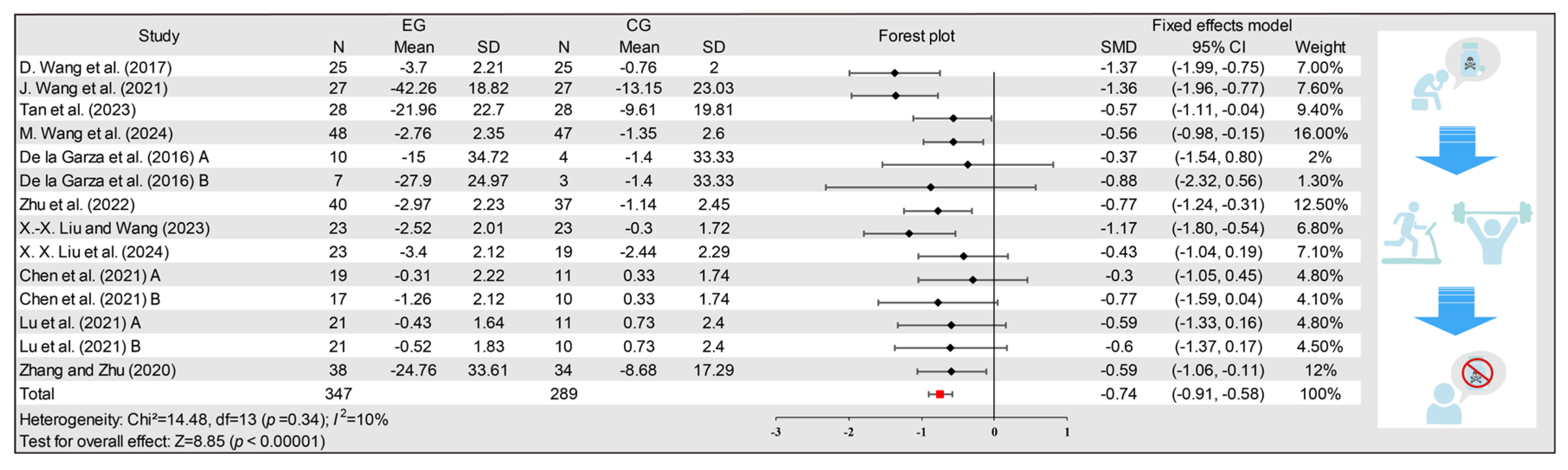
3.3. Effects of Exercise on Drug Craving
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
3.5. Publication Bias
3.6. Meta-Regression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agosti, V., Nunes, E. V., & O’Shea, D. (2012). Do manualized psychosocial interventions help reduce relapse among alcohol-dependent adults treated with naltrexone or placebo? A meta-analysis. The American Journal on Addictions, 21(6), 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5™ (5th ed., Vol. 25, Issue 2, p. 191). American Psychiatric Association Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Bobadilla, A. C., Garcia-Keller, C., Chareunsouk, V., Hyde, J., Medina Camacho, D., Heinsbroek, J. A., & Kalivas, P. W. (2019). Accumbens brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) transmission inhibits cocaine seeking. Addiction Biology, 24(5), 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brellenthin, A. G., Crombie, K. M., Hillard, C. J., & Koltyn, K. F. (2017). Endocannabinoid and mood responses to exercise in adults with varying activity levels. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 49(8), 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, J. D., Chaput, J. P., Sjödin, A. M., & Goldfield, G. S. (2017). Brain on fire: Incentive salience, hedonic hot spots, dopamine, obesity, and other hunger games. The Annual Review of Nutrition, 37, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C. D., Garavan, H., & Bellgrove, M. A. (2009). Insights into the neural basis of response inhibition from cognitive and clinical neuroscience. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(5), 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y. H., Shun, S. C., Chen, M. H., & Chang, Y. F. (2023). Feasibility of different exercise modalities for community-dwelling residents with physical inactivity: A randomized controlled trial. The Journal of Nursing Research, 31(6), e301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., Liu, T., & Zhou, C. (2021). Effects of 12-week aerobic exercise on cue-induced drug craving in methamphetamine-dependent patients and the moderation effect of working memory. Mental Health and Physical Activity, 21, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, S., Gullo, M. J., & Loxton, N. J. (2004). Reward drive and rash impulsiveness as dimensions of impulsivity: Implications for substance misuse. Addictive Behaviors, 29(7), 1389–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Garza, R., Yoon, J. H., Thompson-Lake, D. G. Y., Haile, C. N., Eisenhofer, J. D., Newton, T. F., & Mahoney, J. J., III. (2016). Treadmill exercise improves fitness and reduces craving and use of cocaine in individuals with concurrent cocaine and tobacco-use disorder. Psychiatry Research, 245, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C., Liu, R., Li, R., Huang, Z., & Sun, S. (2024). Effects of traditional chinese exercises on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled Trials. Sports Medicine, 54(9), 2327–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, G. P., & Singleton, E. G. (2009). How long does craving predict use of methamphetamine? Assessment of use one to seven weeks after the assessment of craving: Craving and ongoing methamphetamine use. Substance Abuse, 1, 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2002). Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: Neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(10), 1642–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2011). Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: Neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(11), 652–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S., Bharatha, A., Cohall, D., Rahman, S., Haque, M., & Azim Majumder, M. A. (2024). Aerobic exercise and endocannabinoids: A narrative review of stress regulation and brain reward systems. Cureus, 16(3), e55468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S., Jhanjee, S., & Dhawan, A. (2021). Effectiveness of Interventions Based on Yogic Breathing Practices (IB-YBP) on substance use disorders—A systematic review of the randomized control trials and quasi-experimental trials. Substance Use & Misuse, 56(11), 1624–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, N., Le, L., Abimanyi-Ochom, J., Marel, C., Mills, K., Teesson, M., & Mihalopoulos, C. (2024). Estimating the societal cost of heroin dependence in an Australian population engaged in treatment or harm reduction services. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 264, 112447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M., Yang, S., Miao, Y., Zhang, W., Zhu, D., & Xu, D. (2021). Four-week Tai Chi intervention decreases attention bias to drug cues in individuals with methamphetamine use disorder. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 47(5), 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmati, M., & Russo, S. J. (2015). Anhedonia and the brain reward circuitry in depression. Current Behavioral Neuroscience Reports, 2(3), 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J. P. T., Altman, D. G., Gøtzsche, P. C., Jüni, P., Moher, D., Oxman, A. D., Savovic, J., Schulz, K. F., Weeks, L., & Sterne, J. A. (2011). The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J. P. T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M. J., & Welch, V. A. (Eds.). (2024). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.5 (updated August 2024). Cochrane. Available online: https://methods.cochrane.org/news/release-version-65-cochrane-handbook-systematic-reviews-interventions (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Huang, J., Zheng, Y., Gao, D., Hu, M., & Yuan, T. (2019). Effects of exercise on depression, anxiety, cognitive control, craving, physical fitness and quality of life in methamphetamine-dependent patients. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X., Zhao, X., Li, B., Cai, Y., Zhang, S., Wan, Q., & Yu, F. (2022). Comparative efficacy of various exercise interventions on cognitive function in patients with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Journal of Sport and Health Science, 11(2), 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D., Davies, G., & Willner, P. (2004). The development and initial validation of a questionnaire to measure craving for amphetamine. Addiction, 99(9), 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P., Sun, J., Zhou, X., Lu, L., Li, L., Huang, X., Li, J., Kendrick, K., & Gong, Q. (2021). Functional connectivity abnormalities underlying mood disturbances in male abstinent methamphetamine abusers. Human Brain Mapping, 42(11), 3366–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalivas, P. W., & Volkow, N. D. (2005). The neural basis of addiction: A pathology of motivation and choice. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(8), 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaepen, K., Goekint, M., Heyman, E. M., & Meeusen, R. (2010). Neuroplasticity—Exercise-induced response of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A systematic review of experimental studies in human subjects. Sports Medicine, 40(9), 765–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowiański, P., Lietzau, G., Czuba, E., Waśkow, M., Steliga, A., & Moryś, J. (2018). BDNF: A key factor with multipotent impact on brain signaling and synaptic plasticity. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 38(3), 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H. M., Cleary, M., Sitharthan, T., & Hunt, G. E. (2015). Prevalence of comorbid substance use, anxiety and mood disorders in epidemiological surveys, 1990–2014: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B., Zhou, Y., Qian, Y., & Wu, J. (2025). Impact of exercise on drug cravings: Mediating role of cardiorespiratory fitness and inhibitory control. Frontiers in Psychology, 16, 1540648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. F., & Li, J. X. (2018). Drug addiction: A curable mental disorder? Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 39(12), 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X. X., Huang, P. H., Wang, Y. J., & Gao, Y. (2024). Effects of aerobic exercise combined with attentional bias modification in the care of male patients with a methamphetamine use disorder. Journal of Addictions Nursing, 35(1), E2–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-x., & Wang, S. (2023). Effects of aerobic exercise combined with attentional bias training on cognitive function and psychiatric symptoms of individuals with methamphetamine dependency: A randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 21(3), 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X., Hui-Chan, C. W., & Tsang, W. W. (2016). Changes of heart rate variability and prefrontal oxygenation during Tai Chi practice versus arm ergometer cycling. The Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 28(11), 3243–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y., Qi, X., Zhao, Q., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Li, X., Yu, Y., & Zhou, C. (2021). Effects of exercise programs on neuroelectric dynamics in drug addiction. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 15(1), 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, U. D., Kuwabara, H., Kumar, A., Palermo, M., Abbey, R., Brasic, J., Ye, W., Alexander, M., Dannals, R. F., Wong, D. F., & Ricaurte, G. A. (2008). Persistent cognitive and dopamine transporter deficits in abstinent methamphetamine users. Synapse, 62(2), 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menglu, S., Ruiwen, L., Suyong, Y., & Dong, Z. (2021). Effects of Tai Chi on the executive function and physical fitness of female methamphetamine dependents: A randomized controlled trial. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12, 653229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miron, O., Barda, N., Balicer, R., Kor, A., & Lev-Ran, S. (2022). Association of opioid use disorder with healthcare utilization and cost in a public health system. Addiction, 117(11), 2880–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Rius, J., & Miquel, M. (2017). The cerebellum in drug craving. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 173, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, F., García-Gutiérrez, M. S., Gasparyan, A., Navarro, D., & Manzanares, J. (2021). CB2 receptor involvement in the treatment of substance use disorders. Biomolecules, 11(11), 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A. I., Suri, M. F., Guterman, L. R., & Hopkins, L. N. (2001). Cocaine use and the likelihood of nonfatal myocardial infarction and stroke: Data from the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Circulation, 103(4), 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raichlen, D. A., Foster, A. D., Gerdeman, G. L., Seillier, A., & Giuffrida, A. (2012). Wired to run: Exercise-induced endocannabinoid signaling in humans and cursorial mammals with implications for the ‘runner’s high’. Journal of Experimental Biology, 215 Pt 8, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramo, D. E., & Brown, S. A. (2008). Classes of substance abuse relapse situations: A comparison of adolescents and adults. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 22(3), 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, C. S., Rojas, C. A., Martinez, S., Riascos, R., Marmol-Velez, A., Carrillo, J., & Vargas, D. (2009). Cardiovascular complications of cocaine: Imaging findings. Emergency Radiology, 16(1), 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C. L., Ishibashi, K., Chudzynski, J., Mooney, L. J., Rawson, R. A., Dolezal, B. A., Cooper, C. B., Brown, A. K., Mandelkern, M. A., & London, E. D. (2016). Effect of exercise training on striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptors in methamphetamine users during behavioral treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology, 41(6), 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robison, L. S., Swenson, S., Hamilton, J., & Thanos, P. K. (2018). Exercise reduces dopamine D1R and increases D2R in rats: Implications for addiction. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 50(8), 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayette, M. A. (2016). The role of craving in substance use disorders: Theoretical and methodological issues. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 12, 407–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayette, M. A., Shiffman, S., Tiffany, S. T., Niaura, R. S., Martin, C. S., & Shadel, W. G. (2000). The measurement of drug craving. Addiction, 95(Suppl. S2), S189–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-García, C., Ammendolia, A., Procopio, L., Papaianni, M. C., Sinopoli, F., Bianco, C., De Fazio, P., & Capranica, L. (2010). Body uneasiness, eating disorders, and muscle dysmorphia in individuals who overexercise. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research, 24(11), 3098–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojo, G., Joseph, B., Shah, R., Consolim-Colombo, F. M., De Angelis, K., & Ulloa, L. (2019). Exercise activates vagal induction of dopamine and attenuates systemic inflammation. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 75, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparling, P. B., Giuffrida, A., Piomelli, D., Rosskopf, L., & Dietrich, A. (2003). Exercise activates the endocannabinoid system. Neuroreport, 14(17), 2209–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J., Wang, J., Guo, Y., Lu, C., Tang, W., & Zheng, L. (2023). Effects of 8 months of high-intensity interval training on physical fitness and health-related quality of life in substance use disorder. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 14, 1093106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirado Muñoz, J., Farré, A., Mestre-Pintó, J., Szerman, N., & Torrens, M. (2018). Patología dual en Depresión: Recomendaciones en el tratamiento [Dual diagnosis in depression: Treatment recommendations]. Adicciones, 30(1), 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNODC. (2024). World drug report 2024 (United Nations publication, 2024). Available online: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/world-drug-report-2024.html (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Volkow, N. D., Koob, G. F., & McLellan, A. T. (2016). Neurobiologic advances from the brain disease model of addiction. The New England Journal of Medicine, 374(4), 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N. D., & Morales, M. (2015). The brain on drugs: From reward to addiction. Cell, 162(4), 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D., Zhu, T., Zhou, C., & Chang, Y.-K. (2017). Aerobic exercise training ameliorates craving and inhibitory control in methamphetamine dependencies: A randomized controlled trial and event-related potential study. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 30, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Lu, C., Zheng, L., & Zhang, J. (2021). Peripheral inflammatory biomarkers of methamphetamine withdrawal patients based on the neuro-inflammation hypothesis: The possible improvement effect of exercise. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12, 795073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M., Chen, Y., Xu, Y., Zhang, X., Sun, T., Li, H., Yuan, C., Li, J., Ding, Z.-H., Ma, Z., & Sun, Y. (2024). A randomized controlled trial evaluating the effect of Tai Chi on the drug craving in women. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 22(3), 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M. T., Tang, P. F., Goh, J. O. S., Chou, T. L., Chang, Y. K., Hsu, Y. C., Chen, Y. J., Chen, N. C., Tseng, W. I., Gau, S. S., Chiu, M. J., & Lan, C. (2018). Task-switching performance improvements after Tai Chi chuan training are associated with greater prefrontal activation in older adults. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., & Zhu, D. (2020). Effect of Taijiquan exercise on rehabilitation of male amphetamine-type addicts. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2020, 8886562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y., Zhao, Y., Chen, X., & Li, S. (2024). Effect of physical exercise on the emotional and cognitive levels of patients with substance use disorder: A meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology, 15, 1348224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T., Tao, W., Peng, B., Su, R., Wang, D., Hu, C., & Chang, Y.-K. (2022). Effects of a group-based aerobic exercise program on the cognitive functions and emotions of substance use disorder patients: A randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 20(4), 2349–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author (Year) | Country | Sample Size | Experimental Interventions | Control Interventions | Drug Information | Outcome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise Type | Exercise Intensity | Intervention Period | Intervention Single-Session Duration | Weekly Intervention Frequency | ||||||
| D. Wang et al. (2017) | CHINA | EG: n = 25 CG: n = 25 | Aerobic exercise (AE) | Moderate | 12 weeks | 30 min | 3 times | Routine care | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| J. Wang et al. (2021) | CHINA | EG: n = 27 CG: n = 27 | Resistance and aerobic exercise (ME) | Moderate | 8 weeks | 60 min | 5 times | Safety and health education | Methamphetamine | VR-VAS |
| Tan et al. (2023) | CHINA | EG: n = 28 CG: n = 28 | High-intensity interval training (ME) | High | 8 months | 60 min | 4 times | Routine rehabilitation therapy | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| M. Wang et al. (2024) | CHINA | EG: n = 48 CG: n = 47 | Tai chi (MBE) | Moderate | 3 months | 60 min (per training session 30 min) | 5 times (two training sessions per time) | Traditional addiction treatments | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| De la Garza et al. (2016) A | AMERICA | EG: n = 10 CG: n = 4 | Running (AE) | Moderate | 4 weeks | 30 min | 3 times | Sitting | Cocaine | VAS |
| De la Garza et al. (2016) B | AMERICA | EG: n = 7 CG: n = 3 | Walking (AE) | Light | 4 weeks | 30 min | 3 times | Sitting | Cocaine | VAS |
| Zhu et al. (2022) | CHINA | EG: n = 40 CG: n = 37 | Aerobic gymnastics (AE) | Moderate | 3 months | 36 min (30 min in 1st month) | 5 times | Routine care | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| X.-x. Liu and Wang (2023) | CHINA | EG: n = 23 CG: n = 23 | Aerobic exercise (AE) | Moderate | 8 weeks | 60 min | 5 times | Health Education | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| X. X. Liu et al. (2024) | CHINA | EG: n = 23 CG: n = 19 | Aerobic exercise (AE) | Moderate | 8 weeks | 60 min | 3 times | Health Education | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| Chen et al. (2021) A | CHINA | EG: n = 19 CG: n = 11 | Aerobic exercise (AE) | Moderate | 12 weeks | 30 min | 3 times | Drug rehabilitation education and simple manual labor | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| Chen et al. (2021) B | CHINA | EG: n = 17 CG: n = 10 | Aerobic exercise (AE) | High | 12 weeks | 30 min | 3 times | Drug rehabilitation education and simple manual labor | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| Y. Lu et al. (2021) A | CHINA | EG: n = 21 CG: n = 11 | Resistance exercise (RE) | N/A | 12 weeks | N/A | 3 times | Routine care | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| Y. Lu et al. (2021) B | CHINA | EG: n = 21 CG: n = 10 | Cycling exercise (AE) | Moderate | 12 weeks | 40 min | 3 times | Routine care | Methamphetamine | VAS |
| Zhang and Zhu (2020) | CHINA | EG: n = 38 CG: n = 34 | Tai chi (MBE) | Moderate | 6 months | 1 time 50 min/ 4 times 20 min | 5 times | Routine rehabilitation exercises | Amphetamine | DSQ |
| Potential Confounding Factors | β | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| The publication year | 0.14 | (−0.02, 0.3) | 0.07 |
| The baseline level of EG | 0 | (−0.23, 0.23) | 0.99 |
| The baseline level of CG | −0.01 | (−0.24, 0.22) | 0.94 |
| The method of intervention used in the control group | 0.01 | (−0.1, 0.12) | 0.89 |
| The sample size | 0 | (−0.01, 0.01) | 0.87 |
| The type of drug | −0.67 | (−1.53, 0.19) | 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Jia, Y.; Hong, P.; Sun, T.; Dong, X.; Qian, J.; Qian, J.; Hou, X. Long-Term Exercise Interventions for Reducing Drug Craving in People with Drug Use Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15091272
Chen X, Jia Y, Hong P, Sun T, Dong X, Qian J, Qian J, Hou X. Long-Term Exercise Interventions for Reducing Drug Craving in People with Drug Use Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(9):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15091272
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiang, Yuanyuan Jia, Ping Hong, Tingting Sun, Xiaosheng Dong, Jinghua Qian, Junwei Qian, and Xiao Hou. 2025. "Long-Term Exercise Interventions for Reducing Drug Craving in People with Drug Use Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 9: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15091272
APA StyleChen, X., Jia, Y., Hong, P., Sun, T., Dong, X., Qian, J., Qian, J., & Hou, X. (2025). Long-Term Exercise Interventions for Reducing Drug Craving in People with Drug Use Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Behavioral Sciences, 15(9), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15091272







