Value-Directed Remembering: A Dual-Process Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
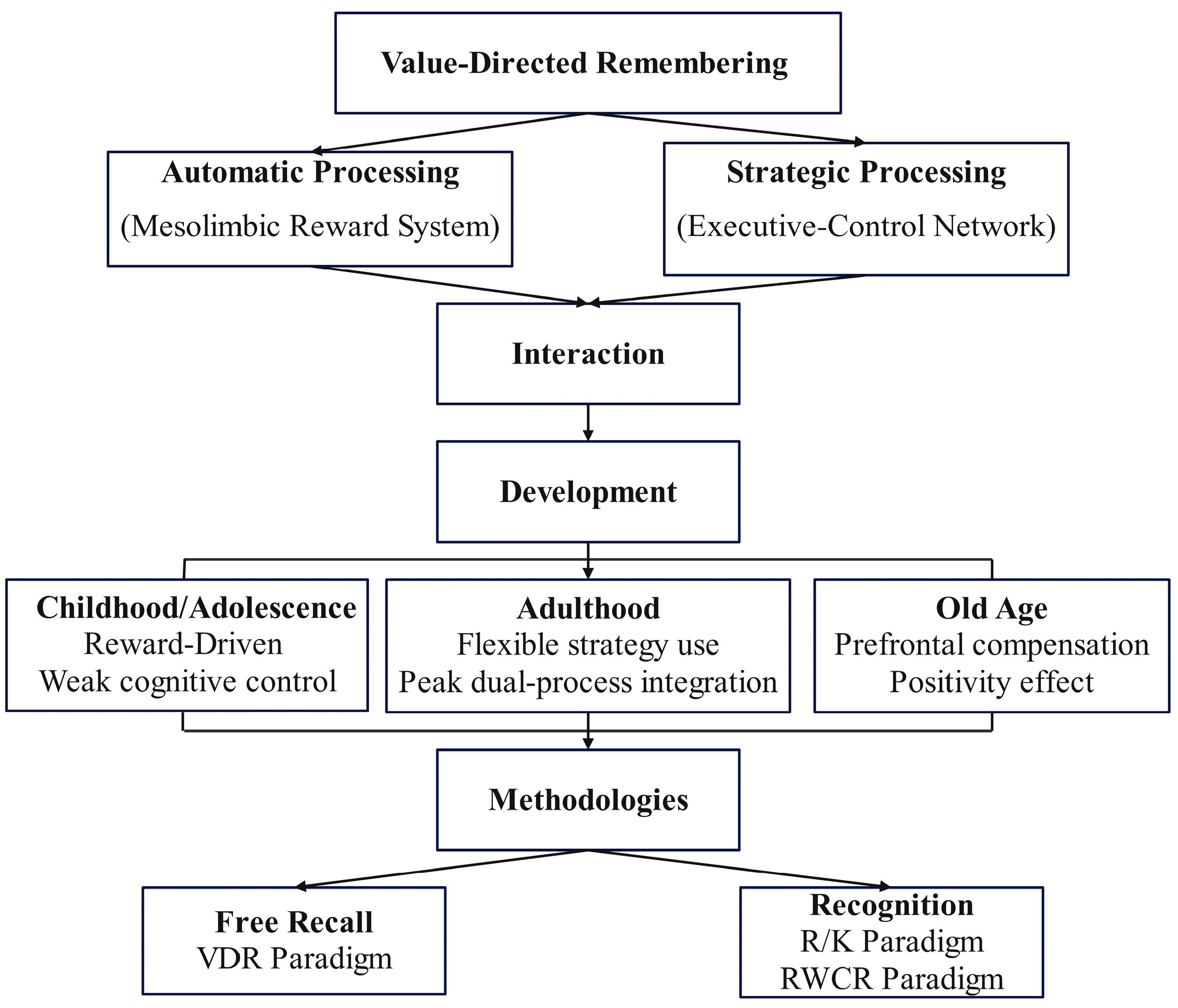
2. The Dual-Process Mechanism of Value-Directed Remembering
2.1. Automatic Processing
2.2. Strategic Processing
2.3. The Interaction Between Automatic and Strategic Processing
3. Development of Value-Directed Remembering
4. Research Methods in Value-Directed Memory
4.1. Free-Recall Tests
4.2. Recognition Tasks
5. General Discussion and Future Directions
5.1. The Interaction of Dual-Process Mechanisms in Adolescents and Adults
5.2. Neural and Cognitive Mechanisms of VDR in Older Adults
5.3. The Shaping Role of Cultural and Contextual Factors on Dual-Processing Mechanisms
5.4. Developmentally Informed Intervention Strategies for Value-Directed Memory
5.5. Directions for Methodological and Experimental Design Optimization
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adcock, R. A., Thangavel, A., Whitfield-Gabrieli, S., Knutson, B., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2006). Reward-motivated learning: Mesolimbic activation precedes memory formation. Neuron, 50(3), 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anquillare, E., & Selmeczy, D. (2023). Developmental differences in value-based remembering: The role of feedback and metacognition. Developmental Psychology, 59(7), 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berntsen, D. (2024). Direct retrieval as a theory of involuntary autobiographical memories: Evaluation and future directions. Memory, 32(6), 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, H. J., Gallant, S. N., & Moon, D. H. (2020). Influence of reward motivation on directed forgetting in younger and older adults. Frontiers in Psychology, 11, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, E. K., Wimmer, G. E., & Shohamy, D. (2018). Retroactive and graded prioritization of memory by reward. Nature Communications, 9(1), 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capa, R. L., Bustin, G. M., Cleeremans, A., & Hansenne, M. (2011). Conscious and unconscious reward cues can affect a critical component of executive control: (Un)conscious updating? Experimental Psychology, 58(5), 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, B. J. (2015). Beyond simple models of self-control to circuit-based accounts of adolescent behavior. Annual Review of Psychology, 66(1), 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, A. D., Farb, N. A. S., & Craik, F. I. M. (2007). Memory for general and specific value information in younger and older adults: Measuring the limits of strategic control. Memory & Cognition, 35(4), 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, A. D., Humphreys, K. L., Lee, S. S., Galván, A., Balota, D. A., & McCabe, D. P. (2011). The development of memory efficiency and valuedirected remembering across the life span: A cross-sectional study of memory and selectivity. Developmental Psychology, 47(6), 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, A. D., Murayama, K., Friedman, M. C., McGillivray, S., & Link, I. (2013). Selecting valuable information to remember: Age-related differences and similarities in self-regulated learning. Psychology and Aging, 28(1), 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S., Jiang, T., Xue, J., Wang, S., Chen, C., & Zhang, M. (2020). The influence of rewards on incidental memory: More does not mean better. Learning & Memory, 27(11), 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, A. M. (2004). Orthography, phonology, and meaning: Word features that give rise to feelings of familiarity in recognition. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 11(3), 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A. O., Glover, M. M., Shen, X., Phaneuf, C. V., Avallone, K. N., Davachi, L., & Hartley, C. A. (2022). Reward enhances memory via age-varying online and offline neural mechanisms across development. The Journal of Neuroscience, 42(33), 6424–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M. S., Rissman, J., Hovhannisyan, M., Castel, A. D., & Knowlton, B. J. (2017). Free recall test experience potentiates strategy-driven effects of value on memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 43(10), 1581–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M. S., Rissman, J., Suthana, N. A., Castel, A. D., & Knowlton, B. J. (2014). Value-based modulation of memory encoding involves strategic engagement of fronto-temporal semantic processing regions. Cognitive, Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(2), 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M. S., Rissman, J., Suthana, N. A., Castel, A. D., & Knowlton, B. J. (2016). Effects of aging on value-directed modulation of semantic network activity during verbal learning. NeuroImage, 125, 1046–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M. X. (2007). Individual differences and the neural representations of reward expectation and reward prediction error. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 2(1), 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Frías, N. S., Nikolova, Y. S., Michalski, L. J., Baranger, D. A. A., Hariri, A. R., & Bogdan, R. (2015). Stress-related anhedonia is associated with ventral striatum reactivity to reward and transdiagnostic psychiatric symptomatology. Psychological Medicine, 45(12), 2605–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, J. L., & Potter, M. C. (2004). Scene consistency in object and background perception. Psychological Science, 15(8), 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidow, J. Y., Foerde, K., Galván, A., & Shohamy, D. (2016). An upside to reward sensitivity: The hippocampus supports enhanced reinforcement learning in adolescence. Neuron, 92(1), 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidow, J. Y., Insel, C., & Somerville, L. H. (2018). Adolescent development of value-guided goal pursuit. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 22(8), 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daw, N. D., O’Doherty, J. P., Dayan, P., Seymour, B., & Dolan, R. J. (2006). Cortical substrates for exploratory decisions in humans. Nature, 441(7095), 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, K. C., & Adcock, R. A. (2018). Motivation and memory. In J. T. Wixted, E. A. Phelps, & L. Davachi (Eds.), Stevens’ handbook of experimental psychology and cognitive neuroscience: Learning and memory (4th ed., Vol. 1, pp. 215–150). John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, B. L., Blais, C., McClure, S. M., & Brewer, G. A. (2020a). Neural correlates underlying the effect of reward value on recognition memory. NeuroImage, 206, 116296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, B. L., & Brewer, G. A. (2019). Divided attention selectively impairs value-directed encoding. Collabra: Psychology, 5(1), 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, B. L., McClure, S. M., & Brewer, G. A. (2020b). Individual differences in value-directed remembering. Cognition, 201, 104275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassett-Carman, A. N., Moser, A. D., Ruzic, L., Neilson, C., Jones, J., Barnes-Horowitz, S., Schneck, C. D., & Kaiser, R. H. (2023). Amygdala and nucleus accumbens activation during reward anticipation moderates the association between life stressor frequency and depressive symptoms. Journal of Affective Disorders, 330, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván, A. (2013). The teenage brain: Sensitivity to rewards. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 22(2), 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, J., Erdeniz, B., & Done, J. (2013). Prediction error in reinforcement learning: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(7), 1297–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, V., Marc, I. B., Ramawat, S., Fontana, R., Fiori, L., Bardella, G., Fagioli, S., Ferraina, S., Brunamonti, E., & Pani, P. (2023). Reward prospect affects strategic adjustments in stop signal task. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1125066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gläscher, J., Hampton, A. N., & O’Doherty, J. P. (2009). Determining a role for ventromedial prefrontal cortex in encoding action-based value signals during reward-related decision making. Cerebral Cortex, 19(2), 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A. L., Parisi, J. M., Spira, A. P., Kueider, A. M., Ko, J. Y., Saczynski, J. S., Samus, Q. M., & Rebok, G. W. (2012). Memory training interventions for older adults: A meta-analysis. Aging & Mental Health, 16(6), 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, M. J., Ritchey, M., Wang, S.-F., Doss, M. K., & Ranganath, C. (2016). Post-learning hippocampal dynamics promote preferential retention of rewarding events. Neuron, 89(5), 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutchess, A. H., Welsh, R. C., Boduroglu, A., & Park, D. C. (2006). Cultural differences in neural function associated with object processing. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 6(2), 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanten, G., Li, X., Chapman, S. B., Swank, P., Gamino, J., Roberson, G., & Levin, H. S. (2007). Development of Verbal Selective Learning. Developmental Neuropsychology, 32(1), 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargis, M. B., Siegel, A. L. M., & Castel, A. D. (2019). Motivated memory, learning, and decision-making in older age: Shifts in priorities and goals. In G. Samanez-Larkin (Ed.), The aging brain: Functional adaptation across adulthood (pp. 135–164). American Psychological Association. [Google Scholar]
- Hedden, T., Ketay, S., Aron, A., Markus, H. R., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2008). Cultural influences on neural substrates of attentional control. Psychological Science, 19(1), 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessee, J. P., Castel, A. D., & Knowlton, B. J. (2017). Recognizing what matters: Value improves recognition by selectively enhancing recollection. Journal of Memory and Language, 94, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessee, J. P., Patterson, T. K., Castel, A. D., & Knowlton, B. J. (2019). Forget me not: Encoding processes in value-directed remembering. Journal of Memory and Language, 106, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudes, R., Rich, J. B., Troyer, A. K., Yusupov, I., & Vandermorris, S. (2019). The impact of memory-strategy training interventions on participant-reported outcomes in healthy older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychology and Aging, 34(4), 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacowitz, D. M., Allard, E. S., Murphy, N. A., & Schlangel, M. (2009). The time course of age-related preferences toward positive and negative stimuli. The Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 64B(2), 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R. L. (2021). The neural correlates of semantic control revisited. NeuroImage, 224, 117444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W., Hernández, S. P., Rahman, M. S., Voigt, K., & Malvaso, A. (2022). Inhibitory control development: A network neuroscience perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 651547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, Q., Mather, M., & Carstensen, L. L. (2004). The role of motivation in the age-related positivity effect in autobiographical memory. Psychological Science, 15(3), 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensinger, E. A., Brierley, B., Medford, N., Growdon, J. H., & Corkin, S. (2002). Effects of normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease on emotional memory. Emotion, 2(2), 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisley, M. A., Wood, S., & Burrows, C. L. (2007). Looking at the sunny side of life: Age-related change in an event-related potential measure of the negativity bias. Psychological Science, 18, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, B. J., & Castel, A. D. (2022). Memory and reward-based learning: A value-directed remembering perspective. Annual Review of Psychology, 73(1), 25–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, B., Adams, C. M., Fong, G. W., & Hommer, D. (2001). Anticipation of increasing monetary reward selectively recruits nucleus accumbens. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21(16), RC159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdziel, L. B. F., Kent, J., & Spencer, R. M. C. (2018). Sleep-dependent enhancement of emotional memory in early childhood. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 12609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H., Lin, S., & Wan, B. (2023). Value-directed attentional refreshing and its mechanism. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 55(8), 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q., Tang, W., & Liu, X. (2025). The modulatory mechanisms of free-recall testing experience on value-directed memory [Manuscript in preparation]. Faculty of Psychology, Tianjin Normal University. [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel, M. A., & Einstein, G. O. (2000). Strategic and automatic processes in prospective memory retrieval: A multiprocess framework. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 14(7), S127–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, I. M., Bui, D. C., Friedman, M. F., & Castel, A. D. (2015). Retrieval monitoring is influenced by information value: The interplay between importance and confidence on false memory. Acta Psychologica, 161, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H. C., & Pattwell, S. S. (2020). Memory across development, with insights from emotional learning: A nonlinear process. In D. Poeppel, G. R. Mangun, & M. S. Gazzaniga (Eds.), The cognitive neurosciences (6th ed., pp. 245–255). MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrooks, C. D., Kerr, T. K., & Castel, A. D. (2017). Selectively distracted: Divided attention and memory for important information. Psychological Science, 28(8), 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y., Nisbett, R. E., & Masuda, T. (2006). Culture and the physical environment: Holistic versus analytic perceptual affordances. Psychological Science, 17(2), 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H. (2023a). Does point value structure influence measures of memory selectivity? Memory, 31(8), 1074–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H. (2023b). Strategic offloading: How the value of to-be-remembered information influences offloading decision-making. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 37(4), 749–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H., Agadzhanyan, K., Whatley, M. C., & Castel, A. D. (2021). Metacognition and fluid intelligence in value-directed remembering. Metacognition and Learning, 16(3), 685–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H., & Castel, A. D. (2020). Responsible remembering: How metacognition impacts adaptive selective memory. Zeitschrift für Psychologie, 228(4), 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H., & Castel, A. D. (2021). Responsible remembering and forgetting as contributors to memory for important information. Memory & Cognition, 49(5), 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D. H., & Castel, A. D. (2022a). Differential effects of proactive and retroactive interference in value-directed remembering for younger and older adults. Psychology and Aging, 37(7), 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H., & Castel, A. D. (2022b). Responsible remembering and forgetting in younger and older adults. Experimental Aging Research, 48(5), 455–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H., & Castel, A. D. (2022c). The role of attention and ageing in the retrieval dynamics of value-directed remembering. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 75(5), 954–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D. H., Huckins, S. C., Rhodes, M. G., & Castel, A. D. (2022a). The effect of perceptual processing fluency and value on metacognition and remembering. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 29(3), 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H., & Knowlton, B. J. (2022). Framing effects in value-directed remembering. Memory & Cognition, 50(6), 1350–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H., Schwartz, S. T., & Castel, A. D. (2022b). Serial and strategic memory processes in goal-directed selective remembering. Cognition, 225, 105178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D. H., Schwartz, S. T., & Castel, A. D. (2024). Value-directed retrieval: The effects of divided attention at encoding and retrieval on memory selectivity and retrieval dynamics. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 50(1), 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, V. P., & Adcock, R. A. (2014). Enriched encoding: Reward motivation organizes cortical networks for hippocampal detection of unexpected events. Cerebral Cortex, 24(8), 2162–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, V. P., DuBrow, S., & Davachi, L. (2019). Decision-making increases episodic memory via postencoding consolidation. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 31(9), 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, C. T., Newcombe, N. S., & Olson, I. R. (2019). Gain-loss framing enhances mnemonic discrimination in preschoolers. Child Development, 90(5), 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L. T., Marini, F., Shende, S. A., Llano, D. A., & Mudar, R. A. (2020). Investigating EEG theta and alpha oscillations as measures of value-directed strategic processing in cognitively normal younger and older adults. Behavioural Brain Research, 391, 112702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L. T., Marini, F., Zacharczuk, L., Llano, D. A., & Mudar, R. A. (2019). Theta and alpha band oscillations during value-directed strategic processing. Behavioural Brain Research, 367, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofen, N., Kao, Y.-C., Sokol-Hessner, P., Kim, H., Whitfield-Gabrieli, S., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2007). Development of the declarative memory system in the human brain. Nature Neuroscience, 10(9), 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, A., Geier, C. F., Ordaz, S. J., Teslovich, T., & Luna, B. (2011). Developmental changes in brain function underlying the influence of reward processing on inhibitory control. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 1(4), 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J. S., Kelly, M. O., Hargis, M. B., & Risko, E. F. (2022). The effect of external store reliance on actual and predicted value-directed remembering. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 29(4), 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A., Murty, V. P., Dunsmoor, J. E., Phelps, E. A., & Davachi, L. (2017). Reward retroactively enhances memory consolidation for related items. Learning & Memory, 24(1), 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessiglione, M., Schmidt, L., Draganski, B., Kalisch, R., Lau, H., Dolan, R. J., & Frith, C. D. (2007). How the brain translates money into force: A neuroimaging study of subliminal motivation. Science, 316, 904–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthuma, D., Baaré, W. F. C., Hulshoff Pol, H. E., Kahn, R. S., Boomsma, D. I., & De Geus, E. J. C. (2003). Genetic correlations between brain volumes and the WAIS-III dimensions of verbal comprehension, working memory, perceptual organization, and processing speed. Twin Research, 6(2), 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, N., Lindenberger, U., Rodrigue, K. M., Kennedy, K. M., Head, D., Williamson, A., Dahle, C., Gerstorf, D., & Acker, J. D. (2005). Regional brain changes in aging healthy adults: General trends, individual differences and modifiers. Cerebral Cortex, 15, 1676–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A. E., & Carstensen, L. L. (2012). The theory behind the age-related positivity effect. Frontiers in Psychology, 3, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, P., Lewinsohn, P. M., Klein, D. N., Seeley, J. R., & Gau, J. M. (2013). Key characteristics of major depressive disorder occurring in childhood, adolescence, emerging adulthood, and adulthood. Clinical Psychological Science, 1(1), 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothkirch, M., Schmack, K., Deserno, L., Darmohray, D., & Sterzer, P. (2014). Attentional modulation of reward processing in the human brain: Attentional Modulation of Reward Processing. Human Brain Mapping, 35(7), 3036–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthouse, T. A. (2019). Trajectories of normal cognitive aging. Psychology and Aging, 34(1), 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanez-Larkin, G. R., & Knutson, B. (2015). Decision making in the ageing brain: Changes in affective and motivational circuits. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 16(5), 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, W., Dayan, P., & Montague, P. R. (1997). A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science, 275(5306), 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S. T., Siegel, A. L. M., & Castel, A. D. (2020). Strategic encoding and enhanced memory for positive value-location associations. Memory & Cognition, 48(6), 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S. T., Siegel, A. L. M., Eich, T. S., & Castel, A. D. (2023). Value-directed memory selectivity relies on goal-directed knowledge of value structure prior to encoding in young and older adults. Psychology and Aging, 38(1), 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A. L. M., & Castel, A. D. (2019). Age-related differences in metacognition for memory capacity and selectivity. Memory, 27(9), 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A. L. M., Schwartz, S. T., & Castel, A. D. (2021). Selective memory disrupted in intra-modal dual-task encoding conditions. Memory & Cognition, 49(7), 1453–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaj, K. M., Agadzhanyan, K., & Castel, A. D. (2023). Value-directed learning: Schematic reward structure facilitates learning. Memory & Cognition, 51(7), 1527–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M. H., Jedd, K., & Luciana, M. (2015). Neural networks involved in adolescent reward processing: An activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. NeuroImage, 122, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D., Xiao, L., & Bechara, A. (2012). Decision making in children and adolescents: Impaired Iowa Gambling Task Performance in early adolescence. Developmental Psychology, 48(4), 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, L. H., & Casey, B. (2011). Developmental neurobiology of cognitive control and motivational systems. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 20(2), 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somerville, S. C., Wellman, H. M., & Cultice, J. C. (1983). Young children’s deliberate reminding. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 143(1), 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidi, A., Ellis, D. M., & Brewer, G. A. (2018). Free recall dynamics in value-directed remembering. Journal of Memory and Language, 100, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, L., Graham, S., O’Brien, L., Woolard, J., Cauffman, E., & Banich, M. (2009). Age differences in future orientation and delay discounting. Child Development, 80(1), 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telzer, E. H., Fuligni, A. J., Lieberman, M. D., & Galván, A. (2014). Neural sensitivity to eudaimonic and hedonic rewards differentially predict adolescent depressive symptoms over time. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(18), 6600–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A. K., & Gutchess, A. (Eds.). (2020). The Cambridge handbook of cognitive aging: A life course perspective. Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Tulving, E. (1985). Memory and consciousness. Canadian Psychology/Psychologie Canadienne, 26(1), 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaeghen, P., Marcoen, A., & Goossens, L. (1992). Improving memory performance in the aged through mnemonic training: A meta-analytic study. Psychology and Aging, 7(2), 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaseñor, J. J., Sklenar, A. M., Frankenstein, A. N., Levy, P. U., McCurdy, M. P., & Leshikar, E. D. (2021). Value-directed memory effects on item and context memory. Memory & Cognition, 49(6), 1082–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q., & Ross, M. (2007). Culture and memory. In S. Kitayama, & D. Cohen (Eds.), Handbook of cultural psychology (pp. 645–667). Guilford Press. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S., Cheng, S., Jiang, T., Liu, X., & Zhang, M. (2023). The effect of external rewards on declarative memory. Advances in Psychological Science, 31(1), 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, A. M. (2023). Reward, motivation and brain imaging in human healthy participants—A narrative review. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 17, 1123733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, S. L., Tennstedt, S. L., Marsiske, M., Ball, K., Elias, J., Koepke, K. M., Morris, J. N., Rebok, G. W., Unverzagt, F. W., Stoddard, A. M., Wright, E., & ACTIVE Study Group. (2006). Long-term effects of cognitive training on everyday functional outcomes in older adults. JAMA, 296(23), 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S., Irish, M., Savage, G., Hodges, J. R., Piguet, O., & Hornberger, M. (2019). Strategic value-directed learning and memory in Alzheimer’s disease and behavioural-variant frontotemporal dementia. Journal of Neuropsychology, 13(2), 328–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y., Jiang, Y., & Yang, L. (2013). The effect of value sequence on value-directed metamemory: The effect of value sequence on value-directed metamemory. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 45(10), 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonelinas, A. P., & Jacoby, L. L. (1995). The relation between remembering and knowing as bases for recognition: Effects of size congruency. Journal of Memory and Language, 34, 622–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., Li, Y., Li, J., & Liu, X. (2023). The influence of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation on memory in adolescents and the underlying neural mechanisms. Advances in Psychological Science, 31(1), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y., & Jiang, Y. (2024). How does value influences memory: A perspective from specificity. Advances in Psychological Science, 32(1), 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Tang, W.; Liu, X. Value-Directed Remembering: A Dual-Process Perspective. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15081113
Li Q, Tang W, Liu X. Value-Directed Remembering: A Dual-Process Perspective. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(8):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15081113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qiong, Weihai Tang, and Xiping Liu. 2025. "Value-Directed Remembering: A Dual-Process Perspective" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 8: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15081113
APA StyleLi, Q., Tang, W., & Liu, X. (2025). Value-Directed Remembering: A Dual-Process Perspective. Behavioral Sciences, 15(8), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15081113





