Does Urban Dialect Ability of Migrant Children Significantly Affect Academic Performance? Analysis of Mediating Effects Based on School Integration
Abstract
1. Research Background and Problem Proposal
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. The Connotation and Influencing Factors of Academic Performance
2.2. Urban Dialect Ability and Academic Performance
2.3. School Integration and Its Mediating Role
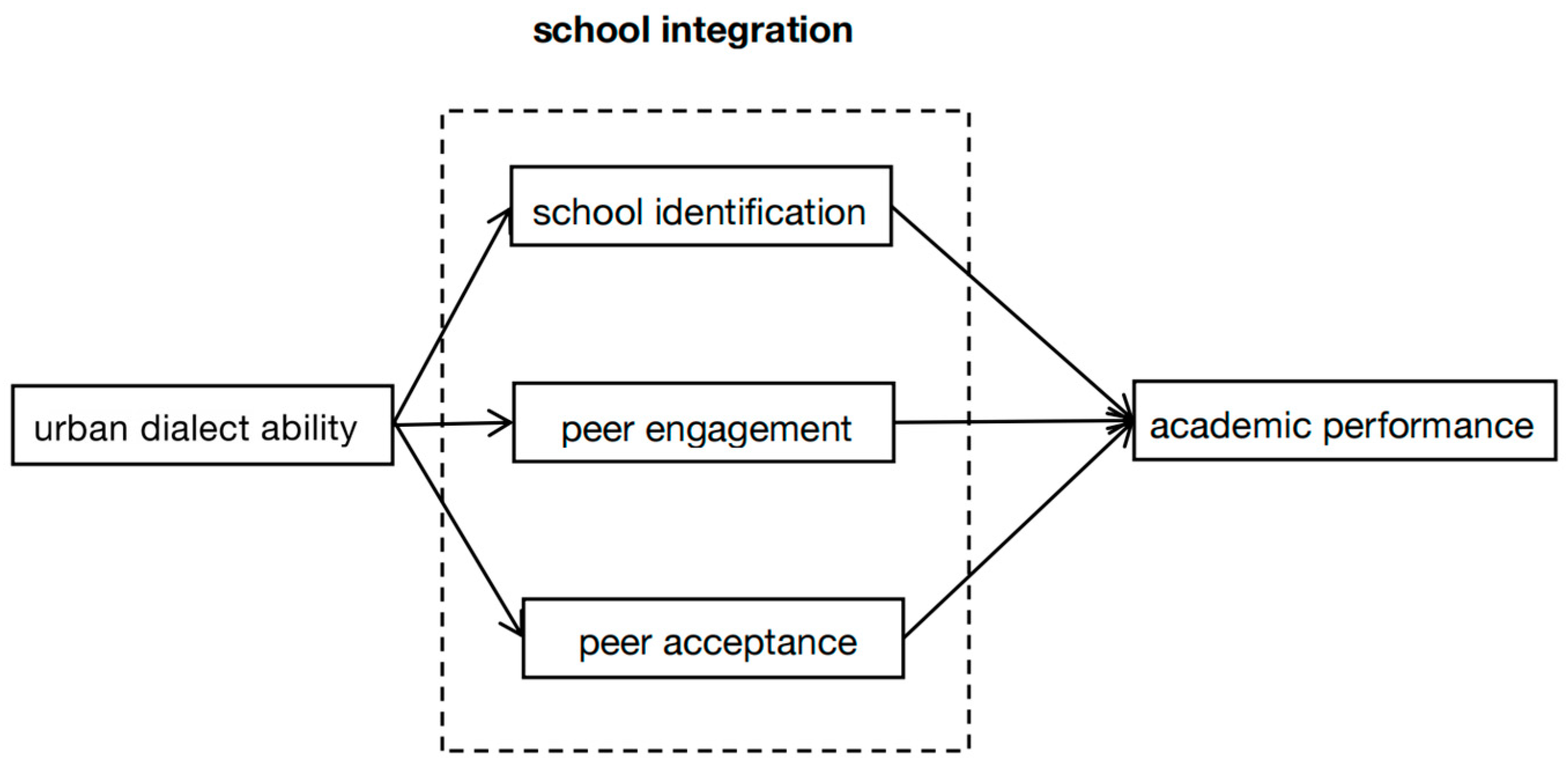
2.3.1. School Integration
2.3.2. The Mediating Role of School Integration
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participants
3.2. Tools
3.2.1. Urban Dialect Ability
3.2.2. Academic Performance
3.2.3. School Integration
3.2.4. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Correlation Analysis
4.2. Regression Analysis
4.2.1. Regression Analysis of Urban Dialect Ability on Academic Performance and School Integration of Migrant Children
4.2.2. Analysis of the Mediating Effect of School Integration on Urban Dialect Ability and Academic Performance
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Practical Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bacete, F. J. G., Tinoco, V. M., Perrin, G. M., & Remírez, J. F. R. (2021). Stability of peer acceptance and rejection and their effect on academic performance in primary education: A longitudinal research. Sustainability, 13(5), 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, R. E. S., & Anderson, J. M. (1974). School context and peer influences on educational plans of adolescents. Review of Educational Research, 44(4), 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, B. (1959). A public language: Some sociological implications of a linguistic form. British Journal of Sociology, 61, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, L. (2019). Reflections on Brown vs. Board of education and school integration today. The Harvard Review of Philosophy, 26, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A. S., & Brown, J. R. (2021). An interprofessional approach to dialect-shifting instruction for early elementary school students. Language Speech and Hearing Services in Schools, 52(1), 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cava, M. J., Povedano, A., Buelga, S., & Musitu, G. (2015). Análisis psicométrico de la Escala de Ajuste Escolar Percibido por el Profesor (PROF-A). Psychosocial Intervention, 24(2), 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire. (2007). Sociolinguistic and pedagogical dimensions of dialects in education. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Chiswick, B. R., & Miller, P. D. (1995). The endogeneity between language and earnings: International analyses. Journal of Labor Economics, 13(2), 246–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, D., Stephen, M., & Uta, S. (2010). Ethnicity and educational achievement in compulsory schooling. The Economic Journal, 120(546), F272–F297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J. S., Campbell, E. Q., Hobson, C. J., McPartland, J., Mood, A. M., Weinfeld, F. D., & York, R. L. (1966). Equality of Educational Opportunity. United States Department of Education. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, R., & Bernstein, B. (1978). Class, codes and control. volume 1: Theoretical studies towards a sociology of language. American Educational Research Journal, 15(4), 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, W. M., & Horesh, U. (2015). Social integration and dialect divergence in coastal Palestine. Journal of Sociolinguistics, 19(4), 460–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, G. B., & Lochner, L. (2012). The impact of family income on child achievement: Evidence from the earned income tax credit. The American Economic Review, 102(5), 1927–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B. (2022). Dialect proficiency, school integration, and psychological health development of migrant children. Journal of China Youth College for Political Sciences, 41(02), 95–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Campos, M. (2004). Context of learning in the acquisition of Spanish second language phonology. Studies in Second Language Acquisition, 26(2), 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J. E., Hillman, C. H., Castelli, D., Etnier, J. L., Lee, S., Tomporowski, P., & Szabo-Reed, A. N. (2016). Physical activity, fitness, cognitive function, and academic achievement in children: A systematic review. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 48(6), 1223–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustmann, C., & Fabbri, F. (2003). Language proficiency and labour market performance of immigrants in the UK. The Economic Journal, 113(489), 695–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekberg, L., & Stman, J. O. (2020). Identity construction and dialect acquisition among immigrants in rural areas—The case of swedish-language finland. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, 46(4), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eric, A. H. (2013). Economic growth in developing countries: The role of human capital. Economics of Education Review, 37, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, S. (2022). Achievement of two cohorts of immigrants: Cognitive mapping changes and the country of origin as moderator. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 51(6), 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, S. (2023). The effect of mobile-assisted learning in real language attainment: A systematic review. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 39(4), 1083–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, S., Brandão, T., & Nunes, O. (2019). Learning styles determine different immigrant students’ results in testing settings: Relationship between nationality of children and the stimuli of tasks. Behavioral Sciences, 9(12), 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geay, C., McNally, S., & Telhaj, S. (2013). Non-native speakers of English in the classroom: What are the effects on pupil performance? The Economic Journal, 123(570), F281–F307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G. C., & Ponce, N. A. (2010). Associations between racial discrimination, limited English proficiency, and health-related quality of life among 6 asian ethnic groups in California. American Journal of Public Health, 100(5), 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G., & Cai, C. (2023). The ability to speak locally and the adaptation of migrant children to schools. Contemporary Youth Research, (02), 85–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, V., Mieszkowski, P., & Sauvageau, Y. (1978). Peer group effects and educational production functions. Journal of Public Economics, 10(1), 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T. (2017). Common tongue: The impact of language on educational outcomes. The Journal of Economic History, 77(2), 473–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S. Z., & Daniel, I. R. (2002). IQ, academic performance, environment, and earnings. The Review of Economics and Statistics, 84(4), 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H. (2011). Korea’s national health insurance—Lessons from the past three decades. Health Affairs, 30(1), 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonah, E. R. (2004). The impact of individual teachers on student achievement: Evidence from panel data. The American Economic Review, 94(2), 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, K., & Danis, W. (2024). Language and identity: The dynamics of linguistic clustering in multinational enterprises. Journal of World Business, 59(4), 101541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, A., & Whitley, E. (2015). Getting there? The effects of functional factors, time and place on the social integration of migrants. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies, 41(13), 2105–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuru, N., Pakarinen, E., Vasalampi, K., Silinskas, G., Aunola, K., Poikkeus, A. M., & Nurmi, J. E. (2014). Task-Focused behavior mediates the associations between supportive interpersonal environments and students’ academic performance. Psychological Science, 25(4), 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpershoek, H., Canrinus, E. T., Fokkens-Bruinsma, M., & de Boer, H. (2019). The relationships between school belonging and students’ motivational, social-emotional, behavioural, and academic outcomes in secondary education: A meta-analytic review. Research Papers in Education, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, H. (2015). School performance. Propósitos y Re-presentaciones, 3(1), 313–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. H., & Shute, V. J. (2010). Personal and social-contextual factors in k–12 academic performance: An integrative perspective on student learning. Educational Psychologist, 45(3), 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, M., Geron, T., & Brighouse, H. (2022). Conceptions of educational equity. AERA Open, 8, 233285842211213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. S., & Jin, X. Y. (2018). A study on the identity of rural migrant children and its influencing factors—Analysis based on the survey data of Shenzhen migrant children. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University (Social Sciences Edition), (06), 112–122+157. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. K., & Zhang, Y. L. (2020). Dialect ability and academic performance of migrant children: Evidence from the China education panel survey. Chinese Journal of Sociology, 40(05), 213–236. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Deng, Z., & Katz, I. (2021). Transmission of educational outcomes across three generations: Evidence from migrant workers’ children in China. Applied Research in Quality of Life, 17(5), 2563–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S., & Chen, Y. (2019). The power of Language: Does speaking the local Language enhance the social integration of migrants? Economic Science, 4, 118–128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, D. P., Warsi, G., & Dwyer, J. H. (1995). A simulation study of mediated effect measures. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 30(3), 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marilou, S. B., & Thelma, P. (2023). Exploring college academic performance of K to12 IT and Non-IT-related strands to reduce academic deficiencies. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA), 14(1), 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, S., Reynolds, K. J., Lee, E., Subasic, E., & Bromhead, D. (2017). The impact of school climate and school identification on academic achievement: Multilevel modeling with student and teacher data. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka, J. (2012). Teaching adolescents to become learners: The role of noncognitive factors in shaping school performance—A critical literature review. Consortium on Chicago School Research. [Google Scholar]
- Orfield, G., & Lee, C. (2005). Why segregation matters: Poverty and educational inequality (p. 47). Civil Rights Project at Harvard University. Available online: https://escholarship.org/content/qt4xr8z4wb/qt4xr8z4wb.pdf?t=n3vdn9 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Park, R. E., & Burgess, E. W. (1970). Introduction to the science of sociology: Including an index to basic sociological concepts. University of Chicago Press. [Google Scholar]
- Pianta, R. C., & Hamre, B. K. (2009). Conceptualization, measurement, and improvement of classroom processes: Standardized observation can leverage capacity. Educational Researcher, 38(2), 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platow, M. J., Foddy, M., Yamagishi, T., Lim, L., & Chow, A. (2012). Two experimental tests of trust in in-group strangers: The moderating role of common knowledge of group membership. European Journal of Social Psychology, 42(1), 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potochnick, S., & Mooney, M. A. (2015). The decade of immigrant dispersion and growth: A cohort analysis of children of immigrants’ educational experiences 1990–2002. International Migration Review, 49(4), 1001–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privado, J., Pérez-Eizaguirre, M., Martínez-Rodríguez, M., & Ponce-de-León, L. (2024). Cognitive and non-cognitive factors as predictors of academic performance. ScienceDirect, 116, 102536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaser, J., & Adger, C. T. (2008). Vernacular language varieties in educational settings: Research and development (pp. 161–173). Blackwell Publishing Ltd. eBooks. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, G. D., & Steib, N. (2013). The personalization effect in multimedia learning: The influence of dialect. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(5), 2022–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B. W. (2006). Personality development and organizational behavior. Research in Organizational Behavior, 27, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J. (2017). Interaction rituals in guanxi practice and the role of instrumental li. Asian Studies Review, 41(4), 664–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryneland, U., & Jensen, B. U. (2020). Dialect acquisition and migration in Norway—Questions of authenticity, belonging and legitimacy. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, 46(2), 937–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sime, D., & Fox, R. (2015). Migrant children, social capital and access to services post-migration: Transitions, negotiations and complex agencies. Children & Society, 29(6), 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. B., Sausi, K., & Kanyane, M. (2014). Theory of segmented assimilation: A comparative study of Nigerian migrants’ integration in kwazulu natal province. Journal of Social Sciences (COES&RJ-JSS), 3(1), 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, L. M., Mavor, K. I., & Platow, M. J. (2017). Learning behaviour and learning outcomes: The roles for social influence and field of study. Social Psychology of Education, 20(1), 69–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syuhudi, A. R. (2019). Constructing identity with dialect diversity. International Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understanding, 6(2), 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrican, S. J., Alleyne, M. L., Smith, P., Cheema, J. R., & King, J. A. (2019). Peer effects in the individual and group literacy achievement of high-school students in a bi-dialectal context. Reading Psychology, 40(2), 117–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, J. A. (2001). Early literacy skills in African-American children: Research considerations. Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 16(4), 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z., & Ye, B. (2014). Mediating effect analysis: Method and model development. Advances in Psychological Science, 22(05), 731–745. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. H., & Li, J. M. (2016). The realistic dilemma and policy options for migrant workers’ accompanying children to receive compulsory education in cities. Educational Research, 37(9), 19–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F., & Liu, Y. M. (2022). Forever outsiders or nominal Shanghainese: Language critique, social class and the ambiguity of local identity. Journal of Shanghai Normal University (Philosophy & Social Sciences Edition), 51(05), 126–136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y., Ohinata, A., & Van Ours, J. C. (2016). The educational consequences of language proficiency for young children. Economics of Education Review, 54, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yao, Y., & Van Ours, J. C. (2015). Language skills and labor market performance of immigrants in the Netherlands. Labour Economics, 34, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L., & Zhao, W. (2022). Impacts of family environment on adolescents’ academic achievement: The role of peer engagement quality and educational expectation gap. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 911959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J., & Grigoriadis, T. N. (2022). Chinese dialects, culture & economic performance. China Economic Review, 73, 101783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Urban Dialect Ability | School Identification | Peer Engagement | Peer Acceptance | Academic Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Dialect Ability | 1 | ||||
| School Identification | 0.087 *** | 1 | |||
| Peer Engagement | 0.010 ** | 0.164 *** | 1 | ||
| Peer Acceptance | 0.037 ** | 0.363 *** | 0.164 *** | 1 | |
| Academic Performance | 0.177 *** | 0.020 ** | 0.032 *** | 0.027 *** | 1 |
| Variables | Academic Performance | School Identification | Peer Engagement | Peer Acceptance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | t | β | t | β | t | β | t | |
| Student Gender | −0.196 | −2.013 | 0.062 | 1.425 | 0.031 | 0.313 | 0.009 | 0.437 |
| Only Child or Not | −0.158 | −1.621 | −0.070 | −1.571 | 0.004 | 0.036 | −0.028 | −1.353 |
| Whether or Not to Live on Campus | 0.235 | 2.414 | 0.105 | 1.877 | 0.227 | 2.043 | −0.015 | −0.596 |
| School Ranking | 0.355 | 3.646 | 0.001 | 0.012 | 0.076 | 0.684 | 0.001 | 0.035 |
| School Location | −0.254 | −2.606 | 0.061 | 1.976 | −0.224 | −2.016 | 0.015 | 1.039 |
| Percentage of Urban Students | −0.763 | −7.836 | −0.120 | −3.277 | 0.117 | 1.053 | −0.014 | −0.809 |
| Teacher Education | 0.831 | 8.534 | −0.001 | −0.022 | 0.005 | 0.045 | 0.003 | 0.346 |
| Teacher Title | 1.342 | 13.786 | 0.021 | 0.471 | 0.014 | 0.126 | 0.033 | 2.011 |
| Faculty Gender | 0.128 | 1.313 | 0.134 | 3.007 | 0.021 | 0.189 | −0.042 | 3.487 |
| Teacher Age | −0.164 | −1.683 | −0.021 | −0.471 | 0.016 | 0.144 | 0.434 | 21.111 |
| Urban Dialect Ability | 1.502 | 15.424 *** | 0.574 | 12.882 *** | 0.797 | 7.173 ** | 0.638 | 31.66 *** |
| ΔR2 | 0.637 | 0.714 | 0.682 | 0.745 | ||||
| F | 145.692 ** | 256.941 *** | 197.453 *** | 345.620 *** | ||||
| Variables | Academic Performance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
| β | t | β | t | β | t | |
| Student Gender | 0.015 | 0.013 | 0.210 | 0.158 | 0.163 | 0.136 |
| Only Child or Not | 0.722 | 0.663 | 0.355 | 0.264 | 0.829 | 0.762 |
| Whether or Not to Live on Campus | 1.360 | 0.972 | 1.249 | 0.743 | 1.161 | 0.832 |
| School Ranking | −0.068 | −0.089 | 0.470 | 0.501 | −0.127 | −0.167 |
| School Location | −2.722 | −7.031 *** | −2.528 | −5.326 *** | −2.734 | −7.067 *** |
| Percentage of Urban Students | 0.020 | 0.702 | −0.014 | −0.402 | 0.020 | 0.715 |
| Teacher Education | 5.655 | 6.158 | 5.003 | 4.582 *** | 5.905 | 6.520 *** |
| Teacher Title | 1.183 | 0.147 | 1.284 | 0.963 | 1.653 | 1.240 |
| Faculty Gender | 0.165 | 0.099 | 0.143 | 0.107 | 0.212 | 0.170 |
| Teacher Age | 0.241 | 0.121 | 0.263 | 0.197 | 0.142 | 0.114 |
| Urban Dialect Ability | 0.560 | 0.423 *** | 0.848 | 0.636 *** | 0.983 | 0.787 *** |
| School Identification | 1.639 | 1.226 *** | ||||
| Peer Engagement | 0.821 | 0.616 ** | ||||
| Peer Acceptance | 0.875 | 0.700 *** | ||||
| ΔR2 | 0.742 | 0.792 | 0.640 | |||
| F | 329.807 *** | 512.934 *** | 147.376 *** | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ming, Y.; Lv, C.; Wang, Z.; Cui, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhi, X. Does Urban Dialect Ability of Migrant Children Significantly Affect Academic Performance? Analysis of Mediating Effects Based on School Integration. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050645
Ming Y, Lv C, Wang Z, Cui H, Zhang K, Zhi X. Does Urban Dialect Ability of Migrant Children Significantly Affect Academic Performance? Analysis of Mediating Effects Based on School Integration. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(5):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050645
Chicago/Turabian StyleMing, Yuelong, Cixian Lv, Zihan Wang, Haoran Cui, Kejun Zhang, and Xiaotong Zhi. 2025. "Does Urban Dialect Ability of Migrant Children Significantly Affect Academic Performance? Analysis of Mediating Effects Based on School Integration" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 5: 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050645
APA StyleMing, Y., Lv, C., Wang, Z., Cui, H., Zhang, K., & Zhi, X. (2025). Does Urban Dialect Ability of Migrant Children Significantly Affect Academic Performance? Analysis of Mediating Effects Based on School Integration. Behavioral Sciences, 15(5), 645. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050645





